
A New Planning Agent Architecture that Efficiently Integrates an Online
Planner with External Legal and Ethical Checkers
∗
Hisashi Hayashi
1
, Yousef Taheri
2
, Kanae Tsushima
3
, Gauvain Bourgne
2
, Jean-Gabriel Ganascia
2
and Ken Satoh
3
1
Advanced Institute of Technology, Tokyo, Japan
2
Sorbonne University, Paris, France
3
Research Organization of Information and Systems, Tokyo, Japan
Keywords:
Planning, Online Planning, Legal Check, Ethical Check, Norm Check, Agent Architecture.
Abstract:
Transferring and using datasets online presents significant legal and ethical challenges, including issues related
to privacy, safety, and bias. Careful planning is essential for compliance with the diverse legal frameworks
and ethical standards of different countries. In our approach, legal and ethical checkers are implemented as
independent modules capable of operating on separate servers if necessary. This structure is logical given the
specialized knowledge required to express legal and ethical norms specific to each country. This paper de-
scribes the integration of a planning agent that employs an online Hierarchical Task Network (HTN) planner
with these legal and ethical checkers. It also introduces, assesses, and compares three different interaction
modes between these modules to facilitate efficient online legal and ethical planning. The assessment em-
phasizes interaction frequency and computation time, with scenarios related to international data transfer and
usage demonstrating the effectiveness of the proposed approach. By exploring these interaction modes, the
paper aims to provide a robust framework for managing the complexities of adhering to diverse legal and eth-
ical requirements in a global context.
1 INTRODUCTION
As data are transferred globally via the Internet for
various services, legal and ethical issues concerning
privacy, security, and other factors have become cen-
tral concerns. Numerous laws and ethical guidelines
have been established to regulate data transfer and
usage. A well-known set of data protection regula-
tions is the European General Data Protection Regu-
lations (GDPR) (European Commission, 2016). Due
to the complexity of laws and ethical guidelines, re-
search has focused on automated compliance checks
for data transfer norms. The policy representation
of the GDPR, in particular, has been studied exten-
sively (Agarwal et al., 2018; Bonatti et al., 2020;
Palmirani et al., 2018; Vos et al., 2019).
Planning the transfer and utilization of datasets is
crucial because these processes are multi-step in na-
ture. Compliance with legal and ethical guidelines is
also essential when constructing data transfer and uti-
∗
This paper is based on our earlier workshop paper
(Hayashi et al., 2024).
lization plans. Several studies have focused on au-
tomated planning that considers ethical and/or legal
norms directly (Berreby et al., 2018; Hayashi and
Satoh, 2022; Hayashi and Satoh, 2023; Lindner et al.,
2020; Taheri et al., 2023a). In particular, the stud-
ies in (Hayashi and Satoh, 2022; Hayashi and Satoh,
2023) utilized a general-purpose online HTN planner
for data transfer planning, adapting it to dynamic situ-
ations where rules describing legal and ethical norms
were included in the planning agent database.
Due to the complexity of legal and ethical norms,
specialized expertise is generally necessary to con-
duct automated compliance checks across different
countries. Unlike previous approaches, we propose
the use of a general-purpose online planner paired
with independently developed norm checkers. Con-
sequently, our problem setting differs from that of
a planner that directly references legal and ethical
norms. In particular, we developed a new planning
agent architecture that utilizes external legal and eth-
ical checkers, which were implemented as separate
modules. Each module shares the same interface but
can be implemented differently within the proposed
Hayashi, H., Taheri, Y., Tsushima, K., Bourgne, G., Ganascia, J.-G., Satoh and K.
A New Planning Agent Architecture that Efficiently Integrates an Online Planner with External Legal and Ethical Checkers.
DOI: 10.5220/0013098300003890
In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2025) - Volume 1, pages 263-272
ISBN: 978-989-758-737-5; ISSN: 2184-433X
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
263

architecture. When these modules are installed on
separate servers, ensuring that they use consistent and
up-to-date information is crucial. High efficiency de-
pends on frequent interactions between these mod-
ules. Each module operates independently, as the de-
velopment of each module requires different special-
izations or domain expertise.
The contributions of this study are as follows:
First, we propose a new architecture that integrates an
online planning agent with legal and ethical check-
ers. Next, we demonstrate efficiency improvements
by adjusting database locations and introducing the
concept of fluent subscription. Finally, the efficiency
gains in terms of the number of interactions between
modules and their computation times are illustrated
through simulations involving multiple scenarios of
planning and replanning for data transfer and utiliza-
tion. Notably, the details regarding the expressiveness
and efficiency of each module are beyond the scope of
this paper.
The remainder of the paper is organized as fol-
lows. Section 2 presents a new architecture that in-
tegrates the three modules discussed earlier. Section
3 introduces the three interaction modes between the
planning agent and the legal and ethical checkers.
Section 4 explains the experimental scenarios, and the
results are presented and discussed in Section 5. Fi-
nally, Section 6 provides the conclusion of the paper.
2 OVERALL ARCHITECTURE
This section introduces the overall architecture
1
sur-
rounding the planning agent, as shown in Figure 1.
The architecture includes a planning agent, a legal
checker, an ethical checker, and an action executor.
The planning agent incorporates an online HTN plan-
ner that generates plans based on its beliefs and adapts
them in response to changes during plan execution.
The agent sends action execution instructions to the
action executor and updates its beliefs and plans based
on feedback from the executor. The legal checker
evaluates each action in a plan against legal norms
to determine whether it is legal. The ethical checker
selects the most ethical plan by comparing multiple
plans based on various ethical norms. The action ex-
ecutor performs the actions and reports the outcomes
back to the planning agent. Additionally, the executor
can identify unexpected fluctuations in server activity,
safety levels, or occupancy levels and report these to
the planning agent.
1
This architecture was first presented at a workshop
(Hayashi et al., 2023).
Given a task (
1
⃝), the planning agent creates a
least-costly plan using a best-first search algorithm
and sends it to the legal checker (
2
⃝). The legal
checker assesses the plan’s legality and reports the re-
sults to the planning agent (
3
⃝). The planning agent
then constructs the next least-costly plan and submits
it to a legal checker for verification (
2
⃝ in the second
iteration). This process (
2
⃝–
3
⃝) repeats until a prede-
fined number of legal plans are obtained or no further
plans are possible.
Once a set of low-cost legal plans is ready, the
planning agent sends them to the ethical checker (
4
⃝)
and requests it to select the most ethical option. The
ethical checker evaluates the plans and reports the
most ethical one back to the planning agent (
5
⃝). At
this stage, the planning agent commits to the plan
deemed both legal and most ethical.
The agent proceeds to sequentially execute each
action in the plan using the action executor (
6
⃝).
Upon receiving an action execution request, the ac-
tion executor attempts to perform the specified action
and/or carry out observations. The results are then re-
ported to the planning agent (
7
⃝), which updates its
beliefs and plans based on the execution outcomes
and/or observations. If the current plan becomes in-
valid or less cost-efficient, the action executor reports
new observations to the planning agent, triggering a
replanning process. Similar to the initial planning
phase, the planning agent engages the legal and ethi-
cal checkers during replanning (
2
⃝-
5
⃝).
2.1 Planning Agent
The planning agent generates plans using the on-
line forward-chaining total-order HTN planning al-
gorithm of Dynagent (Hayashi et al., 2006). Simi-
lar to SHOP (Nau et al., 1999), a standard (offline)
HTN planner, it employs task decomposition through
a best-first search to identify the least-costly plan. The
information used for planning, referred to as belief,
encompasses facts, task preconditions, action effects,
task costs, and task decomposition rules (known as
methods in SHOP).
Due to the simplicity and expressiveness of the
planning domain heuristics, SHOP-like total-order
HTN planners continue to be utilized and studied
for improved computational efficiency (Behnke et al.,
2018; Magnaguagno et al., 2021; Schreiber, 2021).
Another modern online forward-chaining HTN-like
planner employs Monte Carlo tree search techniques
(Patra et al., 2019; Patra et al., 2020) to explore ex-
tensive search spaces in order to find suitable plans.
The planning agent also monitors and controls
plan execution, incrementally modifying alternative
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
264
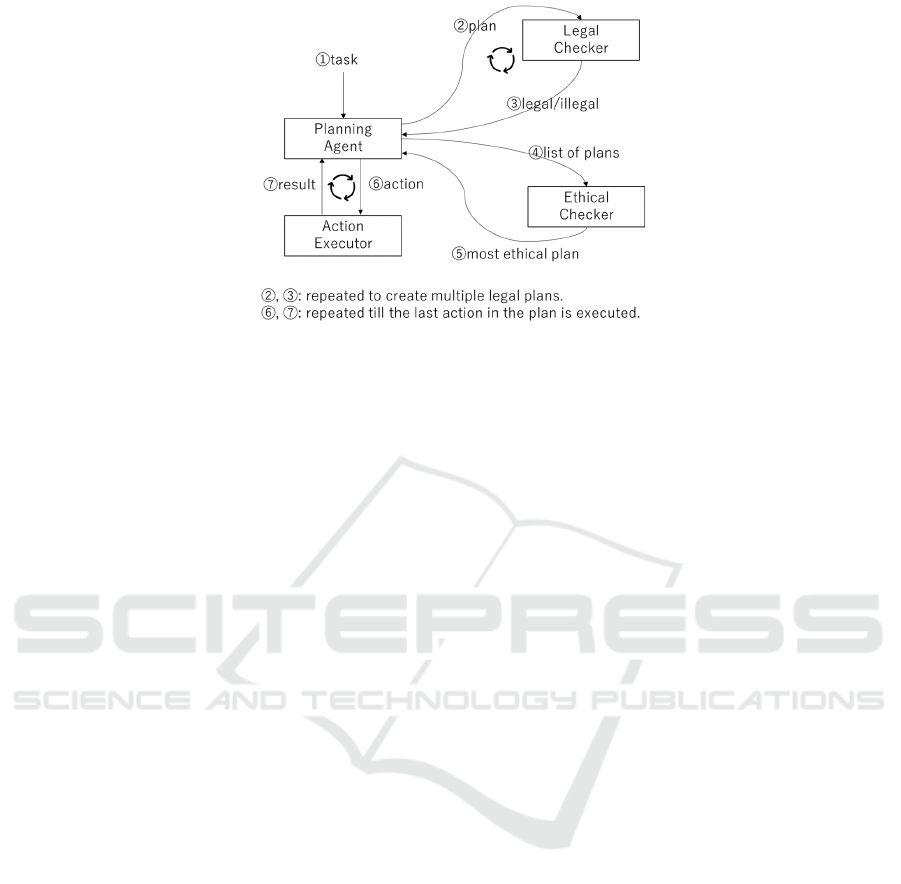
Figure 1: The flow of planning and execution in the proposed architecture.
plans as execution progresses. State changes may af-
fect certain task preconditions within the plans; thus,
the planning agent checks these preconditions, re-
moves invalid plans, and incorporates new valid in-
tentions to adapt to a changing environment. More-
over, the plan is adjusted if it becomes invalid or less
cost-efficient.
To execute actions within the current plan, the
planning agent utilizes the action executor. Each time
an action is successfully executed, the belief is up-
dated based on the action’s effects. The planning
agent first removes the executed action from the head
of each plan and then eliminates invalid alternative
plans, subsequently adding new valid plans. If an ac-
tion execution fails, the current plan becomes nonex-
ecutable, and all plans with the failed action at their
heads are removed from the alternatives.
As mentioned earlier, the planning agent relies on
legal and ethical checkers to filter out illegal plans and
to select the most ethical legal plan, respectively.
2.2 Legal Checker
Research in legal compliance encompasses various
approaches, such as modal (deontic) logics (Governa-
tori et al., 2011; van Riemsdijk et al., 2013), natural
language processing (Contissa et al., 2018), and logic
programming (Chesani et al., 2018). Several lan-
guages have been developed to represent legal rules,
such as Proleg (Satoh and et. al., 2011), which ex-
tends Prolog with exceptions to better accommodate
laws, and Catala (Merigoux et al., 2021), which is de-
signed for representing legal rules including income
tax. In this work, we used the logic programming lan-
guage Prolog in the legal checker for the following
reasons: First, the logic of legal norms with excep-
tions can be effectively expressed as “negation as fail-
ure” in Prolog. Additionally, since we implemented
other components of the system in Prolog, using it
for the legal checker facilitates seamless integration.
However, each module could theoretically be imple-
mented in any programming language.
The legal checker verifies whether a given plan
from the planning agent is legal. Since a plan con-
sists of a list of actions, the legal checker evaluates
each action and considers the plan legal only if all ac-
tions within it are deemed legal. In this work, the le-
gal checker assesses whether the proposed actions are
compliant with GDPR based on the information pro-
vided in the database. This database contains details
about data owners’ permissions, EU member coun-
tries, and relevant nodes within the EU. For instance,
if a data owner restricts data transfers outside the EU,
the legal checker will classify any plan suggesting
such transfers as illegal.
2.3 Ethical Checker
The ethical checker is responsible for evaluating and
selecting the optimal plan from the valid options. The
evaluation mechanism primarily involves an ordering
process based on a model with multiple criteria, as
first introduced in (Taheri et al., 2023b). The or-
dering process considers various moral criteria cor-
responding to distinct ethical dimensions of the prob-
lem. Typically, a moral criterion pertains to a spe-
cific harm or risk that could affect the individuals in-
volved. Additionally, some optimization criteria for
system efficiency may also be incorporated. In our
use case, which involves the transfer and processing
of personal data, the relevant criteria include techni-
cal safety, data sensitivity, processing bias, efficiency,
regulatory protection, and data parsimony.
These criteria are organized into a total preorder of
superiority. If one criterion is deemed superior to an-
other, it is considered strictly more important, with the
A New Planning Agent Architecture that Efficiently Integrates an Online Planner with External Legal and Ethical Checkers
265

inferior criterion serving only to differentiate options
that are equivalent according to the superior criterion.
To evaluate the input plans, they are assessed
against each criterion (see Section 4 for details on this
evaluation process). These measurements are repre-
sented on an ordinal scale through preorders, which
means that each criterion organizes the plans accord-
ing to its underlying standard, allowing for potential
equivalence among them. The use of an ordinal scale
helps avoid inconsistencies and enhances expressive-
ness in ethical evaluations. Next, the global preorder
is obtained by aggregating all these preorders while
considering their relative superiority. If the superi-
ority constitutes a total order, this process amounts to
combining the different criteria lexicographically. For
simplicity, the six criteria are ordered as follows
techn. safety > data sensitivity > bias
> efficiency > regul. safety > data parcimony
The ethical checker manages a superiority relation
defined as a total preorder, which encompasses sev-
eral equivalence classes of criteria ranked in decreas-
ing importance. Within each equivalence class, a
compromise is reached through classical voting rules
from computational social choice theory, such as
Copeland’s method (Pacuit, 2024). The resulting pre-
orders are then combined lexicographically. The eth-
ical checker adopts a relativist view, meaning it does
not determine which input plans are morally right or
wrong. Instead, it selects the best plan among those
proposed by identifying the one most aligned with the
given ethical context.
3 INTERACTION MODES
BETWEEN MODULES
This section introduces three interaction modes be-
tween the planning agent and the legal and ethical
checkers.
As discussed in Section 2, the planning agent in-
teracts with the legal and ethical checkers during both
planning and replanning. The planning agent, legal
checker, and ethical checker are implemented as sep-
arate modules, which can be installed on different
servers. This modular design is practical, given that
ethical and legal norms vary between countries. To
achieve higher efficiency, it is essential to minimize
the number of interactions between these modules and
decrease computation time while ensuring that the
most recent information is reflected in the plans.
The three interaction modes introduced are as fol-
lows. 1: default mode, 2: subscription mode, and
3: all-subscription mode. The interaction modes are
compared in Section 5 through experiments that eval-
uate the number of interactions between modules and
the required computation time. The following subsec-
tions describe each interaction mode in detail.
3.1 Default Mode
The default mode represents the most straightforward
interaction design and serves as the baseline for com-
parison. Figure 2a shows interactions in the default
mode. In this mode, the common knowledge of flu-
ents describing the changing world is recorded in the
planning agent’s database as a belief. Legal and eth-
ical checkers query the planning agent regarding the
truth value of a fluent whenever they need to evaluate
a plan for legal or ethical compliance.
Each time an action is executed or the truth value
of a fluent is updated, the planning agent replans and
updates multiple plans, the legal checker verifies the
legality of each updated plan, and the ethical checker
selects the most ethical plan from these updated legal
plans.
This default interaction mode ensures that the
most recent information is used for planning, replan-
ning, and legal and ethical checks. However, this is
inefficient because the planning agent sometimes re-
quests legal and ethical checks unnecessarily. Addi-
tionally, legal and ethical checkers frequently query
the planning agent for the truth value of a fluent,
thereby increasing the number of interactions.
3.2 Subscription Mode
The subscription mode is designed to improve inter-
action efficiency between the planning agent and the
legal and ethical checkers. While the default mode
is straightforward and easy to implement, it exhibits
inefficiencies for two main reasons. First, legal and
ethical checkers frequently query the planning agent
to verify the truth value of a fluent, which constitutes
part of the planning agent’s beliefs. This results in a
significant increase in the number of interactions be-
tween the modules. Second, the planning agent sends
requests to the legal and ethical checkers each time an
action is executed, increasing unnecessary legal and
ethical evaluations, as well as an increased number of
interactions and computation time. In the subscription
mode, if an action is executed successfully and does
not alter the truth values of the fluents impacting le-
gal and ethical norms, it is unnecessary to modify the
current plan or consult the legal and ethical checkers.
In the subscription mode, legal and ethical check-
ers address the first issue by declaring fluents that
affect their norm checks as subscribed fluents. Fig-
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
266
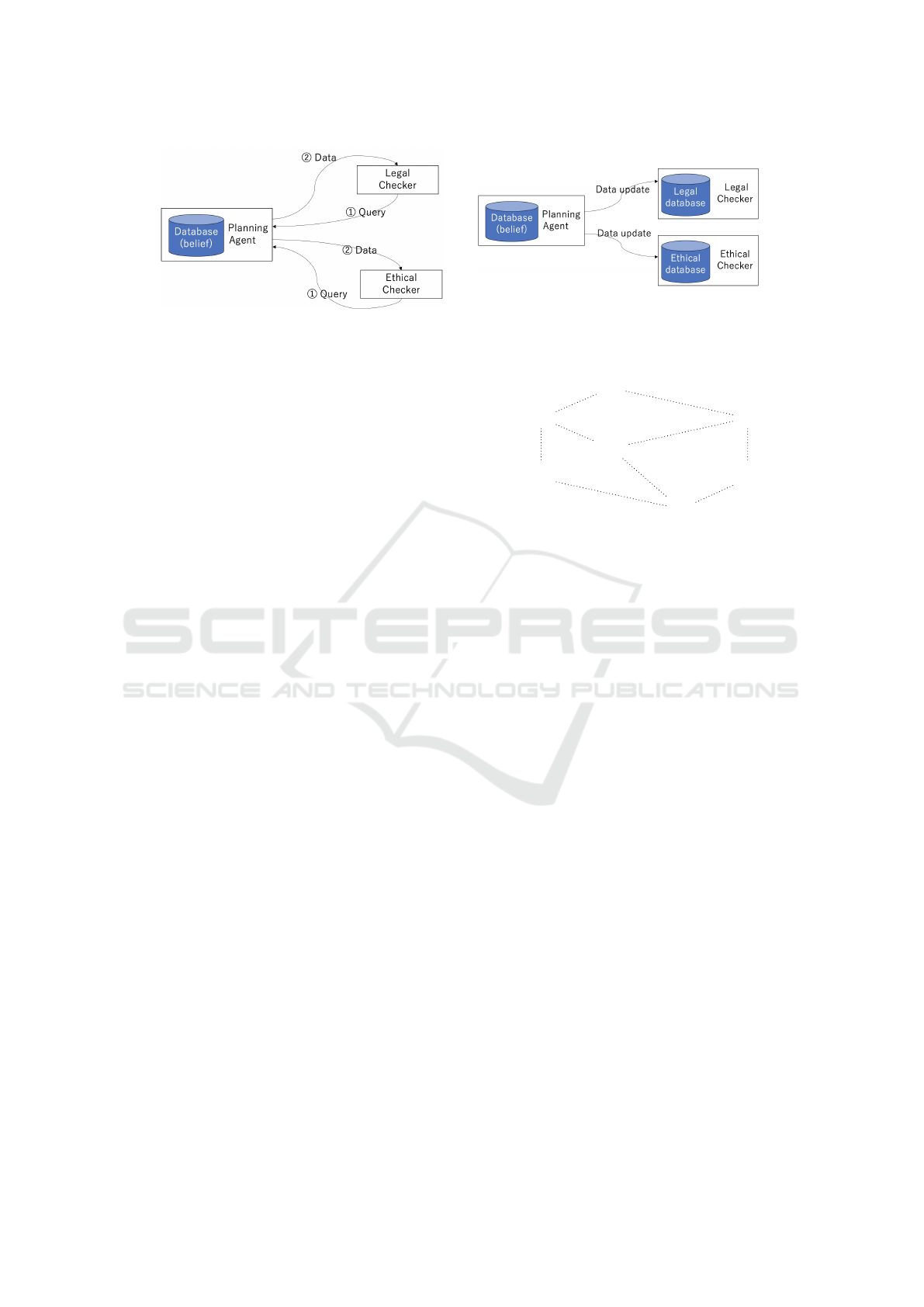
(a) Default mode.
(b) Subscription mode.
Figure 2: Interaction modes between modules.
ure 2b shows the interactions in subscription mode.
The legal (or ethical) checker maintains a separate
database of the subscribed fluents. Initially, the plan-
ning agent, legal checker, and ethical checker syn-
chronize the truth values of each subscribed fluent in
their databases.
To address the second problem, the subscription
mode enables the planning agent to omit legal and
ethical checks when an action is successfully exe-
cuted, as long as the action does not alter the truth val-
ues of the fluents that impact legal or ethical norms.
However, if the execution of the action changes these
truth values, the planning agent requests the legal
checker to re-evaluate the plans for legality and the
ethical checker to select the most ethical legal plan.
In addition, if the truth value of a fluent is updated
through observation, the validity of the existing plans
may be affected. In such instances, the subscription
mode operates similarly to the default mode: the plan-
ning agent replans and generates multiple plans, the
legal checker verifies the legality of each plan, and the
ethical checker identifies the most ethical legal plan.
3.3 All-Subscription Mode
The all-subscription mode is a specialized case of the
subscription mode. In this mode, all fluents are sub-
scribed by the legal and ethical checkers. In this case,
it is unnecessary to declare the subscribed fluents.
4 USE CASE MODEL
To show the characteristics and efficiency of our pro-
posed approach, we apply it in a data transfer and pro-
cessing situation. A similar use case model has been
used in previous works, such as (Taheri et al., 2023a)
and (Hayashi and Satoh, 2022; Hayashi and Satoh,
2023), to illustrate legal and ethical compliance in
data manipulations. The model primarily consists of
multiple nodes used for transferring and processing
•
2
•
1
•
3
■
4
•
6
•
5
•
7
Figure 3: Nodes and connections in the network.
data, as illustrated in Figure 3. Each node represents
a segment of a corporation located either within or
outside the EU. Node 4, indicated by a square, serves
as the central node functioning as a cloud server for
data processing across various purposes. The other
nodes, depicted as circles, are utilized for data storage
and transfer. In this use case, users’ personal data are
stored at the circular nodes. Different sections of the
organization may request data processing and receive
the corresponding outputs at their designated nodes.
To perform a task, the system locates the data,
transfers it to the processing node, and applies the
specified process. After processing personal data, the
system delivers the output to the requested node. The
planner in our architecture generates possible plans to
fulfill the given task, i.e., the potential paths for trans-
ferring and processing data within the network. Each
plan represents a different potential behavior of the
system. In this architecture, these behaviors are ver-
ified by the legal checker for potential infringements
of modeled regulations. The legal checker rules out
the illegal plans, and the remaining plans are ordered
by the ethical checker based on their alignment with
the ethical specification (cf. Section 2.3).
Additional information regarding this use case en-
ables testing of the architecture across various scenar-
ios. Table 1 presents the details of the nodes utilized
in this model. The region indicates geographical lo-
cation of each node, categorized as EU or Non-EU,
reflecting our primary focus on GDPR compliance.
This regional classification is essential for the legal
verification process, as transferring personal data out-
A New Planning Agent Architecture that Efficiently Integrates an Online Planner with External Legal and Ethical Checkers
267

Table 1: The attributes of each node.
Node Region
Safety
Level
Occupancy
Level
1 Non EU medium normal
2 EU medium normal
3 EU medium busy
4 EU high busy
5 EU high normal
6 Non EU low busy
7 Non EU high normal
Table 2: The information of available processing.
Processing Location Purpose
Bias
Level
Required
Categories
p1 node 4 recom 2 [c1,c2,c3,c4]
p2 node 4 recom 1 [c2,c3,c5]
p3 node 4 recom 3 [c1,c3,c6,c7,c8]
Table 3: The information on personal data.
Data Category
Storage
Location
Owner Take-out from EU
du11 c1 node 1 u1 permitted
du12 c2 (sensitive) node 1 u1 permitted
du13 c3 node 1 u1 permitted
du14 c4 node 1 u1 not permitted
du15 c5 (sensitive) node 1 u1 permitted
du16 c6 node 1 u1 permitted
du17 c7 (sensitive) node 1 u1 permitted
du18 c8 node 1 u1 permitted
du21 c1 node 2 u2 permitted
du22 c2 (sensitive) node 2 u2 permitted
du23 c3 node 2 u2 permitted
du24 c4 node 2 u2 permitted
du25 c5 (sensitive) node 2 u2 permitted
du26 c6 node 2 u2 permitted
du27 c7 (sensitive) node 2 u2 permitted
du28 c8 node 2 u2 permitted
side the legislative zone raises ethical implications for
data subjects. It also plays a critical role in the ethical
verification process, particularly for assessing regula-
tory safety (the fifth criterion). The safety level cor-
responds to the safety protocols implemented at each
node, which can be classified as high, medium, or low.
It is crucial to route data through more secure nodes
to prevent potential breaches that could compromise
user privacy. Thus, safety level is integral to the ethi-
cal checking process under technical safety, which is
the most critical criterion. The occupancy level de-
notes whether a node is busy and is employed to min-
imize data management time and enhance the overall
efficiency of the system (the fourth criterion of the eth-
ical checker). This information about occupancy level
is utilized by both the ethical checker and the planning
agent. Additionally, the costs associated with tasks at
busy nodes and data transfer tasks to these nodes are
set at 10, representing a tenfold increase over the de-
fault task cost of 1.
Table 2 shows the processing available to apply to
personal data. It includes information on the location
of processing that is node four and the purpose that is
recommendation for all processing in this case. The
bias level shows the extent to which processing can
be biased with respect to a particular group. We show
this simply by positive integers from which is derived
the bias criterion of the ethical checking (3rd crite-
rion). Each processing requires certain categories of
data, which are indicated by a list and the category
name, e.g., c1, c2, etc.
Last but not least, Table 3 shows information on
personal data. This includes their corresponding cat-
egory, which can be sensitive, the node on which the
data are stored, the data subject who is the owner of
the personal data, and permission from the user to
take the data out of the EU. Note that the data owner
may change permission during execution.
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
268

Based on Tables 2 and 3, data sensitivity (2nd eth-
ical criterion) is computed by counting the number
of sensitive data categories that are moved and pro-
cessed. In contrast, data parcimony (6th ethical crite-
rion) is based on the total number of data units trans-
ferred or processed. We demonstrate the functionality
of our architecture by testing it in some scenarios in
the following section.
4.1 Scenario basecase
Scenario basecase is the baseline scenario. In this sce-
nario, the situation does not change along the way.
The job given to the planning agent is the following:
to load the necessary data, process recommendations,
and deliver the results to node 7. As shown in Figure
3, several routes can be considered. First, the plan-
ning agent creates a number of plans that have differ-
ent data and/or use other routes. The legal checker
performs the following checks on those plans: node
7 is outside the EU, and du14 is prohibited from be-
ing taken out of the EU, so the plans containing du14
(e.g., a plan moving from node 1 to node 7 via node 4
using data [du13, du14, du15]) are rejected. The eth-
ical checker selects the optimal plan among the legal
plans. In our experiment, the plan that uses the fol-
lowing route is chosen: node 1 → node 4 (recommen-
dation process) → node 7, and it does not use du14.
4.2 Scenario precondition-replan-1
This scenario demonstrates how the system responds
to the physical changes in the operating environment.
The objective is to process the personal data of the
user u2 for recommendation. The data is initially
stored in a database at node 2, and the output of the
processing is requested at the same node. The initial
plan is to transfer the data through node 1 to node 4,
apply the processing p2, and transfer the output back
to node 2 via node 1. As shown in Table 1, node 1 and
node 3 have the same values for every attribute ex-
cept occupancy level, where node 1 is less busy than
node 3; therefore, node 1 is selected in the initial plan.
During execution, when the data are loaded from the
database, the system detects that node 1 is suddenly
deactivated. The planner would do a replanning and
select node 3 as an intermediate to send data to node
4, apply the processing, and transfer it back via node
3 again.
4.3 Scenario precondition-replan-2
This scenario is expanded from precondition-replan-
1. After loading the data of u2 and replanning at node
2, the system transfers it to node 4 via node 3. Af-
ter applying the selected processing, suppose that the
system recognizes that node 1 has been reactivated.
The planner considers the new change by forming a
replanning from the current state and chooses node 1
again as the intermediate node to transfer the output
back to node 2.
4.4 Scenario cost-ethical-replan
This scenario demonstrates how the system responds
to the action-execution cost used in planning. As
in Scenario precondition-replan-1, the objective is to
process the personal data of the user u2 for recom-
mendation. The data is initially stored in a database
at node 2, and the processing output is requested at
node 7. The initial plan is to load the data at node
2, transfer it through node 1 to node 4, process the
data, and transfer the output to node 7. Note that the
transfer routes via node 3 are avoided because the oc-
cupancy level of node 3 is busy. Note also that the
ethical checker also considers the occupancy levels of
nodes for plan selection. During execution, when the
data are loaded from the database, the system real-
izes that the occupancy levels of node 1 and node 3
change from ordinary to busy and from busy to nor-
mal, respectively. The planner would do a replanning
and select node 3 as the intermediate to send data to
node 4, apply the processing, and transfer the output
to node 7.
4.5 Scenario ethical-replan
Scenario ethical-replan shows how the system would
react to changes that affect the ordering of plans by
the ethical checker. The task in this scenario is to use
u1’s personal data to generate recommendations and
deliver the result at node 5. u1’s data is stored at node
1. To perform the task, the planner transfers personal
data from node 1 to node 4 to run the selected pro-
cess and chooses an intermediary node between node
3 or 7 to deliver the result to node 5. As node 7 has
a higher safety level, the ethical checker initially se-
lects the plan that transfers data through it. However,
just after processing the data at node 4, the system re-
alizes that, due to some external incidents, the safety
level of node 7 has changed to low. The system then
initiates a re-evaluation, and the ethical checker se-
lects the path that passes through node 3 because it
is safer. In this scenario, the physical constraints are
fixed; however, the properties that affect the ordering
of the ethical checker and, consequently, the selected
plan are changed. The re-evaluation process shows
the functionality of our proposed architecture and the
A New Planning Agent Architecture that Efficiently Integrates an Online Planner with External Legal and Ethical Checkers
269

ethical checker component in similar situations.
4.6 Scenario legal-replan-1
Scenario legal-replan-1 demonstrates how the system
responds to the changes affecting decisions by the
legal checker. In this scenario, the planner discov-
ers that a user has rewritten permission information
in the database during execution. The legal checker
re-evaluates the legality and finds that it is not cur-
rently allowed. So, the planner re-creates different
plans. Specifically, the initial plan selects the dataset
[du21,du23,du26,du27,du28] and the route to take the
data from node 2 to node 7 via the EU to achieve the
goal. However, during execution, just after loading
the dataset at node 2, the permission information for
du28 was rewritten to prohibit taking the data out of
the EU. Because node 7 is outside the EU, it is ille-
gal to move du28 there. So the planner uses another
dataset [du22,du23,du25] to achieve the goal.
4.7 Scenario legal-replan-2
This scenario is expanded from scenario legal-replan-
1. In this scenario, scenario legal-replan-1 is exe-
cuted, and just after the first replan, the user addi-
tionally prohibits another specific piece of data, du25,
from being taken out of the EU. This causes a second
replan, and finally, the data is selected so that neither
du28, which is prohibited in scenario legal-replan-1,
nor du25, which is not permitted in this scenario, is
used.
4.8 Scenario legal-ethical-replan
This scenario occurs in the order of what happens in
scenarios ethical-replan and legal-replan-1: As in sce-
nario legal-replan-1, the user is prohibited from trans-
ferring specific data outside the EU, prompting a re-
plan. The plan selected after the first replan is to move
from node 1 to node 4 to node 7 to node 6, using dif-
ferent data. However, while data is en route to node
7, a change in the security level of node 7 from high
to low is detected, prompting an ethical replan. This
results in the final selection of the route from node 4
to node 1 to node 6.
5 EXPERIMENTS AND
DISCUSSIONS
Tables 4 and 5 present the results obtained from the
scenarios introduced in Section 4. All executions
were performed using SWI-Prolog (threaded, 64 bits,
version 9.0.4) on a MacBook Air running MacOS
14.4.1, Apple M2, eight cores, and 24 GB memory.
All runs used the same maximum number of plans,
16. Thus, the planner generates a maximum of 16
plans. The database information that is shown in Sec-
tion 4 is almost the same, but some parameters are
modified to represent each scenario. Note that each
module can be implemented in any programming lan-
guage and installed on different servers as long as they
can communicate with one another, for example, via
remote procedure calls.
In this implementation, SWI-Prolog is used to run
three modules on a single computer. Therefore, there
is little communication cost between the modules.
However, we can distribute these modules to differ-
ent servers. In this case, the communication cost be-
tween modules will be significant. In this experiment,
we evaluated the communication cost by counting the
number of interactions.
Table 4 presents the total CPU time for planning,
replanning, legal checking, and ethical checking. Ta-
ble 5 indicates the number of interactions between
the planning agent and legal/ethical checkers. Table
6 summarises the results.
In comparing the default and all-subscription
modes, the computation times were almost equal,
but the number of interactions in the all-subscription
mode was significantly lower. In the default mode, the
legal and ethical checkers are called whenever an ac-
tion is executed. The all-subscription mode functions
similarly as action executions typically alter the truth
values of certain fluents subscribed by both checkers.
Furthermore, in the default mode, the legal and
ethical checkers have to request the planning agent
for the truth value of a fluent. Meanwhile, in
all-subscription mode, these checkers consult their
databases and do not need to consult the planning
agent. This significantly reduces the number of in-
teractions. Considering the communication time re-
quired for each interaction, the impact of the all-
subscription mode is enormous. Note that although
the communication times for interaction are not in-
cluded in Table 4, it is possible to estimate them by
multiplying the number of interactions and the ap-
proximated unit communication time.
In the subscription mode, unnecessary legal and
ethical checks are minimized. Compared with the all-
subscription mode, both the number of interactions
and the computation times are lower. This shows
the considerable impact of the subscription mode on
the system efficiency. Overall, the subscription mode
proved to be the most efficient in terms of number of
interactions and computation time.
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
270
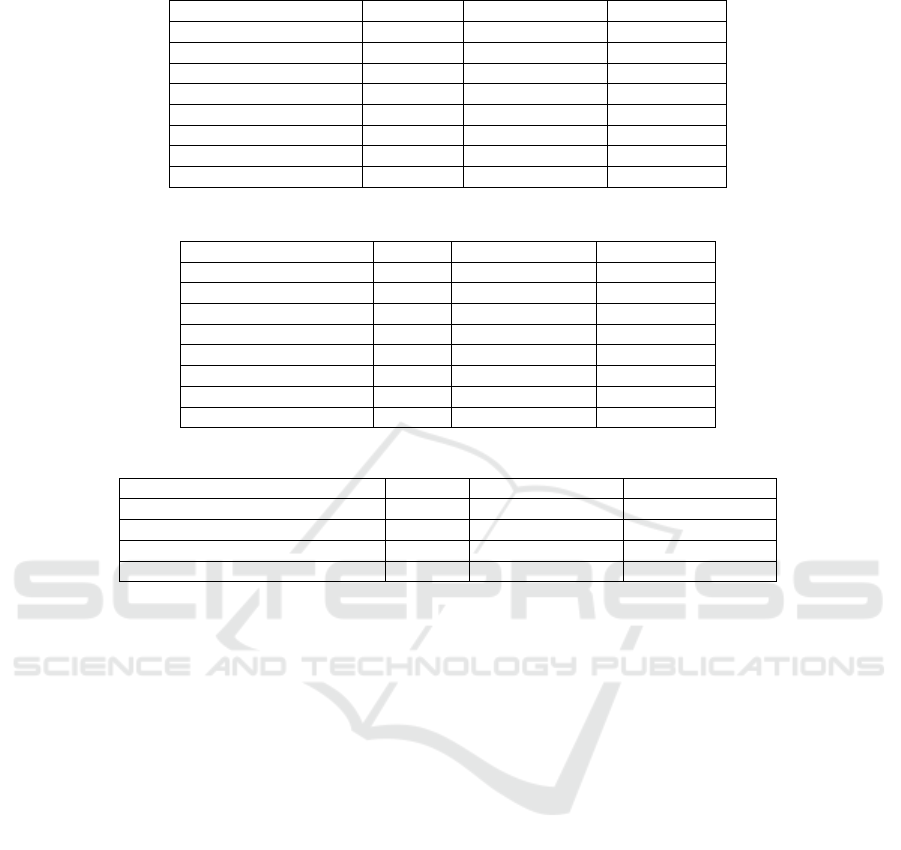
Table 4: Executed results: CPU time (seconds).
default all-subscription subscription
basecase 1.378223 1.373324 0.461348
precondition-replan-1 2.384789 2.299939 1.323991
precondition-replan-2 2.834865 2.746833 1.602472
cost-ethical-replan 2.311678 2.279096 1.154411
ethical-replan 2.709023 2.680235 1.318428
legal-replan-1 3.400821 3.655947 0.831619
legal-replan-2 86.016189 86.042916 49.701664
legal-ethical-replan 19.350356 19.304388 11.013482
Table 5: Executed results: the number of interactions.
default all-subscription subscription
basecase 16916 84 25
precondition-replan-1 46038 121 35
precondition-replan-2 50357 140 51
cost-ethical-replan 24617 104 35
ethical-replan 32760 121 43
legal-replan-1 41069 157 47
legal-replan-2 92655 337 73
legal-ethical-replan 60612 216 107
Table 6: Summary of experiments in different interaction modes.
default all-subscription subscription
Replanning after action always almost always not often
Average CPU time baseline same as baseline 48% of baseline
DBs for legal/ethical checkers no yes yes
Average number of interactions baseline 0.37% of baseline 0.13% of baseline
6 CONCLUSION
In this paper, we demonstrated how to implement
a planning agent that smoothly integrates an online
planner, a legal checker, and an ethical checker. Addi-
tionally, we compared three interaction modes, find-
ing that the fluent subscription technique effectively
reduces the number of interactions and computation
times, which is essential for the efficient integration
of these modules.
Future work will focus on improving integration
methods toward the real-time computation of legal
and ethical planning. For example, a more extensive
map will yield additional alternative plans. Currently,
the planning agent sends a limited number of alter-
native plans to the ethical checker only from the cost
viewpoint. In this case, we might need to send more
alternative plans to the ethical checker so that it can
select the most ethical plan from various points of
view. For this purpose, the planning agent also needs
to pick up the alternative plans from various points of
view before sending them to the ethical checker. An
alternative approach is to call legal and ethical check-
ers during planning to guide the planner’s inferences.
Another future work is to integrate multiple plan-
ning agents, legal checkers, and ethical checkers in
different countries. This topic of multiagent planning
becomes essential as these modules are developed for
each country.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was funded by JST AIP Trilateral
AI Research (JPMJCR20G4); JST Mirai Program
(JPMJMI23B1); JSPS KAKENHI (22H00543 and
21K12144); Agence Nationale de la Recherche
(ANR, French Research Agency) project RECOMP
(ANR-20-IADJ-0004).
REFERENCES
Agarwal, Steyskal, S., Antunovic, F., and Kirrane, S.
(2018). Legislative compliance assessment: Frame-
work, model and GDPR instantiation. In Annual Pri-
vacy Forum, pages 131–149.
Behnke, G., H
¨
oller, D., and Biundo, S. (2018). totSAT —
totally-ordered hierarchical planning through SAT. In
A New Planning Agent Architecture that Efficiently Integrates an Online Planner with External Legal and Ethical Checkers
271

International Conference on Autonomous Agents and
Multiagent Systems, pages 6110–6118.
Berreby, F., Bourgne, G., and Ganascia, J.-G. (2018).
Event-based and scenario-based causality for compu-
tational ethics. In International Conference on Au-
tonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems, pages 147–
155.
Bonatti, P. A., Kirrane, S., Petrova, I. M., and Sauro, L.
(2020). Machine understandable policies and GDPR
compliance checking. KI - K
¨
unstliche Intelligenz,
34(3):303–315.
Chesani, F. et al. (2018). Compliance in business pro-
cesses with incomplete information and time con-
straints: a general framework based on abductive rea-
soning. Fundamenta Informaticae, 161(1-2):75–111.
Contissa, G. et al. (2018). Claudette meets GDPR:
Automating the evaluation of privacy policies us-
ing artificial intelligence. https:// ssrn.com/abstract=
3208596.
European Commission (2016). Regulation (EU) 2016/679
of the European Parliament and of the Council.
Governatori, G. et al. (2011). Designing for compliance:
Norms and goals. In International Joint Conference
on Rules and Reasoning, page 282–297.
Hayashi, H., Mitsikas, T., Taheri, Y., Tsushima, K.,
Sch
¨
afermeier, R., Bourgne, G., Ganascia, J., Paschke,
A., and Satoh, K. (2023). Multi-agent online plan-
ning architecture for real-time compliance. In Inter-
national Rule Challenge, International Joint Confer-
ence on Rules and Reasoning, volume 3485 of CEUR
Workshop Proceedings.
Hayashi, H. and Satoh, K. (2022). Towards legally and eth-
ically correct online HTN planning for data transfer.
In International Workshop on Non-Monotonic Rea-
soning, Federated Logic Conference, volume 3197 of
CEUR Workshop Proceedings, pages 4–15.
Hayashi, H. and Satoh, K. (2023). Online HTN planning
for data transfer and utilization considering legal and
ethical norms: Case study. In International Confer-
ence on Agents and Artificial Intelligence, volume 1,
pages 154–164.
Hayashi, H., Taheri, Y., Tsushima, K., Bourgne, G.,
Ganascia, J., and Satoh, K. (2024). Toward smooth
integration of an online HTN planning agent with le-
gal and ethical checkers. In AICOM track of the In-
ternational Workshop on AI Value Engineering and AI
Compliance Mechanisms (VECOMP), European Con-
ference on Artificial Intelligence (ECAI), pages 1–6.
Hayashi, H., Tokura, S., Hasegawa, T., and Ozaki, F.
(2006). Dynagent: An incremental forward-chaining
HTN planning agent in dynamic domains. In Bal-
doni, M., Endriss, U., Omicini, A., and Torroni, P.,
editors, Declarative Agent Languages and Technolo-
gies III, pages 171–187. Springer.
Lindner, F., Mattm
¨
uller, R., and Nebel, B. (2020). Evalua-
tion of the moral permissibility of action plans. Artifi-
cial Intelligence, 287(103350).
Magnaguagno, M. C., Meneguzzi, F., and Silva, L. (2021).
HyperTensioN: A three-stage compiler for planning.
In International Planning Competition: Planner and
Domain Abstracts – Hierarchical Task Network Plan-
ning Track, pages 5–8.
Merigoux, D., Chataing, N., and Protzenko, J. (2021).
Catala: a programming language for the law. Proc.
ACM Program. Lang., 5(ICFP).
Nau, D., Cao, Y., Lotem, A., and Munoz-Avila, H. (1999).
SHOP: Simple hierarchical ordered planner. In In-
ternational Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence,
volume 2, page 968–973.
Pacuit, E. (2024). Voting Methods. In Zalta, E. N. and
Nodelman, U., editors, The Stanford Encyclopedia
of Philosophy. Metaphysics Research Lab, Stanford
University, Summer 2024 edition.
Palmirani, M., Martoni, M., Rossi, A., Bartolini, C., and
Robaldo, L. (2018). Legal ontology for modelling
GDPR concepts and norms. Legal Knowledge and In-
formation Systems, pages 91–100.
Patra, S., Ghallab, M., Nau, D., and Traverso, P. (2019).
Acting and planning using operational models. In
AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pages
7691–7698.
Patra, S., Mason, J., Kumar, A., Ghallab, M., Traverso, P.,
and Nau, D. (2020). Integrating acting, planning, and
learning in hierarchical operational models. In In-
ternational Conference on Automated Planning and
Scheduling, pages 478–487.
Satoh, K. and et. al. (2011). Proleg: An implementation
of the presupposed ultimate fact theory of Japanese
civil code by prolog technology. In New Frontiers in
Artificial Intelligence, pages 153–164. Springer.
Schreiber, D. (2021). Lilotane: A lifted sat-based approach
to hierarchical planning. Journal of Artificial Intelli-
gence Research, 70:1117–1181.
Taheri, Y., Bourgne, G., and Ganascia, J.-G. (2023a). A
compliance mechanism for planning in privacy do-
main using policies. In Yada, K., Takama, Y., Mi-
neshima, K., and Satoh, K., editors, New Frontiers in
Artificial Intelligence, pages 77–92. Springer Nature.
Taheri, Y., Bourgne, G., and Ganascia, J.-G. (2023b). Mod-
elling integration of responsible ai values for ethical
decision making. In Workshop on Computational Ma-
chine Ethics, International Conference on Principles
of Knowledge Representation and Reasoning.
van Riemsdijk, M. B. et al. (2013). Agent reasoning for
norm compliance: a semantic approach. In Interna-
tional Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multia-
gent Systems, pages 499–506.
Vos, M. D., Kirrane, S., Padget, J., and Satoh, K. (2019).
ODRL policy modelling and compliance checking. In
International Joint Conference on Rules and Reason-
ing, pages 36–51.
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
272
