
BL-MVC: Blockchain Enabled Majority Voting Classifier for Predicting
Heart Diseases
Deepa Kumari
a
, Akshat Kumar K, Ashutosh Wagh, S Shashank, Abhishek Patidar
and Subhrakanta Panda
b
CSIS Department, BITS Pilani, Hyderabad Campus, Shameerpet, Hyderabad, India
Keywords:
Blockchain, IPFS, Majority Voting Classifier, Electronic Health Records, Machine Learning.
Abstract:
This paper introduces an innovative framework merging Block-chain and a Majority Voting Classifier (MVC)
for heart disease detection, aiming to enhance security and accuracy in managing Electronic Health Records
(EHR). The proposed system leverages Blockchain’s distributed ledger and smart contract capabilities to create
a secure, tamper-resistant repository for heart-related patient data. The architecture comprises a user-friendly
React-based front-end and a FastAPI-powered back-end, interfacing with a local blockchain like Ganache.
Solidity smart contracts ensure transparent and secure storage of patient responses, which the framework an-
alyzes through various machine learning models, including hyper-tuned LR, MLP, AdaBoost, CatBoost, and
XGBoost. The proposed approach ensembles the prediction using MVC and achieves diagnostic accuracy
up to 90%. This paper also compares machine learning models’ performance using evaluation metrics such
as accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, precision, F1-measure, Matthew correlation coefficient (MCC), and ROC
curve. This integrated framework can empower physicians to diagnose heart disease patients while safeguard-
ing sensitive health data accurately.
1 INTRODUCTION
Blockchain technology has widespread adoption in
various sectors, including industry and healthcare
(Kumari et al., 2021). Its applications extend to di-
verse areas, such as developing cancer diagnosis and
prognosis systems and systems focused on heart dis-
eases, integrating family history and relevant parame-
ters (Dang et al., 2023). Researchers, including Shab-
bir et al. (Shabbir et al., 2023), have investigated the
impact of factors like allergies, food preferences, age,
and blood pressure on utilizing online health facili-
ties. Intelligent technologies like Machine Learning
(ML), Deep Learning (DL), and Cloud-Assisted ap-
proaches have gained prominence in heart disease de-
tection and prevention (Amin et al., 2021).
Healthcare professionals use Electronic Health
Records (EHRs) and Personal Health Records (PHRs)
to provide informed advice. Health records stored on
the blockchain ensure data integrity and prevent tam-
pering by third parties (Wenhua et al., 2023). The
use of cryptographic notations and public key infras-
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0696-9790
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4768-772X
tructure enhances security in the blockchain network.
Additionally, a social network-based healthcare sys-
tem integrates blockchain and IEEE 802.15.6 proto-
cols for secure health data transfer (Shah et al., 2023).
Other architectures, such as the mHealth communi-
cation framework and blockchain-enabled intelligent
IoT architecture, leverage blockchain for safe stor-
age and effective management of health data (Alam,
2020). Despite the cryptographic solutions provided
by blockchain, challenges such as privacy, scalabil-
ity, and interoperability persist (Shah et al., 2023).
The MedRec system pioneered the use of blockchain
for electronic patient record management. Still, con-
cerns about data accessibility and vulnerabilities due
to third-party databases have led to alternative ap-
proaches, like the healthcare management system pro-
posed by Ivan (Verdonck and Poels, 2020). This sys-
tem prioritizes patient control over data access, en-
suring heightened security and privacy. While multi-
ple platforms and frameworks exist for medical data
management using blockchain, integration with intel-
ligence still needs to be explored, potentially due to
additional associated costs.
The motivation behind the proposed blockchain-
enabled Majority Voting Classifier (MVC) work is
Kumari, D., K., A. K., Wagh, A., Shashank, S., Patidar, A. and Panda, S.
BL-MVC: Blockchain Enabled Majority Voting Classifier for Predicting Heart Diseases.
DOI: 10.5220/0013096800003890
In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2025) - Volume 2, pages 45-56
ISBN: 978-989-758-737-5; ISSN: 2184-433X
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
45

Figure 1: Application Architecture of the proposed system.
rooted in the need to overcome significant challenges
in healthcare data management systems. MVC is an
ensemble learning technique that combines the pre-
dictions of multiple classifiers to make a final decision
based on the majority vote. This approach enhances
predictive accuracy and robustness by leveraging the
strengths of individual models while minimizing the
impact of their weaknesses. Its ability to integrate
results from multiple classifiers makes it a powerful
tool for applications in healthcare, where precision
and reliability are critical. Traditional approaches,
such as those outlined in (Jabarulla and Lee, 2021)
often struggle with critical issues including data secu-
rity, patient privacy, scalability, and the lack of intelli-
gent predictive capabilities. These limitations hinder
the effective use of healthcare data, particularly in the
context of Electronic Health Records (EHRs), where
data breaches and mismanagement can have severe
consequences.
To address these challenges, the proposed MVC
framework integrates machine learning models with
blockchain technology to offer a comprehensive and
secure solution. The blockchain ensures immutable,
decentralized, and transparent storage of EHRs, safe-
guarding patient data from unauthorized access or
tampering. At the same time, the MVC leverages ad-
vanced machine learning algorithms ((Kumari et al.,
2024c)) to accurately predict potential heart ailments
based on patient data, enhancing the predictive capa-
bilities of healthcare systems.
The key contributions of this work are twofold:
(1) a novel integration of blockchain with machine
learning-based prediction models that guarantees both
secure EHR storage and intelligent, data-driven clin-
ical predictions, and (2) an evaluation demonstrating
the efficacy of this approach in terms of improved se-
curity, privacy, and prediction accuracy in healthcare
data management.
The subsequent sections of the paper delve into
the methodology of the proposed system in Section 2,
blockchain storage in Section 3, performance evalua-
tion in Section 4, comparative analysis with existing
frameworks in Section 5, and finally, the conclusion
and future research directions in Section 6.
2 METHODOLOGY
The proposed architecture consists of two integral
components, a front-end and a back-end, designed
to efficiently predict potential heart ailments based
on patient data, as depicted in Figure 1. The
front-end, developed using React, is focused on
user-friendliness, allowing patients to submit health-
related responses seamlessly. These responses are
securely stored on the blockchain through Solidity-
based smart contracts, with deployment on a lo-
cal blockchain environment such as Ganache. This
blockchain integration ensures that patient data is im-
mutably and transparently stored. Once patients sub-
mit their responses, the front-end interacts with the
blockchain to record the transaction and triggers the
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
46

backend for prediction. The technology stack in-
cludes React, HTML, CSS, with Material UI provid-
ing a clean and intuitive interface. The use of the
web3 storage library within React also enables secure
storage of images or other media files on Interplane-
tary File System (IPFS).
The back-end, powered by Python’s FastAPI
framework, manages server-side operations includ-
ing the interaction with blockchain events, API re-
quests, and machine learning predictions. When a
patient submits their data through the front end, it is
passed to the back end, which invokes pre-trained ma-
chine learning models to generate predictions about
potential heart ailments. The classifiers used in-
clude hyper-tuned models such as Logistic Regres-
sion (LR), Multi-layer Perceptron (MLP), AdaBoost,
CatBoost, and XGBoost. The Majority Voting Clas-
sifier (MVC) acts as an ensemble method that aggre-
gates the predictions of individual models to provide a
more accurate overall decision regarding the patient’s
health.
Figure 2 depicts the workflow of the proposed
framework. The interaction between blockchain and
machine learning is pivotal in ensuring both the se-
curity and transparency of patient data, as well as the
trustworthiness of the predictive system. Patient data
is first verified and securely stored on the blockchain,
ensuring that the input data used for machine learning
predictions cannot be tampered with. After predic-
tions are made, the results are similarly stored on the
blockchain to ensure that the integrity of the diagnosis
is maintained. This guarantees a traceable, immutable
log of patient interactions and predictive outcomes.
To ensure system validity and reliability, the sys-
tem architecture is carefully designed and rigorously
tuned. The machine learning models are trained and
tested on publicly available healthcare datasets (as
discussed in 2.1). Feature selection was performed
to optimize model performance, and hyperparame-
ters were tuned using grid search and cross-validation
techniques. The model was evaluated using stan-
dard performance metrics, including accuracy, preci-
sion, recall, F1 score, and the area under the ROC
curve (AUC), to ensure robust predictive capabilities.
Furthermore, the blockchain system was tested using
simulated networks (e.g., Ganache) to verify transac-
tion speed, data integrity, and scalability under vary-
ing loads.
2.1 Dataset
The work relies on a dataset with a comprehensive
history sourced from the Behavioural Risk Factor
Surveillance System (BRFSS), administered by the
Centre for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
since 1984 (Nelson et al., 2001). For the anal-
ysis, the dataset selected corresponds to the 2015
BRFSS (
1
Kaggle Dataset), encompassing a signif-
icant volume of 253,680 survey responses. The
dataset proves particularly valuable for binary clas-
sification tasks related to heart disease, specifically
focusing on the binary target variable ”Heart Dis-
ease or Attack” and 21 feature variables. These fea-
tures combine binary and ordinal variables, ensur-
ing a rich set of information for analysis. The fea-
ture variables include Heart disease attribute, HighBP,
HighCholestrol, CholCheck, BMI, Smoker, Stroke,
Diabetes, PhysActivity, Fruits, Veggies, Heavyal-
cohalConsump, NoDocbcCost, GenHlth, MentHlth,
PhysHlth, DiffWalk, Sex, Age, Education, Income.
The proposed experiment follows 5-fold cross-
validation for a robust evaluation of the model’s per-
formance compared to a single train-test split. Each
fold contains an equal number of samples. In each it-
eration, one fold is held out as the test set, while the
remaining four folds are combined to form the train-
ing set. It mitigates the impact of the data’s initial dis-
tribution and provides a more representative estimate
of the model’s ability to generalize unseen data.
2.2 Hyperparameter Optimization
Hyperparameter tuning aims to identify a given algo-
rithm’s optimal set of hyperparameters. This paper
implements two widely utilized methods for hyperpa-
rameter tuning (Kumari et al., 2023b): random search
and grid search optimization techniques. Table 1 rep-
resents the set of optimal parameters identified using
random search. The performance of these methods is
compared across five distinct machine learning mod-
els such as Logistic Regression (LR), Multi-layer Per-
ceptron (MLP) based on Sigmoid activation function,
AdaBoost, XGBoost, and CatBoost.
Random Search, a dynamic exploration strategy,
proves its strength in efficiently navigating high-
dimensional hyperparameter spaces. This approach
is particularly advantageous when dealing with mod-
els boasting numerous hyperparameters, facilitating
quicker convergence towards optimal or near-optimal
configurations. However, it comes with a trade-off,
as there is no guarantee of comprehensive exploration
of the entire hyperparameter space. Conversely, Grid
Search adopts a systematic approach, meticulously
evaluating all specified combinations of hyperparam-
eter values. While this exhaustive exploration ensures
a thorough understanding of the performance land-
1
https://www.kaggle.com/alexteboul/heart-disease-
health-indicators-dataset
BL-MVC: Blockchain Enabled Majority Voting Classifier for Predicting Heart Diseases
47
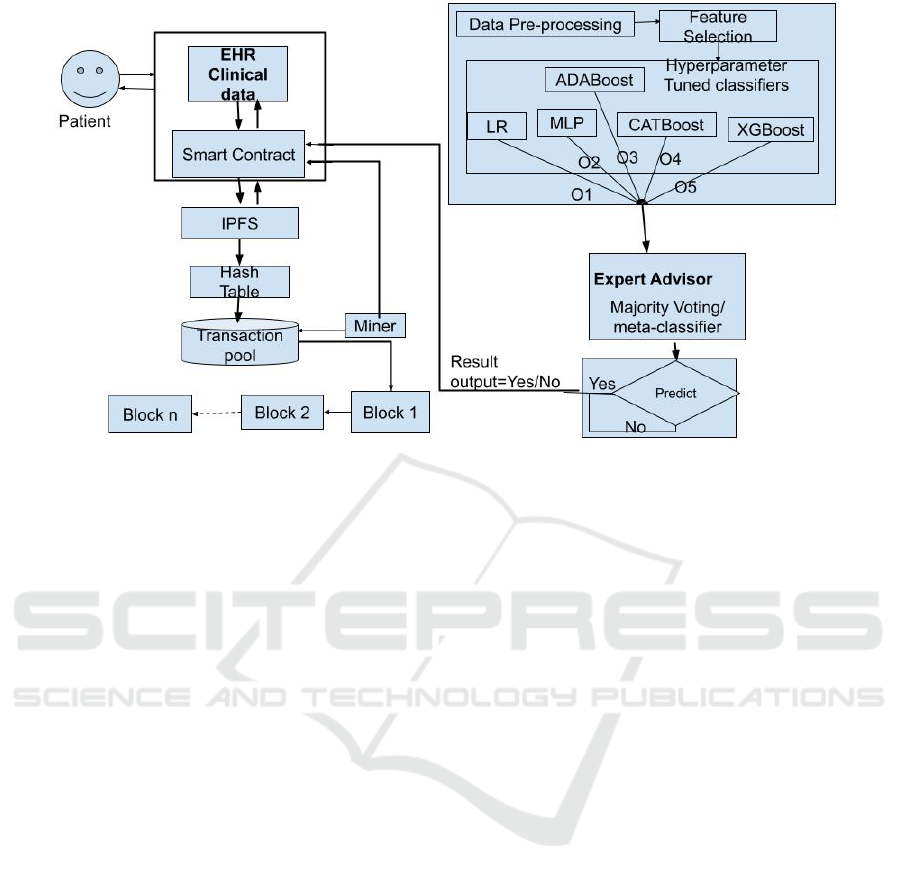
Figure 2: Blockchain enabled ML to predict health diseases.
scape, it can be computationally demanding, partic-
ularly in high-dimensional spaces.
This paper compares the performance with and
without hyperparameter tuning approaches in the
model as shown in Table 2. Without hyperparameter
tuning, model accuracy and other metric values hover
around 75% to 85%. However, using hyperparameter
tuning approaches results in a notable increment in all
performance metric values, reaching around 90-91%.
Random Search outperforms by identifying optimal
parameter values within a more efficient computation
time.
2.3 Feature Selection
The proposed methodology incorporates two widely
adopted feature selection techniques: correlation
heatmap (Chattu, 2021) and Principal Component
Analysis (PCA) (Kumari et al., 2023b) (Gupta et al.,
2012). The correlation heatmap graphically repre-
sents the correlation matrix, unveiling the correlation
coefficients among multiple variables. On the other
hand, PCA aims to reduce the dimensionality of data
by transforming it from a high-dimensional format to
a lower-dimensional representation while preserving
as much of the original data variability as possible.
A subset of 10 features out of the original 21
is selected after applying both correlation analysis
and PCA. These features, including HighBP, High-
Chol, Smoker, Stroke, Diabetes, GenHlth, MentHlth,
PhysHlth, DiffWalk, and Age, are linked significantly
to Heart Disease or Attack.
While Table 3 suggests no substantial improve-
ment in accuracy after employing feature selection.
PCA is the more impactful technique due to its abil-
ity to capture and retain essential information while
compressing the data into a lower-dimensional space.
This dimensionality reduction not only aids in com-
putational efficiency but also ensures that the selected
features contribute significantly to the model’s overall
performance.
2.4 Majority Voting Classifiers (MVC)
MVC in our approach proves particularly advanta-
geous when dealing with scenarios where individ-
ual classifiers may possess diverse strengths or weak-
nesses (Karadeniz et al., 2023). The inherent diversity
among the base classifiers enables the metaclassifier
to leverage the strengths of each while compensating
for any shortcomings they may exhibit. Algorithm
1 represents the steps involved in implementing an
ensemble approach to mitigate the impact of outliers
or anomalies present in the predictions of individual
classifiers. The majority voting meta-classifier is re-
silient and adaptable to different voting schemes. For
instance, it can accommodate weighted voting, where
each base classifier’s confidence or performance is
considered. This flexibility enhances its adaptability
to diverse datasets and varying performance levels of
the base classifiers.
This paper uses soft voting as in MVC, also known
as a weighted average or probabilistic voting classi-
fier, which is a noteworthy aspect of the ensemble
method in machine learning (Awe et al., 2024). In
this approach, multiple models contribute predictions
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
48
Table 1: Hyperparameters tuned with their initial and final values for different classifiers.
Classifier Hyperparameters Epo-
chs
Descriptions
Initial values Final Values
LR
C=[0.001, 0.01, 0.1, 1, 10,
100]
C=0.001 10 C is the regularization parameter. For a given
value of C, the regularization strength de-
creases.
Penalty=[l1, l2, none] Penalty= l2 Penalty determines the type of regularization
applied to the logistic regression model. Reg-
ularization helps prevent overfitting by adding
a penalty term to the loss function.
MLP
hidden layer sizes=[(50,),
(100,), (50, 50), (100, 50,
25)]
hidden layer sizes=
(100,)
1000 hidden layer sizes represent the number of neu-
rons in each hidden layer of the MLP.
activation= [logistic] activation= [logis-
tic]
Activation function for the hidden layer neu-
rons, e.g., logistic (sigmoid).
alpha= [0.0001, 0.001,
0.01]
alpha=0.01 L2 regularization term on weights; it adds a
penalty term to the loss function to prevent
overfitting.
AdaBoost
n estimators= [50, 100,
150, 200]
n estimators= 200 200 n estimators are number of weak learners
(trees) to train in the ensemble.
learning rate= [0.1, 0.5,
1.0]
learning rate= 0.5 learning rate defines as contribution of each
weak learner to the final prediction; a lower rate
requires more weak learners.
CatBoost
learning rate= [0.01, 0.1,
0.2]
learning rate= 0.1 100 learning rate defines as step size shrinkage to
prevent overfitting.
iterations= [50, 100, 200] iterations= 100 iterations are the number of boosting rounds
(trees) to be run.
depth= [3, 5, 7] depth= 3 Depth of the trees in the ensemble.
subsample= [0.8, 0.9, 1.0] subsample= 1.0 Fraction of samples used for training each tree.
colsample bylevel=[0.8,
0.9, 1.0]
colsample bylevel=
1.0
colsample bylevel defines the fraction of fea-
tures used for training each level of the tree.
XGBoost
learning rate= [0.01, 0.1,
0.2]
learning rate= 0.1 100 learning rate is the step size shrinkage to pre-
vent overfitting.
iterations= [50, 100, 200] iterations= 100 iterations define the number of boosting rounds
(trees) to be run.
depth= [3, 5, 7] depth= 3 Maximum depth of a tree in the ensemble.
subsample= [0.8, 0.9, 1.0] subsample= 1.0 Fraction of samples used for training each tree.
colsample bylevel=[0.8,
0.9, 1.0]
colsample bylevel=
1.0
Fraction of features used for training each level
of the tree.
Table 2: Hypertuning approaches.
parameter
Algorithm Accuracy ROC area Specificity Sensitivity NPV PPV Time (in sec)
W/o hyper- LR 76.41 84.20 73.89 78.93 77.76 75.20 44.23
MLP 77.87 85.61 73.82 81.91 80.27 75.84 137.34
AdaBoost 76.87 84.72 75.19 78.56 77.76 76.05 96.21
XGBoost 77.48 85.18 72.96 81.99 80.16 75.26 68.99
CatBoost 85.98 93.48 80.69 91.27 90.21 82.57 85.76
Search
LR 90.77 84.35 99.25 09.08 91.32 55.51 136.47
Random MLP 90.84 85.00 99.16 10.67 91.45 56.93 1054.27
AdaBoost 90.86 84.78 98.70 14.58 91.76 53.83 679.18
XGBoost 90.82 85.00 99.00 11.00 91.00 56.00 56.45
CatBoost 90.85 85.00 99.00 11.00 91.00 57.00 147.08
Grid Search
LR 90.77 85.35 99.25 10.08 91.32 58.51 144.43
MLP 90.84 85.00 99.00 13.00 92.00 61.00 1109
AdaBoost 90.86 85.69 99.22 10.21 91.42 58.63 873.98
XGBoost 90.82 85.00 99.00 09.00 91.00 58.00 1545.56
CatBoost 90.84 85.00 99.00 09.00 91.00 59.00 4185.23
BL-MVC: Blockchain Enabled Majority Voting Classifier for Predicting Heart Diseases
49

Table 3: Before and After Feature Selection.
Classifiers Heatmap correlation PCA
LR 90.64 90.83
MLP (sigmoid) 90.72 90.82
Adaboost 90.84 90.85
XGBoost 90.82 90.83
Catboost 90.82 90.83
Require: Logistic Regression parameters, MLP
parameters, AdaBoost parameters, XGBoost
parameters, CatBoost parameters
Ensure: Majority voting predictions
1: Initialize logistic classifier, mlp classifier,
adaboost classifier, xgboost classifier,
catboost classifier
2: Initialize logistic predictions, mlp predictions,
adaboost predictions, xgboost predictions,
catboost predictions
3: Train logistic classifier on data
4: Train mlp classifier on data
5: Train adaboost classifier on data
6: Train xgboost classifier on data
7: Train catboost classifier on data
8: Predict logistic predictions on data
9: Predict mlp predictions on data
10: Predict adaboost predictions on data
11: Predict xgboost predictions on data
12: Predict catboost predictions on data
13: Initialize majority voting as an empty list
14: for each data point in data do
15: Create a list votes containing
logistic predictions, mlp predictions,
adaboost predictions, xgboost predictions,
catboost predictions
16: Compute majority vote as the mode of votes
using Soft voting
17: Append majority vote to majority voting
18: end for
19: return majority voting
Algorithm 1: Majority Voting Classifier.
for a specific input, and the final prediction is de-
termined through a weighted sum of the individual
models’ probability estimates as shown in Table 4.
The assigned weights signify the perceived reliability
of each model, and the class with the highest com-
bined probability is chosen as the ultimate predicted
outcome. This technique proves valuable in cases in-
volving various models or when uncertainty exists in
individual predictions.
3 BLOCKCHAIN STORAGE
The proposed approach uses blockchain technology
to protect patient’s health records from unauthorized
access or cyber threats (Kumari et al., 2023a). The
Ethereum blockchain is chosen for its security fea-
tures (Kumari et al., 2024b). To handle image files
like ultrasounds and x-rays, the Inter-Planetary File
System (IPFS) (Azbeg et al., 2022) (Dang et al., 2023)
is used, making it efficient for storing and retrieving
large files. Health records are encrypted using sym-
metric key cryptography to ensure privacy. Access to
a patient’s record is tightly controlled, requiring spe-
cific authorization. The relevant authority oversees
this encryption process. Following are the steps for
controlling access:
1. Private Key Decryption: A private key unlocks
and reveals the health record.
2. RSA Key Pair Encryption: The public and sym-
metric keys encrypt the key for added security.
Further, if access needs to be changed or revoked, it
will be performed in following ways:
1. Decryption by Owner’s Private Key: The
owner’s private key decrypts the symmetric key.
2. Record Decryption: The decrypted symmetric
key reveals the Electronic Health Record.
3. Re-encryption with New Symmetric Key: A
new key is used to re-encrypt the health record.
4. Public Key Encryption: The new key is en-
crypted using the public keys of authorized users.
Further, in a blockchain, each block (Figure 3 con-
tains clinical information of the patients that are con-
fined with integrity and security of the entire chain.
The block header is critical as it includes the previ-
ous block’s hash, timestamp, Merkle root (hash of
all transactions), and a nonce for mining, as shown
in Figure 4. Transactions form the core of a block,
representing various data entries. The block also
includes its index, a unique hash, and the previ-
ous block’s hash, creating a secure, chronological
chain. The nonce, adjusted during mining, ensures
the block’s validity. Additional components encom-
pass data or payload, mining information, and the
block’s size. Together, these components establish a
secure, transparent, and immutable ledger, with each
block forming a permanent record of transactions in
the blockchain. Clinical data is analyzed using the
Majority Voting Classifier (MVC) Pickel model. The
Fast API of MVC then sends predictions about the
patient’s health status, notifying the patient through
a user-friendly interface. This approach ensures the
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
50
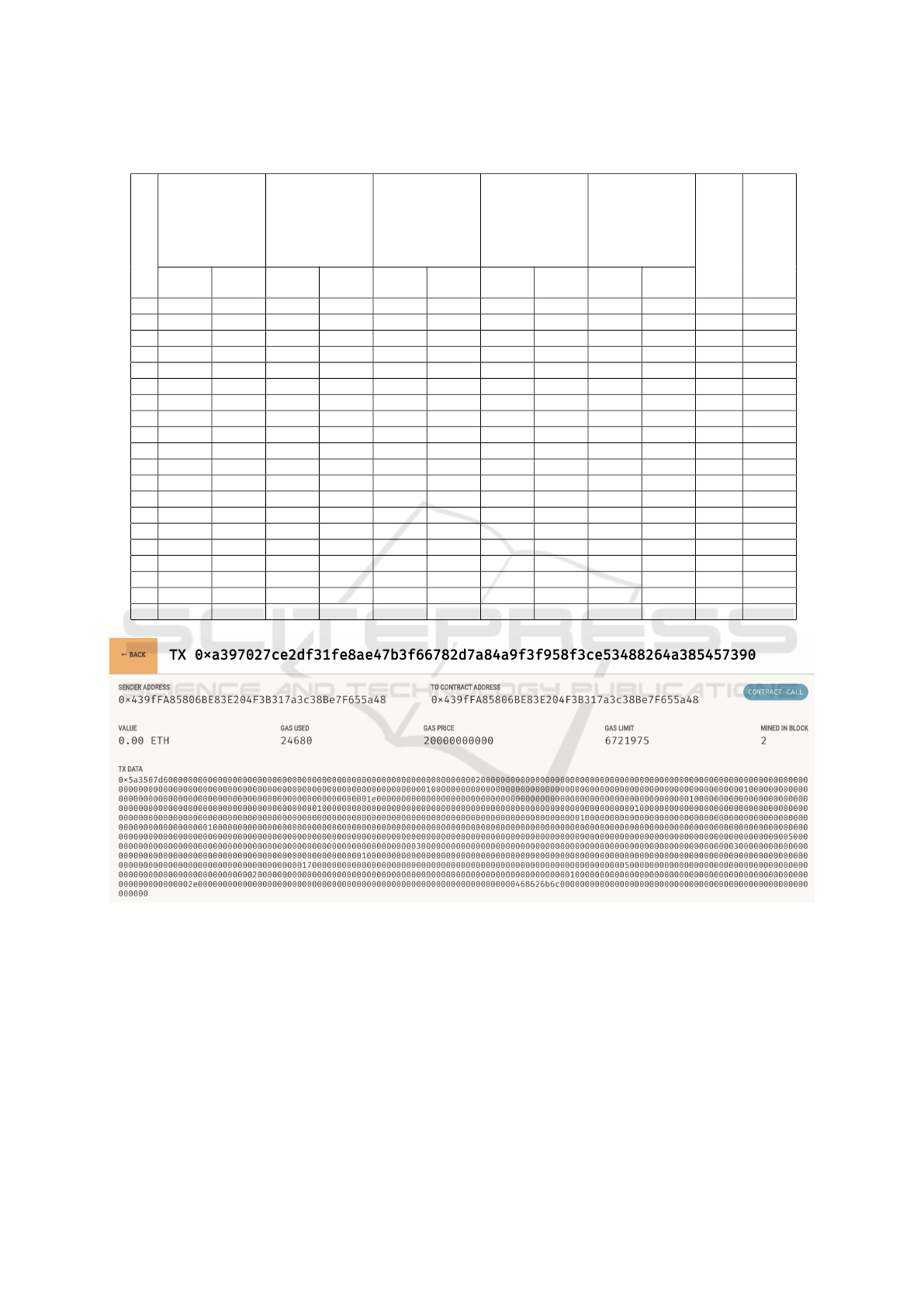
Table 4: Probability results of Majority Voting Classifiers.
Sa-
mp-
le
MLP Adaboost LR Catboost XGboost Final
Pre-
dicted
Class
Predic-
ted
Class
Prob-
abil-
ity
Class
0
Class
1
Class
0
Class
1
Class
0
Class
1
Class
0
Class
1
Class
0
Class
1
1 0.9853 0.0146 0.5932 0.4067 0.9775 0.0224 0.9831 0.0168 0.9750 0.0249 0 0.9028
2 0.8334 0.1665 0.5417 0.4582 0.8140 0.1859 0.8212 0.1787 0.8240 0.1759 0 0.7669
3 0.9989 0.0010 0.6245 0.3754 0.9973 0.0026 0.9972 0.0027 0.9944 0.0055 0 0.9225
4 0.9977 0.0023 0.6135 0.3865 0.9931 0.0069 0.9944 0.0056 0.9920 0.0080 0 0.9181
5 0.1359 0.8641 0.4500 0.8466 0.5500 0.1534 0.8430 0.1570 0.1578 0.8422 1 0.7892
6 0.9244 0.0756 0.5559 0.4441 0.9164 0.0836 0.9213 0.0787 0.9041 0.0959 0 0.8444
7 0.0589 0.9411 0.5675 0.4325 0.0652 0.9348 0.1007 0.8993 0.0771 0.9229 1 0.8531
8 0.8579 0.1421 0.5495 0.4505 0.8746 0.1254 0.8307 0.1693 0.8249 0.1751 0 0.7875
9 0.9697 0.0303 0.5747 0.4253 0.9621 0.0379 0.9573 0.0427 0.9496 0.0504 0 0.8827
10 0.9802 0.0198 0.5886 0.4114 0.9662 0.0338 0.9799 0.0201 0.9760 0.0240 0 0.8982
11 0.0142 0.9858 0.4121 0.5879 0.0313 0.9687 0.0173 0.9827 0.0182 0.9818 1 0.9014
12 0.9642 0.0358 0.5784 0.4216 0.9536 0.0464 0.9701 0.0299 0.9592 0.0408 0 0.8851
13 0.9967 0.0033 0.5988 0.4012 0.9916 0.0084 0.9842 0.0158 0.9861 0.0139 0 0.9115
14 0.9380 0.0620 0.5565 0.4435 0.9106 0.0894 0.9281 0.0719 0.9281 0.0719 0 0.8523
15 0.9899 0.0101 0.6167 0.3833 0.9928 0.0072 0.9878 0.0122 0.9858 0.0142 0 0.9146
16 0.9967 0.0033 0.6197 0.3803 0.9911 0.0089 0.9957 0.0043 0.9931 0.0069 0 0.9193
17 0.9986 0.0014 0.6340 0.3660 0.9965 0.0035 0.9972 0.0028 0.9931 0.0069 0 0.9239
18 0.4832 0.5168 0.4999 0.5001 0.4840 0.5160 0.4992 0.5008 0.4937 0.5063 1 0.5076
19 0.9673 0.0327 0.5731 0.4269 0.9679 0.0321 0.9385 0.0615 0.9438 0.0562 0 0.8781
20 0.9967 0.0033 0.6110 0.3890 0.9909 0.0091 0.9948 0.0052 0.9920 0.0080 0 0.9171
Figure 3: Block 1: Transaction Details with Sender Address, Contract Address, Gas Price, and Gas Used.
security and privacy of medical data, supporting in-
formed healthcare decisions.
Overall, the proposed framework leverages
blockchain not merely as a data registry but as a key
component for enhancing security, transparency, and
integrity beyond what traditional cloud storage can
offer. While cloud storage solutions provide secu-
rity through centralized control, blockchain’s decen-
tralized nature ensures data immutability and prevents
tampering by storing patient records across a dis-
tributed ledger. Moreover, the use of Solidity smart
contracts goes beyond basic read/write operations.
These contracts encapsulate essential business logic
for patient consent management, data access control,
and transaction verification, ensuring that only autho-
rized entities can interact with sensitive medical data.
The smart contracts are designed to automate and en-
force these rules without reliance on intermediaries,
adding an extra layer of trust and security that cen-
tralized cloud solutions cannot fully replicate. This
BL-MVC: Blockchain Enabled Majority Voting Classifier for Predicting Heart Diseases
51
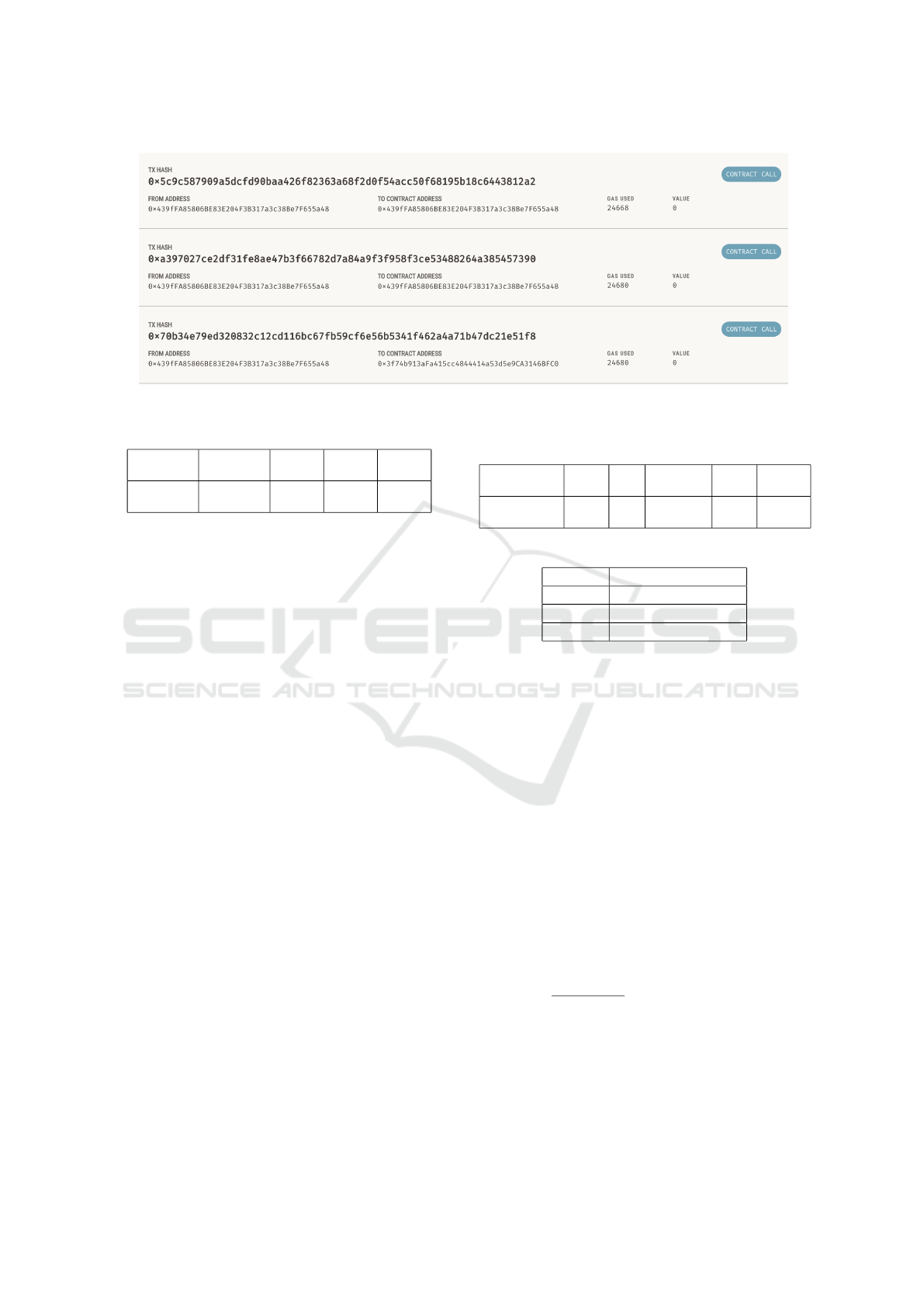
Figure 4: Summary details of 3 blocks.
Table 5: Parameters used for Block header.
Parameter
used
Previous
Hash
Time
Satmp
Nonce Merkel
Root
Length
in Bytes
32 4 4 32
framework also introduces blockchain-integrated ma-
chine learning for predictive healthcare, where each
prediction and its corresponding patient data is veri-
fiably logged on the blockchain, enabling auditability
and traceability for clinical decisions.
4 PERFORMANCE EVALUATION
This section discusses the block capacity and trans-
action processing time, while also conducting a com-
prehensive performance analysis of machine learning
classification models within the majority voting clas-
sifier framework.
4.1 Block Capacity and Its Processing
Time of Transactions
According to (Bhaskaran and Marappan, 2023), cru-
cial parameters such as the Previous Hash length, In-
dex, and Merkle Root are consistently set at 32 Bytes.
On the other hand, the Time Stamp and Nonce ad-
here to a fixed length of 4 Bytes, as outlined in Table
5. Also, the parameter details of the block’s body are
represented in Table 6. Specifically, the User ID,
signature, and Hash are uniformly designated as 32
Bytes each. Additionally, the length of transactions
(tx) and asymmetric Encryption (RSA) are standard-
ized at 32 Bytes and 256 Bytes, respectively. The
table infers that block creation time leads to several
positive outcomes. is lesser that helps Users experi-
ence faster transaction confirmations, enhancing over-
all satisfaction. Lower network latency is achieved,
Table 6: Parameters used for the body of Block of our pro-
posed system.
Parameter
Used
User
ID
tx Signature Hash Encry-
ption
Length in
Bytes
32 132 32 32 256
Table 7: Block creation time.
Blocks Block Time(in sec)
Block 0 0.06132
Block 1 0.05155
Block 2 0.04885
ensuring a synchronized state across nodes. In con-
sensus such as Proof of Authority (PoA) systems,
shorter block times can enhance security by reduc-
ing the window for potential attacks. Miners benefit
from more frequent rewards, sustaining their incen-
tives. Short block times are crucial for time-sensitive
operations in applications and smart contracts, pro-
viding quick responsiveness.
Assessing a blockchain’s throughput, particularly
in transactions per second (TPS), is multifaceted.
Throughput in the proposed approach is calculated us-
ing the system’s capacity to efficiently process a de-
fined amount of work within a given time frame. Ta-
ble 7 represents a block produced within a fraction
of a second; it’s crucial to recognize that the through-
put of a blockchain system is inherently influenced by
both the block time and the block size. The formula
to compute TPS is as follows:
T PS =
1
Block Time
× Transactions per Block
Here, the ”Block Time” denotes the duration re-
quired to produce a single block, while ”Transactions
per Block” signifies the number of transactions en-
compassed within a block.
Since a block is produced every 0.1 seconds, and
each block accommodates 100 transactions:
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
52
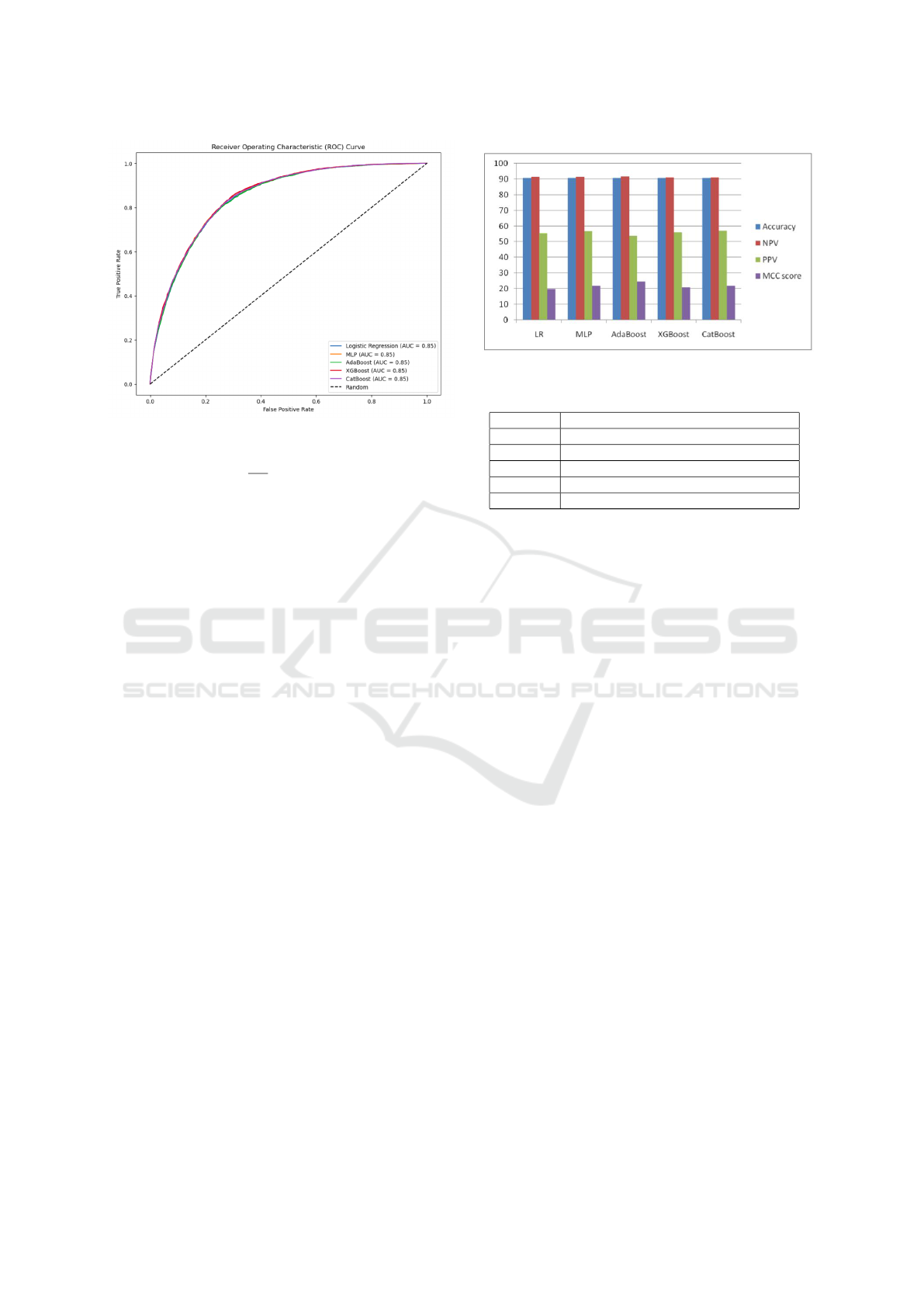
Figure 5: ROC curve analysis of different classifiers.
T PS =
1
0.1
× 100 = 1000
It implies that the system’s throughput is 1000
transactions per second, allowing the system to pro-
cess more transactions quickly. This improved scal-
ability accommodates a larger user base without
compromising performance.. It infers that the pro-
posed approach elevates TPS while considering the
blockchain protocol, consensus algorithm, and the un-
derlying network infrastructure.
4.2 Performance Analysis of ML
Classification Models in Majority
Voting Classifier
• ROC-Curve Analysis. ROC curve analysis is a
valuable tool for assessing the performance of
classifiers, particularly in distinguishing positive
and negative instances (Kumari et al., 2024a). The
goal is to have the ROC curve approach a value of
1, indicating optimal classifier performance. Fig-
ure 5 illustrates that nearly all classifiers yield a
ROC curve value of 0.85. It suggests that classi-
fiers achieve a similar balance between true pos-
itive rate (sensitivity) and false positive rate (1-
specificity).
• Performance metrics: Figure 6 infers that ac-
curacy is almost identical for almost all clas-
sifiers. Amongst all, Adaboost outperforms in
terms of Mathews Correlation Coefficient (MCC)
because of its unique ability to handle imbalanced
datasets. The MCC considers true positive, true
negative, false positive, and false negative predic-
tions, providing a balanced assessment of classi-
fier performance, especially in scenarios with im-
balanced class distributions. Thus, Adaboost ex-
Figure 6: ML performance metrics.
Table 8: MVC Prediction time.
Sno. Prediction Time taken (in milliseconds)
Sample 1 2.69
Sample 2 7.10
Sample 3 4.20
Sample 4 5.04
Sample 5 3.61
cels in achieving a high MCC, indicating its ef-
fectiveness in making accurate predictions while
considering the given dataset.
4.3 Performance Analysis of MVC
Table 8 infers information about the algorithm’s com-
putational efficiency and performance of the proposed
model. However, prediction time for Sample 2 is no-
tably higher at 7.10 milliseconds compared to Sample
1, which recorded a prediction time of 2.69 millisec-
onds. This variation in prediction times are influenced
by factors such as the complexity of the model clas-
sifiers or each sample’s specific characteristics (fea-
tures). The proposed MVC algorithm exhibits an av-
erage time complexity of O(T ), where T represents
the sum of the time complexities of individual oper-
ations involved in the algorithm, including training
classifiers, making predictions, and aggregating re-
sults:
• Training Individual Classifiers: Let T
train
repre-
sent the time complexity of training each individ-
ual classifier. If n is the number of samples and
m is the number of features, and assuming k clas-
sifiers are trained, then the time complexity for
training all classifiers is O(k ·T
train
).
• Making Predictions: Let T
predict
denote the time
complexity of making predictions with each clas-
sifier. If p is the number of samples for which
predictions are made, then the time complexity for
predictions with all classifiers is O(k · p ·T
predict
).
• Aggregating Results: Majority voting typically
BL-MVC: Blockchain Enabled Majority Voting Classifier for Predicting Heart Diseases
53
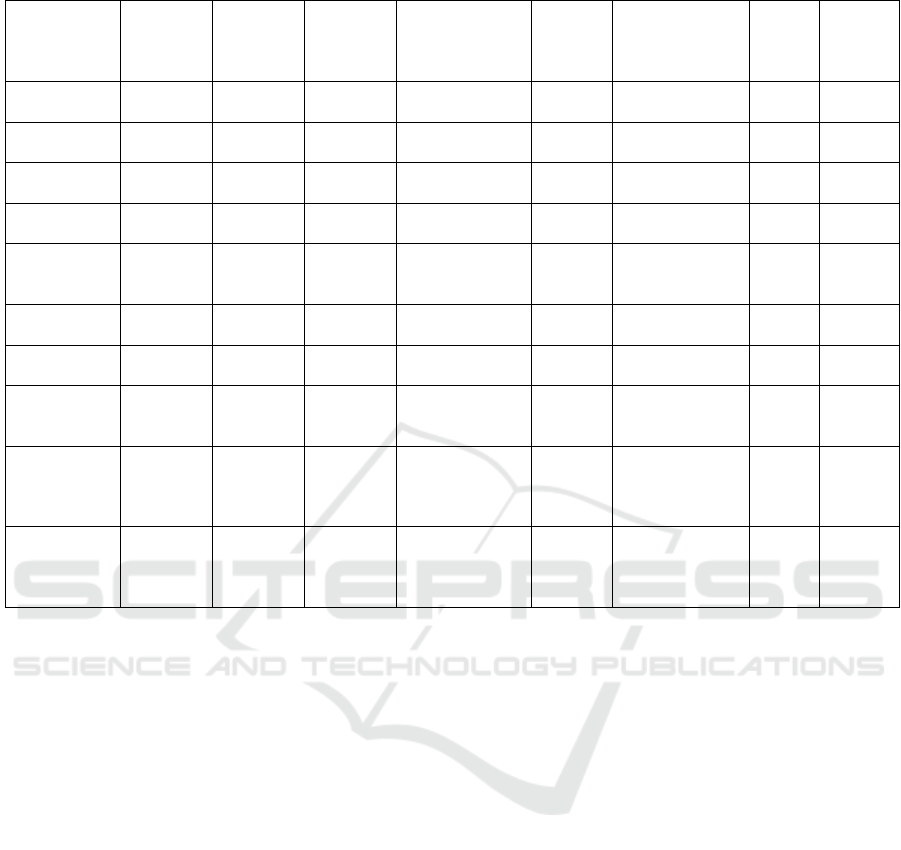
Table 9: Comparison of our system with existing works.
Ref Blockchain Consensus Network
Type
Data storage Data
En-
cryp-
tion
Security Con-
siderations
Implem-
ented
Predic-
tion
(Azaria
et al., 2016)
Ethereum PoW Permission-
less
Centralized DB No Authentication,
Confidentiality
Yes No
(Liang et al.,
2017)
Hyperled-
ger
PBFT Permission Centralized DB No Integrity, Pri-
vacy
Yes No
(Dagher
et al., 2018)
Quorum Quorum-
Chain
Permission Centralized DB Yes Privacy, Access
Control
Yes No
(Dwivedi
et al., 2019)
Ethereum PoA Permission Centralized DB Yes Confidentiality,
Integrity
No No
(Hang et al.,
2019)
Hyperled-
ger
PBFT Permission Centralized DB Yes Confidentiality,
Integrity, Pri-
vacy
Yes No
(Kumar
et al., 2020)
Not
specified
PoW Permission IPFS No Privacy, In-
tegrity
Yes No
(Alamri
et al., 2021)
Not
specified
Not
specified
Permission IPFS Yes Privacy, Access
Control
No No
(Miyachi
and Mackey,
2021)
Ethereum Not
specified
Permission IPFS Yes Privacy No No
(Azbeg
et al., 2022)
Ethereum PoA Permission IPFS Yes Confidentiality,
Integrity, Pri-
vacy, Access
Control
Yes No
Proposed Ethereum PoA Permission IPFS Yes Confidentiality,
Integrity, Pri-
vacy, Access
Control
Yes Yes
has a time complexity of O(k), where k is the
number of classifiers.
• Overall Time Complexity: The overall time com-
plexity T
total
can be expressed as the sum of the
complexities of training, predicting, and aggregat-
ing results:
T
total
= O(k · T
train
+ k · p · T
predict
+ k)
5 COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS
Only two previous works, namely (Azaria et al.,
2016) and (Kumar et al., 2020), utilize the PoW con-
sensus algorithm. However, the PoW algorithm intro-
duces significant drawbacks, such as excessive energy
consumption for block validation and slower transac-
tion speeds. Additionally, these works do not address
key aspects like data encryption or the integration of
IoT medical devices, which are crucial for modern
healthcare systems.
Regarding data storage, most existing works, in-
cluding (Azaria et al., 2016), (Liang et al., 2017),
(Dagher et al., 2018), (Dwivedi et al., 2019), and
(Hang et al., 2019), rely on centralized databases.
This centralization makes them vulnerable to Dis-
tributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks and poten-
tial data tampering. In contrast, our proposed sys-
tem leverages IPFS (InterPlanetary File System) for
decentralized data storage, significantly reducing the
risk of such attacks while ensuring higher resilience
and data integrity.
Our system introduces distinct advantages by in-
tegrating a user-friendly React-based front-end for
seamless patient interaction, secure blockchain stor-
age using Solidity smart contracts, and machine
learning-based heart ailment predictions using the
Majority Voting Classifier (MVC). This holistic inte-
gration of blockchain, decentralized data storage via
IPFS, and advanced predictive models allows us to
provide real-time, accurate predictions while main-
taining data security and transparency. We address
key security requirements, including confidentiality,
integrity, privacy, and access control. This compre-
hensive approach ensures that all aspects of patient
data management, from submission to storage and
prediction, are securely handled.
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
54

6 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
In conclusion, our proposed healthcare data man-
agement system, integrating blockchain and ma-
chine learning technologies, offers a robust and user-
friendly solution for secure storage and predictive
analysis of patient data. The architecture, comprising
a React-based front-end and a FastAPI-powered back-
end deployed on a local blockchain, addresses ex-
isting limitations in user registration, authentication,
and comprehensive disease prediction. The system
demonstrates the potential to revolutionize healthcare
management, empowering patients to control their
health data.
In future work, the authors aspire to develop a
hybrid blockchain for ongoing refinement and opti-
mizing efforts for practical implementation in diverse
healthcare settings.
REFERENCES
Alam, T. (2020). mhealth communication framework using
blockchain and iot technologies. International Jour-
nal of Scientific & Technology Research, 9(6).
Alamri, B., Javed, I. T., and Margaria, T. (2021). A gdpr-
compliant framework for iot-based personal health
records using blockchain. In 2021 11th IFIP Interna-
tional Conference on New Technologies, Mobility and
Security (NTMS), pages 1–5. IEEE.
Amin, R., Al Ghamdi, M. A., Almotiri, S. H., Alruily, M.,
et al. (2021). Healthcare techniques through deep
learning: issues, challenges and opportunities. IEEE
Access, 9:98523–98541.
Awe, O. O., Opateye, G. O., Johnson, C. A. G., Tayo, O. T.,
and Dias, R. (2024). Weighted hard and soft voting
ensemble machine learning classifiers: Application
to anaemia diagnosis. In Sustainable Statistical and
Data Science Methods and Practices: Reports from
LISA 2020 Global Network, Ghana, 2022, pages 351–
374. Springer.
Azaria, A., Ekblaw, A., Vieira, T., and Lippman, A. (2016).
Medrec: Using blockchain for medical data access
and permission management. In 2016 2nd interna-
tional conference on open and big data (OBD), pages
25–30. IEEE.
Azbeg, K., Ouchetto, O., and Andaloussi, S. J. (2022).
Blockmedcare: A healthcare system based on iot,
blockchain and ipfs for data management security.
Egyptian Informatics Journal, 23(2):329–343.
Bhaskaran, S. and Marappan, R. (2023). Enhanced per-
sonalized recommendation system for machine learn-
ing public datasets: generalized modeling, simulation,
significant results and analysis. International Journal
of Information Technology, 15(3):1583–1595.
Chattu, V. K. (2021). A review of artificial intelligence,
big data, and blockchain technology applications in
medicine and global health. Big Data and Cognitive
Computing, 5(3):41.
Dagher, G. G., Mohler, J., Milojkovic, M., and Marella,
P. B. (2018). Ancile: Privacy-preserving framework
for access control and interoperability of electronic
health records using blockchain technology. Sustain-
able cities and society, 39:283–297.
Dang, V. A., Vu Khanh, Q., Nguyen, V.-H., Nguyen, T., and
Nguyen, D. C. (2023). Intelligent healthcare: Integra-
tion of emerging technologies and internet of things
for humanity. Sensors, 23(9):4200.
Dwivedi, A. D., Srivastava, G., Dhar, S., and Singh, R.
(2019). A decentralized privacy-preserving healthcare
blockchain for iot. Sensors, 19(2):326.
Gupta, D., Singh, A. K., Kumari, D., et al. (2012). Hybrid
feature based natural scene classification using neural
network. International Journal of Computer Applica-
tions, 975:8887.
Hang, L., Choi, E., and Kim, D.-H. (2019). A novel emr
integrity management based on a medical blockchain
platform in hospital. Electronics, 8(4):467.
Jabarulla, M. Y. and Lee, H.-N. (2021). A blockchain and
artificial intelligence-based, patient-centric healthcare
system for combating the covid-19 pandemic: Oppor-
tunities and applications. In Healthcare, volume 9(8),
page 1019. MDPI.
Karadeniz, T., Maras¸, H. H., Tokdemir, G., and Ergezer,
H. (2023). Two majority voting classifiers ap-
plied to heart disease prediction. Applied Sciences,
13(6):3767.
Kumar, R., Marchang, N., and Tripathi, R. (2020). Dis-
tributed off-chain storage of patient diagnostic reports
in healthcare system using ipfs and blockchain. In
2020 International conference on communication sys-
tems & networks (COMSNETS), pages 1–5. IEEE.
Kumari, D., Agrawal, D., Nema, A., Raj, N., Panda, S.,
Christopher, J., Singh, J. K., and Behera, S. (2024a).
A study on improving drug–drug interactions predic-
tion using convolutional neural networks. Applied Soft
Computing, 166:112242.
Kumari, D., Jain, C., Saxena, A., Gupta, P., Netke, A., and
Panda, S. (2023a). An experimental analysis of bench-
marking tools for smart contract-based blockchain
application. In International Congress on Informa-
tion and Communication Technology, pages 309–319.
Springer.
Kumari, D., Parmar, A. S., Goyal, H. S., Mishra, K., and
Panda, S. (2024b). Healthrec-chain: patient-centric
blockchain enabled ipfs for privacy preserving scal-
able health data. Computer Networks, 241:110223.
Kumari, D., Rajita, B., and Panda, S. (2021). Blockchain:
A survey on healthcare perspective and its challenges.
Information and Communication Technology for In-
telligent Systems: Proceedings of ICTIS 2020, Volume
1, pages 111–119.
Kumari, D., Vyshnavi, S., Dhar, R., Rajita, B., Panda,
S., and Christopher, J. (2024c). Smart gan: a smart
generative adversarial network for limited imbalanced
dataset. The Journal of Supercomputing, pages 1–42.
BL-MVC: Blockchain Enabled Majority Voting Classifier for Predicting Heart Diseases
55

Kumari, D., Yannam, P. K. R., Gohel, I. N., Naidu, M. V.
S. S., Arora, Y., Rajita, B., Panda, S., and Christopher,
J. (2023b). Computational model for breast cancer
diagnosis using hfse framework. Biomedical Signal
Processing and Control, 86:105121.
Liang, X., Zhao, J., Shetty, S., Liu, J., and Li, D. (2017).
Integrating blockchain for data sharing and collabora-
tion in mobile healthcare applications. In 2017 IEEE
28th annual international symposium on personal, in-
door, and mobile radio communications (PIMRC),
pages 1–5. IEEE.
Miyachi, K. and Mackey, T. K. (2021). hocbs: A
privacy-preserving blockchain framework for health-
care data leveraging an on-chain and off-chain sys-
tem design. Information Processing & Management,
58(3):102535.
Nelson, D. E., Holtzman, D., Bolen, J., Stanwyck, C. A.,
and Mack, K. A. (2001). Reliability and validity of
measures from the behavioral risk factor surveillance
system (brfss). Sozial-und Praventivmedizin, 46:S3–
42.
Shabbir, A., Shabbir, M., Javed, A. R., Rizwan, M., Iwendi,
C., and Chakraborty, C. (2023). Exploratory data anal-
ysis, classification, comparative analysis, case severity
detection, and internet of things in covid-19 telemoni-
toring for smart hospitals. Journal of Experimental &
Theoretical Artificial Intelligence, 35(4):507–534.
Shah, V., Thakkar, V., and Khang, A. (2023). Electronic
health records security and privacy enhancement us-
ing blockchain technology. In Data-Centric AI So-
lutions and Emerging Technologies in the Healthcare
Ecosystem, pages 1–13. CRC Press.
Verdonck, M. and Poels, G. (2020). Decentralized data
access with ipfs and smart contract permission man-
agement for electronic health records. In Business
Process Management Workshops: BPM 2020 Inter-
national Workshops, Seville, Spain, September 13–
18, 2020, Revised Selected Papers 18, pages 5–16.
Springer.
Wenhua, Z., Qamar, F., Abdali, T.-A. N., Hassan, R., Jafri,
S. T. A., and Nguyen, Q. N. (2023). Blockchain tech-
nology: security issues, healthcare applications, chal-
lenges and future trends. Electronics, 12(3):546.
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
56
