
Sampling in CMA-ES: Low Numbers of Low Discrepancy Points
Jacob de Nobel
a
, Diederick Vermetten
b
, Thomas H. W. B
¨
ack
c
and Anna V. Kononova
d
LIACS, Leiden University, Leiden, Netherlands
{j.p.de.nobel, d.l.vermetten, t.h.w.baeck, a.kononova}@liacs.leidenuniv.nl
Keywords:
Benchmarking, CMA-ES, Derandomization, Low Discrepancy Samples.
Abstract:
The Covariance Matrix Adaptation Evolution Strategy (CMA-ES) is one of the most successful examples of
a derandomized evolution strategy. However, it still relies on randomly sampling offspring, which can be
done via a uniform distribution and subsequently transforming into the required Gaussian. Previous work
has shown that replacing this uniform sampling with a low-discrepancy sampler, such as Halton or Sobol
sequences, can improve performance over a wide set of problems. We show that iterating through small,
fixed sets of low-discrepancy points can still perform better than the default uniform distribution. Moreover,
using only 128 points throughout the search is sufficient to closely approximate the empirical performance
of using the complete pseudorandom sequence up to dimensionality 40 on the BBOB benchmark. For lower
dimensionalities (below 10), we find that using as little as 32 unique low discrepancy points performs similar or
better than uniform sampling. In 2D, for which we have highly optimized low discrepancy samples available,
we demonstrate that using these points yields the highest empirical performance and requires only 16 samples
to improve over uniform sampling. Overall, we establish a clear relation between the L
2
discrepancy of the
used point set and the empirical performance of the CMA-ES.
1 INTRODUCTION
Optimization techniques play a crucial role in var-
ious scientific and engineering applications. Exact
methods systematically explore the parameter space
but often suffer from inefficiency due to their exhaus-
tive nature. For example, it has been shown that ran-
domized search is superior to grid search for hyperpa-
rameter tuning (Bergstra and Bengio, 2012). This is
because, especially in higher dimensions, a random-
ized process will provide better coverage of sample
points in the domain than an exhaustive search, given
a limited evaluation budget. While samples generated
uniformly at random provide an improvement in ex-
ploring the search space, such samples can still be
quite suboptimal in covering the domain. Given a
limited number of samples, uniform samples can be
distributed very unevenly (Halton, 1960). This no-
tion of evenly spreading points across a given do-
main motivates the research into Low-Discrepancy
Sequences. These are sequences of pseudo-randomly
generated points that are designed to minimize the
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1169-1962
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3040-7162
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6768-1478
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4138-7024
gaps and clusters that often occur in uniform random
sampling, providing more uniform coverage of the
search space. Specifically, discrepancy measures are
designed to measure how regularly a given point set
is distributed in a given space (Cl
´
ement et al., 2023b).
While early work with low discrepancy point sets
focuses on Monte Carlo integration (Halton, 1960;
Sobol’, 1967), they have subsequently been used in
various domains, such as computer vision (Paulin
et al., 2022) and financial modeling (Galanti and Jung,
1997). Low Discrepancy point sets have been used in
the optimization domain to set up the Design of Ex-
periments (DoE) within a constrained budget (Sant-
ner et al., 2003). One application of particular in-
terest in our context is one-shot optimization, where
low-discrepancy sequences have been shown to out-
perform more traditional uniform sampling (Bous-
quet et al., 2017). Moreover, random search us-
ing quasi-random points has been shown to outper-
form traditional random search (Niederreiter, 1992).
In metaheuristics, randomized search is employed by
many different algorithms, such as Evolution Strate-
gies (ES) (Beyer, 2001). In ES, quasi-random point
sets have been used as an alternative sampling strat-
egy to pure random sampling (Teytaud and Gelly,
2007), specifically for the CMA-ES (Hansen and Os-
120
de Nobel, J., Vermetten, D., Bäck, T. and Kononova, A.
Sampling in CMA-ES: Low Numbers of Low Discrepancy Points.
DOI: 10.5220/0013000900003837
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 16th International Joint Conference on Computational Intelligence (IJCCI 2024), pages 120-126
ISBN: 978-989-758-721-4; ISSN: 2184-3236
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

termeier, 2001). Simplified, the procedure of the
CMA-ES can be divided into two steps, which are re-
peated until convergence:
• Sample λ points from a multivariate normal dis-
tribution N (m,C).
• Adjust the parameters of the multivariate normal
distribution to move towards the µ points with the
highest fitness.
Modifying the sampling step to use points from a
pseudo-random sequence (Teytaud, 2015) demon-
strated increased performance and stability on bench-
mark functions. Moreover, this furthers derandom-
ization, which aims to achieve self-adaptation with-
out any independent stochastic variation of the strat-
egy parameters (B
¨
ack et al., 2023). This paper aims to
extend this work by focusing on the number of sam-
ples drawn from a (pseudo) random sampling strategy
specifically for the CMA-ES. Specifically, we inves-
tigate if repeatedly reusing small subsets of pseudo-
random sequences in a deterministic manner can be
an effective sampling strategy for the CMA-ES. We
provide an analysis for several well-known low dis-
crepancy point sets to investigate the relation between
discrepancy and empirical performance on the BBOB
benchmark functions.
2 PRELIMINARIES
2.1 Low-Discrepancy Sequences
The discrepancy of a set of points quantifies how reg-
ularly they are spaced in the domain. One of the
most common discrepancy measures of a point set
P ⊆ [0,1]
d
is the L
∞
star discrepancy (Cl
´
ement et al.,
2023a), which is defined as follows:
d
∗
∞
(P) = sup
q∈[0,1]
d
|P ∩[0, q)|
|P|
−λ(q)
(1)
Here, λ(q) is the Lebesgu measure of the box [0,q)
and d
∗
∞
(P) measures the worst absolute difference be-
tween λ(q) of a d-dimensional box anchored at the
origin and the proportion of points that fall inside
this box. Note that this measure should be mini-
mized to evenly space points in the domain. Since the
L
∞
star discrepancy can be computationally expen-
sive (Cl
´
ement et al., 2023b), we can also consider the
L
2
star discrepancy, which is defined as follows (Zhou
et al., 2013):
d
∗
2
(P) =
Z
[0,1]
d
|P ∩[0, q)|
|P|
−λ(q)
dq
1/2
(2)
Several pseudo-random sequences have lower star
discrepancies than corresponding uniform sequences.
These methods include Latin Hypercube Sam-
pling (Loh, 1996), Jittered sampling (Pausinger
and Steinerberger, 2016), and Hammersly se-
quences (Peart, 1982). Our work considers the Hal-
ton (Halton, 1960) and Sobol (Sobol’, 1967) se-
quences.
2.2 Derandomization and CMA-ES
While Evolution Strategies (Beyer, 2001) depend
on a random process to sample candidate solutions,
the internal parameter update has been derandom-
ized in state-of-the-art implementations of the algo-
rithm. Derandomization ensures self-adaptation hap-
pens without any independent stochastic variation of
the strategy parameters (Ostermeier et al., 1994). Ef-
fectively, this means the update of the strategy param-
eters is decoupled from the sampling of candidate so-
lutions, moving away from the notion that ‘good so-
lutions have good parameters’ of traditional ES. This
allows modern ES, such as the CMA-ES, to be more
robust and learn good strategy parameters while using
relatively small population sizes (Hansen and Oster-
meier, 2001). Within the CMA-ES, the sampling pro-
cedure is the only remaining source of stochasticity.
At every generation, λ individuals are sampled from
the d-dimensional Gaussian distribution N (m,σ
2
C).
Where m is the mean of the sampling distribution, σ
is the global step size, and C is the covariance matrix.
In practice, C is spectrally decomposed into two ma-
trices, B and D, representing the eigenvectors and in-
verse square root of the eigenvalues of C, respectively.
This allows the sampling of points in the CMA-ES to
happen in a three-stage process:
1. z
k
∼ N (0, 1)
2. y
k
= BDz
k
∼ N (0,C)
3. x
k
= m + σy
k
∼ N (m,σ
2
C)
Given this decomposition, the first step of the sam-
pling process can be practically achieved by sampling
from a uniform distribution u ∼ U(0,1)
d
, and trans-
forming each coordinate u
i
of the sample by:
φ
−1
(u
i
) =
√
2erf
−1
(2u
i
−1) (3)
which is the inverse of the cumulative density func-
tion for a standard Gaussian distribution.
Since the sampling procedure in CMA-ES can
be seen as sampling in [0, 1]
d
, replacing the uniform
sampling with a low-discrepancy sequence is a natural
step. Previous work has shown that scrambled Halton
sequences can improve performance over the standard
sampling procedure on most considered benchmark
problems (Teytaud and Gelly, 2007; Teytaud, 2015).
Sampling in CMA-ES: Low Numbers of Low Discrepancy Points
121
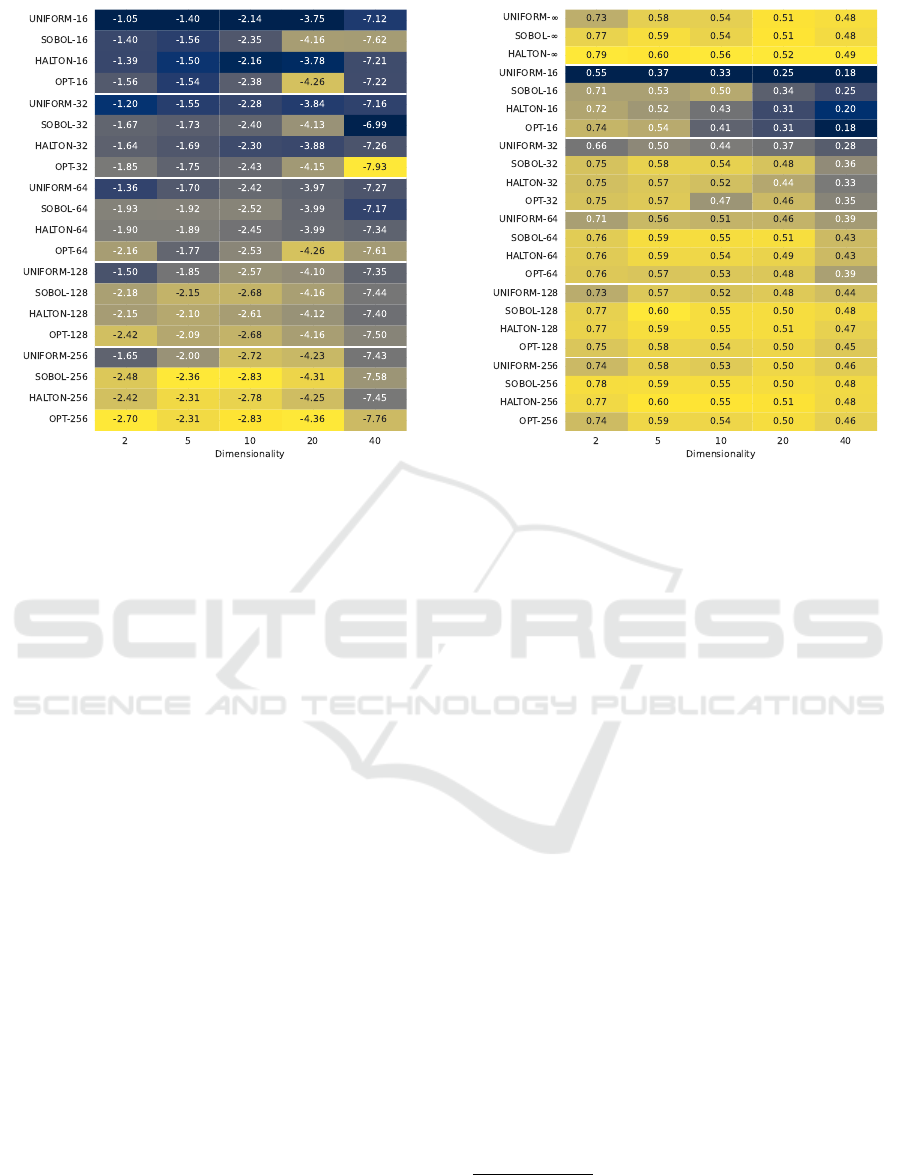
Figure 1: (Average) log
10
(d
∗
2
) star discrepancy for the gen-
erated fixed-size point sets across all dimensionalities. Col-
ors are (min-max) normalized on a per-dimensionality ba-
sis; darker colors indicate a worse (higher) d
∗
2
value.
3 METHODS
3.1 Point Set Generation
For our experiments, we modify how the CMA-ES
samples from a normal distribution by exchanging the
uniform number generator with a selection of points
from a fixed point set stored in a cache. The cache
is randomly permuted once, at the beginning of an
optimization run, and cycled through in steps of size
λ. The permutation is performed to break the bias that
might be present in the ordering of the point set.
We consider four methods for generating point
sets: Sobol, Halton, uniform, and ‘optimized’. Hal-
ton sequences are known to have unwanted correla-
tions in higher dimensional spaces, and as such, we
employ a scrambling method to prevent this (Braaten
and Weller, 1979). For the Sobol sequences, its bal-
ance properties require that the number of points gen-
erated is equal to a power of 2, so we always round
up our number of points sampled to the closest power
of 2. Finally, our ‘optimized’ method for generat-
ing low-discrepancy point sets is split into two parts
based on search space dimensionality. When d =
2, we use optimized Fibonacci sets (Cl
´
ement et al.,
2023a), considered among the best low-discrepancy
point sets available. However, these are only available
for 2D since generating optimized low-discrepancy
Figure 2: Average area under the EAF curve for each
sampling method on the BBOB benchmark, grouped by
dimension. Colors are (min-max) normalized on a per-
dimensionality basis; darker colors indicate a worse (lower)
EAF value.
point sets is a very hard computational problem. We
use the improved Threshold Accepting subset selec-
tion heuristic from (Cl
´
ement et al., 2024) for higher
dimensionalities, using Sobol sequences as the base
sets.
We create point sets of sizes k ∈
{16,32,64,128,256} for each generation mech-
anism and calculate their L
2
star discrepancy
12
.
Figure 1 shows how the discrepancy changes with
increasing dimensionality and size of the point sets.
We observe that, as expected, the standard uniform
sampling has a noticeably higher discrepancy than
both Halton and Sobol sequences, with the optimized
method usually having the lowest discrepancy.
Note that for the optimized method, the relative
difference in discrepancy is largest when d = 2 due
to the different generation mechanism used for this
dimensionality.
3.2 Experimental Setup
To gauge the impact of our derandomization, we
run the Modular CMA-ES (de Nobel et al., 2021)
with each of the generated point sets on the single-
1
We use L
2
instead of L
∞
star discrepancy for computa-
tional reasons.
2
For the uniform points sets, we calculate the average
over 100 samples.
ECTA 2024 - 16th International Conference on Evolutionary Computation Theory and Applications
122
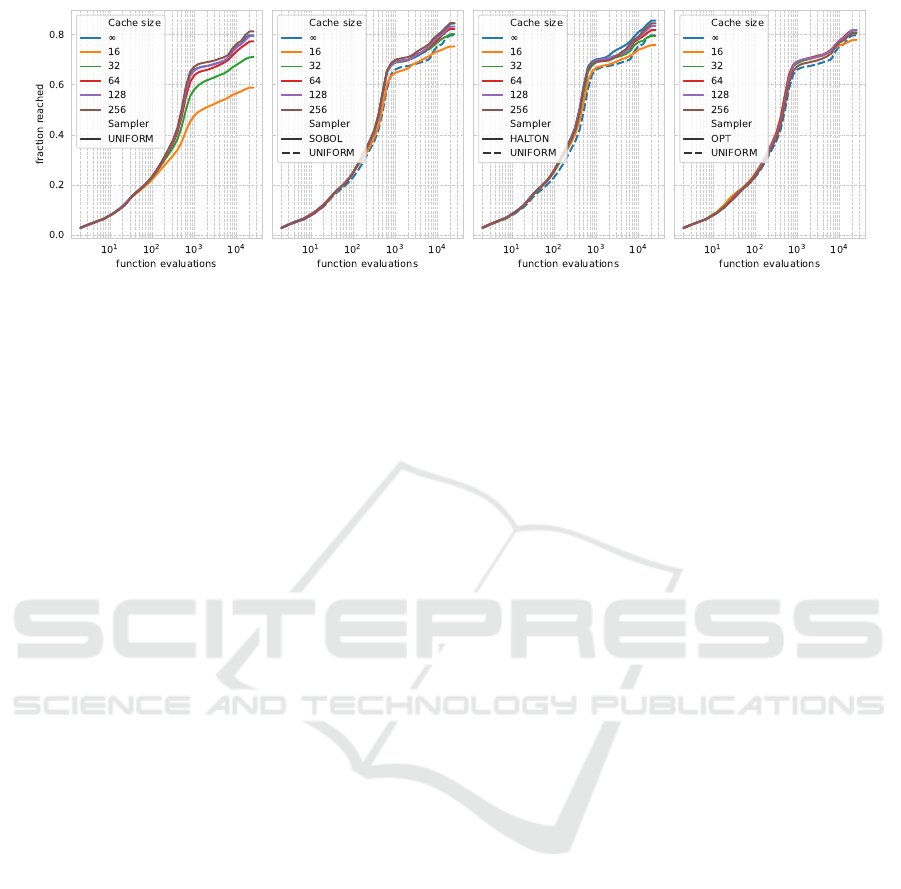
Figure 3: Empirical Attainment Function aggregated over all 24 BBOB functions for dimensionality 2. The methods are
shown in color for each sampling strategy, with cache size indicating the number of points in the cache and ∞ indicating no
caching; every sample is unique. From left to right, the subfigures show results using a uniform sampler, a Sobol sequence,
a scrambled Halton sequence, and the optimized point sets. Note that in the three rightmost figures, the default CMA-ES
sampling strategy, UNIFORM-∞, is included for comparison.
objective, noiseless BBOB suite (Hansen et al., 2009).
This suite consists of 24 functions, of which we use
100 different instances (generated by transformations
such as rotation and translation) in dimensionalities
d ∈ {2, 5, 10, 20,40}. We set our evaluation budget at
B = d ·10000. By using only a single run on each
instance, we only need to generate a single point set
for each (d, N)-pair, while the fact that we use 100 in-
stances ensures a large enough sample size for each
function. Additionally, we benchmark the default
sampling mechanism, UNIFORM-∞, and sampling
from arbitrarily long scrambled Halton and Sobol se-
quences, denoted by the ∞ suffix in our results. No
caching is applied in these cases, and each generated
sample in the optimization process is unique.
To measure performance, we consider the
attainment-based cumulative distribution func-
tion (L
´
opez-Ib
´
a
˜
nez et al., 2024), with bounds 10
2
and
10
−8
for the log-scaled precision values.
Reproducibility
All used point sets, the full experimental code, and
data are in our reproducibility repository (de Nobel
et al., 2024).
4 RESULTS
Figure 2 shows each sampling method’s normalized
area under the EAF curve. Without caching, we
observe that both low-discrepancy sequences outper-
form the uniform sampler, and overall, the scram-
bled Halton shows the highest empirical performance.
Note that the differences tend to decrease with dimen-
sionality. When comparing the results within each
fixed point set size, the uniform sampler often per-
forms notably worse than any of the low-discrepancy
sets. This effect is especially noticeable for smaller
set sizes (lower values of k) but remains observable
for all cache sizes. Interestingly, the optimized point
sets only seem to bring performance benefits in low
dimensionalities and using smaller cache sizes. For
higher dimensionalities, they often perform similarly
to uniform sampling. Overall, increasing the size of
the cached point set increases performance, and using
the complete sequence (∞) yields the highest perfor-
mance for each method. Interestingly, point sets of
only 64 to 128 samples are often enough to get very
close in performance to using the complete sequence
as a sampling strategy. Moreover, we find that such
sequences still outperform the default sampling strat-
egy of the CMA-ES, i.e., UNIFORM-∞, especially in
lower dimensions. In 2D, we can observe that only
using 16 optimized samples can outperform the de-
fault sampling strategy.
When looking at the performance of the algorithm
variants over time, as visualized in Figure 3, we no-
tice that the differences between the different sam-
pling methods occur rather early in the search. While
the used set does not have a noticeable impact on the
initialization, soon after, the small sets with low dis-
crepancy are seen to stagnate, resulting in the much
worse anytime performance observed in Figure 2. By
comparing the different sampler to the dashed line of
the default uniform sequence, we note that all sets
of size 32 and higher outperform this baseline at the
end of the optimization. Additionally, we should note
that the optimized sets perform best among the small-
est sample sizes, but the Halton and Sobol sequences
benefit more from increasing their size. Plots for other
dimensionalities are available in the appendix. Fi-
nally, we show the relation between discrepancy and
performance in Figure 4, where we observe a clear
Sampling in CMA-ES: Low Numbers of Low Discrepancy Points
123
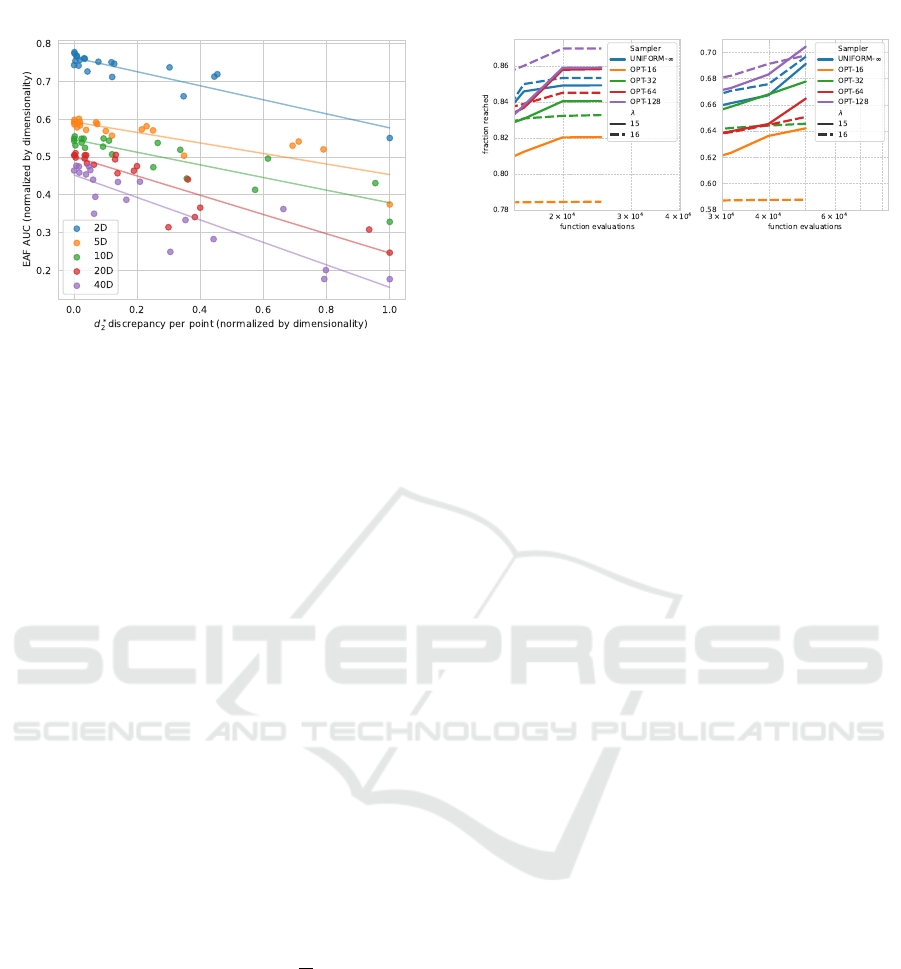
Figure 4: Average area under the Empirical Attainment
Function over all BBOB functions, grouped by dimension
vs. the L
2
star discrepancy, normalized by dimensionality
and the number of points. Lines indicate a linear (least-
squares) model for each dimensionality.
correlation between these two measures. This sup-
ports our previous observation that low discrepancy
point sets are beneficial to the performance of the
CMA-ES.
4.1 Multiples of λ
Since the CMA-ES only requires λ points at every
iteration, a natural assumption would be that only λ
unique points would be required for an effective sam-
pling strategy, given that these points cover the do-
main sufficiently. In our previous experiments, we
have used the default setting for λ, i.e., 4 + ⌊3 +
ln(d)⌋, which is strictly less than 16, the smallest
tested cache size k. This causes the sampler to cy-
cle through the point set, causing variance between
the samples used in each generation. Here, we inves-
tigate this effect using either a population size λ of 15
or 16. In the latter case, λ is a multiple of the cache
size, and for k = 16, this ensures that every genera-
tion uses exactly the same samples. For k < 16, this
causes a cyclic pattern, where every
k
16
-th generation
has the same samples. In figure 5, the empirical per-
formance of this experiment is visualized. The figure
shows that when using the default sampling strategy,
i.e., UNIFORM-∞, using a λ = 16 is better than using
λ = 15. This is reversed for a cache size k = 16, where
there is no variance between the samples in subse-
quent generations. For larger k, this performance of
λ = 15 becomes closer to λ = 16. This indicates
there must be variation between generations, not only
between the samples within each generation, which
aligns with (Teytaud and Gelly, 2007). Intuitively,
this makes sense, as the strategy parameters are be-
ing averaged over multiple generations, making diver-
Figure 5: Empirical Attainment Function aggregated over
all 24 BBOB functions for dimensionality 2 (left) and 5
(right), zoomed to final fraction reached. The default sam-
pling strategy of the CMA-ES, UNIFORM-∞, is shown in
comparison to using a cached sampling strategy, which uses
the ‘OPT’ samples for a cache size k ∈ {16,32,64, 128}.
The solid lines represent λ = 15 and the dashed lines λ = 16.
sity between subsequent populations important. No-
tably, though, using only 4-8 unique populations dur-
ing the entire optimization procedure already yields
higher performance than the UNIFORM-∞ sampling
strategy (for d = 2 and d = 5).
5 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
In this paper, we have shown that replacing the uni-
form sampling with low discrepancy samples in the
offspring generation of the CMA-ES can yield clear
benefits in performance on commonly used bench-
marks. While this matches previous observations
on the advantage of low-discrepancy sequences (Tey-
taud, 2015), our experiments on repeatedly (re-)using
small sets of points show that we don’t necessarily
need to rely on generators when sampling with the
CMA-ES. While we note that, in general, sampling
from an arbitrarily long low discrepancy sequence
is better than using a fixed point set, such sets re-
main competitive when using only 128 points. In
fact, on the two-dimensional problems, where our L
∞
-
optimized point sets can be considered state-of-the-
art (Cl
´
ement et al., 2023a), a cached set consisting of
only 16 samples is enough to outperform the default
sampling strategy of the CMA-ES.
However, our results in higher dimensionalities
show that while there is a clear correlation between
the discrepancy of a point set and the performance
of the CMA-ES using it, this correlation is not per-
fect. While our optimized sets generated by im-
proved Threshold Accptance (Cl
´
ement et al., 2024)
have lower discrepancy than the corresponding Hal-
ton and Sobol sets, their anytime performance is
slightly worse, indicating that there might be other as-
ECTA 2024 - 16th International Conference on Evolutionary Computation Theory and Applications
124

pects of the point sets we should take into account.
We have shown that not only does the discrepancy
of samples within a single generation impact perfor-
mance, but the diversity between subsequent genera-
tions also has an impact. Future work might focus on
diving deeper into the relationship between point set
size, discrepancy, diversity, and performance.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We want to thank Franc¸ois Cl
´
ement and Carola Doerr
for providing us with the optimized low-discrepancy
point sets used in this paper.
REFERENCES
Bergstra, J. and Bengio, Y. (2012). Random search for
hyper-parameter optimization. Journal of machine
learning research, 13(2).
Beyer, H. (2001). The theory of evolution strategies. Natural
computing series. Springer.
Bousquet, O., Gelly, S., Kurach, K., Teytaud, O., and Vin-
cent, D. (2017). Critical hyper-parameters: No ran-
dom, no cry. arXiv preprint arXiv:1706.03200.
Braaten, E. and Weller, G. (1979). An improved low-
discrepancy sequence for multidimensional quasi-
monte carlo integration. Journal of Computational
Physics, 33(2):249–258.
B
¨
ack, T. H. W., Kononova, A. V., van Stein, B., Wang,
H., Antonov, K. A., Kalkreuth, R. T., de Nobel, J.,
Vermetten, D., de Winter, R., and Ye, F. (2023).
Evolutionary Algorithms for Parameter Optimiza-
tion—Thirty Years Later. Evolutionary Computation,
31(2):81–122.
Cl
´
ement, F., Doerr, C., Klamroth, K., and Paquete, L.
(2023a). Constructing optimal l
∞
star discrepancy
sets. arXiv preprint arXiv:2311.17463.
Cl
´
ement, F., Doerr, C., and Paquete, L. (2024). Heuristic
approaches to obtain low-discrepancy point sets via
subset selection. Journal of Complexity, 83:101852.
Cl
´
ement, F., Vermetten, D., De Nobel, J., Jesus, A. D., Pa-
quete, L., and Doerr, C. (2023b). Computing star dis-
crepancies with numerical black-box optimization al-
gorithms. In Proceedings of the Genetic and Evolu-
tionary Computation Conference, pages 1330–1338.
de Nobel, J., Vermetten, D., Kononova, A. V., and B
¨
ack, T.
(2024). Reproducibility files and additional figures.
de Nobel, J., Vermetten, D., Wang, H., Doerr, C., and B
¨
ack,
T. (2021). Tuning as a means of assessing the ben-
efits of new ideas in interplay with existing algorith-
mic modules. In Krawiec, K., editor, GECCO ’21:
Genetic and Evolutionary Computation Conference,
Companion Volume, Lille, France, July 10-14, 2021,
pages 1375–1384. ACM.
Galanti, S. and Jung, A. (1997). Low-discrepancy se-
quences: Monte carlo simulation of option prices. The
Journal of Derivatives, 5(1):63–83.
Halton, J. H. (1960). On the efficiency of certain quasi-
random sequences of points in evaluating multi-
dimensional integrals. Numerische Mathematik, 2:84–
90.
Hansen, N., Finck, S., Ros, R., and Auger, A. (2009).
Real-parameter black-box optimization benchmark-
ing 2009: Noiseless functions definitions. Research
Report RR-6829, INRIA.
Hansen, N. and Ostermeier, A. (2001). Completely deran-
domized self-adaptation in evolution strategies. Evo-
lutionary computation, 9(2):159–195.
Loh, W.-L. (1996). On latin hypercube sampling. The an-
nals of statistics, 24(5):2058–2080.
L
´
opez-Ib
´
a
˜
nez, M., Vermetten, D., Dr
´
eo, J., and Doerr, C.
(2024). Using the empirical attainment function for
analyzing single-objective black-box optimization al-
gorithms. CoRR, abs/2404.02031.
Niederreiter, H. (1992). Random number generation and
quasi-Monte Carlo methods. SIAM.
Ostermeier, A., Gawelczyk, A., and Hansen, N. (1994). A
derandomized approach to self-adaptation of evolu-
tion strategies. Evolutionary Computation, 2(4):369–
380.
Paulin, L., Bonneel, N., Coeurjoly, D., Iehl, J.-C.,
Keller, A., and Ostromoukhov, V. (2022). Mat-
Builder: Mastering sampling uniformity over projec-
tions. ACM Transactions on Graphics (proceedings of
SIGGRAPH).
Pausinger, F. and Steinerberger, S. (2016). On the dis-
crepancy of jittered sampling. Journal of Complexity,
33:199–216.
Peart, P. (1982). The dispersion of the hammersley se-
quence in the unit square. Monatshefte f
¨
ur Mathe-
matik, 94(3):249–261.
Santner, T., Williams, B., and Notz, W. (2003). The De-
sign and Analysis of Computer Experiments. Springer
Series in Statistics, Springer.
Sobol’, I. M. (1967). On the distribution of points in a cube
and the approximate evaluation of integrals. Zhurnal
Vychislitel’noi Matematiki i Matematicheskoi Fiziki,
7(4):784–802.
Teytaud, O. (2015). Quasi-random numbers improve the
CMA-ES on the BBOB testbed. In Bonnevay, S.,
Legrand, P., Monmarch
´
e, N., Lutton, E., and Schoe-
nauer, M., editors, Artificial Evolution - 12th Inter-
national Conference, Evolution Artificielle, EA 2015,
Lyon, France, October 26-28, 2015. Revised Selected
Papers, volume 9554 of Lecture Notes in Computer
Science, pages 58–70. Springer.
Teytaud, O. and Gelly, S. (2007). DCMA: yet another
derandomization in covariance-matrix-adaptation. In
Lipson, H., editor, Genetic and Evolutionary Compu-
tation Conference, GECCO 2007, Proceedings, Lon-
don, England, UK, July 7-11, 2007, pages 955–963.
ACM.
Zhou, Y.-D., Fang, K.-T., and Ning, J.-H. (2013). Mixture
discrepancy for quasi-random point sets. Journal of
Complexity, 29(3-4):283–301.
Sampling in CMA-ES: Low Numbers of Low Discrepancy Points
125
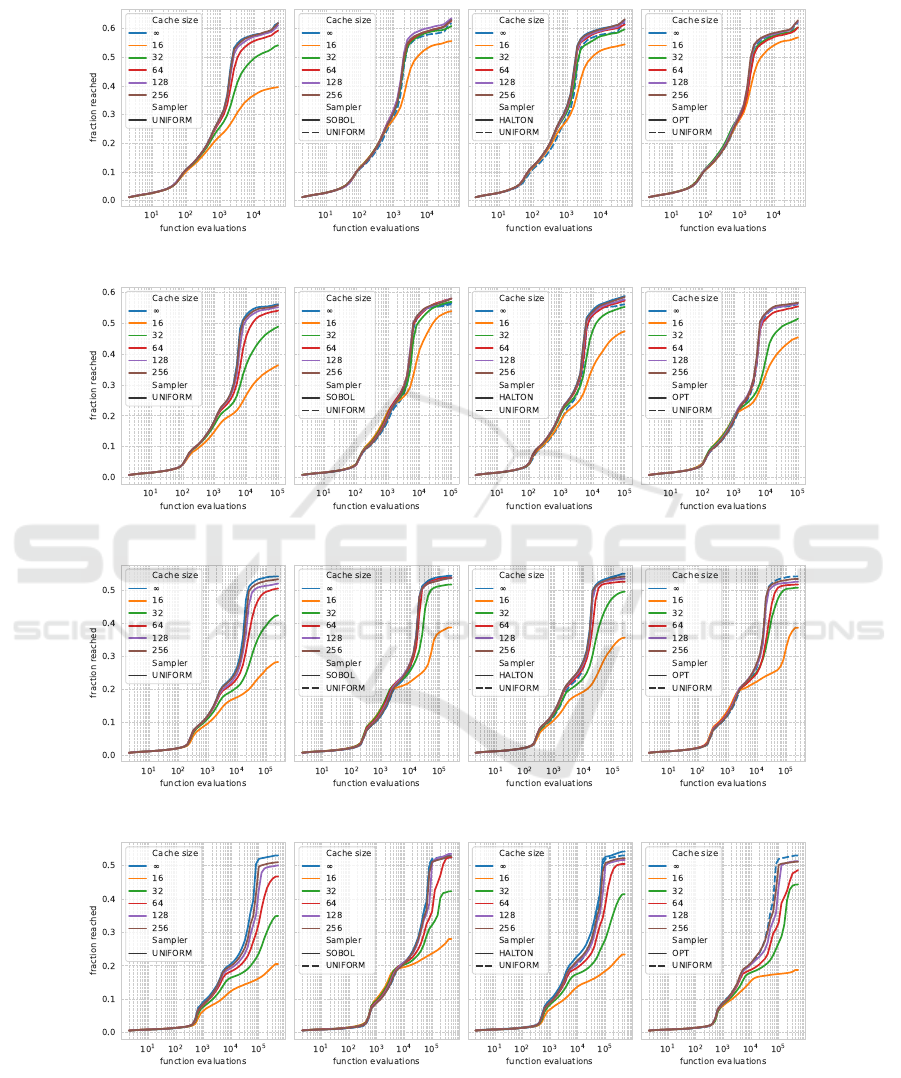
APPENDIX
(a) Dimensionality 5
(b) Dimensionality 10
(c) Dimensionality 20
(d) Dimensionality 40
Figure 6: Empirical Attainment Function aggregated over all 24 BBOB functions for dimensionalities 5, 10, 20, and 40 (from
top to bottom). The methods are shown in color for each sampling strategy, with cache size indicating the number of points in
the cache and ∞ indicating no caching; every sample is unique. From left to right, the subfigures show results using a uniform
sampler, a Sobol sequence, a scrambled Halton sequence, and the optimized point sets. Note that in the three rightmost
figures, the default CMA-ES sampling strategy, UNIFORM-∞, is included for comparison.
ECTA 2024 - 16th International Conference on Evolutionary Computation Theory and Applications
126
