
Preservation and Protection of Cultural Heritage in High
Tourism
Areas Using GIS Technology: A Case Study of the
Medieval City of
Rhodes
Foteini-Pelagia Leventi
1
, Lemonia Ragia
1
and Dorina Moullou
1,2
1
School of Applied Arts, Hellenic Open University, Patras, Greece
2
Ephorate of Antiquities of East Attica, Hellenic Ministry of Culture, Athens, Greece
Keywords: Medieval City of Rhodes, Cultural Heritage, Overtourism, Climate Change, GIS, Protection and Preservation.
Abstract: The Medieval City of Rhodes is one of the most famous destinations in Greece, as it attracts more and more
tourists, especially during the summer season. Given that this particular site is included in the UNESCO list,
its protection and preservation are of utmost importance. Through a literature review, an effort is made to
analyse the phenomenon of overtourism in the area. Both quantitative and qualitative data available on the
topic were used from various sources in order to accurately frame the issues and implications of the
phenomenon. Finally, several proposals are provided using a mix of strategies and mitigation measures
relevant to the issue, emphasizing the importance of using QGIS.
1 INTRODUCTION
The Medieval City of Rhodes, a UNESCO World
Heritage Site, is a remarkable example of medieval
architecture including structures for residential,
military, commercial, public and religious use
(UNESCO, 1988). Specifically, it is particularly
known for the interesting dialogue between these
different kinds of buildings, as it offers a glimpse into
both antiquity and the complex history of the
Crusades and subsequent periods of influence, with
ancient remains, primarily temples, and its impressive
Medieval and Ottoman structures. However, the city
faces increasing challenges that threaten both its
physical integrity and its cultural heritage (UNESCO,
1972) (UNESCO, 2016).
Due to its location and history, the Medieval City
of Rhodes attracts an increasing number of visitors,
which, despite the economic benefits, may lead to
overtourism (Avdikos, 2011). As the city is filled
with narrow streets and ancient and medieval
buildings that were not designed to have large
numbers of tourists, their deterioration is likely.
Additionally, overcrowding impacts visitors'
experience and leads to physical degradation of the
landscape (ICOMOS, 2001-2002), (García-
Hernández, Dela Calle-Vaquero, & Yubero, 2017).
The Medieval City of Rhodes, apart from
overtourism, is facing crucial environmental threats
due to climate change. Higher temperatures are
causing cracks and erosion in the stone structures,
while rising sea levels and storms threaten the city's
fortifications. Furthermore, earthquakes in the region
heighten the risk of damage. These threats require
immediate action to protect the cultural heritage of
Rhodes (European Union, 2019).
In order to address these challenges, the use of
modern technology is necessary. Geographic
Information Systems (GIS), particularly QGIS
(Quantum Geographic Information System), provide
powerful tools for analyzing spatial data and
managing complex urban environments. Some of its
advantages pertain to the capability of mapping,
visualizing, monitoring and analyzing various aspects
of the city’s physical and environmental conditions,
providing researchers with the chance to propose
mitigation strategies and protection measures
(National Geographic, n.d.).
The aim of this report is to examine the various
challenges facing the Medieval City of Rhodes with a
focus on the dual threats of overtourism and
environmental risks driven by climate change. By
understanding the important vulnerabilities of this
historic region, the report seeks to explore how
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) can be used
Leventi, F.-P., Ragia, L. and Moullou, D.
Preservation and Protection of Cultural Heritage in High Tourism Areas Using GIS Technology: A Case Study of the Medieval City of Rhodes.
DOI: 10.5220/0013097300003935
In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Geographical Information Systems Theory, Applications and Management (GISTAM 2025), pages 121-127
ISBN: 978-989-758-741-2; ISSN: 2184-500X
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
121

to monitor, analyze and develop strategies to mitigate
these risks. Ultimately, the purpose is to propose
sustainable solutions to protect both the physical
integrity and the cultural heritage of the Medieval
City of Rhodes for future generations.
2 CASE STUDY
Rhodes is the largest island in the Dodecanese and is
known for its long and important history dating back
to ancient times. Its strategic location in the eastern
Aegean Sea made it a crossroads between East and
West, as well as North and South. Archaeological
evidence indicates that the island of Rhodes has been
inhabited since the New Stone Age, and by the 11th
century BC, it was settled by the Dorians who
established the city-states of Ialysos, Kamiros, and
Lindos. Another important section of island history is
the fact that Rhodes continued to play an important
role in the ancient world, particularly through its
colonies, such as Gela in Sicily (UNESCO, 1988).
The Medieval City of Rhodes, located at the
northern tip of the island, became significant during
the Crusades, when the Knights Hospitaller took
control of the island in 1309. In particular, the island
was initially developed into a fortified stronghold that
used to provide medical services to Crusader knights,
creating its medieval character. Specifically, the
Knights were responsible for the city’s architectural
development, constructing fortifications, gates and
other characteristic buildings that still dominate the
urban landscape. Despite numerous challenges,
including sieges, natural disasters and Ottoman
occupation, Rhodes maintained its historical
significance and integrity (UNESCO, 1988) (Luttrell,
2003).
The historical and architectural value of the Old
Town of Rhodes is the reason why UNESCO
included the site in its World Heritage List. For
instance, its fortifications, influenced by Gothic and
Ottoman architecture, are remarkable examples of
medieval military construction and offer deep insight
into these type of structures in the eastern
Mediterranean. Therefore, it is important to preserve
the original building materials of buildings and the
urban organization in order to maintain the
authenticity of the city. However, modern pressures,
such as overtourism and environmental impacts, pose
threats to the city’s integrity, necessitating mitigation
strategies that could aid in the protection and
preservation of its historical and cultural significance
(García-Hernández, De la Calle-Vaquero, & Yubero,
2017).
Figure 1: The Medieval City of Rhodes (UNESCO, 1988).
2.1
Threats
The island of Rhodes, like many Mediterranean
regions, is characterized by a great number of threats
that are connected to its geographical location and the
effects of climate change that can be observed,
especially in recent years. In general, the results of
climate change are apparent both worldwide and
specifically in Rhodes impacting the natural and
cultural history of the island (European Commission,
n.d.) (Gruber, 2011) (Sesana, Gagnon, Ciantelli,
Cassar, & Hughes, 2020).
2.1.1 Temperature
Extreme weather events, including heatwaves, are a
significant threat. The decade from 2011 to 2020 was
the warmest on record for the island with the data
showing that Rhodes is getting warmer, with 2023
being the warmest year at 20.4
o
C. The increase in
temperature deteriorates heritage materials exposed
to sunlight and promotes invasive species like the
lionfish Pterois miles, affecting local marine life and
tourism (Lindsey & Dahlman, 2024) (Meteoblue,
n.d.).
2.1.2 Wildfires
Higher temperatures contribute to the risk of
wildfires. The EU Environment Program predicts a
14% increase in wildfires by 2030 and 50% by 2100.
In summer 2023, Rhodes faced severe wildfires, with
around 175,000 acres burned, including protected
areas and agricultural land (Jones, Burton, Kelley, &
Doerr, 2023).
2.1.3 Coastal Erosion
Coastal erosion is exacerbated by rising sea levels and
tectonic activity. The island is in a tectonically active
GISTAM 2025 - 11th International Conference on Geographical Information Systems Theory, Applications and Management
122

region, impacting its coastline dynamics. Since 1880,
global sea levels have increased by 21-24 cm,
affecting Rhodes' coastal zones and historical sites,
including the Medieval City (Vandarakis, et al.,
2021).
2.1.4 Precipitation / Rainfalls
Rhodes experiences scarce and heavy rainfalls. In
2023, it had only 332 mm of rain, one of the driest
years in recent history, something that can lead to
wildfires. On the other hand, heavy rains can cause
flooding and landslides, as seen in 2013 and 2023
(Meteoblue, n.d.).
2.1.5 Earthquake
Rhodes has a history of significant earthquakes. In
fact, during the medieval period, some significant
earthquakes occurred in Rhodes affecting island’s
structures. For instance, in 1957, an earthquake
caused a plethora of damages in structures in the Old
Town (Papadopoulos, 2014, p. 181).
2.2
The Negative Impact of
Overtourism
Overtourism is one of the most important threats that
the Old City of Rhodes faces. In fact, increased
tourism is strictly connected with overcrowding. This
phenomenon is mainly visible during summers that
are the peak tourist seasons. In particular, the influx
of visitors leads to congestion in the city’s narrow
streets that originally designed for limited
pedestrians. However, overcrowding not only
diminishes the visitors experience, but also
accelerates the wear and tear on historic buildings and
roads (Alamineh, Hussein, Mulu, & Taddesse, 2023)
(ICOMOS, 2001-2002).
The constant foot traffic can lead to the
deterioration of old stone facades and vibrations in
cobblestone pavements, threatening the structural
integrity of these historical structures. Moreover,
overtourism can result in environmental degradation,
which is another critical issue. Specifically,
overcrowding leads to pollution, including air, water,
and noise pollution, as, for example, the demand for
natural resources, such as water, rises significantly,
often exceeding the area’s capacity (Esteban-Cantillo,
Menendez, & Quesada, 2024).
Another important negative impact of overtourism
pertains to the commercialization of the Old City,
which impacts its authenticity, leading to the loss of
its original purpose and meaning. Commercialization
is also connected with the constant reuse of medieval
buildings of the town in order to create more hotels,
restaurants, shops or anything else that pertains to
tourists’ needs (Giannakopoulos, et al., 2022).
Last but not least, overtourism negatively affects
the local residents. Overcrowding, noise pollution,
and rising rental prices make it increasingly difficult
for locals to maintain their quality of life, especially
during the tourist season. This imbalance highlights
how overtourism affects not only the integrity of the
Medieval City of Rhodes but also the well-being and
the everyday-life of its inhabitants (Shahzalal, 2016).
2.3
Mitigation Strategies
The Medieval City of Rhodes faces significant
challenges from increasing tourism, environmental
degradation, and natural disasters. To address these
issues in an effective way, QGIS (Geographic
Information System) provides a powerful tool for
creating data-driven strategies to mitigate risks and
protect the city's cultural and natural heritage
(National Geographic, n.d.). Here are some key
mitigation strategies utilizing QGIS:
1. Real-Time Visitor Flow Monitoring
Through QGIS, authorities can identify the
most overcrowded areas of the city by
tracking the movements of tourists in real
time. This provides the opportunity of
control visitors flow and propose
redirections to tourists in order to congested
roads be avoided reducing the pressure of
specific areas of the town.
2. Predicting Impact on Vulnerable Areas
The identifications of vulnerable areas to
wear and tear because of overcrowding is
crucial and the QGIS software can help.
Specifically, data analysis through this tool
may aid in predictions regarding these areas
and taking appropriate measures, like
installing protective barriers or limiting
visitor access during peak times.
3. Scenario
Planning for Visitor
Management
This software has the ability to model
various visitor flow scenarios, something
that helps city planners manage the impact
of tourists, including entry time regulations
or proposing alternative routes.
4. Visualizing Environmental Impacts
Through QGIS environmental data are also
available. For instance, the identifications of
alterations in coasts can be visualized,
enabling authorities understand the
Preservation and Protection of Cultural Heritage in High Tourism Areas Using GIS Technology: A Case Study of the Medieval City of
Rhodes
123
development of the phenomenon and take
relevant mitigation measures in order to
protect the integrity of the historical site.
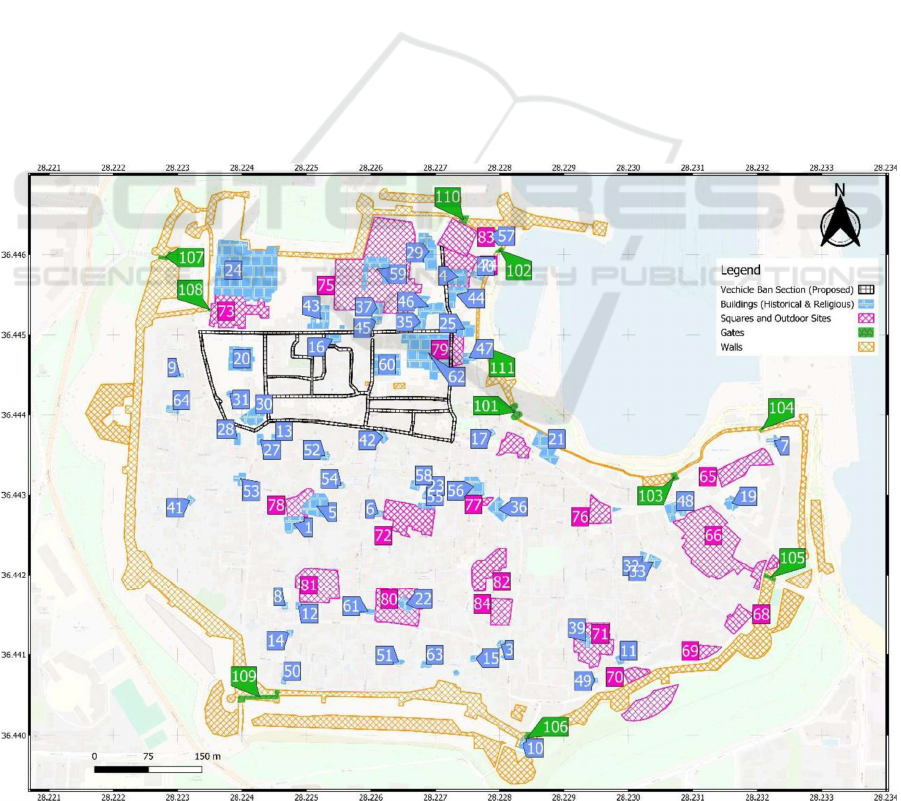
5. Creating Pedestrian-Only Zones
As the use of QGIS provides city planners
with the knowledge of areas of the town with
heavy tourist activity they have the ability to
propose pedestrian-only zones so as to
protect the cobblestone roads and improve
both the visitors’ experience and the
everyday life of locals. Thus, in this map, an
effort is made to present the proposed
Vehicle Ban Section. This specific layer is
depicted with a dotted black line, indicating
sections where vehicle access might be
restricted in the future to preserve the
historical integrity of the area. This map is a
valuable tool for managing tourist flows and
urban planning within the Medieval City. By
distinguishing historical buildings, open
spaces, and proposed vehicle-free areas, it
helps planners balance preservation with
modern demands of overtourism and
overcrowding.
In conclusion, QGIS plays a critical role in
creating and implementing mitigation strategies for
the Medieval City of Rhodes. By integrating data on
visitor flow, environmental impacts, and heritage
vulnerability, QGIS enables authorities to make
informed decisions that protect the city's historical
integrity while ensuring sustainable tourism
practices.
2.4
Using QGIS for
Visualization
The preservation and management of historical sites
like the Medieval City of Rhodes require not only
traditional methods of conservation but also modern
technological tools. Geographic Information System
(GIS) software, particularly QGIS, plays a crucial
role in this process. QGIS is increasingly becoming
an invaluable resource for urban planners,
archaeologists, and conservationists alike, providing
a way to monitor, document, and manage complex
environments like Rhodes (Petrescu, 2007).
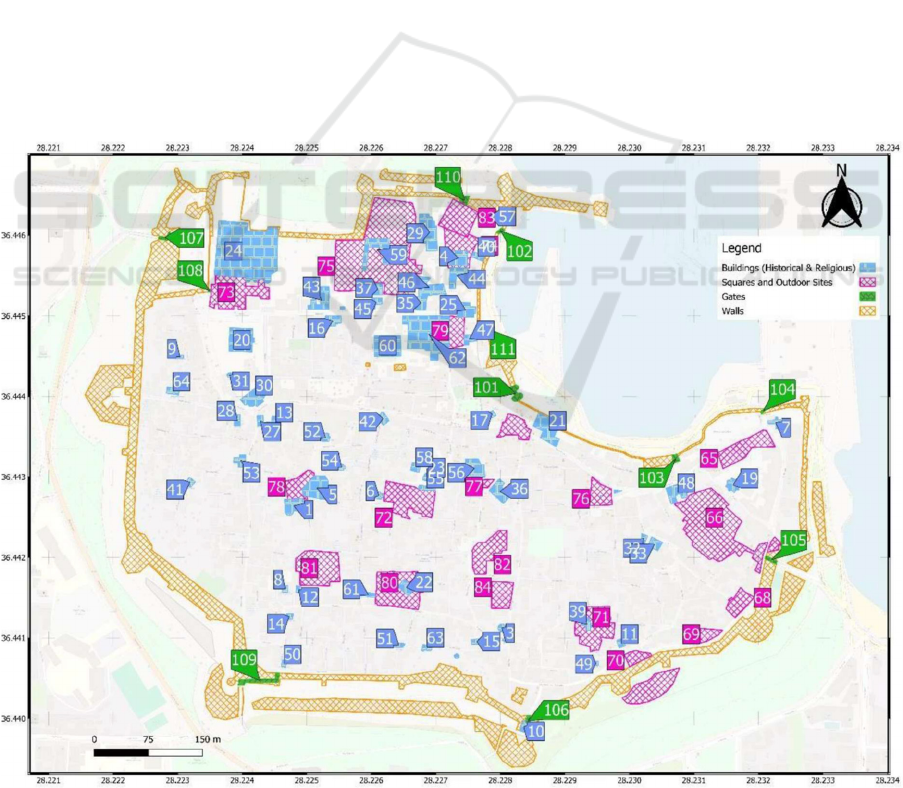
Figure 2: The Medieval City of Rhodes (created using QGIS).
GISTAM 2025 - 11th International Conference on Geographical Information Systems Theory, Applications and Management
124
The current state of the Medieval City of Rhodes
is presented in detail through the use of QGIS. The
use of QGIS is particularly important as it contributes
both to a better understanding of the area and to its
protection, whether from the significant impacts of
natural disasters or from the effects of increasing
tourism in the region. What it especially helps with is
the improved management of the archaeological site.
This is mainly achieved due to the fact that QGIS
allows for the creation of accurate and detailed maps,
including historical buildings, walls, roads or
anything else needed. Essentially, these specific maps
contribute to the continuous monitoring of the
condition of the research points within the
archaeological site, while making it easier to
understand any changes occurring in different zones,
helping to preserve the integrity of the site (Petrescu,
2007).
Of course, it is worth noting that a QGIS map is
particularly helpful in monitoring the medieval city
concerning natural disasters and the impacts of
climate change. In fact, this island is especially
exposed to several natural disasters, such as
earthquakes, extreme temperatures or floods. Thus,
the application of the software can assist in
visualizing specific areas that are more vulnerable
and ultimately create a city plan, helping researchers
prioritize the issues that arise. In addition, the creation
of maps with QGIS for the Old Town of Rhodes is
important for the overall management of the city. For
example, through the different layers, historical
buildings can be easily distinguished from newer
constructions, or even the most frequented by tourists,
streets can be highlighted, aiming for a more effective
management of overtourism on the island. In
conclusion, the use of QGIS for mapping and
visualization of the Medieval City of Rhodes is highly
important for the optimal preservation and protection
of the site, as it enables successful urban planning,
monitoring, and overall management of the
archaeological site.
As one of the most important steps aimed at
addressing various threats and issues related to the
Medieval City of Rhodes is the accurate
understanding of the area and its significant
structures, the mapping process through QGIS is
particularly useful. Thus, in this case, the mapping of
the archaeological site was mainly done to distinguish
certain
buildings,
structures,
and
roads.
Specifically,
Figure 3: The Medieval City of Rhodes with proposed section of pedestrian only zone (created using QGIS).
Preservation and Protection of Cultural Heritage in High Tourism Areas Using GIS Technology: A Case Study of the Medieval City of
Rhodes
125

the buildings, structures, and roads are represented on
the map using different colours and shapes, forming
distinct layers:
• Buildings (Historical & Religious):
Represented in blue. These are significant
structures within the medieval city, likely
indicating historical or religious buildings.
They are marked with numbers for
reference and are scattered throughout the
city. Their distribution offers insight into the
concentration of important buildings within
the medieval city.
• Squares and Outdoor Sites: Depicted in
pink with cross-hatching, these areas
indicate open spaces such as public squares
or other significant outdoor sites. Their
placement on the map highlights the spatial
relationship between the built environment
and open spaces, critical for understanding
the urban area structure of the city.
• Gates: Shown in green, the map identifies
several gates along the city walls. These
gates would have been points of entry and
exit from the medieval city. In fact, the gates
are part of the city’s historic fortifications
and are vital for controlling access to the city.
Their positioning is crucial for analyzing how
people entered and exited the city, both
historically and in modern times, particularly
in relation to tourism flow. Walls: The city
walls are represented by a yellow-orange
cross-hatched line surrounding the city.
These walls form a protective barrier around
the city and are a key feature of its
medieval fortifications, emphasizing its
historical strategic importance.
As mentioned above, the map of the Old Town of
Rhodes created through QGIS facilitates the precise
identification of each building or open space, which
are numbered with details such as their names and
uses. It is worth noting that the visualization of these
current structures contributes to highlighting the city’s
architecture, while also providing information on
how the urban design can impact daily life and
tourist activity within or outside the city.
3 CONCLUSIONS
In conclusion, the important phenomenon of
overtourism has become a significant global concern
that impacts more and more destinations worldwide.
This is primarily because, along with the rise of the
phenomena of climate change affecting our planet, it
may lead to horrible effects, both regarding the
preservation of global cultural and natural heritage
and regarding people’s everyday-lives (Nugroho &
Hardilla, 2020). This basically includes the daily lives
of local communities that are disrupted by
overtourism in affected areas, as well as the
experiences of tourists, who eventually do not enjoy
their trips due to this serious phenomenon. Local
authorities and countries, especially those that have
already affected the consequences of overtourism,
should take specific mitigation measures in order to
protect cultural heritage and themselves. In order to
achieve this, the use of modern technology and
especially the use of GIS are essential.
In Greece, a country renowned for its rich cultural
attractions, the Medieval City of Rhodes stands out as
a prime example of how overtourism along with the
effects of climate change can impact a historically
significant site. The city’s narrow streets and
medieval architecture are particularly vulnerable to
the pressures of heavy tourist traffic. Without
appropriate measures, the integrity of this
archaeological site is at risk.
In conclusion, the future of the Medieval City of
Rhodes depends on a multi-faceted approach that
combines traditional conservation methods with
modern technological innovations. Geographic
Information Systems, specifically QGIS, provide a
crucial platform for analysing, managing, and
protecting this historical site. The lessons learned
from this case study can serve as a model for other
historical cities worldwide that face similar
challenges in balancing preservation with tourism and
environmental pressures.
REFERENCES
Alamineh, G., Hussein, J., Mulu, Y., & Taddesse, B. (2023,
June 17). The negative cultural impact of tourism and
its implication on sustainable development
in
Amhara
Regional State. Retrieved from tandfonline.com:
https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.10
80/23311983.2023.2224597
Avdikos, V. (2011). Local hegemonic blocs: The case of
tourism in Rhodes. Retrieved from academia.edu:
https://www.academia.edu/561874/Local_hegemonic_
blocs_The_case_of_tourism_in_ Rhodes
Esteban-Cantillo, O., Menendez, B., & Quesada, B. (2024,
April 15). Climate change and air
pollution impacts
on cultural heritage building materials in Europe and
Mexico. Retrieved from sciencedirect.com:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/artic
le/pii/S0048969724010842
GISTAM 2025 - 11th International Conference on Geographical Information Systems Theory, Applications and Management
126

European Commission. (n.d.). Causes of climate change.
Retrieved from climate.ec.europa.eu:
https://climate.ec.europa.eu/climate-change/causes-
climate-change_en
European Union. (2019). European framework for
action
on cultural heritage. Retrieved from op.europa.eu:
https://op.europa.eu/en/publication-detail/-
/publication/5a9c3144-80f1-11e9-9f05- 01aa75ed71a1
García-Hernández, M., De la Calle-Vaquero, M., & Yubero,
C. (2017, August 4). Cultural Heritage and Urban
Tourism: Historic City Centres under Pressure.
Retrieved from mdpi.com:
https://www.mdpi.com/2071- 1050/9/8/1346
Giannakopoulos, D., Karekou, Z., Menegaki, E.,
Tsilimantou, E., Ioannidis, C., Maistrou, E.,
Moropoulou, A. (2022, August 1). Reuse of Historic
Buildings in the Medieval City of
Rhodes to Comply
with the Needs of
Sustainable Urban Development.
Retrieved from mdpi.com:
https://www.mdpi.com/2073- 445X/11/8/1214
Gruber, S. (2011). The Impact of Climate Change on
Cultural Heritage Sites: Environmental Law and
Adaptation. In The Impact of Climate Change on
Cultural Heritage Sites: (pp. 209-219). Lexxion
Verlagsgesellschaft
ICOMOS. (2001-2002). Heritage at Risk from
tourism.
Retrieved from icomos.org:
https://www.icomos.org/public/risk/2001/to urism.htm
Jones, M., Burton, C., Kelley, D., & Doerr, S. H. (2023,
July 28). Greece wildfires: how
climate change is
involved, and what we can do about
it.
Retrieved
from
theconversation.com:
https://theconversation.com/greece-wildfires-how-
climate-change-is-involved-and-what-we-can-do-
about-it-210404
Lindsey, R., & Dahlman, L. (2024, January 18). Climate
Change: Global Temperature. Retrieved
from
climate.gov: https://www.climate.gov/news-
features/understanding-climate/climate- change-global-
temperature
Luttrell, A. (2003). The Town of Rhodes 1306-1356.
Rhodes: City of Rhodes Office for the Medieval
Town (Ministry of Culture- Archaeological Receipts
Fund- City of Rhodes Contract).
Meteoblue. (n.d.). Climate Change Rhodes. Retrieved
from
meteoblue.com:
https://www.meteoblue.com/en/climate-
change/rhodes_greece_400666
National Geographic. (n.d.). GIS (Geographic Information
System).
Retrieved
from
education.nationalgeographic.org:
https://education.nationalgeographic.org/resource/geog
raphic-information-system-gis/
Nugroho, A. C., & Hardilla, D. (2020, January). The
Importance
of
Cultural Heritage Conservation in
Society: A Review and Prospect for Future Cities, with
Bandar
Lampung as Cased Study. Retrieved from
researchgate.net:
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/338351963_T
he_Importance_of_Cultural_Heritage_Conservation_in
_Society_A_Review_and_Prospect_for_Future_Cities_
with_Bandar_Lampung_as_Cased_Study
Papadopoulos, G. (2014). Rhodes: Earthquakes and
Tsunamis from Antiquity to the Present Day. Athens:
Aselotos Publications.
Petrescu, F. (2007, October). The Use of GIS Technology in
Cultural Heritage
.
Retrieved from researchgate.net:
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/228636422_T
he_use_of_GIS_technology_in_cultural_heritage
Sesana, E., Gagnon, A. S., Ciantelli, C., Cassar, J., &
Hughes, J. J. (2020, March 31). Climate change impacts
on cultural heritage: A
literature
review.
Retrieved from
wires.onlinelibrary.wiley.com:
https://wires.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/epdf/10.1002/
wcc.710
Shahzalal. (2016). Positive and Negative Impacts of
Tourism on Culture: A Critical Review of
Examples
from the Contemporary
Literature. Retrieved from
https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/234696865.pdf
UNESCO. (1972, November 16). Convention Concerning
the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural
Heritage. Retrieved 2024,
from
whc.unesco.org:
https://whc.unesco.org/en/conventiontext/
UNESCO. (1988). Medieval City of Rhodes. Retrieved from
https://whc.unesco.org/en/list/493/
UNESCO. (2016). The Protection of Cultural Heritage.
Retrieved 2024, from en.unesco.org:
https://en.unesco.org/creativity/policy-monitoring-
platform/protection-cultural- heritage
Vandarakis, D., Panagiotopoulos, I. P., Loukaidi, V., Hatiris,
G.-A., Drakopoulou, P., Kikaki, A., Kapsimalis, V.
(2021, August 7). Assessment of the Coastal
Vulnerability to the Ongoing Sea Level Rise for the
Exquisite Rhodes Island (SE Aegean Sea, Greece).
Retrieved from mdpi.com:
https://www.mdpi.com/2073- 4441/13/16/2169
Preservation and Protection of Cultural Heritage in High Tourism Areas Using GIS Technology: A Case Study of the Medieval City of
Rhodes
127
