
A Model-Checking Framework for
Neuro-Degenerative Deficit Screening and Personalized Training
Elisabetta De Maria and Christopher Leturc
Universit
´
e C
ˆ
ote d’Azur, CNRS, I3S, France
{elisabetta.de-maria, christopher.leturc}@univ-cotedazur.fr
Keywords:
Model-Checking, Probabilistic Model, Neuro-Cognitive Diseases, Medical Application, Serious Game,
Cognitive Training.
Abstract:
Serious games are established as an effective tool to screen cognitive deficits and assess diagnosis in patients
affected by neuro-degenerative diseases such as Alzheimer or Parkinson. They are also known for their cogni-
tive training benefits. According to the latest DSM-5 classification, we can discriminate mild Neuro-Cognitive
Disorders (mild NCDs) and Major Neuro-Cognitive Disorders (Major NCDs). In this article, we consider three
classes of patients: healthy, mild NCD, and Major NCD. For each class, we use Discrete Time Markov Chains
to model the behaviour shown while playing serious games. Model checking techniques allow us to spot the
difference between the expected and the observed behaviour. As a main contribution, we provide a new theo-
retical framework allowing us to evaluate how the confidence level of practitioners on the patient’s Alzheimer
degree evolves after each game session, i.e., help to diagnose, and to set up an experimental protocol in which
the levels of the proposed subsequent game sessions automatically depend on the patient behaviour observed
in the previous sessions, i.e., help to train.
1 INTRODUCTION
Neuro-degenerative pathologies such as the
Alzheimer or Parkinson disease often lead to
the decline of cognitive functions and, more gener-
ally, to cognitive impairments. To provide timely and
individualized actions, the presence of neurocognitive
disorders should be detected as soon as possible and
constantly monitored by clinicians. Presently, an
accurate diagnosis typically involves a comprehen-
sive series of neuropsychological tests, frequently
accompanied by biomarker tests. Conducting these
tests can be demanding and time-consuming, both
for the practitioner and the patient. There is an
increasing interest in discovering behavioral mark-
ers that are objective, quick to conduct, and can
supplement traditional clinical assessments, aiding
in the early detection of alterations in cognitive
performances. Serious games are very promising in
this context (Philippe et al., 2014). They are digital
or physical games designed with a primary purpose
beyond entertainment, such as education, training,
health, or social change, while maintaining engaging
gameplay elements (Alvarez et al., 2007). Several
feasibility studies have demonstrated the value of
serious games in assessing cognitive impairment
(Tong et al., 2016; Vanessa et al., 2017; Kato and
Klerk, 2017). Additionally, research highlights their
potential in Alzheimer’s disease therapy as cognitive
training tools (Anguera et al., 2013; Kathryn et al.,
2014). Furthermore, studies indicate that elderly
people exhibit a preference for games compared to
traditional cognitive exercises (Melenhorst et al.,
2006).
Based on the most recent DSM-5 (American Psy-
chiatric Association, 2013) classification, cognitive
impairments involve both a decline in cognitive func-
tions and behavioral issues that can disrupt everyday
activities. Depending on the severity of these deficits
and on their impact, this classification discriminates
mild Neuro-Cognitive Disorder (mild NCD) and Ma-
jor Neuro-Cognitive Disorder (Major NCD). Patients
with mild NCD and major NCD require supervision
from medical practitioners and psychologists.
In this work we advocate the use of serious games
to help practitioners in screening cognitive deficits
and proposing training activities suited to patients.
For some games, several difficulty levels can be pro-
posed. For each Alzheimer degree (healthy, mild
NCD, Major NCD), the activity of patients while
playing is modeled using discrete Markov chains, in
the style of (De Maria et al., 2019; L’Yvonnet et al.,
De Maria, E. and Leturc, C.
A Model-Checking Framework for Neuro-Degenerative Deficit Screening and Personalized Training.
DOI: 10.5220/0013095300003911
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 18th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2025) - Volume 2: HEALTHINF, pages 351-360
ISBN: 978-989-758-731-3; ISSN: 2184-4305
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
351

2021). As a matter of fact, when patients play serious
games, some scenarios frequently happen while oth-
ers are rare. We quantify these variations in the patient
behaviour by associating probabilities with the impor-
tant actions of games. Certain actions will definitely
be carried out by the patient while other actions de-
pend on the Alzheimer degree of the patient. For these
actions, practitioners provide us with a priori weights
or probabilities according to their experience. These
probabilities are initially integrated into our models
and refined based on clinical study results.
For the correct implementation of our methodol-
ogy, practitioners initially need to give us: (i) for
each game and for each Alzheimer degree, the a pri-
ori weights associated with key activities of the game
(if available, weights coming from clinical experi-
ments will replace a priori weights); (ii) the hypothe-
sis on the Alzheimer degree, i.e., impairment degree,
of each patient, based on a preliminary set of pen
and paper neuropsychological tests. To ensure the
validity of important properties, e.g., all executions
reach a final state, our models are validated thanks to
the use of probabilistic model checking (Hansson and
Jonsson, 1994), which allows to automatically check
if some dynamic properties are respected. By com-
puting probabilities associated with execution traces,
model checking also helps in spotting the differences
between the patient expected behaviour and the ob-
served one.
As a main contribution, we propose the in-
troduction of a meta-automaton whose nodes are
Markov chains representing the expected behaviour
of a class of patients for a given game. Each
state of the meta-automaton represents a game ses-
sion. This meta-automaton allows one: (i) to in-
fer how the confidence level of practitioners on the
patient’s Alzheimer degree evolves after each game
session, and (ii) to set up an experimental protocol
in which the difficulty level of the proposed sub-
sequent game sessions depends on the patient be-
haviour observed in the previous game sessions (im-
provements/regressions/constant behaviour). Some
suited final conditions allow us to determine when
the game sessions should end. At the end of the pro-
tocol, we may suggest to practitioners to reconsider
the patient’s Alzheimer degree provided at the begin-
ning (e.g., a patient known as “Major NCD” could
be considered to be re-classed as “mild MCD” or
vice-versa). Instabilities in the patient performances
(e.g., oscillations) can also be automatically detected
thanks to model checking techniques. Model check-
ing (Clarke et al., 1999b) is thus applied at two levels:
to validate the Markov chains describing the activity
of patients playing serious games, and to detect cru-
Figure 1: Screenshot of the Match Items game.
cial properties of traces of the meta-automaton.
The paper is organized as follows. In Section 2 we
introduce, as a case study, a simple serious game de-
veloped at Claude Pompidou Institute, Nice, France.
In Section 3 we give some preliminaries on the for-
mal tools we adopt: probabilistic automata and tem-
poral logics. Section 4 is devoted to the formal frame-
work we propose to help with diagnosis and training
of Alzheimer patients. In Section 5 we propose a for-
mal validation of our approach and in Section 6 we
outline important future developments.
2 CASE STUDY
As a simple case study, we introduce the Match Items
game (Tran et al., 2015), which has been developed in
2014 at Claude Pompidou Institute, Nice, France and
has already been implied in several clinical protocols.
In particular, one of the clinical experiments validated
this game as a suitable tool to discriminate between
mild NCD patients and healthy ones. The Match
Items game targets selective and sustained visual at-
tention functions. In this game patients interact with a
touch-pad. Their task consists in matching a random
picture shown at the center of the touch-pad with its
corresponding element from a list of pictures located
at the bottom of the screen (see Figure 1). The game
lasts at most five minutes.
When the patient selects the correct picture, a
happy smiley appears, and a new picture is displayed.
In case of an incorrect choice, a sad smiley is dis-
played, prompting the patient to try again. If there
is over 10 seconds of inactivity on the touch-pad, the
game reminds the patient to select a picture. Exiting
the game zone results in the game being stopped. In
the rest of the paper, key actions of this game will
be referred as follows: α := ”the patient chooses the
right picture”, β := ”the patient chooses the wrong
picture”, γ := ”the patient is inactive”, θ := ”the pa-
tient quits the game zone”.
HEALTHINF 2025 - 18th International Conference on Health Informatics
352

3 PRELIMINARIES
In this section, we present the Probabilistic Finite De-
terministic Automata (PDFA) and temporal logics. In
the following subsections, we delve into the details
of these two concepts, laying the groundwork for our
subsequent exploration of model-checking and its ap-
plication to serious game-based neuro-degenerative
screening.
3.1 Probabilistic Deterministic Finite
Automata
Let us consider patients engaged in playing serious
games. Given our focus on studying the patients
activity and the unpredictability of patients’ actions,
we adopt Probabilistic Deterministic Finite Automata
(PDFA) (Rabin, 1963). Given a serious game, we
conceive an automaton for each class of patients. This
automaton serves a dual purpose by representing the
development of the serious game and specifying the
activity the user is supposed to display if she belongs
to the class being tested by the automaton.
Each serious game is represented as a PDFA,
where the states represent the different game config-
urations, e.g., the user has to choose a picture, or the
end of the game. The input symbols of the alphabet
represent the actions the user can make, denoted by
Σ
g
= {α, β, γ, θ}. We note Σ
∗
g
⊆ Σ
N
∗
g
the set of words
we can write with Σ
g
. A word is just a concatenation
of symbols on Σ
g
, w = αβγβγβαβθ is a word that uses
the symbols of Σ
g
, thus w ∈ Σ
∗
g
.
Definition 1. A Deterministic Finite Automaton
(DFA) is a 5-tuple A = (Q, Σ, δ
d
, q
0
, F) where:
• Q is a finite set of states.
• Σ is a finite alphabet of input symbols.
• δ
d
: Q × Σ → Q is the transition function, where
δ
d
(q, a) represents the next state when being in
state q and reading input symbol a.
• q
0
∈ Q is the initial state.
• F ⊆ Q is the set of accepting (final) states.
We define δ
∗
the transition function w.r.t. δ which
operates on a set of words:
δ
∗
d
:Q × Σ
∗
→ Q (1)
δ
∗
d
(q, ()) = q (2)
δ
∗
d
(q, xa) = δ
d
(δ
∗
d
(q, x), a) for x ∈ Σ
∗
, a ∈ Σ (3)
A language L
d
recognized by a DFA is defined as:
L
d
= {w ∈ Σ
∗
| δ
∗
d
(q
0
, w) ∈ F}
We say that A = (Q, Σ, δ
d
, P, q
0
, F) is a Proba-
bilistic Deterministic Finite Automaton (PDFA) if and
only if, A = (Q, Σ, δ
d
, q
0
, F) is a DFA and P : Q × Σ ×
Q → [0, 1] is a probabilistic function such that :
(1) ∀(q, a, q
′
) ∈ Q × Σ × Q, if δ
d
(q, a) ̸= q
′
then P(q, a, q
′
) = 0
(2) ∀q ∈ Q,
∑
(a,q
′
)∈Σ×Q
P(q, a, q
′
) = 1
When the future states of a PDFA depend only
on the present state and are independent of the se-
quence of events that preceded it, the Markov prop-
erty holds (Norris, 1998). In other words, given the
present, the past has no additional information to offer
about the future. A PDFA with the Markov property
is called a Markov chain.
The use of Markov chains provides a powerful
tool for modeling the probabilistic behavior of pa-
tients while playing serious games. In the sequel, we
present probabilistic model-checking, a formal tech-
nique that can be used to automatically analyze the
probabilistic behavior of patients and verify the valid-
ity of specific properties while they are playing.
3.2 Temporal Logics
Temporal logic formulae describe the dynamical evo-
lution of a given system. The Computation Tree Logic
CTL
∗
(Clarke et al., 1999a) allows one to describe
properties of computation trees. Its formulas are ob-
tained by (repeatedly) applying Boolean connectives,
path quantifiers, and state quantifiers to atomic for-
mulas. The path quantifier A (resp., E) can be used
to state that all paths (resp., some path) starting from
a given state have some property. The state quanti-
fiers are the following ones. The next time operator
X can be used to impose that a property holds at the
next state of a path. The operator F (sometimes in
the future) requires that a property holds at some state
on the path. The operator G (always in the future)
specifies that a property is true at every state on the
path. The until binary operator U holds if there is
a state on the path where the second of its argument
properties holds, and, at every preceding state on the
path, the first of its two argument properties holds.
The Branching Time Logic CTL (Clarke et al., 1986)
is a fragment of CTL
∗
that allows quantification over
the paths starting from a given state. Unlike CTL
∗
,
it constrains every state quantifier to be immediately
preceded by a path quantifier. The Linear Time Logic
LTL (Sistla and Clarke, 1985) is another known frag-
ment of CTL
∗
where one may only describe events
along a single computation path. Its formulas are of
the form Aϕ, where ϕ does not contain path quan-
tifiers, but it allows the nesting of state quantifiers.
A Model-Checking Framework for Neuro-Degenerative Deficit Screening and Personalized Training
353

CTL and LTL have a non-empty intersection. As an
example, the property A ((x=1) U (y=3)) belongs
both to CTL and LTL. It holds in a state if, for each
path starting from the state, x equals 1 until the mo-
ment when y equals 3. There exists several tools to
automatically check whether a model verifies a given
CTL or LTL formula, e.g., NuSMV (Cimatti et al.,
1999) and SPIN (Holzmann, 2004).
The dynamics of probabilistic models can be
specified using Probabilistic Computation Tree Logic
(PCTL) (Hansson and Jonsson, 1994), which extends
CTL by replacing the classical CTL path quantifiers
A and E with probabilities. Thus, instead of say-
ing that some property holds for all paths or for
some paths, we say that a property holds for a cer-
tain fraction of the paths. The most important op-
erator in PCTL is P, which allows to reason about
the probability of event occurrences. The property
P bound [prop] is true in a state s of a model if the
probability that the property prop is satisfied by the
paths from state s satisfies the bound bound. As an
example, the PCTL property P =0.4 [X (y = 2)]
holds in a state if the probability that y = 2 is true in
the next state equals 0.4. To compute the likelihood
that some behavior of a model happens, the P operator
can take the form P=?. As an example, the property
P =? [G (y = 1)] assesses the probability that y
always equals 1. Several model-checkers allow to
automatically check whether a given probabilistic
model satisfies a given PCTL formula, or to auto-
matically compute the probability for a given formula
to be satisfied. State-of-the-art probabilistic model
checkers are PRISM (Kwiatkowska et al., 2011), UP-
PAAL (Behrmann et al., 2004), STORM (Dehnert
et al., 2017), and PAT (Sun et al., 2009).
4 THE FRAMEWORK: A
DOXASTIC
META-AUTOMATON
In this section, we present the framework while in-
stantiating it to our medical application. First, we
define three PDFA to model the behaviour of three
classes of patients while playing the game. Second,
we define what we call a “meta-automaton”, whose
aim is to model the protocol. Such a meta-automaton
suggests to practitioners to which class the patient
is supposed to belong and helps the patient to train-
ing. After a game session, based on patient perfor-
mances, the meta-automaton suggests a class the pa-
tient is supposed to belong and the next game ses-
sion for the patient. For the sake of compactness, in
the following, we denote the healthy class with h, the
mild NCD with m, and the Major NCD with M. In
the following, each PDFA is considered as a test the
patient is submitted to.
4.1 Three PDFA for Three Classes of
Patients
In the case study concerning the Match Items game
(see Section 2), we consider the following finite al-
phabet Σ
g
= {α, β, γ, θ}, which represents the differ-
ent possible actions defined in Section 2. As an exam-
ple, a word as w
1
= αββα ∈ Σ
∗
g
signifies that the user
first does action α, then β, then β, and finally α.
In our medical application, we consider three de-
teministic automata Q = {A
h
, A
m
, A
M
} since there
are three classes of Alzheimer patients. Each automa-
ton represents the activity of a class of patients while
playing the serious game. In order to validate or reject
one hypothesis about a state of a patient, we consider
that A
h
represents the test for h, A
m
for m, and A
M
for
M. In these automata we consider one initial state q
0
in which the user has to launch the game, and two final
states: f
1
when the game is over, and f
2
when the user
left the game before it was over. Let F = { f
1
, f
2
} be
the final states. We define the following three PDFAs:
for all x ∈ {M, m, h}, A
x
= (Q
x
∪ F, Σ
g
, δ
x
, P
x
, q
x
, F),
where L
x
is the language recognized by A
x
.
For the Match Items game, clinicians already pro-
vided us with (a priori) empirical probabilities on
the different actions to be performed depending on
the different classes. To obtain these probabilities,
10 clinicians—including medical doctors, nurses, and
psychologists who are familiar with patients’ per-
formance while playing the game—each filled out a
questionnaire. The questionnaire included questions
such as: ”For a patient in a given class, what are
the chances of selecting the correct image at each
step?” and ”For a patient in a given class, what are
the chances of not interacting with the game for at
least 10 seconds?” The responses were given as num-
bers from 0 to 10. Table 1 represents the average
probability given by 10 clinicians. We assume that,
for each of the three automata, the probabilistic func-
tion follows this table, e.g., P
h
is such that for all
(q, q
′
) ∈ (Q
h
\ F)
2
, P
h
(q, α, q
′
) = 0.8, P
h
(q, β, q
′
) =
0.1, P
h
(q, γ, q
′
) = 0.05, P
h
(q, θ, q
′
) = 0.05.
For the sake of clarity, Figure 2 illustrates the au-
tomaton A
h
in a simplified manner by depicting each
transition between states for each action. The initial
state is denoted as q
0
, and there are two final states:
f
1
signifies the normal end of the game, while f
2
indi-
cates the user left the game. Furthermore, let us notice
that A
h
has the Markov chain property as A
m
and A
M
.
HEALTHINF 2025 - 18th International Conference on Health Informatics
354
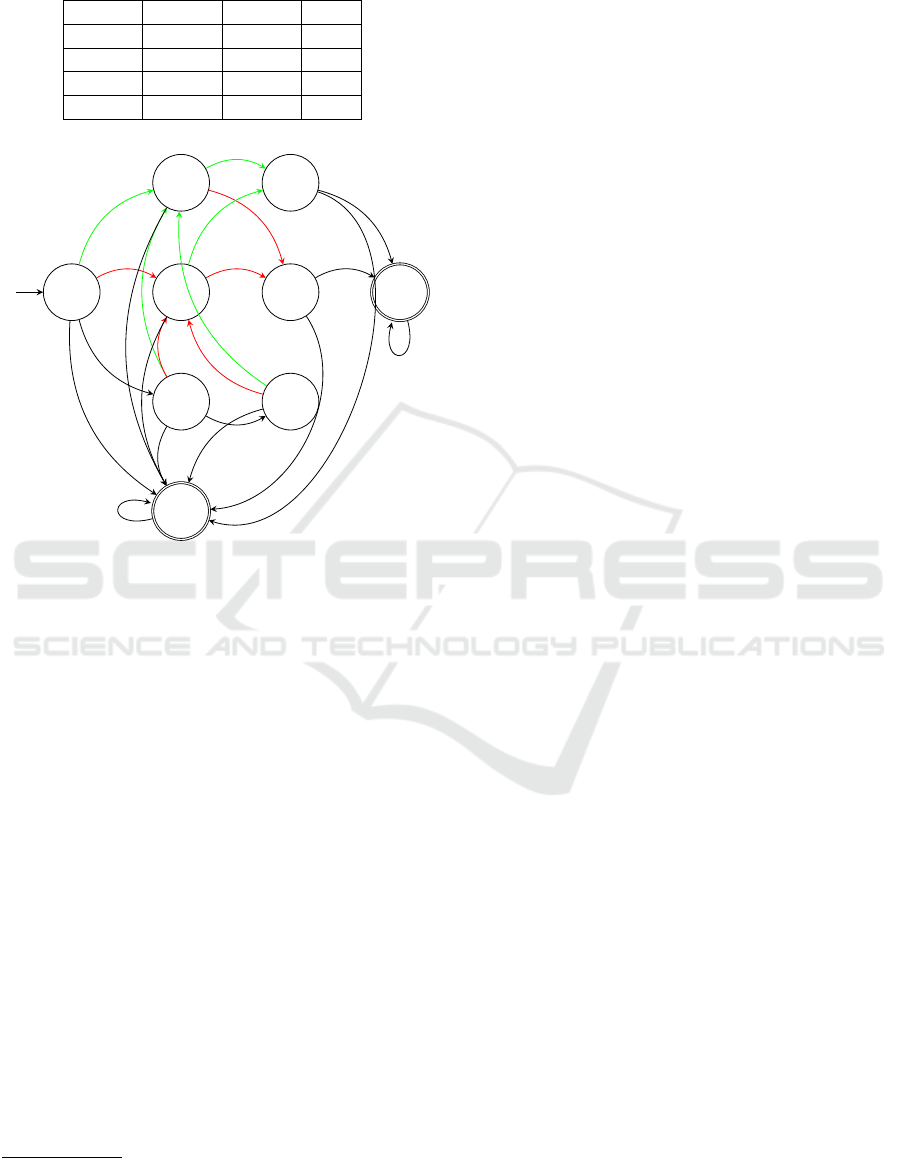
Table 1: Average probability given by 10 clinicians for each
class of patients.
Action h m M
α 0.84 0.5 0.17
β 0.11 0.30 0.58
γ 0.0499 0.1999 0.24
θ 0.0001 0.0001 0.01
q
0
q
11
q
10
q
12
q
121
q
111
q
101
f
1
f
2
α
α
β
α
β
α
β
α
β
. . .
. . .
β
γ
∀
∀
θ
θ
γ
θ
θ
θ
θ
θ
Figure 2: Automaton A
h
describing the expected behaviour
of healthy people while playing the Match Items serious
game.
4.2 An Experimental Protocol as A
Meta-Automaton
The experimental protocol aims to monitor and
assess the patient’s condition. This protocol involves
organizing various tests within a meta-automaton.
After each test, a belief function provides a confi-
dent score about the class the patient belongs to.
Thanks to this score, the meta-automaton informs the
decision-making process for the next test to apply.
Definition 2. A Doxastic Deterministic Finite
Meta-Automaton (DDFMA) is a 7-tuple A =
(Q , Σ
Q
, Σ
A
, δ, {B
q
}
q∈Q
, q
0
, F) where
1
:
• Q is a finite set of PDFA.
• Σ
Q
=
S
q∈Q
Σ
q
is a finite alphabet of input symbols
recognized by all automata in Q.
• Σ
A
is a finite alphabet of input symbols.
• δ : Q × Σ
A
→ Q is the transition function.
1
To distinguish between PDFA and DDFMA, we denote
the latter with a calligraphic letter A
• ∀q ∈ Q , B
q
: L
q
×Σ
A
×Q → [0, 1] is a belief func-
tion that represents from an automaton q, given an
accepted word w ∈ L
q
, the practitioner belief for
the patient to be in the class associated with the
next automaton q
′
. Furthermore B
q
is such that:
(1) ∀q ∈ Q , ∀(a, q
′
) ∈ Σ
A
× Q , if δ(q, a) ̸= q
′
then ∀w ∈ L
q
, B
q
(w, a, q
′
) = 0
(2) ∀q ∈ Q , ∀w ∈ L
q
,
∑
(a,q
′
)∈Σ
A
×Q
B
q
(w, a, q
′
) = 1
• q
0
∈ Q is the initial state, i.e., the first automaton.
• F is the set of final states.
We define δ
∗
the transition function w.r.t. δ which
operates on a set of words defined on the alphabet
Σ = Σ
Q
∪ Σ
A
, and for all q ∈ Q and x ∈ Σ
∗
:
δ
∗
:Q × Σ
∗
→ Q
δ
∗
(q, ()) = q
δ
∗
(q, xa) = δ(δ
∗
(q, x), a) if a ∈ Σ
A
δ
∗
(q, xa) = δ
∗
(q, x) if a ∈ Σ
Q
A language L
A
recognized by a DDFMA is de-
fined as:
L
A
= {w ∈ Σ
∗
| δ
∗
(q
0
, w) ∈ F}
Let us notice that the constraints (1) and (2) for
the function B translate that (1) if a transition does
not exist in the meta-automaton, then the practitioner
belief for the patient to be in the class associated with
this transition cannot be different from 0, and (2) the
sum of all beliefs associated with other transitions is
equal to 1.
For our medical application, we consider the three
classes C = {h, m, M} and the DDFMA A = (Q , Σ
C
,
Σ
A
, δ
exp
, P
exp
, h, F), where
• Q = {A
h
, A
m
, A
M
} is the set of states, which is
composed by the three automata;
• Σ
C
= Σ
h
∪ Σ
m
∪ Σ
M
is the set of all symbols rec-
ognized by the automaton;
• Σ
A
= C : a symbol corresponds to a class that will
be tested in the next state of the automaton
• δ is given in Figure 3;
• for all A
q
∈ Q , for a word w ∈ L
q
recognized by
A
q
, for all O ∈ Σ
exp
, the belief function B
exp
is
A Model-Checking Framework for Neuro-Degenerative Deficit Screening and Personalized Training
355

Table 2: Factors of B
q
, for all q ∈ Q .
q A
h
A
m
A
M
∆
h
q
2.016 0 0
a
h
q
0.5 1 -0.1
b
h
q
-3.6 1.2 0.1
c
h
q
1 0.3 0.1
d
h
q
0.7 2.2 -2.4
v
h
q
0 0 1
z
h
q
0 -1 1.1
∆
M
q
6.256 0 3.769
a
M
q
2.4 -1 -6.6
b
M
q
2.1 1 0.4
c
M
q
-1 1.4 0.01
d
M
q
0.24 0.8 1.6
v
M
q
1 1 1
z
M
q
0 -6.3 0.4
such that for all q ∈ Q , w ∈ L
q
, x ∈ Σ
A
:
B
q
(w, h, A
h
) =
1 if ∆(w) < ∆
h
q
v
h
q
+
a
h
q
b
h
q
+ c
h
q
e
d
h
q
∆(w)+z
h
q
otherwise
B
q
(w, M, A
M
) =
0 if ∆(w) < ∆
M
q
v
M
q
+
a
M
q
b
M
q
+ c
M
q
e
(
d
M
q
∆(w)+z
M
q
)
otherwise
B
q
(w, m, A
m
) = 1 − B
q
(w, h, A
h
) − B
q
(w, M, A
M
)
• h ∈ Q is the initial state, that corresponds to the
initial hypothesis on the class in which the patient
belongs to.
• F = Q: we consider each state to be an accepting
state.
We defined a function ∆ : L
q
→ R representing a
confidence score for the patient not to belong to the
class tested by the automata A
q
. The domain of this
function is defined on [0, m], with m ∈ R which is the
max score (here m = 10). 0 indicates that the patient
did not do any mistake, while m indicates that the pa-
tient did 100% mistakes or left the game, i.e., she did
the θ action. We consider a factor for each action:
k
β
= 1 and k
α
= 1 since we aim to count the number
of mistakes. However, since we have also θ and γ as
possible, to count these actions we associate a factor
to each one. We consider a factor k
γ
= 0.2 indicat-
ing that five γ are equivalent to do one mistake. Fi-
nally, k
θ
= 1 × 10
9
: if the patient leaves the game, we
consider it as 100% mistakes. Thus, ∆ computes the
number of mistakes (i.e., β actions) and weights the
number of waiting actions (i.e., γ actions). To do so,
we introduce a function for each x ∈ Σ
C
, |.|
x
: Σ
∗
C
→ N
that counts the number of x in a word w ∈ Σ
∗
C
and we
note |w|
x
this number. The formal definition is the
following one, for all words w ∈ Σ
⋆
C
:
∆(w) =
(
m if θ ∈ w
m×(k
β
×|w|
β
+k
γ
×|w|
γ
+k
θ
×|w|
θ
)
k
α
×|w|
α
+k
β
×|w|
β
+k
γ
×|w|
γ
+k
θ
×|w|
θ
otherwise
In Table 2, we give the factors defined for each
B
q
. These factors considered in each B
q
have been
computed based on Table 1 so that the output class
from a test corresponds to the class given by this ta-
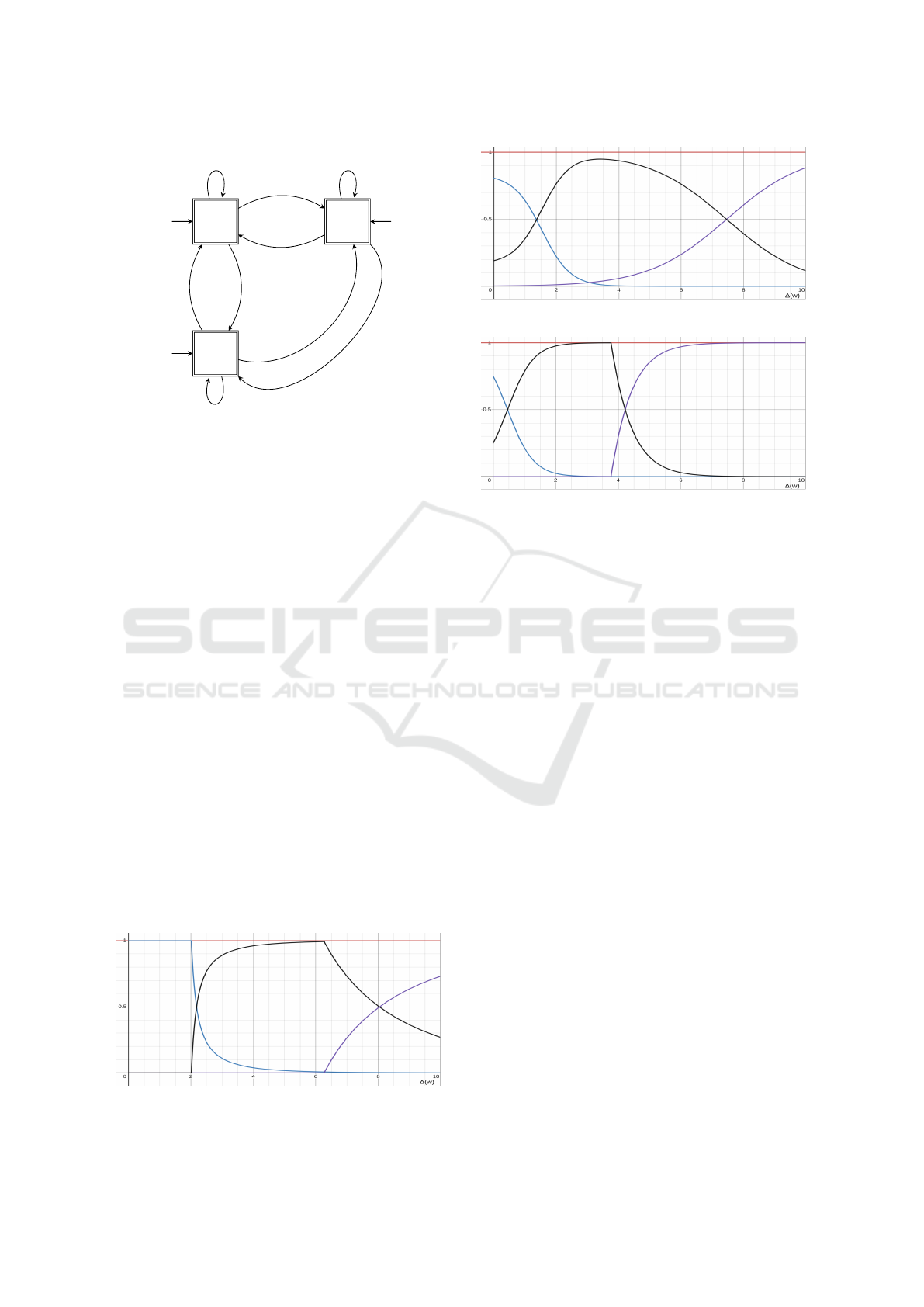
ble. Figure 4, 5 and 6 represent the different be-
lief functions for each automaton A
h
, A
m
and A
M
,
respectively. Thus, to be considered in h, the pa-
tient has to produce at least 80% of good answers
(the value given in Table 1 is 0.84). So, the delta
is computed as 1 − 0.84 = 0.16. This value corre-
sponds to the abscissa of the first intersection be-
tween the green and the black curves in Figure 5.
The green curve represents the variation of the belief
B
A
m
(w, h, A
h
), i.e., when we believe the patient could
be in h. The black curve represents the variation of
the belief B
A
m
(w, m, A
m
), i.e., when we believe the
patient could be in m. This intersection between the
green curve and the black one is approximately for
a ∆(w) = 0.16, it represents the moment where the
practitioner considers the patient in m and should do
the test again. After 75% mistakes, we believe that
the patient could be in M and this is represented by
the intersection between the black curve and the pur-
ple curve. The purple curve represents the variation
B
A
m
(w, M, A
M
). Figure 4 represents the change of
belief in function of the result w of the patient when
the test A
h
has been done. The green curve represents
B
A
h
(w, h, A
h
), the black curve B
A
h
(w, m, A
m
), and the
purple curve B
A
h
(w, M, A
M
). After more than 20%
mistakes, the belief to be in h decreases a lot to reach
the intersection with the belief to be in m. Let us no-
tice that, contrary to the green curve in Figure 5, the
belief to be in h is slightly shifted to the right, since
we consider the test A
h
to be harder, and therefore
tolerate the patient to make a few more errors. Af-
ter 80% mistakes, we start to believe the patient could
belong to the class M and we would have to do the
M transition. Figure 6 represents the change of be-
lief in function of the result w of the patient when the
test A
M
has been done. We do not tolerate more than
13% mistakes to be in class h. This is depicted by
HEALTHINF 2025 - 18th International Conference on Health Informatics
356
A
h
h = h
A
m
h = m
A
M
h = M
h
m
h
m
h
M
m
M
M
Figure 3: Automaton of the experimental protocol.
the intersection point between the green curve and the
black curve. Let us notice that, since we applied the
easiest test A
M
, we cannot fully believe the patient
belongs to the class h even if the patient does no mis-
take. This is represented by the fact that, for ∆(w) = 0,
B
A
M
(w, h, A
h
) = 0.8.
Figure 3 represents the experimental protocol as a
DDFMA. The transitions represent the next test to ap-
ply. To know the next transition, i.e., the next test to
apply, we compute a score from the current test with
the ∆ function. Then, this score is considered as an in-
put for the belief function B. This function represents
the beliefs of a clinician or a set of clinicians about
the results obtained from the test.
The first test to apply, i.e., the initial state, depends
on the initial hypothesis h we consider. Then, we start
by the corresponding test q to validate or reject h and
get a score; then this score is considered as an input
for the function B
q
that returns the next test to apply.
Let us admit the initial hypothesis is h = h, i.e., the
patient is assumed to be in the class h. We then apply
the test A
h
: after the test is over, we have evaluated if
the patient is in h or if we have to reject the hypoth-
esis. To compute the score we consider the ∆ func-
tion previously defined, which computes the number
of actions that are not the right action (i.e., α).
Figure 4: Evolution of B
A
h
in function of ∆(w).
Figure 5: Evolution of B
A
m
in function of ∆(w).
Figure 6: Evolution of B
A
M
in function of ∆(w).
If we could not reject the hypothesis, the evalua-
tion is h, which means we confirm the hypothesis as
acceptable w.r.t. the test. If the result is m, it is highly
possible that the patient is in m. The change of class
will be suggested to practitioners
5 FORMAL VALIDATION
In this section, we apply the DDFMA framework to
the serious game introduced in Section 2, employing
a PDFA-based representation to describe the expected
behavior of each class of patients while playing the
game. Firstly, we provide examples of PCTL proper-
ties to test the aptitude of the models to dispaly some
interesting behaviours. Secondly, we apply LTL to
the execution traces of the meta-automaton in order to
define stopping conditions for the protocol. Thirdly,
we give concrete decision-making capabilities of the
meta-automaton and show some properties holding in
our medical application, including examples of ac-
ceptable and unacceptable traces.
5.1 Using PCTL to Assess Model
Probabilistic Behavior
The behaviour of the game for each class of patients
is modelled with a PDFA that has the Markov Chain
Property. In order to apply model-checking to our ap-
plication, we define PDFA models :
Definition 3. Let Atm be a set of symbols called
atomic propositions. We call M = (A, V ) a PDFA
A Model-Checking Framework for Neuro-Degenerative Deficit Screening and Personalized Training
357

model iff A is PDFA and V : Atm → 2
Q
is a valua-
tion function where Q is the set of states of A. We call
M = (A, V ) a DDFMA model iff A is a DDFMA and
V : Atm → 2
Q
is a valuation function where Q is the
set of states of A.
We define the following PDFA models: M
h
=
(A
h
, V
h
), M
m
= (A
m
, V
m
) and M
M
= (A
M
, V
M
), for
each automaton A
h
,A
m
and A
M
. We consider each
action to be represented as an atomic proposition, de-
noted by Atm = { α, β, γ, θ}, verified in the acces-
sible state with the corresponding transition. Given
a PDFA model M ∈ {M
h
, M
m
, M
M
}, if we access a
state s with the action β, then the atom β is veri-
fied in s, denoted by M, s |= β. Each final state f
1
(resp. f
2
) has a corresponding atom a
1
(resp. a
2
),
i.e., M, f
1
|= a
1
and M, f
2
|= a
2
. Given a model M
c
,
with c ∈ {h, m, M}, and a state s in M
c
, we check if
the state s in M
c
satisfies the following PCTL useful
property examples.
Reachability of a Final State. Is the probability of
reaching a final state equal to 1? The PCTL formula
to test is P =1 [F (a1 or a2)].
Reachability of a State Without Violating Some
Constraints. Is the probability to reach a certain
state d without violating some constraints c greater
than 0? The PCTL formula to test is P >0[c U d].
Reachability of a State Without Passing From An-
other. Which is the probability to reach a state d
without passing from a state b? The PCTL formula to
test is P =?[(not b) U d].
5.2 LTL Analysis of Patient
Experiences: Protocol Stop
Conditions
In this section we consider the DDFMA A defined in
Section 4.2 and we note its corresponding DDFMA
model M = (A, V ). The valuation function V is
such that each transition t ∈ C (where C = {h, m, M})
is associated with an atomic proposition verified in a
state q ∈ Q . For instance, if we do a transition m
to reach a state q
m
, then the corresponding atomic
proposition m is verified in q
m
, i.e., M , q
m
|= m.
5.2.1 Oscillating Behaviour
If we detect a trace τ = (q
0
, q
1
, . . . , q
n
) ∈ Q
n+1
showing that the patient alternated between different
classes, then we want to stop the protocol. Hereafter
we provide some examples of traces we aim to detect
by providing a regular expression: (m . ∗ M)
4
(resp.
(h . ∗ M)
4
, (h . ∗ m)
4
), i.e., the patient oscillates be-
tween m and M (resp. h and M, h and m) four consec-
utive times. Here ”.” denotes any character of C and
∗ is the quantification ”zero or more occurrences”.
Let q
0
be the first state of a trace τ. q
0
verifies
the stop condition if it satisfies the following LTL for-
mula: m and F (M and F (m and F (M and
F(m and F (M and F (m and F M )))))).
5.2.2 The Permitted Number of Tests Has Been
Exceeded
We consider that a patient will not do more than 10
tests. Given an initial state q
0
for a trace τ, q
0
verifies
this stop condition if it satisfies the LTL formula: X
10
true and not X
11
false, where X
n
is a shortcut
for X...X with n occurrences of X.
5.2.3 Reaching A Steady-State Condition
If a patient stays in the same class for at least 3
tests, we stop the test. For instance, given a trace
τ = (q
0
, . . . , q
n
), a state q
n−2
verifies this stop condi-
tion for the healthy class if it verifies the LTL formula:
h and X(h and X h).
5.3 Acceptable and Unacceptable
Traces
Some traces are unacceptable. For instance, if the pa-
tient gives wrong answers but he is considered as h,
then we do not want her to stay in the class h. In the
same way, if the patient has a very positive outcome
but is considered as m, then we would like to check in
a more accurate way if she could be classed as h. But
we allow a mitigated outcome to make the patient stay
in the same state. In the following, given a DDFMA
model M = (A, V ), we formally show that our belief
functions are compatible with these properties.
5.3.1 An Extremely Poor Outcome In A
h
Cannot
Classify a Patient as h
A trace in the DDFMA looks like τ = hβγ ∗ βγ ∗ βh.
This trace recognized by a DDFMA means that we
initialize the DDFMA in the state A
h
to make the pa-
tient perform this test. In this test, the word recog-
nized by the automaton A
h
is βγ ∗ βγ ∗ β. This trace
signifies that the patient only does wrong answers β,
and may wait between actions, i.e., γ∗.
We formally show that, according to the DDFMA
model defined in Section 4.2, this is impossible. Let
consider a word w = βγγβββγβ
5
γβ recognized by the
HEALTHINF 2025 - 18th International Conference on Health Informatics
358

test A
h
, i.e., this is the execution of actions of the pa-
tient. Here obviously ∆(w) = m = 10. Thus accord-
ing to Figure 4, the belief B
A
h
(w, M, A
M
) = 0.72 and
B
A
h
(w, m, A
m
) = 0.28. Since the belief of belonging
to M is stronger than belonging to m, the automaton
should propose a transition towards A
M
and so τ can-
not be verified in this configuration for our DDFMA.
5.3.2 A Very Good Outcomes In A
M
Can
Classify a Patient as h
Let consider that a patient does 100% of α in the au-
tomaton A
M
. A word recognized by A
M
could be
w = α
10
. Thus, ∆(w) = 0 and B
A
M
(w, h, A
h
) = 0.75
if we look at Figure 6. In such situation an acceptable
trace would be Mwh.
5.3.3 A Medium Outcomes In A
m
Can Classify
A Patient As m
A medium outcome in A
m
corresponds to all words w
recognized by A
m
such that ∆(w) ∈ [1.364, 7.45]. For
instance a word w = (αβ)
5
have a ∆(w) = 5 and so
B
A
m
(w, m, A
m
) = 0.8765. In such situation an accept-
able trace by the DDFMA would be mwm.
6 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
WORK
Artificial intelligence is increasingly being embraced
for medical applications, revolutionizing healthcare
with its innovative capabilities. In this work we
proposed a framework to model the behaviour of
Alzheimer patients while playing serious games over
several game sessions. The utility of the proposed
methodology is twofold: (i) complement the diag-
nosis of medical doctors thanks to our formal analy-
sis of the patient performances while playing serious
games; (ii) help practitioners by dynamically suggest-
ing the next step, i.e., game or difficulty level, to pro-
pose to the patient after each game session. One of
the main strengths of the proposed methodology is to
be very general, and thus suited to be exploited for
other kinds of medical protocols, e.g., diagnosis and
training of children affected by attention disorders.
The approach we propose in this article was de-
vised after numerous discussions with the clinicians
of Claude Pompidou Institute, Nice, France. Before
implementing the methodology, we need a theoretical
model to present to practitioners. As a next step, we
intend to implement all the models in the Probablistic
Model Checker PRISM (Kwiatkowska et al., 2011)
and to develop an automated tool at the clinicians’
disposal. For the sake of simplicity, we provided only
one game and one difficulty level. Actually, the pro-
tocol can include the possibility to alternate different
games, and different difficulty levels for each game.
We dispose of several games targeting different cogni-
tive functions which may be affected in Alzheimer pa-
tients, such as memory or inhibitory control. Finally,
the formal approach presented in this work opens an
avenue in automating medical protocols and allows to
dynamically keep practitioners aware about the pos-
sible evolution on the patient disease severity level.
The meta-automaton dynamically evaluates the confi-
dence levels of practitioners regarding a patient’s di-
agnosis by analyzing the consistency and progression
of their in-game performance across sessions. This
adaptive mechanism not only enhances diagnostic ac-
curacy over time but also personalizes the therapeu-
tic aspect of the games. By automatically adjust-
ing the complexity and nature of subsequent game
sessions based on prior performance, our protocol
ensures that each patient receives tailored cognitive
training. This personalized approach maximizes the
therapeutic benefits, making serious games a power-
ful dual-purpose tool for both diagnosing and training
patients with neurodegenerative diseases.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We thank Valeria Manera from Institut Claude Pompi-
dou, Nice, France, for her valuable insights and fruit-
ful discussions on Alzheimer’s patients.
REFERENCES
Alvarez, J., Jessel, J.-P., and M
´
ethel, G. (2007). Pbl and se-
rious game. In Moore, G. and Hernandez, A., editors,
7th ALE International Workshop, Toulouse.
American Psychiatric Association (2013). Diagnostic and
Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. Number 21.
American Psychiatric Association, 5th edition.
Anguera, J. A., Boccanfuso, J., Rintoul, J. L., Al-Hashimi,
O., Faraji, F., Janowich, J., Kong, E., Larraburo, Y.,
Rolle, C., Johnston, E., and Gazzaley, A. (2013).
Video game training enhances cognitive control in
older adults. Nature, 501(7465):97–101.
Behrmann, G., David, A., and Larsen, K. G. (2004). A Tuto-
rial on UPPAAL. In Formal Methods for the Design of
Real-Time Systems: 4th International School on For-
mal Methods for the Design of Computer, Communi-
cation, and Software Systems, SFM-RT 2004, number
3185 in LNCS, pages 200–236. Springer.
Cimatti, A., Clarke, E. M., Giunchiglia, F., and Roveri, M.
(1999). NUSMV: A new symbolic model verifier. In
A Model-Checking Framework for Neuro-Degenerative Deficit Screening and Personalized Training
359

Computer Aided Verification, 11th International Con-
ference, CAV ’99, Trento, Italy, July 6-10, 1999, Pro-
ceedings, pages 495–499.
Clarke, E., Grumberg, O., and Peled, D. (1999a). Model
Checking. MIT Press.
Clarke, E. M., Emerson, E. A., and Sistla, A. P. (1986). Au-
tomatic verification of finite-state concurrent systems
using temporal logic specifications. ACM Trans. Pro-
gram. Lang. Syst., 8(2):244–263.
Clarke, E. M., Grumberg, O., and Peled, D. A. (1999b).
Model Checking. MIT Press.
De Maria, E., L’Yvonnet, T., Moisan, S., and Rigault, J.
(2019). Probabilistic activity recognition for serious
games with applications in medicine. In Hasan, O.
and Mallet, F., editors, Formal Techniques for Safety-
Critical Systems - 7th International Workshop, FTSCS
2019, Shenzhen, China, November 9, 2019, Revised
Selected Papers, volume 1165 of Communications in
Computer and Information Science, pages 106–124.
Springer.
Dehnert, C., Junges, S., Katoen, J.-P., and Volk, M. (2017).
A storm is coming: A modern probabilistic model
checker. In Computer Aided Verification, pages 592–
600. Springer.
Hansson, H. and Jonsson, B. (1994). A logic for reasoning
about time and reliability. Formal aspects of comput-
ing, 6(5):512–535. Springer.
Holzmann, G. J. (2004). The SPIN Model Checker - primer
and reference manual. Addison-Wesley.
Kathryn, J. M., Ewbank, D. C., Wang, H., and Trojanowski,
J. Q. (2014). The impact of exercise, cognitive activ-
ities, and socialization on cognitive function: Results
from the national long-term care survey. American
Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease & Other Dementias,
29.
Kato, P. and Klerk, S. (2017). Serious games for assess-
ment: Welcome to the jungle. Journal of Applied Test-
ing Technology, 18.
Kwiatkowska, M., Norman, G., and Parker, D. (2011).
PRISM 4.0: Verification of Probabilistic Real-time
Systems. In Proc. 23rd Int. Conf. on Computer Aided
Verification (CAV’11), volume 6806, pages 585–591.
Springer.
L’Yvonnet, T., Maria, E. D., Moisan, S., and Rigault, J.
(2021). Probabilistic model checking for human activ-
ity recognition in medical serious games. Sci. Comput.
Program., 206:102629.
Melenhorst, A.-S., Rogers, W. A., and Bouwhuis, D. G.
(2006). Older adults’ motivated choice for technologi-
cal innovation: Evidence for benefit-driven selectivity.
Psychology and Aging, 21.
Norris, J. R. (1998). Markov chains. Number 2.
Philippe, R., K
¨
onig, A., Amieva, H., Andrieu, S., Bremond,
F., Bullock, R., Ceccaldi, M., Dubois, B., Gauthier,
S., Kenigsberg, P.-A., Nave, S., Orgogozo, J. M., Pi-
ano, J., Benoit, M., Touchon, J., Vellas, B., Yesavage,
J., and Manera, V. (2014). Recommendations for the
use of serious games in people with alzheimer’s dis-
ease, related disorders and frailty. Frontiers in Aging
Neuroscience, 6:54.
Rabin, M. O. (1963). Probabilistic automata. Information
and control, 6(3):230–245.
Sistla, A. P. and Clarke, E. M. (1985). The complex-
ity of propositional linear temporal logics. J. ACM,
32(3):733–749.
Sun, J., Liu, Y., Dong, J. S., and Pang, J. (2009). PAT:
Towards Flexible Verification under Fairness. In 21th
International Conference on Computer Aided Verifi-
cation, volume 5643, pages 709–714. Springer.
Tong, T., Chignell, M., Tierney, M. C., and Lee, J. (2016). A
serious game for clinical assessment of cognitive sta-
tus: Validation study. JMIR Serious Games, 4(1):e7.
Tran, M. K. P., Br
´
emond, F., and Robert, P. (2015). As-
sistance for Older Adults in Serious Game Using an
Interactive System. In 4th Int. Conf. on Games and
Learning Alliance (GALA), pages 286–291. Springer.
Vanessa, V., Wyss, P., Rampa, L., Mitache, A. V., M
¨
uri,
R. M., Mosimann, U. P., and Nef, T. (2017). Evalua-
tion of a novel serious game based assessment tool for
patients with alzheimer’s disease. PLOS ONE, 12.
HEALTHINF 2025 - 18th International Conference on Health Informatics
360
