
Enhancing Answer Attribution for Faithful Text Generation with Large
Language Models
Juraj Vladika
a
, Luca M
¨
ulln and Florian Matthes
b
Technical University of Munich, School of Computation, Information and Technology, Department of Computer Science,
Germany
{juraj.vladika, luca.muelln, matthes}@tum.de
Keywords:
Natural Language Processing, Large Language Models, Information Retrieval, Question Answering, Answer
Attribution, Text Generation, Interpretability.
Abstract:
The increasing popularity of Large Language Models (LLMs) in recent years has changed the way users
interact with and pose questions to AI-based conversational systems. An essential aspect for increasing the
trustworthiness of generated LLM answers is the ability to trace the individual claims from responses back to
relevant sources that support them, the process known as answer attribution. While recent work has started
exploring the task of answer attribution in LLMs, some challenges still remain. In this work, we first perform
a case study analyzing the effectiveness of existing answer attribution methods, with a focus on subtasks of
answer segmentation and evidence retrieval. Based on the observed shortcomings, we propose new methods for
producing more independent and contextualized claims for better retrieval and attribution. The new methods are
evaluated and shown to improve the performance of answer attribution components. We end with a discussion
and outline of future directions for the task.
1 INTRODUCTION
As Large Language Models (LLMs) rise in popularity
and increase their capabilities for various applications,
the way users access and search for information is no-
ticeably changing (Kaddour et al., 2023). The impres-
sive ability of LLMs to produce human-sounding text
has led to new applications but also raised concerns.
They sometimes generate responses that sound con-
vincing but lack accuracy or credible sources, so-called
hallucinations (Ji et al., 2023). This poses challenges
to their reliability, especially in critical applications
like law or healthcare, as well as in day-to-day usage
(Wang et al., 2024a).
Additionally, the opaque nature of these models
complicates understanding their decision-making pro-
cesses and interpretability of generated outputs (Singh
et al., 2024). As these models continue to permeate var-
ious sectors, from education (Kasneci et al., 2023) to
healthcare (Nori et al., 2023) — the need for verifiable
and accountable information becomes increasingly cru-
cial. If LLMs provide incorrect information or biased
content, the inability to trace back the origin of such re-
sponses can lead to misinformation and potential harm
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4941-9166
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6667-5452
or infringe on copyrighted material (Lewis, 2023).
A promising avenue for increasing the trustworthi-
ness and transparency of LLM responses is the idea
of answer attribution. It refers to the process of trac-
ing back (”attributing”) the claims from the output to
external evidence sources and showing them to users
(Rashkin et al., 2023). Distinct from usual methods
of hallucination mitigation, which focus on altering
the model’s output, answer attribution is oriented to-
wards end users. It aims to equip users with a list of
potential sources that support the output of the LLM to
increase its transparency and leaves quality assurance
to the users. This process usually involves segmenting
LLM answers into claims and linking them to relevant
evidence. While many attribution systems have started
emerging in recent years (Li et al., 2023), we observe
they still suffer from drawbacks limiting their appli-
cability. The retrieved sources for specific claims and
their respective entailment can be inaccurate due to
inadequate claim formulation (Liu et al., 2023; Min
et al., 2023).
To address these research gaps, in this study, we
provide incremental contributions to the answer attri-
bution process by enhancing its components. We: (1)
perform a case study of current answer attribution com-
ponents from literature and detect their shortcomings;
Vladika, J., Mülln, L. and Matthes, F.
Enhancing Answer Attribution for Faithful Text Generation with Large Language Models.
DOI: 10.5220/0013066600003838
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 16th International Joint Conference on Knowledge Discovery, Knowledge Engineering and Knowledge Management (IC3K 2024) - Volume 1: KDIR, pages 147-158
ISBN: 978-989-758-716-0; ISSN: 2184-3228
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
147

(2) propose improvements to the answer-segmentation
and evidence-retrieval components; and (3) provide a
numerical and qualitative analysis of improvements.
We involve human annotation on subsets when possi-
ble and consider multiple competing approaches. Our
research builds on top of recent LLM factuality and
answer attribution works and outlines open challenges,
leaving the door open for further advancements and
refinement of the process.
2 RELATED WORK
A lot of ongoing NLP work is devoted to ensuring the
trustworthiness of LLMs in their everyday use (Liu
et al., 2024), including their reliability (Zhang et al.,
2023a), safety (Wei et al., 2024), fairness (Li et al.,
2023), efficiency (Afzal. et al., 2023), or explainability
(Zhao et al., 2024a). An important aspect hindering the
trust in LLMs are hallucinations – described as model
outputs that are not factual, faithful to the provided
source content, or overall nonsensical (Ji et al., 2023).
A recent survey by (Zhang et al., 2023b) di-
vides hallucinations into input-conflicting, context-
conflicting, and fact-conflicting. Our work focuses
on fact-conflicting, which are hallucinations in which
facts in output contradict the world knowledge. De-
tecting hallucinations is tied to the general problem
of measuring the factuality of model output (Augen-
stein et al., 2023; Zhao et al., 2024b) and automated
fact-checking of uncertain claims (Guo et al., 2022;
Vladika and Matthes, 2023). The recently popular
method FactScore evaluates factuality by assessing
how many atomic claims from a model output are sup-
ported by an external knowledge source (Min et al.,
2023). Hallucinations can be corrected in the LLM
output by automatically rewriting those claims found
to be contradicting a trusted source, as seen in recent
CoVe (Dhuliawala et al., 2023) or Factcheck-Bench
(Wang et al., 2024b).
A middle ground between pure factuality evalu-
ation and fact correction is answer attribution. The
primary purpose of answer attribution is to enable
users to validate the claims made by the model, pro-
moting the generation of text that closely aligns with
the cited sources to enhance accuracy (Li et al., 2023).
One task setting is evaluating whether the LLMs can
cite the references for answers from their own memory
(Bohnet et al., 2023). A more common setup involves
retrieving the references either before the answer gen-
eration or after generating it (Malaviya et al., 2024).
When attributing claims to scientific sources, the more
recent and better-cited publications were found to be
the most trustworthy evidence (Vladika and Matthes,
2024). Some approaches to the problem include fine-
tuning smaller LMs on NLP datasets (Yue et al., 2023)
or using human-in-the-loop methods (Kamalloo et al.,
2023). Our work builds on top of (Malaviya et al.,
2024) by utilizing their dataset but improves the indi-
vidual components of the attribution pipeline.
3 FOUNDATIONS
We provide a precise description for the task of attribu-
tion in the context of LLMs for this work as follows:
Answer Attribution is the task of providing a set
of sources
s
that inform the output response
r
of a
language model for a given query
q
. These sources
must be relevant to the model’s response and should
contain information that substantiates the respective
sections of the response. This definition provides a
comprehensive overview of the task and encapsulates
its constituent subtasks:
1.
Response Segmentation. Segmenting the response
r
into individual claims c
i
.
2.
Claim Relevance Determination. Determining the rele-
vance of each claim
c
i
for the need of attribution (”claim
check-worthiness”).
3.
Finding Relevant Evidence. Retrieving a list of rele-
vant evidence sources s
i
for each claim c
i
.
4.
Evidence-Claim Relation. Determining whether the
evidence sources from the list of sources
s
i
actually
refer to the claim c
i
.
In our work, we focus on analyzing and improving
subtasks 1 and 4, and to a lesser extent, subtasks 2
and 3, leaving further improvements to future work.
We take the recent dataset ExpertQA (Malaviya et al.,
2024) as a starting point for our study. Moving away
from short factoid questions, this dataset emulates how
domain experts in various fields interact with LLMs.
Thus, the questions posed to the model are longer and
more complex, can contain hypothetical scenarios, and
elicit long, descriptive responses. This makes it a real-
istic benchmark for modern human-LLM interaction.
We take the responses generated by GPT-4 (”gpt-4”
in OpenAI API) from ExpertQA and perform attribu-
tion evaluation based on claims found in its responses.
Two main setups for attribution are post-hoc retrieval
(PHR), which first generates the response and then
does retrieval to attribute the facts; and retrieve-then-
read (RTR), which first retrieves the sources and then
generates the response (i.e., RAG). In our work, we
focus on the PHR system (Fig. 1, because it is closer
to the definition of attribution. Still, the challenges in
claim formulation and evidence retrieval apply to both
settings, so our findings also hold for RTR.
KDIR 2024 - 16th International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Information Retrieval
148

Table 1: High-level comparison of the different answer segmentation systems.
Segmentation System Number of c Unique #c avg. len(c) c / Sentence
spaCy sentences 938 855 103.2 1.00
gpt35 factscore 3016 2684 61.4 3.2
segment5 propsegment 2676 2232 54.2 2.85
Figure 1: The complete answer attribution process (in
the Post-Hoc-Retrieval setup).
4 CASE STUDY OF EXISTING
SOLUTIONS
This section provides a case study of recently popular
approaches for different components of the answer
attribution pipeline.
4.1 Answer Segmentation
As described above, the first step for attribution in PHR
systems is to segment the provided LLM response into
claims (atomic facts). We define a claim as ”a state-
ment or a group of statements that can be attributed to
a source”. The claim is either a word-by-word segment
of the generated answer or semantically entailed by the
answer. To validate the segmentation, we sample 20
random questions from the ExpertQA dataset. Three
different segmentation systems are evaluated based on
the number of atomic facts each claim contains and
the number of claims they generate.
The first (i) and most intuitive way of segmenting
an answer into claims is to use the syntactic struc-
ture of the answer, segmenting it into sentences, para-
graphs, or other syntactic units. Following ExpertQA
(Malaviya et al., 2024), this segmentation is done us-
ing the sentence tokenizer from the Python library
spaCy
.
1
The second approach (ii) for answer seg-
mentation that we analyze is based on the work of
PropSegment (Chen et al., 2023a), where text is seg-
mented into propositions. A proposition is defined as
a unique subset of tokens from the original sentence.
We use the best-performing model from the paper,
SegmenT5-large (Chen et al., 2023b), a fine-tuned ver-
sion of the T5 checkpoint 1.1 (Chung et al., 2022).
The third approach (iii) of segmenting an answer into
claims utilizes pre-trained LLMs and prompting, as
found in FactScore (Min et al., 2023). In their ap-
proach, the model is prompted to segment the answer
into claims, and the resulting output is subsequently
revised by human annotators. We replicate this method
by using GPT-3.5 (turbo-0613) and the same prompt
(”Please breakdown the following sentence into inde-
pendent facts:”), amended with meta-information and
instructions for the model on formatting the output.
The prompt is in Appendix 7, Table 10.
Table 1 shows the differences between the three
answer segmentation approaches. As expected, the
average number of characters of the atomic facts cre-
ated by GPT-3.5 and T5 is significantly smaller than
the original sentence length. It is also noteworthy that
the claims generated by GPT-3.5 are longer in charac-
ters and more numerous per sentence. In addition, the
number of unique claims per answer and the number
of claims per answer differ significantly by an aver-
age of 12% and up to 16.5% for SegmenT5. An error
we observed is that the segmentation systems create
duplicated claims for the same answer.
For a qualitative analysis of these segmented
claims, we manually annotate 122 claims that the three
systems generated for a randomly selected question
”A 55 year old male patient describes the sudden ap-
pearance of a slight tremor and having noticed his
handwriting getting smaller, what are the possible
ways you’d find a diagnosis?”. The categories for
annotations are aligned with (Chen et al., 2023a) and
(Malaviya et al., 2024), and describe important claim
properties. The properties are as follows: (1) Atomic:
the claim contains a single atomic fact; (2) Indepen-
dent: the claim can be verified without additional con-
text; (3) Useful: the claim is useful for the question;
(4) Errorless: the claim does not contain structural
1
https://spacy.io/
Enhancing Answer Attribution for Faithful Text Generation with Large Language Models
149

errors, e.g., being an empty string; (5) Repetition: the
claim is a repetition of another claim from the same
segmentation system. Each category is binary, mean-
ing a claim can be annotated with multiple categories.
Given that the question is from the medical domain,
the claims are expected to be more complex and re-
quire domain knowledge.
Table 2 shows the result of the qualitative analy-
sis. The most noticeable outcome is that the
spaCy
segmentation system performs significantly differently
compared to other systems. It simply tokenizes the re-
sponses into sentences and considers every sentence to
be a claim, which is not realistic given the often quite
long sentences generated by LLMs. Consequently,
the score for ”Atomic” claims stands at 20% (3/15).
Intriguingly, only 20% (3/15) of the sentences from
the response are independently verifiable without ad-
ditional context from the question or the rest of the
response. Due to the complexity of the answer, most
sentences reference a preceding sentence in the re-
sponse, mentioning ”the patient” or ”the symptoms”.
The usefulness of the claims in answering the given
questions is relatively high for spaCy sentence segmen-
tation and GPT-3.5 segmentation but diminishes for
the SegmenT5 segmentation. Although most claims
are errorless, it is notable that all systems produce er-
roneous outputs. Specifically, for this question,
spaCy
segments four empty strings as individual sentences.
It is plausible that errors in the other two segmenta-
tion systems stem from this issue, as they also rely on
spaCy
-tokenized sentences as input. This dependency
also results in repetitions, primarily based on incorrect
answer segmentation. This list provides a positive and
a negative example claim for each category to give an
idea of errors:
1.
Atomic — Positive: ”Seeking a second opinion helps”
(
gpt35 factscore
) – Negative: ”Brain tumors or struc-
tural abnormalities are among the possible causes that
these tests aim to rule out.” (gpt35 factscore)
2.
Independent — Positive: ”Parkinson’s dis-
ease is a cause of changes in handwriting.”
(
segment5 propsegment
) – Negative: ”Imaging
tests may be ordered.” (segment5 propsegment)
3.
Useful — Positive: ”There are several possible
diagnoses that could explain the sudden appear-
ance of a slight tremor and smaller handwriting.”
(
gpt35 factscore
) – Negative: ”The patient is a 55-
year-old male.” (segment5 propsegment)
4.
Errorless — Positive: ”The patient is expe-
riencing smaller handwriting.” (
gpt35 factscore
)
– Negative: ”The sentence is about something.”
(segment5 propsegment)
Based on these findings, we conclude that auto-
matic answer segmentation faces three main chal-
lenges and we give three desiderata for successful
answer segmentation: (1) To provide independently
verifiable claims, the segmentation system requires
more context than just the sentence, possibly the entire
paragraph and the question; (2) the segmentation sys-
tem needs to be capable of handling domain-specific
language, such as the complex medical domain; (3) if
the goal is to identify individual atomic facts, the seg-
mentation system needs to operate at a more granular
level than sentences.
4.2 Claim Relevance
The relevance (usefulness) of a claim is evaluated
based on its relation to the question. We define it
as: Given a question or query
q
and a correspond-
ing answer
a
, a claim
c
with
c ∈ a
is relevant if it
provides information to satisfy the user’s information
need. Most attribution publications do not perform the
relevance evaluation automatically, relying instead on
annotators (Min et al., 2023). Due to limited resources,
we want to investigate whether this can be performed
automatically. We adopt the approach of FactCheck-
Bench (Wang et al., 2024b), who implement it with a
GPT-3.5 prompt – the prompt is in Appendix 7, Table
10. They classify a claim into four classes of ”check-
worthiness”: factual claim, opinion, not a claim (e.g.,
Is there something else you would like to know?), and
others (e.g., As a language model, I cannot access
personal information).
To evaluate the performance, we use the same 122
claims from Table 2 and annotate with the LLM and
manually. The agreement for ”factual claim” class is
very high (79 annotations the same out of 85), while
the biggest confusion is between ”not a claim” and
”other”. This shows that automatic assessment can re-
liably be used to determine the claim relevance. There-
fore, we apply the prompt to automatically label all the
claims from Table 1. The results are shown in Table 3.
We observe that 86.3% claims generated by GPT3.5
FactScore system are factual. These 2,317 claims will
be used in further steps for attribution evaluation.
4.3 Evidence Retrieval
The evidence retrieval step in the attribution process is
arguably the most important, especially in a post-hoc
retrieval system – its goal is to find the evidence to
which a claim can be attributed to. Evidence sources
can be generated directly from LLM’s memory (Ziems
et al., 2023), retrieved from a static trusted corpus
like Sphere (Piktus et al., 2021) or Wikipedia (Peng
et al., 2023), or dynamically queried from Google
(Gao et al., 2023). We use the Google approach: we
take each claim (labeled as unique and factual in the
KDIR 2024 - 16th International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Information Retrieval
150

Table 2: Comparison of different claim properties for the different segmentation systems. The fractions show the number of
occurrences divided by the total number of atomic claims generated by that system.
Atomic Independent Useful Errorless Repetition
gpt35 factscore 53/56 8/56 44/56 48/56 13/56
segment5 propsegment 40/53 6/53 28/53 34/53 18/53
spaCy sentences 3/15 3/15 10/15 11/15 3/15
Table 3: Claim relevance distribution of different segmentation systems.
Segmentation System Unique #c # factual # not a claim # opinion # other
spaCy sentences 855 550 244 26 35
gpt35 factscore 2684 2317 258 68 41
segment5 propsegment 2232 1878 290 36 28
previous steps) and query Google with it, take the top 3
results, scrape their entire textual content from HTML,
and split it (with NLTK) into chunks of either 256 or
512 character length. We embed each chunk with a
Sentence-BERT embedder all-mpnet-base-v2 (Song
et al., 2020) and store the chunks into a FAISS-vector
database (Douze et al., 2024). After that, we query
each claim against the vector store for that question
and retrieve the top 5 most similar chunks.
Table 4: NLI predictions between a claim and its respective
evidence snippets found on Google.
Method & CW Contr. Entail. No Relation
GPT3.5 - 256 2 111 82 (36.0%)
GPT3.5 - 512 1 126 88 (38.6%)
DeBERTa - 256 12 37 179 (78.5%)
DeBERTa - 512 11 64 153 (67.1%)
Human - 256 8 54 166 (72.8%)
Human - 512 9 81 138 (60.5%)
We want to automatically determine whether the
retrieved evidence chunk is related to the claim. We
model this as a Natural Language Inference (NLI) task,
following the idea from SimCSE (Gao et al., 2021),
where two pieces of text are semantically related if
there is an entailment or contradiction relation between
them and unrelated otherwise. For this purpose, we
use GPT-3.5 with a few-shot prompt (Appendix 7,
Table 11) and DeBERTa-v3-large model fine-tuned
on multiple NLI datasets from (Laurer et al., 2024),
since DeBERTa was shown to be the most powerful
encoder-only model for NLI.
We take 228 claim-evidence pairs and annotate
them both manually and automatically with the two
models (GPT and DeBERTa). The results are in Table
4. The results show that the DeBERTa-NLI model
was by far more correlated with human judgment and
that GPT-3.5 was overconfident in predicting the entail-
ment relation, i.e., classifying a lot of irrelevant chunks
as relevant. Additionally, the longer context window
led to these longer evidence chunks being more re-
lated to the claim. The stricter nature of DeBERTa
predictions makes it better suited for claim-evidence
relation prediction. Therefore, we will use DeBERTa
as the main NLI model in the next section, with a
512-character context window.
5 DEVELOPING SOLUTIONS
In this section, we propose certain solutions for se-
lected key issues identified in the previous section. We
use the existing answer attribution pipeline and en-
hance individual components to assess their effects on
the overall system.
5.1 Answer Segmentation
One of the primary reasons for the weak performance
of previous systems was the lack of independence
among claims. Even when tasked to create atomic
claims, most existing systems fail to provide sufficient
context, making it difficult for the claims to stand
alone. This leads to significant error propagation and
misleading outcomes in evidence retrieval and attri-
bution evaluation. There are three different types of
claims produced by current systems that require addi-
tional context for accurate evaluation:
1.
Anaphoric References (Coreference Resolution). Claims that include
one or more anaphors referring to previously mentioned entities or
concepts. — Example: ”The purpose of these strategies is to reduce
energy consumption.”, ”They ensure the well-being of everyone.”
2.
Conditioning (Detailed Contextualization). Claims that lack entire
sentences or conditions necessary for proper contextualization. While
not always obvious from the claim itself, this information is crucial for
accurately evaluating the claims. — Example: ”Chemotherapy is no
longer the recommended course of action.”
3.
Answer Extracts (Hypothetical Setup). Claims that arise from ques-
tions describing a hypothetical scenario. Current answer systems often
replicate parts of the scenario in the answer, leading to claims that can-
not be evaluated independently of the scenario itself. — Example: ”A
young girl is running in front of cars.”
Enhancing Answer Attribution for Faithful Text Generation with Large Language Models
151
We propose two strategies to provide more con-
text during answer segmentation: (1) claim enrich-
ment, and (2) direct segmentation with context. In the
first approach, we edit extracted claims to incorporate
the necessary context from both the answer and the
question. A system employing this strategy would im-
plement the function
f
enrich
(q, r, c
non-independent
)
, where
c
non-independent
is the non-independent claim,
r
is the re-
sponse, and
q
is the question. In the second approach,
we suggest a system that directly segments the answer
into multiple independent claims, each supplemented
with the required context. This system would use the
function
f
segment
(r, q)
, differing from the initial sys-
tems (as in Section 4), by incorporating the entire an-
swer and question rather than basing the segmentation
on individual sentences.
5.1.1 Claim Enrichment
We want to enrich only the non-independent claims. In
the previous section, we manually labeled the claims
for independence (Table 2). We now want to auto-
mate this task. For this purpose, we test whether the
GPT-3.5 (turbo-0613) and GPT-4 (turbo-1106) sys-
tems can perform this task with a one-shot prompt (in
Appendix 7, Table 13) that assesses the independence.
The results are compared with human evaluation from
Table 2. Table 5 shows the results. It is evident that
both GPT-3.5 and GPT-4 exhibit significantly high
precision, with GPT-4 outperforming in terms of re-
call and F1 score. We conclude that claim indepen-
dence can be detected by LLMs (0.84 F1 in GPT4)
and utilize the claims classified as ”non-independent”
by GPT-4 to assess the performance of the function
f
enrich
(q, r, c
non-independent
).
Table 5: Non-Independence detection performance com-
pared to human evaluation.
GPT3.5 GPT4
System Prec. R F1 Prec. Rec. F1
Overall 0.94 0.27 0.42 0.96 0.74 0.84
factscore 0.93 0.29 0.44 0.95 0.75 0.84
segmenT5 0.90 0.19 0.32 0.96 0.66 0.78
spaCy 1.0 0.5 0.67 1.0 1.0 1.0
To test the enrichment, we utilize only the GPT-
3.5 system, as described in Table 3. From the 2,317
unique and factual claims, as segmented by the original
GPT-3.5 system, we take a random sample of 500 and
assess their independence using the GPT-4 prompt
from the previous step. We observe 290 out of 500
were deemed to be ”not independent” by GPT-4. We
then perform the enrichment by applying a one-shot
prompt with both GPT-3.5 and GPT-4 to implement
the function
f
enrich
(q, a, c
non-independent
)
and compare
the results to the original claims. The comparison
is conducted using the non-independence detection
system described above. The quality of this step is
measured in the reduction of non-independent claims.
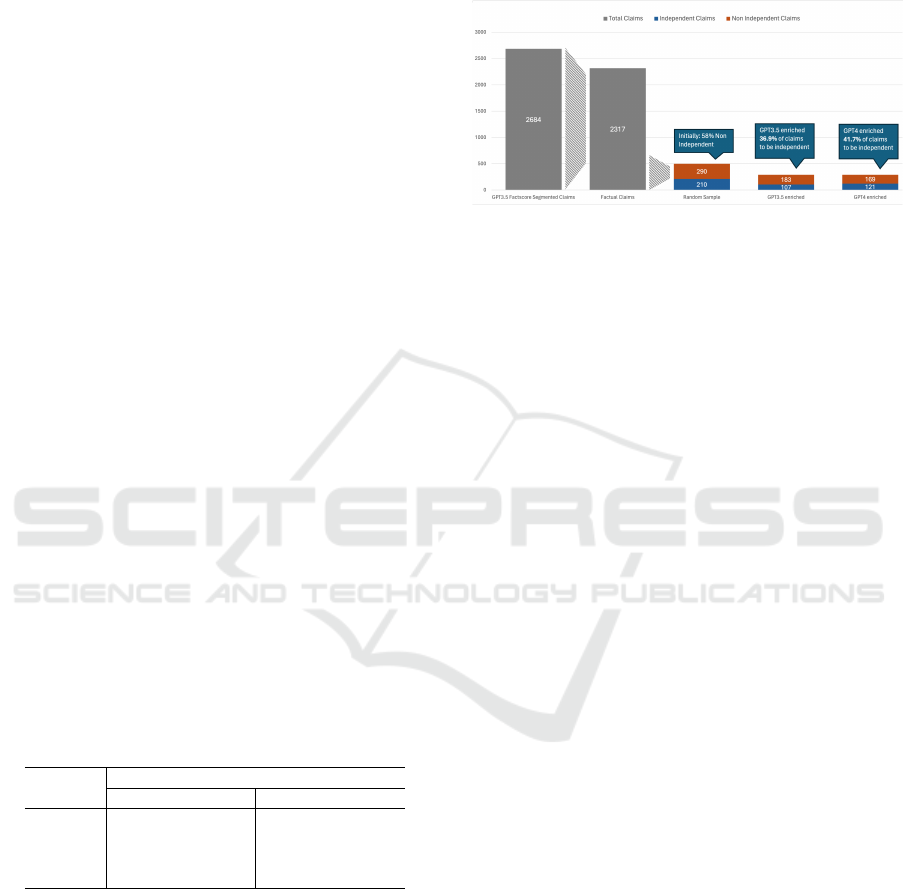
The results are presented in Figure 2.
Figure 2: Statistics of contextualization of the 290 created
claims by GPT3.5 and GPT4, evaluated by GPT4.
The enrichment function managed to make an addi-
tional 107/290 with GPT-3.5 and 121/290 with GPT-4
claims independent, i.e., further reducing the number
of non-independent claims by 36.9% (GPT-3.5) and
41.7% (GPT-4). This is a considerable improvement
that increases the number of claims usable for later
attribution steps. Nevertheless, many claims still re-
mained without context. Another observation is that
the enrichment has noticeably increased the average
number of characters of the claims. Initially, the aver-
age number of characters for independent claims was
66.0 and 59.4 for non-independent claims. The revi-
sion by GPT-4 increased it to 155.6 characters, and
the enrichment by GPT-3.5 to 145.9 characters. Later,
we evaluate the impact of claim enrichment on the
evidence retrieval process (Section 5.3).
5.1.2 Answer Segmentation with Context –
Direct Segmentation
An alternative to enrichment is directly segmenting the
answer into multiple independent claims with context.
This approach implements the function
f
segment
(r, q)
by using a one-shot prompt and GPT3.5 and GPT4
as LLMs. To evaluate the result quantitatively, we
compare the average number of claims and the length
of claims with those from alternative approaches to
answer segmentation. This step is done on a subset
of 100 question-answer pairs from ExpertQA. The
prompt requests the model to print out a structured list
of claims. The exact prompt can be found in Appendix
7, Table 14. The results are presented in Table 6.
Upon applying the segmentation to the responses
from GPT-4, an increase in the number of claims was
observed, aligning with the levels obtained through
the original FactScore segmentation. This implementa-
tion aims to diminish non-independence, given that the
original FactScore segmentation relied on SpaCy sen-
KDIR 2024 - 16th International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Information Retrieval
152
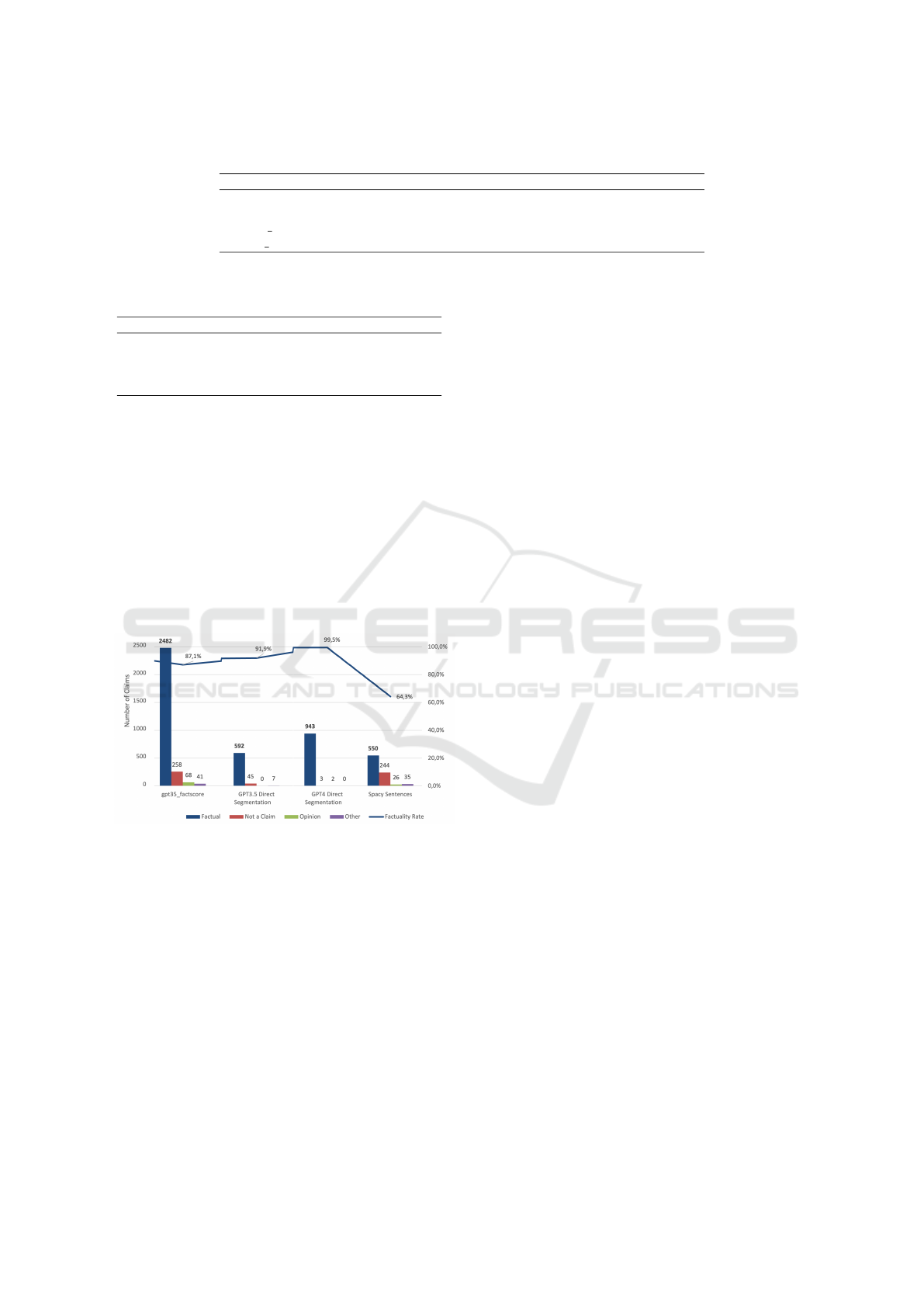
Table 6: Descriptive comparison of adopted answer segmentation approaches.
Segmentation System Number of c Unique #c avg. len(c) c / Sentence
GPT3.5 direct 644 644 102.8 0.75
GPT4 direct 948 948 84.1 1.11
spaCy sentences 938 855 103.2 1.00
gpt35 factscore 3016 2684 61.4 3.22
Table 7: Comparison of claim enrichment on the retrieval
performance.
Model Contr. Entail. No Rel.
Original Independent 5.6% 42.2% 52.2%
Original Non-Ind. 3.6% 24.1% 71.3%
Enriched Independent 6.1% 35.4% 58.6%
Enriched Non-Ind. 1.3% 20.5% 78.2%
tences, which exhibited non-independence in 80% of
instances. As generating independent claims from non-
independent inputs is not possible, employing GPT-4
as a baseline may mitigate this issue.
5.2 Factuality & Independence
The next step in the evaluation involves analyzing the
factuality of individual claims. This is done employing
the same methodology as described in Section 4.2,
with previous results in Table 3. The outcomes of the
direct answer segmentation are depicted in Figure 3.
Figure 3: Visualization of the factuality evaluation statistics
for the four different systems.
This figure clearly demonstrates an improvement
in the factuality rate of the claims generated by both
GPT-4 and GPT-3.5 compared to SpaCy sentence seg-
mentation, with the factuality rate increasing from
64.3% to 99.5% for GPT-4 and to 91.9% for GPT-3.5.
These results suggest that this approach is a signifi-
cantly better alternative to spaCy tokenization.
5.3 Impact on Evidence Retrieval
The evaluation of the impact of claim enrichment on
evidence retrieval is conducted using the same 2,317
(question, response, claim) triplets, which were clas-
sified by the GPT-3.5 system as factual, as in the pre-
vious setup. The retrieval process is conducted us-
ing the same GPT-3.5 enriched claim-based retrieval
system For assessing the impact of claim enrichment
on retrieval (function
f
enrich
(q, a, c
non-independent
)
), we
compare a sampled yet stratified set of claims across
four categories: originally independent, originally non-
independent, enriched (by GPT4) non-independent,
and enriched (by GPT4) independent claims. The
enriched claims are based on the originally non-
independent claims. We utilize DeBERTa to evaluate
the claim-evidence relation.
The findings are presented in Table 7. The table
reveals several interesting findings: Firstly, it is ev-
ident that originally independent claims highly out-
perform originally non-independent claims in the evi-
dence retrieval pipeline. Upon enriching the originally
non-independent claims with GPT-4, as described in
the previous section (
f
enrich
(q, a, c
non-independent
)
), the
claims that were successfully enriched show a big im-
provement in performance within the retrieval pipeline.
This indicates that enriching (contextualizing) claims
enhances the retrieval performance. The successfully
enriched claims approach the performance of the orig-
inally independent claims, with a ”No Relation” share
of 58.6%. However, claims that were not successfully
enriched exhibit worse performance than the originally
non-independent claims, with a ”No Relation” share
of 78.2%. Overall, the effect of claim enrichment is
a 16.2 percentage point reduction (69.9 to 53.7) of
claim-source pairs with no relation.
Additionally, we evaluate the impact of direct an-
swer segmentation on the retrieval process. For that,
we use the random sample of 40 (question, response,
claim) triplets per direct segmentation system, as de-
scribed in Section 5.1.2. The results are presented in
Table 8. As above, we analyze the share of (claim,
evidence) pairs that are classified as ”Missing” or ”No
Relation” by DeBERTa; a lower share means a better
retrieval process. The table shows the claims were yet
again enhanced when compared to the previous enrich-
ment approach. Direct segmentation by GPT-4 records
a combined ”Missing + No Relation” share of 48.5%
for independent claims and 81.6% for non-independent
claims. This represents a significant improvement for
independent claims compared to both enriched and
original claims.
Enhancing Answer Attribution for Faithful Text Generation with Large Language Models
153

Table 8: Comparison of direct answer segmentation on the retrieval performance (more Entailment is better).
Model Contradiction Entailment Missing No Relation
Original Independent 5.6% 42.2% 0.0% 52.2%
Original Non-Ind. 3.6% 24.1% 2.4% 69.9%
GPT3.5 Direct – Independent 4.2% 47.2% 0% 48.6%
GPT3.5 Direct – Non-Ind. 0% 27.0% 2.7% 70.3%
GPT4 Direct – Independent 0% 51.5% 0% 48.5%
GPT4 Direct – Non-Ind. 2.0% 14.3% 2.0% 81.6%
Table 9: Comparison of different embedding models and context window splitters on the retrieval performance (more Entailment
indicates better performance).
Model Contradiction Entailment No Relation
Ada 2.0 2.9% 41.0% 56.0%
AnglE 2.9% 39.5% 57.5%
SBert + Recursive CW 0.0% 22.1% 76.1%
SBert Baseline (Macro) 0.9% 35.7% 62.5%
To summarize the findings, it can be concluded
that direct segmentation with context by GPT-4 signifi-
cantly surpasses both the original and enriched claims
and outperforms comparative methods in aspects of
retrieval, time efficiency, and independent claim gen-
eration. It nearly matches the performance of GPT-4
in enriching non-independent claims regarding the cre-
ation of independent claims and surpasses it in the
retrieval process at the macro level.
5.4 Analysis of Evidence Retrieval
As a final step, we briefly evaluate the evidence re-
trieval process itself, analyzing different embedding
models and context window sizes. We utilize claims
generated by GPT-4 Direct, as this system was shown
to be the best performer in the previous steps. We
use the same random sample of 40 questions. We
modify two dimensions of the retrieval process: the
embedding model and the context window splitter. In-
stead of Sentence-BERT, we employ OpenAI Ada 2.0,
which provides embeddings from GPT-3.5, and AnglE-
Embeddings (Li and Li, 2023) from a pre-trained
sentence-transformer model optimized for retrieval.
Rather than using a simple sliding window approach,
we implement a recursive text splitter with overlap to
capture more relevant information.
The search engine (Google Search Custom Search
Engine) remains unchanged. The results are presented
in Table 9. The results demonstrate that the Ada 2.0
Embeddings with the fixed 512c-size context window
splitter outperform the overall SBert baseline, which
was used in our previous experiments and depicted the
best performance. The AnglE embeddings, optimized
for retrieval, also outperform the Sentence-BERT base-
line but fall behind the GPT-based Ada 2.0 embed-
dings. Interestingly, the recursive context window
splitter with SBert embeddings performs significantly
worse than the fixed context window splitter.
6 DISCUSSION
The evaluation of various attribution methods revealed
that the main challenge lies in the precise retrieval
of relevant evidence snippets, especially considering
the complexity of the query or the intended user need.
A crucial aspect of effective retrieval is in formulat-
ing claims for subsequent search in a way that they
are atomic, independent, and properly contextualized.
Additionally, addressing the shortcomings in answer
segmentation and independence was essential for im-
proving the attribution process. Segmenting answers
into independent (contextualized) claims was most ef-
fectively done using GPT-4, yet it did not achieve an
80% success rate. This indicates that a general-purpose
language model might not be the best choice for this
task and could be improved in the future by a more
specialized and smaller model tailored specifically for
this purpose. Future work could involve fine-tuning
models for detecting non-independent claims and ex-
ploring alternative approaches for source document
retrieval. Additionally, future research should focus on
expanding the scope of embedding models and their
context windows for semantic search of evidence.
7 CONCLUSION
In this paper, we analyzed automated answer attribu-
tion, the task of tracing claims from generated LLM
responses to relevant evidence sources. By splitting the
task into constituent components of answer segmenta-
tion, claim relevance detection, and evidence retrieval,
we performed a case analysis of current systems, de-
KDIR 2024 - 16th International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Information Retrieval
154

termined their weaknesses, and proposed essential im-
provements to the pipeline. Our improvements led to
an increase in performance in all three aspects of the
answer attribution process. We hope our study will
help future developments of this emerging NLP task.
REFERENCES
Afzal., A., Vladika., J., Braun., D., and Matthes., F. (2023).
Challenges in domain-specific abstractive summariza-
tion and how to overcome them. In Proceedings of
the 15th International Conference on Agents and Artifi-
cial Intelligence - Volume 3: ICAART, pages 682–689.
INSTICC, SciTePress.
Augenstein, I., Baldwin, T., Cha, M., Chakraborty, T.,
Ciampaglia, G. L., Corney, D., DiResta, R., Ferrara,
E., Hale, S., Halevy, A., Hovy, E., Ji, H., Menczer, F.,
Miguez, R., Nakov, P., Scheufele, D., Sharma, S., and
Zagni, G. (2023). Factuality challenges in the era of
large language models.
Bohnet, B., Tran, V. Q., Verga, P., Aharoni, R., Andor, D.,
Soares, L. B., Ciaramita, M., Eisenstein, J., Ganchev,
K., Herzig, J., Hui, K., Kwiatkowski, T., Ma, J., Ni, J.,
Saralegui, L. S., Schuster, T., Cohen, W. W., Collins,
M., Das, D., Metzler, D., Petrov, S., and Webster, K.
(2023). Attributed question answering: Evaluation and
modeling for attributed large language models.
Chen, S., Buthpitiya, S., Fabrikant, A., Roth, D., and Schus-
ter, T. (2023a). PropSegmEnt: A large-scale corpus for
proposition-level segmentation and entailment recogni-
tion. In Findings of the Association for Computational
Linguistics: ACL 2023.
Chen, S., Zhang, H., Chen, T., Zhou, B., Yu, W., Yu, D.,
Peng, B., Wang, H., Roth, D., and Yu, D. (2023b).
Sub-sentence encoder: Contrastive learning of propo-
sitional semantic representations. arXiv preprint
arXiv:2311.04335.
Chung, H. W., Hou, L., Longpre, S., Zoph, B., Tay, Y.,
Fedus, W., Li, Y., Wang, X., Dehghani, M., Brahma, S.,
Webson, A., Gu, S. S., Dai, Z., Suzgun, M., Chen, X.,
Chowdhery, A., Castro-Ros, A., Pellat, M., Robinson,
K., Valter, D., Narang, S., Mishra, G., Yu, A., Zhao, V.,
Huang, Y., Dai, A., Yu, H., Petrov, S., Chi, E. H., Dean,
J., Devlin, J., Roberts, A., Zhou, D., Le, Q. V., and
Wei, J. (2022). Scaling instruction-finetuned language
models.
Dhuliawala, S., Komeili, M., Xu, J., Raileanu, R., Li, X.,
Celikyilmaz, A., and Weston, J. (2023). Chain-of-
verification reduces hallucination in large language
models.
Douze, M., Guzhva, A., Deng, C., Johnson, J., Szilvasy, G.,
Mazar
´
e, P.-E., Lomeli, M., Hosseini, L., and J
´
egou, H.
(2024). The faiss library.
Gao, L., Dai, Z., Pasupat, P., Chen, A., Chaganty, A. T., Fan,
Y., Zhao, V., Lao, N., Lee, H., Juan, D.-C., and Guu,
K. (2023). RARR: Researching and revising what lan-
guage models say, using language models. In Rogers,
A., Boyd-Graber, J., and Okazaki, N., editors, Proceed-
ings of the 61st Annual Meeting of the Association for
Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers),
pages 16477–16508, Toronto, Canada. Association for
Computational Linguistics.
Gao, T., Yao, X., and Chen, D. (2021). SimCSE: Simple con-
trastive learning of sentence embeddings. In Empirical
Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP).
Guo, Z., Schlichtkrull, M., and Vlachos, A. (2022). A survey
on automated fact-checking. Transactions of the Asso-
ciation for Computational Linguistics, 10:178–206.
Ji, Z., Lee, N., Frieske, R., Yu, T., Su, D., Xu, Y., Ishii, E.,
Bang, Y. J., Madotto, A., and Fung, P. (2023). Survey
of hallucination in natural language generation. ACM
Computing Surveys, 55(12):1–38.
Kaddour, J., Harris, J., Mozes, M., Bradley, H., Raileanu, R.,
and McHardy, R. (2023). Challenges and applications
of large language models.
Kamalloo, E., Jafari, A., Zhang, X., Thakur, N., and Lin, J.
(2023). HAGRID: A human-llm collaborative dataset
for generative information-seeking with attribution.
arXiv:2307.16883.
Kasneci, E., Seßler, K., K
¨
uchemann, S., Bannert, M.,
Dementieva, D., Fischer, F., Gasser, U., Groh, G.,
G
¨
unnemann, S., H
¨
ullermeier, E., et al. (2023). Chatgpt
for good? on opportunities and challenges of large lan-
guage models for education. Learning and individual
differences, 103:102274.
Laurer, M., van Atteveldt, W., Casas, A., and Welbers, K.
(2024). Less annotating, more classifying: Addressing
the data scarcity issue of supervised machine learn-
ing with deep transfer learning and bert-nli. Political
Analysis, 32(1):84–100.
Lewis, M. (2023). Generative artificial intelligence and
copyright current issues. Morgan Lewis LawFlash.
Li, D., Sun, Z., Hu, X., Liu, Z., Chen, Z., Hu, B., Wu, A.,
and Zhang, M. (2023). A survey of large language
models attribution.
Li, X. and Li, J. (2023). Angle-optimized text embeddings.
Liu, N., Zhang, T., and Liang, P. (2023). Evaluating verifi-
ability in generative search engines. In Bouamor, H.,
Pino, J., and Bali, K., editors, Findings of the Associ-
ation for Computational Linguistics: EMNLP 2023,
pages 7001–7025, Singapore. Association for Compu-
tational Linguistics.
Liu, Y., Yao, Y., Ton, J.-F., Zhang, X., Guo, R., Cheng,
H., Klochkov, Y., Taufiq, M. F., and Li, H. (2024).
Trustworthy llms: a survey and guideline for evaluating
large language models’ alignment.
Malaviya, C., Lee, S., Chen, S., Sieber, E., Yatskar, M., and
Roth, D. (2024). ExpertQA: Expert-curated questions
and attributed answers. In 2024 Annual Conference
of the North American Chapter of the Association for
Computational Linguistics.
Min, S., Krishna, K., Lyu, X., Lewis, M., Yih, W.-t., Koh, P.,
Iyyer, M., Zettlemoyer, L., and Hajishirzi, H. (2023).
FActScore: Fine-grained atomic evaluation of factual
precision in long form text generation. In Bouamor,
H., Pino, J., and Bali, K., editors, Proceedings of the
2023 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural
Language Processing, pages 12076–12100, Singapore.
Association for Computational Linguistics.
Enhancing Answer Attribution for Faithful Text Generation with Large Language Models
155

Nori, H., King, N., McKinney, S. M., Carignan, D., and
Horvitz, E. (2023). Capabilities of gpt-4 on medical
challenge problems.
Peng, B., Galley, M., He, P., Cheng, H., Xie, Y., Hu, Y.,
Huang, Q., Liden, L., Yu, Z., Chen, W., and Gao, J.
(2023). Check your facts and try again: Improving
large language models with external knowledge and
automated feedback.
Piktus, A., Petroni, F., Karpukhin, V., Okhonko, D.,
Broscheit, S., Izacard, G., Lewis, P., O
˘
guz, B., Grave,
E., Yih, W.-t., et al. (2021). The web is your oyster-
knowledge-intensive nlp against a very large web cor-
pus. arXiv preprint arXiv:2112.09924.
Rashkin, H., Nikolaev, V., Lamm, M., Aroyo, L., Collins,
M., Das, D., Petrov, S., Tomar, G. S., Turc, I., and
Reitter, D. (2023). Measuring attribution in natural lan-
guage generation models. Computational Linguistics,
49(4):777–840.
Singh, C., Inala, J. P., Galley, M., Caruana, R., and Gao, J.
(2024). Rethinking interpretability in the era of large
language models.
Song, K., Tan, X., Qin, T., Lu, J., and Liu, T.-Y. (2020). Mp-
net: masked and permuted pre-training for language
understanding. In Proceedings of the 34th Interna-
tional Conference on Neural Information Processing
Systems, NIPS’20, Red Hook, NY, USA. Curran Asso-
ciates Inc.
Vladika, J. and Matthes, F. (2023). Scientific fact-checking:
A survey of resources and approaches. In Rogers, A.,
Boyd-Graber, J., and Okazaki, N., editors, Findings of
the Association for Computational Linguistics: ACL
2023, pages 6215–6230, Toronto, Canada. Association
for Computational Linguistics.
Vladika, J. and Matthes, F. (2024). Improving health ques-
tion answering with reliable and time-aware evidence
retrieval. In Duh, K., Gomez, H., and Bethard, S., ed-
itors, Findings of the Association for Computational
Linguistics: NAACL 2024, pages 4752–4763, Mexico
City, Mexico. Association for Computational Linguis-
tics.
Wang, B., Chen, W., Pei, H., Xie, C., Kang, M., Zhang, C.,
Xu, C., Xiong, Z., Dutta, R., Schaeffer, R., Truong,
S. T., Arora, S., Mazeika, M., Hendrycks, D., Lin, Z.,
Cheng, Y., Koyejo, S., Song, D., and Li, B. (2024a).
Decodingtrust: A comprehensive assessment of trust-
worthiness in gpt models.
Wang, Y., Reddy, R. G., Mujahid, Z. M., Arora, A., Ruba-
shevskii, A., Geng, J., Afzal, O. M., Pan, L., Boren-
stein, N., Pillai, A., Augenstein, I., Gurevych, I., and
Nakov, P. (2024b). Factcheck-bench: Fine-grained
evaluation benchmark for automatic fact-checkers.
Wei, A., Haghtalab, N., and Steinhardt, J. (2024). Jailbroken:
How does llm safety training fail? Advances in Neural
Information Processing Systems, 36.
Yue, X., Wang, B., Chen, Z., Zhang, K., Su, Y., and Sun, H.
(2023). Automatic evaluation of attribution by large
language models. In Bouamor, H., Pino, J., and Bali,
K., editors, Findings of the Association for Computa-
tional Linguistics: EMNLP 2023, pages 4615–4635,
Singapore. Association for Computational Linguistics.
Zhang, J., Bao, K., Zhang, Y., Wang, W., Feng, F., and
He, X. (2023a). Is chatgpt fair for recommendation?
evaluating fairness in large language model recommen-
dation. In Proceedings of the 17th ACM Conference
on Recommender Systems, pages 993–999.
Zhang, Y., Li, Y., Cui, L., Cai, D., Liu, L., Fu, T., Huang, X.,
Zhao, E., Zhang, Y., Chen, Y., Wang, L., Luu, A. T.,
Bi, W., Shi, F., and Shi, S. (2023b). Siren’s song in the
ai ocean: A survey on hallucination in large language
models.
Zhao, H., Chen, H., Yang, F., Liu, N., Deng, H., Cai, H.,
Wang, S., Yin, D., and Du, M. (2024a). Explainability
for large language models: A survey. ACM Transac-
tions on Intelligent Systems and Technology, 15(2):1–
38.
Zhao, Y., Zhang, J., Chern, I., Gao, S., Liu, P., He, J., et al.
(2024b). Felm: Benchmarking factuality evaluation of
large language models. Advances in Neural Informa-
tion Processing Systems, 36.
Ziems, N., Yu, W., Zhang, Z., and Jiang, M. (2023). Large
language models are built-in autoregressive search en-
gines. In Rogers, A., Boyd-Graber, J., and Okazaki, N.,
editors, Findings of the Association for Computational
Linguistics: ACL 2023, pages 2666–2678, Toronto,
Canada. Association for Computational Linguistics.
APPENDIX
This is the appendix with additional material.
Technical Setup and Manual Annotation
All GPT 3.5 and GPT 4 models were accessed through
the official OpenAI API. Version turbo-0125 for GPT
3.5 and 0125-preview for GPT 4, or as indicated in
the text. For local experiments (such as model em-
beddings with sentence transformers, DeBERTa entail-
ment prediction, etc.), one A100 GPU with 40GB of
VRAM was used, for a duration of one computation
hour per experiment. No fine-tuning was performed
by us, models like SegmenT5 and DeBERTa-v3 were
used out-of-the-box, found in cited sources and Hug-
gingFace.
Whenever we refer to manual annotation of data
examples, this was done by two paper authors, who
have a master’s degree in computer science and are
pursuing a PhD degree in computer science. None of
the annotations required in-depth domain knowledge
and were mostly reading comprehension tasks.
Prompts
The used prompts are given in Tables 10–14.
KDIR 2024 - 16th International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Information Retrieval
156

Table 10: Overview of applied prompts for GPT answer segmentation and claim relevance (check-worthiness) detection.
Use Case Prompt Content
FactScore Answer Seg-
mentation with GPT 3.5
Please breakdown the following sentence into independent facts.
Don’t provide meta-information about sentence or you as a system. Just list the facts and strictly stick to the following
format:
1. ”Fact 1”
2. ”Fact 2”
3. ”...”
The sentence is:
Claim Relevance / Check-
Worthiness Detection
You are a factchecker assistant with task to identify a sentence, whether it is 1. a factual claim; 2. an opinion; 3. not a
claim (like a question or a imperative sentence); 4. other categories.
Let’s define a function named checkworthy(input: str).
The return value should be a python int without any other words, representing index label, where index selects from [1, 2,
3, 4].
For example, if a user call checkworthy(”I think Apple is a good company.”) You should return 2
If a user call checkworthy(”Friends is a great TV series.”) You should return 1
If a user call checkworthy(”Are you sure Preslav is a professor in MBZUAI?”) You should return 3
If a user call checkworthy(”As a language model, I can’t provide these info.”) You should return 4
Note that your response will be passed to the python interpreter, no extra words.
checkworthy(”input”)
Table 11: Overview of applied prompt for claim-evidence relation detection, i.e., entailment recognition (NLI) between the
claim and retrieved evidence chunk with GPT 3.5.
Use Case Prompt Content
Claim-Evidence En-
tailment Recognition
Your task is to determine if a claim is supported by a document given a specific question. Implement the function nli(question:
str, claim: str, document: str) -> str which accepts a question, a claim, and a document as input.
The function returns a string indicating the relationship between the claim and the document in the context of the question.
The possible return values are:
”entailed” if the claim is supported by the document, ”contradicted” if the claim is refuted by the document, ”no relation” if
the claim has no relevant connection to the document given the question.
Your evaluation should specifically consider the context provided by the question. The output should be a single string value
without additional comments or context, as it will be used within a Python interpreter.
Examples:
Question: ”You are patrolling the local city center when you are informed by the public about a young girl behaving
erratically near traffic. What are your initial thoughts and actions?”
Claim: ”Trained professionals should handle situations like this.”
Document: ”Every trained professional football player should be adept at managing high-stress situations on the field.”
Output: ”no relation”
Question: ”You are patrolling the local city center when you are informed by the public about a young girl behaving
erratically near traffic. What are your initial thoughts and actions?”
Claim: ”Trained professionals should handle situations like this.”
Document: ”Standard police officer training includes procedures for managing public disturbances and emergencies.”
Output: ”entailed”
Table 12: Overview of applied prompt for the claim independence detection.
Use Case Prompt Content
Claim Independence
Detection
You are tasked with determining whether a given claim or statement can be verified independently. A claim is considered ”independent” if it
contains sufficient information within itself to assess its truthfulness without needing additional context or external information. Your response
must strictly be either ”independent” or ”not independent.” Adhere to this format precisely, as your output will be processed by a Python
interpreter.
Guidelines:
Evaluate if the claim provides enough detail on its own to be verified. Do not consider external knowledge or context not present in the claim.
Respond only with ”independent” if the claim is self-sufficient for verification; otherwise, respond with ”not independent.” The below examples
contain Rationales for explanation, which are not allowed in your response.
Examples:
Input: ”The sun rises in the east.”
Output: independent
Input: ”Chemotherapy is no longer the recommended course of action.”
Output: not independent
Rationale: The claim would require additional context, for example the type of cancer or the patient’s medical history.
Input: ”Opening up the aperture can overexpose the image slightly.”
Output: independent
Input: ”A young girl is running in front of cars.”
Output: not independent
Rationale: The claim is situational and lacks specific details that would allow for independent verification.
Input: ”They ensure the well-being of everyone involved.”
Output: not independent
Rationale: The claim is vagues, it is not known who ”They” are.
Enhancing Answer Attribution for Faithful Text Generation with Large Language Models
157

Table 13: Overview of applied prompt for the claim enrichment process.
Use Case Prompt Content
Claim Enrichment
Prompt
Your task involves providing context to segmented claims that were originally part of a larger answer, making each claim
verifiable independently.
This involves adding necessary details to each claim so that it stands on its own without requiring additional information
from the original answer. The claim should stay atomic and only contain one specific statement or piece of information. Do
not add new information or more context than necessary! Ensure that all pronouns or references to specific situations or
entities (e.g., ”He,” ”they,” ”the situation”) are clearly defined within the claim itself. Your output should consist solely of
the context-enhanced claim, without any additional explanations, as it will be processed by a Python interpreter.
Example:
Question: ”How to track the interface between the two fluids?”
Answer: ”To track the interface between two fluids, you can use various techniques depending on the specific situation and
the properties of the fluids. Here are a few common methods:
...
4. Ultrasonic Techniques: Ultrasonic waves can be used to track the interface between fluids. By transmitting ultrasonic
waves through one fluid and measuring the reflected waves, you can determine the position of the interface.
...
It’s important to note that the choice of method depends on the specific application and the properties of the fluids involved.”
Claim: ”Reflected waves can be measured.”
Revised Claim: ”Reflected waves can be measured to determine the position of the interface between two fluids.”
Table 14: Overview of the prompt for direct claim segmentation with added context.
Use Case Prompt Content
Direct Claim Segmen-
tation with Context
Objective: Transform the answer to a question into its discrete, fundamental claims. Each claim must adhere to the
following criteria:
Conciseness: Formulate each claim as a brief, standalone sentence.
Atomicity: Ensure that each claim represents a single fact or statement, requiring no further subdivision for evaluation of
its truthfulness. Note that most listing and ”or-combined” claims are not atomic and must be split up.
Independence: Craft each claim to be verifiable on its own, devoid of reliance on additional context or preceding
information. For instance, ”The song was released in 2019” is insufficiently specific because the identity of ”the song”
remains ambiguous. Make sure that there is no situational dependency in the claims.
Consistency in Terminology: Utilize language and terms that reflect the original question or answer closely, maintaining
the context and specificity.
Non-reliance: Design each claim to be independent from other claims, eliminating sequential or logical dependencies
between them.
Exhaustiveness: Ensure that the claims cover all the relevant information in the answer, leaving no important details
unaddressed.
Strictly stick to the below output format, which numbers any claims and separates them by a new line. This is important,
as the output will be passed to a python interpreter.
Don’t add any explanation or commentary to the output.
Example:
Input:
Question: As an officer with the NYPD, I am being attacked by hooligans. What charges can be pressed?
Answer: If you’re an NYPD officer and you’re being assaulted by hooligans, you have the right to press charges for
assault on a police officer, which is recognized as a criminal offense under New York law. Specifically, the act of
assaulting a police officer is addressed under New York Penal Law § 120.08, designating it as a felony. Offenders may
face severe penalties, including time in prison and monetary fines.
Output:
1. An NYPD officer assaulted by hooligans has the right to press charges for assault on a police officer.
2. Assault on a police officer is deemed a criminal offense in New York.
3. The act of assaulting a police officer is specified under New York Penal Law § 120.08.
4. Under New York law, assaulting a police officer is categorized as a felony.
5. Conviction for assaulting a police officer in New York may result in imprisonment.
6. Conviction for assaulting a police officer in New York may lead to monetary fines.
KDIR 2024 - 16th International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Information Retrieval
158
