
Hate Speech Detection Using Cross-Platform Social Media Data in
English and German Language
Gautam Kishore Shahi
1 a
and Tim A. Majchrzak
2 b
1
University of Duisburg-Essen, Germany
2
University of Agder, Norway
Keywords:
Hate Speech, YouTube, User Comments, Cross-Platform, Multilingual Data.
Abstract:
Hate speech has grown into a pervasive phenomenon, intensifying during times of crisis, elections, and social
unrest. Multiple approaches have been developed to detect hate speech using artificial intelligence, however,
a generalized model is yet unaccomplished. The challenge for hate speech detection as text classification
is the cost of obtaining high-quality training data. This study focuses on detecting bilingual hate speech in
YouTube comments and measuring the impact of using additional data from other platforms in the performance
of the classification model. We examine the value of additional training datasets from cross-platforms for
improving the performance of classification models. We also included factors such as content similarity,
definition similarity, and common hate words to measure the impact of datasets on performance. Our findings
show that adding more similar datasets based on content similarity, hate words, and definitions improves
the performance of classification models. The best performance was obtained by combining datasets from
YouTube comments, Twitter, and Gab with an F1-score of 0.74 and 0.68 for English and German YouTube
comments.
1 INTRODUCTION
Hate speech on social media has become a
widespread problem on the Web (Jahan and Ous-
salah, 2023). With easy access to social media plat-
forms, such as Twitter (now X), YouTube, or Gab, the
amount of hate speech has been increasing (Shahi and
Kana Tsoplefack, 2022) for decades. The topic of
hate speech is linked to global developments and re-
cent crises, such as hate speech on the Russia-Ukraine
conflict (Di F
´
atima et al., 2023), COVID-19 (Shahi
and Kana Tsoplefack, 2022), and ongoing elections in
different countries of the world. Different social me-
dia platforms have their own data formats and guide-
lines, allowing users to post content in various media
types and languages. For example, on YouTube, users
can post hate speech as videos or comments.
Hate speech detection is mainly studied in En-
glish and for specific platforms such as Twitter
(Siegel, 2020), Facebook (Del Vigna et al., 2017),
and YouTube (D
¨
oring and Mohseni, 2020). A hate
speech classification model needs fine-grained anno-
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6168-0132
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2581-9285
tated training data. Gathering high-quality training
data is expensive and time-consuming (Shahi and Ma-
jchrzak, 2022) for training machine learning models.
Previous research shared hate speech datasets in dif-
ferent languages (Poletto et al., 2021; Al-Hassan and
Al-Dossari, 2019; Fortuna and Nunes, 2018). How-
ever, such data sets vary considerably by social me-
dia platform, annotation goal (such as offensive lan-
guage, abusive language, hate speech), period of data
collection, and other dimensions (Al-Hassan and Al-
Dossari, 2019). There are notable differences in the
linguistic style of comments posted on different plat-
forms (such as adherence to standard spelling and
grammar and usage of emojis). Hence, prior research
and datasets are dissimilar and not readily generaliz-
able, especially across different languages.
With the advancement of Generative Artificial
Intelligence (GAI), mainly Large Language Models
(LLMs) such as ChatGPT
1
, data annotation data have
been tested for hate speech (Wullach et al., 2020).
However, there is a need for ground truth to verify the
annotation quality; annotation quality depends on the
given definition, ethical implications, and local law
1
https://chat.openai.com/
Shahi, G. K. and Majchrzak, T. A.
Hate Speech Detection Using Cross-Platform Social Media Data in English and German Language.
DOI: 10.5220/0013070000003825
In Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies (WEBIST 2024), pages 131-140
ISBN: 978-989-758-718-4; ISSN: 2184-3252
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
131

(Li et al., 2023). Hence, quality annotated data is
still challenging when developing a classifier for hate
speech detection.
Social media platforms are mandated in some ju-
risdictions to delete hateful messages within a cer-
tain time frame once they are reported as part of con-
tent moderation (Wang and Kim, 2023). As a re-
sult, thousands of posts need to be checked automat-
ically for whether or not they contain hateful content
(Bayer and Petra, 2020). This study proposes a hate
speech detection model for bilingual YouTube com-
ments. User comments were collected from YouTube
videos in English and German and covered different
social topics, such as politics, LGBT rights, and im-
migration. Comments are annotated for hate speech.
To solve the problem of data annotation on a large
scale, we collected and annotated a small number of
YouTube comments and explored our approach by
reusing existing datasets to enhance the performance
of the classifier. We propose the following research
question:
RQ: How does the performance of the Classifier for
hate speech detection change by adding additional
training data?
To answer the RQ, we searched 190 YouTube
videos on different topics and collected users’ com-
ments from YouTube videos. We annotated 1,892 En-
glish and 6,060 German comments. Along with that,
we used eight existing datasets from different plat-
forms in German and English. First, we compute the
dataset similarity based on definition, text, and hate
words. In similarity measures, text and hate speech
provide content similarity from datasets, and defini-
tion similarity provides choices for hate speech. Fur-
ther, we systematically compare the predictive per-
formance of hate speech classifiers when the training
data is augmented with various kinds of external data
across different platforms in two different settings.
We employed cross-data set training, i.e., augment-
ing the training data with an external data set (from
the same social media platform and in the same lan-
guage). Finally, we used cross platform training, i.e.,
augmenting the training data with external data from
a different social media platform.
For evaluation, we considered the performance of
the machine learning model in terms of precision, re-
call, and F1 score, the similarity of hate words from
the dataset, and the definition of hate speech in the
dataset. Apart from the performance of the classifi-
cation model, the definition and hate word similarity
provide an overview of linguistic content. The key
contribution of this work is twofold. First, we pro-
vide a dataset for hate speech on YouTube comments
in English and German. Second, we explore existing
hate speech datasets to enhance the performance of
the hate speech classification model.
This article is organized as follows. We discuss
related work in Section 2 followed by the research
method in Section 3. We then show our experiment
and results in Section 4 before discussing the findings
in Section 5. Finally, we discuss the ideas for future
work in Section 6.
2 RELATED WORK AND
BACKGROUND
Machine learning is the dominant approach to text
classification in various domains such as political sen-
timent analysis (R
¨
ochert et al., 2020), detecting in-
civility and impoliteness in online discussions (Stoll
et al., 2020) as well as the classification of political
tweets (Charalampakis et al., 2016). Especially the
state-of-the-art technique BERT (Deep Bidirectional
Transformers for Language Understanding) (Malmasi
and Zampieri, 2017) has been used for the detec-
tion of hate speech (Salminen et al., 2020; Aggar-
wal et al., 2019; Liu et al., 2019; Zampieri et al.,
2019). The text classifier aims to train a robust classi-
fier to recognize hate comments globally, i.e., on dif-
ferent platforms and languages. For the identification
and training of the models, several studies classify
hate speech using deep neural network architectures
or standard machine learning algorithms. Wei et al.
compare machine learning models on different public
datasets (Wei et al., 2017). The results indicate that
their approach of a convolution neural network out-
performs the previous state-of-the-art models in most
cases (Wei et al., 2017). A recent study used trans-
fer learning (Yuan et al., 2023) to train 37,520 En-
glish tweets, showing a trend towards more complex
models and better results. Prior studies have analyzed
hate speech on YouTube; one study highlights the hate
speech on YouTube on Syrian refugees (Aslan, 2017).
In another study, hate speech on gender is studied on
a small dataset quantitatively (D
¨
oring and Mohseni,
2019).
Previous studies have mainly focused on detect-
ing hate speech in different languages (Ousidhoum
et al., 2019) and on comparing different social me-
dia platforms (Salminen et al., 2020). Considering
the past studies about hate speech, it is noticeable
that many studies only concentrate on one platform or
specific language, such as English (Waseem, 2016),
German (Ross et al., 2016), Spanish (Ben-David and
Matamoros-Fern
´
andez, 2016) and Italian (Del Vigna
et al., 2017) to train a machine learning model to au-
tomatically classify and predict which unseen texts
WEBIST 2024 - 20th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
132

can be considered hate speech. Ousidhoum et al.
applied a multilingual and multitasking approach to
train a classifier on three languages (English, French,
and Arabic) based on Twitter tweets using a compari-
son of traditional machine learning and deep learning
models (Ousidhoum et al., 2019).
Previous research uses human-annotated datasets
for supervised hate speech detection. Besides the dif-
ferent methods for training the model, different code
books are used for data annotation. At the same time,
(Davidson et al., 2017; Waseem and Hovy, 2016)
opted for a multi-label procedure (hateful, offensive
(but not hateful), and neither (Davidson et al., 2017);
racist, sexist (Waseem and Hovy, 2016)), the annota-
tion of the data of (Ross et al., 2016) was collected
with a binary labeling schema (hate speech as yes or
no).
However, research is needed considering the clas-
sifier’s performance in multilingual contexts in com-
bination with datasets from social media platforms.
Salminen et al. (Salminen et al., 2020) points out that
the mono-platform focus in hate speech detection re-
search is problematic, as there are no guarantees that
the models developed by researchers will generalize
well across platforms. This issue underscores the im-
portance of our research in exploring cross-platform
generalization.
Fortuna et al. have shown that merging and
combining different datasets can enhance the over-
all performance of classification models (Fortuna and
Nunes, 2018). However, a more systematic evalu-
ation is needed to determine the extent of improve-
ment when a classifier is trained on one dataset, and
then another is added. This approach could poten-
tially lead to significant advancements in hate speech
detection.
The role of generative AI models such as chatGPT
in generated annotated data without any background
truth is still under exploration (Li et al., 2023). Conse-
quently, hate speech detection still depends on gath-
ering human-annotated data to build a classification
model.
3 RESEARCH METHOD
This section explains the approach used for building
the classification model in the study, i.e., data col-
lection, data annotation, similarity measurement, the
classification approach, and the evaluation strategy.
The research method is depicted in Figure 1.
3.1 Data Collection
First, we collected datasets in two steps: 1) Collect-
ing YouTube comments in English and German. 2)
Compiling publicly available data published in prior
research on Twitter, Wikipedia, and Gab.
YouTube is a video-sharing platform where videos
from across the world are uploaded. We used a self-
developed Python crawler using pytube
2
(a Python li-
brary) and searched keywords on YouTube to gather
video and their comments (R
¨
ochert et al., 2021). To
maintain the diversity in the dataset, we chose dif-
ferent controversial topics, such as politics, LGBT,
immigration, abortion, war, sex education, entertain-
ment, and sports, the probability of having hate com-
ments is more on videos on these topics. A total of
49,074 comments were extracted from 101 English
YouTube videos and 89 German videos in multiple
languages. Furthermore, we identified the language
of comments and filtered German and English com-
ments using fastText (Joulin et al., 2016). Overall,
we got 30,663 and 18,441 English and German com-
ments, respectively, which are further filtered for data
annotation, further explained in section 3.2.
For external datasets, the criteria were to get pub-
licly accessible datasets and use binary class for hate
speech detection. We considered ten datasets from
three different platforms (Twitter, Gab, Wikipedia)
and provided a three-letter ID to each of them; the
first letter indicates the language, the second the plat-
form, and the third the number. For example, ET1 is
the 1st English Twitter dataset. Overall, we used ten
datasets; eight datasets were collected from external
sources, and we collected and annotated two datasets
(EY1 and GY1). Table 1 gives an overview of the col-
lected dataset. For each dataset, we provide the lan-
guage, platform name, size of data, and percentage of
hate speech annotated in the dataset.
3.2 Data Annotation
Each social media platform, community, organiza-
tion, and government defines hate speech differ-
ently (Fortuna and Nunes, 2018). Before develop-
ing our codebook, several definitions of hate speech
were studied, such as given by the EU code of
conduct (Wigand and Voin, 2017), ILGA (Europe,
2014), Nobata (Nobata et al., 2016), Facebook (Face-
book, 2024), YouTube (YouTube, 2024) and Twitter
(X.com, 2024).
Multiple definitions of hate speech have been pro-
posed. Nockleby defines hate speech as any commu-
nication that disparages a person or a group based
2
https://pytube.io/en/latest/
Hate Speech Detection Using Cross-Platform Social Media Data in English and German Language
133
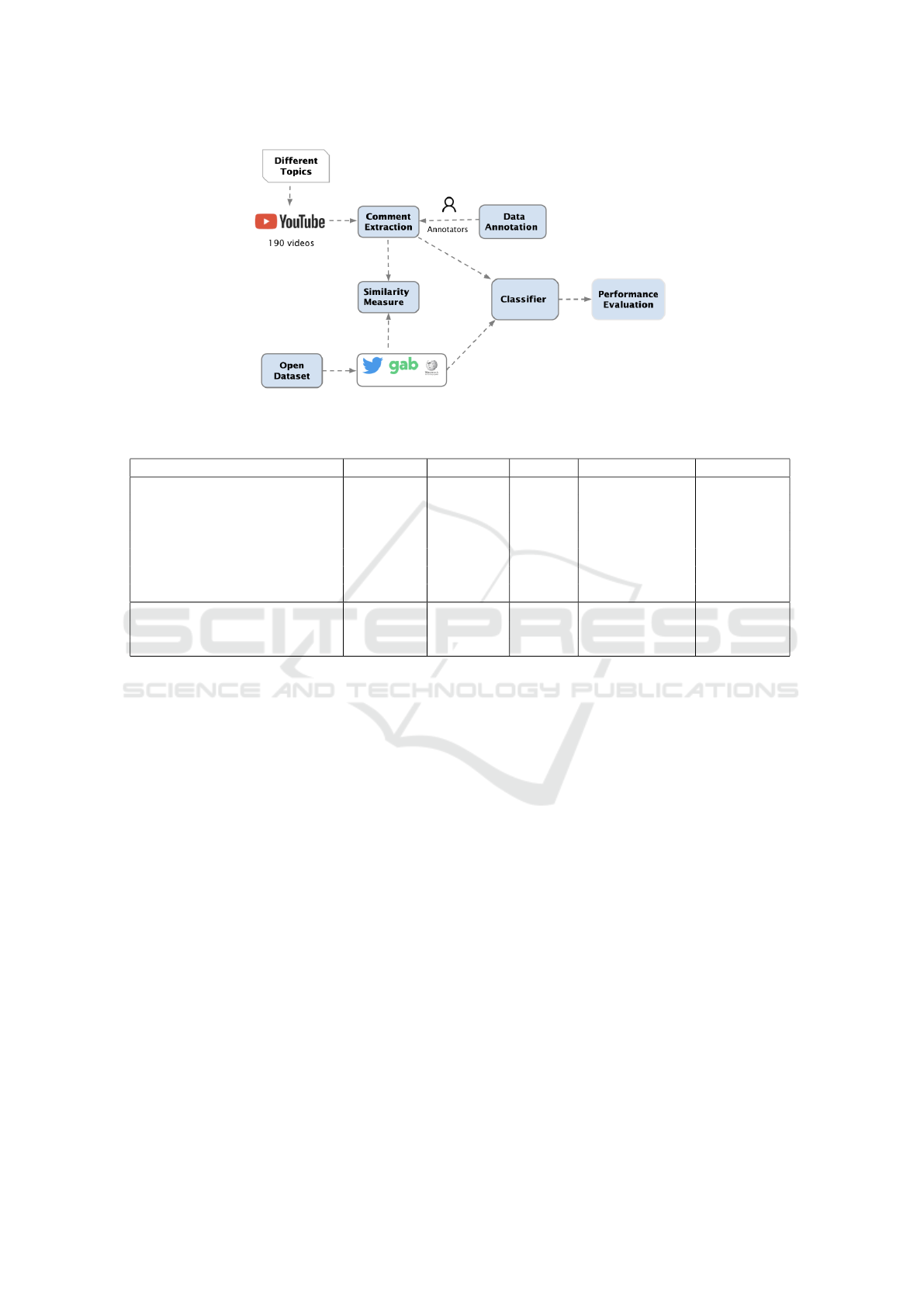
Figure 1: Methodolodoy used for the hate speech detection.
Table 1: Datasets compiled from different platforms in German and English.
Data set Language Platform Size % Hate speech Availability
EY1 English YouTube 1,892 37.36 Partial
ET1 (Mandl et al., 2019) English Twitter 7,005 16.31 Partial
ET2 (Davidson et al., 2017) English Twitter 24,783 5.77 Open
ET3 (Basile et al., 2019) English Twitter 12,971 42.10 Partial
ET4 (Waseem and Hovy, 2016) English Twitter 10,498 27.35 Partial
EW1 (AI, 2018) English Wikipedia 312,735 6.8 Open
EG1 (Gaffney, 2018) English Gab 27,265 8.4 Open
GY1 German YouTube 6,060 4.6 Partial
GT1 (Mandl et al., 2019) German Twitter 4,469 2.3 Partial
GT2 (Ross et al., 2016) German Twitter 470 11.7 Partial
on some characteristics such as race, color, ethnic-
ity, gender, sexual orientation, nationality, religion,
or other characteristics (Nockleby, 2000). Fortuna &
Nunes discuss the definition of hate speech, and the
criteria to remove it varies across each social media
platform (Fortuna and Nunes, 2018), ILGA Europe
(Europe, 2014) and code of conduct between Euro-
pean Union and companies (European Commission,
1999).
We found a lack of generic definitions that apply
to cross-platform and different languages. We, thus,
define hate speech as: Language that expresses prej-
udice against a person from a group (e.g., Barack
Obama for being black) or a particular group (such
as black people), primarily based on ethnicity, reli-
gion, or sexual orientation. The message should be
about a specific group based on skin color (e.g. black,
white), religion (e.g., Hindu, Muslim, Christian), gen-
der (e.g., male, female, non-binary), class (e.g. rich,
poor), ethnicity (e.g., Asian, European), sexual orien-
tation (e.g., lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender), na-
tionality (e.g., Indian, German), physical appearance
(e.g., beautiful, ugly, short, tall), disability (e.g. hand-
icapped) or disease (e.g., ill or fit).
The proposed definition was used to annotate hate
speech in YouTube comments. Annotators were pro-
vided with different sets of examples of hate speech
and non-hate speech in both languages. Three annota-
tors with a bachelor’s degree in computer science and
backgrounds in both languages carried out the annota-
tion process. We conducted a test annotation for both
languages and found that the number of hate speech
comments is less for German, so we randomly filtered
2000 and 6,500 comments for English and German.
While annotating, we also identify the hateful words
mentioned in the comment. The majority vote out
of three annotators is considered for the final label.
To measure the reliability among annotators, Cohen’s
kappa (McHugh, 2012) is used for intercoder reliabil-
ity. We got 1,892 English and 6,060 German YouTube
comments, resulting in Cohen’s kappa of 0.86, indi-
cating acceptable interrater reliability.
3.3 Similarity Measurement
We collected eight different datasets for evaluating
cross-platform bilingual classification models. Each
dataset was collected differently on various contro-
versial topics, so we computed the similarity among
datasets based on definition, hate words, and content
WEBIST 2024 - 20th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
134

as described below. The similarity measures are de-
cided based on the factors affecting the dataset, such
as the definition mentioned in the codebook, textual
content, and the number of hate words that are con-
tent and region-dependent.
Definition Similarity. Each dataset was anno-
tated based on a different codebook (extracted from
a scientific publication mentioning the dataset), so
we measured the similarity of the definition of hate
speech on each dataset. The annotation codebook sig-
nificantly affects the quality of annotated data. For the
definition similarity, we conducted an online study us-
ing Prolific (Prolific, 2024) as discussed in Section 4.
Content Similarity. We measured the similar-
ity between the content among two datasets. Con-
tent similarity indicates common words mentioned in
a different dataset. We used a sentence-transformer
model for computing the content similarity (Kazemi
et al., 2022). We converted text from each dataset
into vectors and simultaneously computed the cosine
similarity between the two datasets. The content sim-
ilarity measures the semantic similarity of datasets.
Hate Word Similarity. In hate speech detection,
the text contains hate words referring to a person or
group of people. First, we collected the hate words
from literature and added hate words from YouTube
comments defined by annotators. Using these hate
words, we filtered hate words from each dataset, com-
puted the intersection of hate words between two data
sets, and divided it by the total number of hate words
in the two datasets. It helps to analyze the similarity
of the presence of hateful content within two datasets.
The definition similarity score was calculated us-
ing user study; basic details were provided to partic-
ipants, and they were asked to vote for similarity on
a 10-point scale. Finally, we normalized the average
value using the formula (n-1)/9, where n is the aver-
age of the similarity score to show the similarity score
for the definition. For content similarity, we used sen-
tence embeddings of text as discussed by (Kazemi
et al., 2022); for hate words, we used text matching
using Python. A detailed description of all three sim-
ilarities is discussed in Section 4.
3.4 Classification Model
We followed the traditional natural language process-
ing (NLP) data cleaning technique method using the
Natural Language Toolkit (NLTK) library (Loper and
Bird, 2002). This includes removing short words (i.e.,
less than three characters), emails, and hyperlinks.
We used different machine models for the classi-
fication model, such as the Support Vector Machine
(SVM), Long short-term memory (LSTM), Logis-
tic Regression, and the state-of-the-art Bidirectional
encoder representations from transformers (BERT)
model. First, we used the annotated YouTube com-
ments and measured performance. Later, we added
the dataset in different combinations (from same and
cross-platform) to the YouTube comments and mea-
sured the performance of the classification model.
We evaluated the performance of the classification
model generated model in terms of precision, recall,
and F1. We provided the model evaluation for both
positive and negative classes.
4 EXPERIMENT AND RESULTS
We computed the similarity of datasets based on def-
inition, content, and hate words. All three measures
indicate the similarity of the different datasets con-
cerning YouTube comments. The goal is to find the
relationship between these similarities and classifica-
tion performance. The result obtained from similarity
measures is shown in Tables 2, 3, and 4 for English,
as well as 5 for German.
Definition Similarity. We conducted an online sur-
vey with 100 participants on Prolific. The participants
were from all over the globe, with an average age
of 26 years: 60% male and 40% female, 66% work-
ing professionals, and the remaining students. Out of
eight external datasets, only six defined hate speech
explicitly. A combination of two definitions from six
datasets, 15 combinations of definitions of similarity,
was provided to participants, and they were asked to
vote for similarity on a 10-point scale. Average votes
from 90 participants (10 participants were excluded
because their response time was too fast, indicating
they voted without really pondering about it) were
calculated to measure the similarity for each similar-
ity. Finally, we normalized the average value using
the formula (n-1)/9, where n is the average of the sim-
ilarity score to show the similarity of the definition
used in the data annotation. The result shows that the
definition used in English YouTube comments is sim-
ilar to the definition of ET4, followed by ET5.
For Hate Word Similarity: we filtered the hate
words mentioned in our datasets using Hurtlex
(Bassignana et al., 2018). We also screened the hate
words mentioned in other datasets. We computed
common hate words using text matching and repre-
sented the hate word similarity in percent. Based on
the hate word similarity, most datasets share similar
hate word datasets, and English Wikipedia contains
words that are more similar to EY1. However, EG1
contains the maximum number of similar hate words
in English, and GT2 is more similar to all datasets.
Hate Speech Detection Using Cross-Platform Social Media Data in English and German Language
135

So, for English, Gab has more hateful content, which
is not true for German.
For the Content Similarity: we converted each
dataset into a vector using the XLM-RoBERTa sen-
tence transformer model (Reimers and Gurevych,
2020) and computed the cosine similarity of each pair
of datasets. The content similarity indicates the over-
all common words present in different datasets con-
cerning our dataset. After computing the content sim-
ilarity, EG1 has maximum similarity to EY1 for En-
glish. For German, GT1 has a definition that is more
similar to GY1.
To implement classification models for traditional
machine learning models, SVM has been imple-
mented using the scikit-learn library (Pedregosa et al.,
2011). For LSTM, we applied Text-to-Sequences to
vectorize the data; for CNN, a Document-Term Ma-
trix was used. We used Hugging Face’s pre-trained
distilbert-base-uncased (DistilBERT base model (un-
cased), 2024) model for the BERT model. The BERT
model outperforms others, so the result and training
procedures describe the BERT model.
For training, we first used EY1 for English and
GY1 for German; we used 70% of the corpus for
training and the remaining 30% for testing. The test
dataset was kept separate for each dataset combina-
tion for evaluation. First, we trained the classifier for
EY1 and GY1 and tested the performance separately;
then, for further training, we added different datasets
along with the training set of EY1 and GY1 to keep
the test set the same for evaluation. The class distribu-
tion of each dataset except ET4 and EG1 was highly
imbalanced; most of the collected datasets needed to
be balanced. We used undersampling with equal class
distribution and the overall dataset for implementa-
tion because it gives better performance than the orig-
inal dataset. We noted the number of hate classes
and randomly filtered the same number from non-hate
classes.
We used a pre-trained BERT model with fine-
tuning as a learning rate 3e
−5
, batch size of 32, and
sequence length of 128 to six epochs. We report the
precision, recall, and F1 scores in both classes. In Ta-
ble 6, we present the result obtained from the classi-
fication model on different combinations of datasets:
Adding more datasets helps in increasing precision,
recall, and F1 score. We emphasized the maximum
score obtained for the evaluation measures as bold in
Table 6. The Table presents results from the best com-
binations of datasets for the BERT model only.
5 DISCUSSION
Collecting the data set from the social media plat-
form and annotating the data is time-consuming. To
overcome the problem, we collected and annotated
YouTube comments built a classification model, and
further used the existing dataset for training. To mea-
sure the role of the additional datasets in the perfor-
mance of the classifier, we looked at literature works
for finding datasets. However, only a few research
share datasets as open-access. Even when it is par-
tially available (for instance, only the tweet IDs in
Twitter (X) data sets), the user needs to write a pro-
gram to collect the data or have access to an existing
one and know how to use it. With time, many social
media posts are deleted by either social media plat-
forms or users (cf. e.g. (Waseem, 2016)). We could
crawl only 10,498 out of 16,914 labeled entries. Due
to platform restrictions from YouTube, prior work did
not share users’ comments publicly which makes it
difficult to explore the performance of the classifier
by adding users’ comments from other hate speech.
A publicly accessible dataset will ease the workload
to detect hate speech on social media.
During content similarity, we observed that a
dataset that contains hate speech on general topics
such as sexism, racism, targeted populations, vulgar-
ity, and framing helps to improve the performance of
the classification model. We found that Class imbal-
ance is a problem for hate speech detection; so far, all
data sets are imbalanced. We observed that under-
sampling data with an equal distribution of classes
gives better results.
We have evaluated the role of additional datasets
for the performance of the classifier on different crite-
ria. For English datasets, based on the similarity mea-
sure, Definition Similarity often improves the clas-
sifier performance. For example, ET3 is very sim-
ilar to EY1, but EG1 is dissimilar, and it still im-
proves classification performance as a precision of
hate class. There is no direct relation in the perfor-
mance model that a dataset with a similar definition
gives the highest precision. Content Similarity is di-
rectly related to enhancing the performance of the
classification model; ET4 from the same platform im-
proves the classification model, while the EG1 from
cross-platform has the maximum similarity with EY1,
which enhances the overall performance of the mode.
So, there is a direct relation; the similar content im-
proves the performance. Hate word Similarity also
does not help to conclude that EW1 does not improve
the performance but hate word similarity with content
similarity, and the performance increases such as EG1
increases the performance.
WEBIST 2024 - 20th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
136
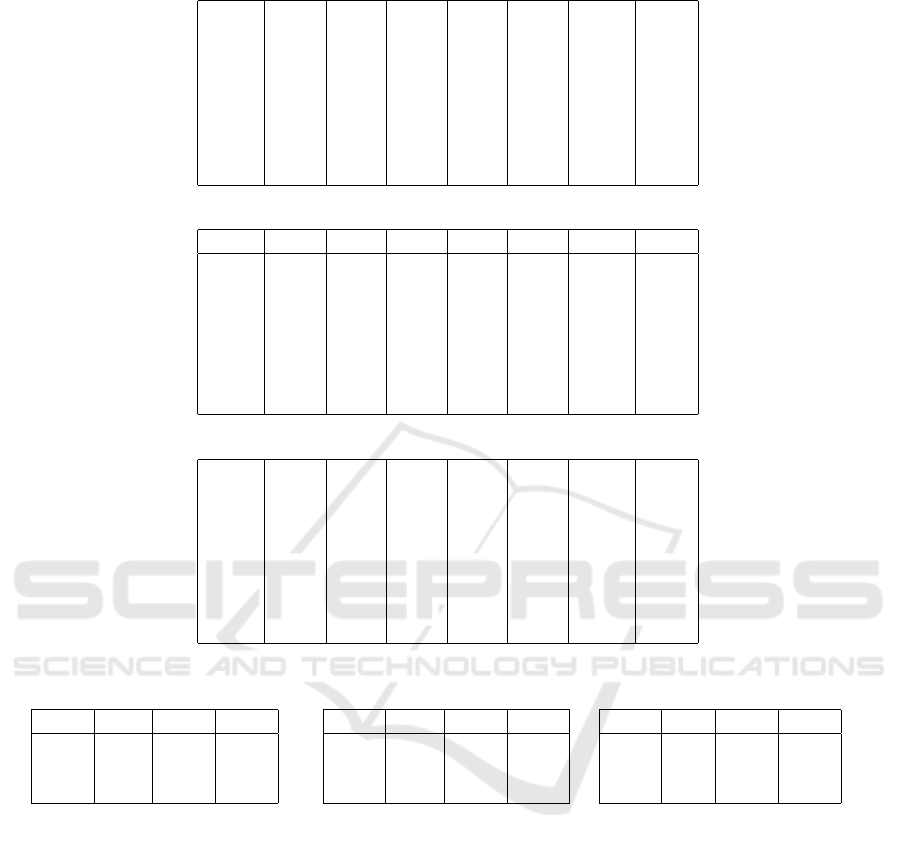
Table 2: Content similarity measures for the English dataset.
EY1 ET1 ET2 ET3 ET4 EW1 EG1
EY1 1.00 0.31 0.29 0.36 0.44 0.47 0.56
ET1 1.00 0.15 0.77 0.28 0.24 0.73
ET2 1.00 0.49 0.43 0.30 0.35
ET3 1.00 0.38 0.30 0.72
ET4 1.00 0.53 0.63
EW1 1.00 0.54
EG1 1.00
Table 3: Hate word similarity measures for the English dataset.
EY1 ET1 ET2 ET3 ET4 EW1 EG1
EY1 1.00 0.72 0.88 0.86 0.78 0.92 0.91
ET1 1.00 0.71 0.75 0.73 0.77 0.80
ET2 1.00 0.83 0.84 0.89 0.88
ET3 1.00 0.83 0.89 0.90
ET4 1.00 0.83 0.84
EW1 1.00 0.92
EG1 1.00
Table 4: Definition similarity measures for the English dataset.
EY1 ET1 ET2 ET3 ET4 EW1 EG1
EY1 X 0.66 0.63 0.76 0.70 X 0.56
ET1 X 0.64 0.72 0.62 X 0.57
ET2 X 0.64 0.63 X 0.63
ET3 X 0.61 X 0.59
ET4 X X 0.59
EW1 X X
EG1 X
Table 5: Similarity measures for the German dataset.
a) Content Similarity
GY GT1 GT2
GY 1.00 0.14 0.10
GT1 1.00 0.11
GT2 1.00
b) Hateword Similarity
GY GT1 GT2
GY 1.00 0.35 0.24
GT1 1.00 0.10
GT2 1.00
c) De f inition Similarity
GY GT1 GT2
GY X 0.56 0.44
GT1 X 0.54
GT2 X
However, for German, based on the similarity in
content, the performance of the classifier improved
by adding GT1. The same trend follows for the hate
word similarity and definition similarity. However,
the similarity between datasets regarding content and
hate words is less than that of English.
Therefore, if the dataset is similar in terms of sim-
ilarity measures, additional data improves the perfor-
mance of the classification model. Overall, data anno-
tation is a key challenge, but combining datasets hav-
ing a similar issue with similar content and hate words
improves the classification performance. A heuristic
combination of a balanced dataset could improve pre-
cision, recall, and f1-score. There is no direct relation
in increasing the dataset from the same platform, but
cross-platform datasets improve performance, such as
ET4 and EG1, jointly improving recall and F1-score.
In this study, the classification model was based on the
traditional machine learning approach; however, the
performance might change if a large language model
such as ChatGPT is applied. LLMs are pre-trained on
vast amounts of data from the web, which might cap-
ture deeper contextual and semantic interpretations of
the text. By fine-tuning an LLM on the specific task,
the classification model could better handle complex-
ities, which could potentially lead to better perfor-
mance than traditional methods.
Improvements to hate speech detection will ulti-
mately have organizational and social consequences.
If detecting hate speech is easier, there will be less
room for social media platforms to not remove hate-
ful content. The consequences this will have on social
media users – those affected by hate speech, those be-
ing “bystanders”, and those posting hate speech – will
Hate Speech Detection Using Cross-Platform Social Media Data in English and German Language
137
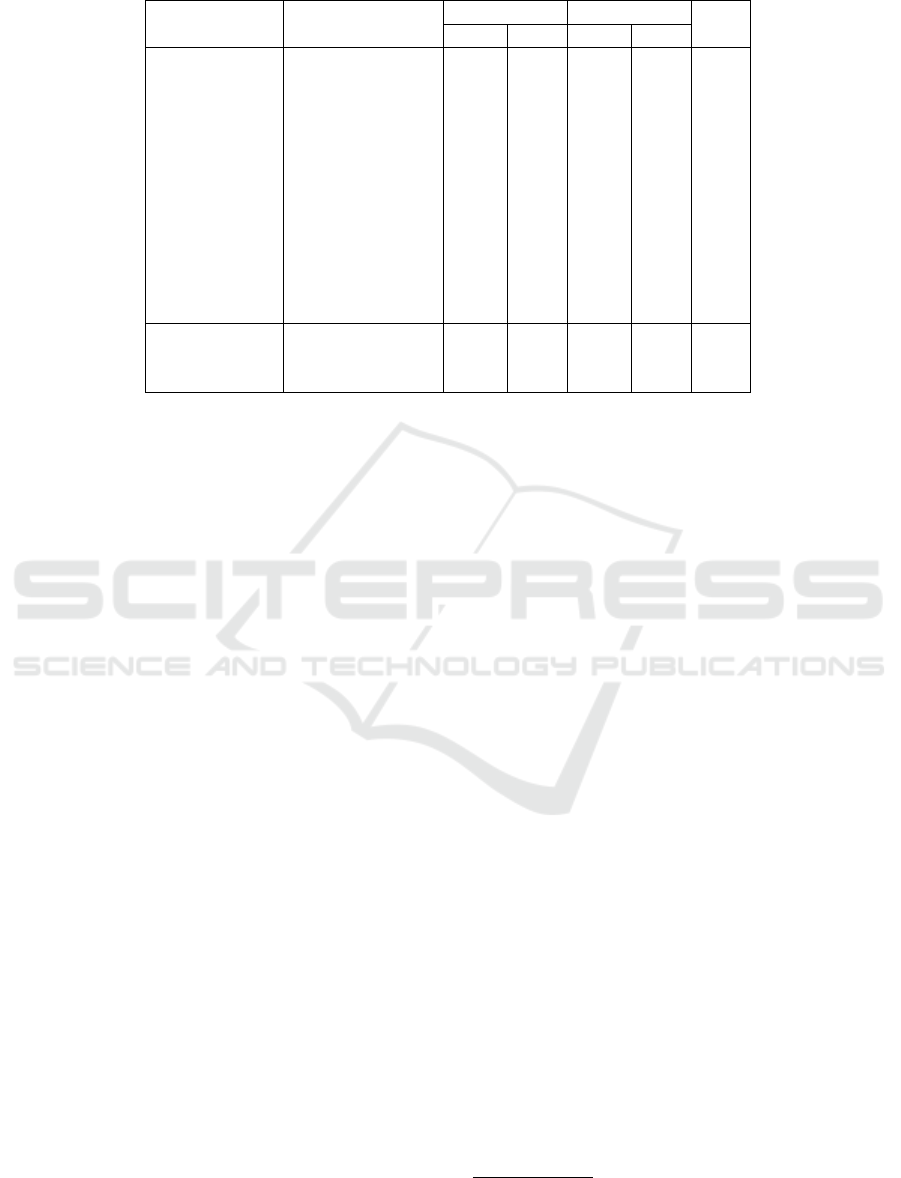
Table 6: Summary of the Precision, Recall, F1 Score of classification model.
Target Dataset Trainig Datasets
Non-Hate Hate
F1
Prec. Rec. Prec. Rec.
EY1 EY1 0.67 0.55 0.62 0.73 0.64
EY1 EY1+ET1 0.72 0.14 0.52 0.95 0.51
EY1 EY1+ET2 0.61 0.87 0.77 0.43 0.64
EY1 EY1+ET3 0.60 0.93 0.84 0.38 0.62
EY1 EY1+ET4 0.79 0.67 0.71 0.82 0.74
EY1 EY1+EW1 0.55 0.86 0.68 0.30 0.54
EY1 EY1+EG1 0.80 0.57 0.67 0.85 0.71
EY1 EY1+ET1+ET4 0.70 0.73 0.72 0.69 0.71
EY1 EY1+ET2+ET4 0.71 0.66 0.69 0.73 0.70
EY1 EY1+ET3+ET4 0.54 0.88 0.68 0.26 0.52
EY1 EY1+ET4+EW1 0.81 0.47 0.63 0.89 0.66
EY1 EY1+ET4+EG1 0.83 0.61 0.69 0.87 0.74
GY1 GY1 0.77 0.60 0.67 0.82 0.71
GY1 GY1+GT1 0.82 0.38 0.59 0.92 0.62
GY1 GY1+GT1+GT2 0.72 0.60 0.66 0.76 0.68
need to be targeted by further research. The conse-
quences of potentially many posts being deleted are
not clear, either. However, neither removal nor de-
tection changes much of the roots of hate speech sur-
facing on social media. While the work we present
here is mainly technological in nature, countering
hate speech requires truly interdisciplinary efforts.
6 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
WORK
In this study, we presented hate speech detection on
YouTube comments and explored the classification
model by adding external data from the same plat-
form and cross-platform in English and German. We
provided datasets with 1,892 and 6,060 English and
German human-annotated. We tested the combina-
tion of different data sets and measured performance
in terms of precision, recall, and F1 score. Along with
the performance metric, we have used similarity mea-
sures to conclude the role of the external datasets in
enhancing classifier performance.
We also measured the similarity metrics to find the
relationship between additional data and with perfor-
mance of the classification model. We computed the
similarity of datasets based on definition, content, and
hate words and explored their importance for the clas-
sification models. Overall, the results show the per-
formance of the hate speech classifier gets improved
by adding an existing hate speech dataset and differ-
ent patterns for both languages, especially if datasets
are similar.
The practical application of this approach is to cre-
ate a generalized classification model for hate speech
detection over bilingual cross-platform. Our approach
can be tested with a heuristic dataset combination in
future work. One of the further extensions of our
work is to extend to use of additional datasets in dif-
ferent languages, such as Spanish and Italian. An-
other extension could be multi-class hate speech clas-
sification with classes such as hate speech, offensive,
or profane.
DATA SHARING
We have conducted all experiments on a macro level
following strict data access, storage, and auditing pro-
cedures for the sake of accountability. Following the
guidelines of the YouTube data-sharing policy, we
will release comment IDs, YouTube video IDs, and
a replication package to download the data. We share
the link to the existing dataset for the data collected
from another source at GitHub
3
.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We thank our annotators, Alexander Kocur and Jes-
sica Priesmeyer for completing the annotating task.
3
https://github.com/Gautamshahi/BilingualYouTube
HateSpeech
WEBIST 2024 - 20th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
138

REFERENCES
Aggarwal, P., Horsmann, T., Wojatzki, M., and Zesch, T.
(2019). Ltl-ude at semeval-2019 task 6: Bert and two-
vote classification for categorizing offensiveness. In
Proceedings of the 13th International Workshop on
Semantic Evaluation, pages 678–682.
AI, J. (2018). Toxic Comment Classification Challenge.
Al-Hassan, A. and Al-Dossari, H. (2019). Detection of hate
speech in social networks: a survey on multilingual
corpus. In 6th International Conference on Computer
Science and Information Technology.
Aslan, A. (2017). Online hate discourse: A study on hatred
speech directed against syrian refugees on youtube.
Journal of Media Critiques, 3(12):227–256.
Basile, V., Bosco, C., Fersini, E., Nozza, D., Patti, V.,
Pardo, F. M. R., Rosso, P., and Sanguinetti, M. (2019).
Semeval-2019 task 5: Multilingual detection of hate
speech against immigrants and women in twitter. In
Proceedings of the 13th International Workshop on
Semantic Evaluation, pages 54–63.
Bassignana, E., Basile, V., and Patti, V. (2018). Hurtlex:
A multilingual lexicon of words to hurt. In 5th Ital-
ian Conference on Computational Linguistics, CLiC-
it 2018, volume 2253, pages 1–6. CEUR-WS.
Bayer, J. and Petra, B. (2020). Hate speech and hate crime
in the eu and the evaluation of online content regula-
tion approaches. EPRS: European Parliamentary Re-
search Service.
Ben-David, A. and Matamoros-Fern
´
andez, A. (2016). Hate
speech and covert discrimination on social media:
Monitoring the facebook pages of extreme-right po-
litical parties in spain. International Journal of Com-
munication, 10:1167–1193.
Charalampakis, B., Spathis, D., Kouslis, E., and Ker-
manidis, K. (2016). A comparison between semi-
supervised and supervised text mining techniques on
detecting irony in greek political tweets. Engineering
Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 51:50–57.
Davidson, T., Warmsley, D., Macy, M., and Weber, I.
(2017). Automated hate speech detection and the
problem of offensive language. In Eleventh interna-
tional aaai conference on web and social media.
Del Vigna, F., Cimino, A., Dell’Orletta, F., Petrocchi,
M., and Tesconi, M. (2017). Hate me, hate me
not: Hate speech detection on facebook. Proceed-
ings of the First Italian Conference on Cybersecurity
(ITASEC17), Venice, Italy.
Di F
´
atima, B., Munoriyarwa, A., Gilliland, A., Msughter,
A. E., Vizca
´
ıno-Verd
´
u, A., G
¨
okaliler, E., Capoano,
E., Yu, H., Alikılıc¸,
˙
I., Gonz
´
alez-Aguilar, J.-M., et al.
(2023). Hate Speech on Social Media: A Global Ap-
proach. Pontificia Universidad Cat
´
olica del Ecuador.
DistilBERT base model (uncased) (2024).
https://huggingface.co/distilbert/distilbert-base-
uncased.
D
¨
oring, N. and Mohseni, M. R. (2019). Fail videos and
related video comments on youtube: a case of sexu-
alization of women and gendered hate speech? Com-
munication research reports, 36(3):254–264.
D
¨
oring, N. and Mohseni, M. R. (2020). Gendered hate
speech in youtube and younow comments: Results of
two content analyses. SCM Studies in Communication
and Media, 9(1):62–88.
Europe, I. (2014). Hate crime & hate speech retrieved from.
European Commission (1999). Speech by Commissioner
Jourov
´
a - 10 years of the EU Fundamental Rights
Agency: a call to action in defence of fundamental
rights, democracy and the rule of law retrieved from.
Facebook (2024). How do i report inap-
propriate or abusive things on facebook.
https://www.facebook.com/help/212722115425932.
Fortuna, P. and Nunes, S. (2018). A survey on automatic
detection of hate speech in text. ACM Computing Sur-
veys (CSUR), 51(4):85.
Gaffney, D. (2018). The pushshift Gab dataset.
Jahan, M. S. and Oussalah, M. (2023). A systematic re-
view of hate speech automatic detection using natural
language processing. Neurocomputing, page 126232.
Joulin, A., Grave, E., Bojanowski, P., Douze, M., J
´
egou,
H., and Mikolov, T. (2016). Fasttext.zip: Com-
pressing text classification models. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1612.03651.
Kazemi, A., Garimella, K., Shahi, G. K., Gaffney, D., and
Hale, S. A. (2022). Research note: Tiplines to uncover
misinformation on encrypted platforms: A case study
of the 2019 indian general election on whatsapp. Har-
vard Kennedy School Misinformation Review.
Li, L., Fan, L., Atreja, S., and Hemphill, L. (2023). ”hot”
ChatGPT: The promise of chatgpt in detecting and dis-
criminating hateful, offensive, and toxic comments on
social media. arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.10619.
Liu, P., Li, W., and Zou, L. (2019). Nuli at semeval-2019
task 6: transfer learning for offensive language detec-
tion using bidirectional transformers. In Proceedings
of the 13th International Workshop on Semantic Eval-
uation, pages 87–91.
Loper, E. and Bird, S. (2002). Nltk: the natural language
toolkit. arXiv preprint cs/0205028.
Malmasi, S. and Zampieri, M. (2017). Detecting hate
speech in social media. In Proceedings of the Inter-
national Conference Recent Advances in Natural Lan-
guage Processing, RANLP 2017, pages 467–472.
Mandl, T., Modha, S., Majumder, P., Patel, D., Dave, M.,
Mandlia, C., and Patel, A. (2019). Overview of the
hasoc track at fire 2019: Hate speech and offensive
content identification in indo-european languages. In
Proceedings of the 11th Forum for Information Re-
trieval Evaluation, pages 14–17.
McHugh, M. L. (2012). Interrater reliability: the kappa
statistic. Biochemia medica, 22(3):276–282.
Nobata, C., Tetreault, J., Thomas, A., Mehdad, Y., and
Chang, Y. (2016). Abusive language detection in on-
line user content. In Proceedings of the 25th interna-
tional conference on world wide web, pages 145–153.
Nockleby, J. T. (2000). Hate speech. Encyclopedia of the
American constitution, 3:1277–1279.
Ousidhoum, N., Lin, Z., Zhang, H., Song, Y., and Ye-
ung, D.-Y. (2019). Multilingual and multi-aspect hate
Hate Speech Detection Using Cross-Platform Social Media Data in English and German Language
139

speech analysis. In Proceedings of the 2019 Con-
ference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language
Processing and the 9th International Joint Conference
on Natural Language Processing (EMNLP-IJCNLP),
pages 4675–4684.
Pedregosa, F., Varoquaux, G., Gramfort, A., Michel, V.,
Thirion, B., Grisel, O., Blondel, M., Prettenhofer,
P., Weiss, R., Dubourg, V., Vanderplas, J., Passos,
A., Cournapeau, D., Brucher, M., Perrot, M., and
Duchesnay, E. (2011). Scikit-learn: Machine learning
in Python. Journal of Machine Learning Research,
12:2825–2830.
Poletto, F., Basile, V., Sanguinetti, M., Bosco, C., and Patti,
V. (2021). Resources and benchmark corpora for hate
speech detection: a systematic review. Language Re-
sources and Evaluation, 55:477–523.
Prolific (2024). www.prolific.com.
Reimers, N. and Gurevych, I. (2020). Making monolin-
gual sentence embeddings multilingual using knowl-
edge distillation. In Proceedings of the 2020 Confer-
ence on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Pro-
cessing (EMNLP), pages 4512–4525.
R
¨
ochert, D., Neubaum, G., Ross, B., Brachten, F., and
Stieglitz, S. (2020). Opinion-based homogeneity on
youtube. Computational Communication Research,
2(1):81–108.
R
¨
ochert, D., Shahi, G. K., Neubaum, G., Ross, B., and
Stieglitz, S. (2021). The networked context of covid-
19 misinformation: informational homogeneity on
youtube at the beginning of the pandemic. Online So-
cial Networks and Media, 26:100164.
Ross, B., Rist, M., Carbonell, G., Cabrera, B., Kurowsky,
N., and Wojatzki, M. (2016). Measuring the Reliabil-
ity of Hate Speech Annotations: The Case of the Eu-
ropean Refugee Crisis. In Beißwenger, M., Wojatzki,
M., and Zesch, T., editors, Proceedings of NLP4CMC
III: 3rd Workshop on Natural Language Processing
for Computer-Mediated Communication, volume 17
of Bochumer Linguistische Arbeitsberichte, pages 6–
9, Bochum.
Salminen, J., Hopf, M., Chowdhury, S. A., Jung, S.-g.,
Almerekhi, H., and Jansen, B. J. (2020). Develop-
ing an online hate classifier for multiple social media
platforms. Human-centric Computing and Informa-
tion Sciences, 10(1):1.
Shahi, G. K. and Kana Tsoplefack, W. (2022). Mitigating
harmful content on social media using an interactive
user interface. In Social Informatics: 13th Interna-
tional Conference, SocInfo 2022, Glasgow, UK, Pro-
ceedings, pages 490–505. Springer.
Shahi, G. K. and Majchrzak, T. A. (2022). Amused: an an-
notation framework of multimodal social media data.
In Intelligent Technologies and Applications: 4th In-
ternational Conference, INTAP 2021, Grimstad, Nor-
way, October 11–13, 2021, Revised Selected Papers,
pages 287–299. Springer.
Siegel, A. A. (2020). Online hate speech. Social media
and democracy: The state of the field, prospects for
reform, pages 56–88.
Stoll, A., Ziegele, M., and Quiring, O. (2020). Detecting in-
civility and impoliteness in online discussions. Com-
putational Communication Research, 2(1):109–134.
Wang, S. and Kim, K. J. (2023). Content moderation on
social media: does it matter who and why moderates
hate speech? Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social
Networking, 26(7):527–534.
Waseem, Z. (2016). Are you a racist or am i seeing things?
annotator influence on hate speech detection on twit-
ter. In Proceedings of the first workshop on NLP and
computational social science, pages 138–142.
Waseem, Z. and Hovy, D. (2016). Hateful symbols or hate-
ful people? predictive features for hate speech detec-
tion on twitter. In Proceedings of the NAACL student
research workshop, pages 88–93.
Wei, X., Lin, H., Yang, L., and Yu, Y. (2017).
A convolution-lstm-based deep neural network for
cross-domain mooc forum post classification. Infor-
mation, 8(3):92.
Wigand, C. and Voin, M. (2017). Speech by commis-
sioner jourov
´
a—10 years of the eu fundamental rights
agency: A call to action in defence of fundamental
rights, democracy and the rule of law.
Wullach, T., Adler, A., and Minkov, E. (2020). Towards
hate speech detection at large via deep generative
modeling. IEEE Internet Computing, 25(2):48–57.
X.com (2024). The twitter rules.
https://help.twitter.com/en/rules-and-policies/x-rules.
YouTube (2024). Hate speech policy: Youtube community
guidelines.
Yuan, L., Wang, T., Ferraro, G., Suominen, H., and Rizoiu,
M.-A. (2023). Transfer learning for hate speech detec-
tion in social media. Journal of Computational Social
Science, 6(2):1081–1101.
Zampieri, M., Malmasi, S., Nakov, P., Rosenthal, S., Farra,
N., and Kumar, R. (2019). Semeval-2019 task 6: Iden-
tifying and categorizing offensive language in social
media (offenseval). In Proceedings of the 13th In-
ternational Workshop on Semantic Evaluation, pages
75–86.
WEBIST 2024 - 20th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
140
