
Q-Learning Based LQR Occupant-Centric Control of Non-Residential
Buildings
Oumaima Ait-Essi
1
, Joseph J. Yam
´
e
1,∗ a
, Hicham Jamouli
2 b
and Fr
´
ed
´
eric Hamelin
1 c
1
CRAN, CNRS, UMR 7039, Universit
´
e de Lorraine, Campus Sciences, Vandoeuvre-l
`
es-Nancy, France
2
LISAD, ENSA, Universit
´
e Ibn Zohr, Agadir, Morocco
Keywords:
Reinforcement Learning, Q-Learning, Data-Based Linear Quadratic Control, HVAC-VAV Systems, Building
Occupants, Occupant-Centric Control.
Abstract:
We propose a novel approach to the control of variable-air-volume (VAV)-HVAC systems for the regulation of
thermal comfort in rooms of a non-residential building where the number of occupants may vary considerably
and randomly during the day. Specifically, we develop a reinforcement learning control algorithm based
on model-free optimal linear quadratic control. We leverage the quality function, the so-called Q-function,
derived from Bellman dynamic programming, to develop a learning control algorithm based solely on system-
generated data including building dynamics and its occupants. Simulations are carried out on a new HVAC-
VAV system installed in a building at the University of Lorraine, demonstrating the potential of the proposed
method for maintaining climatic conditions and the comfort of room occupants while optimizing the airflow
demand of VAV boxes, which is correlated with the energy consumed per room.
1 INTRODUCTION
Energy consumption in buildings accounts for over
36.9% of primary energy consumption, of which
17.2% is accounted for by commercial and non-
residential buildings (EIA, 2024). Heating, ventila-
tion, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems account
for 40% of total building energy consumption. En-
suring occupant comfort while achieving energy sav-
ings is a key objective in optimal building opera-
tion, as comfort plays a vital role in human well-
being and productivity. Recent contributions regard-
ing human-building interactions highlight the impact
of occupant information, such as occupancy and be-
havior, on building energy consumption. The poten-
tial for improving the operation of buildings and their
control systems through such human-building interac-
tions is now well recognized, and has led to occupant-
centric control (OCC) as an important research topic
(Soleimanijavid et al., 2024; Ouf et al., 2021; Yu
et al., 2024; Xu et al., 2023; Jia et al., 2017). Al-
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4349-6240
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9064-0372
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5535-5680
∗
Corresponding author: joseph.yame@univ-
lorraine.fr.
though the concept of OCC is not perfectly defined, it
can be categorized in two main ways (Ouf et al., 2021)
: occupant-centric controls and occupant behavior-
centric controls. In the first meaning, OCC deals with
the presence/absence of occupants and HVAC control
based on occupants counts while in its second mean-
ing OCC focuses on occupant behaviors and prefer-
ences from occupant’s interactions with building sys-
tems, e.g., thermostats setpoints adjusting, windows
openings, exercising, etc. With regards to the behav-
ioral aspects of OCC, information and potential char-
acteristics can be extracted from energy consumption
data using machine learning methods which are sub-
sequently used to identify and classify typical behav-
ior patterns (Yu et al., 2024). However, occupant be-
haviors are highly stochastic and unpredictable, with
temporal complexities in the process of identifying
consistent behavioral strategies (Xu et al., 2023). To
meet these challenges, reinforcement learning is in-
creasingly becoming one of the most effective ways
of developing control strategies that take occupant be-
havior into account to ensure thermal comfort and
optimize building energy consumption (Han et al.,
2020), (Liu and Gou, 2024), (Wang et al., 2023).
In the work presented here, OCC is addressed un-
der its first categorization as the presence/absence and
the number of occupants in a building have a direct
494
Ait-Essi, O., Yamé, J. J., Jamouli, H. and Hamelin, F.
Q-Learning Based LQR Occupant-Centric Control of Non-Residential Buildings.
DOI: 10.5220/0013066800003822
In Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics (ICINCO 2024) - Volume 1, pages 494-502
ISBN: 978-989-758-717-7; ISSN: 2184-2809
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
impact on its energy consumption, and strongly in-
fluence the operation of energy systems throughout
the building. Buildings with highly variable occu-
pancy profiles, such as classrooms, computer rooms
or university laboratories, and with occupancy vary-
ing throughout the day all along the year, raise is-
sues for the design and implementation of control
strategies aimed at balancing comfort and energy ef-
ficiency. Among these issues, the lack of an accurate
model of building dynamics is a barrier to the design
of optimal controllers to ensure thermal comfort and
optimum energy consumption. Optimal controllers,
such as the linear quadratic controller (LQR), are fre-
quently used for systems with known dynamics. In
the case of unknown dynamics, a basic approach is
to fit a model to the system using input/output obser-
vations and then use the fitted model for control pur-
poses. A more direct approach would be to design the
optimal controller directly from observations, with-
out the intermediate step of a fitted plant model. Such
an approach, driven by advances in machine learning,
is currently undergoing significant growth, with LQR
control being considered as a standard benchmark for
learning-based control of systems with unknown dy-
namics (Farjadnasab and Babazadeh, 2022). It is in
this context that this research project was carried out
on thermal comfort and the reduction of energy con-
sumption in a university building where classroom oc-
cupancy varies greatly from one day to the next.
2 SYSTEM DESCRIPTION AND
MODELING
2.1 System Description
The system under consideration is an HVAC instal-
lation recently commissioned in a central building,
called ATELA building, comprising practical electri-
cal, electronics and control engineering laboratories
with lectures and computer rooms at the Faculty of
Science and Technology of the University of Lorraine
in Nancy, France.
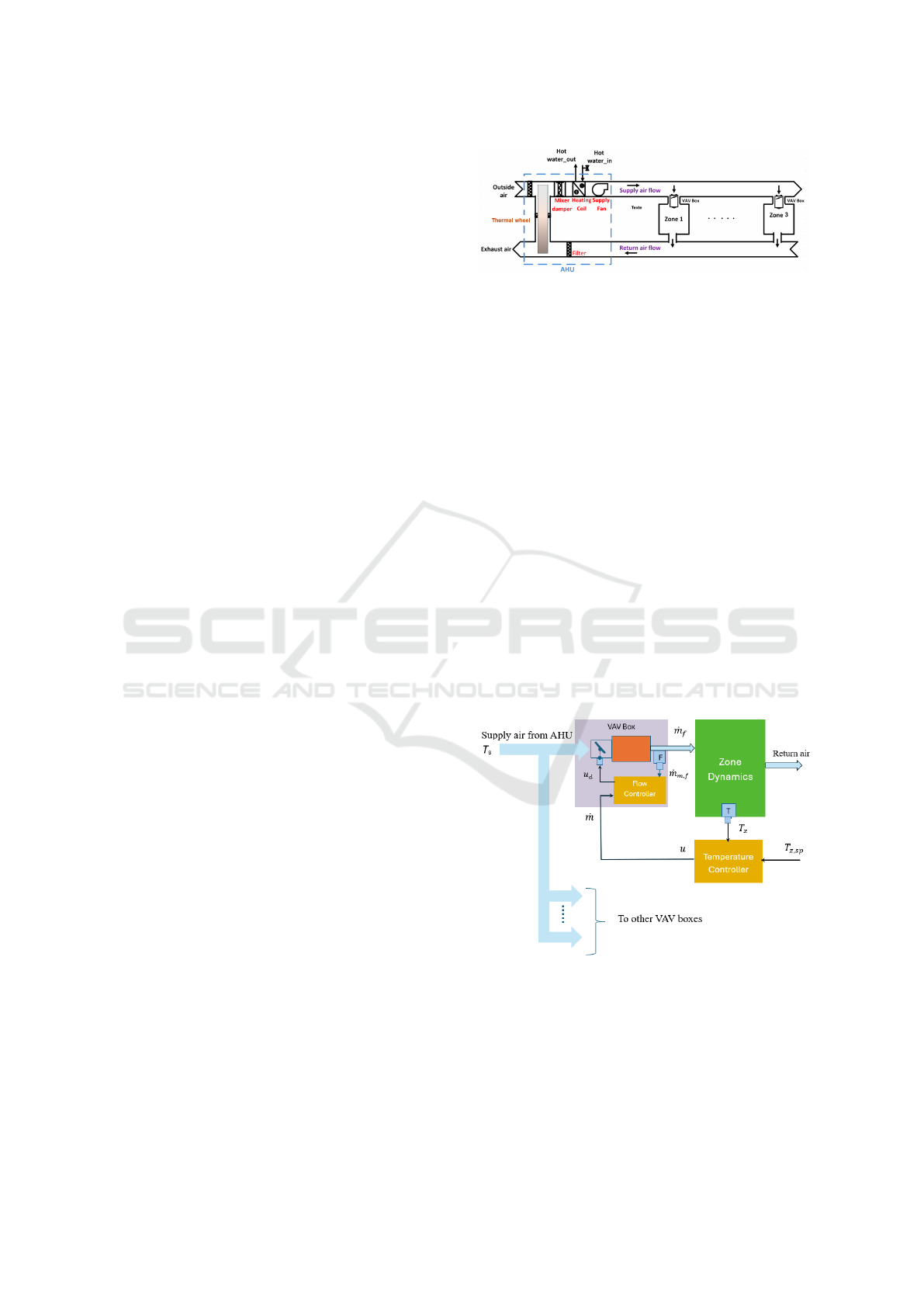
The air-conditioning system is a typical VAV-
based HVAC system for a multizone building as de-
picted in figure 1
Each zone is equipped with a VAV terminal box
which receives conditioned air from a central air han-
dling unit (AHU) at a constant temperature, called the
supply air-temperature. The AHU consists mainly of
a thermal wheel, i.e., a rotary heat exchanger, heat-
ing and cooling coils and a supply fan. The thermal
wheel recovers heat from the exhaust air and trans-
fers it to the fresh air stream coming from outside.
Figure 1: Multizone VAV-based HVAC system.
The heating and cooling coils are water to air heat ex-
changers which control the temperature of supply air
flow by varying hot or chilled water flow of constant
temperature supplied by a district heating network or
a local chiller for the chilled water. Each VAV box
has a damper which regulates the volume of condi-
tioned air delivered to the box according to the ther-
mal needs of the zone. As all VAV boxes regulate their
air volume independently, the total air volume deliv-
ered by the AHU varies according to the demands of
the VAV boxes. Consequently, the fan speed is con-
trolled to meet the overall demand of all zones. Figure
2 shows the closed-loop structure for controlling ther-
mal conditions in each zone. Note that VAV boxes
are equipped with embedded electronic air-mass flow
controllers. The temperature controller tracks the
zone temperature setpoint T
z,sp
by providing the re-
quired air mass flow rate setpoint u = ˙m to the VAV
box depending on the zone temperature measurement
T
z
. The VAV’s embedded flow controller then mod-
ulates the VAV-damper opening, through signal u
d
to
deliver the required air-mass flow rate ˙m
f
to the zone.
Figure 2: Closed-loop structure at each zone.
2.2 Thermal System Modeling
To gain the understanding needed to formulate the
data-driven control problem in section 4.1 within the
reinforcement learning framework, we now establish
a basic model of zone thermal dynamics, in winter
Q-Learning Based LQR Occupant-Centric Control of Non-Residential Buildings
495

season, based on the principles of heat transfer. Con-
sidering a zone as a thermodynamic control volume
(Amende et al., 2021; Bergman and Lavine, 2017),
the principle of energy conservation is simply ex-
pressed by the differential equation
ρc
p
υ
i
dT
z
i
dt
= ˙m
i
c
p
(T
s
−T
z
i
) −
˙
Q
load,i
(1)
In this equation, ρ and c
p
are the air density and the
specific heat of air at constant pressure, respectively.
The supply air temperature to the zone is constant
and equal to T
s
, and all other variables indexed by
i = 1,...,N
b
, where N
b
is the number of zones, are
zone-specific. These variables are the zone volume υ
i
,
the zone temperature T
z
i
and the zone sensible heat-
ing load
˙
Q
load,i
. The sensible heating load is the net
amount of energy that must be supplied to the zone
to maintain a specified thermal state for the zone, and
this is nothing more than the net sum of heat losses.
The first term of the right-hand side of (1) is the en-
ergy supplied by the AHU to the zone to heat it and
this is expressed in terms of the mass flowrate, spe-
cific heat and temperature difference between the sup-
ply air and the zone. In this work, we assume that
heat losses are mainly to the environment at ambient
temperature T
oa
and to the adjacent zones whilst heat
gains are mainly due to occupancy and solar gains
through the glazings. Therefore, the net sensible heat-
ing load of zone i reads as
˙
Q
load,i
= UA
i
(T
z
i
−T
oa
) +UA
i j
(T
z
i
−T
z
i j
) −η
i
φ
h
− ˙q
sol,i
(2)
where T
z
i j
is the temperature of zones j adjacent to
zone i, φ
h
is the average rate of heat flow from a hu-
man (ASHRAE, 2021, Chapter 9), η
i
the number of
occupants of the zone, A
i
the total area of the enve-
lope of the zone surrounded by the environment, A
i j
the area of the wall of zone i adjacent to zones j, U
the overall U-value of the zone, T
oa
the outside air
temperature, and ˙q
sol,i
the solar gain of the zone. Let
C
i
= ρc
p
υ
i
be the thermal capacitance of zone i and
define the following constants
α
i
= UA
i
/C
i
α
i j
= (U
i j
A
i j
)/C
i
, j ̸= i
α
ii
= −
α
i
+
∑
N
b
j̸=i
α
i j
γ
i
= c
p
/C
i
β
i
= γ
i
T
s
φ
i
= φ
h
/C
i
Construct the N
b
-dimensional column vectors α, β, γ
whose elements are respectively the α
′
i
s, β
′
i
s, γ
′
i
s, i =
1,..., N
b
. Now, introduce the following matrices
A = [α
i j
]
N
b
i, j=1
, B(T
z
) = diag
β −γ ⊙T
z
where T
z
is the N
b
-dimensional vector of zone tem-
peratures and the symbol ⊙ denotes the Hadamard
product. Matrix B(T
z
) is the diagonal matrix whose
diagonal elements are the components of vector β −
γ ⊙T
z
. The combination of (1) and (2) written for the
N
b
zones results into the following state-space equa-
tion for the multizone building dynamics
˙
T
z
= AT
z
+ B (T
z
) ˙m + Φη + αT
oa
+ E˙q
sol
(3)
where Φ is the diagonal matrix whose diagonal ele-
ments are the φ
′
i
s and E is the thermal elastance ma-
trix which is the inverse of the capacitance matrix
diag
C
1
,...,C
N
b
. Clearly, the dynamics is nonlinear
but appears as a linear-type dynamic system with a
state-dependent input matrix which is characteristic
of bilinear systems.
3 RECAP ON THE STANDARD
DISCRETE TIME LINEAR
QUADRATIC REGULATOR
AND THE Q-FUNCTION
The linear quadratic control problem is the following
constrained optimization problem
min
u
k
V (x
k
) =
∑
∞
j=k
ℓ(x
j
,u
j
)
s.t. x
k+1
= A
d
x
k
+ B
d
u
k
(4)
where the constraint is a linear dynamics with x
k
∈R
n
and u
k
∈ R
m
its state and control input at time step
k ≥ 0 and A
d
∈ R
n×n
and B
d
∈ R
n×m
being the state
transition matrix and the control input matrix, respec-
tively, of that system. The objective function of the
optimization problem is a long-run cost in which the
stage cost at time step k, ℓ(x
k
,u
k
) is given by the
quadratic form
ℓ(x
k
,u
k
) = x
T
k
Q
d
x
k
+ u
T
k
R
d
u
k
(5)
in which the parameters Q
d
∈ R
n×n
and R
d
∈ R
m×m
are weighting matrices that are chosen symmetric and
positive semidefinite and positive definite, i.e., Q
d
≥
0 and R
d
> 0. The cost in (4) can be written in a
recursive form, known as the Bellman equation
V (x
k
) = ℓ(x
k
,u
k
) +V (x
k+1
) (6)
from which, the Bellman optimality principle states
that the optimal value function V
opt
(x
k
) satisfies the
following relationship called the Bellman optimality
equation
V
opt
(x
k
) = min
u
k
ℓ(x
k
,u
k
) +V
opt
(x
k+1
)
(7)
For the optimization problem (4), solving the Bellman
optimality equation (7) amounts to solving a discrete-
time algebraic Ricatti equation (DARE)
A
T
d
PA
d
−P+Q
d
−A
T
d
PB
d
(R
d
+B
T
d
PB
d
)
−1
B
T
d
PA
d
= 0
(8)
ICINCO 2024 - 21st International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
496

whose unique positive definite solution, P
opt
> 0,
yields the optimal value function
V
opt
(x
k
) = x
T
k
P
opt
x
k
(9)
and the corresponding optimal control policy
u
opt
k
= −K
opt
x
k
(10)
with the gain K
opt
= (R
d
+B
T
d
P
opt
B
d
)
−1
B
T
d
P
opt
A
d
. At
this point, it is interesting to see that the minimizing
argument in Bellman’s optimality equation (7), i.e.,
u
opt
k
written as a function of x
k
, u
opt
k
= π(x
k
), is
π(x
k
) = argmin
u
k
Q
π
(x
k
,u
k
) (11)
where Q
π
(x
k
,u
k
), called the Q-function, is given by
Q
π
(x
k
,u
k
) = ℓ(x
k
,u
k
) +V
π
(x
k+1
) (12)
Now, given the optimal value function V
π
in (9),
it is immediately seen that the optimal K
opt
can be
computed through the Q-function (12) which is ac-
tually the cost of executing an arbitrary control u
k
at
time k, and then following the optimal policy π from
time k + 1 to all future times. The optimal control
u
opt
k
which minimizes the cost is obtained by solving
the first-order necessary optimality condition (FONC)
∇
u
k
Q
π
(x
k
,u
k
) = 0, where ∇
u
k
stands for the gradi-
ent w.r.t u
k
. For the LQR policy, straightforward cal-
culations using the dynamics system in (4) and (9)
show that the Q-function (12) is a quadratic form in
z
k
= col(x
k
,u
k
) denoting the column vector obtained
by stacking vectors x
k
and u
k
,
Q
π
(x
k
,u
k
) = z
T
k
Qz
k
(13)
and
Q =
A
T
d
P
π
A
d
+ Q
d
A
T
d
P
π
B
d
B
T
d
P
π
A
d
B
T
d
P
π
B
d
+ R
d
(14)
with P
π
being the unique positive definite solution of
the DARE (8). The FONC yields consequently the
optimal control (10).
4 Q-LEARNING BASED
MODEL-FREE LQR
SYNTHESIS
4.1 Problem Formulation
The main problem addressed in this paper can be
formulated as follows:
Problem. Consider the multizone building system
(3) with unknown parameters. Given discrete-time
measurements of the zone temperatures and the
air mass flows, design an optimal controller that
will maintain setpoint temperatures independent of
occupancy while minimizing the energy demand of
each zone.
As the building dynamics is unknown and strongly
influenced by the high variability of occupancy dur-
ing the day, the objective is to learn the optimal con-
troller directly on the basis of time series from the
system and reinforcement learning techniques. Let’s
formalize the problem by setting x(t) = T
z
(t) and
u(t) = ˙m(t) in (3) for notation convenience. The
building normally operates around an operating point
for thermal comfort, and it can be assumed that it
has linear dynamics in the region around the set point
temperature, say T
r
, so that the unknown dynamics
(3) reads
˙x = Ax + Bu + Φη + αT
oa
+ E˙q
sol
y = x
(15)
where A = A, B is the Jacobian matrix of B (x) at
the operating point, and y is the output of the system.
A key signal for comfort monitoring is the real-time
deviation between setpoint and temperature measure-
ment. This signal is available in the building automa-
tion system controlling the HVAC plant, and is given
by
e = T
r
−y (16)
To define the environment to be controlled within the
reinforcement learning framework, gather all signals
that exist outside the controller, the so-called agent,
to be designed. The environment will therefore be ev-
erything that exists outside the agent, and constitutes
a system with a boundary through which the agent
sends actions and receives observations and penal-
ties. The setpoints T
r
and the occupancy profile η (t),
t ≥ 0, determined by the number of occupants, are
seen as provided by the environment and generated
by a signal generator given by
˙
T
r
˙
η
=
A
r
0
0 A
η
T
r
η
(17)
where matrices A
r
and A
η
are non-Hurwitz matrices.
The problem stated above can be reformulated as
having the objective of designing a model-free opti-
mal feedback control u(t) such that
(i) the closed-loop system is stable
(ii) for all initial conditions of the signal generator
and the building states, e(t) → 0 as t → ∞
(iii) properties (i) and (ii) are robust to variations in
building dynamics
Q-Learning Based LQR Occupant-Centric Control of Non-Residential Buildings
497
4.2 Method
Towards solving the problem, we select a structure
based on the internal model principle (IMP) (Francis
and Wonham, 1976; Davison and Goldenberg, 1975),
which states that a necessary condition for achiev-
ing the above objectives is that the open loop system
contains the modes of the dynamic structure of the
setpoint T
r
(t) and the occupancy profile η(t). Such
modes are to be embedded in a filter driven by the
error signal (16), and this will enable us to set the en-
vironment to be used for reinforcement learning con-
trol.
Let δ
r
(s) and δ
η
(s) be the minimal polynomials of A
r
and A
η
, and let δ(s) be the least common multiple of
δ
r
(s) and δ
η
(s) given by
δ(s) = s
p
+ λ
p−1
s
p−1
+ ... + λ
1
s + λ
0
(18)
Define the pN
b
-dimensional IMP-filter by
˙
ξ = Λξ + Γe (19)
where Λ and Γ are block diagonal matrices compris-
ing N
b
blocks given by
Λ = block diag
Λ
∗
Λ
∗
···
| {z }
N
b
−times
Γ = block diag
Γ
∗
Γ
∗
···
| {z }
N
b
−times
with Λ
∗
a p ×p matrix and Γ
∗
a p-dimensional vector
given by
Λ
∗
=
0
p−1,1
I
p−1
−λ
0
−λ
1
···−λ
p−1
Γ
∗
=
0 0 ··· 1
T
where 0
m,n
and I
n
denotes the zero matrix of size
(m ×n) and the identity matrix of dimension n, re-
spectively. The error-driven IMP-filter is used to aug-
ment the original system as shown in figure 3 to create
the environment of the problem to be solved. Then,
the augmented plant has the following composite dy-
namics
˙x
˙
ξ
=
A 0
−Γ Λ
x
ξ
+
B
0
u (20)
+
0 Φ
Γ 0
T
r
η
+
α E
0 0
T
oa
˙q
sol
which is written compactly as
˙
ζ = A ζ + Bu + D ω + E d (21)
where ζ = col(x, ξ), ω = col
T
r
,η
, d =
col
T
oa
, ˙q
sol
and matrices A , B, D , and E
are self-explanatory with regards to equation (20).
The following theorem, adapted from (Davison and
Goldenberg, 1975), solves the problem stated when a
model of the system is available
Theorem 1. (Davison’s Theorem) If the composite
dynamics (20) is controllable, Then
(i) it can be stabilized by a state feedback control
u = −Kζ
(ii) for such stabilizing state feedback, lim
t→∞
e(t) = 0
for any initial conditions of x, ξ, T
r
, and η
(iii) properties (ii) is robust for any variations in the
building parameters (A, B), the controller pa-
rameter K and the IMP-filter parameter Γ pro-
vided the closed-loop is stable.
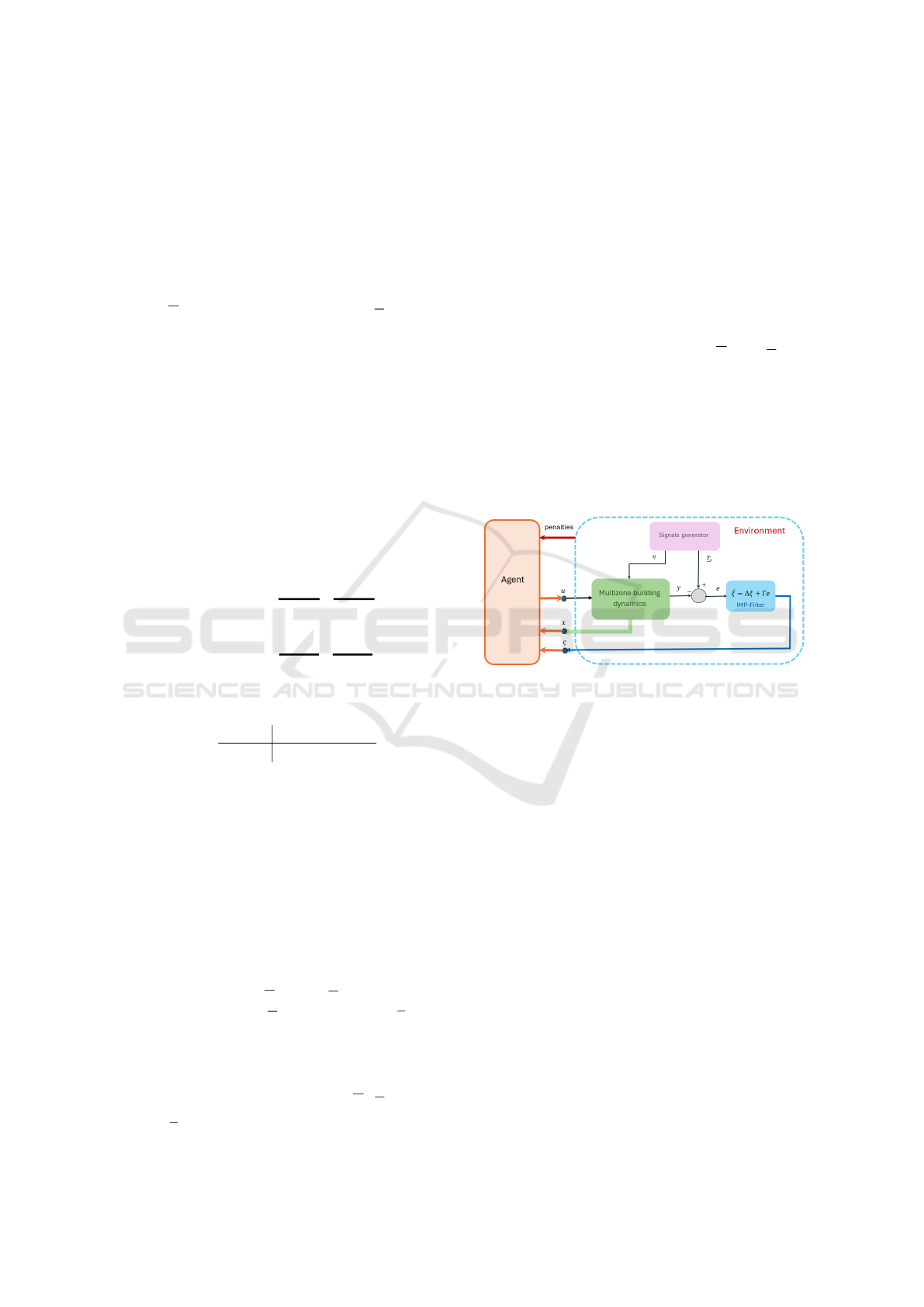
4.3 Results
The setup of the problem is shown in fig. 3
Figure 3: Reinforcement learning control structure.
where the agent, i.e. the controller, is to be designed
based on the states ζ
k
= col (x
k
,ξ
k
) of the unknown
environment. The optimization problem to be solved
reads
min
u
k
∑
∞
j=k
ζ
T
k
Q
d
ζ
k
+ u
T
k
R
d
u
k
under Unknown environment dynamics
(22)
Referring to the Q-function defined for discrete-time
LQR in section 3, it can be written here as
Q
π
(ζ
k
,u
k
) =
ζ
k
u
k
T
Q
11
Q
12
Q
21
Q
22
ζ
k
u
k
(23)
and the FONC ∇
u
k
Q
π
(x
k
,u
k
) = 0 yields the optimal
control
u
opt
k
= π(ζ
k
) = −Q
−1
22
Q
21
ζ
k
(24)
Thus, if the kernel matrix Q were known, the optimal
control could be computed without resorting to the
dynamical equations of the environment. To achieve
such a model-free system control design, assume that
there exists a kernel
ˆ
Q that approximates the kernel
Q of the unknown environment, so that Q
π
(ζ
k
,u
k
) ≈
z
T
k
ˆ
Qz
k
and Q
π
(ζ
k+1
,π (ζ
k+1
)) ≈ ˜z
T
k+1
ˆ
Q˜z
k+1
with z
k
=
ICINCO 2024 - 21st International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
498

col(ζ
k
,u
k
) and ˜z
k+1
= col (ζ
k+1
,π (ζ
k+1
)). From (12),
the following approximate equality holds
(z
k
− ˜z
k+1
)
T
ˆ
Q (z
k
− ˜z
k+1
) −ℓ(ζ
k
,u
k
) ≈ 0 (25)
The left-hand side of the above approximate equation
is linear in
ˆ
Q, and setting it as a residual ε
k
and using
the handy property of vectorization (Graham, 2018)
leads to the error equation
ψ
T
k
vec(
ˆ
Q) −ℓ(ζ
k
,u
u
) = ε
k
(26)
where ψ
k
= (z
k
− ˜z
k+1
) ⊗ (z
k
− ˜z
k+1
), ⊗ being the
Kronecker product, and vec(
ˆ
Q), is the column vec-
tor of dimension (N
b
(p + 2))
2
obtained by stacking
the columns of the matrix
ˆ
Q on top of one another.
From (26), it is seen that matrix
ˆ
Q can be estimated
by minimizing the sum of squares of N residuals,
min
ˆ
Q
k+N−1
∑
j=k
ε
2
k
= min
ˆ
Q
Ψvec(
ˆ
Q) −ℓ
2
2
(27)
with data matrices,
Ψ =
−ψ
T
j
−
−ψ
T
j+1
−
.
.
.
−ψ
T
j+N−1
−
, ℓ =
ℓ
j
ℓ
j+1
.
.
.
ℓ
j+N−1
(28)
Note that the size of matrix Ψ is (N ×n
Ψ
) with n
Ψ
=
(N
b
(p + 2))
2
. For future reference, the conditions un-
der which problem (27) has a unique solution is stated
below as a lemma.
Lemma 2. The solution of problem (27) is unique so-
lution if and only if matrix Ψ is of full column-rank,
and this requires at least that N ≥ n
Ψ
.
An important practical issue here is that, due to
the IMP-filter, the environment is not stable and con-
sequently the time series
{
ζ
k
,u
k
}
, k = 0,1,..., gen-
erated in an open-loop experimental setting, are un-
bounded. Therefore, the agent cannot be trained with
open-loop data. However, this problem can be cir-
cumvented in a closed-loop experimental setting with
a stabilizing controller, i.e., u
k
= −K
s
ζ
k
with K
s
be-
ing a stabilizing feedback gain. Unfortunately, these
closed-loop data are such that ζ
k
and u
k
are highly
dependent on each other due to feedback, and this is
likely to prevent a large part of the state space of the
environment to be explored. A common technique for
relieving this problem is to add a dither (noise) to the
feedback control signal to promote exploration of the
state space, i.e., u
k
= −K
s
ζ
k
+ ˜n
k
, with ˜n
k
the additive
noise. This is related to persistently exciting inputs
in system identification and dual control in stochastic
control (Yam
´
e, 1987). A key observation here is that,
despite the additive noise to enforce non-collinearity
between the columns of matrix Ψ, this matrix has a
particular rigid structure in this respect revealed by
the following proposition.
Proposition 3. Let matrix Ψ be given by (28) with
N ≥ n
Ψ
. Then, Ψ is rank-deficient, i.e., rank (Ψ) =
r
Ψ
< n
Ψ
.
Proof. The proof is omitted for lack of space, see
(Yam
´
e, 2024).
The rank deficiency of matrix Ψ makes problem
(27) ill-posed, as it does not satisfy Hadamard’s cri-
teria for the existence of a solution, the uniqueness
of this solution and its continuous dependence on the
input data (Vogel, 2002). This ill-posedness is tack-
led here by augmenting matrix Ψ with a scalar matrix
√
λI
n
Ψ
, λ ≥ 0, leading to the optimization problem
min
ˆ
Q
Ψ
√
λI
n
Ψ
vec
ˆ
Q
−
ℓ
0
n
Ψ
,1
2
2
(29)
Note that the rank of the augmented ”Ψ-matrix” is
equal to n
Ψ
, and from lemma 2, the minimization
problem (29) admits a unique solution given analyt-
ically by
vec
ˆ
Q
=
Ψ
T
λ
Ψ
λ
−1
Ψ
T
λ
ℓ
λ
(30)
with Ψ
λ
and ℓ
λ
being the augmented Ψ-matrix and
augmented ℓ-vector, respectively, in (29). This solu-
tion is also known as Tikhonov’s regularized solution
to the original problem (27) and λ is the regularized
parameter (Vogel, 2002). The problem as formulated
in (29) is not merely a bulwark against the rank de-
ficiency of the original problem’s data matrix Ψ, but
it allows also to deal with the noise in this data ma-
trix (El Ghaoui and Lebret, 1997), resulting from the
noise injection into the control signal as expounded
above to facilitate exploration of the state space of
the environment. The solution (30) is implemented
in a batch-processed form through the following al-
gorithm
5 SIMULATION STUDIES
The building automation system (BAS) of the ATELA
classrooms has been commissioned using simple PID
controllers tuned by trial and error. The main chal-
lenge was to tune the zone temperature controllers
that controls the VAV damper openings via the set-
point of the mass airflow controllers, see fig. 2. It
should be noted that the mass airflow controllers,
which are internal to the VAV boxes, were factory-
set. To improve thermal comfort and minimize the
Q-Learning Based LQR Occupant-Centric Control of Non-Residential Buildings
499

energy demand of each zone, given the high variabil-
ity of their occupancy and the number of occupants
during the day, the model-free Q-learning based LQR
control developed in the previous section was imple-
mented. In this experimental simulation study, which
served as a first test for the implementation of the Q-
learning control algorithm in the BAS, only zone 1
was concerned, see fig. 1. For this zone, a database
of time series in closed-loop has been generated con-
sisting of
˜
N = 1000 sample points, see fig 4. The
room temperature setpoint was T
r
= 22
◦
C and noise
was added to the control input signal to promote ex-
ploration of the system dynamics. These time series
can also be generated by a building simulator.
Algorithm 1: Q-Learning based model-free LQR.
1: Build a database of times series
{ζ
0
,u
0
,ζ
1
,u
1
,..., ζ
˜
N
} obtained in a stable
closed-loop with noise added to the control
inputs u
k
, k = 0, ...,
˜
N −1,
˜
N sufficiently large
2: Take a sub-series of length N ≥ n
Ψ
from step 1.
3: Choose a regularization parameter λ > 0
4: Initialization: Select any stabilizing policy π
t
(ζ)
5: repeat
6: for k = 1,2, ... ,N do
7: Construct :
z
k
= col (ζ
k
,u
k
)
˜z
k+1
= col (ζ
k+1
,π
t
(ζ
k
))
8: Compute :
ψ
k
= (z
k
− ˜z
k+1
) ⊗(z
k
− ˜z
k+1
)
ℓ
k
= z
T
k
diag(Q
d
,R
d
)z
k
9: end for
10: Build data matrices Ψ and ℓ from (28)
11: Solve (29) for
ˆ
Q
12: Update policy to π
t+1
(ζ) from (24)
13: π
t
← π
t+1
14: until Convergence of the policy, and set the opti-
mal policy as π
opt
(ζ) = π
t
(ζ)
Figure 4: Closed-loop time-series for the Q-learning pro-
cess for zone 1.
To apply the method developed in section 4, the
temperature set-point and occupancy signals of zone
1 are described as piecewise constant signals, i.e.,
˙
T
r
(τ) = 0, τ ∈ [t
i
,t
i+1
)
˙
η(τ) = 0,τ ∈ [t
j
,t
j+1
)
T
r
(t
i
) = T
r,i
η(t
j
) = η
j
(31)
where indices i, j belong to a subset of N and
T
r
(t
i
),η(t
j
) are the initial conditions of T
r
(τ),η(τ)
on the intervals [t
i
,t
i+1
) and [t
j
,t
j+1
), respectively.
Clearly, the least common multiple of the minimal
polynomials of the state matrices of the two first-order
differential equations in (31) is δ(s) = s, so that ,
p = 1. The IMP-filter is therefore a 1-dimensional
filter simply given by
˙
ξ = e, and the environment
state reads ζ = col(x,ξ) with x = T
z
1
, the tempera-
ture of zone 1. The LQR parameters are chosen as
Q
d
= I
2
, R
d
= ρ = 10
4
and the sampling period equal
h = 60s. The regularization parameter λ is chosen as
the square of the smallest singular value of the rank-
deficient data matrix Ψ. The controller was learned
by running algorithm 1 which yields the optimal Q-
learning based LQR feedback gain K =
ˆ
Q
−1
22
ˆ
Q
21
=
[0.5022,−0.0055].
A test was carried out on the system on January
15, 2024, from 00:00 to 23:00, with a temperature set-
point profile and the measured zone occupancy (num-
ber of occupants) as shown in the figure 5. During the
typical hours when the room is unoccupied, i.e., be-
tween midnight (00:00) and 06:00 and between 20:00
and midnight, the setpoint is set to 17°C for energy-
savings. Between 06:00 and 08:00, the setpoint fol-
lows a linear time profile to reach the comfort tem-
perature of 22°C. During lunchtime (12:00- 14:00),
the setpoint is lowered to 20°C, and then set back
to 22°C in the afternoon, until classes end at 18:00.
From 18:00 onwards, the setpoint again follows a lin-
ear time profile, being gently reduced to 17°C from
20:00 onwards.
As it can be seen from figure 5, the learned con-
troller performs very well and allows the temperature
setpoint to be correctly maintained regardless of oc-
cupancy and outside temperature. More surprisingly,
although the setpoint model used for the design is that
of piecewise-constant signals, it is found that the con-
troller is capable of perfectly tracking a setpoint that
varies linearly with time. It is also seen that the VAV’s
air mass flow demand remains contained due to the
formulation of the optimal control problem, thus en-
suring a low energy demand for room heating.
ICINCO 2024 - 21st International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
500
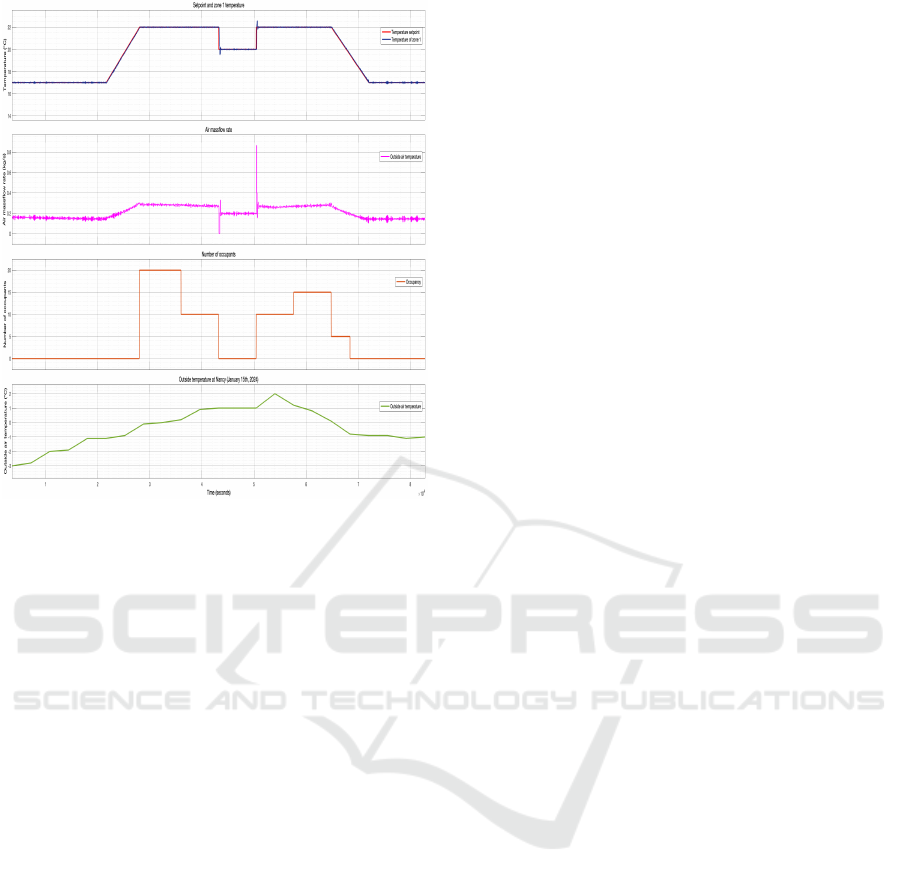
Figure 5: One-day simulation results with the Q-learning-
based LQR controller.
6 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, we have developed a Q-learning based
LQR controller from time series generated by a
building-HVAC system. The main objective was to
design the control of VAV terminal boxes to guarantee
thermal comfort despite climatic variations and large,
random variations in building rooms occupancy. The
test results obtained on the building with the model-
free Q-learning controller show the excellent behav-
ior of this controller in setpoint tracking, regardless
of occupancy and external climatic conditions. From
a mathematical viewpoint with regards to the estima-
tion of the parameters of the quality function, inter-
esting questions arise concerning the rank-deficiency
of the data matrix. These issues will be addressed and
reported elsewhere.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This project is funded by the French Ministry of Eu-
rope and Foreign Affairs (MEAE) and the Ministry of
Higher Education and Research (MESR) and the Mo-
roccan Ministry of Higher Education, Scientific Re-
search and Innovation (MESRSI), under the frame-
work of the Franco-Moroccan bilateral program PHC
TOUBKAL TBK/23/165, with Grant number: Cam-
pus N° 48604PM.
REFERENCES
Amende, K. L., Keen, A. J., Catlin, L. E., Tosh, M., Sneed,
A. M., and Howell, R. H. (2021). Principles of
Heating, Ventilating and Air-Conditioning. ASHRAE,
Peachtree Corners, GA.
ASHRAE (2021). ASHRAE Handbook, Fundamentals, vol-
ume 2021.
Bergman, T. L. and Lavine, A. S. (2017). Fundamentals of
Heat and Mass Transfer. John Wiley & Sons, Hobo-
ken, NJ, 8th edition.
Davison, E. J. and Goldenberg, A. (1975). Robust control of
a general servomechanism problem: The servo com-
pensator. Automatica, 11(5):461–471.
EIA (2024). How much energy is consumed in U.S. build-
ings? https://www.eia.gov/tools/faqs.
El Ghaoui, L. and Lebret, H. (1997). Robust solu-
tions to least-squares problems with uncertain data.
SIAM Journal on Matrix Analysis and Applications,
18(4):1035–1064.
Farjadnasab, M. and Babazadeh, M. (2022). Model-
free lqr design by q-function learning. Automatica,
137:110060.
Francis, B. A. and Wonham, W. M. (1976). The inter-
nal model principle of control theory. Automatica,
12(5):457–465.
Graham, A. (2018). Kronecker Products and Matrix Calcu-
lus with Applications. Dover Publications Inc, Mine-
ola, N. Y.
Han, M., May, R., Zhang, X., Wang, X., Pan, S., Da, Y.,
and Jin, Y. (2020). A novel reinforcement learning
method for improving occupant comfort via window
opening and closing. Sustainable Cities and Society,
61:102247.
Jia, M., Srinivasan, R. S., and Raheem, A. A. (2017).
From occupancy to occupant behavior: An analyti-
cal survey of data acquisition technologies, modeling
methodologies and simulation coupling mechanisms
for building energy efficiency. Renewable and Sus-
tainable Energy Reviews, 68:525–540.
Liu, X. and Gou, Z. (2024). Occupant-centric hvac and win-
dow control: A reinforcement learning model for en-
hancing indoor thermal comfort and energy efficiency.
Building and Environment, 250:111197.
Ouf, M. M., Park, J. Y., and Gunay, H. B. (2021). On
the simulation of occupant-centric control for building
operations. Journal of Building Performance Simula-
tion, 14(6):688–691.
Soleimanijavid, A., Konstantzos, I., and Liu, X. (2024).
Challenges and opportunities of occupant-centric
building controls in real-world implementation: A
critical review. Energy and Buildings, 113958.
Vogel, C. R. (2002). Computational Methods for Inverse
Problems. SIAM series on Frontiers in Applied Math-
ematics.
Q-Learning Based LQR Occupant-Centric Control of Non-Residential Buildings
501

Wang, Z., Calautit, J., Tien, P. W., Wei, S., Zhang, W.,
Wu, Y., and Xia, L. (2023). An occupant-centric
control strategy for indoor thermal comfort, air qual-
ity and energy management. Energy and Buildings,
285:112899.
Xu, X., Yu, H., Sun, Q., and Tam, V. W. (2023). A critical
review of occupant energy consumption behavior in
buildings: How we got here, where we are, and where
we are headed. Renewable and Sustainable Energy
Reviews, 182:113396.
Yam
´
e, J. (1987). Dual adaptive control of stochastic sys-
tems via information theory. In 26th IEEE Con-
ference on Decision and Control, pages 316–320.
doi:10.1109/CDC.1987.272811.
Yam
´
e, J. J. (2024). On the rank-deficiency of the data matrix
of the q-learning based lqr problem. Technical Report
02-24, CRAN.
Yu, H., Tam, V. W., and Xu, X. (2024). A systematic re-
view of reinforcement learning application in building
energy-related occupant behavior simulation. Energy
and Buildings, 114189.
ICINCO 2024 - 21st International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
502
