
Implementing AI for Enhanced Public Services Gov.br: A Methodology
for the Brazilian Federal Government
Ma
´
ısa Kely de Melo
1,6,∗ a
, Silvia Ara
´
ujo dos Reis
1,7 b
, Vin
´
ıcius Di Oliveira
2,11,12 c
,
Allan Victor Almeida Faria
1,4 d
, Ricardo de Lima
3,12 e
, Li Weigang
2,12,∗ f
,
Jose Francisco Salm Junior
1,13 g
, Joao Gabriel de Moraes Souza
1,9 h
, V
´
erica Freitas
8 i
,
Pedro Carvalho Brom
2,10,12 j
, Herbert Kimura
1,7 k
, Daniel Oliveira Cajueiro
1,5 l
,
Gladston Luiz da Silva
1,4 m
and Victor Rafael R. Celestino
1,7,∗ n
1
LAMFO - Lab. of ML in Finance and Organizations, University of Bras
´
ılia, Campus Darcy Ribeiro, Bras
´
ılia, Brazil
2
TransLab, Department of Computer Science, University of Bras
´
ılia, Campus Darcy Ribeiro, Bras
´
ılia, Brazil
3
Ministry of Management and Innovation in Public Services, Federal District, Brazil
4
Department of Statistics, University of Bras
´
ılia, Campus Darcy Ribeiro, Bras
´
ılia, Brazil
5
Department of Economics, University of Bras
´
ılia, Campus Darcy Ribeiro, Bras
´
ılia, Brazil
6
Department of Mathematics, Federal Institute of Education, Science and Technology of Minas Gerais, Formiga, Brazil
7
Department of Business Administration, University of Bras
´
ılia, Campus Darcy Ribeiro, Bras
´
ılia, Brazil
8
School of Business and Management, Uberlandia Federal University, Uberl
ˆ
andia, Brazil
9
Department of Economics and Business Administration, Brazilian Institute of Education Development and Research -
IDP, Bras
´
ılia, Brazil
10
Department of Mathematics, Federal Institute of Education, Science and Technology of Bras
´
ılia, Campus Estrutural,
Bras
´
ılia, Brazil
11
Federal District Secretariat of Economy, Bras
´
ılia, Brazil
12
Department of Computer Science, University of Bras
´
ılia, Campus Darcy Ribeiro, Bras
´
ılia, Brazil
13
University of the State of Santa Catarina, Florian
´
opolis, Santa Catarina, Brazil
Keywords:
Brazil, Design Sprint, Public Administration, AI, Machine Learning, LLM.
Abstract:
The website portal of the Brazilian federal government (Gov.br) consists of pages from almost 40 ministries,
180 public agencies and up to 5000 public services for all citizens, posing a significant challenge in improving
service quality. This article presents an innovative methodology to implement artificial intelligence (AI) to
address these challenges, to enhance the efficiency, accessibility, and quality of services to the population.
The methodology combines elements of Lean Office, Design Sprint, Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP), and
advanced AI techniques, particularly Large Language Models (LLMs), making it flexible and adaptable to
the needs of government entities. Developed in collaboration with project managers, public servants, and
stakeholders, the methodology includes a survey of demands, selection, and prototyping of AI projects in a
complex government context. The practical application selected the Gov.br portal for prototyping, involving
the development of an advanced generative agent to interact with citizens, clarify doubts, direct to the re-
quested services, and provide human interaction when necessary. The recommended practices offer a valuable
contribution to other developing countries seeking to integrate AI solutions into their public services.
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8120-9778
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1646-4454
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1295-5221
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4300-9334
e
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9269-3558
f
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1826-1850
g
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8492-1645
h
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0685-3082
i
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3035-9738
j
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1288-7695
k
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6772-1863
l
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5898-1655
m
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9650-2993
n
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5913-2997
∗
Corresponding author
90
Kely de Melo, M., Reis, S. A., Di Oliveira, V., Faria, A. V. A., de Lima, R., Weigang, L., Salm Junior, J. F., Souza, J. G. M., Freitas, V., Brom, P. C., Kimura, H., Cajueiro, D. O., Luiz da Silva, G.
and Celestino, V. R. R.
Implementing AI for Enhanced Public Services Gov.br: A Methodology for the Brazilian Federal Government.
DOI: 10.5220/0012997000003825
In Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies (WEBIST 2024), pages 90-101
ISBN: 978-989-758-718-4; ISSN: 2184-3252
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

1 INTRODUCTION
In recent years, the public sector has increasingly ex-
plored artificial intelligence (AI) to enhance opera-
tions and improve service delivery (Maragno et al.,
2023). There are at least 142 AI applications in fed-
eral administrations (Engstrom et al., 2020). Some
focus on making government information more acces-
sible, while others aim to improve citizen interaction
through Information and Communication Technolo-
gies (ICTs) (Kitsios et al., 2023). AI technologies,
such as machine learning (ML), natural language pro-
cessing (NLP), and computer vision, hold great po-
tential for automating tasks, analyzing large datasets,
and offering more efficient, personalized services.
The disruptive potential of AI in the public sec-
tor is evident in three main areas: enhancing internal
efficiency, improving decision-making, and strength-
ening citizen-government interaction. AI applications
in the public sector include facial recognition in polic-
ing (Blount, 2024), recidivism prediction in criminal
justice (Wang et al., 2023), virtual agents for process
automation (Scutella et al., 2024), forecasting social
service needs (Dwivedi et al., 2023), chatbots (Chen
et al., 2024), healthcare (Yu et al., 2018), public trans-
port (Jevinger et al., 2024), education (Cohen et al.,
2023), environmental management (Fan et al., 2023),
and agribusiness (Kutyauripo et al., 2023). These
initiatives promote more inclusive services and en-
hance citizen participation in public sector activities
(Samoili et al., 2020).
Integrating artificial intelligence into the public
sector is evolving, with much still unknown about its
full potential and optimal strategies. Existing research
on AI adoption highlights three key values: trans-
parency, effectiveness, and efficiency (Rocha et al.,
2022; Faria et al., 2022; Chen et al., 2023). Rec-
ognizing the need for clear guidelines, the Brazilian
federal government aims to identify the best practices
for selecting AI projects in public agencies.
This paper presents the methodology developed
for the project “Artificial Intelligence Research Ap-
plied to the Prototyping of Solutions for the Fed-
eral Government’s Artificial Intelligence Office.” The
methodology focuses on mapping, prototyping, and
documenting AI solutions for public administration
issues, aligning with the responsibilities of the Secre-
tariat of Digital Government (SGD) (BRASIL, 2023),
under the Ministry of Management and Innovation in
Public Services. The proposed solution supports AI
governance and the development of data models, pro-
cesses, and standards, including data mining, analy-
sis, and visualization technologies. These practices
enhance the public policy management cycle and the
provision of services. Given that these responsibili-
ties are part of other countries’ digital transformation
strategies, the methodology offers a valuable contri-
bution to governmental agencies developing AI solu-
tions for public services.
It also details the step-by-step methodology for
selecting and prototyping projects in AI Decision-
Making in the Public Sector. This methodology was
developed and applied in collaboration with AI and
project management expert researchers, members of
the SGD, and other bodies comprising the Brazil-
ian Government’s Artificial Intelligence Hub (NIA).
Figure 1 illustrates NIA, highlighting partner insti-
tutions’ diversity. The results of the methodology’s
application in federal government agencies are re-
ported, highlighting recommended practices and ob-
tained outcomes. The project selected for prototyp-
ing, arising from the demands identified by the public
agencies participating in the research, was the Gov.br
portal service (BRASIL, 2024). This portal com-
prises pages from nearly 40 ministries and 180 pub-
lic agencies, integrating up to 5000 public services.
Over 150 million Brazilians access it and records ap-
proximately four thousand accesses per second (Gov,
2024). The prototyping involved the development of
an Advanced Generative Agent to interact with citi-
zens, assist them, clarify doubts, and direct them to
the requested service pages, with human overflow in
necessary cases.
2 RELATED WORK
We present the following works that explore various
aspects of AI solutions for public services and the
techniques used in the proposed methodology. Ad-
ditionally, we contextualize the application of AI in
public services within the Brazilian framework.
2.1 Public Service with AI
Implementing AI in the public sector requires un-
derstanding its capabilities and addressing challenges
like explainability, data governance, and infrastruc-
ture. Human-AI collaboration can improve tasks and
create new jobs, but caution is essential to avoid
mistrust. Engaging stakeholders, such as citizens
and suppliers, foster innovation but demands effec-
tive ecosystem management and clear regulations
(Maragno et al., 2023). Currently, there is no uni-
fied global approach to determining AI’s legal status
(Atabekov, 2023), and most countries focus on the
process rather than the final result generated by AI
(Atabekov, 2023).
Implementing AI for Enhanced Public Services Gov.br: A Methodology for the Brazilian Federal Government
91
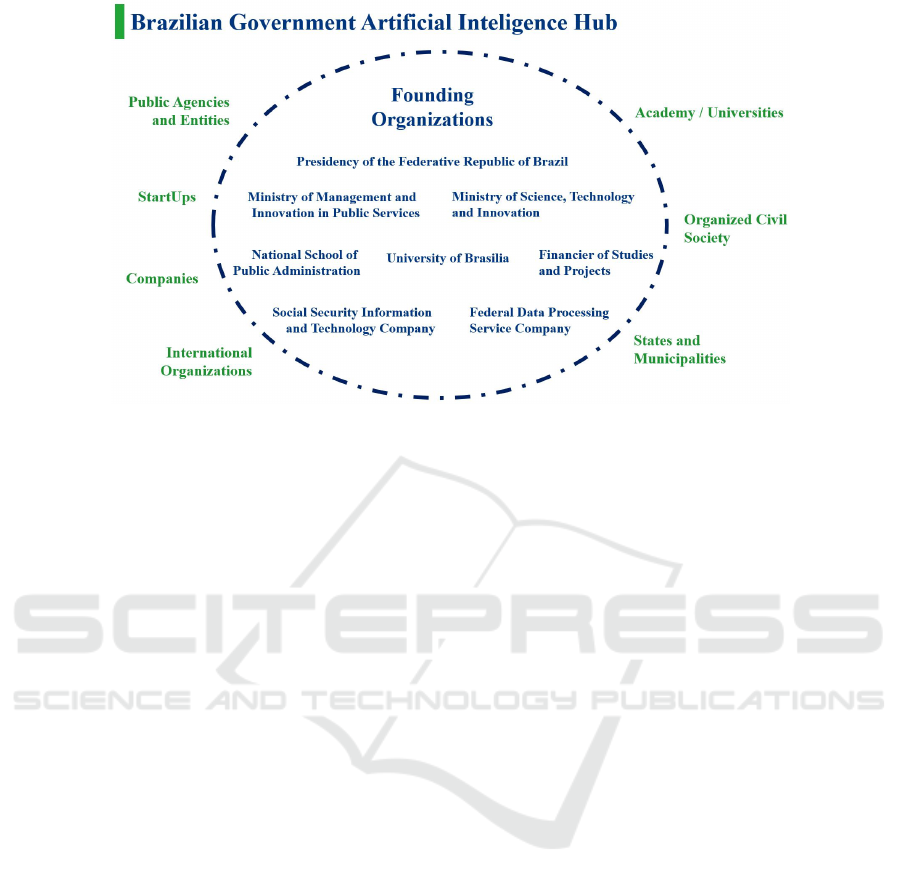
Figure 1: Brazilian Government Artificial Intelligence Hub (NIA).
There is a knowledge gap in academic research
concerning AI’s influence on public values and the
governance challenges that arise from this interac-
tion (Chen et al., 2023; Kitsios et al., 2023; Maragno
et al., 2023; Neumann et al., 2024). Insights into how
government employees perceive AI’s impact on pub-
lic values and governance challenges remain limited.
The debate over whether AI will transform the pub-
lic sector and its operational environments continues
(Kitsios et al., 2023).
The rising interest in AI within government spans
various scholarly fields. While this diversity is en-
riching, it can cause fragmentation in theoretical and
terminological approaches as researchers from dif-
ferent disciplines work independently (Straub et al.,
2023). Technical research often neglects broader per-
spectives and real-world contexts. Additionally, the
increasing number of typologies and taxonomies to
interpret AI’s role in government sometimes needs
to be more interconnected, reinforcing a fragmented
knowledge base (Straub et al., 2023).
Despite growing debate, AI diffusion in the public
sector remains limited compared to the private sector
(Neumann et al., 2024). Interdisciplinary AI scholar-
ship in government is still emerging, and theory has
yet to offer significant value to practitioners (Birhane
et al., 2022). Humans remain crucial as decision-
makers and rule enforcers, including public safety and
fraud investigations (Chen et al., 2023). The abun-
dance of conceptual terms and lack of integration be-
tween social sciences and AI’s technical aspects leave
governments uncertain about which principles to pri-
oritize in AI governance (Straub et al., 2023). Glob-
ally, AI in government is still in early implementa-
tion, with key decisions shaping future expectations
(Straub et al., 2023).
2.2 AI in Public Service in Brazil
Brazil has advanced its digital agenda since the
1990s, starting with the 1991 Information Technol-
ogy Program, which offered tax incentives for R&D
in hardware and automation and promoted company-
university collaboration (Filgueiras and Junquilho,
2023). In 2018, the Brazilian Strategy for Digital
Transformation (E-Digital) (BRASIL, 2018) outlined
actions for advancing public policies, emphasizing
AI, big data, 5G, and modernizing production. It also
highlighted the need for ICT training and assessing
the impacts of disruptive technologies. In 2021, the
Brazilian Strategy for Artificial Intelligence (EBIA)
(BRASIL, 2021) was introduced, focusing on AI re-
search, public security, legislation, and international
governance (Anna, 2023). EBIA promotes innova-
tion by fostering knowledge exchange through coun-
cils and networks (Nonato et al., 2024).
Brazil has made significant strides in innova-
tion potential (Anna, 2023), with growing social in-
terest in enhancing public sector innovation to im-
prove efficiency, quality, and accessibility (Guedes
and J
´
unior, 2024). The Brazilian government has
established AI centers of excellence, funded univer-
sity research, created collaborative networks, and de-
veloped ecosystems while ensuring privacy and data
protection (Filgueiras and Junquilho, 2023). The
public sector leads in policy formulation, promotes
data transparency, fosters innovation, supports profes-
sional training, and invests in emerging technologies
to build effective governance ecosystems (BRASIL,
2021).
WEBIST 2024 - 20th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
92

Despite various initiatives to promote digital de-
velopment, Brazil’s efforts need coherence and align-
ment with its social reality (Filgueiras and Junquilho,
2023). Key challenges hindering EBIA’s implementa-
tion include a clear timeline for strategic goals (Anna,
2023) and unclear governance structures (Gaspar and
Mendonc¸a, 2021). As emphasized in the public con-
sultation, regulatory bodies, specific authorities, and
existing structures are needed. The lack of policy inte-
gration leads to non-cooperation among actors, mak-
ing EBIA more of an ineffective document than a col-
laborative strategy for problem-solving (Gaspar and
Mendonc¸a, 2021).
Several AI initiatives have been identified in
Brazil’s public agencies. The Conecte SUS project
aims to modernize public health management (Lemes
and Lemos, 2020), while the EB S@
´
ude Project uses
AI to optimize military health databases (Lemes and
Lemos, 2020). Regulatory sandboxes are advanced
in the financial sector, with institutions like the Min-
istry of Economy and the Central Bank of Brazil
implementing models since 2019 (Kubota and Rosa,
2024). The Brazilian Federal Revenue Service uses
SISAM for real-time processing of over 2.5 million
import declarations (Guedes and J
´
unior, 2024). Vari-
ous agencies, including the Federal Court of Accounts
and the Federal Police, employ AI robots to boost pro-
ductivity (Desordi and Della Bona, 2020). Additional
AI use cases are documented in an OECD.AI inven-
tory (OECD.AI, 2022).
Although broad social participation contributed to
the national AI strategy, it has yet to be fully imple-
mented nationwide. To address this, the Federal Gov-
ernment established the AI Hub (NIA), tasked with
creating a list of Priority AI Projects, defining projects
eligible for funding, and promoting academic stud-
ies to solve public sector challenges. The project dis-
cussed in this paper is an initiative of the NIA SubHub
for Prospecting Strategic Projects, executed by the
University of Bras
´
ılia (UnB) through LAMFO under
a Decentralized Execution Agreement (DEA). This
SubHub comprises professionals from various fields,
as described in Figure 1.
3 EMPOWERING SERVICES: AI
FRAMEWORK
A standardized methodology is necessary for imple-
menting AI in public services. To meet the goals of
the National Artificial Intelligence Strategy, this pa-
per proposes a comprehensive process for deploying
AI solutions. The following sections outline steps for
identifying demands, selecting projects, designing so-
lutions, prototyping, and validation. This methodol-
ogy was developed through a literature review, high-
lighting key findings and limitations of AI in pub-
lic administration. By exploring best practices and
emerging technologies, we applied the concept of
Meta AI—learning to learn about AI—through thor-
ough applied research to achieve the project’s objec-
tives.
To address the challenge, the proposed methodol-
ogy aimed to answer the following question: What
is the best method for selecting AI projects in gov-
ernment with subjective issues to be judged and
more than ten alternative options? Initially, a lit-
erature review was conducted on methods for se-
lecting AI projects in government with subjective
judgment criteria, highlighting Multicriteria Decision
Analysis (MCDA) methods, particularly the Analytic
Hierarchy Process (AHP) (Saaty, 1977), due to its
widespread use for project selection. AHP Express
was selected for cases with many alternatives (Leal,
2020).
In addition to the method for selecting AI projects,
after the evaluation was completed, Lean Office prac-
tices were incorporated to improve public administra-
tion services and reduce bureaucratic overhead. Two
literature reviews were conducted to advance this re-
search: one focused on digitalization and the other on
Lean practices.
This resulted in the development of the AI so-
lution selection and prototyping process for public
services, which was designed based on the proposed
methods in the literature and enriched through discus-
sions among the AI scientists, who are the authors of
this paper, and members of the SGD, the institution
responsible for promoting AI project development in
the Brazilian federal government. Consequently, a
methodology was proposed that reflects cutting-edge
knowledge and addresses the specific and complex
peculiarities of public administration in a country as
large as Brazil. The steps of the proposed method-
ology are illustrated in Figure 2, with each phase’s
objective described below.
Step 1: Survey. Conduct a comprehensive survey
of federal public administration agencies’ AI needs.
This step investigates departmental challenges and
identifies areas where AI can enhance public service
efficiency and effectiveness. The research should be
thorough, incorporating interviews, questionnaires,
and analysis of existing data.
Step 2: Elimination. Following the application of
the Survey (Step 1), various project proposals for ap-
plying AI are identified. At this step, an initial filter
is used to ensure that the proposed projects can in-
deed be addressed through AI. This filter eliminates
Implementing AI for Enhanced Public Services Gov.br: A Methodology for the Brazilian Federal Government
93
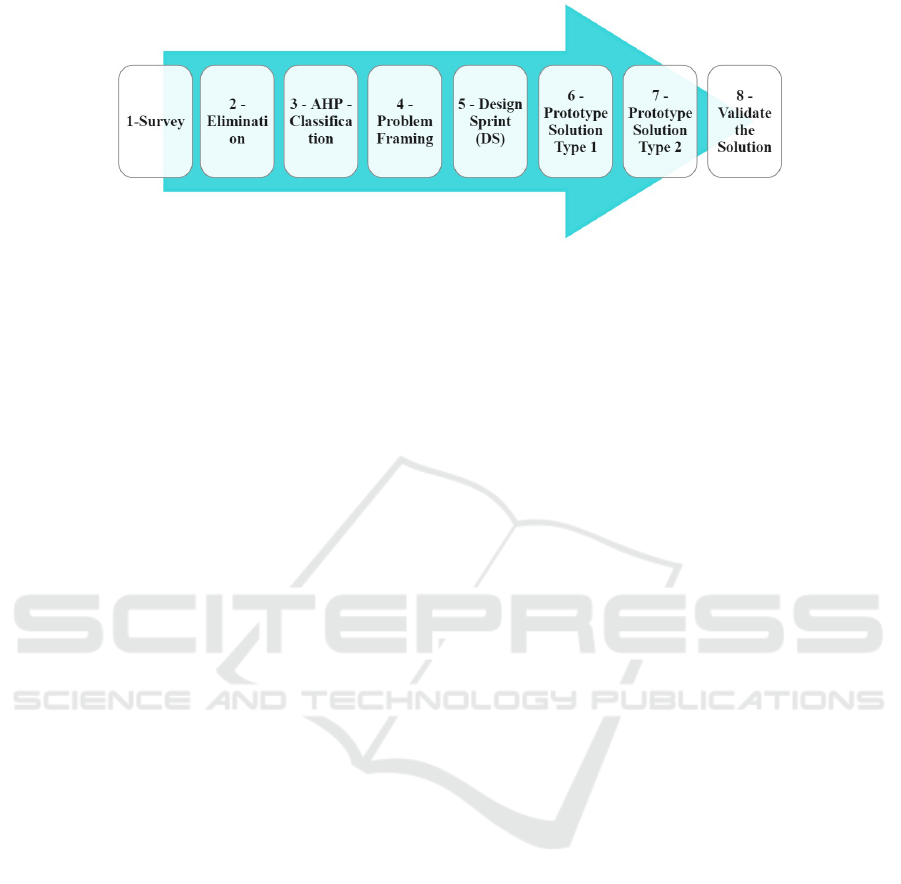
Figure 2: Steps of the Project Selection Process for Prototyping.
proposals failing to meet the established criteria, en-
suring that only viable projects proceed to the next
phase.
Step 3: AHP - Classifier. The proposals filtered
in the elimination step proceed to prioritization. In
this step, the proposals are ranked in order of prior-
ity and preference, considering the subjective aspects
of stakeholders, such as expected impact, urgency,
and feasibility. The AHP is utilized here to structure
and facilitate decision-making, ensuring that the most
promising and strategic projects are selected.
Step 4: Problem Framing. In the proposed ap-
proach presented in this paper, Problem Framing was
used - for (Bardwell, 1991), Problem Framing helps
structure and provide information organization to un-
derstand the problem, which people do not do daily.
Hence, it helps create a data management and analy-
sis environment that aims to solve problems. A lack
of understanding of the problem can lead to solu-
tions that do not bring the desired effects (Robertson,
2016).
Step 5: Design Sprint. Afterward, an adapted ver-
sion of the Design Sprint was used (Knapp et al.,
2016). A study (Mendonc¸a de S
´
a Ara
´
ujo et al., 2019)
mentions that the computer systems industry has
widely adopted Design Sprint to minimize the prob-
lems in defining requirements in software projects.
Another study (Larusdottir et al., 2021) highlights the
focus on adapting the design of the product, usually
a computational application, to the users’ needs and
adds that, in the Design Sprint proposal, a relatively
small team, which initially has a superficial idea of
the users’ requirements, intends to, at the end of the
process, have a prototype solution.
Step 6: Prototyping the Solution - Type 1. Aiming
at the prototyping of the solution selected in Step 5,
a theoretical and summarized prototype of the solu-
tion is conceptualized. This conceptualization occurs
through collaborative brainstorming sessions between
the project researchers and the team from the SGD.
In this step, the existing computational and scientific
methods in the literature that are most suitable for im-
plementing the solution are identified and discussed.
The definition of requirements and the initial system
architecture are outlined.
Step 7: Prototyping the Solution - Type 2. The
researchers, specialists in artificial intelligence, im-
plement the computational framework conceptualized
in Step 6 as a Minimum Viable Product (MVP). The
MVP is a functional version of the solution with ba-
sic functionalities sufficient for initial tests and vali-
dations. This step includes selecting and identifying
databases, developing AI algorithms, system integra-
tion, and preliminary testing.
4 DETAILED EXECUTION:
PHASE GUIDE
A detailed guide on the applicability of the methodol-
ogy defined in Section 3 is presented below.
4.1 Survey
The development of the survey was based on the aca-
demic experience of the project team, as no specific
survey was identified in the literature. At the grantor’s
request, a preamble to the survey was prepared, with
guidelines for the application and use of AI mod-
els in public administration. The preamble includes
content on the premises for preparing guidelines, the
definition of generative AI, applications of generative
AI in government, and the limitations of generative
AI and large language models (LLMs). This survey
was carefully designed to accommodate varying lev-
els of AI maturity in agencies, aiming to collect spe-
cific knowledge about public sector processes related
to problems and needs that can be framed as strategic
projects and addressed with AI-based solutions.
WEBIST 2024 - 20th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
94

4.2 AHP Express
The Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) is a multicri-
teria decision-making method that uses hierarchical
or network structures to represent a decision problem
and develops priorities for the alternatives based on
the decision maker’s judgments (Saaty, 1987). AHP
should be understood as a facilitator, a thought struc-
turing process, rather than an algorithm that solves
problems (Colin, 2007). According to (Colin, 2007),
the application of the AHP comprises four phases:
1. Hierarchy representation: involves the develop-
ment of the decision hierarchy that relates the various
levels of interrelated elements. 2. Pairwise compar-
isons: includes evaluating preferences for each deci-
sion element at a given hierarchy level. 3. Eigen-
vector method: encompasses using the eigenvector
method to estimate the relative weights of decision el-
ements at a particular level and assess the consistency
of preferences established in pairwise comparisons.
4. Aggregation of priorities: concerns the aggre-
gation of relative priorities to evaluate the outcome
related to the objective.
In addition to the formula for calculating the in-
consistency of judgments and the maximum accept-
able level, (Saaty, 1977) indicates that when there are
comparisons involving more than nine elements, the
expectation is that consistency will be low. In line
with the proposal of (Saaty, 2006), Step 2 - Elimina-
tion was devised by the authors of this paper for cases
involving more than nine alternatives.
The step-by-step application of the AHP Express
method is detailed in (Leal, 2020). It follows the prin-
ciples of traditional AHP, whose framework can be
seen in (Saaty, 1987; Colin, 2007). The main dif-
ference is that, as the AHP Express method assumes
judgment consistency, there is no need to calculate in-
consistency. From the judgment of the preferred al-
ternative, obtaining the values of the other pairwise
comparisons through the relationship established in
the initial judgment line is possible. The AHP Ex-
press method was chosen for being suitable for the
agile project management model.
4.2.1 Elimination
This phase was developed to address two main objec-
tives: firstly, to eliminate AI project proposals identi-
fied during the Survey phase that are deemed infeasi-
ble, and secondly, to classify the remaining proposals
according to their maturity levels in descending order.
A set of criteria and sub-criteria were established to
achieve these goals, comprising a suitable model for
an AI solution. AI specialists, including the authors
of this study, initially formulated these criteria and
subsequently refined them through input from stake-
holders within the NIA. Notable contributors included
leaders from SGD/MGI, MCTI, Enap, Finep, Serpro,
Dataprev and other entities.
Table 1 (Appendix) outlines the specific criteria
and sub-criteria utilized to assess the feasibility of
each project proposal for AI implementation. These
criteria encompass technical feasibility, data require-
ments, proposed solutions, societal impact, and strate-
gic alignment. Possible answers to the questions are:
YES NO I DON’T KNOW
• If any proposal receives a “NO” response for any
sub-criteria, it is automatically eliminated from
the process.
• “YES” responses are scored as “1”.
• “I DON’T KNOW” responses are scored as “0”.
• All proposals must pass through this elimination
phase.
• At the end, the scores of the proposals will be
summed-up and placed in descending order.
Initially, the nine highest-scoring projects will be
considered for the AHP-Classifier step, as these indi-
cate higher maturity levels. If there is a tie among the
top nine, the criteria weights can be adjusted based
on stakeholder input. It is recommended that weights
be adjusted only in the case of a tie, with the most
relevant criterion assigned a weight of 2.
4.2.2 AHP Express Classifier
The criteria used in the AHP-Express method to clas-
sify/select AI projects from each Government area
are described below. Although only the criteria were
scored, since the methodology needed to be adapted
for agile project management, they were described
through sub-criteria presented to stakeholders during
the AHP application interviews.
1. Urgency of Solution: Time to solve the problem
without AI: How long will it take without AI? Impact
of delay: What are the consequences of not address-
ing the problem? Future urgency: Will the problem
become more urgent?
2. Availability of Data Sources: Internal data qual-
ity: Are internal data reliable? Cost of external data:
How much will external data acquisition cost? Time
to acquire external data: How long will it take?
3. Broader Population Reach: People impacted:
How many people will be affected? Geographical
reach: Will the AI solution be available nationwide?
Accessibility: Will it be accessible across income lev-
els and digital skills?
Implementing AI for Enhanced Public Services Gov.br: A Methodology for the Brazilian Federal Government
95

4. Greater User Value: User benefits: What advan-
tages does the AI provide? User satisfaction: Is it
user-friendly and does it meet needs? Time saved:
How much time will users save?
5. Projected Access Volume - Cost Estimate: Es-
timate per period: What is the estimated access vol-
ume? Growth curve: How is access expected to grow?
Seasonality: Is demand seasonal?
6. Lower Technical Effort: Problem complex-
ity: Does the problem need advanced AI techniques?
Tools and libraries: Are there tools available for de-
velopment? Expertise: Is there AI expertise? Repli-
cability: Can the solution be used for other problems?
Maintenance: Is maintenance challenging?
7. Ease of Implementation: System integration:
Does the solution integrate with existing systems?
Regulation: Is it compliant with laws?
8. Risks, Ethics, and LGPD: Are risks mapped? Are
there ethical concerns? How does LGPD impact the
solution?
Meetings with process stakeholders are essential
for applying AHP Express. It is recommended to hold
three meetings for each segment (Area, Department,
Ministry): one with expert researchers, one with seg-
ment members, and one with the SGD group, each
consisting of two to four members.
The process starts with presenting up to nine
project proposals from Step 2 - Elimination, the eight
criteria, the Saaty Scoring Table, and a brief expla-
nation of the dynamics. Participants first assess the
importance of each criterion in response to the ques-
tion “Which AI project should be selected?” and then
evaluate each project based on these criteria. AHP
Express uses the Saaty scale (1-9), where one indi-
cates equal preference, and nine indicates extreme
preference.
4.3 Problem Framing
To carry out this step, a meeting was held with the
individuals most directly involved with the identified
and prioritized problem, including people from vari-
ous areas since the problem is cross-functional. These
participants were instructed beforehand to identify the
causes and characteristics of the problem, enabling
a fruitful conversation and ensuring everyone under-
stood its context and relevant aspects. Considering
the project’s objective, the availability of data is es-
sential. Databases with relevant data were analyzed to
illustrate the problem, and the currently implemented
solution was examined to identify strengths and areas
for improvement.
4.4 Design Sprint
Three of the five traditional Design Sprint steps were
carried out in two days, with a multidisciplinary team
(the Squad) - made up of people involved in the
problem: Understand/Map, Sketch, and Decide. In
“Understand/Map”, the long-term objectives were de-
fined, the questions established for the Sprint were an-
swered, the user map was created, interviews with ex-
perts were carried out, and the target user was defined.
In “Sketch”, there was a division into two groups,
which analyzed all available information and came
up with proposals – the entire group analyzed this in
“Decide”, arriving at a solution definition.
4.5 Prototyping
This step pertains to the mapping and development of
prototypes considering the agile approach in a demon-
stration environment and the documentation of AI
solutions obtained in Step 5. The experimentation
through prototyping aims to evaluate the feasibility
of an MVP solution. The requirements and specifica-
tions will be developed closely with the requesting en-
tity during the design sprint phase. The Type 2 proto-
type, conceived in Step 6, is delivered through Python
code, developed in a controlled environment that sim-
ulates the user’s real-world problem. This prototype
accompanies a detailed technical report and a presen-
tation for the main stakeholders and interested parties.
4.6 Validation
Validating AI solutions in the public sector demands
a rigorous approach to ensure effectiveness and ef-
ficiency. This paper describes the validation pro-
cess of an MVP prototype for an interactive chatbot
providing information and virtual addresses for pub-
lic agency services. MVP validation for AI applica-
tions, like chatbots, requires a systematic process that
combines functionality tests, user evaluations in con-
trolled settings, and real-world deployments. Robust
development, testing, and monitoring tools are es-
sential for successful validation and final implemen-
tation, ensuring the solution effectively meets user
needs.
The process begins by defining the chatbot’s ob-
jectives and success criteria, measured by metrics
such as correct response rate, interaction time, and
user feedback. Internal tests validate functionality,
including conversation flow and database integration.
This is followed by user testing in controlled envi-
ronments, gathering qualitative and quantitative feed-
back for improvements. Adjustments are made be-
WEBIST 2024 - 20th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
96

fore large-scale deployment. The chatbot is then beta-
tested in a real environment, where performance is
monitored through continuous user feedback. After
validation, a crucial monitoring plan is established to
ensure the chatbot adapts to new demands and up-
dates, maintaining its effectiveness.
Based on its specifications, the prototype’s user
interface is also designed for evaluation. This struc-
tured approach ensures AI solutions meet technical
and operational standards and are validated under
near-real conditions, providing a foundation for large-
scale implementations.
5 RESULTS
This study proposes an innovative methodology for
improving Brazilian public services using AI, as out-
lined earlier. Developed in collaboration with SGD
members, AI researchers, the authors, and NIA col-
laborators, this methodology follows the steps de-
tailed in Section 3. Below are the results from each
step of its application.
Initially, discussions between project executors
and stakeholders determined that the Executive Sec-
retaries of the Ministries would select the agencies for
the survey. To ensure the survey was comprehensive
and precise, we meticulously crafted 16 open-ended
questions, focusing on the Service Context, Problem
Characterization, AI Needs, and AI Solution.
The survey was conducted in the Department of
Digital Public Service Platforms (DESER) of SGD,
and three project proposals were raised. Subse-
quently, four people from the General Coordination
of Automation and Service (CGATE), two AI profes-
sors, a facilitator professor, and SGD staff carried out
the elimination step, in which all three projects passed
the filter. After the filter, the process proceeded to
the AHP Express. Three groups of respondents were
interviewed for the application of AHP Express: 1)
professors specialized in AI, 2) SGD public servants,
and 3) public servants from the originating area of the
proposal/demand. The respondent teams consisted of
2 to 4 participants. Each stakeholder from each group
had their response recorded during an interview, in
which the questions contained in Table 1 were asked.
In the AHP Classification, the three projects selected
in Step 2 were analyzed:
• Automated Recovery of the Gov.br Account ac-
cess
• CGATE citizen support channels
• Citizen support channel for public services on the
Gov.BR Portal
These projects focus on the need for high citizen
interaction through digital platforms, particularly the
Gov.br Portal. Consequently, the classification pro-
cess results highlight the importance of impacting a
large portion of the population. The three groups
evaluated the projects based on the criteria in Sec-
tion 4.2.2. The final AHP Express results, detailed in
Figure 3, represent the geometric means of the three
scores for each criterion. The project “Citizen service
channel for public services on the Gov.br Portal” was
selected for the prototyping phase.
Figure 3: AHP Express Result.
The Problem Framing and Design Sprint steps
were conducted as described in Sections 4.3 and 4.4.
As a result, after the Problem Framing of Problem 3,
the following answers were reached for Problem 3:
• Where do we want to be in 1 year? Increase
public service engagement rate by 100% through
Gov.Br.
• What is the product? Generative AI chatbot.
• What does the product do? Assists and answers
citizens’ questions about the public service they
need and directs them to the service page.
• What problem is the team trying to solve with
the product? Better direct citizens to the service
they are looking for.
• Who currently uses the product, and who
would we like to use it? Citizens (Gov.br users).
• What is the best phrase to communicate the
long-term goal? Reduce requests to support
channels: Gov account support and ombudsman
by 25%.
The prototyping will involve developing an Ad-
vanced Generative Agent to interact with citizens on
the Gov.br Portal, assisting, clarifying doubts, and di-
recting them to the appropriate service pages. Proto-
typing will occur in two steps, as outlined in Section
4.5. Below are the results of the strategy and archi-
tecture developed by AI experts and stakeholders for
this generative agent:
Data Collection and Structuring: Identify and or-
ganize data communication. Attach and restructure
additional information. Summarize documents. Pro-
pose a FAQ document.
Document Processing: Extract text, topics, key-
words, and structure using document intelligence
tools (e.g., Azure).
Implementing AI for Enhanced Public Services Gov.br: A Methodology for the Brazilian Federal Government
97

Vector Database: Generate semantic chunking with
layout. Create embeddings. Organize the database by
themes and problems. Define indexes in the vector
database.
Prompt Embedding: Define settings for the genera-
tive agent to communicate inclusively with polite, ac-
cessible language tailored to different user profiles.
Specify topics the agent won’t respond to, such as po-
litical matters or prejudices. Provide examples for In-
context Learning, like step-by-step guides for public
services, responses about losing Gov.br access, pro-
cesses needing human intervention, and complaint in-
structions. Enable human overflow by offering sup-
port links, operating hours, and contact info. Ensure
system status is informed to users before starting a
conversation.
Advanced Semantic Search: To enhance the gen-
erative agent’s precision, a specific LLM, LLaMA,
trained on a Portuguese-language database, will be
used. This model will optimize Retrieval-Augmented
Generation with Fine-Tuning (RAFT) (Zhang and
et al., 2024), combining supervised fine-tuning with
RAG (Lewis and et al., 2020). RAFT adjusts train-
ing data for better question responses using Chain-of-
Thought reasoning from specific documents, enhanc-
ing RAG by integrating external database retrieval
with pre-trained models.
The proposed RAFT solution, which combines su-
pervised fine-tuning with RAG, introduces an inno-
vative approach to improving the accuracy of inter-
actions between generative AI and citizens. Validat-
ing a chat intelligent agent with an LLM includes
testing its functionality, performance, user experi-
ence, domain-specific knowledge, ethical considera-
tions, benchmark comparisons, and ongoing monitor-
ing to ensure it meets requirements and provides sat-
isfactory interactions (Xi et al., 2023). At the time of
writing, Step 8 is under development, as described in
Section 4.6.
6 DISCUSSION
This paper presents a comprehensive methodology for
deploying AI solutions in public services, incorpo-
rating Lean Office waste elimination methods, pro-
cess optimization, and standardization before evaluat-
ing workflow automation. Once automated, a contin-
uous improvement (kaizen) loop optimizes the NLP
chatbot’s workflow. Digitization enables the automa-
tion of standardized processes, eliminating waste and
embedding intelligence through smarter control algo-
rithms. Key questions addressed include the link be-
tween operational excellence in public administration
and AI in workflows and the driving forces behind im-
proved performance and efficiency in public services
through AI.
Beyond portal access benefits, the Brazilian gov-
ernment can gain additional advantages. Using Webo-
metrics (Saeidnia et al., 2024), interactions between
citizens and the generative agent will produce valu-
able data. Authorities can leverage this to:
• Identify patterns in citizen behavior, needs, and
preferences.
• Understand popular services and common com-
plaints.
• Create data-driven public policies.
• Personalize services and improve efficiency.
• Monitor service trends and conversion rates for
successful demand resolutions.
• Enhance metrics for “Gov.br” portal usage.
Data privacy and security are crucial when apply-
ing AI in public administration. The information col-
lected covers healthcare, smart cities, and public ser-
vice forecasting at varying levels of maturity. These
challenges emphasize the need for robust safeguards
to protect sensitive data and ensure adherence to data
protection regulations.
Other projects have been selected using the pro-
posed methodology across different agencies and sec-
retariats. To harmonize the selection process at a na-
tional level, one option is to apply uniform weights
to all criteria for each project. This would standard-
ize the selection process, ensuring that each crite-
rion is equally evaluated from a national perspective
rather than from an individual secretariat’s viewpoint.
Consequently, the process would better align with
the broader objective: identifying which AI project
should be prioritized for Brazil as a whole.
7 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
WORK
This paper presented an innovative methodology for
implementing AI solutions in Brazilian public ser-
vices, aimed at enhancing efficiency, accessibility,
and service quality. Integrating Lean Office, Design
Sprint, and advanced AI techniques, the methodology
is both flexible and adaptable to diverse governmen-
tal needs, ensuring inclusivity. Collaboration among
AI experts, public servants, and stakeholders was key
to ensuring technical feasibility and alignment with
public policies.
WEBIST 2024 - 20th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
98

The methodology addresses a specific demand
from the SGD, part of the National Digital Gov-
ernment Strategy. Given Brazil’s numerous federal
agencies, it includes the selection and prototyping of
projects within a complex government structure. Its
flexibility allows application in other countries with
extensive governmental frameworks, promoting digi-
tal transformation in varied contexts.
The development of a generative agent for the
Gov.br Portal meets the demand and transforms cit-
izen interactions into valuable data. This data pro-
vides insights for personalizing services. We propose
using LLaMA X, trained on Portuguese documents,
with RAFT for improved accuracy. Future work in-
cludes developing a ChatGPT-based AI for compar-
ison and exploring integrations with programs like
Bolsa Fam
´
ılia and systems such as CPF (Social Secu-
rity Number), CNPJ (National Registry of Legal En-
tities), SEI (Electronic System of Information), and
institutions payroll.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Acknowledgments and recognition are extended to
the Ministry of Management and Innovation in Public
Services, especially the Secretaria de Governo Digi-
tal (SGD), for financially supporting this project and
enabling the practical feasibility of solution identifi-
cation and prototyping.
REFERENCES
Anna, U. (2023). Artificial intelligence landscape in south
america. AARMS–Academic and Applied Research in
Military and Public Management Science, 22(1):101–
114.
Atabekov, A. (2023). Artificial intelligence in contempo-
rary societies: legal status and definition, implemen-
tation in public sector across various countries. Social
Sciences, 12(3):178.
Bardwell, L. V. (1991). Problem-framing: A perspective on
environmental problem-solving. Environmental Man-
agement, 15(5):603–612.
Birhane, A., Kalluri, P., Card, D., Agnew, W., Dotan, R.,
and Bao, M. (2022). The values encoded in machine
learning research. In Proceedings of the 2022 ACM
Conference on Fairness, Accountability, and Trans-
parency, pages 173–184.
Blount, K. (2024). Using artificial intelligence to prevent
crime: implications for due process and criminal jus-
tice. AI & SOCIETY, 39(1):359–368.
BRASIL (2023). Decreto Nº 11.437, de 17 de marc¸o
de 2023. https://www.planalto.gov.br/ccivil 03/
ato2023-2026/2023/decreto/D11437.htm#art5. [On-
line; accessed 27-June-2024].
BRASIL, M. d. C. T. e. I. (2018). Estrat
´
egia Brasileira
para a Transformac¸
˜
ao Digital. https://www.gov.br/
mcti/pt-br/centrais-de-conteudo/comunicados-mcti/
estrategia-digital-brasileira/estrategiadigital.pdf.
BRASIL, M. d. G. e. I. e. S. P. (2024). Servic¸os e
informac¸
˜
oes do brasil. https://www.gov.br/pt-br. Ac-
cessed: 27 June 2024.
BRASIL, Minist
´
erio da Ci
ˆ
encia, T. e. I. (2021). Estrat
´
egia
brasileira de intelig
ˆ
encia artificial: Ebia. https://bit.
ly/3C6LgY4.
Chen, T., Gasc
´
o-Hernandez, M., and Esteve, M. (2024).
The adoption and implementation of artificial intelli-
gence chatbots in public organizations: Evidence from
us state governments. The American Review of Public
Administration, 54(3):255–270.
Chen, Y.-C., Ahn, M. J., and Wang, Y.-F. (2023). Arti-
ficial intelligence and public values: value impacts
and governance in the public sector. Sustainability,
15(6):4796.
Cohen, S., Manes Rossi, F., and Brusca, I. (2023). Debate:
Public sector accounting education and artificial intel-
ligence. Public Money & Management, 43(7):725–
726.
Colin, E. C. (2007). Pesquisa operacional: 170 aplicac¸
˜
oes
em estrat
´
egia, financ¸as, log
´
ıstica, produc¸
˜
ao, market-
ing e vendas. Livros T
´
ecnicos e Cient
´
ıficos.
Desordi, D. and Della Bona, C. (2020). A intelig
ˆ
encia arti-
ficial e a efici
ˆ
encia na administrac¸
˜
ao p
´
ublica. Revista
de Direito, 12(02):01–22.
Dwivedi, Y. K., Sharma, A., Rana, N. P., Giannakis, M.,
Goel, P., and Dutot, V. (2023). Evolution of artifi-
cial intelligence research in technological forecasting
and social change: Research topics, trends, and fu-
ture directions. Technological Forecasting and Social
Change, 192:122579.
Engstrom, D. F., Ho, D. E., Sharkey, C. M., and Cu
´
ellar,
M.-F. (2020). Government by algorithm: Artificial
intelligence in federal administrative agencies. NYU
School of Law, Public Law Research Paper, (20-54).
Fan, Z., Yan, Z., and Wen, S. (2023). Deep learning and ar-
tificial intelligence in sustainability: a review of sdgs,
renewable energy, and environmental health. Sustain-
ability, 15(18):13493.
Faria, A. V. A., de Melo, M. K., de Oliveira, F. A. R.,
Weigang, L., and Celestino, V. R. R. (2022). Auto-
mated slr with a few labeled papers and a fair work-
load metric. In International Conference on Web
Information Systems and Technologies, pages 1–23.
Springer.
Filgueiras, F. and Junquilho, T. A. (2023). The brazilian
(non) perspective on national strategy for artificial in-
telligence. Discover Artificial Intelligence, 3(1):7.
Gaspar, W. B. and Mendonc¸a, Y. C. d. (2021). A in-
telig
ˆ
encia artificial no brasil ainda precisa de uma es-
trat
´
egia.
Gov, A. (2024). Gov.br
´
e a p
´
agina de
governo mais acessada do mundo.
Implementing AI for Enhanced Public Services Gov.br: A Methodology for the Brazilian Federal Government
99

https://agenciagov.ebc.com.br/noticias/202403/gov-
br-e-a-pagina-de-governo-mais-acessada-do-mundo.
Accessed: 27 June 2024.
Guedes, L. and J
´
unior, M. O. (2024). Artificial intelligence
adoption in public organizations: a case study. Fu-
ture Studies Research Journal: Trends and Strategies,
16(1):e860–e860.
Jevinger,
˚
A., Zhao, C., Persson, J. A., and Davidsson,
P. (2024). Artificial intelligence for improving pub-
lic transport: a mapping study. Public Transport,
16(1):99–158.
Kitsios, F., Kamariotou, M., and Mavromatis, A. (2023).
Drivers and outcomes of digital transformation: The
case of public sector services. Information, 14(1):43.
Knapp, J., Zeratsky, J., and Kowitz, B. (2016). Sprint: o
m
´
etodo usado no Google para testar e aplicar novas
ideias em apenas cinco dias. Editora Intr
´
ınseca Ltda.
Kubota, L. C. and Rosa, M. B. (2024). Intelig
ˆ
encia
artificial no brasil: Adoc¸
˜
ao, produc¸
˜
ao cient
´
ıfica
e regulamentac¸
˜
ao. digitalizac¸
˜
ao e tecnologias da
informac¸
˜
ao e comunicac¸
˜
ao. Digitalizac¸
˜
ao e tecnolo-
gias da informac¸
˜
ao e comunicac¸
˜
ao: oportunidades e
desafios para o Brasil. Rio de Janeiro: Ipea.
Kutyauripo, I., Rushambwa, M., and Chiwazi, L. (2023).
Artificial intelligence applications in the agrifood sec-
tors. Journal of Agriculture and Food Research,
11:100502.
Larusdottir, M., Roto, V., and Cajander, A. (2021). Intro-
duction to user-centred design sprint. In Ardito, C.
e. a., editor, Human-Computer Interaction – INTER-
ACT 2021, volume 12936 of Lecture Notes in Com-
puter Science, pages 283–293. Springer, Cham.
Leal, J. E. (2020). Ahp-express: A simplified version of the
analytical hierarchy process method. MethodsX, 7.
Lemes, M. M. and Lemos, A. N. L. E. (2020). O uso
da intelig
ˆ
encia artificial na sa
´
ude pela administrac¸
˜
ao
p
´
ublica brasileira. Cadernos Ibero-Americanos de Di-
reito Sanit
´
ario, 9(3):166–182.
Lewis, P. and et al. (2020). Retrieval-augmented genera-
tion for knowledge-intensive nlp tasks. In Advances in
Neural Information Processing Systems, volume 33,
pages 9459–9474.
Maragno, G., Tangi, L., Gastaldi, L., and Benedetti, M.
(2023). Exploring the factors, affordances and con-
straints outlining the implementation of artificial in-
telligence in public sector organizations. International
Journal of Information Management, 73:102686.
Mendonc¸a de S
´
a Ara
´
ujo, C. M., Miranda Santos, I.,
Dias Canedo, E., and Favacho de Ara
´
ujo, A. P. (2019).
Design thinking versus design sprint: A comparative
study. In Marcus, A. and Wang, W., editors, Design,
User Experience, and Usability. Design Philosophy
and Theory, volume 11583 of Lecture Notes in Com-
puter Science, pages 335–344. Springer, Cham.
Neumann, O., Guirguis, K., and Steiner, R. (2024). Explor-
ing artificial intelligence adoption in public organiza-
tions: a comparative case study. Public Management
Review, 26(1):114–141.
Nonato, S. D. O., de Souza Figueiredo, S. d. S.,
de Melo Alves, C. A., and Dias, C. N. (2024).
Cooperac¸
˜
ao interorganizacional em planos es-
trat
´
egicos de intelig
ˆ
encia artificial: uma an
´
alise
comparativa. Future Studies Research Journal:
Trends and Strategies, 16(1):e838–e838.
OECD.AI (2022). Ai use case in the public sector. Re-
trieved on 29-Jun-2024.
Robertson, S. I. (2016). Problem Solving: Perspectives from
Cognition and Neuroscience. Psychology Press, 2nd
edition.
Rocha, C. A. A., Weigang, L., Dib, M. V. P., Faria, A. V. A.,
Cajueiro, D. O., de Melo, M. K., and Celestino, V.
R. R. (2022). Leveraging transfer learning for long
text classification with limited data. In International
Conference on Web Information Systems and Tech-
nologies, pages 98–120. Springer.
Saaty, R. W. (1987). The analytic hierarchy process—what
it is and how it is used. Mathematical Modelling,
9(5):161–176.
Saaty, T. L. (1977). A scaling method for priorities in hier-
archical structures. Journal of Mathematical Psychol-
ogy, 15.
Saaty, T. L. (2006). Rank from comparisons and from rat-
ings in the analytic hierarchy/network processes. Eu-
ropean Journal of Operational Research, 168(2):557–
570.
Saeidnia, H. R., Hosseini, E., Abdoli, S., and Ausloos, M.
(2024). Unleashing the power of ai: a systematic re-
view of cutting-edge techniques in ai-enhanced scien-
tometrics, webometrics and bibliometrics. Library Hi
Tech.
Samoili, S., Cobo, M. L., G
´
omez, E., De Prato, G.,
Mart
´
ınez-Plumed, F., and Delipetrev, B. (2020). Ai
watch. defining artificial intelligence. towards an op-
erational definition and taxonomy of artificial intelli-
gence.
Scutella, M., Plewa, C., and Reaiche, C. (2024). Vir-
tual agents in the public service: examining citizens’
value-in-use. Public Management Review, 26(1):73–
88.
Straub, V. J., Morgan, D., Bright, J., and Margetts, H.
(2023). Artificial intelligence in government: Con-
cepts, standards, and a unified framework. Govern-
ment Information Quarterly, 40(4):101881.
Wang, C., Han, B., Patel, B., and Rudin, C. (2023). In pur-
suit of interpretable, fair and accurate machine learn-
ing for criminal recidivism prediction. Journal of
Quantitative Criminology, 39(2):519–581.
Xi, Z., Chen, W., Guo, X., He, W., Ding, Y., Hong, B.,
Zhang, M., Wang, J., Jin, S., Zhou, E., et al. (2023).
The rise and potential of large language model based
agents: A survey. arXiv preprint arXiv:2309.07864.
Yu, K.-H., Beam, A. L., and Kohane, I. S. (2018). Artifi-
cial intelligence in healthcare. Nature biomedical en-
gineering, 2(10):719–731.
Zhang, T. and et al. (2024). Raft: Adapting lan-
guage model to domain specific rag. arXiv preprint
arXiv:2403.10131.
WEBIST 2024 - 20th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
100

APPENDIX
Table 1: Criteria and Subcriteria for Feasibility of AI Implementation in Public Services.
Criteria Subcriteria
1- Is There Technical Feasibility?
a. Cost: The AI solution’s development, implementation, and mainte-
nance are economically viable.
b. Time: The solution can be implemented within the PBIA timeline;
c. Maintenance: The AI solution is feasible to maintain and update;
d. Operationalization: Necessary resources for implementation (human,
material, infrastructure) are available;
2- Will the data not be a limiting
factor for the model?
a. Data Quality: Some data patterns can be learned to help solve the
problem;
b. Data Quality: The available data tend to be sufficiently accu-
rate, complete, and reliable once preprocessed so as not to impede the
progress of the project;
c. Data Quantity: There is sufficient data to train and test the AI solu-
tion.
d. Data Diversity: The data significantly represent the target popula-
tion’s characteristics.
3- Can AI improve the solution?
a. Effort: The current solution to the problem is unsatisfactory, and the
AI-based solution will increase process efficiency.
b. Effort: The solution cannot be found using simple rules (e.g., through
spreadsheets, If..else) or basic statistical analysis.
c. Effort: There is a need for prediction, classification, or the use of
language models (like ChatGPT) based on input data.
d. Measurability: The outcome of the process and/or service is measur-
able.
4- Will there be a good Impact on
society?
a. Benefits: The AI solution will bring real benefits to society, either
directly or indirectly through improved management;
b. Threats: The AI solution considers and mitigates negative impacts
on society;
c. Acceptance: The AI solution will be accepted by society;
d. Regulation: The AI solution complies with existing laws and regula-
tions.
5- Is it in line with Strategic Align-
ment?
a. Alignment with the organisation’s mission: The AI solution aligns
with the organisation’s mission;
b. Strategic priorities: The AI solution contributes to the organisation’s
strategic priorities;
c. Reputation risk: The AI solution will not harm the organisation’s
reputation;
d. Governance: The solution contributes to advancing specific public
policies and government-established goals.
Implementing AI for Enhanced Public Services Gov.br: A Methodology for the Brazilian Federal Government
101
