
How Organizational Improvisational, Transformational Leadership
Styles Impact Innovation Performance of Start-Up Companies in
VUCA Environments
Wenxi Xiong
a
and Yongzhong Yang
Business School, Sichuan University, China
Keywords: Organizational Improvisation, Transformational Leadership, Start-Ups, Innovation Performance.
Abstract: Entering the competitive VUCA environment, the traditional management model with prediction and control
as the main measures has not adapted to the needs of the times in certain situations, and it has become a hot
topic for start-ups to survive and grow in the current unpredictable environment and achieve breakthrough
innovation. This study constructs a correlation model between organizational improvisation, transformational
leadership, and innovation performance of start-ups, and uses the VUCA environment as a moderating
variable. The findings confirm that all dimensions of organisational improvisation and transformational
leadership significantly affect the innovation performance of start-ups; Organizational improvisation and
transformational leadership positively interact to influence innovation performance of start-ups, i.e.
organizational improvisation and transformational leadership reinforce each other's influence on innovation
performance of start-ups; The VUCA environment positively moderates the impact of organizational
improvisation and transformational leadership on innovation performance of start-ups. This study will help
start-ups to fully grasp the fleeting opportunities and respond to the changing external environment in a timely
manner to further enhance the competitive advantage of start-ups, and provide practical guidance for top
managers of start-ups to enhance their innovation performance.
1 INTRODUCTION
The international situation is characterized by
"Volatility", "Uncertainty", "Complexity" and
"Ambiguity". VUCA environment characteristics are
becoming more and more obvious. Under the VUCA
era environment, how start-ups can turn crisis into
safety, survive and grow in the crisis has become an
issue of concern for all sectors of society.
The first thing that start-ups in dynamically
changing environments need to do to achieve
sustainable and healthy growth is to change the
decision-making paradigm away from the traditional
strategic thinking of planning, execution, feedback
and review, and to think and act, practice and
improve, innovate and integrate with more flexible
and improvised strategies (Tang & Zhou, 2017).
The concept of organizational improvisation
refers to the key elements of an organization's
strategic actions in a complex environment, and it
differs from the traditional strategic decision-making
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0005-5551-3959
model in that it integrates planning, decision-making,
and execution. Organizational improvisation can help
organizations better complete the decision-making
process when unexpected events or changes in the
environment deviate from expectations.
Organizational improvisation also reflects the
richness of a leader's experience, judgment, and
decisiveness.
Weick (1993) points out that transformational
leaders give their employees more autonomy and
encourage them to think outside the box and promote
improvisation. In today's competitive world,
transformational leaders are one of the most
responsive types of leaders and are valued more than
ever for building strong confidence through advance
learning and preparation, and for learning by
experience without fear of failure, so that
organizations can adjust quickly in a VUCA
environment, calming immediate fluctuations while
making intuitive and rational decisions to seize future
opportunities.
Xiong, W. and Yang, Y.
How Organizational Improvisational, Transformational Leadership Styles Impact Innovation Performance of Start-Up Companies in VUCA Environments.
DOI: 10.5220/0012997300003838
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 16th International Joint Conference on Knowledge Discovery, Knowledge Engineering and Knowledge Management (IC3K 2024) - Volume 3: KMIS, pages 295-304
ISBN: 978-989-758-716-0; ISSN: 2184-3228
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
295

Based on this, this paper will focus on the
relationship between organizational improvisation,
transformational leadership and innovation
performance of start-ups, and explore the
mechanisms of organizational improvisation and
transformational leadership on innovation
performance of start-ups.
2 BACKGROUND OF THE
STUDY
VUCA was first proposed by the U.S. military to
describe the complex and changing military
environment at that time, and with the development
of information technology such as big data, artificial
intelligence and cloud computing, as well as the
constant changes in the international market, the
external environment in which the organization
operates has become more and more characteristic of
VUCA. Bennett & Lemoin (2014) mentioned VUCA
as "Volatility", "Uncertainty", "Complexity",
"Ambiguity" in " Harvard Business Review", which
will become a trend in the future, and explains its
meaning. Troise et al.(2022) used digital
technological capabilities, relational capabilities, and
innovative capabilities premised on organizational
agility - the ability to quickly anticipate or respond to
external changes - is critical to surviving and
competing in today's turbulent VUCA environment
characterized by technological advancement and
digitalization.
The study of improvisation first began with jazz
metaphors, so early research on organizational
improvisation was mainly based on the perspective of
jazz metaphors. Through specific studies, researchers
attempted to summarize the characteristics of the
concept of improvisation in jazz improvisation,
differentiate the degree and form of improvisation,
explore the mechanisms of improvisational
behaviors, and discover the role of improvisational
metaphors in jazz performances in organizational
practices. Weick (1998) firstly blended improvisation
with organizational management by observing top
managers and found that they would, like jazz
musicians, identify and aim at the goals and make and
follow rules, engage in directed activities, and
suggested characteristics of groups with high
improvisation skills. When improvisation is
combined with team and environmental moderators,
it has a positive impact on team innovation, as well as
suggesting that organizational members can improve
their improvisational skills through training. Fultzz &
Hmieleski (2021) established a model linking
organizational improvisation with new venture
performance, demonstrating that improvisation
ability is a resourceful means for startups to identify
new opportunities and gain performance advantages.
For the transformational leadership research. At
the individual level, the main areas involved are job
performance, job satisfaction, employee happiness,
individual knowledge sharing, employee creativity,
employee emotions, and self-coordination. Stanescu
et al. (2019) point out the positive and significant
relationship between transformational leadership and
employee innovative behavior and psychological
empowerment by creating a greater sense of
empowerment, leaders can have a higher positive
impact on the employee's level of employee
innovation. At the organizational level, current
research focuses on the study of transformational
leadership on organizational performance. Ng (2017)
developed an integrative model using five theoretical
driving mechanisms to explain the impact of
transformational leadership on performance
outcomes. Mach et al. (2021) explored how
transformational leadership affects team performance
through team cohesion and how this relationship is
moderated by prior team performance. The results of
the study indicated that transformational leadership
indirectly affects team performance through the
mediating role of team cohesion, and that when the
level of prior performance is high, the this indirect
effect is more significant.
In exploring the relationship between work
environment and creativity, Amabile (1996)
suggested that an innovative organizational climate
promotes team support, which in turn promotes
innovation. Scott & Bruce (1994) and Xie et al.
(2007) argued that an innovative culture within an
organization has a positive impact on performance in
new tasks. The latter's empirical study found that a
good innovation culture can improve the business
quality and innovation level of the organization,
which in turn can help firms to better improve their
performance level. Leadership behavior is another
important factor in influencing innovation
performance. Scott (2011) supported this view by
showing that innovative leadership behaviors are
believed to promote an innovative and creative
climate in the organization, which, in turn, improves
employees' innovation ability. Wang (2021) points
out that when individual employees have a higher
degree of forgetfulness, it is more conducive to digital
transformation to promote organizational innovation
performance through dynamic capabilities.
KMIS 2024 - 16th International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Systems
296

In a VUCA environment filled with turbulence,
disruption and uncertainty, start-ups are actively
implementing change and innovation to cope with
various changes, but encountering many difficulties
and resistance in the process. These dilemmas of
change and innovation have received increasing
attention in management practices and theoretical
studies, and have become the focus of attention for
academics, researchers and managers. However, the
current empirical research is still in a relatively
imperfect stage, the existing research is not deep and
systematic enough, and scholars and practitioners
need to further integrate the research on
transformational leadership and innovation
performance. Meanwhile, scholars need to further
integrate research on organizational change and
innovation behavior and consider how to enhance
transformational leadership in the spirit of
organizational improvisation to promote innovation
in startups; on the other hand, practitioners consider
how to systematically introduce the theory of
enhancing transformational leadership into the
process of organizational improvisation. Overall, the
relationship between organizational improvisation,
transformational leadership, and innovation
performance of start-ups in VUCA environments
does not seem to have been systematically studied in
academia.
To sum up, there are still certain black holes and
deficiencies in the academic research on the related
concepts, for example, the lack of integrated research
on the relationship between organizational
improvisation, transformational leadership and
innovation performance, and the failure to organically
combine the VUCA environment with organizational
change and innovation management. Based on this,
this paper will focus on the relationship between
organizational improvisation, transformational
leadership and innovation performance, and explore
the mechanism of organizational improvisation and
transformational leadership on the new performance
of start-ups under the VUCA environment.
3 THEORETICAL MODEL AND
RESEARCH
HYPOTHESISSECTION
HEADINGS
3.1 Theoretical Model
In the VUCA environment, it brings great impact to
the survival, competition and development of start-
ups. Faced with the coupling effect of external
environment complexity and organizational
complexity, it is especially important to create a
diversified and inclusive internal environment to
properly handle the crisis and turn it into a driving
force for development. Responding quickly and
ruling with dynamics is even more crucial for leaders
of start-ups to lead their organizations to success.
Based on dynamic capability theory, when an
organization has the ability to react quickly to the
internal and external environment, its core
competitiveness will be greatly enhanced. In addition,
practice has shown that in the face of new challenges
and threats, the effectiveness of traditional response
strategies is greatly reduced and may even fail.
A review of the literature on leadership and team
performance suggests that leadership behaviors are a
key factor in team innovation performance and that
the right leadership behaviors can maximize team
innovation performance. Bass describes
transformational leaders as “leaders who make
subordinates aware of the importance and
responsibility of the tasks they undertake by making
them leaders whose needs are met, and who also
create a greater vision for their subordinates,
encourage and support them to go beyond
themselves, adopt new ideas and approaches,
creatively solve new challenges and problems, and
create an atmosphere of mutual support and
harmonious innovation within the organization to
promote organizational innovation” (Bass, 1985).
Therefore, transformational leadership style is
important for accelerating organizational
innovativeness and improving organizational
innovation performance.
Based on the above review of the literature and
related theories, this paper argues that organizational
improvisation and transformational leadership may
interact to produce influencing factors on innovation
performance of start-ups, while the relationship
between the two and innovation performance of start-
ups may be mediated by the VUCA environment,
therefore, the paper proposes the following
theoretical model, as shown in Fig 1.
3.2 Theoretical Model
3.2.1 Organizational Improvisation and
Innovation Performance of Start-Ups
Organizational improvisation as a "time pressure" and
"environmental uncertainty" triggered by the ability to
respond quickly to unexpected events has a strong
immediate, spontaneous, creative characteristics,
How Organizational Improvisational, Transformational Leadership Styles Impact Innovation Performance of Start-Up Companies in VUCA
Environments
297
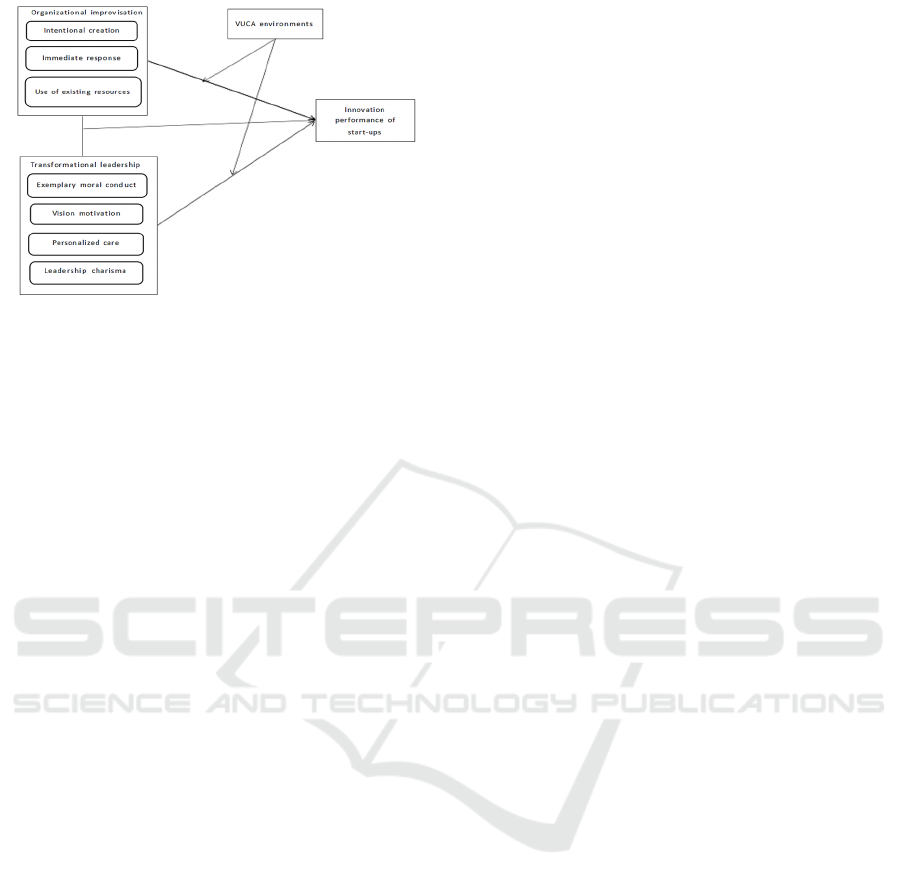
Figure 1: Conceptual model.
through the current problem facing the specificity of a
timely response, and The existing resources are
successfully integrated and utilized to avoid missed
opportunities and problem complications. Based on
the view of flexible human resource management and
technological variability, Shan et al. (2021) pointed
out that in an uncertain environment, technology-
based firms use improvisation capabilities to enhance
technology commercialization by efficiently
integrating existing resources, thus positively
influencing organizational innovation performance.
Xiang (2021) confirmed a strong positive influence
between organizational improvisational capabilities
and innovation performance using the supportive
incubation environment and environmental dynamics
as moderating variables. Based on the moderating role
of improvisational skills, Chen (2013) investigated the
relationship between time-based competition and
organizational performance and found that
improvisational skills deepened the organization's
understanding of time-based competitive cognition
through rapid and immediate innovation responses,
and the study found that improvisational skills
effectively contributed to organizational innovation
performance.
Based on this, this paper proposes the following
research hypothesis: H1, H1a, H1b, as shown in Table
1.
3.2.2 Transformational Leadership and
Innovation Performance of Start-Up
Firms
In general, organizational development is influenced
by the entrepreneurial leadership style,i.e., the leader's
vision, wisdom and motivation to innovate affect the
organization's performance indicators; therefore,
innovation performance is closely related to the
entrepreneur's values and beliefs, i.e., innovation
performance is influenced by the entrepreneurial
leadership style. Transformational leaders, on the
other hand, tend to actively cultivate their own
innovation consciousness and capabilities, inspire
organizational members through their own images,
attitudes, beliefs and behaviors, correct employees'
work attitudes, build employees' collective cognition
and perceptions of the organization, help promote
mutual cognition among members, and guide the
organization to accomplish innovative tasks, which is
a key factor in improving organizational innovation
performance. Numerous studies have shown that
transformational leaders have an impact on
organizational innovation performance by influencing
to increase the creativity of their subordinates. For
example, Nguyen (2022) showed that there is a
significant correlation between transformational
leadership and employee creativity. Shafi et al. (2020)
stated that transformational leadership has a
significant positive effect on employee creativity
through idealizing influence, intellectual stimulation
and motivational motivation. Zhang & Wang (2020)
showed that transformational leaders improve
organizational innovation performance by increasing
their own work engagement. Rong et al. (2018) stated
that CEO transformational leadership style has a
significant positive impact on organizational
innovation performance.
Based on the above analysis, the following
hypotheses are proposed in this study: H2, H2a, H2b,
H2c, H2d, as shown in Table 1.
3.2.3 Interactive Effects of Organizational
Improvisation and Transformational
Leadership on Innovation
Performance of Start-up Firms
By collating the existing literature in English and
Chinese, there is a gap in the current research on the
interaction between the two. However, based on the
existing research by scholars, it is not difficult to find
that both organizational improvisation and
transformational leadership have a reinforcing effect
on each other to positively influence organizational
innovation performance.
From the perspective of organizational
improvisation, when an organization has the ability to
react quickly to the internal and external
environment, its core competitiveness will be greatly
enhanced. In addition, the organization or its
members must meet challenges with new
organizational strategies through the exercise of
individual creativity and improvisation, and take
advantage of market opportunities to creatively solve
KMIS 2024 - 16th International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Systems
298
problems, which also indirectly enhances the
innovation capability of the whole organization. The
transformational leader supports and facilitates the
rapid growth of employees by providing them with
personalized guidance, making them aware of their
self-worth, and developing their ability to improve
their self-leadership.
From the perspective of transformational leaders,
the creative thinking, immediate responsiveness of
organizational members is greatly enhanced when
their behavior is unrestrained and maximizes their
ability to improvise, which will help transformational
leaders, through their personal charisma, build trust
with employees, motivate them, and prompt them to
further creatively solve new challenges and problems,
creating in the organization a mutually supportive and
harmonious innovation climate within the
organization to achieve better organizational
innovation performance. It is evident that
organizational improvisation positively reinforces the
role of transformational leaders on organizational
innovation performance.
In summary of the analysis, the following
hypothesis is proposed in this study: H3, as shown in
Table 1.
3.2.4 Moderating Effect of VUCA
In the VUCA environment, various characteristics
have brought a huge impact on the survival,
competition and development of the company. Facing
the coupling effect of external environmental
complexity and organizational complexity, it is
especially important to create a diverse and inclusive
internal environment to properly handle the crisis and
turn it into a driving force for development. Krupp &
Schoemaker (2014), Bennett& Lemoine (2014), and
Livingston (2014) have each made Troise et al. (2022)
and others presuppose that organizational agility - the
ability to quickly anticipate or respond to external
changes - premised on digital technology capabilities,
relational capabilities, and innovation capabilities, is
essential in today's environment characterized by
technological advancement and digitization as the
hallmark of today's turbulent VUCA environment is
critical to survive and compete. In addition to this,
due to the rapidly changing domestic and
international environment, start-up leaders must meet
challenges with fresh organizational strategies and
take advantage of market opportunities to creatively
solve problems through the exercise of personal
creativity and improvisation. Khan et al. (2021)
showed that under the VUCA environment,
knowledge workers enter the workplace more often,
so leader-member exchange and leader identification
play a mediating role between authentic leadership
and employees' innovative work behaviors, and states
that by building strong relationships with employees,
managers can motivate employees to pursue
innovative work behaviors.
Therefore, the following research hypotheses are
proposed in this paper: H4, H5, as shown in Table 1.
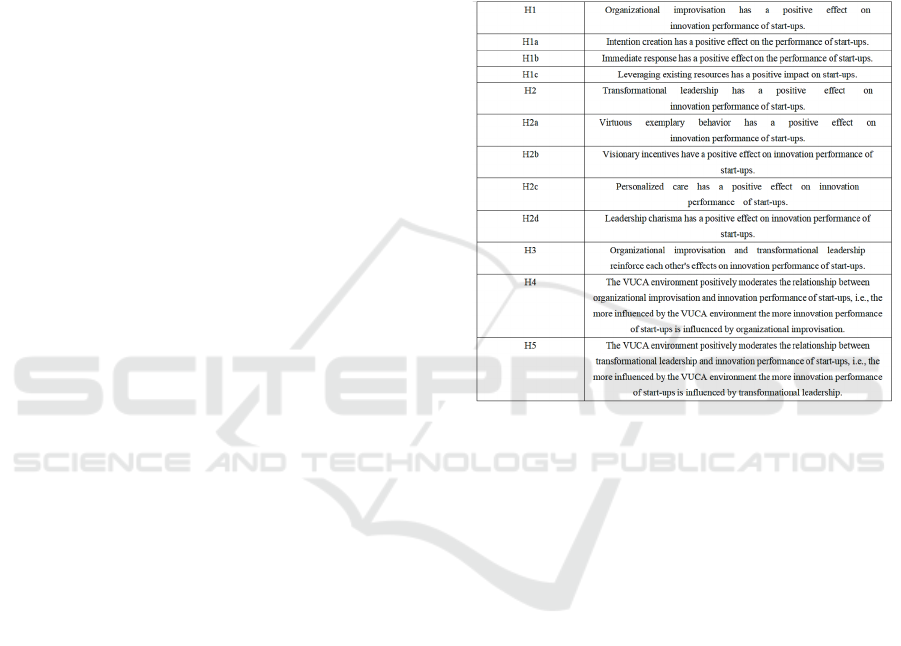
Table 1: Research hypothesis.
4 STUDY DESIGN
4.1 Data Collection
AKumar & Das (2020) point out that enterprises that
are active and founded within 8 years are new.
Domestic scholars such as Cheng, Song-Song et al.
(2019) and Zhang (2018) also generally define
enterprises that have been established for less than 8
years as start-ups. Therefore, this study defines the
investigated start-up enterprises as those whose
enterprise age is less than or equal to 8 years.
In this study, 396 official questionnaires were
distributed by telephone and email to the middle and
senior management of a start-up enterprise in an
industrial development zone in Chengdu, Sichuan
Province (China) through the introduction of
acquaintances, and 308 valid questionnaires were
obtained after excluding invalid questionnaires such
as incomplete completion or enterprises not meeting
the conditions. From the viewpoint of the sample
itself, the survey targets are widely distributed,
covering manufacturing, service, information
transmission, new energy materials, etc. From the
How Organizational Improvisational, Transformational Leadership Styles Impact Innovation Performance of Start-Up Companies in VUCA
Environments
299
viewpoint of the enterprise characteristics, 38
questionnaires were distributed to state-owned
enterprises, 130 to private enterprises, 102 to foreign-
funded enterprises, and 38 to other enterprises. 42.5%
of businesses with 100 or more employees, 32.5%
with 51-100 employees, 10.7% with 21-50 employees
and 14.3% with less than 20 employees.
4.2 Questionnaire Design
The reliability test of the scales often uses Cronbach's
α coefficient. In this paper, the reliability of each
variable scale was analyzed using SPSS 27.0, and the
results showed that the reliability values of each scale
of organizational improvisation, transformational
leadership, VUCA, and innovation performance were
0.952, 0.983, 0.940, and 0.904, respectively. The total
reliability value was 0.975, thus indicating a high
quality of reliability of the study data.
The validity tests were divided into exploratory
factor analysis and validation factor analysis. In the
exploratory factor analysis, KMO and Bartlett's
spherical tests were conducted for the scales of
organizational improvisation, transformational
leadership, VUCA, and innovation performance, and
the results showed that the KMO of all variables was
greater than 0. 8, and the factor loadings of each
measurement question item were greater than 0. 6,
indicating good structural validity of the scales, as
shown in Table 1. Validation factor analysis was
conducted for each variable and the model fit was
tested by indicators, in which the value of chi-square
degrees of freedom was 1.143, which was less than 3,
the value of RMSEA was 0.022, which was less than
0.10, the value of RMR was 0.050, which was less
than 0.08, and the values of CFI, GFI, NFI, and TLI
were all greater than 0.9, indicating that the absolute
and value-added fitness of the model was better.
5 EMPIRICAL STUDY
5.1 Results of the Regression Ana
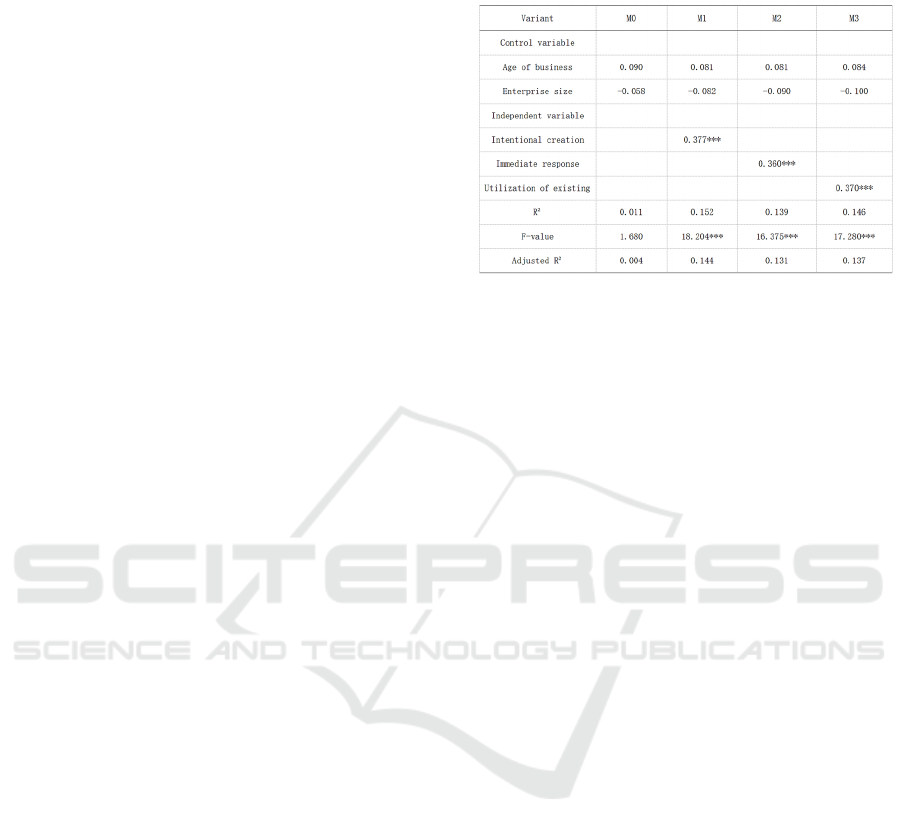
As can be seen from the table 2, in model M0, the
adjusted R ² is 0.004, indicating that the explained
variance of firm age and firm size on individual
innovation performance is 0.4%, and after adding the
intention creation variable in model M1, the adjusted
from R ² increases to 0.144, and the regression
coefficient P = 0.377 of virtue draping on the
innovation performance of new start-up firms in
model M1 is significant at the P = 0.001 level It
indicates that intention creation is significantly and
Table 2: Table of regression analysis (independent variable
is organizational improvisation).
positively related to innovation performance of start-
ups, and hypothesis H1a holds; after adding
immediate response variable in model M2, the
adjusted R²is 0.131, which has significantly improved
the explanatory strength of innovation performance of
start-ups compared with the basic model M0, and the
regression coefficient of immediate response on
innovation performance of start-ups P= 0.360, which
is significant at the P = 0.001 level. It indicates that
immediate response is significantly and positively
related to innovation performance of start-ups, and
hypothesis H2b holds; the addition of personalized
care in model M3 increases the moderated R²to 0.137
and the regression coefficient on innovation
performance is 0.370 (p=0.001), indicating that using
available resources is significantly and positively
related to innovation performance, and hypothesis
H2c holds.
5.2 Results of Regression Analysis of
Transformational Leadership and
Innovation Performance
From the table 3, it can be seen that after adding the
virtue pendant variable in model M1, the adjusted
from R²increases from 0.004 in M0 to 0.213, and the
regression coefficient P = 0.459 of virtue pendant on
innovation performance of start-up firms in model
M1 is significant at the 0.001 level, indicating that
virtue pendant positively affects innovation
performance of start-up firms, and hypothesis H2a
holds; after adding the vision incentive variable in
model M2, the adjusted from R²variable in model
M2, the adjusted R²is 0.186, which has significantly
improved the explanatory strength of innovation
performance of start-ups compared with the basic
model M0, and the regression coefficient P = 0.428
for vision incentive innovation performance of start-
ups
is
significant
at
the
0.001
level,
indicating
that
KMIS 2024 - 16th International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Systems
300
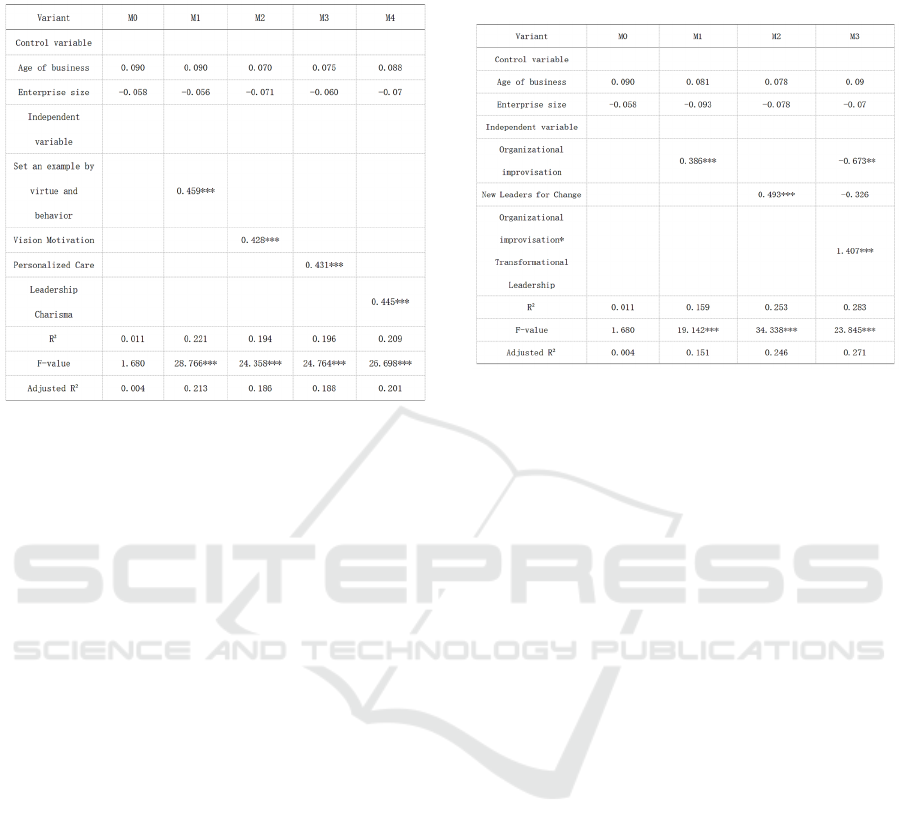
Table 3: Results of regression analysis of transformational
leadership and innovation performance).
vision incentive positively affects innovation
performance of start-ups, and the hypothesis H2b
holds; adding personalized care in model M3, the
adjusted R ² increases to 0.188 and the regression
coefficient on innovation performance is 0.431
(p=0.001), indicating that personalized care is
significantly and positively related to innovation
performance, and hypothesis H2c holds; after adding
leadership charisma in model M4, the adjusted R²is
0.201 and the regression coefficient on innovation
performance is 0.445 (p=0.001), indicating that
leadership charisma and innovation performance also
show a significant positive correlation, and the
hypothesis H2d holds.
5.3 Results of Interaction Effect
Analysis
From the table 4, we can see that the adjusted R²
values are 0.004,0.151,0.246,0.271, i.e., the model can
explain 0.4%,15.1%,24.6%,27.1% of the variance,
i.e., the model fits well; this paper constructs model
M0 as the regression equation with the control
variable as the independent variable, model M1 as the
regression equation with the introduction of the
independent variable organizational improvisation,
and M2 is the regression equation with the
introduction of the independent variable change-
oriented leadership, and M3 is the product term with
the introduction of organizational improvisation and
change-oriented leadership. According to the table 4,
the regression coefficient of M1 independent variable
organizational
improvisation
is
0.386
(p <
0.001),
Table 4: Test table of the relationship between
organizational improvisation, transformational leadership
and innovation performance.
based on the results of this analysis, it can be
concluded that organizational improvisation
positively affects organizational innovation
performance, i.e., the hypothesis H1 of this study is
verified. the regression coefficient of M2 independent
variable transformational leadership is 0.493 (p <
0.001), which indicates that transformational
leadership positively affects organizational
innovation performance, i.e., the hypothesis H1 of
this study is verified. The regression coefficient of
M3 product term was 1.407 (p < 0.001), and the
hypothesis H3 of this study was supported.
5.4 Results of Analysis of Moderating
Effects
To reduce the problem of non-essential
multicollinearity in the regression analysis, this study
decentered the independent variable Organizational
Improvisation and Transformational Leadership and
the moderating variable VUCA Environment (mean
center) before constructing the interaction terms, and
then calculated the product of the independent and
moderating variables after decentering and
constructed interaction term 1 and interaction term 2,
respectively. From the table 5, we can see that the
adjusted R2 values are 0.004, 0.248, 0.271, 0.304,
0.315, i.e. the model can explain 4%, 24.8%, 27.1%,
30.4%, 31.5% of the variance, i.e. the model fit is
good; model M0 is constructed as the regression
equation with the control variable as the independent
variable, model M1 is the regression equation with the
introduction of the independent variable Organization
improvisation and the regression equation of equation
of
the
moderating
variable
VUCA
environment,
M2
How Organizational Improvisational, Transformational Leadership Styles Impact Innovation Performance of Start-Up Companies in VUCA
Environments
301
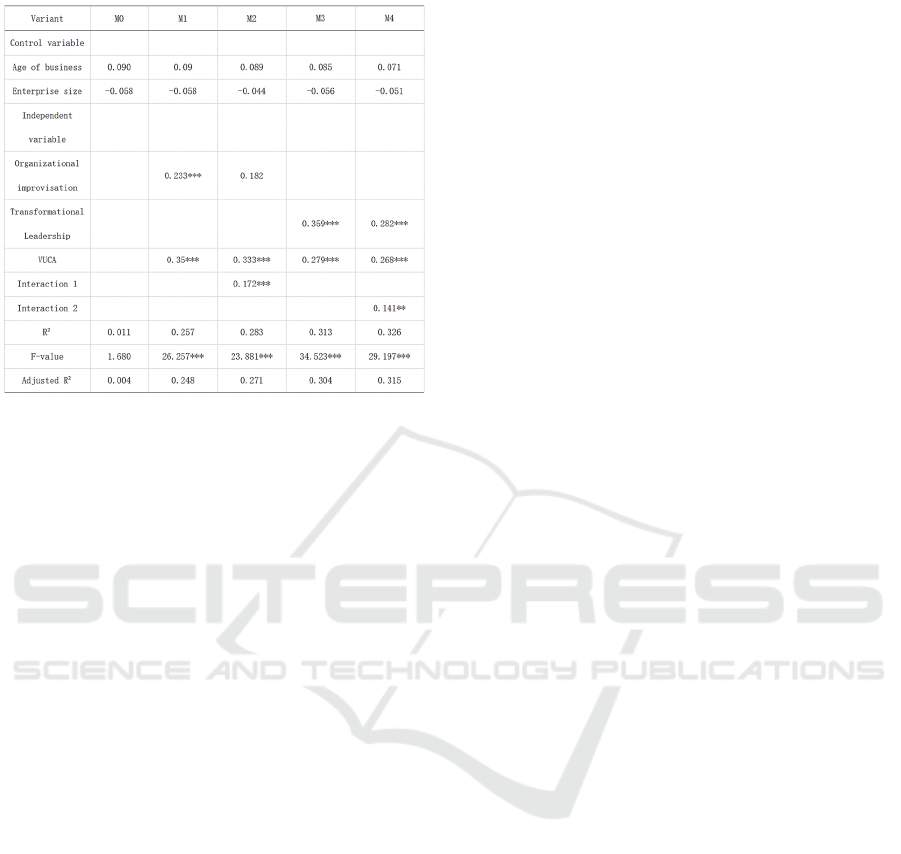
Table 5: Table of tests for moderating effects.
is the regression equation of the interaction term 1
after the introduction of the independent variable
organizational improvisation, the moderating
variable VUCA environment, and decentering, model
M3 is the regression equation of the introduction of
the independent variable transformational leadership
and the moderating variable VUCA environment, and
M4 is the regression equation of the interaction term
2 after the introduction of the independent variable
organizational improvisation, the moderating
variable VUCA environment, and decentering .
According to the above table, the regression
coefficient of interaction term M2 is 0.172 (p <
0.001), and based on the results of this analysis, it can
be concluded that VUCA environment reinforces the
positive effect of organizational improvisation on
innovation performance, thus supporting this paper's
research hypothesis H4. The regression coefficient of
interaction 2 in the M4 model is 0.141 (p < 0.01),thus
being able to support this paper's research hypothesis
H5, thus it can be concluded that the VUCA
environment positively moderates the positive effect
of transformational leadership on innovation
performance.
6 CONCLUSION
Firstly, Organizational improvisation can positively
affect the innovation performance of start-ups: if an
organization facing uncertain environmental
conditions and time pressures can efficiently
coordinate internal and external organizational
resources based on integrating and reconfiguring
existing resources, react quickly and effectively, and
dare to break the rules and respond to unpredictable
environmental changes in innovative ways and
means, it can take advantage of the business
opportunities brought by environmental changes and
create new competitive advantages and thus improve
the innovation performance of the firm, which is
consistent with the study of Cunha &Vera (2005) .
Secondly, transformational leaders can positively
influence the performance of start-ups:
transformational leaders tend to actively develop their
own innovative awareness and capabilities, inspire
organizational members through their own images,
attitudes, beliefs and behaviors, correct employees'
work attitudes, build employees' collective
perceptions and ideas about the organization, help
promote mutual perceptions among members, and
guide the organization to accomplish innovative tasks,
which is a key factor in improving organizational
innovative performance A key factor in improving
organizational innovation performance.
Thirdly, Organizational improvisation and
transformational leadership can positively interact to
influence the innovation performance of start-ups:
transformational leaders create the conditions for
organizational improvisation through personal
leadership charisma, thereby gaining the trust of
employees while they strive to create a harmonious,
supportive, innovative and entrepreneurial culture
within the organization that promotes change and
innovation.
Fourthly, the VUCA environment plays a
significant moderating role between organizational
improvisation and innovation performance of start-
ups: the more volatile, uncertain, complex and
ambiguous the competitive environment is, the
greater the role of organizational improvisation on
innovation performance of start-ups, which proves
that the volatility of the environment is one of the
necessary conditions for organizational improvisation.
The degree of VUCA in the environment is an
external factor that is difficult for the organization to
control, but by improving the dynamic capabilities of
the organization, the organization can take advantage
of market opportunities, creatively solve challenges,
and improve the innovative performance of start-ups.
Fifthly, the VUCA environment plays a
significant moderating role between transformational
leadership and innovation performance of start-ups:
the more volatile, uncertain, complex and ambiguous
the competitive environment in which a company is
operating, the greater the role of transformational
leadership on innovation performance of start-ups.
KMIS 2024 - 16th International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Systems
302

7 DISCUSSION
7.1 Theoretical Significance
Firstly, we explore the role relationship and evolution
mechanism between transformational leadership style
and innovation performance from the perspectives of
management, leadership, organizational behavior,
and innovation performance of start-ups, and explore
the effective path and influencing factors to enhance
the innovation performance of start-ups under the
perspective of organizational improvisation from the
perspective of transformational leadership style.
Secondly, the concept of organizational
improvisation is still in its infancy in China, and most
of the qualitative studies on the relationship between
organizational improvisation and performance have
been conducted. In addition to this, the current
research mainly focuses on organizational
performance and competitive advantage, and few
scholars have conducted research on the impact of
organizational improvisation on the innovation
performance of start-ups.
Thirdly, because start-ups are less able to
withstand risks compared to mature firms, start-ups
usually face problems such as fierce market
competition and difficulty in predicting current
market demand (Li & Cao, 2021), and with the further
intensification of the VUCA environment, start-ups
face even more serious competitive pressures and
threats to their resources
7.2 Research Limitations and Future
Directions
Firstly, due to objective reasons in terms of time and
funding, the sample of this study is mainly from
Southwest China, while the degree of environmental
turbulence and the organisations themselves exist in
different countries and regions with large
characteristics. In addition, the industries in this study
include both high-tech and traditional industries, and
whether or not there are large differences caused by
different industries may all affect the generalizability
of the study's findings. One of the directions for future
research is to conduct comparative studies by industry
as well as by region.
Secondly, the questionnaire research method
mainly used in this study, the scales are scoring mode,
some employees may have concerns when it comes to
the leader and the company performance related
questions, which can not fully reflect the objective
facts of the enterprise, with the limitations of first-
hand data, and at the same time, the indexof the
organization's innovation performance is also
subjective measurement, which inevitably causes the
bias of the research data. Future research can combine
rooted theory with questionnaire research, thus
making up for the shortcomings in this area.
Third, the data obtained in this study were only
static cross-sectional data, which were analyzed to
explore the relationship between the independent and
dependent variables, without longitudinal data
collection and dynamic tracking analysis. In order to
obtain more accurate research results, future research
needs to conduct longitudinal studies with specific
time spans, as well as case studies exploring deeper
associations between variables, in order to reduce
errors arising from single cross-sectional data with a
multi-faceted, cross-level research approach.
7.3 Management Suggestions for
Practice
Firstly, this study confirms that innovation
performance of start-ups is positively and positively
influenced by transformational leadership. Therefore,
organizations can determine whether existing leaders
need transformational leadership training by
analyzing the different needs of team leaders, develop
training programs based on their needs and change
behaviors in practice after training, create scenarios
conducive to transformational leadership traits, and
strengthen the effectiveness of the training by
recognizing and rewarding transformational
leadership behaviors.
Secondly, using modern Internet technology and
other means, the company can effectively simulate
and practice the difficulties and blows it may face,
and require the employees of the new venture to make
timely responses, and shorten the response time each
time through repeated training, thus putting forward
more requirements for improving the improvisation
ability of the company's employees.
Thirdly, new start-ups should detach themselves
from the previous independent perspective of
transformational leadership and organizational
improvisation, and pay attention to the positive
effects generated by the integration of the two, and
give full play to the complementary advantages of the
two in the VUCA environment. At the same time, this
paper finds that the impact of both on the innovation
performance of start-ups is moderated by VUCA, and
the role of both has a strong correlation with the
turbulent environment in which the enterprise is
located. At the same time, it is necessary to focus on
the cultivation of innovation ability, break the
inherent routine, avoid the rigidity of the
How Organizational Improvisational, Transformational Leadership Styles Impact Innovation Performance of Start-Up Companies in VUCA
Environments
303

organization, and maintain the creativity of the
organization.
REFERENCES
Bass, B. M. (1985). Leadership and Performance beyond
Expectations. The Academy of Management Review,
Chen, C. (2013). The impact of time-based competition on
organizational performance from a cognitive
perspective (Master's thesis, Northeast University of
Finance and Economics).
Chowdhury, M. M. H., & Quaddus, M. (2017). Supply
chain resilience:
Conceptualization and scale development using dynamic
capability theory. International Journal of Production
Economics, 188, 185–204.
Crossan, M. M., Vieira da Cunha, J., Cunha, M. P. E., &
Vera, D. (2002). Time and Organizational
Improvisation. SSRN Electronic Journal.
Fultz, A. E. F., & Hmieleski, K. M. (2021). The art of
discovering and exploiting unexpected opportunities:
The roles of organizational improvisation and
serendipity in new venture performance. Journal of
Business Venturing, 36(4), 106121.
Leybourne, S., & Sadler-Smith, E. (2006). The role of
intuition and improvisation in project management.
International Journal of Project Management, 24(6),
483–492.
Li, J.S., & Zhao, S.M. (2021)Orientation and path of human
resource management model innovation in the VUCA
era - focusing on the "three pillars" model. Journal of
Jianghai (05), 90-96.
The NTL Handbook of Organization Development and
Change: Principles, Practices, and Perspectives: Second
Edition,2014,76(6):659-672.
Mach, M., Ferreira, A. I., & Abrantes, A. C. M. (2021).
Transformational Leadership and Team Performance in
Sports Teams: A Conditional Indirect Model. Applied
Psychology, 71(2).
Ng, T. W. H. (2017). Transformational leadership and
performance outcomes: Analyses of multiple mediation
pathways. The Leadership Quarterly, 28(3), 385–417.
Nguyen, T. P. L., Nguyen, T. T., Duong, C. D., & Doan, X.
H. (2022). The effects of transformational leadership on
employee creativity in Vietnam telecommunications
enterprises. Management Decision, 60(3), 837–857.
Nielsen, K., & Daniels, K. (2012). Does shared and
differentiated transformational leadership predict
followers' working conditions and well-being?.
Leadership Quarterly, 23(3), 383-397.
Rong, P. F., Su, Y., & Wang, X. L. (2018). CEO leadership
style, TMT behavioral integration and firm innovation
performance. Xuehai (01), 196-206.
Scott, S. G., & Bruce, R. A. (1994, October 1). Creating
innovative behavior among R&D professionals: the
moderating effect of leadership on the relationship
between problem-solving style and innovation. IEEE
Xplore.
Shafi, M., Zoya, Lei, Z., Song, X., & Sarker, M. N. I.
(2020). The effects of transformational leadership on
employee creativity: Moderating role of intrinsic
motivation. Asia Pacific Management Review, 25(3).
ScienceDirect.
Shan, B. A., Pu, Y., Yan, S., & Liang, B. M. (2021). A study
on the impact of improvisational ability on the
performance of technology-based new ventures under
uncertainty. Journal of Management (07), 1032-1039
Stanescu, D. F., Zbuchea, A., & Pinzaru, F. (2020).
Transformational leadership and innovative work
behaviour: the mediating role of psychological
empowerment. Kybernetes.
Tang, Y., & Zhou, P. (2017). And so on and so forth:
Corporate improvisation strategy in a dynamic
environment. Tsinghua Management Review (05), 84-
90
Troise, C., Corvello, V., Ghobadian, A., & O’Regan, N.
(2022). How can SMEs successfully navigate VUCA
environment: The role of agility in the digital
transformation era. Technological Forecasting and
Social Change,2022, 174, 121227.
Wang, C. (2021). Research on the Role Mechanism of
Digital Transformation on Corporate Innovation
Performance. Contemporary Economic Management
(03), 34-42.
Weick, K. E. (1993). The Collapse of Sensemaking in
Organizations: The Mann Gulch Disaster.
Administrative Science Quarterly, 38(4), 628.
Xiang, Y. Y. (2021). The impact of resource patchwork and
organizational improvisation on innovation
performance of start-up firms (Master's thesis,
Chongqing University of Technology and Business).
Zhang, J., &Wang, G. H. (2020). Analysis of the impact
mechanism of transformational leadership on team
innovation performance. Enterpris Economics (09), 37-
43.
Zhang, X. E., & Zhang, K. (2018). The impact of
entrepreneurial orientation on the performance of
newly created social enterprises - The mediating role of
resource collocation and the moderating role of
regulation. Science and Technology Progress and
Countermeasures (09), 91-99
KMIS 2024 - 16th International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Systems
304
