
Enhancing Post-Incarceration Support: A Custom Chatbot Solution for
the Brazilian Prison System
Geovana Ramos Sousa Silva
a
, Lurian Correia Lima, Guilherme Pereira Paiva
and Edna Dias Canedo
b
University of Bras
´
ılia (UnB), Department of Computer Science, Bras
´
ılia–DF, Brazil
Keywords:
Chatbot, Conversational Interface, Social Support.
Abstract:
This paper presents the development and implementation of a dedicated chatbot to assist former inmates of the
Brazilian prison system, integrated into the ESVirtual application. This initiative addresses the multifaceted
challenges faced by this vulnerable group by providing a comprehensive and sustainable approach to support
their social reintegration. The proposed architecture leverages Docker Compose, Rasa NLU, Stories, and
Actions, creating a robust and scalable framework capable of understanding natural language, adapting to
diverse interaction scenarios, and executing customized actions. By integrating the chatbot into ESVirtual, we
enhance its utility and accessibility, offering former inmates a reliable and accessible channel for obtaining
information and support. The decision to manually craft the chatbot’s content, rather than using generative AI,
ensures the accuracy, relevance, and reliability of the provided information, allowing for quick adaptation to
changes in policies, legislation, and available services. Socially, this project aims to significantly contribute
to the reintegration of former inmates into society, reducing recidivism rates and fostering a more just and
inclusive community. By providing essential support and resources, the chatbot empowers individuals to
overcome the challenges they face after leaving the prison system and to build dignified and productive lives.
This work underscores the potential of technology and innovation to promote social well-being and justice,
marking a significant step towards a more humanized approach to former inmates reintegration in Brazil.
1 INTRODUCTION
In Brazil, the issue of reintegrating former inmates is
a multifaceted challenge that requires a holistic and
innovative approach. The transition of individuals
who have served their sentences back into society is
often marked by a series of obstacles, ranging from
stigmatization to lack of access to employment oppor-
tunities, adequate housing, education, and healthcare
(Storck, 2023; Tharshini et al., 2024). These chal-
lenges significantly contribute to the high recidivism
rates in the country.
In this context, there is a need to develop effec-
tive solutions that can support former inmates in their
journey of social reintegration. Among these solu-
tions, technology plays a crucial role, providing ac-
cessible and scalable tools that can meet the diverse
needs of this vulnerable group (Dores and Dores,
2019).
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0304-0804
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2159-339X
This project proposes the development of a chat-
bot dedicated exclusively to providing information
and support to former inmates of the Brazilian prison
system and introduced through an existing app for
their assistance (Canedo et al., 2024). A chatbot is
an artificial intelligence application designed to simu-
late human conversations, offering automatic and in-
teractive responses to users’ questions and requests
(Al Husaeni et al., 2024).
By using a chatbot, it is expected to offer former
inmates a reliable source of information and guid-
ance, available at any time and place through mobile
devices or computers connected to the internet. This
is particularly relevant given the difficulties former in-
mates face in accessing traditional support and coun-
seling services, often limited by geographical, finan-
cial, or social stigma barriers (Benard et al., 2023).
The proposed chatbot will provide a variety of
resources and functionalities, including guidance on
their legal rights, information on reintegration pro-
grams, access to employment and education oppor-
tunities, emotional support, and connection to rele-
Silva, G. R. S., Lima, L. C., Paiva, G. P. and Canedo, E. D.
Enhancing Post-Incarceration Support: A Custom Chatbot Solution for the Brazilian Prison System.
DOI: 10.5220/0013086800003929
In Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS 2025) - Volume 1, pages 423-433
ISBN: 978-989-758-749-8; ISSN: 2184-4992
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
423

vant social services. By offering this comprehensive
support, the chatbot aims to empower former inmates,
helping them overcome the challenges they face dur-
ing the reintegration process. It is believed that by
promoting autonomy, confidence, and access to es-
sential resources, the chatbot can help its users to rein-
tegrate themselves into society and reduce recidivism.
2 BACKGROUND
2.1 ESVirtual
In 2021, the CNJ launched the Social Office Virtual
(ESVirtual) app (UNDP, 2024), which aims to ex-
pand the reach and enhance the availability of ser-
vices for individuals reintegrating from the prison
system. It complements the in-person assistance pro-
vided at Social Offices, which are present in 17 states,
and the psychosocial services offered prior to release,
especially during the Covid-19 pandemic (Canc¸ado
et al., 2022). The app uses georeferencing to help
users locate social public service facilities, including
healthcare units, social services, shelters, community
restaurants, legal aid centers, and civil documentation
offices (Portal CNJ, 2022).
The app is also integrated with the Unified Elec-
tronic Execution System (SEEU), allowing former in-
mates and their families to track the progress of their
sentences quickly and easily through the app (Portal
CNJ, 2022). Additionally, it offers free courses in
various fields of knowledge and content specifically
focused on job and income generation. Beyond its
diverse range of services, the app aims to boost the
implementation of physical Social Offices, which are
currently established in over 20 municipalities across
the country. The Social Office Virtual app is available
for both Android and iOS devices (PlayStore, 2024)
and its interface is shown in Figure 1.
2.2 Chatbot
A chatbot is an artificial intelligence (AI) software
designed to simulate human-like conversation with
users through text or voice interactions (Al Husaeni
et al., 2024; Silva and Canedo, 2024; Gonc¸alves et al.,
2024). Chatbots are increasingly popular due to their
ability to provide instant responses, handle multiple
queries simultaneously, and operate 24/7, thereby en-
hancing user experience and operational efficiency
(Misischia et al., 2022). There are two primary types
of chatbots: generative and retrieval-based (Pandey
and Sharma, 2023).
Figure 1: ESVirtual app.
Generative chatbots use machine learning algo-
rithms, particularly neural networks, to generate re-
sponses in real-time (Pandey and Sharma, 2023).
These chatbots are capable of producing more flex-
ible and varied responses as they do not rely on pre-
defined scripts. However, they require extensive train-
ing data and computational power, and their responses
can sometimes be unpredictable or less accurate.
Retrieval-based chatbots, on the other hand, oper-
ate by selecting the most appropriate response from a
set of predefined replies (Bachtiar et al., ). They lever-
age machine learning models to match user queries
with the best possible answers from a database. While
they may lack the flexibility of generative models,
retrieval-based chatbots are generally more reliable
and easier to control, making them suitable for many
practical applications.
One of the most widely used frameworks for
building retrieval-based chatbots is Rasa. Rasa is an
open-source framework that provides tools for devel-
oping and managing conversational AI applications
(Joshi and Sharma, 2020). It supports both intent
ICEIS 2025 - 27th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
424

recognition and entity extraction, enabling developers
to create sophisticated dialogue systems. The choice
of Rasa can be justified by its robust architecture, ac-
tive community support, and the flexibility it offers in
customizing and deploying chatbots (Dagkoulis and
Moussiades, 2022). Additionally, Rasa’s ability to in-
tegrate with various messaging platforms and APIs
makes it a versatile choice for building chatbots tai-
lored to specific business needs.
2.3 Related Work
Brazil has seen a growing interest in the development
of chatbots aimed at addressing various social issues,
particularly in health, education, and community en-
gagement. These initiatives leverage artificial intel-
ligence and natural language processing to facilitate
communication and provide essential services to di-
verse populations.
In response to the COVID-19 pandemic, a chatbot
was developed by a large telehealth service in Brazil
to assist with screening and monitoring (Chagas et al.,
2023). This chatbot provided users with evidence-
based information regarding COVID-19 symptoms
and facilitated web-based assessments of symptom
severity. Evaluations conducted through a mixed-
methods approach highlighted the usability of the
chatbot, revealing strengths and areas for improve-
ment based on user feedback. This initiative show-
cased the potential of chatbots to deliver timely health
information and support public health efforts during a
crisis. Key challenges included ensuring the chatbot
provided accurate, up-to-date information and creat-
ing a user-friendly interface for a wide range of users.
Adapting the chatbot to the Portuguese language and
cultural context was likely crucial for its success.
Another significant project is the Amanda Selfie
chatbot (Massa et al., 2023), designed specifically to
create demand for pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP)
among adolescent men who have sex with men
(AMSM) and transgender women in Brazil. Devel-
oped through a participatory process that included in-
put from the target demographic, Amanda Selfie func-
tions as a virtual peer educator. The chatbot’s design
reflects cultural sensitivity, as it embodies a Black
transgender woman, making it relatable to its audi-
ence. The development process spanned 21 months
and involved rigorous testing to assess acceptabil-
ity, functionality, and usability. The results indicated
that Amanda effectively increased awareness and de-
mand for PrEP services among adolescents, illustrat-
ing the power of targeted digital interventions in pub-
lic health.
The work of (Tueiv and Schmitz, 2023) focused
on optimizing the value delivered by Chatbots, a cru-
cial tool in the digitalization of government services.
By applying the Incremental Funding Method (IFM)
alongside the Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP)
technique, the study developed a method tailored to
the unique characteristics of Chatbot and Machine
Learning projects. The approach demonstrated that,
using a customized optimization delivery sequencing
method, Chatbot-enabled services, such as those im-
plemented in the Institute of Social Security and Pen-
sion of Brazil (INSS) application, couldcan enhance
the efficiency and effectiveness of government ser-
vices. This research highlights the significant role of
Chatbots in advancing digital inclusion and accelerat-
ing the transformation of government services to bet-
ter serve citizens.
IAraBot is an architectural model and proactive
chatbot developed to detect misinformation in real-
time on WhatsApp and Telegram in Brazil (Cacabro
et al., 2023). The chatbot aims to provide media
education and help users critically evaluate content.
Key challenges include accurately identifying misin-
formation, providing relevant examples and explana-
tions in Portuguese, and encouraging users to develop
critical thinking skills. Adapting the chatbot’s lan-
guage and approach to different age groups and edu-
cation levels is also important.
The work of (Andrade et al., 2020b) presents a
novel approach to enhancing user support for the
EV.G platform through the development of a special-
ized chatbot. This chatbot is designed to handle fre-
quently asked questions and reduce the burden on
human support staff by utilizing an architecture that
adapts to new information and user requests. Lever-
aging open-source tools customized for EV.G’s needs,
the chatbot, named Eva, aims to improve service qual-
ity by providing rapid responses, which is crucial
for customer satisfaction. Notably, EvaTalk is tasked
with understanding and processing Portuguese writ-
ten text, including its variations and informal usage
such as shortcuts, misspellings, and acronyms often
encountered in online communication. These chal-
lenges are underscored by the need for the chatbot
to handle the diverse linguistic expressions used by
users, which deviates from standard Portuguese and
impacts the coherence of interactions. Despite its ca-
pabilities in managing repetitive queries, EvaTalk’s
effectiveness is contingent on addressing these lan-
guage complexities and ensuring that more intricate
issues are escalated to human support.
These examples highlight the innovative use of
chatbots in Brazil for social purposes, demonstrat-
ing their potential to enhance communication, pro-
mote health awareness, and improve access to essen-
Enhancing Post-Incarceration Support: A Custom Chatbot Solution for the Brazilian Prison System
425

tial services. Developing chatbots for Portuguese in-
volves overcoming a range of challenges due to the
language’s diverse dialects, regional variations, and
cultural nuances (D’
´
Avila, 2018). Portuguese is spo-
ken across multiple countries, each with distinct vo-
cabularies and idiomatic expressions, making it diffi-
cult for chatbots to universally understand and gen-
erate appropriate responses. These challenges are
compounded by varying cultural expectations; for in-
stance, among Brazilian users and Portuguese users
(Thom
´
e-Williams, 2004). Still, language-specialized
models have a tendency to perform worse than multi-
lingual models (Shaitarova et al., 2023).
Additionally, the grammatical complexities of
Portuguese, such as gendered nouns and intricate verb
conjugations (Wilkens et al., 2024), pose significant
hurdles for chatbots in accurately interpreting and re-
sponding to user inputs. The scarcity of high-quality,
annotated datasets for Portuguese further hampers the
development of robust natural language processing
models (Trajano et al., 2023). Most existing chatbot
frameworks and AI tools are designed primarily for
English (Liang et al., 2023), requiring developers to
invest extra time and resources to adapt these tools
for Portuguese. This adaptation process can increase
development costs and extend deployment timelines,
complicating the creation of effective chatbot solu-
tions.
3 CHATBOT PROPOSAL
This section presents the chatbot proposal, outlining
the key requirements and the proposed architecture
designed to meet these needs. It details the specific
functional and technical requirements that the chatbot
must fulfill. Following this, it presents the proposed
architecture, which includes a robust framework and
technology stack intended to support these require-
ments efficiently. This section will provide a compre-
hensive overview of how the proposed design aligns
with the objectives and operational demands, ensur-
ing a seamless and effective implementation of the
chatbot.
3.1 Requirements
The project proposes an innovative and comprehen-
sive solution to address the challenges faced by for-
mer inmates in Brazil by integrating a dedicated chat-
bot into the ESVirtual application (Canedo et al.,
2024). ESVirtual is already recognized as a robust
platform aimed at providing support and resources for
people in vulnerable situations, and the inclusion of a
specialized chatbot will further expand its utility and
effectiveness in supporting former inmates.
To ensure accessibility and flexibility in imple-
mentation, the chatbot will be developed using a free
open-source framework. This strategic choice will not
only reduce costs but also allow for smoother inte-
gration with the existing ESVirtual app infrastructure.
Moreover, utilizing an open-source framework offers
the advantage of an active developer community and
constantly evolving resources, ensuring the continu-
ous maintenance and improvement of the chatbot over
time.
The chatbot’s scope will be comprehensive, ad-
dressing a variety of crucial topics for former inmates.
This will include information and guidance on shelter,
food, access to healthcare services, ways to contact
support organizations, available benefits (such as so-
cial programs and financial assistance), professional
training opportunities, and legal assistance. By offer-
ing support in a wide range of areas, the chatbot aims
to meet the diverse needs of former inmates, provid-
ing them with tangible resources to help them reinte-
grate into society.
A distinctive aspect of this project is the decision
not to use generative artificial intelligence to gener-
ate responses. Instead, the chatbot’s responses will be
crafted and managed by the project team. This ap-
proach was adopted to ensure the accuracy, relevance,
and consistency of the information provided, as well
as to enable quick responses to changes in policies,
legislation, or services available to former inmates.
Although this requires additional effort from the team,
we believe it is crucial to ensure the quality and relia-
bility of the service offered.
3.2 Architecture
The proposed architecture for the chatbot integrated
with the ESVirtual application is designed to be mod-
ular, scalable, and easy to maintain. To achieve these
goals, we opted to use Docker Compose, a tool that
simplifies and standardizes the definition and execu-
tion of multi-container Docker applications. There
will be containers for Rasa and the Action Server. The
full architecture is presented in Figure 2.
Docker Compose is a tool that allows for the
easy and consistent definition and execution of multi-
container Docker applications. It uses a YAML file
to configure the application’s services and dependen-
cies, ensuring that the development environment is
replicable and consistent across different machines.
This simplifies the installation, update, and mainte-
nance of the chatbot, while also allowing for more
efficient scalability by adding or removing containers
ICEIS 2025 - 27th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
426

Figure 2: Architecture of the proposed chatbot.
as needed.
Rasa is an open-source framework for building
chatbots based on machine learning and natural lan-
guage processing (NLP). It enables the development
of highly customized chatbots capable of understand-
ing and responding to questions contextually. The
Rasa chatbot will be the core of our solution, pro-
viding interaction and response capabilities to users.
Rasa allows for the creation of machine learning mod-
els specifically trained for the chatbot’s context, en-
suring that responses are relevant and accurate. Ad-
ditionally, Rasa supports the implementation of com-
plex conversation flows, allowing for a more natural
and intuitive interaction with users.
The Action Server is a component of Rasa that
allows for the integration of custom actions into the
chatbot. It will be responsible for executing specific
actions, such as performing complex operations that
cannot be directly handled by the chatbot. The Ac-
tion Server will be crucial for extending the chatbot’s
capabilities and providing more sophisticated and per-
sonalized responses to users.
These components, when combined using Docker
Compose, form a cohesive and scalable architecture
for the chatbot integrated with the ESVirtual applica-
tion. The use of Docker containers ensures that the
development environment is consistent and easily re-
producible across different machines, while the use
of Rasa and the Action Server provides the flexibil-
ity and customization capabilities needed to meet the
specific demands of users. This modular approach
facilitates the update and maintenance of individual
components without affecting the entire system, pro-
moting greater operational efficiency and the ability
to adapt the chatbot to new needs and challenges.
Although there was a choice of not adding addi-
tional components for data tracking, as seen in (An-
drade et al., 2020a), the architecture is flexible enough
to be incremented in the future. This choice was due
to privacy concerns of storing user data, which may
be sensitive since users are free to send any message.
Therefore, data is only in memory during the course
of conversation, and it is not persisted after the con-
versation is over.
4 RESULTS
This section presents the results of the chatbot devel-
opment, emphasizing both its content and interface. It
details how the chatbot’s responses have been refined
for relevance and engagement, and how the interface
has been designed to ensure user-friendliness. Addi-
tionally, we will discuss the challenges encountered
in evolving the chatbot, including maintaining perfor-
mance while integrating new features and adapting to
content changes.
4.1 Knowledge Base
To ensure that the chatbot provides accurate and rel-
evant responses to users, it is essential to supply it
with appropriate content and train it to understand and
adequately respond to user queries. This is achieved
through the use of Rasa NLU (Natural Language Un-
derstanding), Stories, and Actions, which together
form the core intelligence of the chatbot. Below, we
detail each of these components and how they con-
tribute to the chatbot content feeding process.
Rasa NLU is responsible for understanding the in-
tents and entities in user messages. It utilizes ad-
vanced natural language processing (NLP) techniques
to extract relevant information from messages and
map them to the intents and entities defined in the
chatbot model. To feed Rasa NLU with content, it is
necessary to provide examples of user messages along
with the associated intents and entities. These exam-
ples are used to train the Rasa NLU model, enabling
it to recognize similar patterns and contexts in future
messages.
Stories are representations of dialogues between
the user and the chatbot. They describe sequences of
interactions between the user and the chatbot, includ-
ing user messages, actions performed by the chatbot
in response to these messages, and the conditions for
transitioning between different dialogue states. Sto-
ries are used to train the chatbot’s conversation model,
allowing it to learn to follow specific conversation
flows and make appropriate decisions based on the
context of the interaction. To feed the chatbot with
content, it is necessary to create and provide a variety
of stories that cover different conversation scenarios
and relevant use cases for users.
Actions are the tasks that the chatbot can perform
in response to user messages. These may include
Enhancing Post-Incarceration Support: A Custom Chatbot Solution for the Brazilian Prison System
427

sending a text message, asking a follow-up question,
calling an external API to retrieve additional infor-
mation, among others. Actions are defined and im-
plemented by the developer and are triggered based
on the decisions made by the chatbot’s conversation
model during user interaction. To feed the chatbot
with content, it is necessary to define and implement
the actions required to respond to the different user
intents and achieve the chatbot’s objectives.
By feeding the chatbot content using Rasa NLU,
Stories, and Actions, we ensure that the chatbot can
understand and adequately respond to user queries,
providing a natural and effective conversational ex-
perience. The chatbot’s design ensures it covers a
comprehensive range of topics relevant to the needs
of former inmates, providing them with a reliable and
accessible source of information and support. Below,
we outline the main topics covered by the chatbot:
1. General Interactions
(a) Greeting and Farewell: The chatbot can ini-
tiate conversations, greet users, and bid them
farewell.
(b) Affirmations and Negations: It handles user af-
firmations and negations, ensuring smooth in-
teraction flow.
(c) Bot Challenges: Users can verify the chatbot’s
identity and capabilities.
2. Legal and Documentation Support
(a) Fine Penalties: Information on penalties and
fines.
(b) Document Regularization: Assistance with reg-
ularizing various personal documents, includ-
ing birth certificates, voter registration, CPF,
CTPS, and military service certificates.
(c) Legal Assistance: Guidance on obtaining legal
support, including assistance from public de-
fenders and legal assistants.
3. Employment and Professional Development
(a) Job Opportunities: Information on finding job
opportunities.
(b) Professional Training: Details on obtaining
scholarships for courses, finding vocational
courses, and the requirements and documenta-
tion needed for these courses.
4. Housing and Shelter
(a) Temporary Housing: Information on temporary
shelters, including locations, availability, oper-
ating hours, and acceptance policies.
(b) Social Housing Programs: Assistance with so-
cial housing programs, rental subsidies, and re-
lated services.
5. Health and Welfare
(a) Public Health System: Access to information
about the public health system, including how
to obtain a SUS card, schedule appointments,
and find medical establishments.
(b) Psychological Support: Access to psycholog-
ical support services for former inmates and
their families.
6. Food and Nutrition
(a) Food Assistance: Information on finding food,
community restaurants, and food cards.
(b) Basic Food Supplies: Guidance on obtaining
basic food supplies.
7. Community and Social Support
(a) Support Services: Information about CRAS,
CREAS, and Centro Pop services.
(b) Connecting with Other Former Inmates: Facili-
tating contact and support networks among for-
mer inmates.
8. Children and Family
(a) Childcare and School Enrollment: Assistance
with enrolling children in school and accessing
childcare services.
(b) Parental Support: Support for parenting and
custody issues.
9. Social Programs and Benefits
(a) Social Benefits: Information on various social
programs like BPC, PBF, social electricity tar-
iffs, and reclusion assistance.
(b) Eligibility and Registration: Guidance on eligi-
bility and registration for social programs and
subsidies.
10. Miscellaneous Support
(a) Transportation and Mobility: Information on
transportation options and mobility assistance.
(b) Leisure and Recreation: Details on accessing
free leisure and recreational activities.
(c) Emergency Assistance: Support for emergen-
cies, including drug addiction help and domes-
tic violence reporting.
A significant number of intents needed to be inte-
grated into the chatbot to meet the requirements of so-
cial offices. We examined the progression of training
examples and their impact on intent prediction confi-
dence across multiple releases of the model. Figure
3 illustrates the number of training examples used in
each release. This visual representation highlights the
increasing volume of data incorporated into the train-
ing process, driven by the high volume of intents re-
quired.
ICEIS 2025 - 27th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
428
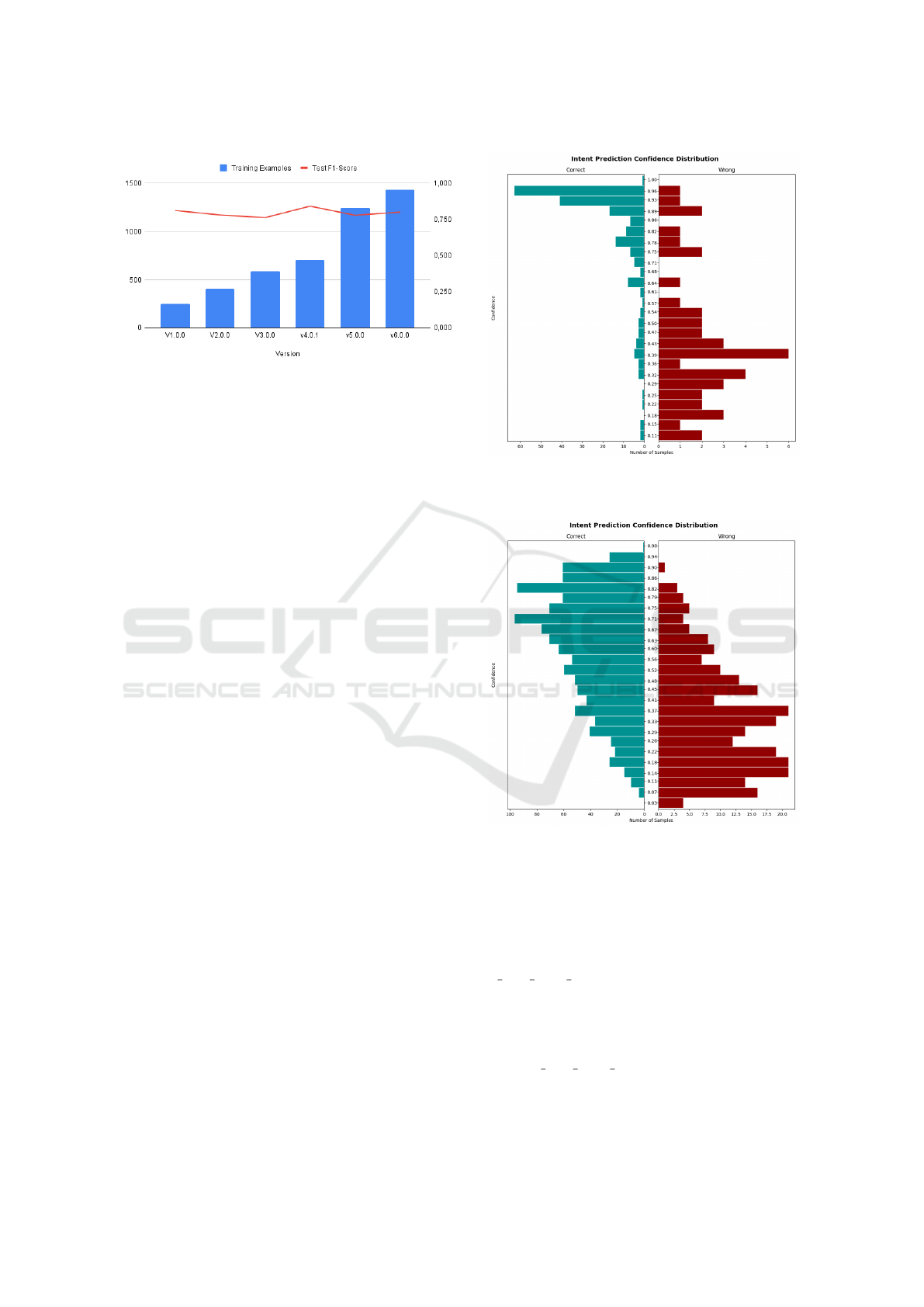
Figure 3: Number of training examples per release.
To assess the model’s performance, we analyzed
the distribution of intent prediction confidence at dif-
ferent stages of development. Figure 4 shows the con-
fidence distribution for the first release. The initial
distribution reveals insights into the model’s baseline
performance and the areas needing further refinement.
As the model evolved, the intent prediction confi-
dence distribution showed some stability, despite the
subtle increase in data volume depicted in Figure 3.
Maintaining this stability was a challenge. It required
constant updates to the pipeline to accommodate the
incoming new data. This stability was not coinciden-
tal but rather the result of continuous adjustments to
the pipeline, including modifications to the base train-
ing model and its hyperparameters.
Furthermore, with the large volume of intents, it
became necessary to progressively reduce the fall-
back threshold. This threshold determines when the
chatbot will return an “I didn’t understand” response.
Lowering it helped improve the chatbot’s ability to
handle the increasing number of intents accurately.
Figure 5 presents the confidence distribution for the
last release, showcasing the improvements achieved
through these ongoing adjustments. Although the ad-
justments helped in the keeping the confidence ratings
acceptable, the high volume of intents to predict still
resulted in some decrease in performance, which was
expected.
The evolution of the pipeline for the chatbot re-
flects the growing sophistication in handling the nu-
ances of the Portuguese language and improving over-
all performance. Each iteration of the pipeline has
introduced advancements aimed at enhancing both
language understanding and user interaction quality.
Here’s a closer look at the progression and the rea-
sons behind these changes:
The initial pipeline was quite basic, relying heav-
ily on traditional NLP techniques, with Rasa’s de-
fault tokenizers, featurizers, classifiers and response
selector. The second pipeline made significant strides
Figure 4: Intent prediction confidence distribution for the
first release.
Figure 5: Intent prediction confidence distribution for the
last release.
in handling the Portuguese language more effectively
by integrating specialized tools and feature extraction
techniques using spaCy’s robust NLP tools, such as
SpacyNLP and SpacyTokenizer.
Introducing spaCy’s portuguese NLP model
(pt core news sm) and tokenizer enhanced the
pipeline’s ability to handle Portuguese text more
effectively, thanks to spaCy’s pretrained language
models and more sophisticated tokenization. Later,
the spaCy model was changed to the medium-sized
model (pt core news md) for better performance but
longer training duration. Additionaly, adding the
RegexEntityExtractor allowed for the extraction of
Enhancing Post-Incarceration Support: A Custom Chatbot Solution for the Brazilian Prison System
429

named entities based on regular expressions, improv-
ing the model’s ability to recognize specific terms
and entities in Portuguese through regex patterns and
the list of works provided in the custom lookup table.
The third pipeline represents a more advanced and
modern approach to building a Portuguese chatbot.
The RegexEntityExtractor was updated to be case-
insensitive, improving its flexibility and accuracy in
identifying entities regardless of case variations. The
third pipeline’s use of advanced models like BERT
highlights a shift towards leveraging deep learning for
more nuanced language understanding and contextu-
ally appropriate responses. This version also reflects a
greater emphasis on improving entity recognition and
feature extraction capabilities, which are crucial for
handling the complexities of Portuguese.
4.2 Custom Actions
In the realm of conversational AI, custom actions
are pivotal in extending the capabilities of chatbots
beyond predefined responses and static dialogues.
These actions enable chatbots to perform complex
tasks, interact with external APIs, and provide per-
sonalized user experiences. By leveraging custom ac-
tions, developers can tailor chatbot functionalities to
meet specific user needs and integrate seamlessly with
existing workflows and systems.
In the context of the ESVirtual application, cus-
tom actions play a crucial role in enhancing user inter-
action, ensuring that the chatbot can deliver accurate
information and handle nuanced queries effectively.
This section delves into the development of two such
custom actions, highlighting their design and imple-
mentation to bolster the ESVirtual chatbot’s perfor-
mance and user satisfaction.
The ActionPhoneNumber custom action was de-
veloped to enhance the ESVirtual chatbot’s ability to
provide users with relevant contact information for
various essential services. This action is triggered
when a user requests a phone number for a specific
entity, such as emergency services or public institu-
tions. The ActionPhoneNumber class, extending the
Action class from rasa sdk, is designed to retrieve and
deliver phone numbers based on user queries. The ac-
tion operates as follows:
1. Entity Extraction: It extracts the entity (e.g.,
”SAMU”, ”Pol
´
ıcia Militar”) from the user’s
message using the tracker.get slot( ”enti-
dade telefone”) method.
2. Phone Number Retrieval: It calls the
obter telefone method, which contains a prede-
fined dictionary of service phone numbers, to
fetch the appropriate contact number for the given
entity.
3. Response Generation: If a valid phone number
is found, the action constructs a response mes-
sage with the phone number. For certain entities
like ”SAMU” and ”Disque Sa
´
ude,” the response
includes additional information about health ser-
vices. For ”Defensoria P
´
ublica,” the message pro-
vides further details about legal assistance ser-
vices. If the phone number is not found, the ac-
tion prompts the user to try again with a different
keyword.
4. Message Dispatch: The response is
then sent to the user using the dis-
patcher.utter message(text=response) method.
This design ensures that users receive precise and
helpful information promptly, improving the overall
utility and responsiveness of the chatbot.
The ActionFallbackWithSuggestions custom ac-
tion addresses scenarios where the chatbot fails to
understand the user’s input. By offering alternative
suggestions, this action aims to guide the user to-
wards more recognizable queries, enhancing user ex-
perience and interaction efficiency. The ActionFall-
backWithSuggestions class, also extending the Action
class from rasa sdk, operates as follows:
1. Intent Ranking Retrieval: It accesses the
ranking of the latest message’s intents using
tracker.latest message[’intent ranking’].
2. Top Intent Selection: It selects the top three in-
tents (excluding the fallback intent itself) for sug-
gesting to the user.
3. Intent Mapping: It loads a mapping of intent
names to their display names from a CSV file us-
ing the load intent mapping method. This ensures
that the suggestions are user-friendly and easily
understandable.
4. Button Generation: For each of the top intents, it
constructs a button with a title (display name) and
a payload (intent name).
5. Fallback Message Dispatch: The action
sends a fallback message to the user, in-
cluding the generated buttons, using the
dispatcher.utter message(text=message, but-
tons=buttons) method. This message encourages
the user to rephrase their query or select one of
the suggested options.
6. Utterance Reversion: It reverts the user’s utter-
ance to maintain the conversation flow, ensuring
that the chatbot remains responsive and helpful.
ICEIS 2025 - 27th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
430
Figure 6: Initial presentation of the chatbot section in the
ESVirtual app.
By incorporating these mechanisms, the Action-
FallbackWithSuggestions custom action significantly
enhances the chatbot’s ability to handle misunder-
standings and guide users effectively, thereby improv-
ing the overall conversational experience.
4.3 User Interface
As shown in Figure 2, the chatbot was developed as a
standalone service to facilitate easy maintenance and
evolution. It was made accessible to the ESVirtual
app via a REST API, ensuring that the chatbot in-
terface remained entirely separate from the question-
answer processing. Figures 6 and 7 illustrate the sec-
tions of the app where the chatbot is available.
Although the service and interface were modular-
ized, certain details needed to be synchronized for a
successful integration. For example, some keywords
in the chatbot responses were used to redirect users to
the corresponding help pages for additional informa-
tion. This was necessary because some topics were
Figure 7: Message exchange with the chatbot.
too extensive to be fully addressed in a chatbot mes-
sage.
Due to the limitations of mobile screen size, we
faced the challenge of balancing the amount of in-
formation in the chatbot responses to avoid excessive
scrolling, which could confuse users or cause them to
overlook previous interactions. This required careful
content curation and UX writing to ensure that infor-
mation was presented clearly and concisely.
5 CONCLUSION
The development and implementation of a chatbot
dedicated to assisting former inmates of the Brazilian
prison system, integrated with the ESVirtual applica-
tion, represents a crucial initiative in the search for in-
novative solutions to the challenges faced by this vul-
nerable group. Throughout this project, we explored a
comprehensive and sustainable approach to providing
support and resources to former inmates, considering
technical, functional, and ethical aspects.
Enhancing Post-Incarceration Support: A Custom Chatbot Solution for the Brazilian Prison System
431

The proposed architecture, based on the use of
Docker Compose, Rasa NLU, Stories, and Actions,
offers a solid and scalable framework for the chatbot,
ensuring its ability to understand natural language,
adapt to different interaction scenarios, and execute
customized actions. Integrating the chatbot with the
ESVirtual application further enhances its utility and
accessibility, providing former inmates with a reliable
and accessible channel to obtain information and sup-
port on their journey to social reintegration.
The decision not to use generative artificial intel-
ligence to generate responses, opting instead to man-
ually craft the chatbot’s content, demonstrates our
commitment to the accuracy, relevance, and reliability
of the information provided to users. This allows for
a quick response to changes in policies, legislation, or
services available to former inmates, ensuring that the
chatbot remains effective and useful over time.
On a social level, the implementation of this
project has the potential to significantly contribute to
the reintegration of former inmates into society, re-
ducing recidivism rates and promoting the building of
a more just and inclusive society. By providing essen-
tial support and resources to former inmates, we em-
power these individuals to overcome the challenges
they face after leaving the prison system and to build
a dignified and productive life.
In summary, this work represents an important
step towards a more humanized and effective ap-
proach to dealing with the reintegration of former in-
mates of the Brazilian prison system, demonstrating
the power of technology and innovation to promote
social well-being and justice.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This study was financed in part by the FUNDAC¸
˜
AO
DE APOIO
`
A PESQUISA DO DISTRITO FED-
ERAL (FAPDF), Brasil – Finance Code 01/2023.
REFERENCES
Al Husaeni, D. F., Haristiani, N., Wahyudin, W., and Rasim,
R. (2024). Chatbot Artificial Intelligence as Educa-
tional Tools in Science and Engineering Education: A
Literature Review and Bibliometric Mapping Analy-
sis with Its Advantages and Disadvantages. ASEAN
Journal of Science and Engineering, 4(1):93–118.
Andrade, G. G., Silva, G., J
´
unior, F. D., Santos, G.,
de Mendonc¸a, F. L., and J
´
unior, R. S. (2020a).
EvaTalk: A Chatbot System for the Brazilian Govern-
ment Virtual School, volume 2. SCITEPRESS, Portu-
gal.
Andrade, G. G., Silva, G., J
´
unior, F. D., Santos, G.,
de Mendonc¸a, F. L., and J
´
unior, R. S. (2020b).
Evatalk: A chatbot system for the brazilian govern-
ment virtual school. In Proceedings of the 22nd Inter-
national Conference on Enterprise Information Sys-
tems - Volume 1: ICEIS,, pages 556–562. INSTICC,
SciTePress.
Bachtiar, F. A., Dysham, A. A., Fauzulhaq, A. D., Az-
zam, J. S., and Aryadita, H. FLUENT: Factoid Re-
trieval Based Chatbot Using LSTM. In 2023 1st In-
ternational Conference on Advanced Engineering and
Technologies (ICONNIC), page 14. IEEE.
Benard, A. K., Msomba, G., and Pesha, J. (2023). Social
Challenges Facing Ex-Prisoners During their Integra-
tion into Societies in Iringa Municipality, Tanzania.
Asian Res. J. Arts Soc. Sci., 21(3):78–89.
Cacabro, M., Franco, W., Monteiro, J. M., and Machado,
J. (2023). Iara - an architectural model to assist the
development of advising bots for misinformation de-
tection. In Proceedings of the 29th Brazilian Sym-
posium on Multimedia and the Web, WebMedia ’23,
page 168–176, New York, NY, USA. Association for
Computing Machinery.
Canc¸ado, E. C. R., Bandeira, I. N., Costa, P. H. T., Fortes,
J., Moreira, D. C., Amaral, L. H. V., and Canedo,
E. D. (2022). Exploring user-centered requirements
validation and verification techniques in a social inclu-
sion context. In Filipe, J., Smialek, M., Brodsky, A.,
and Hammoudi, S., editors, Proceedings of the 24th
International Conference on Enterprise Information
Systems, ICEIS 2022, Online Streaming, April 25-27,
2022, Volume 1, pages 85–92. SCITEPRESS.
Canedo, E. D., Canc¸ado, E. C. R., Mota, A. P. B., Ban-
deira, I. N., Costa, P. H. T., Lima, F., Amaral, L., and
Bonif
´
acio, R. (2024). Using Design Thinking to break
social barriers: An experience report with former in-
mates. J. Software: Evol. Process, 36(7):e2648.
Chagas, B. A., Pagano, A. S., Prates, R. O., Praes, E. C.,
Ferreguetti, K., Vaz, H., Reis, Z. S. N., Ribeiro,
L. B., Ribeiro, A. L. P., Pedroso, T. M., Beleigoli, A.,
Oliveira, C. R. A., and Marcolino, M. S. (2023). Eval-
uating User Experience With a Chatbot Designed as a
Public Health Response to the COVID-19 Pandemic
in Brazil: Mixed Methods Study. JMIR Human Fac-
tors, 10.
D’
´
Avila, T. C. (2018). KINO: an approach for rule-based
chatbot development, monitoring and evaluation. Uni-
versidade Federal de Minas Gerais.
Dagkoulis, I. and Moussiades, L. (2022). A Comparative
Evaluation of Chatbot Development Platforms. In
ACM Other conferences, pages 322–328. Association
for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA.
Dores, A. P. and Dores, A. P. (2019). The Role of Infor-
mation and Communications Technology in the Social
Reintegration of Ex-Prisoners. IGI Global.
Gonc¸alves, L. P., Silva, G. R. S., and Canedo, E. D. (2024).
Documentation artifacts for conversation-related re-
quirements specification in chatbots. In Lucena, M.,
Lencastre, M., and Ballejos, L. C., editors, Anais do
WER24 - Workshop em Engenharia de Requisitos,
ICEIS 2025 - 27th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
432

Buenos Aires, Argentina, August 7-9, 2024. Even3,
Brasil.
Joshi, M. and Sharma, R. K. (2020). An Analytical
Study and Review of open Source Chatbot frame-
work, RASA. International Journal of Engineering
Research & Technology, 9(6).
Liang, W., Yuksekgonul, M., Mao, Y., Wu, E., and Zou, J.
(2023). GPT detectors are biased against non-native
English writers. PATTER, 4(7).
Massa, P., de Souza Ferraz, D. A., Magno, L., Silva, A. P.,
Greco, M., Dourado, I., and Grangeiro, A. (2023). A
Transgender Chatbot (Amanda Selfie) to Create Pre-
exposure Prophylaxis Demand Among Adolescents
in Brazil: Assessment of Acceptability, Functionality,
Usability, and Results. J. Med. Internet Res., 25.
Misischia, C. V., Poecze, F., and Strauss, C. (2022). Chat-
bots in customer service: Their relevance and impact
on service quality. Procedia Comput. Sci., 201:421–
428.
Pandey, S. and Sharma, S. (2023). A comparative study
of retrieval-based and generative-based chatbots us-
ing Deep Learning and Machine Learning. Healthcare
Analytics, 3:100198.
PlayStore (2024). Escrit
´
orio Social Virtual ESV – Apps no
Google Play. [Online; accessed 23. Jul. 2024].
Portal CNJ (2022). Escrit
´
orio Social Virtual - Portal CNJ.
[Online; accessed 23. Jul. 2024].
Shaitarova, A., Zaghir, J., Lavelli, A., Krauthammer, M.,
and Rinaldi, F. (2023). Exploring the Latest High-
lights in Medical Natural Language Processing across
Multiple Languages: A Survey. Yearbook of Medical
Informatics, 32(1):230.
Silva, G. R. S. and Canedo, E. D. (2024). Towards user-
centric guidelines for chatbot conversational design.
Int. J. Hum. Comput. Interact., 40(2):98–120.
Storck, W. (2023). More Education of Juvenile Offenders
In Sentences Of Imprisonment: A Reform And Justi-
fication Approach As A Consequence Of Niklas Luh-
mann’s Systems Theory. Issue 3/2023, 8(0).
Tharshini, N. K., Wong, S. K., Mas’ud, F. H., Ali, K., and
Ahmad, N. A. (2024). Readiness for re-entry among
pre-release prisoners in Sarawak, Malaysia. Journal
of Forensic Practice, ahead-of-print(ahead-of-print).
Thom
´
e-Williams, A. C. (2004). Sociolinguistic aspects of
forms of address in portugal and brazil: Tu or voce.
Intercultural Communication Studies, 13(3):85–99.
Trajano, D., Bordini, R. H., and Vieira, R. (2023).
OLID-BR: offensive language identification dataset
for Brazilian Portuguese. Lang. Resources &. Eval-
uation, pages 1–27.
Tueiv, M. and Schmitz, E. (2023). Maximizing the value
delivered of chatbots in e-gov using the incremental
funding method. In Proceedings of the 16th Inter-
national Conference on Theory and Practice of Elec-
tronic Governance, ICEGOV ’23, page 242–246, New
York, NY, USA. Association for Computing Machin-
ery.
UNDP (2024). CNJ e parceiros lanc¸am aplicativo para
apoio a pessoas egressas do sistema prisional. [On-
line; accessed 23. Jul. 2024].
Wilkens, R., Zilio, L., and Villavicencio, A. (2024). As-
sessing linguistic generalisation in language models:
a dataset for Brazilian Portuguese. Lang. Resources
&. Evaluation, 58(1):175–201.
Enhancing Post-Incarceration Support: A Custom Chatbot Solution for the Brazilian Prison System
433
