
Empirical Analysis of Trade Cost Impacts on Cross-Border
e-Commerce Competitiveness: A Case Study of China and 'Belt and
Road' Countries in the Digital Economy
Yiyuan Hu
a
School of Statistics, Capital University of Economics and Business, Taipingqiao Street, Beijing Fengtai, China
Keywords: Digital Economy, Cross-Border e-Commerce, Trade Costs, Belt and Road.
Abstract: Trade expenses significantly influence the growth of the digital economy and international e-commerce.
Minimizing the expenses associated with international transactions and enhancing the efficacy of digital
commerce are crucial strategies for international e-commerce platforms to boost their profitability. Moreover,
it represents a vital approach for nations to foster external economic engagement and achieve lasting economic
progress. This study utilizes the dataset from China and the nations involved in the "Belt and Road" initiative
to perform an empirical examination of how lowering trade expenses can enhance the competitiveness of
international e-commerce. The research identifies that several elements, including geographical distance,
regulatory differences, levels of economic development, and economic liberty, impact the expenses of
international e-commerce. Specifically, strategies like diminishing the costs of information retrieval,
streamlining delivery and logistics expenses, and reducing the costs associated with sales channels can offer
significant opportunities and competitive advantages for the growth of international e-commerce.
1 INTRODUCTION
At a time when inflationary pressure continues to rise
and the cost of production and living is rising, solving
the problem of economic development has become an
increasingly urgent global challenge. In the
meantime, the swift advancement in information
technologies, including artificial intelligence, big
data, blockchain, and cloud computing, is propelling
a significant information technology revolution
globally (Zhichao, Xue, 2019; Peiyao and Tao, 2019).
In the face of simultaneous economic and
technological shifts, the concept of the digital
economy has taken centre stage. It significantly
contributes to the enhancement of supply chain and
industrial chain efficiency by enabling swift and
effective data flow and distribution. This role of the
digital economy is critical for optimizing and
upgrading these chains, thus playing a key role in the
ongoing transformation. Furthermore, it supports the
seamless development of economic and industrial
activities both domestically and internationally
(Yanghua, 2024), and has become an important
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0001-0370-4973
engine to boost economic growth and pull the
recovery of the global economy.
Over the last ten years, swift progress in digital
technologies and infrastructure has dramatically
transformed the realm of business operations,
modifying organizational structures and corporate
culture. These alterations have paved the way for new
methods of innovation, marketing strategies, and
product categories (Zeljko and Dmitry, 2019).
Additionally, the widespread adoption and
convenience of social media have catalyzed the
inclination towards online purchases on an
international level, laying a foundational stone for e-
commerce expansion and propelling the growth of
cross-border online trade. This surge in e-commerce
activity has notably impacted global commerce. E-
commerce, benefiting from its low entry costs, offers
an advantageous platform for small and medium-
sized enterprises to generate global revenue, marking
a significant stride in their development. E-commerce
promotes the optimization of supply chain
management, further reduces logistics costs, and its
platform attributes also increase the transparency of
Hu, Y.
Empirical Analysis of Trade Cost Impacts on Cross-Border e-Commerce Competitiveness: A Case Study of China and ’Belt and Road’ Countries in the Digital Economy.
DOI: 10.5220/0012938000004508
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Engineering Management, Information Technology and Intelligence (EMITI 2024), pages 349-353
ISBN: 978-989-758-713-9
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
349

market prices, reduce the cost of obtaining
information for all parties, bring a fierce and healthy
competitive environment, and give entrepreneurs the
opportunity to start and expand their business.
On the whole, big data technology has broken the
information barriers in the trade market, and e-
commerce enterprises can obtain valuable
information by means of information technology so
as to effectively reduce information search, sales
channels, delivery and transportation and many other
operating costs, and make innovative decisions for
consumer behavior, opening up the living space of
enterprises and ushering in new trade development
opportunities. Therefore, the digital economy, as an
emerging economic form, can not only reduce
enterprise costs and improve economic profits, but
also promote the development of the overall cross-
border e-commerce trade.
China has leveraged policy support, tax
incentives, and streamlined customs procedures to
effectively lower the trading costs associated with e-
commerce. Additionally, the development of a robust
electronic payment system, data protection
mechanisms, and network security infrastructure has
contributed to market standardization. Hence, this
investigation seeks to analyze the transaction costs
involved in e-commerce interactions between China
and a selection of Belt and Road Initiative nations. It
endeavors to formulate a strategy that elevates the
competitive edge of cross-border e-commerce
transactions and bolsters the development of the
national economy.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
China's total foreign trade ranks among the top in the
world, and the scale of digital economy development
is also relatively large. According to preliminary
statistics in 2023, there will be 645,000 enterprises
with export and import performance in China, among
which more than 100,000 cross-border e-commerce
entities (Shouwen, 2024). This shows that China, as
the world's largest exporter, has a large scale of digital
economy development and has made important
contributions to global digital economy growth.
Therefore, the current trade performance of China's
cross-border e-commerce has important research
significance under the topic of how to achieve "cost
reduction and efficiency increase".
Since its inception in 2013, the Belt and Road
Initiative has acted as a catalyst for expanding trade
relations between China and the countries along the
BRI route. According to data from China's General
Administration of Customs, trade volumes have
surged from 6.46 trillion yuan at the outset of the
initiative to 11.6 trillion yuan, marking an average
annual growth rate of 7.5%. This growth has elevated
China's trade with BRI countries from 25% to 29.7%
of its total international trade. Notably, in 2023, cross-
border e-commerce transactions between China and
these countries amounted to 2.38 trillion yuan, with
exports accounting for 1.83 trillion yuan (a 19.6%
increase) and imports totaling 548.3 billion yuan (a
3.9% increase). The consumer base engaging in
cross-border e-commerce imports expanded to 163
million in 2023, further underscoring the initiative's
impact on the digital commerce economy.
A plethora of academic investigations have
underscored the pivotal role digital commerce plays
in the economic advancement of nations.
Contemporary studies predominantly shed light on
the determinants shaping cross-border electronic
commerce within the digital economy paradigm and
their effects on global trade dynamics. In a seminal
work, a scholar delineates the framework for the
elevated progression of China’s cross-border e-
commerce under the digital economy umbrella,
pinpointing hurdles including regulatory oversight,
the breadth of support services, and the cultivation of
premier brand identities, make a blueprint for
enhancing trade development via digital innovations
is proposed (Peng, 2024). Researcher Wang, Y.
delves into the repercussions of the digital economy
on China’s cross-border e-commerce evolution,
mediated by factors such as transaction costs and
productive efficacy. Research indicates a significant
boost provided by the digital economy to China's
cross-border e-commerce, particularly affecting trade
exports (Yu and Yi, 2017). Additionally, another
study uses an enhanced trade gravity model to
measure the logistics performance index, offering
empirical insight into the factors affecting transaction
volumes in cross-border e-commerce between China
and the Belt and Road countries. This analysis
demonstrates that factors such as geographical
closeness, per capita income, and consumer
demographics play a crucial role in influencing the
scale of cross-border e-commerce transactions
(Yanan, 2020).
To sum up, there is a lot of empirical research on
international trade, so as to provide references and
suggestions for theoretical practice. But a closer look
can also reveal some shortcomings:
Initially, the prevailing research largely focuses
on the effects of digital trade development, focusing
on the impact of cross-border e-commerce on
international trade, considerable attention has been
EMITI 2024 - International Conference on Engineering Management, Information Technology and Intelligence
350

paid to the role of the digital economy in facilitating
the growth of cross-border trade and the prospective
expansion of cross-border e-commerce. Nonetheless,
these analyses often overlook the specific factors
contributing to the competitiveness of cross-border e-
commerce or the ways in which digital trade costs can
affect the competitive advantage of e-commerce
transactions. Furthermore, there is a notable scarcity
of comparative analyses regarding various trade
costs. While the influence of disparate trade costs on
the growth of cross-border e-commerce is
acknowledged, there exists a lack of detailed
comparison regarding the prioritization of trade cost
management.
Hence, the unique contribution of this manuscript
lies in its utilization of empirical analysis techniques
to investigate the effects of different trade costs on
both cross-border e-commerce and the broader digital
trade landscape. It aims to pinpoint critical factors by
evaluating the positive and negative impacts of
various trade costs and their management approaches,
thereby offering insights into optimizing cross-border
e-commerce operations.
3 RESEARCH
3.1 Research Design
The investigation bifurcates into two distinct
segments: Firstly, examining the effect of trade costs
on the proliferation of domestic e-commerce trade
within China, and secondly, analyzing the disparity in
digital competitiveness and trade costs across various
nations in the international trading arena. The
examination of e-commerce trade at the provincial
level in China utilizes data extracted from the "China
Statistical Yearbook" and information from six issues
of the "Cross-border E-commerce Comprehensive
Pilot Zone List" published by The State Council,
covering the development of cross-border e-
commerce pilot zones and per capita GDP from 2015
to 2022. In parallel, the analysis of digital
competitiveness among countries employs data from
the World Development Indicators (WDI) of the
World Bank, the CEPII database, the China Customs
database, and relevant scholarly works. It is crucial to
acknowledge that barriers to trade between two
countries can appear in different guises, such as
tariffs, quotas, and an assortment of non-tariff
barriers, including import licenses or technical
standards. Additionally, the time it takes to ship
goods can act as another type of trade barrier
(François, Alen, Siobhan, Nadia and Michele,
2019). Otherwise, as supply chains increasingly
globalize, it's critical to account for the geographical
positions of supply chain participants in evaluating
the performance advantages of supply chain practices,
such as purchasing tools (Frank and Eamonn, 2017).
Therefore, another section includes data on China's
GDP and that of 36 other countries and regions
connected to the "Belt and Road" initiative. This data
elaborates on the geographical and institutional
distances, differences in economic freedom, and the
export values between China and these entities,
emphasizing the data from the year 2019.
The challenge arises from the inability to directly
quantify the alleged costs, leading researchers to
predominantly utilize indirect methodologies. They
propose models that simulate bilateral trade flows and
associate these flows with surrogate variables
designed to signify trade barriers (David, 1999). In
assessing countries' digital competitiveness, most of
the previous studies used the traditional gravity model
to study the trade flow between two countries, which
can estimate the influence of geographical distance,
economic scale, economic freedom and other factors
on the trade flow. However, considering that the
logarithmic transformation of the independent
variable is carried out and there may be more complex
nonlinear relationships between variables, this paper
chooses to establish the following generalized
additive model for analysis:
log(Exports + 1) = β₀+ s(log(GDP + 1)) +
s(log(Dist + 1)) + s(Policy) + s(Freedom) + ϵ
(1)
Exports represent China's exports in countries or
regions along the Belt and Road, and s(GDP) is a
smooth term of GDP to capture the non-linear
relationship between GDP and exports. s(Dist) is the
smoothing term of geographical distance from China,
s(Policy) is the smoothing term of institutional
differences, and s(Freedom) is the smoothing term of
economic freedom.
3.2 Empirical Research
Analyzing the annual changes in average metrics of
digital economic growth across China's provinces
uncovers a deliberate extension of cross-border e-
commerce pilot zones from coastal areas to a wider
expanse of the country. This expansion correlates
with economic disparities, where coastal provinces
typically exhibit superior economic performance
compared to their inland counterparts, a trend that
aligns with the establishment of these pilot zones.
Furthermore, an upward trajectory in the Gross
Domestic Product of these provinces over time
Empirical Analysis of Trade Cost Impacts on Cross-Border e-Commerce Competitiveness: A Case Study of China and ’Belt and Road’
Countries in the Digital Economy
351
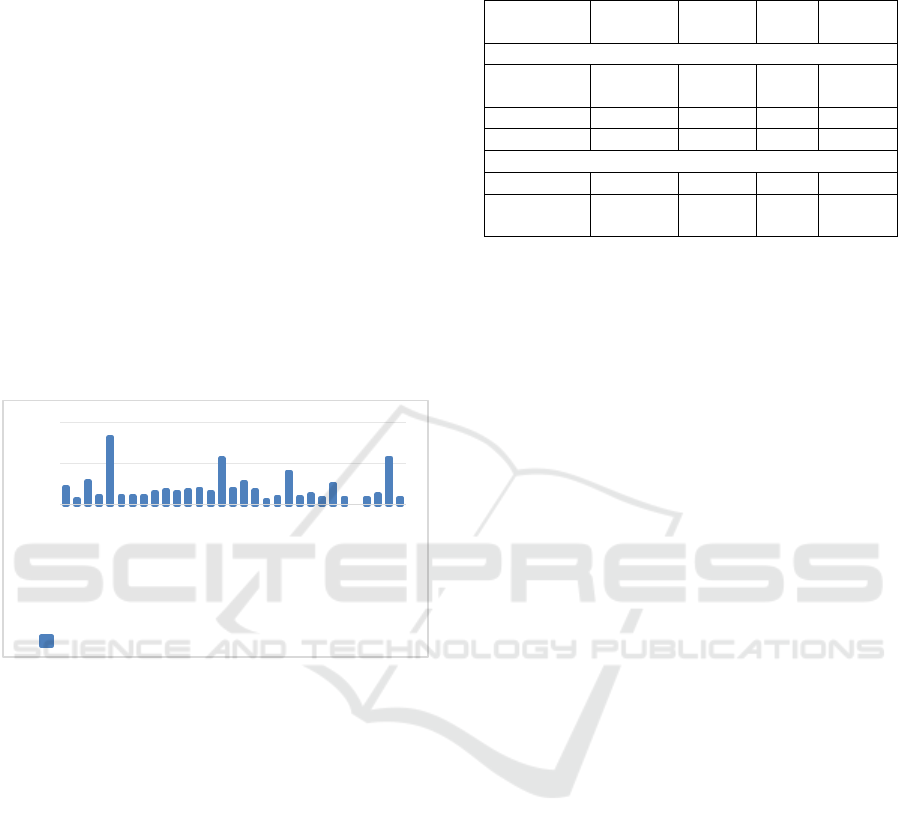
suggests a linkage to the pilot zones' establishment, a
hypothesis supported by linear model analysis which
fails to refute this association. The advent of the
digital economy has significantly bolstered the trade
competitiveness of provinces by streamlining
information search costs, marketing channel
expenditures, and management services, thereby
mitigating governance costs and influencing cross-
border trade expenses to achieve cost reduction and
efficiency enhancement.
The inception of cross-border e-commerce pilot
zones has catalyzed investments in infrastructure,
digital innovation, digital industry, and governance.
The adoption of a clustered development approach
coupled with favorable policy frameworks has
curtailed operational and managerial expenses for e-
commerce enterprises, thereby fostering a
competitive and collaborative development
atmosphere among e-commerce entities.
Figure 1: Construction of cross-border trade pilot zones in
China's provincial-level administrative regions.
Recent empirical findings on a country's digital
competitiveness indicate that boosting digital trade
competitiveness markedly lowers the expenses
associated with cross-border commerce between
China and the "Belt and Road" affiliated countries.
The economic growth level, extent of economic
liberty, geographical proximity, and institutional
variances between China and its trading counterparts
each play a role in shaping the costs linked to China's
cross-border e-commerce trade. A greater alignment
in cultural and economic progression levels enhances
the efficiency of cross-border trade relations.
Consequently, e-commerce entities tend to favor
trading partners that are geographically nearer, as this
choice leads to diminished logistics costs.
Table 1: Regression result of digital competitiveness of Belt
and Road countries.
Term Estimate
Std.
Error
t value Pr(>t)
Parametric Coefficients
Intercept 20.31924 3.26022 6.232
<0.0001
***
Polic
y
-0.48604 0.39872 -1.219 0.235
Freedom 0.03078 0.04549 0.677 0.505
A
pp
roximate Si
g
nificance of Smooth Terms
s(log_GDP) 0.0807 .
s(log_Dist)
<0.0001
***
P.S. Note: *** p < 0.001, **p < 0.01. *p < 0.1
The Gross Domestic Product of a nation serves as
a robust indicator of its economic and trade prowess,
facilitating enterprises within that nation to leverage
digital trade platforms for publicity, negotiation, and
transactions, thereby enhancing trade pairings
between parties. This mechanism also permits the
efficient oversight and management of the
transportation process through real-time data
exchange, elevating the efficiency of customs
processes in cross-border trade. It underscores the
pivotal role of GDP in diminishing costs and
augmenting efficiency within cross-border trade
enterprises, markedly influencing export volumes.
Moreover, the relationship between geographical
distance and trade volumes exhibits a nonlinear
dynamic, where increased distances escalate trade
costs, consequently diminishing trade volumes.
Given the significant impact of geographical distance
on logistics expenses for cross-border e-commerce,
effective communication and matching strategies are
crucial in the preliminary stages. Selecting cost-
efficient transport solutions and negotiating
appropriate contracts are imperative measures to
minimize the tangible distances involved.
Conversely, while the effects of institutional
disparities and economic freedom levels on trade
volumes appear minimal, macro-level observations
indicate a trend where countries boasting higher
economic freedom often register superior trade
volumes. This insight underscores the complex
interplay between regulatory environments and trade
outcomes.
4 CONCLUSIONS
In light of the research conducted, it becomes evident
that prompting traditional enterprises towards digital
transformation holds critical importance. This
transition is pivotal for optimizing resource allocation
0
50
100
Anhui
Gansu
Guizhou
Henan
Hunan
Jiangxi
Ningxia
Shanxi
Sichuan
Xinjiang
Chongq…
Number of comprehensive pilot zones for cross-…
EMITI 2024 - International Conference on Engineering Management, Information Technology and Intelligence
352

and bolstering the competitiveness of products. The
path to research, development, and innovation within
digital technologies is marked by lengthy cycles,
substantial investment requirements, and uncertain
returns. Consequently, the effective employment of
digital technology across various domains such as
production, logistics, payment systems, and
management is paramount to achieving cost
efficiency and enhanced productivity (Saeed, 1998).
Furthermore, the development and refinement of
current cross-border trade pilot zones and e-
commerce systems reveal substantial opportunities
for cost reduction and efficiency enhancement. It
necessitates a comprehensive coordination among
customs, national taxation bodies, and inspection
agencies. It's essential to prioritize the development
of public information service platforms to create an
enabling environment for cross-border e-commerce.
Improving the integration and efficiency of cross-
border trade pilot zones, as well as boosting industrial
competitiveness, are crucial measures for maintaining
strong international connections. Such efforts not
only refine the operational structure but also lay the
groundwork for future innovations in cross-border
trade.
Third, the establishment of relevant trade
cooperation mechanisms between countries is
conducive to reducing tariff barriers, providing free
and convenient space for trade exchanges, and
effectively reducing trade costs. Combined with
geographical advantages, trade cooperation has
driven the digital competitiveness of countries along
the "Belt and Road", narrowing the marginal trade
differences between different countries, and is a
feasible way to maximize the function of digital trade
competitiveness in cross-border trade of "reducing
costs and increasing efficiency".
In order to effectively alleviate the trade cost
problems caused by cultural and institutional
differences, do a good job in the language
construction of cross-border e-commerce network
platforms to ensure the accuracy and popularity of
translation (Anqi, 2020). Vigorously introduce
language professionals, deeply understand the
cultural and institutional differences of different
countries and solve the obstacles of online
transactions while reducing logistics costs.
REFERENCES
Dallocchio, M., Lambri, M., Sironi, E.,Teti, E., 2024. The
Role of Digitalization in Cross-Border E-Commerce
Performance of Italian SMEs. Sustainability, 16(2),
508.
Dennis, A, 2007. Trade costs, barriers to entry, and export
diversification in developing countries (Vol. 4368).
World Bank Publications.
François de Soyres, Alen Mulabdic, Siobhan Murray, Nadia
Rocha, Michele Ruta, 2019. How much will the Belt
and Road Initiative reduce trade costs?. International
Economics, Volume 159, Pages 151-164, ISSN 2110-
7017.
Gwartney, J., Lawson, R, 2003. The concept and
measurement of economic freedom. European Journal
of Political Economy, 19(3), 405-430.
Hummels, D. L, 1999. Toward a geography of trade
costs. Available at SSRN 160533.
Kristjánsdóttir, H., Guðlaugsson, Þ. Ö., Guðmundsdóttir,
S., Aðalsteinsson, G. D., 2020. Cultural and
geographical distance: Effects on UK exports. Applied
Economics Letters, 27(4), 275-279.
Limao, N., Venables, A. J., 2001. Infrastructure,
geographical disadvantage, transport costs, and
trade. The world bank economic review, 15(3), 451-
479.
Samiee, S., 1998. The internet and international marketing:
is there a fit?. Journal of Interactive Marketing, 12(4),
5-21.
Tekic, Z., Koroteev, D., 2019. From disruptively digital to
proudly analog: A holistic typology of digital
transformation strategies. Business Horizons, 62(6),
683-693.
Wang, Y., Wang, Y., Lee, S. H., 2017. The effect of cross-
border e-commerce on China’s international trade: An
empirical study based on transaction cost
analysis. Sustainability, 9(11), 2028.
Wei Anqi, 2020. Research on the development of cross-
border e-commerce in ASEAN based on the perspective
of "Maritime Silk Road". International Public Relations
(01), 295.
Wiengarten, F., Ambrose, E., 2017. The role of
geographical distance and its efficacy on global
purchasing practices. International Journal of
Operations & Production Management, 37(7), 865-881.
Wu Xin, Fei Zhou, 2024. The mechanism of digital
economy affecting the development of cross-border e-
commerce trade in my country from the perspective of
double intermediary effect. Business Economics
Research, (01),154-157.
Yanan Zhao, 2020. Influencing Factors of Cross-Border E-
Commerce Trade between China and “Belt and Road”
Coastal and Inland Countries. Journal of Coastal
Research 1 June 2020; 103 (SI): 70–73.
Zhang Peng, 2024. Exploration on the high-quality
development of China’s cross-border e-commerce in
the era of digital economy. Northern Economics and
Trade (02), 121-124.
Empirical Analysis of Trade Cost Impacts on Cross-Border e-Commerce Competitiveness: A Case Study of China and ’Belt and Road’
Countries in the Digital Economy
353
