
Modeling Sunlight in Gazebo for Vision-Based Applications Under
Varying Light Conditions
Ramir Sultanov
1 a
, Ramil Safin
1 b
, Edgar A. Mart
´
ınez-Garc
´
ıa
2 c
and Evgeni Magid
1,3 d
1
Intelligent Robotics Department, Kazan Federal University, 35 Kremlin Street, Kazan, Russian Federation
2
Institute of Engineering and Technology, Department of Industrial Engineering and Manufacturing, Autonomous
University of Ciudad Juarez, Manuel D
´
ıaz H. No. 518-B Zona Pronaf Condominio, Chihuahua, 32315 Cd Ju
´
arez, Mexico
3
HSE University, 20 Myasnitskaya str , Moscow, Russian Federation
fi
Keywords:
Robotics, Vision, the Sun, Lighting Conditions, Simulation, Localization, Gazebo.
Abstract:
Vision is one of the well-researched sensing abilities of robots. However, applying vision-based algorithms
can be challenging when used in different environmental conditions. One such challenge in vision-based
localization is dynamic lighting conditions. In this paper, we present a new Gazebo plugin that enables re-
alistic illumination changes depending on a current Sun’s position. A plugin’s underlying algorithm takes
into account various parameters, such as date, time, latitude, longitude, elevation, pressure, temperature, and
atmospheric refraction. Virtual experiments demonstrated effectiveness of the proposed plugin, and the source
code is available for free academic use.
1 INTRODUCTION
Vision is one of key sensing abilities and is actively
researched in robotics. In the medical field, robots
equipped with visual sensors can assist during surgi-
cal operations (Komatsu et al., 2024). In the industrial
sector, vision-enabled robots can accelerate assem-
bly processes (Duan et al., 2024). In transportation,
robotic vision can be utilized for autonomous navi-
gation (Artono et al., 2024). Autonomous navigation
algorithms rely on localization algorithms, which, in
turn, are influenced by operating conditions. One of
these conditions is dynamic lighting, which changes
throughout a day, presenting a challenge for local-
ization algorithms to overcome (Piasco et al., 2021;
Oishi et al., 2019).
Testing algorithms in all possible conditions can
be challenging. In order to reduce software costs, al-
gorithms could be verified in a simulation before be-
ing tested in a real-world setting. Yet, the simulation
environment should be reproducible in the real world,
i.e., it needs to be realistic enough.
Objectives of this paper are to simulate realistic
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9319-0728
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1429-1876
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9163-8285
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7316-5664
sunlight in the Gazebo simulator and to evaluate an
impact of varying lighting conditions on vision-based
localization algorithms. This work presents a newly
developed solar position plugin for the Gazebo sim-
ulator and examines its effects on vision-based local-
ization algorithms’ performance.
2 RELATED WORK
2.1 Vision-Based Localization
Localization is not limited to vision-based algorithms.
Some works use other algorithms for localization,
e.g., 2D (Yue et al., 2024) or 3D structure-based ap-
proaches (Sarlin et al., 2021). This paper focuses on
vision-based algorithms.
Typically, vision-based localization (Safin et al.,
2020; Mingachev et al., 2020) employs visual infor-
mation (such as multi-color or gray-color images) or a
combination of visual information and supplementary
data (such as depth or odometry information).
A variety of features can be used for vision-based
localization. For example, in (Drupt et al., 2024) the
simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) al-
gorithm used ORB features and was designed for un-
derwater robots. Similarly, in (Zhang et al., 2024; Ji
Sultanov, R., Safin, R., MartıÌ ˛Anez-GarcıÌ ˛Aa, E. A. and Magid, E.
Modeling Sunlight in Gazebo for Vision-Based Applications Under Varying Light Conditions.
DOI: 10.5220/0013068700003822
In Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics (ICINCO 2024) - Volume 1, pages 519-526
ISBN: 978-989-758-717-7; ISSN: 2184-2809
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
519

et al., 2024), SLAM systems employed ORB features
but aimed at ground robots operating in dynamic en-
vironments. In (Adkins et al., 2024), ORB features
were used for ground robots engaged in long-term ac-
tivities. Other works employed SIFT (Lowe, 2004),
SURF (Bay et al., 2006), and BRISK (Leutenegger
et al., 2011) features.
Additionally, challenges in localization include
dynamic obstacles (e.g., cars, pedestrians, or ani-
mals), weather conditions (e.g., rain, snow, or fog),
changing lighting conditions and others.
Dynamic obstacles can introduce additional un-
certainty of a transformation estimated by a local-
ization algorithm if not properly addressed. Weather
conditions, such as rain, snow, and fog, can reduce
visibility over large distances and may cause a sensor
lens to become occluded with water droplets, limiting
its field of view and/or distorting obtained images.
Lighting affects data acquired by visual sensors,
often resulting in multiple different representations
of a same location. Common solutions to this issue
include a use of lighting-invariant image representa-
tions (Corke et al., 2013), estimating differences in
sequential data (Milford and Wyeth, 2012), and map-
ping an environment over multiple sessions (Labb
´
e
and Michaud, 2022).
Effects of different lighting conditions on local-
ization algorithms can vary from minor to major, de-
pending on a disparity of the lighting conditions of
a query image used for localization and a reference
image used for mapping. For example, in (Irie et al.,
2012), the FAB-MAP algorithm achieved a recall rate
of 0.6% when applied to datasets with large light-
ing changes, compared to a 20.2% recall rate with
datasets experiencing small lighting changes. There-
fore, lighting conditions can be a crucial factor in
achieving accurate localization.
Furthermore, vision-based detection and segmen-
tation algorithms typically rely on visual features such
as color, texture, and contrast, which can be drasti-
cally affected by illumination changes.
2.2 Light Simulation in Virtual
Environments
Light simulation in virtual environments is commonly
referred to as rendering. There are several rendering
techniques, including ray casting (Roth, 1982), ray
tracing (Shirley and Morley, 2008), radiosity (Goral
et al., 1984; Nishita and Nakamae, 1984), path tracing
(Lafortune, 1996), and others. These techniques gen-
erally use rays to simulate light propagation. In our
research, experiments were conducted using the Cas-
caded Image Voxel Cone Tracing global illumination
approach, which is provided by the Gazebo simulator
(Koenig and Howard, 2004).
The Gazebo simulator (Koenig and Howard,
2004) can be configured to use different graphics ren-
dering engines, including OGRE, OGRE-next (Rojt-
berg, Pavel and Rogers, David and Streeting, Steve
and others, 2024), or OptiX (Parker et al., 2010).
The light is simulated according to techniques used
in a selected graphics rendering engine. In this work,
OGRE-next graphics rendering engine was used.
3 METHODOLOGY
The Gazebo simulator (Koenig and Howard, 2004)
is an open-source software widely used in robotics
and is compatible with the Robot Operating System
(ROS). Gazebo is featured by a large community sup-
port and numerous ready-to-use plugins – extensions
that allow modifying simulator’s behavior.
Additionally, Gazebo’s abstraction layer enables
use of different rendering engines, making it a valu-
able tool for research of lightning conditions’ simula-
tion.
3.1 Simulation of Light
To simulate realistic lighting in Gazebo, we imple-
mented our own solar position plugin. This plugin
creates a virtual Sun in the simulated environment,
with its position calculated using the Solar Position
Algorithm (SPA) (Reda and Andreas, 2004), which
has an uncertainty of ±0.0003°. The algorithm allows
calculating solar zenith and azimuth angles within a
time frame from the year 2000 B.C. to 6000 A.D.
The algorithm consists of the steps that calculate: Ju-
lian and Julian Ephemeris Day, century, and millen-
nium; Earth heliocentric longitude, latitude, and ra-
dius vector; geocentric longitude and latitude; nuta-
tion in longitude and obliquity; true obliquity of the
ecliptic; aberration correction; apparent sun longitude
and apparent sidereal time at Greenwich; geocentric
and right ascension; geocentric sun declination; ob-
server local hour angle; topocentric sun right ascen-
sion; topocentric local hour angle; topocentric zenith
and azimuth angles.
The Solar Algorithm includes calculations for in-
cidence angle and sunrise, transit, and sunset times.
However, these were not used in our plugin, as they
are not necessary for calculating a solar zenith angle,
an azimuth angle, and a distance.
The solar position plugin uses the following pa-
rameters, as required by the SPA, to calculate a solar
zenith angle, an azimuth angle, and a distance: a year,
ICINCO 2024 - 21st International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
520

a month, a day, an hour, a minute, a second, a time-
zone, a latitude, a longitude, an elevation, an annual
average local pressure, an annual average local tem-
perature, an atmospheric refraction at a sunrise and a
sunset, a fractional second difference between UTC
and UT (Delta UT1), a difference between Earth’s ro-
tation time and terrestrial time (Delta T).
3.2 Vision-Based Localization
Algorithms
In this paper, two approaches of localization algo-
rithms were tested: a direct image matching and an
image features matching. In the direct image match-
ing, intensity values of images are directly compared.
In the image features matching, sets of detected fea-
tures are compared. In this study, SIFT, SURF, ORB,
and BRISK features were tested. Feature extraction
and description were performed using the OpenCV
(version 4.5.4) library (Bradski, 2000). Using the
SPA, three datasets were collected at different times
of the day: at 4 AM, at 12 PM, at 8 PM.
3.3 Performance Metrics
To analyze effects of the solar position plugin, two
metrics were used: a mean difference between
datasets and a standard deviation between datasets.
The mean difference between two datasets is calcu-
lated using the following equation:
E =
1
n
n
∑
i=1
D(A
i
, B
i
) (1)
where E is the mean difference, n is a number of im-
ages in the dataset, D(A
i
, B
i
) is a difference between
corresponding images, and A and B are the datasets.
The standard deviation between two datasets is
calculated using the following equation:
s =
s
1
n − 1
n
∑
i=1
(D(A
i
, B
i
) − E)
2
(2)
where s is the standard deviation, n is the number
of images in a dataset, D(A
i
, B
i
) is a difference be-
tween corresponding images in the datasets A and B,
A
i
and B
i
are the i-th images of the corresponding
datasets, and E is the mean difference between the
two datasets.
A difference between two images using the direct
image matching approach is calculated using the fol-
lowing equation:
D =
1
wh
w
∑
x=1
h
∑
y=1
distance(a
xy
, b
xy
) (3)
where D is the difference between the two images,
w is a width of an image, h is a height of an im-
age, distance(a
xy
, b
xy
) is a distance function applied
to pixel values, and a and b are images with a
xy
and
b
xy
representing pixel values at corresponding coordi-
nates.
A distance between two pixels using the boolean
approach is calculated based on the following equa-
tion:
distance =
0 i f a
xy
== b
xy
1 i f a
xy
! = b
xy
(4)
where a
xy
and b
xy
are pixel values.
A distance between two pixels in gray-scale im-
ages using the Euclidean approach is calculated based
on the following equation:
distance =
(a
xy
− b
xy
)
2
255
2
(5)
where a
xy
and b
xy
are pixel values.
A distance between two pixels in RGB images us-
ing Euclidean approach is calculated based on the fol-
lowing equation:
distance =
1
255
2
∗ 3
3
∑
c=1
(a
xyc
− b
xyc
)
2
(6)
where a
xyc
and b
xyc
are pixel values in channel c. RGB
images contain three channels.
A difference between two images using the image
features matching approach is calculated based on the
following equation:
D =
F
total
− F
matched
F
total
(7)
where D represents a difference between the two im-
ages, F
total
is a total number of features, F
matched
is a
number of features that were matched.
A total number of features is calculated using the
following equation:
F
total
= F
a
+ F
b
− F
matched
(8)
where F
total
is the total number of features, F
a
is a
number of features detected in image a, F
b
is a num-
ber of features detected in image b, F
matched
is a num-
ber of features that were matched.
Lowe’s ratio was used for feature matching, mean-
ing that features are matched if a distance of the clos-
est match candidate is sufficiently different from that
of the second closest match candidate. A threshold
value was set to 0.5, meaning the closest match is ac-
cepted if it is at least twice as close as the next closest
candidate.
Modeling Sunlight in Gazebo for Vision-Based Applications Under Varying Light Conditions
521
3.4 Experimental Setup
To the best of our knowledge, there is no common
standard environment for testing localization algo-
rithms. While exploring existing environment models
for our experiments in Gazebo, we noted that some
models lack a roof (which allows a sunlight to leak
from above), other models are too simple (containing
only a few objects) or too complex to be processed
quickly by a typical PC. Finally, a model (Nicolas-
3D, 2024) shown in Fig. 1 was selected.
Lighting in the Gazebo simulator can be improved
using global illumination techniques, which typically
yield more realistic results. Currently, the Gazebo
simulator supports only Voxel Cone Tracing (VCT)
and Cascaded Image Voxel Cone Tracing (CIVCT).
Both approaches were tested in the proposed environ-
ment, and the CIVCT approach was chosen because it
subjectively produced more visually realistic results.
The source code of the Gazebo simulator was
modified to use CIVCT for global illumination. These
modifications were necessary because the CIVCT ap-
proach requires binding a camera, and at the time, no
method was found to bind a non-GUI camera other
than modifying the source code directly. The modi-
fied source code is available on GitLab
1
.
The chosen trajectory of the camera used in the
experiments is marked in red in Fig. 2. Camera poses
were calculated along this trajectory at 1-meter inter-
vals, except cases where the camera performs a turn;
in those instances, the pose was set at the beginning
of the next line segment. The camera was always
pointed toward the next trajectory point. As a result,
each dataset contained 991 images, which were man-
ually checked for consistency.
A PC with Intel Core i3 processor, 8 GB of RAM,
and Nvidia GeForce GTX 950 GPU was used for the
evaluation. The simulation included the testing en-
vironment, the camera with a resolution of 640x480
pixels, and the proposed solar position plugin. The
parameters used during the experiments are presented
in Table 1.
4 RESULTS
Tables 2 and 3 present results of the experiments. Ta-
ble 2 shows mean difference values for each algo-
rithm, while Table 3 provides standard deviation val-
ues. In both tables, ”4-12,” ”4-20,” and ”12-20” cor-
respond to matching pairs of images acquired at 4:00
1
https://gitlab.com/lirs-kfu/gazebo-solar-position-plu
gin/-/tree/main/gz-sim
Table 1: Parameters of the solar position plugin used in the
experiments.
Parameter Value
Year 2024
Month 7
Day 1
Hour 4, 12, or 20
Minute 0
Second 0
Timezone +3 hours
Latitude +55.792115°
Longitude +49.122254°
Elevation 90 meters
Pressure 1013.25 millibars
Temperature 0° Celsius
Atmospheric refraction 0.5667
Delta UT1 0 seconds
Delta T 69.184 seconds
AM vs 12:00 PM, 4:00 AM vs 8:00 PM, and 12:00
PM vs 8:00 PM, respectively.
Table 2: Mean difference values in the experiments.
Algorithm 4-12 4-20 12-20
Boolean-rgb 0.70159 0.69474 0.70102
Boolean-grey 0.70078 0.66502 0.70063
Euclidean-rgb 0.06425 0.00308 0.07117
Euclidean-grey 0.06308 0.00295 0.07000
SIFT 0.84577 0.63501 0.83832
SURF 0.94056 0.81301 0.93860
ORB 0.97809 0.89677 0.97376
BRISK 0.95350 0.86339 0.95288
Table 3: Standard deviation of differences in the experi-
ments.
Algorithm 4-12 4-20 12-20
Boolean-rgb 0.06709 0.07227 0.06767
Boolean-grey 0.06680 0.10038 0.06752
Euclidean-rgb 0.00917 0.00190 0.01036
Euclidean-grey 0.00862 0.00176 0.01014
SIFT 0.04907 0.14882 0.05197
SURF 0.01816 0.10936 0.02048
ORB 0.01723 0.09651 0.02059
BRISK 0.01580 0.09893 0.01765
Tables 4 and 5 present the results of the tests. Ta-
ble 4 shows the mean difference values for each algo-
rithm, while Table 5 provides the standard deviation
values. In both tables, ”4-4,” ”12-12,” and ”20-20”
correspond to tests using images acquired at 4:00 AM,
12:00 PM, and 8:00 PM, respectively, to evaluate the
deterministic behavior of the algorithms.
Equation 4 was used to calculate a difference be-
tween images in the boolean-rgb algorithm and in the
ICINCO 2024 - 21st International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
522
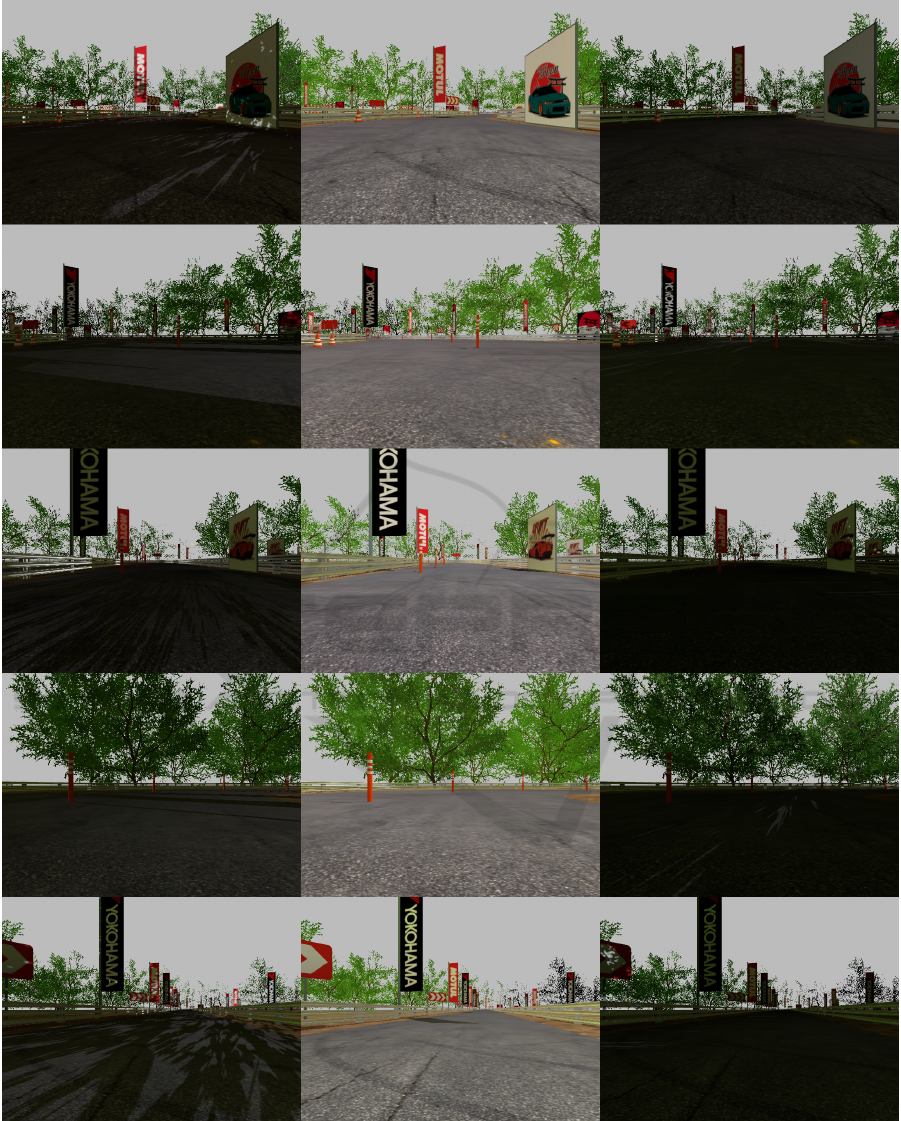

Figure 1: Virtual environment images. The left column shows morning (4 AM) images, the middle column shows day (12
PM) images, and the right column shows evening (8 PM) images. Rows correspond to images with IDs 264, 394, 573, 741,
and 800.
Modeling Sunlight in Gazebo for Vision-Based Applications Under Varying Light Conditions
523
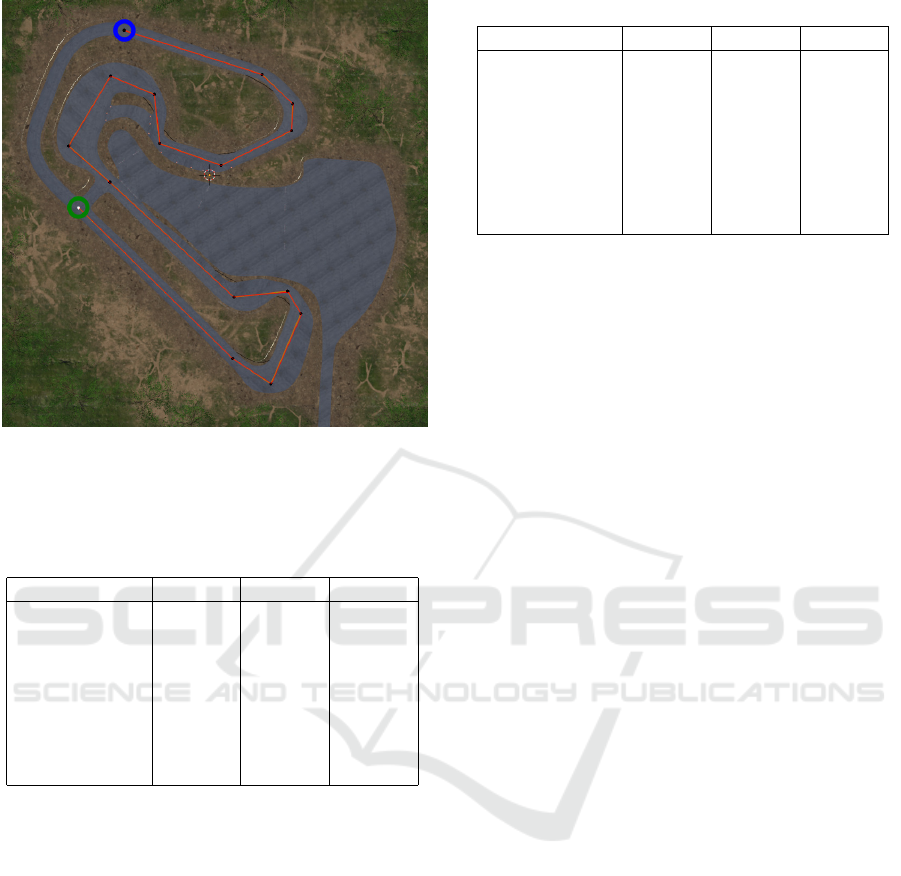

Figure 2: Trajectory of the camera used in the experiments
is marked in red. The camera starts at the point marked
with the blue circle and finishes at the point marked with
the green circle.
Table 4: Mean difference values in the tests.
Algorithm 4-4 12-12 20-20
Boolean-rgb 0 0 0
Boolean-grey 0 0 0
Euclidean-rgb 0 0 0
Euclidean-grey 0 0 0
SIFT 1.19e-5 0 4.54e-6
SURF 0 0 0
ORB 8.04e-6 0 8.04e-6
BRISK 0.01224 0.00751 0.01274
boolean-grey algorithm. Equation 6 was used to cal-
culate a difference between images in the Euclidean-
rgb algorithm. Equation 5 was used to calculate the
difference between images in the Euclidean-grey al-
gorithm. For SIFT, SURF, ORB, and BRISK, the
default parameters provided by the OpenCV library
were used.
5 DISCUSSION
5.1 Limitations
In the experiments, the Sun’s position was not ad-
justed according to the simulation time. However,
with some source code modifications, the solar posi-
tion plugin can be configured to move the Sun based
on simulation time. These modifications are expected
to be included in future versions of the plugin.
Table 5: Standard deviation of differences in the tests.
Algorithm 4-4 12-12 20-20
Boolean-rgb 0 0 0
Boolean-grey 0 0 0
Euclidean-rgb 0 0 0
Euclidean-grey 0 0 0
SIFT 0.00023 0 0.00014
SURF 0 0 0
ORB 0.00025 0 0.00025
BRISK 0.00655 0.00324 0.00578
The background color (sky color) in the experi-
ments was set to grey. Unfortunately, the sky pro-
vided by the Gazebo simulator was not influenced by
the angle of sunlight; for instance, it remained mostly
blue when it should have been red. As a result, the
default sky was not used in the experiments. This
limitation should be considered when interpreting the
experimental results, as the sky color remained con-
stant and did not affect any of the algorithms. The sky
occupied up to 50% of the image area (as the camera
was parallel to the ground), which suggests that the
algorithms might be more significantly affected if the
sky was adjusted according to the angle of sunlight.
To achieve more realistic results, a sky model that re-
sponds to the sunlight angle is necessary. Addition-
ally, the Gazebo simulator lacks a night sky model.
Incorporating a night sky, with the Moon and stars,
could improve accuracy of results during nighttime
and possibly during twilight.
The experiments did not include the robot’s shad-
ows. Shadows were turned off because only a cam-
era was used, and the shadows cast by the camera
alone did not appear realistic. The shadow area of a
robot in an image can range from small to large. Since
robot shadows are dependent on the angle of sunlight,
enabling them in future experiments could result in
significant image differences at different times of the
day.
It was observed during the simulation that sunlight
could pass through the virtual ground plane from be-
low and illuminate objects above it. The model used
in the experiments did not include any textures be-
neath the ground, which may have resulted in slightly
less realistic outcomes. It is believed that using light-
absorbing textures on the underside of the virtual
ground plane could help eliminating some unrealis-
tic effects, such as objects being lit from below by a
Sun.
Default parameters provided by the OpenCV were
used for feature detection and description. As a re-
sult, it is unclear whether the optimal parameters were
used and how these may have affected the results.
ICINCO 2024 - 21st International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
524
5.2 Analysis
Despite all the factors mentioned above, the experi-
mental results clearly demonstrated the effects of sun-
light on the algorithms. Notations from Table 6 are
used in analysis presented in this subsection.
Table 6: Notations for results’ analysis.
Value Notation
Mean difference between morning
images and day images
E
md
Mean difference between morning
images and evening images
E
me
Mean difference between day images
and evening images
E
de
Standard deviation of difference be-
tween morning images and day im-
ages
s
md
Standard deviation of difference be-
tween morning images and evening
images
s
me
Standard deviation of difference be-
tween day images and evening im-
ages
s
de
It can be observed that E
me
is less than E
md
or
E
de
. The morning images were taken approximately
one hour after the sunrise, while the evening images
were taken about half an hour before the sunset. As
a result, the morning and evening images were darker
compared to those taken in the middle of the day.
The Euclidean algorithms demonstrated differ-
ences between images using the Euclidean distance.
It can be observed that E
de
is slightly larger than E
md
.
This can be explained by a fact that the evening im-
ages were taken only half an hour before the sunset,
while the morning images were taken an hour after
the sunrise. Therefore, the morning conditions were
closer to the day conditions. However, this was not
the case for the boolean algorithms, where E
md
and
E
de
are approximately the same. It is believed that
the boolean algorithms do not handle image matching
well enough and, as a result, produce poorer results.
The difference measured using feature-based al-
gorithms is not expected to be fully accurate because
these algorithms do not account for ground-truth re-
lationships between features in images from different
datasets. Unfortunately, manual dataset labeling was
not possible at the time. Nevertheless, the results of
feature-based algorithms still show correlations with
each other. It can be observed that the SIFT algorithm
performed well, while the SURF, BRISK, and ORB
algorithms performed worse. The poor results may
be attributed to a lack of experience with these fea-
tures, as only the default parameters provided by the
OpenCV library were used, and no parameter analysis
was conducted.
As for the standard deviation results, s
me
is the
largest, except for the Euclidean algorithms. The
large value of s
me
indicates that, even though the mean
difference between images was not significant, some
individual images exhibited more variation than oth-
ers. This suggests that the morning and evening im-
ages may not be interchangeable. Although darkness
levels in the morning and evening images are approx-
imately the same, the angle of sunlight and shadows
still differ, leading to the greater deviation. For the
Euclidean algorithms, s
me
is smaller than s
md
and s
de
,
indicating that the darkness levels in the morning and
evening images are similar, while the day images are
brighter.
The experimental results indicated that SIFT,
ORB, and BRISK produce different features for the
same dataset across different runs. Since the SURF
algorithm does not produce noticeable differences for
a single dataset, and the source code of the experi-
ments was thoroughly reviewed, it was concluded that
SIFT, ORB, and BRISK are either not deterministic
algorithms or are not properly configured to be deter-
ministic. As a result, the differences between datasets
may vary slightly.
6 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, the solar position plugin for the Gazebo
simulator was presented. The Sun’s position in the
sky depends not only on gravitational forces but also
on light propagation parameters, such as a speed of
light in a particular environment, atmospheric condi-
tions, and time-related errors. Therefore, the SPA was
used to accurately model the Sun’s position in the vir-
tual environment. Virtual experiments with the de-
veloped solar position plugin demonstrated that SIFT,
SURF, ORB, and BRISK algorithms were affected by
dynamic lighting. The plugin is available for free aca-
demic use at Gitlab account of our Laboratory of In-
telligent Robotic Systems (LIRS)
2
.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This paper has been supported by the Kazan Federal
University Strategic Academic Leadership Program
(”PRIORITY-2030”).
2
Laboratory of Intelligent Robotic Systems, GitLab,
https://gitlab.com/lirs-kfu/gazebo-solar-position-plugin
Modeling Sunlight in Gazebo for Vision-Based Applications Under Varying Light Conditions
525

REFERENCES
Adkins, A., Chen, T., and Biswas, J. (2024). Obvi-slam:
Long-term object-visual slam. IEEE Robotics and Au-
tomation Letters.
Artono, B., Nugroho, W., and Wahyudi, R. (2024). Color-
based image processing for autonomous human fol-
lowing trolley robot navigation with camera vision. J.
of Computer Science and Engineering, 5(1):20–38.
Bay, H., Tuytelaars, T., and Van Gool, L. (2006). Surf:
Speeded up robust features. In 9th European Conf. on
Computer Vision, Part I 9, pages 404–417. Springer.
Bradski, G. (2000). The OpenCV Library. Dr. Dobb’s Jour-
nal of Software Tools.
Corke, P., Paul, R., Churchill, W., and Newman, P. (2013).
Dealing with shadows: Capturing intrinsic scene ap-
pearance for image-based outdoor localisation. In
2013 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelli-
gent Robots and Systems, pages 2085–2092. IEEE.
Drupt, J., Comport, A. I., Dune, C., and Hugel, V. (2024).
Mam3slam: Towards underwater-robust multi-agent
visual slam. Ocean Engineering, 302:117643.
Duan, J., Fang, Y., Zhang, Q., and Qin, J. (2024). Hrc for
dual-robot intelligent assembly system based on mul-
timodal perception. Proceedings of the Institution of
Mechanical Engineers, Part B: Journal of Engineer-
ing Manufacture, 238(4):562–576.
Goral, C. M., Torrance, K. E., Greenberg, D. P., and Bat-
taile, B. (1984). Modeling the interaction of light be-
tween diffuse surfaces. ACM SIGGRAPH computer
graphics, 18(3):213–222.
Irie, K., Yoshida, T., and Tomono, M. (2012). Outdoor
localization using stereo vision under various illumi-
nation conditions. Advanced Robotics, 26(3-4):327–
348.
Ji, Q., Zhang, Z., Chen, Y., and Zheng, E. (2024). Drv-slam:
An adaptive real-time semantic visual slam based on
instance segmentation toward dynamic environments.
IEEE Access, 12:43827–43837.
Koenig, N. and Howard, A. (2004). Design and use
paradigms for Gazebo, an open-source multi-robot
simulator. In Int. Conf. on intelligent robots and sys-
tems, volume 3, pages 2149–2154. Ieee.
Komatsu, H., Sawada, M., Iida, Y., Wada, I., Azuma, Y.,
Kudoh, A., Sato, S., Harada, T., and Taniguchi, F.
(2024). New surgery technique combining robotics
and laparoscopy using the hugo™ ras system. Asian
Journal of Endoscopic Surgery, 17(3):e13344.
Labb
´
e, M. and Michaud, F. (2022). Multi-session visual
slam for illumination-invariant re-localization in in-
door environments. Frontiers in Robotics and AI,
9:801886.
Lafortune, E. (1996). Mathematical models and monte carlo
algorithms for physically based rendering. Depart-
ment of Computer Science, Faculty of Engineering,
Katholieke Universiteit Leuven, 20(74-79):4.
Leutenegger, S., Chli, M., and Siegwart, R. Y. (2011).
Brisk: Binary robust invariant scalable keypoints. In
Int. Conf. on computer vision, pages 2548–2555.
Lowe, G. (2004). Sift-the scale invariant feature transform.
Int. J, 2(91-110):2.
Milford, M. J. and Wyeth, G. F. (2012). Seqslam: Visual
route-based navigation for sunny summer days and
stormy winter nights. In IEEE Int. Conf. on robotics
and automation, pages 1643–1649.
Mingachev, E., Lavrenov, R., Magid, E., and Svinin, M.
(2020). Comparative analysis of monocular slam al-
gorithms using tum and euroc benchmarks. In 15th
International Conference on Electromechanics and
Robotics” Zavalishin’s Readings”, pages 343–355.
Springer.
Nicolas-3D (2024). Drift race track (sketchfab. http
s :// s k e tchf a b.com / 3 d - mode l s /dri f t- r a ce- tra
ck-free-b4108132c93f4736957d97e274fbd11e. Ac-
cessed: 14-08-2024.
Nishita, T. and Nakamae, E. (1984). Half-tone represen-
tation of 3-d objects with smooth edges by using a
multi-scanning method. J. Information Processing (in
Japanese), 25(5):703–711.
Oishi, S., Inoue, Y., Miura, J., and Tanaka, S. (2019). Seqs-
lam++: View-based robot localization and navigation.
Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 112:13–21.
Parker, S. G. et al. (2010). Optix: a general purpose ray
tracing engine. Acm transactions on graphics (tog),
29(4):1–13.
Piasco, N., Sidib
´
e, D., Gouet-Brunet, V., and Demonceaux,
C. (2021). Improving image description with aux-
iliary modality for visual localization in challenging
conditions. International Journal of Computer Vision,
129(1):185–202.
Reda, I. and Andreas, A. (2004). Solar position algo-
rithm for solar radiation applications. Solar energy,
76(5):577–589.
Rojtberg, Pavel and Rogers, David and Streeting, Steve and
others (2001 – 2024). Ogre scene-oriented, flexible 3d
engine. https://www.ogre3d.org/.
Roth, S. D. (1982). Ray casting for modeling solids. Com-
puter graphics and image processing, 18(2):109–144.
Safin, R., Lavrenov, R., and Mart
´
ınez-Garc
´
ıa, E. A. (2020).
Evaluation of visual slam methods in usar applica-
tions using ros/gazebo simulation. In Proceedings
of 15th International Conference on Electromechan-
ics and Robotics” Zavalishin’s Readings” ER (ZR)
2020, Ufa, Russia, 15–18 April 2020, pages 371–382.
Springer.
Sarlin, P.-E. et al. (2021). Back to the feature: Learn-
ing robust camera localization from pixels to pose.
In IEEE/CVF Conf. on computer vision and pattern
recognition, pages 3247–3257.
Shirley, P. and Morley, R. K. (2008). Realistic ray tracing.
AK Peters, Ltd.
Yue, X., Zhang, Y., Chen, J., Chen, J., Zhou, X., and He, M.
(2024). Lidar-based SLAM for robotic mapping: state
of the art and new frontiers. Industrial Robot: Int. J.
of robotics research and application, 51(2):196–205.
Zhang, B., Dong, Y., Zhao, Y., and Qi, X. (2024). Dynpl-
slam: A robust stereo visual slam system for dynamic
scenes using points and lines. IEEE Transactions on
Intelligent Vehicles.
ICINCO 2024 - 21st International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
526
