Finding Strong Lottery Ticket Networks with Genetic Algorithms
Philipp Altmann, Julian Sch
¨
onberger, Maximilian Zorn and Thomas Gabor
LMU Munich, Germany
Keywords:
Evolutionary Algorithm, Neuroevolution, Lottery Ticket Hypothesis, Pruning, Neural Architecture Search.
Abstract:
According to the Strong Lottery Ticket Hypothesis, every sufficiently large neural network with randomly
initialized weights contains a sub-network which – still with its random weights – already performs as well
for a given task as the trained super-network. We present the first approach based on a genetic algorithm to
find such strong lottery ticket sub-networks without training or otherwise computing any gradient. We show
that, for smaller instances of binary classification tasks, our evolutionary approach even produces smaller and
better-performing lottery ticket networks than the state-of-the-art approach using gradient information.
1 INTRODUCTION
A central aspect to the wide success of artificial neu-
ral networks (ANNs) is that they are usually designed
to be overparametrized (Aggarwal et al., 2018). That
means that they feature more parameters (weights)
than are strictly necessary to represent the function
they are meant to approximate. However, it is also
that overparametrization that constructs a solution
landscape that is friendly towards relatively simple
optimization strategies like stochastic gradient de-
scent (Shevchenko and Mondelli, 2020), whose ap-
plication is also enabled by the fact that neural net-
works are usually differentiable and can thus pro-
vide gradient information to the optimization algo-
rithm. The Lottery Ticket Hypothesis (Frankle and
Carbin, 2018) and its variants (Ramanujan et al.,
2020) have provided a different perspective on the
properties of neural networks: Among the randomly
initialized weights (before any optimization), some
weights have already “won the lottery” by being eas-
ily trainable. Furthermore, in any sufficiently over-
parametrized network, there already exist — at the
point of random initialization — certain subnetworks
that (when unhinged from the rest of the network) ap-
proximates the desired function as accurately as the
whole network would after optimization. Thus, if
these subnetworks or strong lottery tickets could be
found easily, the whole training process of neural net-
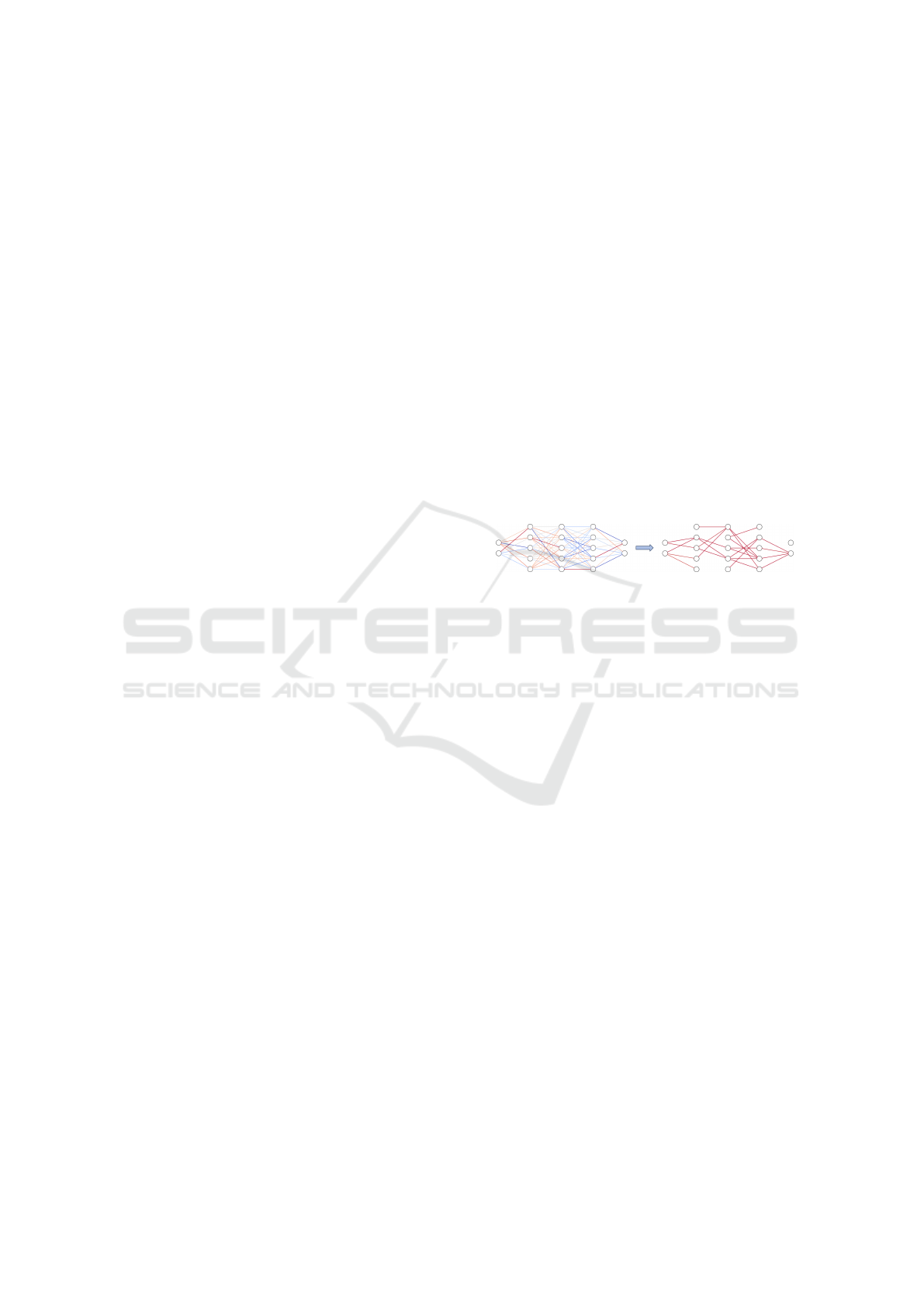
works could be skipped. Figure 1 illustrates a lottery
ticket network evolved from a full network with much
more active (i.e., non-zero) connections.
Finding such subnetworks naturally requires a
Figure 1: Illustration of a lottery ticket network. Top: Full
network graph. Red connections persist in most evolved lot-
tery ticket networks in an example population (blue connec-
tions do not). Bottom: Example of an evolved lottery ticket
subnetwork with only a fraction of active connections.
substantial computational load, as the number of pos-
sible combinations of connections to prune from the
subnetwork grows exponentially with the network
size. This makes it difficult for a lottery-ticket-based
optimization alternative to succeed in practice. In
fact, state-of-the-art methods for finding lottery tick-
ets tend to utilize regular training steps of the full net-
work (without changing the weights) to identify more
important connections to be kept in the subnetwork.
This paper presents a novel approach to find-
ing strong lottery tickets based purely on combina-
torial evolutionary optimization without training the
weights or utilizing gradient information. To the best
of our knowledge, this is the first approach in this di-
rection. We summarize our contribution as follows:
• We show that a basic genetic algorithm (GA) can
already produce strong lottery ticket networks.
• Our approach yields sparser and more accurate
networks compared to the gradient-based state-of-
the-art in exemplary binary classification tasks.
• Uncovering scenarios where the utilized GA op-
erations are insufficient, we hope to pave the way
for further investigating the applicability of GAs
for optimizing neural networks or similar entities.
Altmann, P., Schönberger, J., Zorn, M. and Gabor, T.
Finding Strong Lottery Ticket Networ ks with Genetic Algorithms.
DOI: 10.5220/0013010300003837
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 16th International Joint Conference on Computational Intelligence (IJCCI 2024), pages 449-460
ISBN: 978-989-758-721-4; ISSN: 2184-3236
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
449

2 RELATED WORK
The Lottery Ticket Hypothesis has received consider-
able attention in recent years, and as such, many con-
nections to adjacent fields have been discovered. In
this section, we will elaborate on the existing litera-
ture and how it relates to our work.
Lottery Ticket Hypothesis. Frankle and Carbin
(2018) discovered that a network that was pruned af-
ter training and then had its remaining weights reset
to their original random-initialized value could then
be trained again to achieve a comparable test accu-
racy to the original network in a similar number of
iterations. They called this phenomenon the Lottery
Ticket Hypothesis (LTH) and the pruned subnetwork
a winning ticket. They developed an algorithm based
on iterative magnitude pruning to find these winning
tickets. Since then, many approaches have been de-
veloped to find these winning tickets: Jackson et al.
(2023) use an evolutionary algorithm where they cal-
culate the fitness based on the network density and
validation loss in an attempt to deal with the trade-
off between the sparsity and the accuracy of the sub-
network. Other subsequent work (Zhou et al., 2019;
Wang et al., 2020b) extended the LTH by empiri-
cally showing that it is possible to find subnetworks
that already have better accuracy than random guess-
ing within randomly initialized networks without any
training. Zhou et al. (2019) identify neural network
masking as an alternative form of training and intro-
duce the notion of “supermasks.”
Strong Lottery Ticket Hypothesis. Ramanujan
et al. (2020) built upon this idea and proposed the
Strong Lottery Ticket Hypothesis (SLTH): A suffi-
ciently overparameterized neural network with ran-
dom initialization contains a subnetwork, the strong
lottery ticket (SLT), that achieves competitive accu-
racy (w.r.t. the large, trained network) without any
training (Malach et al., 2020). Additionally, they in-
troduced edge-popup, an algorithm for finding strong
lottery tickets by approximating the gradient of a so-
called pop-up score for every network weight. These
popup scores are then updated via stochastic gra-
dient descent (SGD). A series of theoretical works
studied the degree of required overparameterization
(Malach et al., 2020; Orseau et al., 2020; Pensia
et al., 2020) and proved that a logarithmic overparam-
eterization is already sufficient (Orseau et al., 2020;
Pensia et al., 2020). On the quest for more effi-
cient methods for finding SLTs, Whitaker (2022) pro-
posed three theoretical quantum algorithms that are
based on edge-popup, knowledge distillation (Hinton
et al., 2015), and NK Echo State Networks (Whit-
ley et al., 2015). Finally, Chen et al. (2021) intro-
duced an additional type of high-performing subnet-
work called “disguised subnetworks” that differ from
regular SLTSs in the way that they first need to be
“unmasked” through certain weight transformations.
They retrieve these special subnetworks via a two-
step algorithm performing sign flips on the weights of
pruned networks using Synflow (Tanaka et al., 2020).
Weak Lottery Ticket Hypothesis. Only a few
methods for finding strong lottery tickets have been
developed to this point, and most of the empirical
work has been focused on the original LTH. They
identify so-called weak lottery tickets that can achieve
competitive accuracies (on the much smaller sub-
networks), but only when the subnetworks’ weights
are re-trained. This cycle of training, pruning, and
re-training is generally expensive, and the advan-
tages compared to standard training are less obvi-
ous. In contrast, searching for strong lottery tick-
ets allows one to uncover high-accuracy scoring sub-
networks without any (potentially expensive) (re-
)training steps. Furthermore, its combination with
meta-heuristic optimization allows the application to
structures of discontinuous functions that would not
be learnable via gradient-based approaches. In this
paper, we propose a method for finding strong lot-
tery tickets that is based purely on genetic algorithms.
Existing methods often use heuristics and pseudo-
training algorithms that work with some form of gra-
dient descent and usually fix pruning ratios before-
hand. In contrast, our approach does not require
gradient information, can directly optimize the sub-
network encoding, and does not apply any artificial
bound to the maximum number of pruned weights.
Moreover, genetic algorithms frequently excel at dis-
covering high-quality solutions to NP-hard problems
and due to their stochastic nature and global search
capabilities are generally well suited for optimizing
non-convex objective functions with many local min-
ima, saddle points and plateaus. In the case of the
SLTH the optimization landscape is highly complex,
with potential non-convexity due to masking, ran-
dom initialization and the loss function. Note that the
method of Jackson et al. (2023), although very similar
to our method, applies the evolutionary algorithm to
the original LTH and can thus only find weak lottery
tickets that have to be trained.
Extreme Learning Machine. Huang et al. (2006)
proposed Extreme Learning Machine (ELM), an ap-
proach conceptually similar to the SLTH, where the
random parameter values of the hidden layer in a
NCTA 2024 - 16th International Conference on Neural Computation Theory and Applications
450

single-hidden-layer neural network are fixed, while
the optimal weights of the output layer are calculated
using the closed-form solution for linear regression.
In comparison to SLTs, the dense models are less
parameter-efficient, do not scale well to deep architec-
tures requiring complex adaptations e.g. based on Au-
toencoders (Kasun et al., 2013) and include the calcu-
lation of the matrix inverse which is computationally
intensive.
Neural Architecture Search. There are parallels
between neural architecture search (NAS) and search-
ing for lottery tickets since, in both cases, we generate
a network of previously unknown structures and un-
trained (but perhaps selected) weights. Gaier and Ha
(2019) investigated the influence of the network ar-
chitecture compared to the initialization of its param-
eters when it comes to solving a specific task. They
initialized all parameters with a single value sampled
from a uniform distribution and concluded they could
find architectures that achieved higher-than-random
accuracy on the MNIST dataset. Wortsman et al.
(2019) developed a method that enables continuous
adaptation of a network’s connection graph and its
parameters during training. They showed that the
resulting networks outperform manually engineered
and random-structured networks. Compared to our
approach, Gaier and Ha (2019) use a single fixed
value for the parameters instead of drawing values
from a random distribution. The approach presented
by Wortsman et al. (2019) is an alternative to find-
ing winning tickets. Ramanujan et al. (2020) then in-
troduced edge-popup inspired by that work, but since
their learning of the network structure and its param-
eterization is inseparable, their approach cannot be
used to find a pruning mask for strong lottery tickets.
Evolutionary Pruning. In contrast to NAS or the
related field of neuroevolution, both of which typi-
cally include evolving the topology of the network,
evolutionary pruning solely focuses on pruning the
network, i.e., removing connections and possibly
whole neurons from the network graph. With such
techniques, many networks can be reduced in size
without affecting their performance. This branch of
research consists of methods that differ in the choice
of solution representation (direct encoding or indirect
encoding) and the number of objectives. Methods that
use direct encoding often work with binary masks that
are applied to structures of the network, e.g., single
weights or convolution filters (Wu et al., 2021). Typi-
cal multi-objective tasks include, apart from the spar-
sity goal, also things like accuracy improvement or
energy consumption (Wang et al., 2021b). Our ap-
proach also works with binary pruning masks and the
two objectives, accuracy and sparsity, but to the best
of our knowledge, we are the first to apply evolution-
ary pruning to the setting of the SLTH.
Other Pruning Methods. According to Wang et al.
(2021a), besides the classic LTH, which applies static
pruning masks on trained networks, and the SLTH,
which does not involve any training, there is a third
branch of methods that prune at initialization using
pre-selected masks (Lee et al., 2018; Wang et al.,
2020a; Tanaka et al., 2020). For example, Lee et al.
(2018) created a pruning mask before training, which
zeroed out all structurally unimportant connections,
as determined by a new saliency criterion called con-
nection sensitivity. Like our approach, their approach
is one-shot since the network only needs to be pruned
once, but there is still training involved, and very spe-
cific pruning criteria are required to determine good
subnetworks.
3 METHOD
In the following, we will discuss the components of
the genetic algorithm, including the structure of our
solution candidates, the way we determine their fit-
ness and select parents and survivors accordingly, as
well as the different genetic operations that guide the
evolutional process.
Solution Representation. Our approach generates
strong lottery ticket networks via an evolutionary al-
gorithm. We assume that the task that the network
is meant to solve is fixed (e.g., given by a classifi-
cation accuracy function L). We are also given the
architecture graph of the full network and the vec-
tor of its n ∈ N randomly initialized weights w =
⟨w
0
,...,w
n
⟩ with w
i
∈ R for all i. Our approach then
produces a (genotype) bit mask b = ⟨b
1
,...,b
n
⟩ with
b
i
∈ {0,1} for all i so that the (phenotype) masked
network w
′
= ⟨b
i
· w
i
⟩
i=1,...,n
is significantly smaller
than the full network w.r.t. non-zero weights, but per-
forms approximately as well as a trained successor of
the full network w.r.t. L. Formally, let w
∗
be the n
weights of the trained full network, then b should ful-
fill
∑
n
i=0
b
i
<< n and L(w
′
) ≈ L(w
∗
). Note that we
only consider weights in the parameter vector and not
any of the potential bias nodes of the network. Yet, al-
though the biases do not get pruned, we still initialize
them using our chosen initialization method.
Finding Strong Lottery Ticket Networks with Genetic Algorithms
451

Fitness and Selection. To drive the evolution of
strong lottery tickets, we perform lexicographic evo-
lutionary optimization. We define two objectives: Our
primary goal is to find subnetworks that match the
accuracies achieved by standard training. Our sec-
ondary goal is to retrieve subnetworks that are as
sparse as possible without having a negative impact
on the accuracy. This multi-objective approach al-
lows us to prune subnetworks by a considerable mar-
gin even after very high accuracies have already been
achieved. The evaluation of the individuals happens
in two places in our evolutionary pipeline: For parent
selection (i.e., selecting the individuals for recombi-
nation), we only consider the accuracy goal, whereas
for survivor selection (i.e., selecting the individuals
for the next generation), we also consider the sparsity
goal. This accounts for the fact that recombination
is the main contributor to better-performing individ-
uals throughout the evolution. Focussing solely on
the accuracy goal for parent selection leads to an ef-
fective prioritization. The fitness corresponds to the
measured accuracy on the train dataset, and the indi-
viduals are ranked accordingly. Even though we also
consider the sparsity for survivor selection, accuracy
is still the main determinant, i.e., for survivor selec-
tion, we prefer individuals with a higher sparsity value
within groups of individuals with the same accuracy.
We use (elitist) cut-off selection for survivor se-
lection
1
. This method selects the top k individuals of
the current population and transfers them to the next
generation’s population. In our case, k = N where N
is the original population size; since none of our ge-
netic operators are in place, the population typically
grows beyond its original size N in between gener-
ations and needs to be reduced for the next genera-
tion. For parent selection, any individual may be cho-
sen as a first parent with a chance rec rate ∈ [0,1]
and matched with a second parent chosen randomly
from the top l individuals in the current population
where l = N · par rate is defined via a hyperparam-
eter par rate.
Genetic Operators. We implement two steps to
generate our initial population: First, the individu-
als are generated randomly, i.e., each bit has an equal
likelihood of being chosen at any given point in the
pruning mask. Second, from the randomly gener-
ated individuals, we discard those that do not reach
a certain accuracy bound. In our implementation, we
choose to use an adaptive bound that can decrease dy-
namically if too few individuals match the boundary
1
We also tried other selection methods, like roulette or
random walk selection, but we found that the choice of se-
lection method had no significant impact.
value, following the shape of a pre-defined exponen-
tial function, to reduce the effects that random sam-
pling has on runtime. Using the adaptive accuracy
bound allows for a higher initial bound and proved to
have a positive influence on the final accuracies. For
the following, we refer to the configuration that per-
forms only the first step as GA, and the configuration
that uses an adaptive accuracy bound (i.e., the first and
the second step) is named GA (adaptive AB)
2
.
We perform single-point mutation, randomly se-
lecting individuals from the current population at a
chance mut rate and generating a mutant via one
random bit flip. For recombination, we use ran-
dom crossover on two parents. Note that mutants
and children are always added to the population and
never directly replace their parents. Finally, to fur-
ther increase the diversity in the population, we add
m freshly generated individuals to the population in
each generation. The value of m = N · mig rate is
given by the hyperparameter mig rate.
4 EXPERIMENTAL SETUP
To evaluate the capabilities of the previously dis-
cussed genetic algorithm in finding SLTs, we apply
it to multiple datasets and different network architec-
tures. The performance is then compared to the state-
of-the-art approach. We conclude with an analysis of
the implications of having more than two classes.
Hyperparameters. For the following experiments,
our GA works with a fixed population size of N = 100
individuals. Additionally, we use fixed rates for par-
ent selection, recombination, mutation, and migra-
tion: For recombination, we use a rec rate = 0.3,
which implies that around 30% of individuals from
the whole population are chosen to become a first
parent. Due to par rate = 0.3, then the recombi-
nation mate of any first parent is randomly chosen
from the top 30% of the population. We choose
mute rate = 0.1 so that approximately 10% of the
individuals generate a mutant to be added to the pop-
ulation. That is a fairly high value, but we intend to
generate highly explorative runs. For the same rea-
son, we set the mig rate = 0.1 so that around 10%
of the interim population before survivor selection is
made up of freshly generated individuals. Table 1
summarizes the chosen hyperparameter values. Our
GA terminates if the population evolved for at least
100 generations with no accuracy improvement in the
2
All required implementations are available at https://
github.com/julianscher/SLTN-GA.
NCTA 2024 - 16th International Conference on Neural Computation Theory and Applications
452

(a) Moons (b) Circles
Architecture moons, circles digits
A [2, 20, 2] [64, 20, 10]
B [2, 75, 2] [64, 75, 10]
C [2, 100, 2] [64, 100, 10]
D [2, 50, 50, 2] [64, 50, 50, 10]
(c) Network architectures
Figure 2: Overview of our datasets and network architectures we use on them: The moons ((a)) test dataset consisting of
16000 2d-datapoints, normalized on the interval [−0.7,0.7], and the circles ((b)) test dataset consisting of two different-
sized rings with 16000 2d-datapoints from scikit-learn (Pedregosa et al., 2011), and the network architectures ((c)) with a
single-lettered identification code. The bracket notation describes the number of neurons in the different network layers. The
first number corresponds to the number of input neurons. The last is the number of output neurons.
last 50. When using GA (adaptive AB), we restrict
the evolution to take at maximum 200 generations,
due to us observing that from that point forward the
accuracy improvement usually is only marginally and
does not justify the additional runtime costs. We did
not perform any explicit hyperparameter search for
determining optimal values, but based our decisions
on observations made throughout the implementation
phase. This allows us to reason about the general per-
formance of the GA, which can be expected even with
potentially suboptimal hyperparameter values.
Table 1: The used hyperparameters for our GA evaluation.
Hyperparameter Value
pop size N 100
rec rate 0.3
par rate 0.3
mut rate 0.1
mig rate 0.1
Datasets. Our experiments are built on three
datasets with varying complexities. We chose clas-
sification tasks as they can be easily interpreted and
come with a clear and tried evaluation metric. The
two-dimensional moons dataset with only two classes,
depicted in Figure 2a, consists of two moon-shaped
point clusters with little to no overlap. A 2-layered
network with only 6 hidden cells trained via back-
propagation already achieves approximately 100%
accuracy in some runs. In contrast to this rather sim-
ple dataset, we selected the circles dataset, pre-
sented in Figure 2b as a more challenging 2d binary
classification problem. The two classes are arranged
as two Gaussian-shaped rings, where the bigger ring
surrounds the smaller ring. The transition is imme-
diate, and there are many overlapping points, which
is a challenging task even for the trained dense net-
work. We generate 66000 random data points for
both datasets and add Gaussian noise with σ = 0.07.
As a third dataset, we use the digits dataset, which
consists of 1797 images with size 8 × 8 pixels each
and class labels {0,..., 9}. We split the datasets into
a training and a test dataset, using 25% of the data
points for testing. Additionally, we perform min-max
normalization on the moons and the digits datasets
to mitigate potentially negative scaling effects for the
networks, which can arise from non-Gaussian distri-
butions.
Network Architectures. We only use classical
feed-forward ANNs with ReLU activation for the
neurons in the input and hidden layers. Since for
the GA we are primarily interested in the final accu-
racies and not the class probabilities we do not use
a softmax activation function, but instead, calculate
the accuracies directly using the class of the highest
valued network output. In order to get a better intu-
ition about the GA’s behavior across different model
sizes, we test 4 network architectures as listed in Ta-
ble 2c in our experiments. For simplicity, we only de-
note the analyzed network architectures by “A”, “B”,
“C”, and “D” in the later plots. Our studies showed
that the choice of the network parameter initialization
method greatly impacts the achieved final accuracies.
We sample the network weights from a uniform dis-
tribution over the interval [−1,1] for all our GA ex-
periments. This method proved to yield the best over-
all results on the considered datasets. Additionally,
there already exist proofs for the existence of SLTs
based on uniform parameter initializations (Malach
et al., 2020; Pensia et al., 2020). Although most of
the work on the SLTH works with zeroed-out biases,
we experienced a significant performance boost when
we initialized the biases by sampling from the same
uniform distribution.
Baselines. Finally, since, by definition of strong lot-
tery tickets, we are particularly interested in the com-
parative performance of a network that was trained
using a gradient-based method, we use backpropaga-
Finding Strong Lottery Ticket Networks with Genetic Algorithms
453

tion as a baseline. To compare against a sophisticated
implementation of a trainable feed-forward network,
we used the MLPClassifier module from scikit-learn
and performed hyperparameter tuning on all 4 archi-
tectures using their RandomizedSearchCV function.
We employ random search because of its computa-
tional efficiency in exploring large parameter spaces
with a limited computation budget. The chosen pa-
rameter ranges were selected based on prior knowl-
edge and preliminary experiments. Specifically, the
tuned hyperparameters include solvers, learning rates,
batch sizes, momentum, alphas (for l2 regulariza-
tion) and epsilon values (for numerical stability). An
overview of the resulting values is provided by Table
2. The search and the subsequent training lasted 1000
epochs to ensure convergence. Our studies compare
the mean accuracies of the backpropagation trained
networks from Table 2c on the test datasets.
Table 2: Listing of the determined backpropagation hyper-
parameters for the MLPClassifier model from scikit-learn
using random search.
Dataset Solver Learning Rate Learning Rate Init Epsilon Batch Size Alpha Momentum
moons
adam constant 0.021544 4.64e-09 128 0.0001 -
adam constant 0.001 4.64e-09 64 0.000215 -
adam constant 0.001 4.64e-09 64 0.000215 -
adam constant 0.001 4.64e-09 64 0.000215 -
circles
sgd adaptive 0.1 - 64 0.046416 0.0
sgd adaptive 0.004642 - 128 0.046416 0.5, nesterov
adam constant 0.001 4.64e-09 64 0.000215 -
sgd adaptive 0.1 - 128 0.046416 0.0, nesterov
5 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
5.1 GA Performance Analysis
As mentioned previously, we use 4 different network
architectures in our experiments (cf. Table 2c). The
general intuition would be that networks with higher
parameter counts are more likely to contain param-
eters with lucky initializations, leading to higher-
scoring subnetworks. Additionally, we are interested
in whether the usage of an accuracy bound for the
generation of the initial population has a noticeable
impact on the subsequent evolution.
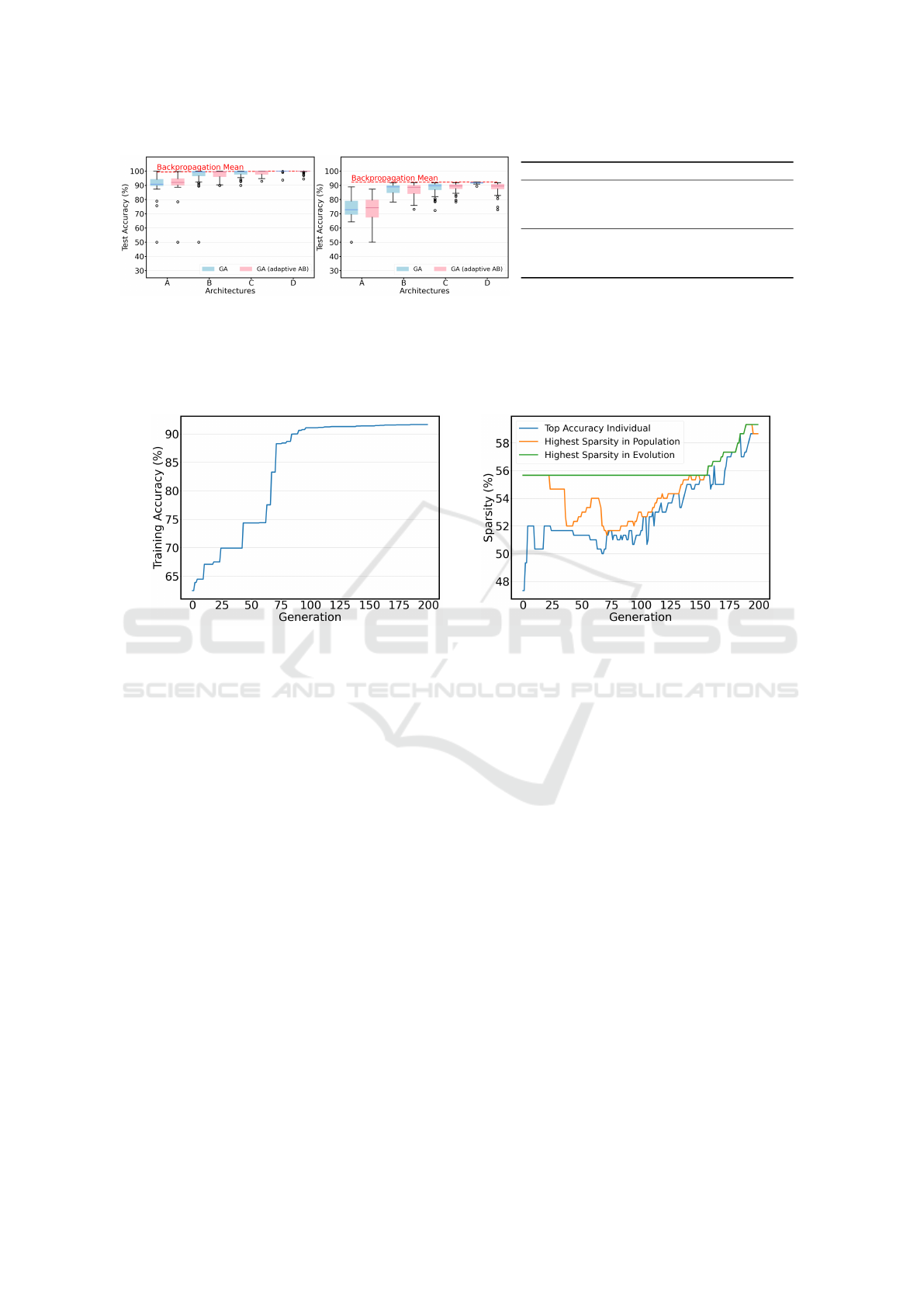
The results for the moons dataset are shown in
Fig. 3a. We observe that the GA is able to achieve
very high final accuracies, reaching almost 100%
mean accuracy for network D. Examining the distri-
bution of the different GA runs for the various net-
work architectures, there exists a clear connection be-
tween the number of network parameters and the per-
formance. Whereas, for the smallest network A with
only 80 parameters, the mean difference to backprop-
agation is around 9%. The difference diminishes con-
tinuously with increasing parameter count. For net-
works C and D, the mean approximately matches that
of backpropagation, and for network D, there remains
only little variance between the runs. The difference
in performance between the different GA configura-
tions is less prominent. In general, the mean for the
runs using an accuracy bound is a little higher than
those that did not use it, but for increasing network
sizes, this effect plays less of a role.
The results on the circles dataset, illustrated in
Fig. 3b, mostly support these findings. Consider-
ing the mean performance of backpropagation, it be-
comes clear that the circles dataset has higher com-
plexity than the moons dataset. The GA, again, scores
the lowest accuracies on network architecture A but
reaches higher final accuracies on the larger networks.
The highest mean accuracy of 91.6% is achieved on
network D, but this time without using an accuracy
bound. Also, there seems to be a certain minimum
threshold for the parameter count before which the fi-
nal accuracies are noticeably lower, but increasing the
network size has less of an effect after exceeding it.
Still, we can say that there exist situations where the
GA is able to score very similar accuracies to back-
propagation.
To get an impression of the typical behavior of the
GA regarding the development of our accuracy and
sparsity objectives, we selected one high-performing
example run from the runs on the circles dataset;
that run was performed on network architecture B us-
ing the GA configuration with an adaptive accuracy
bound. In Fig. 4a, we see that the individual with the
highest fitness in the initial population had less than
65% accuracy. This accuracy is then successively im-
proved in the first 100 generations, taking a set of
big leaps until the final accuracy reaches a plateau
at around 91% accuracy. This clearly shows the op-
timization capabilities of the genetic algorithm. For
the next 100 generations, until the generation thresh-
old for GA (adaptive AB) is reached, only minor im-
provements are made. Meanwhile, Fig. 4b shows how
the sparsity develops over the course of the evolution.
Typical behavior is that the sparsity decreases in the
first half of the generations since we prioritize achiev-
ing our accuracy goal, and only when the improve-
ment of the accuracy slows down does the optimiza-
tion of the sparsity really start to show. GA really
started to improve on the sparsity objective. That is
because, at that point, the population is very homoge-
neous, and there are many individuals with the same
accuracy. In this run, the GA achieved an additional
improvement of around 10% in sparsity compared to
the top individual in the initial population.
Scalability. Calculating the fitness of the individu-
als in the population is the decisive factor on runtime
NCTA 2024 - 16th International Conference on Neural Computation Theory and Applications
454
(a) moons, R = 50 (b) circles, R = 50
Arch. GA GA (adaptive AB) Backprop.
moons
A 90.7% ± 7.2 90.9% ± 9.1 99.4% ± 2.4
B 96.9% ± 7.3 97.5% ± 3.3 99.6% ± 1.9
C 98.4% ± 2.5 98.9% ± 1.7 99.8% ± 1.4
D 99.8% ± 0.9 99.6% ± 1.0 99.9% ± 0.0
circles
A 73.9% ± 8.1 73.7% ± 8.6 92.3% ± 0.1
B 87.3% ± 3.6 86.8% ± 4.4 92.4% ± 0.0
C 88.0% ± 4.3 88.5% ± 3.2 92.3% ± 0.0
D 91.6% ± 0.5 88.3% ± 4.0 92.4% ± 0.0
(c) Reached mean accuracies ± standard deviation
Figure 3: Overview of the performance of the GA in the moons (a) and circles (b) datasets. The blue boxes contain different
runs for every architecture using the default GA configuration. The pink boxes contain the results of R runs for the GA
configuration that uses the adaptive accuracy bound with initial threshold value 0.85. For comparison, we added the mean
accuracies that were achieved with the trained networks using backpropagation. (c) summarizes the achieved accuracies.
(a) Accuracy (b) Sparsity
Figure 4: Optimization progress of one well-performing run using “GA (adaptive BA)” on network architecture B = [2,75, 2]
in the circles dataset with regard to the accuracy (a), and the sparsity (b). The blue line shows the sparsity of the fittest
individual in the current population. The orange line displays the top sparsity in the current population, and the green line
represents the current best sparsity found in all previous generations.
complexity with O(g ∗ N ∗ (d ∗l ∗b
2
)) multiplications
for an evolution with g generations, a population of
size N, d dataset samples and a worst case network
architecture with l ∗ b
2
parameters (i.e., length of the
bit-vector). Typically N < g and (l ∗ b
2
) ≪ d. In prac-
tice, the effect of g ∗ N on the runtime can be reduced
by efficient parallelization. A compressed version of
the subnetwork encoding reduces the complexity for
the other GA operations.
5.2 Edge-Popup & Weight Initialization
In the previous subsection, we saw that the GA per-
forms well on the given binary classification tasks,
achieving accuracies that are very close to or even
match the accuracies obtained by training via back-
propagation, given a sufficient network architecture
is chosen. To get an idea of how well the GA per-
forms in comparison to other methods that search
for SLTs in a randomly initialized neural network,
we repeat our previous experimental setup using the
well-known edge-popup algorithm (Ramanujan et al.,
2020). Edge-popup assigns a score to each weight
of the neural network and constructs subnetworks by
only choosing the top k% scoring edges in each layer
for the forward pass. The scores are updated in the
backward pass by using the straight-through gradi-
ent estimator (Bengio et al., 2013). Once pruned,
edges can re-appear in a subnetwork since the edges’
contribution to the loss is continuously re-evaluated
when approximating the gradients. The parameter
k in the forward pass denotes a fixed value, which
is also called the pruning rate. Therefore, a prun-
ing rate of 60% corresponds to a subnetwork where
(1 − k) = 40% of weights are pruned. Note that the
sparsity metric we use in our work works the other
way around. A subnetwork with a sparsity of 60%
means 60% of weights are pruned.
We use the default settings from the authors and
train for a total of 100 epochs. Every configuration
is evaluated on 25 random seeds. The authors found
two initialization methods that worked particularly
Finding Strong Lottery Ticket Networks with Genetic Algorithms
455
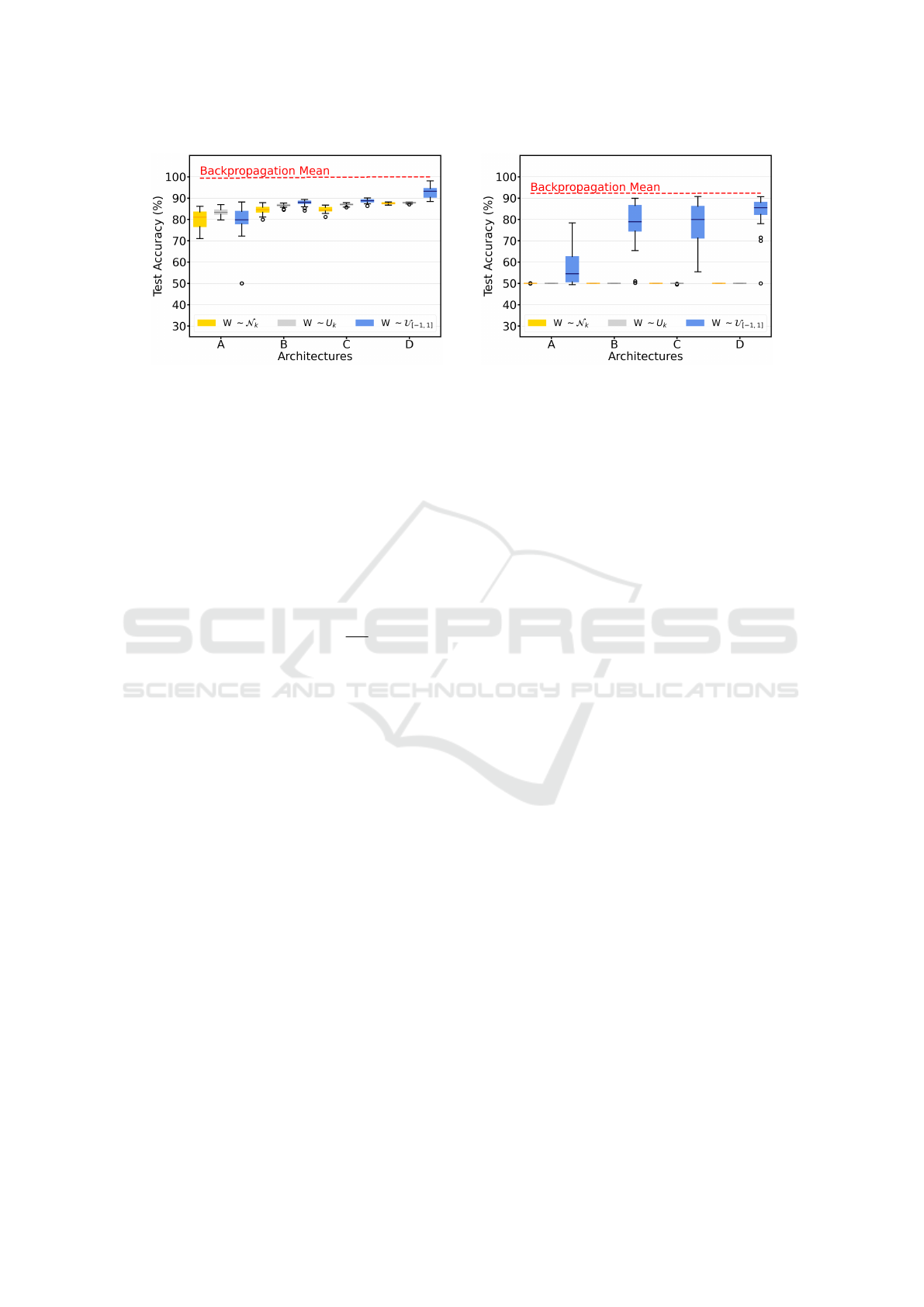
(a) moons, R = 25 (b) circles, R = 25
Figure 5: Illustration of the performance of edge-popup on shown datasets using the different color-coded initializations with
R runs each. The backpropagation mean accuracies on the respective architectures (dashed line) are provided for comparison.
well for their experiments: initializing the network
parameters from a Kaiming normal distribution (also
known as He initialization (He et al., 2015)), which
(following the notation of Ramanujan et al. (2020))
we refer to as “Weights ∼ N
k
”, or sampling from a
signed Kaiming constant distribution, which we refer
to as “Weights ∼ U
k
”. Thus, in addition to using our
initialization method, which we indicate as “Weights
∼ U
[−1,1]
”, we also consider runs where the networks
are initialized using both of their methods. Note that
we use the scaled versions of these methods, where
the standard deviation is scaled by
p
1/k. For the ex-
act definitions of these methods, refer to Ramanujan
et al. (2020). As with our GA, we also sample the
biases from the uniform distribution when using our
parameter initialization method with edge-popup.
Due to the considerable performance difference
between alternative parameter initializations for our
GA, which is also supported by the findings of Ra-
manujan et al. (2020), we start with an ablation study
to determine the highest accuracy achieving initial-
ization technique for edge-popup before proceeding
with the actual comparison studies. Fig. 5a shows
the results of the different runs edge-popup on the
moons dataset. The trend that the larger the network,
the higher the final accuracies on the moons dataset
typically are, seems to apply here as well. It is also
noticeable that the runs using our parameter initial-
ization method (apart from network A) generally out-
performed the other run-throughs. In the case of net-
work D, it did so by quite a significant margin (≈ 5%
mean difference). Nevertheless, in none of the set-
tings, edge-popup’s mean accuracy comes close to
the performance of backpropagation. The same holds
for the circles experiment, as shown in Fig. 5b, ex-
cept here, the Kaiming normal and signed Kaiming
constant distributions proved to be completely insuf-
ficient. There is no run where the classification accu-
racy is better than random, i.e., the predicted class la-
bel is correct in only 50% of cases. Considering these
results, one might assume that this is an algorithmic
issue, but since edge-popup performs well with our
initialization method, the issue has to be the Kaim-
ing normal or Kaiming singed constant distributions.
A potential reason might be the Gaussian nature of
the rings, which has a distorting effect on the meth-
ods. Finding the exact cause remains subject to future
work. In summary, it seems that at least for the moons
and circles datasets, edge-popup benefits from us-
ing uniform initialization. Going forward, we, there-
fore, decided to sample the parameters for both the
GA and edge-popup from the same distribution.
Considering the contrary development of the ac-
curacy and sparsity levels at the beginning of the evo-
lution (cf. Fig. 4b), we hypothesize a correlation. This
also implies a potential connection between the num-
ber of pruned parameters throughout the evolution
and the final achieved fitness. Opposed to us, edge-
popup works with fixed pruning rates. To rule out any
performance deficits that might arise because of this
inflexibility, we include additional edge-popup runs in
our comparison study, where we set the pruning rates
to the mean sparsity levels that can be achieved with
the two GA configurations. We chose that configura-
tion for every architecture and dataset, which scored
the highest mean accuracy, and reran the edge-popup
experiments with the derived mean sparsity levels.
The results of our comparison study are depicted
in Fig. 6. For an extensive evaluation, we plotted the
mean accuracy of the best-performing GA configura-
tion for the respective architecture, together with the
mean accuracies of backpropagation and the original
edge-popup runs. The shaded area around the line
plots represents the 95% confidence intervals for the
estimation of the mean. Relevant for the compari-
son of edge-popup with the adapted pruning rates, we
NCTA 2024 - 16th International Conference on Neural Computation Theory and Applications
456
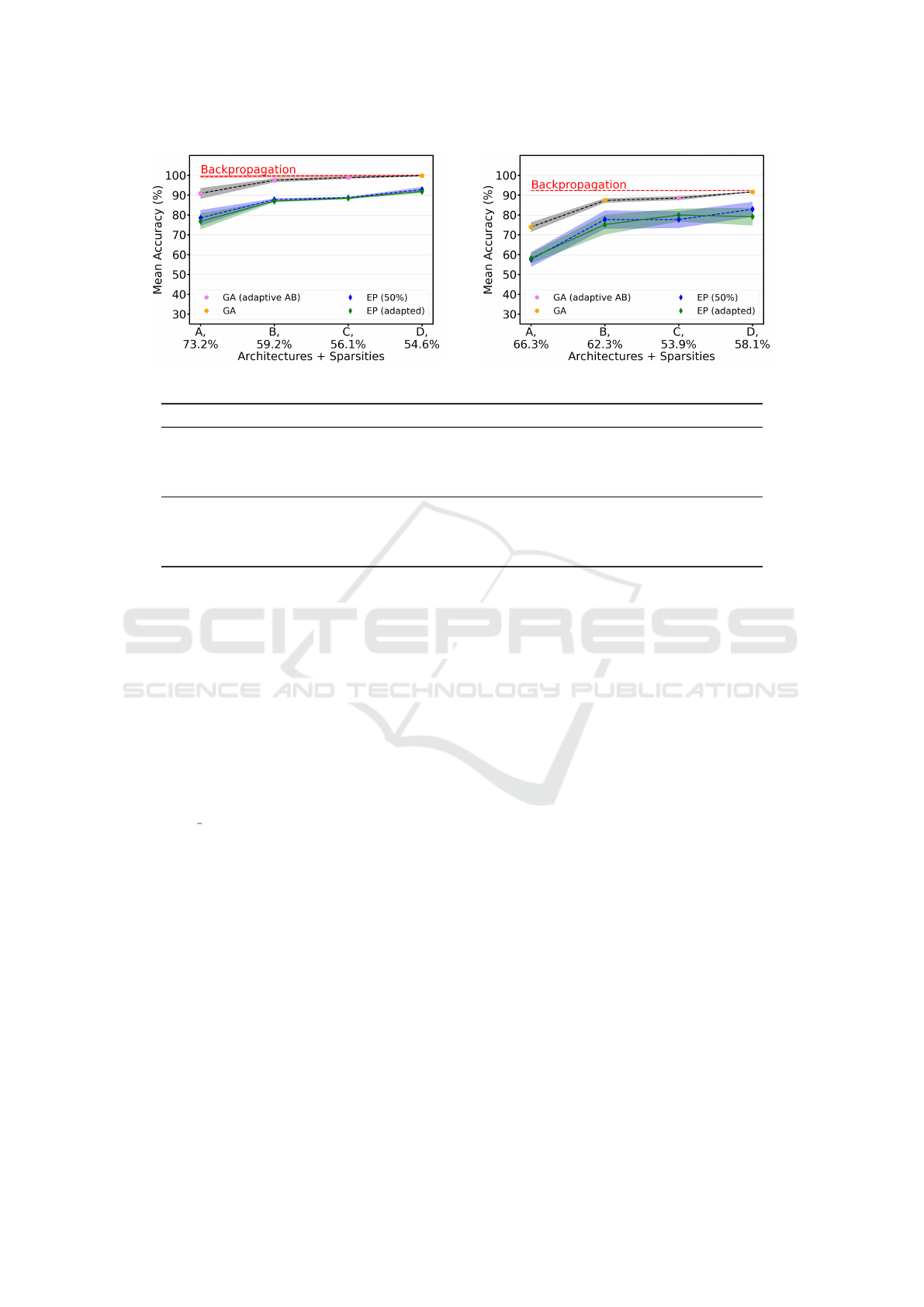
(a) moons (b) circles
Dataset Reference Target Coef. Std. Err. z P > |z| 95%-Conf.
moons
GA GA (adaptive AB) 0.042 0.083 0.507 0.612 [-0.121, 0.205]
EP (50%) EP (adapted) -0.133 0.095 -1.405 0.160 [-0.320, 0.053]
GA EP (50%) -1.185 0.081 -14.697 0.000 [-1.343, -1.027]
GA Backpropagation 0.661 0.087 7.609 0.000 [0.491, 0.831]
circles
GA GA (adaptive AB) -0.106 0.064 -1.670 0.095 [-0.231, 0.018]
EP (50%) EP (adapted) -0.062 0.102 -0.609 0.543 [-0.263, 0.138]
GA EP (50%) -0.964 0.074 -13.095 0.000 [-1.109, -0.820]
GA Backpropagation 1.030 0.071 14.595 0.000 [0.892, 1.168]
(c) Statistical analysis
Figure 6: Performance evaluation of the GA against edge-popup on shown datasets, using the respective sparsity levels that
were achieved with our GA configurations as new values for the fixed pruning rates. Depending on the achieved mean ac-
curacy, we either adapt the mean sparsity levels from “GA” or from “GA (adaptive AB)”, which is indicated by the different
colored dots. For comparison, we plot the mean accuracies and 95% confidence intervals for the corresponding GA config-
uration, backpropagation, and the original edge-popup variant using the default prune-rate of 0.5. A final statistical analysis
evaluates the performance difference of combinations of algorithms based on p-values for the GA and edge-popup configura-
tions, as well as the backpropagation baseline. (c) shows the performance deviation of the target algorithm from the reference.
specified the respective mean sparsity levels our GA
configurations achieved on the x-axis in addition to
the architectures. We can see in Fig. 6a that for moons,
these levels dropped with increasing network sizes,
converging to 0.5, which corresponds to edge-popup’s
default prune rate value. This suggests that the influ-
ence of the varied pruning rate should be higher for
smaller architectures. Indeed, we observe the biggest
relative change for network A. The varied prune rate
appears to have a negative effect as it resulted in mul-
tiple low-accuracy runs, which negatively influenced
the mean. Yet, because of the high variance, there are
also some instances that scored higher compared to
EP (50%). For the other networks, there was little to
no change regarding the mean accuracy, and if there
was, it was only negative. The same holds true for
the circles dataset, as can be seen in Fig. 6b except
for architecture C. Since there is considerable vari-
ance between runs that use the same pruning rate and
the confidence intervals mostly overlap, it cannot be
concluded with certainty that these changes are due to
the varied pruning rates. Overall, none of the changes
lead to a significant performance improvement.
If we compare edge-popup against the GA con-
figurations, it becomes apparent that the GA outper-
forms for every dataset and architecture, even if we
enable edge-popup to find sparser subnetworks. In
fact, the adapted pruning rates lead to a worse perfor-
mance. Based on this, we can conclude that the GA
can find higher accuracy scoring subnetworks that are
also sparser and approximately match backpropaga-
tion for larger networks. To test the statistical signif-
icance of our findings, we fit a linear mixed model to
our accuracy data. We are mainly interested in com-
paring the different algorithms across different archi-
tectures on the same dataset. That’s why we model the
algorithms as fixed effects and treat the four architec-
tures and varying network initializations as random
effects to account for the variability across runs. We
perform our statistical analysis using the MixedLM
module from (Seabold and Perktold, 2010). To fit
the data and ensure proper convergence, we employ
Powell’s algorithm, use the restricted maximum like-
lihood (REML), and standardize the accuracies. The
Finding Strong Lottery Ticket Networks with Genetic Algorithms
457

results of our analysis are listed in Table 6c.
For assessing the statistical significance, we con-
sider various statistics, including coefficients and p-
values, to determine the relationship between the ref-
erence algorithm and the target algorithm. Starting
with the moons dataset, we can see that the coefficient
for GA (adaptive AB) is positive. This indicates that it
performs slightly better than the GA, considering all
architectures and initializations. Yet, because the p-
value is > 0.05, this performance difference is statis-
tically insignificant. The same holds for edge-popup
with the varied prune rate, although in this case, the
negative coefficient indicates a slightly worse per-
formance of EP (adapted), supporting our previous
findings. Because both GA (adaptive AB) and EP
(adapted)’s performances deviate insignificantly from
the reference algorithms, we only compare GA and
EP (50%) against each other. Doing so, we observe
a large negative coefficient, implying a considerably
worse performance of EP (50%). This result is sta-
tistically significant, as the p-value is 0. Compared
to backpropagation, the GA configuration performs
moderately worse, which is also a statistically sig-
nificant result. For the circles dataset, the analysis
draws a very similar picture. Although, in this case,
GA (adaptive AB) has a negative coefficient, support-
ing the (almost statically significant) result that the
base GA configuration is a more appropriate choice
for this dataset. Accounting for all random effects,
backpropagation here clearly outperforms the GA.
We conclude that the GA performs significantly
better than edge-popup in the given scenarios and per-
forms only moderately worse than backpropagation
on the moons dataset regarding the final accuracy.
5.3 Multi-Class Performance
So far, we only considered datasets for binary clas-
sification. It turns out that our approach has a much
harder time finding suitable lottery tickets for multi-
class classification problems. We first analyze that be-
havior by comparing the performance of the GA using
network architecture B
3
and the 2-, 3-, 4-, 5-, and 10-
class variants of the digits dataset.
The results are depicted in Fig. 7a. We observe
that, at least in the binary case, the GA still reaches
perfect accuracy in most of the runs; however, us-
ing just one more class label leads to a considerable
increase in variance. There are still runs that reach
approximately 100% accuracy, which is not the case
anymore for the 4-class and 5-class settings, where
3
Preliminary experiments showed the highest GA accu-
racies on this architecture in the computationally less inten-
sive base configuration.
the variance further increases, and there is a notice-
able drop in achieved accuracy. When we reach the
10-class setting, the mean accuracy is only a little
above 54%. The increasing number of class labels
seems to pose a considerable challenge to the GA.
These observations also hold for much simpler
multi-class problems: For a follow-up experiment,
we introduce the blobs dataset consisting of up to
10 different 2-dimensional Gaussian-shaped clusters
with different class labels 1,...,10. These clusters are
uniformly distributed in the feature space and do not
overlap, as shown in Figure 7b. For this experiment,
we used a neural network architecture that consists of
2 input neurons, 100 hidden units, and as many output
neurons as required, given the number of classes. For
the classification of points in 2d space, backpropaga-
tion is able to reach 100% accuracy regardless of the
number of classes. The results are shown in Fig. 7c
and draw a similar picture as the first experiment:
While instances with fewer classes can reach perfect
accuracy, trying to distinguish more class labels leads
to increasingly bad final accuracies. However, in con-
trast to the digits dataset, the GA can find high-
accuracy subnetworks for a higher maximum number
of class labels (up to 6 classes), which suggests that
the GA can indeed deal with more classes when the
input space is less complex.
Aside from that, we observe a unique multi-modal
distribution of the accuracies, whose detailed analysis
is left for future work. At the moment, we reckon that
since the type of training we perform with our GA is
at its core just the task of solving a complex combi-
natorial problem, i.e., the problem of sampling proper
decision boundaries, the complexity of this task grows
superlinearly with an increasing number of decision
boundaries that need to be arranged in the feature
space. One observation we made during the GA runs
is that the accuracy is improved in only very small
steps, and the GA takes a long time to converge. This
behavior could partly be explained by the low popu-
lation diversity that leads to very homogenous popu-
lations already early in the evolution. In that phase,
the main driver of change is the mutation operation,
which can only lead to small accuracy improvements.
We hypothesize that it needs more sophisticated GA
operations, including proper diversity retention tech-
niques, to deal with complex multi-class datasets.
6 CONCLUSION
We have presented a GA-based approach for find-
ing strong lottery ticket networks without any training
steps on the network. We have analyzed different con-
NCTA 2024 - 16th International Conference on Neural Computation Theory and Applications
458
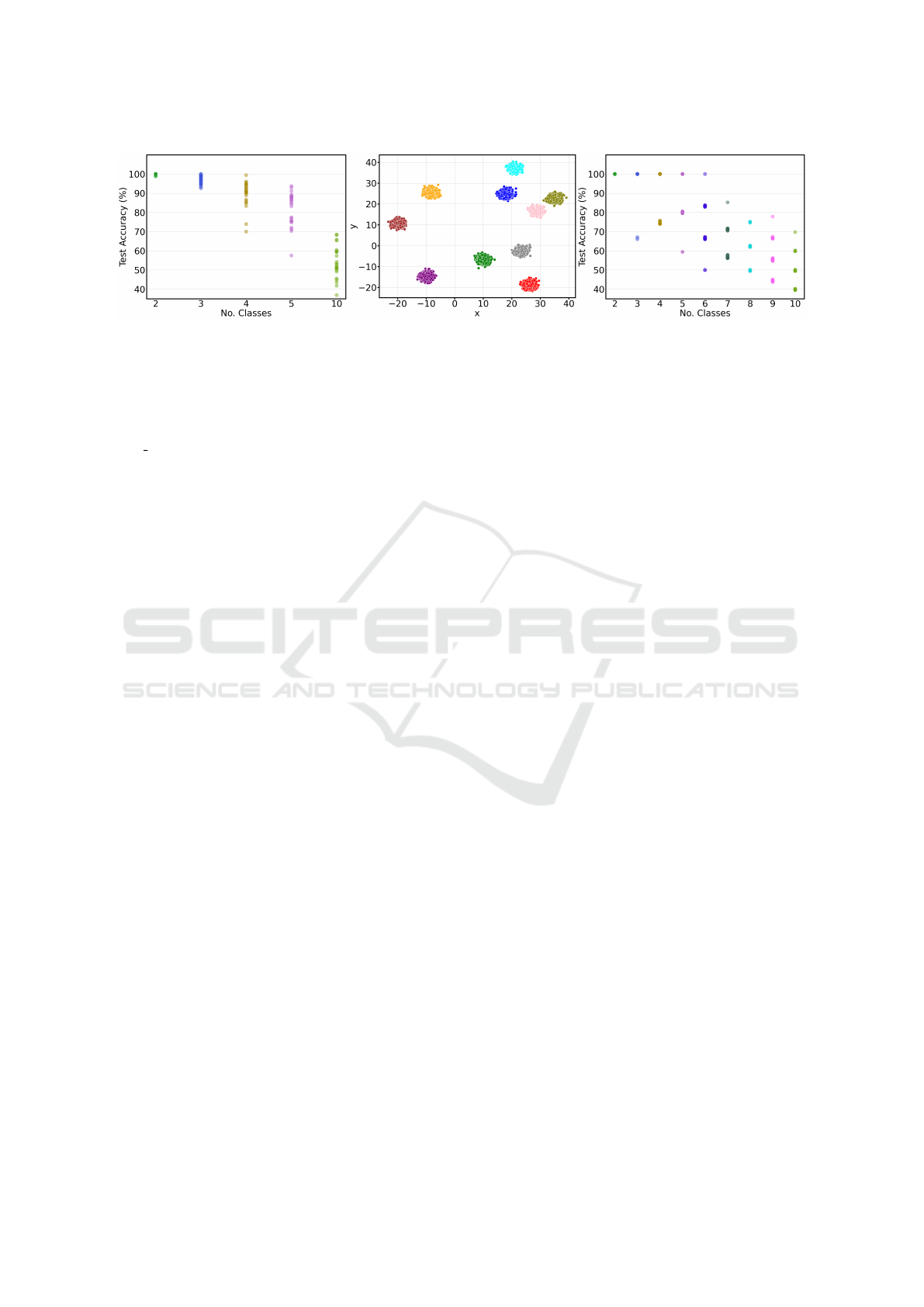
(a) digits, R=25 (b) blobs test dataset (c) blobs
Figure 7: Mutli-class performance on R runs: (a) Overview of the distribution of final accuracies achieved by the GA (without
accuracy bound) for different variants of the digits dataset. For the binary case we consider class labels 0 and 1, for the
ternary case 0, 1, and 2, and so on. All runs were performed on architecture B (cf. Table 2c), but we adapted the number of
output neurons according to the number of class labels. (b) illustrates the blobs test dataset for 10 differently labeled cluster
of 2d points, generated using scikit-learn (Pedregosa et al., 2011). (c) Performance of default GA configuration without
accuracy bound on the blobs dataset with varying class labels. The dataset was generated using the scikit-learn function
make blobs and consists of differently labeled clusters, each containing 1250 datapoints. For this experiment, we used a
network architecture [2,100, n] where n is the number of class labels.
figurations and behaviors of the GA and have shown
that, for simple binary classification problems, our ap-
proach outperforms the start-of-the-art method edge-
popup by producing smaller and more accurate sub-
networks. This holds even when the latter is given a
more beneficial weight initialization procedure. Fur-
thermore, we found that forcing edge-popup to pro-
duce subnetworks that possess the same sparsity lev-
els as the ones produced by the GA leads to a drop
in accuracy. Although integrating an adaptive accu-
racy bound resulted in slightly better accuracies on the
moons dataset, in our experiments, this effect is sta-
tistically insignificant and comes with reduced com-
putational efficiency, favoring the standard GA. Fi-
nally, we have also observed that the performance of
our approach breaks down when finding networks for
multi-class classification problems. This poses sub-
stantial questions about the relationship between net-
work structure and learnability for future research.
Notably, in the shown example datasets, our GA-
based approach has the advantage over edge-popup,
which implements training steps via backpropagation
and thus depends on gradient information, which our
approach does not. This can be seen as a call to revisit
alternative methods of evolving neural networks, at
least for special cases. Since our approach effectively
frames the problem of finding a good neural network
as a problem of binary combinatorial optimization, it
may also open up new solving methods to this appli-
cation (see Whitaker (2022)) or allow for better inte-
gration of neural networks in scenarios where combi-
natorial optimization is already employed.
We would also like to point out that — since the
GA is not using gradient information — it is likely
that our approach has applications beyond classical
neural networks, which are built on functions that al-
low gradient information to pass through. We hypoth-
esize that using our GA, it should be possible to use
non-differentiable evaluation functions like the edit
distance (Levenshtein et al., 1966) for strings or logi-
cal consistency checks for propositional logic directly
as loss functions without requiring a potentially sub-
optimal differentiable surrogate (cf. Patel and Matas
(2021); Li and Srikumar (2019)) which would have
important implications for fields like natural language
processing or neural reasoning. To allow for the com-
parison to the state of the art, we chose classifica-
tion problems for this paper; however, future work
should aim for more complex network structures that
allow for non-differentiable functions and test if our
approach — and thus a variant of the lottery ticket
hypothesis – still functions there.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was partially funded by the Bavarian Min-
istry for Economic Affairs, Regional Development
and Energy as part of a project to support the thematic
development of the Institute for Cognitive Systems.
REFERENCES
Aggarwal, C. C. et al. (2018). Neural networks and deep
learning. Springer, 10(978):3.
Bengio, Y., L
´
eonard, N., and Courville, A. (2013). Es-
timating or propagating gradients through stochastic
neurons for conditional computation. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1308.3432.
Finding Strong Lottery Ticket Networks with Genetic Algorithms
459

Chen, X., Zhang, J., and Wang, Z. (2021). Peek-a-boo:
What (more) is disguised in a randomly weighted neu-
ral network, and how to find it efficiently. In Interna-
tional Conference on Learning Representations.
Frankle, J. and Carbin, M. (2018). The lottery ticket hypoth-
esis: Finding sparse, trainable neural networks. arXiv
preprint arXiv:1803.03635.
Gaier, A. and Ha, D. (2019). Weight agnostic neural net-
works. Advances in neural information processing
systems, 32.
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., and Sun, J. (2015). Delv-
ing deep into rectifiers: Surpassing human-level per-
formance on imagenet classification. In Proceedings
of the IEEE international conference on computer vi-
sion, pages 1026–1034.
Hinton, G., Vinyals, O., and Dean, J. (2015). Distilling
the knowledge in a neural network. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1503.02531.
Huang, G.-B., Zhu, Q.-Y., and Siew, C.-K. (2006). Extreme
learning machine: theory and applications. Neuro-
computing, 70(1-3):489–501.
Jackson, A., Schoots, N., Ahantab, A., Luck, M., and
Black, E. (2023). Finding sparse initialisations using
neuroevolutionary ticket search (nets). In Artificial
Life Conference Proceedings 35, volume 2023, page
110. MIT Press One Rogers Street, Cambridge, MA
02142-1209, USA journals-info . . . .
Kasun, L. L. C., Zhou, H., Huang, G.-B., and Vong, C. M.
(2013). Representational learning with elms for big
data. IEEE Intelligent Systems.
Lee, N., Ajanthan, T., and Torr, P. H. (2018). Snip: Single-
shot network pruning based on connection sensitivity.
arXiv preprint arXiv:1810.02340.
Levenshtein, V. I. et al. (1966). Binary codes capable of cor-
recting deletions, insertions, and reversals. In Soviet
physics doklady, volume 10, pages 707–710. Soviet
Union.
Li, T. and Srikumar, V. (2019). Augmenting neural net-
works with first-order logic. In Proceedings of the
57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Compu-
tational Linguistics.
Malach, E., Yehudai, G., Shalev-Schwartz, S., and Shamir,
O. (2020). Proving the lottery ticket hypothesis: Prun-
ing is all you need. In International Conference on
Machine Learning, pages 6682–6691. PMLR.
Orseau, L., Hutter, M., and Rivasplata, O. (2020). Loga-
rithmic pruning is all you need. Advances in Neural
Information Processing Systems, 33:2925–2934.
Patel, Y. and Matas, J. (2021). Feds-filtered edit distance
surrogate. In International Conference on Document
Analysis and Recognition, pages 171–186. Springer.
Pedregosa, F., Varoquaux, G., Gramfort, A., Michel, V.,
Thirion, B., Grisel, O., Blondel, M., Prettenhofer,
P., Weiss, R., Dubourg, V., et al. (2011). Scikit-
learn: Machine learning in python. Journal of ma-
chine learning research, 12(Oct):2825–2830.
Pensia, A., Rajput, S., Nagle, A., Vishwakarma, H., and
Papailiopoulos, D. (2020). Optimal lottery tickets via
subset sum: Logarithmic over-parameterization is suf-
ficient. Advances in neural information processing
systems, 33:2599–2610.
Ramanujan, V., Wortsman, M., Kembhavi, A., Farhadi, A.,
and Rastegari, M. (2020). What’s hidden in a ran-
domly weighted neural network? In Proceedings
of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and
pattern recognition, pages 11893–11902.
Seabold, S. and Perktold, J. (2010). statsmodels: Econo-
metric and statistical modeling with python. In 9th
Python in Science Conference.
Shevchenko, A. and Mondelli, M. (2020). Landscape con-
nectivity and dropout stability of sgd solutions for
over-parameterized neural networks. In International
Conference on Machine Learning, pages 8773–8784.
PMLR.
Tanaka, H., Kunin, D., Yamins, D. L., and Ganguli, S.
(2020). Pruning neural networks without any data by
iteratively conserving synaptic flow. Advances in neu-
ral information processing systems, 33:6377–6389.
Wang, C., Zhang, G., and Grosse, R. (2020a). Picking
winning tickets before training by preserving gradient
flow. arXiv preprint arXiv:2002.07376.
Wang, H., Qin, C., Bai, Y., Zhang, Y., and Fu, Y. (2021a).
Recent advances on neural network pruning at initial-
ization. arXiv preprint arXiv:2103.06460.
Wang, Y., Zhang, X., Xie, L., Zhou, J., Su, H., Zhang, B.,
and Hu, X. (2020b). Pruning from scratch. In Pro-
ceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelli-
gence, volume 34, pages 12273–12280.
Wang, Z., Luo, T., Li, M., Zhou, J. T., Goh, R. S. M., and
Zhen, L. (2021b). Evolutionary multi-objective model
compression for deep neural networks. IEEE Compu-
tational Intelligence Magazine, 16(3):10–21.
Whitaker, T. (2022). Quantum neuron selection: find-
ing high performing subnetworks with quantum al-
gorithms. In Proceedings of the Genetic and Evolu-
tionary Computation Conference Companion, pages
2258–2264.
Whitley, D., Tin
´
os, R., and Chicano, F. (2015). Optimal
neuron selection: Nk echo state networks for rein-
forcement learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:1505.01887.
Wortsman, M., Farhadi, A., and Rastegari, M. (2019). Dis-
covering neural wirings. Advances in Neural Informa-
tion Processing Systems, 32.
Wu, T., Li, X., Zhou, D., Li, N., and Shi, J. (2021).
Differential evolution based layer-wise weight prun-
ing for compressing deep neural networks. Sensors,
21(3):880.
Zhou, H., Lan, J., Liu, R., and Yosinski, J. (2019). De-
constructing lottery tickets: Zeros, signs, and the su-
permask. Advances in neural information processing
systems, 32.
NCTA 2024 - 16th International Conference on Neural Computation Theory and Applications
460
