
A Tool for Mass Generation of Random Step Environment Models with
User-Defined Landscape Features
Ruslan Gabdrahmanov
1 a
, Tatyana Tsoy
1 b
, Edgar A. Mart
´
ınez-Garc
´
ıa
2 c
and Evgeni Magid
1,3 d
1
Intelligent Robotics Department, Kazan Federal University, 35 Kremlin Street, Kazan, Russian Federation, Russia
2
Institute of Engineering and Technology, Department of Industrial Engineering and Manufacturing, Autonomous
University of Ciudad Juarez, Manuel D
´
ıaz H. No. 518-B Zona Pronaf Condominio, Chihuahua, 32315 Cd Ju
´
arez, Mexico
3
HSE University, 20 Myasnitskaya str, Moscow, Russian Federation
Keywords:
Robotics, Mobile Robotics, USAR, Modeling, Gazebo, Webots, Machine Learning, Tool.
Abstract:
Computer simulations are growing in popularity in robotics research due to their near-zero cost of error and
lower labor intensity. One of necessary components of a simulation, in addition to a robot model, is a model
of a world in which the robot operates. While it is always possible to construct a world model manually, a
demand for automatic tools that generate multiple testing environments with particular user-defined features
grows together with integration of data hungry machine learning techniques into robotic algorithms. This
article presents a next generation of LIRS-RSEGen tool for constructing virtual random step environments
(RSE). The new tool can simultaneously generate multiple RSE models with user-defined specific features that
are declared via an intuitive graphical user interface. The resulting models simulate an urban search and rescue
environment and can be used with robot models for developing and testing software for localization, mapping,
navigation and locomotion, and are applicable for machine learning due to their relatively low impact on
performance and random elements in RSE generation. The constructed worlds’ performance was successfully
tested with robot models in the Webots and Gazebo simulators.
1 INTRODUCTION
Urban search and rescue (USAR) was first intro-
duced as a distinct area of robotics in DARPA/NSF
Human-Robot Interaction study (Burke et al., 2004).
USAR deals with rescuing victims in environments
that are represented by man-made structures, includ-
ing partially or completely destroyed ones. Naviga-
tion and localization in such environments is com-
plicated: in some locations onboard sensors of an
unmanned ground vehicle (UGV) become unreliable
due to a large amount of dust and smoke in the
air together with frequent occlusion cases within de-
bris (Safin et al., 2021). Additionally, locomotion
is complicated by damaged buildings and debris as
USAR environments are generally not designed to
support robot motion (Isaacs et al., 2022).
Computer modeling and simulation in robotics
employ a digital model of a robot, physics, and a
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9276-2034
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5715-7768
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9163-8285
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7316-5664
typical environment for a particular task, while try-
ing to achieve a behavior of the model and environ-
ment characteristics to be as close to real ones as
possible with available computing power (Le Lidec
et al., 2024). Simulations allow calculating a robot
model behavior in a digital environment as if it was a
real world experiment with a physical robot, but with
lower costs and risks (Choi et al., 2021). Among the
drawbacks, one can highlight a discrepancy with the
reality and therefore problems may arise when trying
to use algorithms of a virtual world in the real world
(Zhao et al., 2020; Rao et al., 2020).
2 RELATED WORK
2.1 Robotics Simulators
Gazebo is a specialized robotics simulator with robot
operating system (ROS) support and a wide variety
of development libraries. It includes several physics’
engines with DART (a default one (Lee et al., 2018)),
TPE, ODE, Bullet and Simbody, OGRE graphics ren-
Gabdrahmanov, R., Tsoy, T., Martínez-García, E. A. and Magid, E.
A Tool for Mass Generation of Random Step Environment Models with User-Defined Landscape Features.
DOI: 10.5220/0013068600003822
In Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics (ICINCO 2024) - Volume 1, pages 511-518
ISBN: 978-989-758-717-7; ISSN: 2184-2809
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
511

dering, and has built-in tools for generating clean or
noisy sensor data (Open Source Robotics Foundation.
Gazebo official site, 2024). Webots is an open-source
robotics simulator that positions itself as a tool for
professionals, yet relatively easy to learn and use (Cy-
berbotics. Cyberbotics webots page, 2024); it is based
on the ODE physics engine. There are several other
popular simulators whose support we did not consider
in this study (Collins et al., 2021).
The Gazebo simulator was already supported in
the previous version of our tool, LIRS-RSEGen (Gab-
drahmanov et al., 2022a), and this paper presents its
further upgrade. We initially chose Gazebo for its
powerful DART physics engine, ROS compatibility,
and popularity. For LIRS-RSEGen-2, we also added
Webots because of its ease of use, ROS compatibility,
and a variety of resources in a default installation.
At the time of writing, two other tools for gener-
ating virtual Gazebo worlds were considered: an au-
tomatic tool for world construction LIRS-WCT (Ab-
byasov et al., 2020) and a tool for building a world
from arbitrary images and laser scans (Lavrenov and
Zakiev, 2017). The earlier generates a Gazebo world
from a 2D grayscale image that serves as a top-down
view of the world; this approach gives a lot of free-
dom, but resulting models have a high computational
complexity and significantly reduce a real-time fac-
tor (RTF, which is simulation time compared to real
physical time) of the simulation. The later tool con-
verts arbitrary images and laser scans into a Gazebo
world that demonstrates a critically low RTF due to a
nature of object models, which require a physics en-
gine to perform a lot of self-collision checks.
2.2 Random Step Environment
The Random Step Environment (RSE) or stepfield
pallets is an approximation of a typical USAR en-
vironment, littered with debris and rubble, which
was developed by the National Institute of Standards
and Technology (NIST) to evaluate a performance of
USAR robots (Jacoff et al., 2008). A classic RSE pal-
let (Figure 1) consists of a wooden frame of 120x120
cm with a margin height and width of 10 cm, and 100
wooden blocks inside the frame; the blocks are 10x10
cm in width and length, and the height has four op-
tions: 5, 10, 20, 30, 40 cm. Multiple pallets can be
placed next to each other to form a larger RSE.
RSE, like any approximation, has its advantages
and disadvantages. The advantages include:
• Simplicity of creation and simulation;
• Repeatability: with the scheme and required
blocks it’s possible to rebuild the exact copy;
Figure 1: Real world classic RSE.
• Diversity of possible forms of the final RSE;
• A small number of polygonal surfaces, that re-
sult in a high performance in simulations (with a
proper implementation).
The disadvantages include:
• Inability to create some typical structures and ob-
stacles, e.g., an inclined plane;
• Need to assemble a large number of blocks if a
large test site area is required;
• Simplicity of the model implies simpler localiza-
tion and mapping, compared to the real USAR en-
vironment, which may lead to a decrease in ef-
ficiency of developed algorithms when they are
tested in a real environment.
2.3 LIRS-RSEGen
LIRS-RSEGen is a simple open-source tool that gen-
erates virtual models of RSE environments (Gabdrah-
manov et al., 2022a). The tool, unlike most of its
peers, does not require a low-level input such as a
mapping or scheme of a desired environment or pre-
cise characteristics for each part of it. Instead, as an
input the tool uses obstacles, which are typical ba-
sic structures of a RSE, such as walls, peaks, pits,
etc. (Magid and Tsubouchi, 2010). Obstacles are de-
fined by their position (which can be randomized),
height, and other parameters. With this approach,
only a few obstacles can be specified instead of defin-
ing a height of each RSE block one by one. LIRS-
RSEGen can generate several different environments
from a single input layout using randomization in a
short period of time. This property is useful for devel-
oping and testing machine learning based algorithms,
e.g., for localization, mapping, navigation, and lo-
comotion. Visual and physical models are identical,
which allows an easier sim-to-real transfer. The tool
ICINCO 2024 - 21st International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
512

is implemented in Python 3 programming language
with PyQt6 and numpy libraries.
This paper further extends the previous version of
the LIRS-RSEGen. Algorithms for calculating RSE
blocks’ heights were completely redesigned, respon-
siveness and appearance of an interface was signifi-
cantly improved. A number of new functions were
added, such as support for the Webots simulator, sav-
ing schemes to a file and loading from it, a graphical
preview of a RSE structure, an ability to customize
base files of a world, which allows a user generating
worlds in which entities that are necessary for a task
are already placed.
3 RSE GENERATOR
3.1 Graphical User Interface and Input
The generator creates RSE models in .obj format,
which is suitable for import into most simulators and
3D editors, as well as individual blocks based mod-
els exclusively for Gazebo and Webots. Generation is
configured by setting global parameters that affect an
entire RSE: its size, and parameters of individual ob-
stacles, such as a location or a height of an obstacle.
The interface is designed for a fast and comfortable
work that does not require programming skills or an
interaction with a console (Figure 2).
Figure 2: LIRS-RSEGen-2 GUI.
The left side of the Graphical user interface (GUI)
contains fields for entering the generation parameters.
At the top part of the GUI are located fields for enter-
ing global parameters:
• Target simulator: a simulator for which worlds
with RSE will be generated. There is also an op-
tion to generate only the obj models.
• Amount: a number of worlds or models that will
be created. Randomized obstacles will be recal-
culated for each world.
• Pallet boundary: Pallets will be separated from
each other by boundaries of 1 RSE block of a
height that is equal to parameter Step height (cm),
if the parameter is enabled. Although it may seem
useless, this parameter is important if it is nec-
essary to perfectly reproduce a generated RSE in
a real world. Without a supporting frame, RSE
blocks will crumble under even a small force.
• Pallet size: a size of a single pallet that a final
RSE consists of. Pallets will be separated from
each other by borders of 1 block of height 1 if
Pallet boundary is enabled. Otherwise, the Size
parameter is used.
• Size in pallets: a size of the RSE in pallets. For
example, Pallet size 3 and Size in pallets 2x3 will
create a RSE of size 6x9, or 9x13 taking into ac-
count the borders. This is used if Pallet boundary
is enabled. Otherwise, the Size parameter is used.
• Size: Determines a size of the RSE in 10x10cm
blocks, by XY coordinates.
• Mesh type: A user can choose between a single
mesh (mesh is a set of vertices, edges, and faces
that define an object shape) or many individual
block-like meshes. For the second option, Target
simulator must be selected.
• Step height (cm): A minimum difference in height
of two blocks; e.g., with Step height 10, blocks
can be 10, 20, 30, etc.
Input fields for selected obstacle parameters are
located at the bottom of the GUI :
• Selected obstacle: shows which obstacle is cur-
rently being edited.
• Save: a button that saves the edited obstacle.
• Type: obstacle type.
• Height in steps: obstacle height in steps from Step
height (cm) parameter
• Angle of slope: a slope angle of the obstacle; 90
will create steep walls, 0 will cover the entire map
evenly to the specified height. With intermediate
values, the height will gradually decrease while
moving away from specified coordinates of the
obstacle, according to a selected angle (for more
details, refer to Subsection 3.3).
• Random range: Allows setting upper and lower
boundaries of coordinates in which this obstacle
can appear, instead of a fixed value.
A Tool for Mass Generation of Random Step Environment Models with User-Defined Landscape Features
513

• Point 1 pos and Point 2 pos: set a position of the
obstacle within the RSE. Random range doubles
a number of input fields, allowing a user to spec-
ify a range of values. Any additional slopes may
appear only in points that have perpendicular to a
defined segment (Figure 3).
Figure 3: Slopes positioning, heights grid.
The right side of the GUI contains a graphical pre-
view and a table that lists all created obstacles. The
graphical preview in the upper part shows a view from
above of a RSE that will be generated with current pa-
rameters. Blue-green-red gradients were used to show
different heights with blue meaning a lowest height
and red meaning a highest one. The lower right part
consists of a table and control buttons. The table con-
tains all created obstacles with one row per obstacle.
Each obstacle can be clicked to select it, then control
buttons can be used. The left control buttons can be
used to move the selected obstacle relatively to other
ones in the table. Since each obstacle is added to RSE
one by one (in order they appear in the table), moving
the obstacle can affect a final RSE world. The bottom
control buttons can be used to create a new default ob-
stacle, copy, edit or delete the selected one. New or
copied obstacles are displayed at the end of the table.
3.2 Obstacles and Options
The matrix generator supports six different types of
obstacles, which determine a created RSE structure:
• Random. (Figure 4) is a random distribution
of blocks is generated throughout the RSE. The
height ranges from 0 to the selected height in steps
as a random distribution.
• Random Gaussian (normal). (Figure 5) gen-
erates a random Gaussian distribution of blocks
across the entire RSE. This results in a smoother
RSE than with Random.
• Peak. (Figure 6) is a point obstacle that consists
of a single RSE block.
• Pit. (Figure 7) is a peak with the opposite effect.
• Wall. (Figure 8) is a diagonal obstacle between
two points on the RSE.
• Long Pit. (Figure 9) is a wall with the opposite
effect (reduces height, creating pits and lowlands).
Figure 4: A random obstacle.
Figure 5: A normal random obstacle.
Figure 6: A peak obstacle.
Figure 7: 0 degree (flat) peak and pit obstacles.
3.3 Generator Mathematics
Initially the matrix is zero, each obstacle is imposed
on the matrix in order according to the obstacle table.
An intersection of obstacles is calculated according
ICINCO 2024 - 21st International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
514

Figure 8: A wall obstacle.
Figure 9: Wall and perpendicular long pit obstacles.
to the maximum rule, i.e., the largest of two values is
taken, with an exception of a pit and a long pit, which
subtract a height from the current matrix. Each of
the six obstacles uses its own algorithm to modify the
current matrix as follows:
• The Random obstacle with height H fills the RSE
with random height values generated as a contin-
uous uniform distribution U(0,H).
• The Random Gaussian obstacle with height H fills
the RSE with random height values generated as
a Gaussian (normal) distribution, with the mathe-
matical expectation u = H/2 and standard devia-
tion q = 1. Values lower than 0 or higher than H
are truncated to 0 and H, respectively.
• The Wall obstacle is defined by two points of a
segment. The height of the blocks is maximum in
blocks close to the given segment, while in blocks
located farther it decreases according to a spec-
ified angle. The height of such blocks is calcu-
lated as follows: first, a distance from the defining
segment to the block d is calculated, then a right
triangle is formed, where d is an opposite leg of
an angle a from the Angle of slope field. Thus, if
distance d >
√
2
2
a block height h is calculated as:
h = max(H −d ∗tan(a),0) (1)
Otherwise, h = H
Distance d is calculated using the equation:
d = ||
(s
1
−s
0
) ×(s
0
−p)
||s
1
−s
0
||
||∗S (2)
where s
0
and s
1
are points of the wall segment, p
is the selected point and S is a constant block size.
Data: segment matrix S, RSE block heights
2D matrix M, max height H, angle A
Result: block height for each point [x, y] in
matrix M;
x = 0;
y = 0;
tan = tangent(A);
while x < length(M) do
while y < length(M[0]) do
if x is equal(S) and y not in
y range(S) then
continue;
end
if y is equal(S) and x not in
x range(S) then
continue;
end
side = S[0] - S[1];
projection side = [x, y] - S[0];
scalar1 = scalar product(side,
projection side);
scalar2 = scalar product(side, side);
if 0 ≤ scalar1 ≤ scalar2 then
dist = distance(S, [x, y]);
M[x][y] = max(M[x][y],
H-dist*tan);
end
x = x + 1;
y = y + 1;
end
end
Algorithm 1: Distance based height calculation.
where x is equal(S) and y is equal(S) are func-
tions that check if points of segment S have iden-
tical x and y coordinates respectively; x range(S)
and y range(S) return array of numbers between
maximum and minimum x and y coordinates; dis-
tance(S, [x, y]) is a function based on equation 2.
• The peak type obstacle is specified by a single
point. The height of the blocks will be maximum
in the selected block, and in the blocks located
nearby it will decrease according to the specified
angle using equation 1 for height and distance
equation 3 as follows:
d = ||s −p||∗S (3)
• The long pit type obstacle is calculated similarly
to the wall, but unlike it, the resulting height is
subtracted from the current height matrix; yet, the
result cannot be negative.
A Tool for Mass Generation of Random Step Environment Models with User-Defined Landscape Features
515

• The pit type obstacle is calculated similarly to the
peak, but unlike it, the resulting height is sub-
tracted from the current height matrix; yet, the re-
sult cannot be negative.
3.4 Saving and Importing RSEs
The program allows saving and loading created RSE
configurations. The configurations are stored as csv
files containing a table of obstacles (one row per ob-
stacle) and can be opened and edited with any text
editor. Such format is chosen for its simplicity and
compatibility with obstacles data without additional
processing.The program comes with a set of sample
configurations to help a user understanding its work.
3.5 Static Data and Their Modification
If Target simulator is selected, in addition to the obj
models, several files are generated, which together
make the simulation world. The generator uses a con-
cept of dividing data into static and dynamic. Thus,
the RSE model itself and the world name are dy-
namic data that change with each generation, and
other world data are static that are simply copied for
each world. Basic static files for each simulator are
stored in separate directories and have a structure sim-
ilar to that of the generated world. Thus, static data
of the world can be changed; for example, its pos-
sible to add a robot model to the world in advance,
change an initial position of the RSE, introduce addi-
tional objects, etc. All these changes are copied to the
generated models, allowing a user to immediately get
ready-to-use simulation worlds in large quantities.
4 EVALUATION OF MODELS
To evaluate generated models performance, we gener-
ated numerous RSE worlds of various configurations.
Only single mesh RSE models were used for testing.
Performance was measured using RTF and CPU load.
Experiments were conducted with a single robot and
a group of robots, in static and dynamic modes plac-
ing robots above the constructed RSE model without
contacting any other objects (e.g., a default flat plane
or, in case of Turtlebot3, other robots).
Each test consisted of five runs per one robot
model and RSE size option; one run lasted one sim-
ulation minute. RTF was measured as minimal and
maximal values spotted in all five runs; CPU load was
measured as an average in all five runs; Physics errors
were measured as an accumulated number of collision
errors’ incidents (clearly visually noticeable as one
object intersects another or as an object is launched
at a high speed in a random direction for no reason)
and joint errors’ incidents (clearly visually noticeable
as one or more joints of a robot become disconnected
or appear at a position that is not possible during its
normal operation) that occurred through all five runs.
Control measurements were performed as a single 1-
minute run with the same robot in the world with a
single flat plane. The testing computer characteristics
are listed in Table 1; the GPU is mentioned because it
was used for rendering a simulation scene.
Table 1: Testing computer specifications.
Module Model Characteristics
CPU AMD Ryzen 7 2700X 8x3.70GHz
GPU Nvidia GeForce 1660 6GB 1830MHz
RAM Kingston hyperX fury 16GB
4.1 Webots
For Webots we created RSE worlds of various sizes
and evaluated them with several different robot mod-
els. Boston dynamics spot (Boston dynamics. Boston
dynamics spot page, 2024) quadrupedal robot model
was used as a complex model with a high impact on
performance; Bluebotics shrimp robot (Estier et al.,
2000) was used as a simpler model with a smaller re-
source consumption. Both robot models are available
in Webots default distribution. The results of the tests
are shown in Table 2; superscript a denotes that a sin-
gle CPU Thread was loaded at 100% in most of the
tests, therefore we assume that a single core perfor-
mance is main bottleneck in RTF; superscript b em-
phasizes that some contact joints between materials
were skipped during tests in multiple occasions.
Figure 10: Spot on 50x50 RSE in Webots.
The experiments showed that large RSEs affect
performance more than small ones due to a larger
amount of triangles for collision check calculation
and rendering. Despite a fact that a CPU load re-
mained the same due to software not allocating all
ICINCO 2024 - 21st International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
516
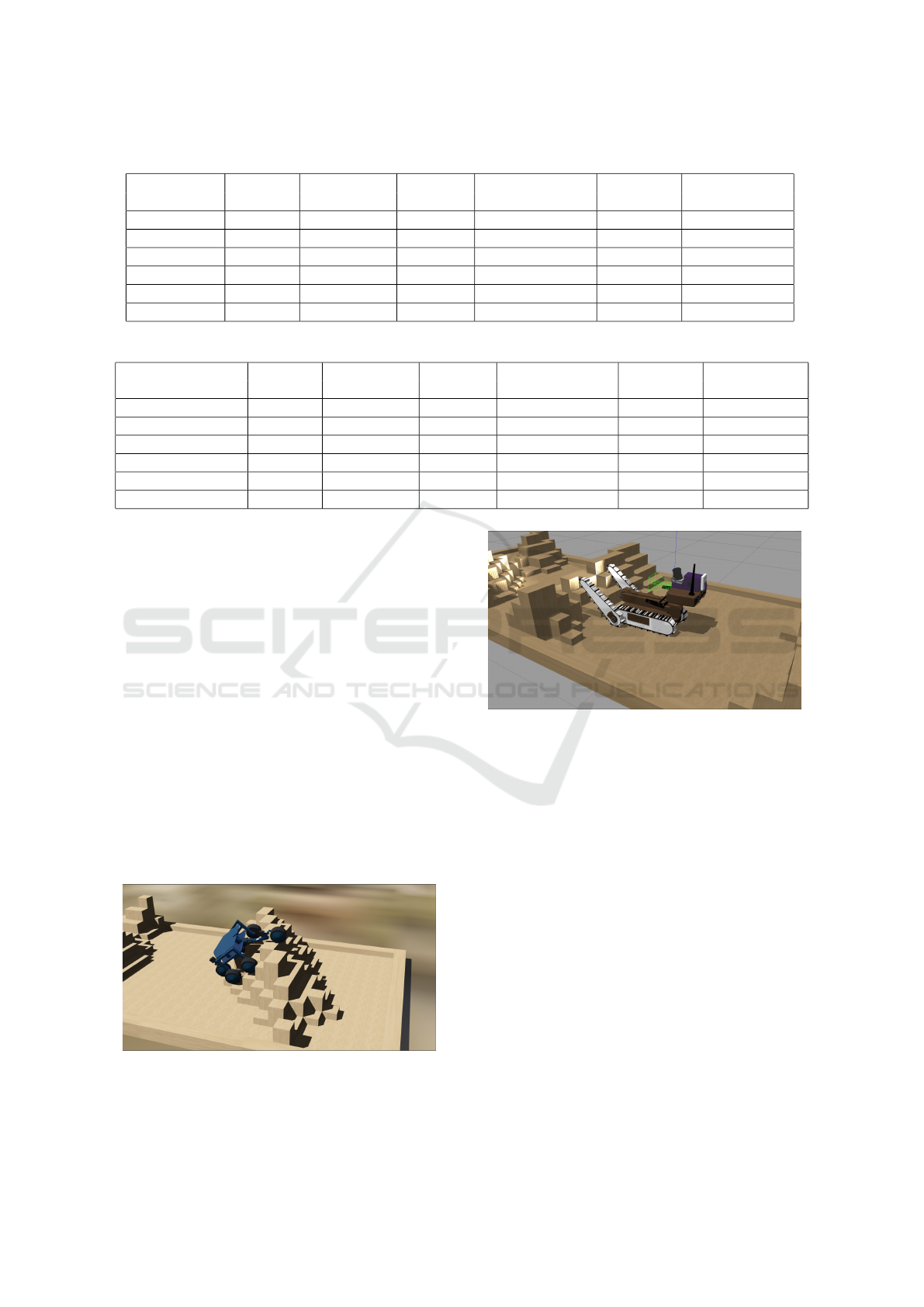
Table 2: Webots testing results.
Robot model RSE size Control RTF RTF Contr. CPU load CPU load
a
Physics errors
b
Name X,Y Min-max Min-max % % Occasions
Spot 10x10 1.12-1.45 1.10-1.42 5% 6% 0
Spot 15x60 1.12-1.45 1.06-1.38 5% 7% 0
Spot 50x50 1.12-1.45 0.95-1.36 5% 7% 2
Shrimp 10x10 6.12-8.34 4.45-8.25 5% 6% 0
Shrimp 15x60 6.12-8.34 3.87-7.64 5% 7% 0
Shrimp 50x50 6.12-8.34 3.23-6.89 5% 7% 0
Table 3: Gazebo testing results.
Robot model RSE size Control RTF RTF Contr. CPU load CPU load
a
Physics errors
Name X,Y Min-max Min-max % % Occasions
Servosila engineer 10x10 0.76-0.9 0.69-0.85 24% 25% 0
Servosila engineer 15x60 0.76-0.9 0.58-0.74 24% 26% 0
Servosila engineer 50x50 0.76-0.9 0.42-0.57 24% 26% 0
turtlebot3*3 10x10 0.99-1 0.99-1 8% 8% 0
turtlebot3*3 15x60 0.99-1 0.98-1 8% 8% 0
turtlebot3*3 50x50 0.99-1 0.96-1 8% 9% 0
available threads, an obvious RTF drop was detected.
4.2 Gazebo
For Gazebo Servosila Engineer crawler robot model
(Moskvin et al., 2020) with its higher performance
gear wheels platform (Gabdrahmanov et al., 2022b)
was used as a complex model with high impact on
performance and groups of 3 Turtlebot3 (Amsters
and Slaets, 2020) differential drive robot models were
used as simpler model with less resource consump-
tion. All runs were performed with default physics
settings and the results are presented in Table 3. A
higher CPU load and a lower RTF were detected for a
complex robot model, with a proportional decrease of
RTF’s values with the increase of the RSE size. Yet,
even the minimal values of the RTF stayed within a
comfortable for a user zone of above 0.3 (Abbyasov
et al., 2020).
Figure 11: Bluebotics Shrimp on 15x60 RSE in Webots.
Figure 12: Servosila Engineer on 15x60 RSE in Gazebo.
5 CONCLUSIONS
This article presented a next generation of LIRS-
RSEGen tool for constructing virtual random step
environments (RSE). The new tool can simultane-
ously generate multiple RSEs with user-defined spe-
cific features that are declared via an intuitive graph-
ical user interface. The new version of the genera-
tor, LIRS-RSEGen-2, has a richer and more respon-
sive interface, a graphical preview allows a user to
clearly see an appearance of the expected model. The
generated RSE models have a relatively small impact
on performance, random elements allow generating
thousands of unique worlds with just one configura-
tion, and the visual and physical body of the models
are identical, which together allows the tool to be used
for developing machine learning algorithms, includ-
ing reinforcement learning.
The constructed worlds were successfully tested
for teleoperation tasks in Webots simulator using Spot
A Tool for Mass Generation of Random Step Environment Models with User-Defined Landscape Features
517

and Bluebotics shrimp robots and in Gazebo simula-
tor using Servosila Engineer and a group of 3 Turtle-
bot3 Burger robots. The tests demonstrated that small
RSE models do not have a critical impact on perfor-
mance and can be effectively used in the time ac-
celeration mode. However, large and complex mod-
els of 2500+ RSE blocks cause a drop in perfor-
mance, and larger size values combined with com-
plex robot model can lead to errors in calculating
physics by Gazebo and Webots simulators. LIRS-
RSEGen-2 is available for free academic use at Git-
lab account of our Laboratory of Intelligent Robotic
Systems (LIRS)
1
.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This paper has been supported by the Kazan Federal
University Strategic Academic Leadership Program
(”PRIORITY-2030”).
REFERENCES
Abbyasov, B., Lavrenov, R., Zakiev, A., Yakovlev, K.,
Svinin, M., and Magid, E. (2020). Automatic tool for
gazebo world construction: from a grayscale image to
a 3d solid model. In 2020 IEEE International Con-
ference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pages
7226–7232. IEEE.
Amsters, R. and Slaets, P. (2020). Turtlebot 3 as a robotics
education platform. In Robotics in Education: Cur-
rent Research and Innovations 10, pages 170–181.
Springer.
Boston dynamics. Boston dynamics spot page (2024). https:
//bostondynamics.com/products/spot/. Accessed:
2024-09-02.
Burke, J., Murphy, R., Rogers, E., Lumelsky, V., and
Scholtz, J. (2004). Final report for the darpa/nsf in-
terdisciplinary study on human–robot interaction. Sys-
tems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part C: Applications and
Reviews, IEEE Transactions on, 34:103 – 112.
Choi, H., Crump, C., Duriez, C., Elmquist, A., Hager, G.,
Han, D., Hearl, F., Hodgins, J., Jain, A., Leve, F., et al.
(2021). On the use of simulation in robotics: Oppor-
tunities, challenges, and suggestions for moving for-
ward. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sci-
ences, 118(1):e1907856118.
Collins, J., Chand, S., Vanderkop, A., and Howard, D.
(2021). A review of physics simulators for robotic
applications. IEEE Access, 9:51416–51431.
Cyberbotics. Cyberbotics webots page (2024). https://
cyberbotics.com/. Accessed: 2024-09-02.
1
Laboratory of Intelligent Robotic Systems RSE Gen-
erator, GitLab, https://gitlab.com/lirs-kfu/lirs-rsegen-2
Estier, T., Piguet, R., Eichhorn, R., and Siegwart, R. (2000).
Shrimp, a rover architecture for long range martian
mission. In ESA Workshop on Advanced Space Tech-
nologies for Robotics and Automation, pages 5–7.
Gabdrahmanov, R., Tsoy, T., Bai, Y., Svinin, M., and
Magid, E. (2022a). Automatic generation of random
step environment models for gazebo simulator. In
Robotics for Sustainable Future: CLAWAR 2021 24,
pages 408–420. Springer.
Gabdrahmanov, R., Tsoy, T., Bai, Y., Svinin, M. M., and
Magid, E. (2022b). Gear wheels based simulation
of crawlers for mobile robot servosila engineer. In
ICINCO, pages 565–572.
Isaacs, J., Knoedler, K., Herdering, A., Beylik, M., and
Quintero, H. (2022). Teleoperation for urban search
and rescue applications. Field Robotics, 2(1):1177–
1190.
Jacoff, A., Downs, A., Virts, A., and Messina, E. (2008).
Stepfield pallets: Repeatable terrain for evaluating
robot mobility. In 8th Workshop on Performance Met-
rics for Intelligent Systems, pages 29–34.
Lavrenov, R. and Zakiev, A. (2017). Tool for 3d gazebo map
construction from arbitrary images and laser scans.
In 2017 10th International Conference on Develop-
ments in eSystems Engineering (DeSE), pages 256–
261. IEEE.
Le Lidec, Q., Jallet, W., Montaut, L., Laptev, I., Schmid,
C., and Carpentier, J. (2024). Contact models in
robotics: a comparative analysis. IEEE Transactions
on Robotics.
Lee, J., X. Grey, M., Ha, S., Kunz, T., Jain, S., Ye,
Y., S. Srinivasa, S., Stilman, M., and Karen Liu, C.
(2018). Dart: Dynamic animation and robotics toolkit.
The Journal of Open Source Software, 3(22):500.
Magid, E. and Tsubouchi, T. (2010). Static balance for res-
cue robot navigation-translation motion discretization
issue within random step environment. In ICINCO
(2), pages 415–422.
Moskvin, I., Lavrenov, R., Magid, E., and Svinin, M.
(2020). Modelling a crawler robot using wheels as
pseudo-tracks: model complexity vs performance. In
IEEE 7th International Conference on Industrial En-
gineering and Applications (ICIEA), pages 1–5. IEEE.
Open Source Robotics Foundation. Gazebo official site
(2024). http://gazebosim.org/. Accessed: 2024-09-02.
Rao, K., Harris, C., Irpan, A., Levine, S., Ibarz, J., and
Khansari, M. (2020). Rl-cyclegan: Reinforcement
learning aware simulation-to-real. In Proceedings of
the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and
Pattern Recognition, pages 11157–11166.
Safin, R., Lavrenov, R., and Mart
´
ınez-Garc
´
ıa, E. A. (2021).
Evaluation of visual slam methods in usar applica-
tions using ros/gazebo simulation. In Proceedings of
15th International Conference on Electromechanics
and Robotics” Zavalishin’s Readings”, pages 371–
382. Springer.
Zhao, W., Queralta, J. P., and Westerlund, T. (2020). Sim-
to-real transfer in deep reinforcement learning for
robotics: a survey. In IEEE symposium series on com-
putational intelligence, pages 737–744. IEEE.
ICINCO 2024 - 21st International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
518
