
Research on Factors Influencing Indoor Air Quality in Houses: Case
Study of Shanghai
Jiaxi Gao
Shanghai Pinghe School, Shanghai, 200000, China
Keywords: Indoor Air Quality, Multiple Linear Regression, Random Forest.
Abstract: Although the current studies have identified and comprehensively summarized several factors that may affect
indoor air quality, the extent of these factors’ impact on indoor air quality hast been explored. In this paper, a
multiple linear regression model is used to analyze 15 factors with 100 samples from Shanghai. It is finally
concluded that the ventilation rate, cooking habits, furniture characteristics, recent renovations, occupancy
durations, smoking, construction characteristics, humidity, heating fuels, and natural ventilation are positively
correlated to IAQ, while cleaning frequency, air conditioning systems, location, temperature, and attached
garage are negatively correlated to IAQ. The furniture characteristics and humidity have a relatively weaker
effect on IAQ. This research also uses a Random Forest Regression model to verify the results obtained earlier,
as this method is capable of addressing the varied nature of IAQ impacts. Some unexpected results imply that
the impact of certain variables need further research to provide more precise conclusions.
1. INTRODUCTION
Indoor air quality (IAQ) describes the environmental
conditions within houses, buildings, and other indoor
spaces. It is a significant consideration given that
people spend a large portion of their time indoors.
Research has shown that American adults spend
approximately 86.9% of their time indoors each day,
about 5.5% in vehicles, and only 7.6% outdoors
(Klepeis et al., 2001). The importance of IAQ is
underscored by its close relationship with residents’
health conditions, making it a key factor in creating a
comfortable living environment (Cincinelli and
Martellini, 2017).
Despite its importance, IAQ receives
considerably less attention in China compared to
outdoor air quality. Many people remain unaware that
the risks associated with indoor air pollution can be
more serious than those of outdoor pollution (Haden,
2016). Understanding the impact of indoor pollutants
on comfort and health is crucial. Consequently, this
paper aims to investigate the factors affecting IAQ in
houses, assisting people in evaluating pollution levels
in their homes and making decisions to improve their
living standards and quality of life.
The factors affecting IAQ are complex and
diverse. IAQ levels can be influenced by the existence
of new furniture, room arrangements, and the location
of diffusers (Haghighat et al., 1996). More research
also found that natural ventilation and air-
conditioning, and human activities such as cooking
are also influencing IAQ level (Wong and Huang,
2004 & Langer and Bekö, 2013). Heating fuels and
attached garages are also factors that contribute to
changing IAQ (Semple et al., 2012 & Funk et al.,
2014). Mannan et al. conducted a review on the
factors impacting IAQ, analyzing 14 factors in both
residential and commercial buildings (ventilation,
cleaning, cooking systems, furniture characteristics,
renovation, air conditioning systems, occupancy
duration, location, smoking, construction
characteristics, temperature, humidity, heating fuels,
attached garage) (Funk et al., 2014). Although their
paper comprehensively summarized these factors, it
did not explore the extent of their impact on IAQ
levels (Mannan and Al-Ghamdi, 2021). Vilčeková et
al. used statistical analysis to examine the dependence
between building characteristics (year of
construction, year of renovation, smoking, and
heating system) and IAQ in Macedonia (Vilčeková et
al., 2017). However, the small sample size limits the
Gao, J.
Research on Factors Influencing Indoor Air Quality in Houses: Case Study of Shanghai.
DOI: 10.5220/0013035900004601
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Innovations in Applied Mathematics, Physics and Astronomy (IAMPA 2024), pages 209-215
ISBN: 978-989-758-722-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
209

generalizability of their results, and their study
focused only on a subset of factors.
In conclusion, this paper aims to investigate the
factors affecting indoor air quality in houses in
Shanghai, China. Using a multiple linear regression
model and statistical methods, this study will identify
and evaluate the effects of 15 factors on IAQ,
examining the extent to which they influence IAQ in
residential areas
.
2. METHODS
2.1 Data Source
To investigate the factors affecting indoor air quality
(IAQ) in residential areas in Shanghai, China, data
were collected primarily through detailed household
surveys. These surveys provided comprehensive and
context-specific information essential for analyzing
IAQ in the study area. The survey method was chosen
for its ability to gather detailed and diverse data
directly from residents, ensuring a thorough
understanding of various indoor environmental
conditions and factors influencing IAQ.
The household surveys were conducted across
multiple districts in Shanghai, targeting a random
sample of households to ensure representative
coverage of different residential settings. The surveys
were designed to collect data on several key aspects
(Table 1).
The survey data were meticulously recorded and
verified to ensure accuracy and reliability. This rich
dataset provided a robust foundation for subsequent
analysis.
2.2 Variable Selection
Based on the literature review and preliminary data
analysis, fourteen variables were selected for
inclusion in the study. These variables were identified
as potential factors influencing IAQ in residential
buildings. The selected variables are listed in Table 2.
Table 1. List of Key Aspects.
Aspects Meaning
Household Characteristics
Information on the number of occupants, age distribution, and occupancy duration was
gathered. This data helped in understanding how human presence and activities might
affect IAQ.
Building Features
Detailed questions were asked about the age of the building, recent renovations, types of
materials used in construction and furnishing, and the presence of attached garages. These
factors are known to influence the levels of pollutants and ventilation efficiency within
homes.
Occupant Activities
The surveys included questions about daily activities such as cooking habits, smoking, use
of cleaning products, and the operation of heating and air conditioning systems. These
activities can significantly impact the concentration of indoor pollutants.
Ventilation and Air
Conditioning
Residents provided information about their use of ventilation systems, frequency of
window opening, and the types of air conditioning systems used. These variables are
critical in understanding how air exchange rates and mechanical systems contribute to IAQ.
Table 2. List of Variables.
Variable Logogram Meaning
Ventilation Rate
𝑥
The frequency of window opening and the use of mechanical ventilation systems
Cleaning Frequency
𝑥
How often the household is cleaned
Cooking Habits
𝑥
Frequency of cooking
Furniture
Characteristics
𝑥
Presence of new furniture
Recent Renovations
𝑥
Any recent construction or renovation activities (binary: 0 or 1)
Air Conditioning
Systems
𝑥
Types and usage patterns of air conditioning units
IAMPA 2024 - International Conference on Innovations in Applied Mathematics, Physics and Astronomy
210

Occupancy Duration
𝑥
The amount of time residents spend indoors
Location
𝑥
Geographic location within Shanghai (categorical variable (urban to suburban)
converted to numerical(1 to 0)
Smoking
𝑥
Presence of smokers in the household (binary: 0 or 1)
Construction
Characteristics
𝑥
Building materials and construction methods
Temperature
𝑥
Indoor temperature in degrees Celsius
Humidity
𝑥
Indoor relative humidity percentage
Heating fuels
𝑥
Types of heating fuels used (binary: 0 or 1)
Attached Garage
𝑥
Presence and use of attached garages (binary: 0 or 1)
Natural Ventilation
𝑥
Use of natural ventilation methods such as opening windows
Table 3. List of Data Distribution.
Variable mean SD Min Q1 Median Q3 Max
Ventilation Rate 4.73 2.90 0.05 2.06 4.67 6.84 9.88
Ckeaning Frequency 2.64 1.39 0.06 1.48 2.88 3.65 4.99
Cooking Habits 1.53 0.91 0.04 0.72 1.51 2.37 2.97
Furniture Characteristics 1.89 1.14 0.05 0.98 1.83 2.90 3.84
Recent Renovations 0.54 0.50 0.00 0.00 1.00 1.00 1.00
Air Conditioning Systems 1.58 0.92 0.02 0.89 1.65 2.24 2.98
Occupancy Duration 11.95 6.83 0.15 5.27 12.22 18.03 23.71
Location 2.53 1.14 1.00 2.00 2.00 3.00 4.00
Smoking 0.50 0.50 0.00 0.00 0.50 1.00 1.00
Construction Characteristics 1.51 0.91 0.04 0.77 1.56 2.22 2.97
Temperature 18.13 9.85 0.18 8.39 17.59 27.32 34.92
Humidity 51.36 27.47 0.60 26.38 551.91 75.52 99.77
Heating Fuels 0.55 0.50 0.00 0.00 1.00 1.00 1.00
Attached Garage 0.53 0.50 0.00 0.00 1.00 1.00 1.00
Natural Ventilation 4.90 2.88 0.04 2.52 4.99 7.25 9.77
IAQ 12.52 7.54 -2.33 6.78 12.85 17.76 28.92
2.3 Model Selection
To analyze the relationship between these variables
and IAQ, a multiple linear regression model was
employed. Multiple linear regression was chosen due
to its effectiveness in quantifying the influence of
multiple independent variables on a single dependent
variable, in this case, IAQ.
The dependent variable for the model was the IAQ
level, measured as a composite score based on
concentrations of particulate matter (PM2.5 and
PM10), volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and
CO2 levels. The independent variables were the
fifteen factors identified earlier. The multiple linear
regression model was formulated as follows:
𝐼𝐴𝑄 = 𝛽
+ 𝛽
𝑥
+ 𝛽
𝑥
+ ⋯ + 𝛽
𝑥
+ 𝜖 (1)
Where: 𝛽
is the intercept. 𝛽
, 𝛽
,..., 𝛽
are the
coefficients for each independent variable. 𝜖 is the
error term.
3. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Descriptive Analysis
Below is the data of each variable’s distribution, 100
data is collected (Table 3). Table 3 shows the
descriptive statistics of these variables.
Research on Factors Influencing Indoor Air Quality in Houses: Case Study of Shanghai
211
3.2 Multiple Linear Model Results
To evaluate the coefficients in the linear regression
model that is chosen, the Python built-in ordinary
least squares (OLS) method is used, which minimizes
the sum of the squared differences between the
observed and predicted IAQ values (Table 4).
This high R-squared value (close to 1) suggests a
strong fit of the model to the data, and the author gets
the resultant model:
𝐼𝐴𝑄 = −0.415 + 1.8618𝑥
− 1.4443𝑥
+ ⋯−
1.0781 𝑥
+ 1.2108 𝑥
+ 𝜖 (2)
Table 4. OLS regression results
Variable coef std err t P>|t| [0.025 0.975]
Ventilation Rate -0.4150 0.346 -1.199 0.234 -1.103 0.273
Ckeaning Frequency 1.8618 0.183 10.201 0.000 1.499 2.225
Cooking Habits -1.4443 0.188 -7.662 0.000 -1.819 -1.069
Furniture Characteristics 0.7111 0.185 3.845 0.000 0.343 1.079
Recent Renovations 1.4693 0.191 7.710 0.000 1.090 1.848
Air Conditioning Systems 0.7599 0.176 4.329 0.000 0.411 1.109
Occupancy Duration -0.7805 0.182 -4.300 0.000 -1.141 -0.420
Location 1.9306 0.206 9.398 0.000 1.522 2.339
Smoking -1.0533 0.193 -5.450 0.000 -1.438 -0.669
Construction Characteristics 1.0088 0.105 9.603 0.000 0.800 1.218
Temperature 1.1318 0.190 5.945 0.000 0.753 1.510
Humidity -0.4658 0.186 -2.508 0.014 -0.835 -0.097
Heating Fuels 0.8330 0.175 4.767 0.000 0.485 1.180
Attached Garage 0.6737 0.106 6.370 0.000 0.463 0.884
Natural Ventilation -1.0781 0.105 -10.236 0.000 -1.288 -0.869
IAQ 1.2108 0.180 6.741 0.000 0.854 1.568
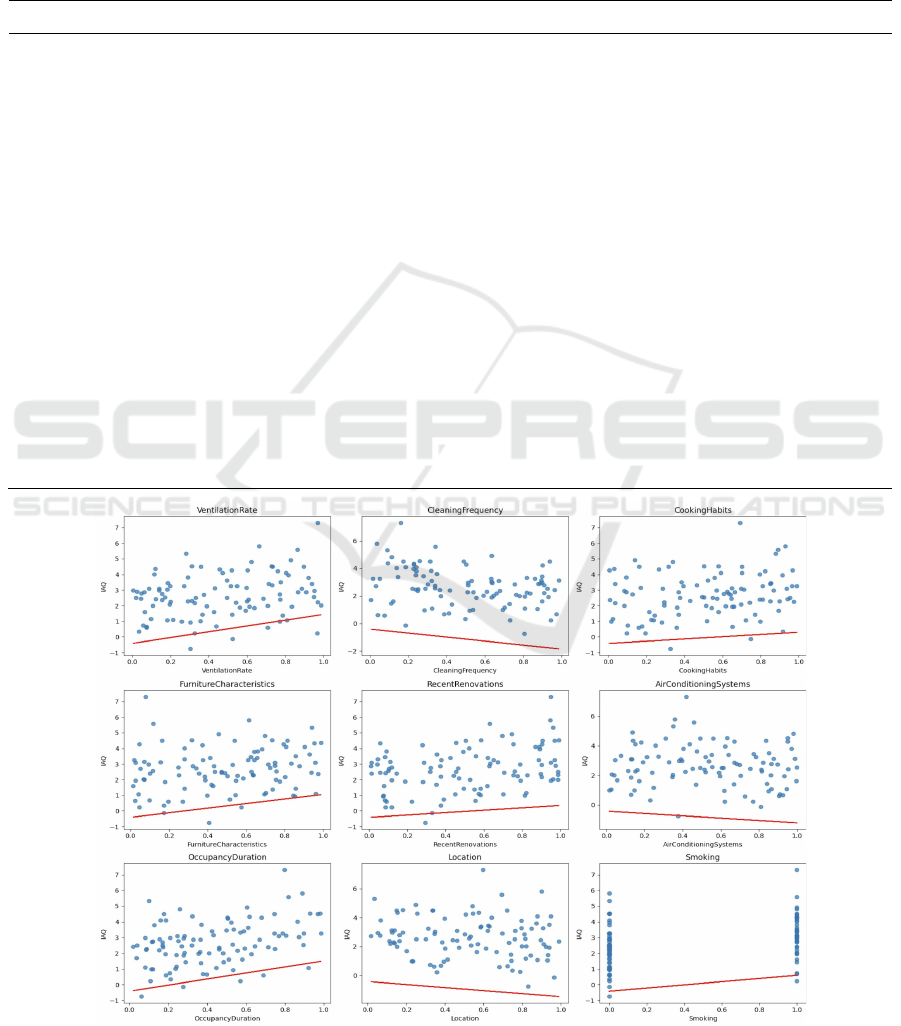
Figure 1: Variable Correlation 1.
IAMPA 2024 - International Conference on Innovations in Applied Mathematics, Physics and Astronomy
212
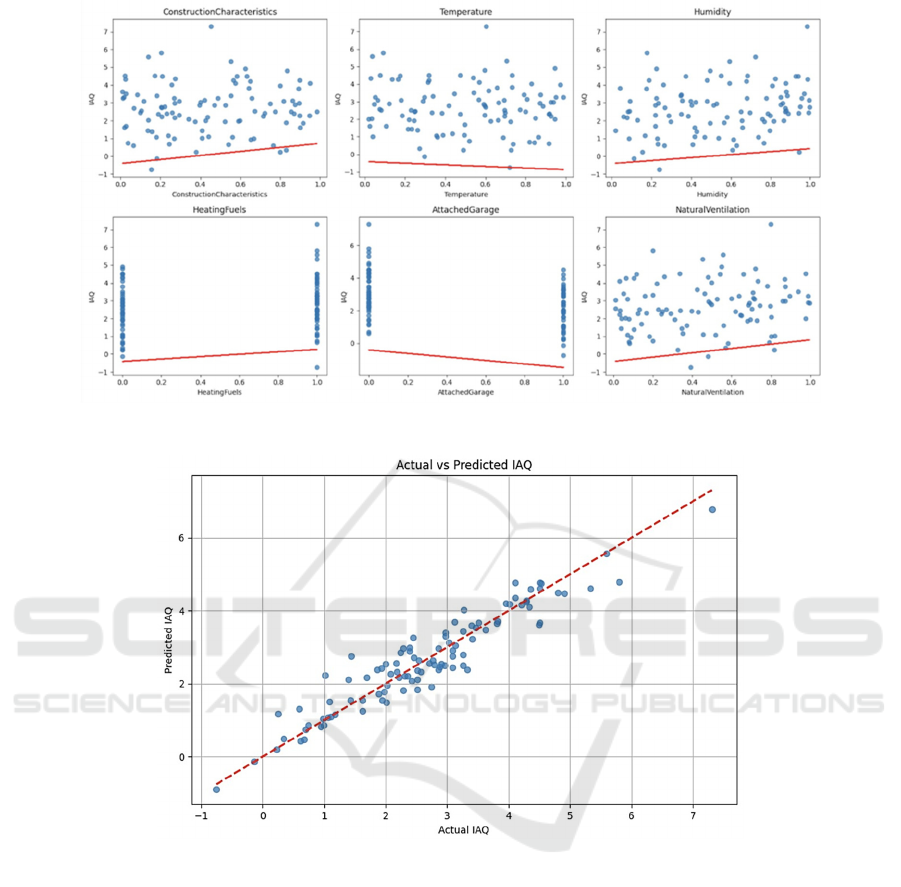
Figure 2: Variable Correlation 2
Figure 3: Linear model fitting results.
To conclude, each variable’s own relationship
with IAQ from data (the yellow points) combined
with the OLS calculated coefficients (red lines) is
depicted in the two following graphs. The red lines
match the trend of the data, which validates the
results.
Fig 1 and 2 show the scatterplot of these variables
against IAQ. Also, the model is compared with the
real data, with generated results shown in Fig 3. The
plot indicates a strong correlation between the actual
and predicted IAQ values, further validating the
model’s effectiveness in predicting IAQ based on the
identified factors.
Based on the multiple linear regression analysis,
several key factors significantly affect indoor air
quality (IAQ) in residential areas in Shanghai. The
results indicate that: There is a strong positive
relationship between ventilation rate and IAQ. Higher
ventilation rates lead to better air quality, which
aligns with expectations as increased ventilation
helps remove indoor pollutants. Surprisingly, a higher
cleaning frequency is associated with lower IAQ.
This could be due to the use of cleaning products that
release VOCs, negatively impacting air quality. More
intensive cooking activities are positively correlated
with IAQ, suggesting that proper ventilation during
cooking can mitigate the release of pollutants. The
presence of new furniture, which can emit VOCs,
shows a positive but relatively weaker effect on IAQ.
Homes with recent renovations exhibit significantly
Research on Factors Influencing Indoor Air Quality in Houses: Case Study of Shanghai
213
higher IAQ, likely due to the introduction of new
materials and the potential temporary effects of dust
and chemicals. Effective use of air conditioning
systems improves IAQ, possibly due to filtration and
controlled air circulation.
Longer occupancy durations correlate positively
with IAQ, indicating that homes occupied for longer
periods may have better-managed indoor
environments. Urban vs. suburban locations show a
negative impact on IAQ, with urban settings
generally having poorer air quality. As expected,
smoking within homes significantly degrades IAQ,
contributing to higher levels of indoor pollutants. The
quality and type of building materials used also
significantly affect IAQ, with better materials leading
to improved air quality. Higher temperatures are
associated with lower IAQ, while higher humidity
levels show a slight positive impact, possibly due to
reduced dust. The type of heating fuels used
significantly impacts IAQ, with cleaner fuels
contributing to better air quality. Homes with
attached garages show higher IAQ, which might be
counterintuitive but could be related to better
ventilation practices in such homes. Increased use of
natural ventilation negatively impacts IAQ, possibly
due to the infiltration of outdoor pollutants.
3.3 Random Forest Results
To analyze the relationship between these variables
and IAQ, another method can be introduced to further
confirm the built model, which is called Random
Forest Regression model. Random Forest Regression
was chosen for its ability to handle complex
interactions between variables and its robustness
against overfitting, making it suitable for capturing
the multifaceted nature of IAQ influences.
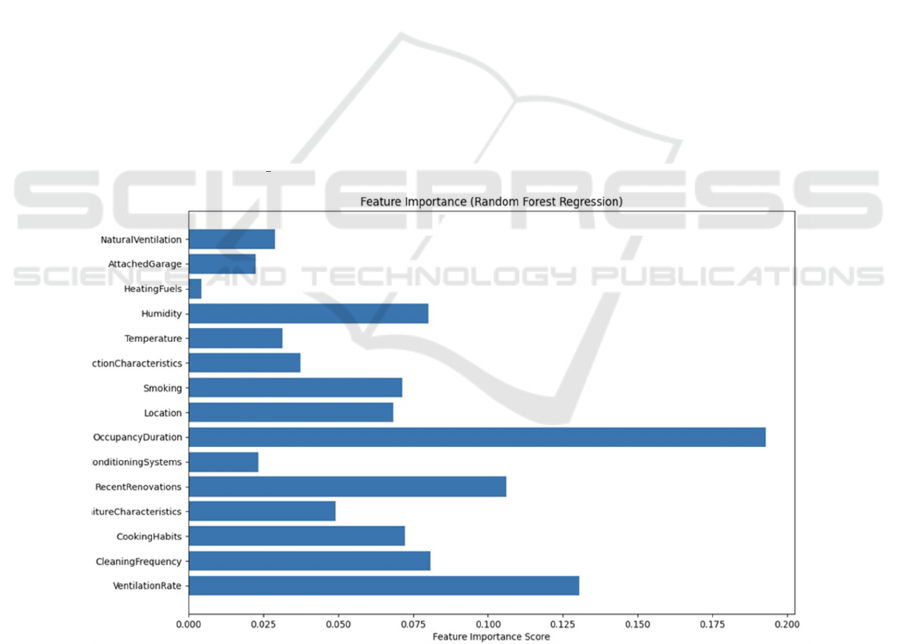
From Fig 4, the author can further confirm our
built model above that the importance features match
the calculated coefficients in multi linear regression
model. Generated results shown in the graph
demonstrates that the occupancy duration has the
highest feature importance, which is about 0.190. A
few other factors also show high feature importance,
such as ventilation rate, recent renovations, and
humidity. The factor with the least feature importance
is heating fuels, with a score at about 0.005. Also, the
generated predictor matches the trend of our previous
model, which is shown by the comparison in Figure
5, which performs a relatively well fitness.
Figure 4: Feature Importance.
IAMPA 2024 - International Conference on Innovations in Applied Mathematics, Physics and Astronomy
214
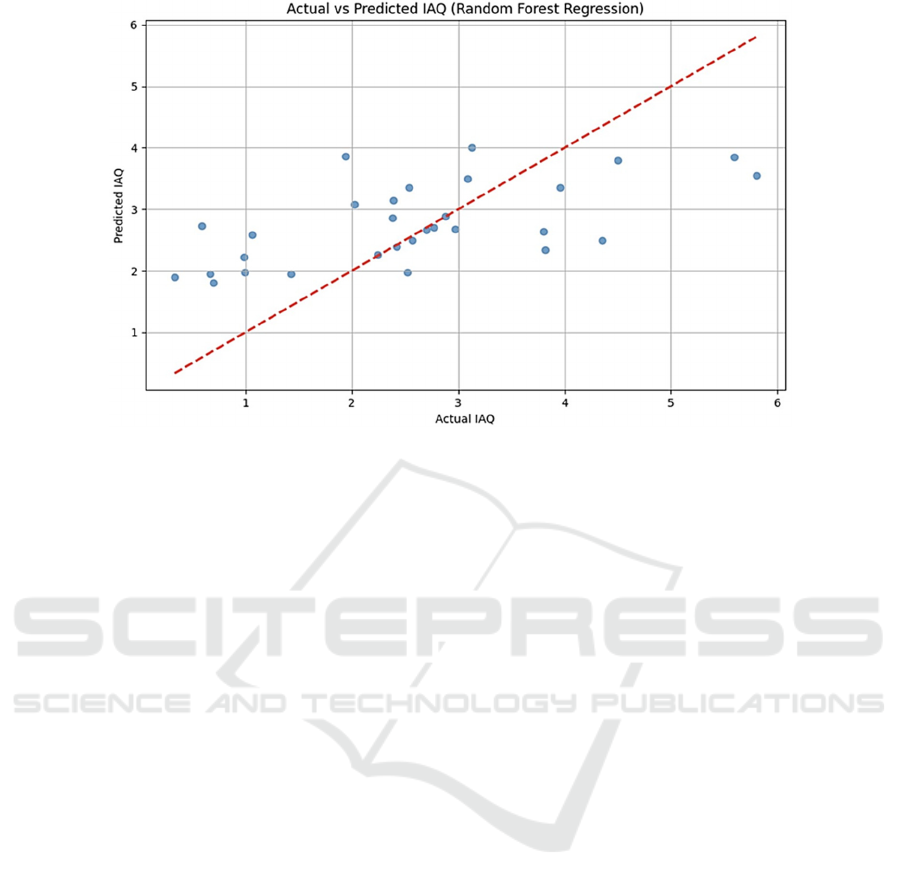
Figure 5: Random Forest model fitting results.
4. CONCLUSION
Overall, the paper identifies critical factors affecting
IAQ in residential areas in Shanghai and gives the
convincing predicting model for IAQ, which provides
a foundation for residents and policymakers to make
informed decisions. By building and applying the
Multiple Linear Regression model and the Random
Forest Regression model, the conclusion of the
relationship between the influencing factors and IAQ
levels can be reached. Specifically, 10 of the factors,
including ventilation rate, cooking habits, furniture
characteristics, recent renovations, occupancy
durations, smoking, construction characteristics,
humidity, heating fuels, and natural ventilation are
found to have a positive relationship with IAQ levels;
while 5 other factors, which are cleaning frequency,
air conditioning systems, location, temperature, and
attached garage, are negatively correlated to IAQ
levels. Furniture characteristics and humidity have
quite weak effects on IAQ levels. However, some
unexpected results and limitations suggest the need
for further research, especially concerning cleaning
products, cooking methods, and the specific
characteristics of attached garages and natural
ventilation practices. By addressing these deficits,
future studies can provide even more precise
recommendations for improving indoor air quality.
REFERENCES
Klepeis N E, et al. The National Human Activity Pattern
Survey (NHAPS): a resource for assessing exposure
to environmental pollutants. Journal of exposure
science & environmental epidemiology, 2001, 11(3):
231-252.
Cincinelli A, Martellini T. Indoor air quality and health.
International journal of environmental research and
public health, 2017, 14(11): 1286.
Haden R. Indoor Air vs. Outdoor Air. Medical Associates
of Northwest Arkansas, 2016.
Haghighat F, Huo Y, Zhang J, Shaw C Y. The influence of
office furniture, workstation layouts, diffuser types
and location on indoor air quality and thermal comfort
conditions at workstations. Indoor Air, 1996, 6(3):
188-203.
Wong N H, Huang B. Comparative study of the indoor air
quality of naturally ventilated and air-conditioned
bedrooms of residential buildings in Singapore.
Building and Environment, 2004, 39(9): 1115-1123.
Langer S, Bekö G. Indoor air quality in the Swedish
housing stock and its dependence on building
characteristics. Building and Environment, 2013, 69:
44-54.
Semple S, et al. Contribution of solid fuel, gas combustion,
or tobacco smoke to indoor air pollutant
concentrations in Irish and Scottish homes. Indoor air,
2012, 22(3): 212-223.
Funk W E, et al. Indoor air quality in the United Arab
Emirates. Journal of Environmental Protection, 2014.
Mannan M, Al-Ghamdi S G. Indoor air quality in buildings:
A comprehensive review on the factors influencing
air pollution in residential and commercial structure.
International Journal of Environmental Research and
Public Health, 2021, 18(6): 3276.
Vilčeková S, et al. Investigation of indoor air quality in
houses of Macedonia. International Journal of
Environmental Research and Public Health, 2017,
14(1): 37.
Research on Factors Influencing Indoor Air Quality in Houses: Case Study of Shanghai
215
