
Approximations of the Sigmoid Function Beyond the Approximation
Domains for Privacy-Preserving Neural Networks
Shusaku Uemura, Kazuhide Fukushima
a
and Shinsaku Kiyomoto
b
KDDI Research, Inc., Saitama, Japan
Keywords:
Polynomial Approximation, Sigmoid Function, Fully Homomorphic Encryption, Privacy-Preserving Neural
Network.
Abstract:
Artificial intelligence and data analysis have recently attracted attention, but privacy is a serious problem when
sensitive data are analyezed. Privacy-preserving neural networks (PPNN) solve this problem, since they can
infer without knowing any information about the input. The PPNN promotes the analyses of sensitive or
confidential data and collaboration among companies by combining their data without explicitly sharing them.
Fully homomorphic encryption is a promising method for PPNN. However, there is a limitation that PPNN
cannot easily evaluate non-polynomial functions. Thus, polynomial approximations of activation functions are
required, and much research has been conducted on this topic. The existing research focused on some fixed
domain to improve their approximation accuracy. In this paper, we compared seven ways in total for several
degrees of polynomials to approximate a commonly used sigmoid function in neural networks. We focused
on the approximation errors beyond the domain used to approximate, which have been dismissed but may
affect the accuracy of PPNN. Our results reveal the differences of each method and each degree, which help
determine the suitable method for PPNN. We also found a difference in the behavior of the approximations
beyond the domain depending on the parity of the degrees, the cause of which we clarified.
1 INTRODUCTION
In recent decades, information systems have broadly
played an important role in daily life. People use
smartphones, PCs and other devices, and companies
provide their own systems, applications and so on.
Cloud platformers help the market of information sys-
tems rapidly grow. In such situations, a significant
amount of data is being generated. This leads to the
era of big data, where there are many demands to
perform advanced analyses on these data. Emerg-
ing technology of artificial intelligence (AI) satis-
fies these demands. In recent years, many AI-based
data analyzing systems such as market research tools
and customer relationship management systems have
huge potential for improving current business and
cross-domain customer analyses between companies
using AI systems and opening new business avenues.
Nonetheless, people are not necessarily willing to
provide their sensitive information such as health data
to AI even if it will give them useful information for
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2571-0116
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0268-0532
tasks such as disease prediction. In addition, compa-
nies and organizations tend to hesitate to share their
confidential data with third-party AI systems. This re-
luctance also prevents collaborative analyses among
several companies by combining their data, even if
they provide useful insights that cannot be obtained
by individual analyses.
Privacy-preserving machine learning (PPML) pro-
vides a solution to this problem of the trade-off be-
tween privacy and convenience. PPML performs
training and/or inference without knowing anything
about the input data. PPML can be realized using
privacy-preserving computation technologies such as
multiparty computation (MPC) and fully homomor-
phic encryption (FHE). Although both MPC and FHE
enable PPML, each method has its own strength.
MPC is a computation system that composes of sev-
eral computing servers. Each server computes on a
secret piece of data, with which the servers cannot
retrieve the original data. To perform complex opera-
tions, they communicate and jointly compute. Finally,
by combining the secret pieces of data, MPC can han-
dle the data without knowing them. FHE is an encryp-
tion scheme, which enables operations on encrypted
Uemura, S., Fukushima, K. and Kiyomoto, S.
Approximations of the Sigmoid Function Beyond the Approximation Domains for Privacy-Preserving Neural Networks.
DOI: 10.5220/0013100700003899
In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy (ICISSP 2025) - Volume 2, pages 445-454
ISBN: 978-989-758-735-1; ISSN: 2184-4356
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
445

values without decryption. Since the data are en-
crypted, a server can evaluate them without knowing
them and does not require communication for compu-
tation. Although MPC can compute faster than FHE,
there is a risk that malicious servers may retrieve the
data by jointly combining all of their secret pieces.
In addition, if computing servers are owned by one
company, that company can potentially retrieve the
data, which forces data owners to trust the company.
FHE does not have this risk because the data are en-
crypted by the secret key of the client. Even if a mali-
cious server attempts to retrieve the data, they cannot
decrypt the data without the key. The data owners,
which are clients in this case, do not necessarily need
to trust the server. Therefore, FHE-based PPML can
promote joint analyses among companies since it can
secrete confidential data and does not require trust in
the servers.
Among many AI technologies, neural networks
are fundamental and used in recent AI systems. One
of major problems in implementing neural networks
with FHE is how to compute activation functions.
Neural networks are combination of operations on
vectors and matrices and activation functions. Since
activation functions are not arithmetic, FHE cannot
directly adopt them because of the limitation of the
operational functions. FHE allows only a few types
of operation such as addition and multiplication. It
requires additional processes to execute complicated
operations such as divisions and conditional branches.
One major method to homomorphically compute an
activation function is to approximate it with polyno-
mials. Among several types of activation functions,
the sigmoid function is a popular option. It is ex-
pected to go well with polynomial approximations be-
cause it is differentiable function. Therefore, exam-
ining the accuracy of polynomial approximations of
the sigmoid function is important to make neural net-
works with FHE more accurate.
1.1 Related Works
Many studies on PPML have been conducted in recent
years. CryptoNets (Dowlin et al., 2016) uses homo-
morphic encryption called YASHE (Bos et al., 2013)
to realize privacy-preserving neural networks. It em-
ploys a monomial x
2
as an activation function to re-
duce the computational complexity. The authors of
(Cheon et al., 2020) proposed polynomials that ap-
proximate the sign function in the interval [−1,1],
with which a comparison function and ReLU func-
tion can be constructed. In 2022, the authors of (Lee
et al., 2022) improved the approximating polynomial
by composing several polynomials.The research of
(Stoian et al., 2023) proposed neural networks that
utilized a property of TFHE (Chillotti et al., 2020)
called programmable bootstrapping to evaluate ac-
tivation functions. This method enables evaluation
of arbitrary function without decryption but is time-
consuming. The proposed scheme was implemented
in ConcreteML(Meyre et al., 2022). In (Trivedi et al.,
2023), the authors approximated the sigmoid function
with several methods and examined the errors in the
approximation. They fixed the degree of approximat-
ing polynomials as three and used intervals [−10,10]
and [−50,50] as the target ranges to approximate.
1.2 Our Contribution
Although previous research working on privacy-
preserving neural networks has been conducted, some
studies compromised the accuracy for efficiency by
using a nonlinear monomial, whereas others made
the approximation function only accurate inside the
designated range, which we will call an approxima-
tion domain in the remainder of this paper. On the
other hand, input values of activation functions may
be too large or too small and lie outside the approx-
imation domain. In that case, the error can have a
non-negligible impact on the inference result of the
privacy-preserving neural networks. Therefore, there
is necessity to explore the behaviors of approximation
functions outside the approximation domain, which
can lead to more accurate privacy-preserving neural
networks.
We conducted experiments on the approximations
of the sigmoid function with seven types of approxi-
mations for various degrees of polynomials. We com-
pared each method in terms of L
2
and L
∞
errors both
in the domain used for approximations and beyond
the domain. Our results show that limit approxima-
tion is the best method when the parameter is set to
the same value as other polynomial approximations.
Our results also show that the errors outside the ap-
proximation domain behave differently depending on
the approximations although those inside the domain
behave similarly. By closely examining the behav-
iors, we clarified the cause of this difference, which
provides information to avoid unexpected inference
errors in privacy-preserving neural networks.
1.3 Organization
This paper consists of six sections including this sec-
tion. In the following section, we quickly review the
information used in this paper such as a fully ho-
momorphic encryption scheme and a sigmoid func-
tion. In Section 3, four methods to approximate
ICISSP 2025 - 11th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy
446

the sigmoid function are explained. Then, Section
4 presents the result of experiments on the accuracy
of the approximations of the sigmoid function outside
the range used for approximation. Section 5 discusses
our experimental results. Finally, Section 6 concludes
this paper.
2 PRELIMINARIES
In this section, we review a fully homomorphic en-
cryption (FHE) scheme that is often used for privacy-
preserving machine learning. We also review the def-
inition of the sigmoid function, which is often used as
an activation function in neural networks.
In the remainder of this paper, R denotes the set
of real numbers.
2.1 Fully Homomorphic Encryption
A homomorphic encryption (HE) is an encryption
scheme that enables operations on encrypted values
without decryption. Technically, HE schemes consist
of three functions that are identical to those of a pub-
lic key encryption scheme, key generation (KeyGen),
encryption (Enc), and decryption (Dec). For addition
and multiplication, the following equation holds for
an HE scheme: Dec(Enc(m
1
) ◦ Enc(m
2
)) = m
1
◦ m
2
for any messages m
1
and m
2
in the message space
where the operation ◦ can be both addition and mul-
tiplication. Multiplication over two encrypted values
is not straightforward. It sometimes requires a special
key called or/and special operations.
While the number of homomorphic operations is
limited for some HE schemes, other HE scheme do
not have this limit. The former is called somewhat ho-
momorphic encryption or leveled homomorphic en-
cryption. The latter is called fully homomorphic
encryption (FHE). A fully homomorphic encryption
scheme allows an arbitrary number of operations on
encrypted data using an operation called bootstrap-
ping. Bootstrapping reduces the noise of an encrypted
value, which is increased by homomorphic operations
and can cause decryption failure if it exceeds a thresh-
old. As machine learning requires a number of oper-
ations, FHE schemes are often employed to realize
privacy-preserving machine learning.
Several FHE schemes have been created thus
far, such as Brakerski-Gentry-Vaikuntanathan (BGV)
(Brakerski et al., 2012), Cheon-Kim-Kim-Song
(CKKS) (Cheon et al., 2019; Cheon et al., 2017),
and a torus fully homomorphic encryption (TFHE)
(Chillotti et al., 2020). All of these FHE schemes are
based on the Learning With Errors (LWE) encryption
scheme (Regev, 2005). The message space of BGV,
BFV and TFHE is restricted to the set of integers.
Strictly speaking, it is a set of integers represented by
certain bits prefixed by the parameter of the scheme.
Meanwhile, the message space of the CKKS scheme
is the set of complex numbers. Thus, CKKS enables
operations on approximate numbers, instead of inte-
gers.
TFHE has an outstanding function called pro-
grammable bootstrapping (PBS), which enables to
evaluate any discrete function on encrypted data dur-
ing bootstrapping without extra computation. Al-
though this property is suitable for privacy-preserving
neural networks, which require many nonlinear func-
tions such as activation functions, TFHE can han-
dle only integers. This does not suit for neural net-
works, which require decimal computations. How-
ever, CKKS can handle decimals. Although CKKS
cannot execute PBS, it can rapidly evaluate polyno-
mials. Thus, CKKS can approximate nonlinear func-
tions through polynomial approximation.
For these reasons, both CKKS and TFHE are com-
mon options of FHE for privacy-preserving machine
learning (Lou and Jiang, 2019; Meyre et al., 2022).
For more information about privacy-preserving neural
networks including FHE-based and multiparty com-
putation, see (Ng and Chow, 2023). In this paper,
we focus on CKKS-based privacy-preserving neural
networks since they can handle decimals and approx-
imate nonlinear functions with high accuracy.
2.2 Cheon-Kim-Kim-Song Scheme
As mentioned in the previous subsection, Cheon-
Kim-Kim-Song (CKKS) is a fully homomorphic en-
cryption scheme that allows operations on approx-
imate numbers. Although CKKS has an efficient
variant making use of residue number system (RNS)
(Cheon et al., 2019), this modification does not es-
sentially affect our research; we quickly explain the
original CKKS (Cheon et al., 2017).
CKKS is composed of three basic operations: key
generation, encryption and decryption. A sketch of
these three algorithms is presented below.
• KeyGen: Sample a,s,e from certain polynomial
rings. Set b
:
= −as + e. Output pk
:
= (a, b) as a
public key and sk
:
= (1,s) as a secret key.
• Enc
pk
(m): Sample v,e
1
,e
2
from polynomial rings
of small coefficients. Output c
:
= (vb + m +
e
0
,va + e
1
) as a ciphertext for a message m.
• Dec
sk
(c): Output b + as as a decrypted message.
Since the detailed algorithms do not matter in our re-
search, we omit them. See (Cheon et al., 2017) for
Approximations of the Sigmoid Function Beyond the Approximation Domains for Privacy-Preserving Neural Networks
447

details.
The addition of two encrypted values can be per-
formed by simply adding them. However, the mul-
tiplication of two encrypted values is not straightfor-
ward. It requires an additional key called the evalua-
tion key.
• EvalKeyGen
sk,P
: Sample a
′
,e
′
from certain poly-
nomial rings. Output evk
:
= (−a
′
s + e
′
+ Ps
2
,a).
• Mult
evk,P
(c
1
, c
2
): For c
1
= (b
1
,a
1
), c
2
= (b
2
,a
2
),
compute (d
0
,d
1
,d
2
)
:
= (b
1
b
2
,a
1
b
2
+ a
2
b
1
,a
1
a
2
).
Output (d
0
,d
1
) +
P
−1
· d
2
· evk
CKKS can efficiently compute polynomials and
inverses, which enables CKKS to evaluate many func-
tions including sigmoid function through polynomial
approximation and division. Polynomials are combi-
nations of additions and multiplications. Thus, they
can be constructed via the above homomorphic addi-
tion and multiplication. To homomorphically evaluate
the inverse function, approximation is required. The
following equation can be used to approximate the in-
verse of x. Setting ˆx
:
= p − x for some p ∈ R, it holds
that
x(p + ˆx)(p
2
+ ˆx
2
)···(p
2
r−1
+ ˆx
2
r−1
) = p
2
r
− ˆx
2
r
. (1)
Assuming |x| < p/2,
p
−2
r
·
r−1
∏
k=0
(p
2
k
+ ˆx
2
k
) =
1
x
·
1 −
ˆx
2
r
p
2
r
≈
1
x
. (2)
Thus, by computing the left-hand side of Equation
(2), one obtains the approximation of 1/x.
2.3 Sigmoid Function
The sigmoid function σ(x) is a continuous function
that asymptotically approaches 1 as x goes to positive
infinity and asymptotically approaches 0 as x goes to
negative infinity. This function is used as an activa-
tion function in neural networks. The sigmoid func-
tion can be expressed as follows: σ(x) =
1
1+exp(−αx)
,
where α is a parameter. Because this parameter does
not have a significant influence on the accuracy of the
polynomial approximation, we set α = 1 for the re-
mainder of this paper, thus σ(x) = 1/(1 + exp(−x)).
To evaluate neural networks, three operations are
necessary: vector addition, multiplication between a
matrix and vector, and the evaluation of activation
functions. Among these three operations, additions
and multiplications can be performed homomorphi-
cally with the aforementioned procedures. However,
the evaluation of activation functions is not straight-
forward since a non-arithmetic function requires addi-
tional process. Previous research on neural networks
uses the approximation of activation functions. For
example, (Dowlin et al., 2016) uses x
2
for simplicity
and efficiency.
Rectified Linear Unit (ReLU) is one option of ac-
tivation function, which outputs the same value as the
input if it is positive and 0 if it is negative. The ReLU
function cannot be expressed with Taylor expansion
at the origin, which makes it require complicated pro-
cedure to approximate with polynomials. Therefore,
we focus on the sigmoid function, which is infinitely
differentiable.
3 POLYNOMIAL
APPROXIMATION OF
SIGMOID FUNCTION
This section explains the methods that we employed
to approximate the sigmoid function. We used four
approximation methods: Taylor expansion, Lagrange
interpolation, Remez algorithm (Remez, 1934), and
approximation of limit.
In order to approximate the sigmoid function with
the above methods, there exist two major ways. One
is to approximate the sigmoid function directly, and
the other is to approximate via an approximation of
the exponential function as we will explain in detail
below.
3.1 Two Ways to Approximate Sigmoid
Function
As mentioned above, there exist two ways to approx-
imate the sigmoid function, directly and via exponen-
tial function. The asymptotic behaviors of the sig-
moid function and polynomials differs from those of
polynomials. For x → ∞ (resp. x → −∞), the sigmoid
function σ(x) → 1 (resp. σ(x) → 0). On the other
hand, for x → ±∞, p(x) → ±∞ for any polynomial
p(x). Thus, it is expected that the error between the
sigmoid function and approximating polynomials in-
creases when x increases or decreases.
When x tends to the positive infinity, the behavior
of an exponential function and polynomials is simi-
lar in that both go to the positive infinity if the lead-
ing coefficient of the polynomial is positive. There-
fore, both sigmoid and approximation approach zero
asymptotically when x → −∞. Thus, approximation
via an exponential function is superior to the direct
approximation. However, the inverse with FHE re-
quires additional computations as explained in Sec-
tion 2.2.
ICISSP 2025 - 11th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy
448

3.2 Taylor Expansion
Taylor expansion is a well-known analytic method
for approximating functions. In order to execute
Taylor expansion, the target function should be at
least infinitely differentiable. Taylor expansion of a
function f at a ∈ R is expressed as f (x) = f (a) +
(x−a)
1!
d f
dx
(a) + ··· +
(x−a)
n−1
(n−1)!
d
n−1
f
dx
n−1
(a) + R
n
where R
n
is
a residue. It can be expressed as R
n
=
(x−a)
n
n!
d
n
f
dx
n
(θ)
where a < θ < x. If R
n
converges as n → ∞, then
f (x) can be written as Taylor expansion. That is,
f (x) =
∑
∞
n=0
(x−a)
n
n!
d
n
f
dx
n
(a) where we set d
0
f /dx
0
= f
and 0! = 1.
The sigmoid function can be written as Taylor ex-
pansion. To approximate the sigmoid function with
the Taylor series, it is sufficient to use Taylor se-
ries at most degree n. Since the sigmoid function is
symmetric at the origin, it appears accurate when it
is approximated with Taylor series at the origin. In
other words, the polynomial approximation
˜
σ
n
with
Taylor series of the sigmoid function is written as
˜
σ
n
(x) =
∑
n
k=0
x
k
k!
d
k
σ
dx
k
(0). In the above approximation,
the residue is cut off. In the case of the exponential
function, the formula is clearer because the derivative
of the exponential function is the exponential func-
tion. Therefore, the approximation ˜e
n
of the degree n
is ˜e
n
(x) =
∑
n
k=0
x
k
k!
.
3.3 Lagrange Interpolation
Lagrange interpolation is a numerical method to ap-
proximate a function with polynomials. It constructs
an approximating polynomial that coincides with the
target function at the given points. To construct the
polynomial, one can sum up polynomials that coin-
cide with the target function at a certain given point
and take 0 at the other given points. When n points
x
1
,x
2
,..., x
n
are given, the polynomial obtained via
Lagrange interpolation of f (x) is
p(x)
:
=
n
∑
k=1
f (x
k
)
∏
j̸=k
(x − x
j
)
(x
k
− x
j
)
. (3)
When x
1
,x
2
,..., x
n
are different, p(x) is a polynomial
of the degree of at most n − 1, because each product
part
∏
j̸=k
(x − x
j
)/(x
k
−x
j
) is a polynomial of the de-
gree n − 1. In addition, p(x
k
) = f (x
k
) holds for all
x
k
∈ (x
1
,...x
n
). This is because the product part for
k is equal to 1 and for the other j ̸= k it is equal to
0. Therefore, in the above sense, Lagrange interpo-
lation constructs a polynomial that approximates the
target function. Note that the approximation error of
Lagrange interpolation does not necessarily decrease
when the degree of polynomial increases, since it is a
numerical method of approximation.
3.4 Remez Algorithm
Remez algorithm (Remez, 1934) is also a numerical
method to obtain an approximating polynomial the L
∞
error of which is minimum among fixed-degree poly-
nomials. Since L
∞
norm is the maximum of a function
in a certain domain, a polynomial that minimizes the
error in terms of L
∞
norm is called a minimax polyno-
mial. Therefore, we can paraphrase that Remez algo-
rithm is suitable to obtain a minimax polynomial of a
specific degree.
An improved variant of this algorithm is used for
RNS-CKKS bootstrapping (Lee et al., 2021). The im-
proved variant supports the union of intervals as its
approximation domain. Since the domain in which
the sigmoid function is approximated is a single inter-
val, we use the simpler one. Refer (Lee et al., 2021,
Algorithm 1) for the details of the algorithm we im-
plemented.
Remez algorithm clearly aims to minimize the er-
ror ”within” the given domain. Thus, it guarantees the
accuracy inside the domain but does not guarantee the
accuracy outside the approximation domain.
3.5 Approximation of Limit
The last approximation method used is an approxi-
mation of the limit. This method approximates an
exponential function by truncating a sequence that
converges to an exponential function. The sequence
{(1 + x/n)
n
}
n
converges to an exponential function,
i.e., exp(x) = lim
n→∞
1 +
x
n
n
. Thus, the n-th term of
the sequence is expected to be a good approximation
for a large integer n.
In order to obtain the approximation of a larger
number, it is efficient to repeat squaring the base.
Starting from (1+x/2
r
), to repeat squaring for r times
results (1 + x/2
r
)
2
r
. This is much more efficient than
just multiplying the base 2
r
times.
Note that this method is different from the other
three approximations as this is not a explicit poly-
nomial approximation. For the same parameter n,
the other methods can obtain polynomials of the de-
gree n whereas this method implicitly yields a poly-
nomial of degree 2
n
if (1 + x/2
n
)
2
n
is expanded. In
order to compare this method to the others, one must
be careful about this difference. Furthermore, this
method only applies to approximations of the sig-
moid function via an exponential function. This can-
not be extended to direct an approximation of the sig-
moid function since there does not exist a well-known
Approximations of the Sigmoid Function Beyond the Approximation Domains for Privacy-Preserving Neural Networks
449
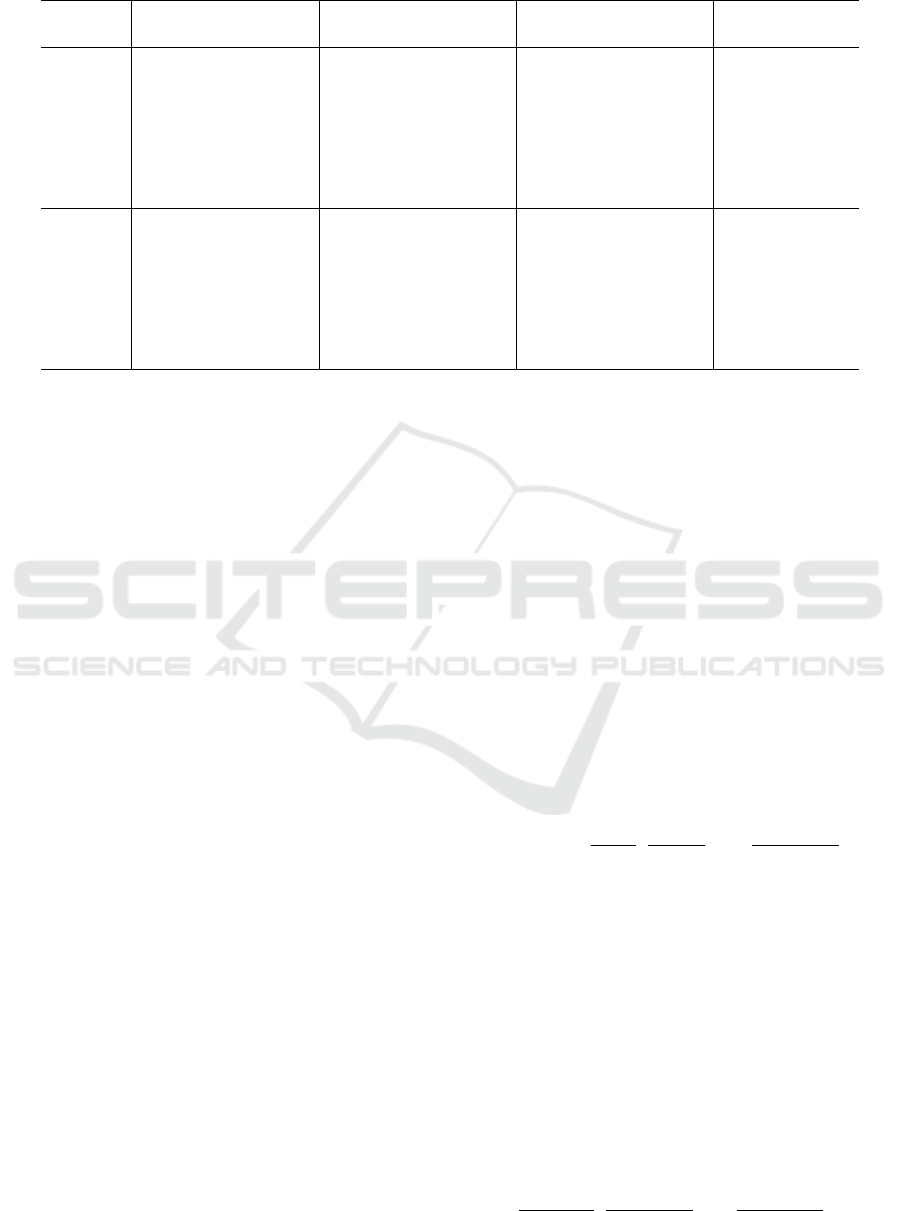
Table 1: Approximation errors inside the approximation domain [−3,3].
Taylor Lagrange Remez Limit
n via exp sig via exp sig via exp sig via exp sig
L
2
2 0.142 0.0899 4.1 0.0589 3.71 0.0386 0.0343 -
5 0.0783 0.0336 0.00905 0.00184 0.00999 0.000996 0.00431 -
8 0.00184 0.024 7.62e-05 0.000249 6e-05 0.00016 0.000539 -
11 3.13e-05 0.014 3.2e-07 2.33e-05 1.45e-07 4.14e-06 6.74e-05 -
14 2.61e-07 0.011 7.9e-10 3.95e-06 1.73e-10 6.65e-07 8.43e-06 -
17 1.24e-09 0.00727 4.82e-11 5.65e-07 9e-13 1.72e-08 1.05e-06 -
20 3.7e-12 0.00601 2.75e-08 1.25e-07 3.16e-14 2.76e-09 1.32e-07 -
L
∞
2 0.667 0.297 5.82e+03 0.0913 6.3e+03 0.0626 0.0607 -
5 1.9 0.241 0.0525 0.00624 0.0429 0.00157 0.00695 -
8 0.0362 0.22 0.000826 0.00119 0.000245 0.000252 0.000859 -
11 0.000817 0.183 5.33e-06 0.000197 5.92e-07 6.51e-06 0.000107 -
14 8.37e-06 0.167 1.79e-08 4.3e-05 7.05e-10 1.04e-06 1.34e-05 -
17 4.74e-08 0.139 1.5e-09 8.2e-06 2.69e-11 2.7e-08 1.68e-06 -
20 1.63e-10 0.126 7.8e-07 2.19e-06 1.08e-12 4.33e-09 2.09e-07 -
exponential sequence that converges to the sigmoid
function as far as authors’ knowledge.
4 EXPERIMENTS
In this section, we describe the details of our experi-
ments and the results. In summary, the four methods
explained in the previous section were implemented
for both the exponential function and the sigmoid
function. We conducted experiments for several de-
grees and approximation domains to measure the er-
rors of approximation both inside and outside the ap-
proximation domain.
Since σ(x) − 1/2 is an odd function, polynomials
of odd degrees appear appropriate for approximation.
However, even polynomials were also used because
the exponential function is not an odd function. To
compare the direct approximations and approxima-
tions via exponential functions, it is natural to include
even polynomials.
The experiments were conducted on a Mac mini
with an Apple M2 CPU, 24 GB RAM and macOS
Ventura 13.6.3. Python 3.10.11 was used for all ex-
periments.
4.1 Details of Implementation
Since Lagrange interpolation and Remez algorithm
are numerical methods, the coefficients of the approx-
imating polynomials depend on how to implement
them. We explain the details of the implementation
of each method.
4.1.1 Taylor Expansion
Since the Taylor expansion is an analytic method,
there are few things to note. For both sigmoid and
exponential functions, we used Taylor series at the
origin, thus it is also known as Maclaurin expansion.
The residue term R
n+1
in Taylor expansion was cut off
to obtain the approximating polynomials of degree n.
We used SymPy 1.12.1 (Meurer et al., 2017) to obtain
the derivatives of both functions and substituted 0 for
x to obtain the coefficients.
4.1.2 Lagrange Interpolation
As Section 3.3 describes, Lagrange interpolation re-
quires n + 1 points to obtain approximating polyno-
mials. We used the points that equally divided the
approximation domain. More specifically, since we
used the interval [−3, 3] as the approximation domain,
we used {−3,
−3n+6
n
,
−3n+2·6
n
,...,
−3n+(n−1)·6
n
,3} for
n-th polynomial .
4.1.3 Remez Algorithm
In addition to Lagrange interpolation, Remez algo-
rithm also requires initial points to obtain an ap-
proximation function. Unlike Lagrange interpola-
tion, the Remez algorithm requires n + 2 points in-
stead of n + 1 to obtain an n-th polynomial. As
this difference does not matter, we initialized the
input points in the almost same way as Lagrange
interpolation, i.e., we divided the approximation
domain equally. The approximation domain was
set to be identical to the Lagrange interpolation:
the interval [−3,3]. Thus, the initial points are
{−3,
−3(n+1)+6
n+1
,
−3(n+1)+2·6
n+1
,...,
−3(n+1)+n·6
n+1
,3}. The
ICISSP 2025 - 11th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy
450
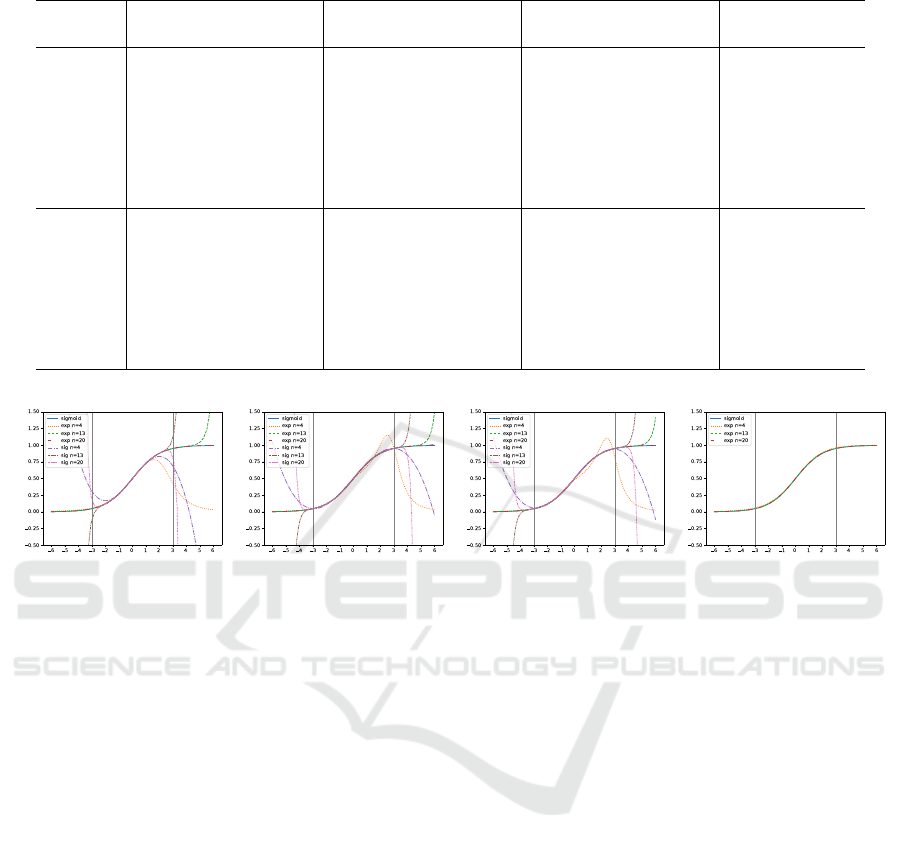
Table 2: Approximation Errors outside the approximation domain[−6,−3) ∪ (3,6].
Taylor Lagrange Remez Limit
n via exp sig via exp sig via exp sig via exp sig
L
2
2 0.443 0.64 0.391 0.194 0.446 0.288 0.0279 -
5 2.07 3.85 1.85 0.832 2.28 0.618 0.0036 -
8 0.266 10.9 0.204 1.46 0.204 1.08 0.000451 -
11 3.18 98.7 1.36 8.38 1.17 3.74 5.64e-05 -
14 0.0145 3.11e+02 0.00687 16.0 0.00572 7.24 7.05e-06 -
17 0.000641 3.24e+03 0.000243 1.03e+02 0.000241 28.6 8.81e-07 -
20 1.54e-05 1.07e+04 0.00101 2.05e+02 8.02e-05 57.8 1.1e-07 -
L
∞
2 0.926 1.0 0.943 0.408 0.96 0.533 0.0564 -
5 3.51e+03 12.7 5.65e+03 3.26 1.01e+04 2.48 0.00635 -
8 0.942 46.3 0.921 7.34 0.924 5.53 0.000794 -
11 2.01e+04 6.16e+02 3.51e+03 59.6 1.71e+03 27.7 9.93e-05 -
14 0.206 2.25e+03 0.115 1.32e+02 0.1 61.9 1.24e-05 -
17 0.0121 2.99e+04 0.00515 1.07e+03 0.0051 3.1e+02 1.55e-06 -
20 0.000335 1.09e+05 0.017 2.36e+03 0.00189 6.94e+02 1.94e-07 -
(a) Taylor expansion (b) Lagrange interpolation (c) Remez algorithm (d) Limit approximation
Figure 1: Comparisons between the sigmoid function and approximating polynomials of the degrees 4, 13, 20.
approximation parameter δ was set to be 10
−3
. Ad-
ditionally, the algorithm was terminated when the L
∞
error fell below 10
−10
to avoid the instability of the
algorithm.
4.1.4 Approximation of Limit
As Section 3.5 explains, this method only applies to
approximations via the exponential function. Hence,
we conducted experiments with this method only on
approximations via the exponential function. Unlike
the two previous methods, which are identical to Tay-
lor expansion, performing this method requires only
one parameter, which is the number of squares. Al-
though this parameter is not the degree of the ap-
proximating polynomial as described in Section 3.5,
we handle it similarly to the degree parameter for the
other methods for comparison because these parame-
ters are regarded as similar in the sense that they are
closely related to the number of computations.
4.2 Accuracy Inside Approximation
Domain
Here, we compare the accuracies of the obtained ap-
proximations. We use two criteria to measure the ac-
curacy of the approximation: the L
2
error, which is
also known as mean squared error (MSE) and L
∞
er-
ror, which is the maximum absolute error in a certain
range. These errors were measured inside the approx-
imation domain [−3,3]. Although the Taylor expan-
sion and limit approximation do not depend on the ap-
proximation domain, we compared all methods using
identical criteria. The errors were numerically mea-
sured instead of analytically measured. We evaluated
the function for 10,000 points that uniformly sepa-
rated the domain, and computed the mean squared
errors for L
2
and took the maxima for the L
∞
error
respectively.
Table 1 shows the results of the approximation
inside the approximation domain [−3,3]. In the ta-
ble, ”via exp” columns show the results of approx-
imations via the exponential function while ”sig”
columns show those of direct approximation of sig-
moid function. The ”n” column shows the degree of
Approximations of the Sigmoid Function Beyond the Approximation Domains for Privacy-Preserving Neural Networks
451

(a) Approximation via exponential (b) Direct approximation
Figure 2: Comparisons among approximating polynomials of the degree 13.
the approximating polynomials. Since the limit ap-
proximation cannot be applied to the direct approxi-
mation, the column is filled with ”-”. Table 1 shows
that three noteworthy points. First, the error decreases
as the degree of the approximating polynomial in-
creases for all methods of both direct and via exp.
This is natural because it is expected that a polyno-
mial of a larger degree can express broader range of
functions. Second, Table 1 shows the approximation
via the exponential function of the limit approxima-
tions is the best method among all approximation.
Note that the comparison between the limit approx-
imation and the other methods is not straightforward
because parameter n is not simply the degree of poly-
nomials. Third, for almost all methods and degrees,
the approximations via the exponential function have
better L
2
and L
∞
errors than the direct approximations
of the sigmoid function.
4.3 Accuracy Outside Approximation
Domain
To examine the errors outside the approximation do-
mains, we used a union of intervals [−6, −3) ∪ (3, 6]
as the outside so that the lengths of the approxima-
tion domain and outside had equal lengths. When the
outside is set to be broader, the errors are expected
to increase because the polynomials diverge while the
sigmoid function saturates.
Table 2 illustrates the L
2
and L
∞
errors of the ap-
proximating polynomials within [−6,−3) ∪ (3,6] in
the same manner as Table 1. These results have three
noticeable points. First, the limit approximation is the
best method, which is consistent with the inside case.
Second, almost all results show that the approxima-
tions via the exponential function are better than the
direct approximation of the sigmoid function. Third,
the L
∞
errors for approximations via exponential of
odd degrees should be closely examined. Despite
these observation, these approximations have much
larger errors than the direct approximations. We dis-
cuss the details of this phenomenon in the following
section.
Fig 1 shows the comparisons between the sigmoid
function and the approximating polynomials of de-
grees 4, 13, 20. In the figure, the curves with the
label ”exp n = ∗” are the polynomials of the approx-
imation via the exponential function, those with label
”sig n = ∗” are polynomials of the direct approxima-
tions. The gray vertical lines are the bounds of the
approximation domain, i.e. −3 and 3. Although the
approximations fit the sigmoid function well within
the approximation domain [−3,3] for higher degrees,
they do not fit well outside the domain. This figure
also shows that the error grows rapidly outside the do-
main.
Fig 2 illustrates the comparisons among approx-
imating polynomials of degree 13. In the figure, the
gray vertical lines represent the bounds of the approx-
imation domain, i.e., −3 and 3. This result shows
that Taylor expansion is the worst approximation for
the same degree. The Lagrange interpolation and the
Remez algorithm fit fairly well, and the limit approxi-
mation has the best performance. The approximations
via the exponential function in the range of negative
values are quite accurate. We discuss the reasons in
detail in the next section.
5 DISCUSSION
In this section, we discuss the details and reasons for
the observed phenomena in our experiments as shown
in the previous section. There are two points to dis-
cuss: the L
∞
error of approximations via the exponen-
tial function of the odd degree and the difference in
behaviors of approximations via the exponential func-
tion in the ranges of positive and negative values.
5.1 L
∞
Error of Odd Degrees
As Section 4.3 shows, the L
∞
error of approximations
via the exponential function of the odd degree tends
to be overwhelmingly larger. Here, we provide an ex-
ICISSP 2025 - 11th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy
452
Figure 3: Polynomial approximation of odd and even degrees constructed with Remez algorithm.
planation and discuss how to overcome this issue.
Before the discussion, we must ensure that the
aforementioned phenomenon is observed for other
odd degrees and not observed for even degrees. Fig
3 shows the approximations via the exponential func-
tion by Remez algorithm. This figure contains the
results of various degrees, half of which are odd,
3,9,15, and the other half are even, 6,12,18. Fig 3
illustrates that the phenomenon is observed for other
odd degrees.
The reason is the division performed when the ap-
proximated sigmoid functions is constructed from the
approximated exponential functions. Specifically, a
polynomial p(x) of an odd degree diverges to the pos-
itive infinity or negative infinity when x → ∞ and to
the opposite infinity when x → −∞. Thus, there exists
a real number a ∈ R that satisfies p(a) = −1 from the
continuity of the polynomial. This leads to the reason
for the phenomenon for the approximated sigmoid
function
˜
σ(x) constructed from p(x) ≈ exp(x). Since
˜
σ(x) = 1/(1 + p(−x)), it holds lim
x↗−a
˜
σ(x) = ∞ and
lim
x↘−a
˜
σ(x) = −∞. Since the exponential function
rapidly increases in the positive range, the leading
coefficient of approximating polynomial is set to be
positive to fit this trend. Hence, the divergent point
−a is positive, and the approximated sigmoid func-
tions of odd degrees diverge at certain positive val-
ues. Additionally, Fig 3 implies that the divergent
point moves toward the right, i.e., to a larger value,
as the degree increases. This is considered to be
because the accuracy of the approximation increases
even outside the approximation domain as the degree
increases. Note that for even degrees, this diverging
phenomenon does not occur because the approximat-
ing polynomials do not take −1 due to their convexity.
In Fig 3, the gray vertical lines represent the
bounds of the approximation domain, −3 and 3, and
the gray horizontal dotted lines represent asymptotic
values of the sigmoid function, 0 and 1.
5.2 Behavioral Differences in Positive
and Negative Ranges
As mentioned in Section 4.3 and Figs 2a and 3 show,
the approximations via the exponential function fit the
sigmoid function well in the negative range, but not in
the positive range. The reason is that the division of
larger values relatively reduces the influence of the
approximation error. The denominator of the sigmoid
function becomes large in the negative range, e.g.,
1 + exp(−(−3)) ≈ 21 and larger for smaller values.
Thus, even though there is an approximation error, it
will be cancelled out by the relatively large denomi-
nator. However, in the positive range the denominator
is relatively small, 1 + exp(−3) ≈ 1.05 for example.
Therefore, the approximation error has a significant
impact on the approximated sigmoid function. This
is the reason for the difference in the behaviors of
the approximations via the exponential function in the
positive and negative ranges.
The sigmoid functions approximated by both odd-
and even-degree polynomials converge to 0 instead of
1 as x → ∞. Any polynomial tends to either positive
or negative infinity as x → −∞, which implies that
the denominator of the approximated sigmoid func-
tion also goes to negative or positive infinity as x → ∞.
Therefore, the approximated sigmoid function con-
verges to 0. This also applies to the negative range,
i.e., it converges to 0 in both negative and positive
ranges.
6 CONCLUSION
In this paper, we compared four methods in two man-
ners to approximate the sigmoid function, which is
an important component of privacy-preserving neu-
ral networks. We measured two types of errors of
these methods with several degrees of polynomials
Approximations of the Sigmoid Function Beyond the Approximation Domains for Privacy-Preserving Neural Networks
453

and showed the relationship between accuracy and
degrees of polynomials. This research also reveals
the behavior of the approximated function outside the
designated range to approximate, which potentially
impacts on the inference result of privacy-preserving
neural networks. We discuss the reasons for this un-
preferable behavior. This discussion helps prevent un-
expected behaviors of privacy-preserving neural net-
works caused by approximation errors. Overall, our
results provides important knowledge about polyno-
mial approximations of the sigmoid function that are
used for FHE-based privacy-preserving neural net-
works.
REFERENCES
Bos, J. W., Lauter, K., Loftus, J., and Naehrig, M. (2013).
Improved security for a ring-based fully homomor-
phic encryption scheme. In Cryptography and Cod-
ing: 14th IMA International Conference, IMACC
2013, Oxford, UK, December 17-19, 2013. Proceed-
ings 14, pages 45–64. Springer.
Brakerski, Z., Gentry, C., and Vaikuntanathan, V. (2012).
(leveled) fully homomorphic encryption without boot-
strapping. In Proceedings of the 3rd Innovations in
Theoretical Computer Science Conference, ITCS ’12,
page 309–325, New York, NY, USA. Association for
Computing Machinery.
Cheon, J. H., Han, K., Kim, A., Kim, M., and Song, Y.
(2019). A full RNS variant of approximate homomor-
phic encryption. In Selected Areas in Cryptography
– SAC 2018: 25th International Conference, Calgary,
AB, Canada, August 15–17, 2018, Revised Selected
Papers, page 347–368, Berlin, Heidelberg. Springer-
Verlag.
Cheon, J. H., Kim, A., Kim, M., and Song, Y. (2017). Ho-
momorphic encryption for arithmetic of approximate
numbers. In Takagi, T. and Peyrin, T., editors, Ad-
vances in Cryptology – ASIACRYPT 2017, pages 409–
437, Cham. Springer International Publishing.
Cheon, J. H., Kim, D., and Kim, D. (2020). Efficient homo-
morphic comparison methods with optimal complex-
ity. In Moriai, S. and Wang, H., editors, Advances
in Cryptology – ASIACRYPT 2020, pages 221–256,
Cham. Springer International Publishing.
Chillotti, I., Gama, N., Georgieva, M., and Izabach
`
ene, M.
(2020). TFHE: Fast fully homomorphic encryption
over the torus. Journal of Cryptology, 33:34–91.
Dowlin, N., Gilad-Bachrach, R., Laine, K., Lauter, K.,
Naehrig, M., and Wernsing, J. (2016). CryptoNets:
Applying neural networks to encrypted data with high
throughput and accuracy. In Proceedings of the 33rd
International Conference on International Conference
on Machine Learning - Volume 48, ICML’16, page
201–210. JMLR.org.
Lee, E., Lee, J.-W., No, J.-S., and Kim, Y.-S. (2022).
Minimax approximation of sign function by compos-
ite polynomial for homomorphic comparison. IEEE
Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing,
19(6):3711–3727.
Lee, J.-W., Lee, E., Lee, Y., Kim, Y.-S., and No, J.-
S. (2021). High-precision bootstrapping of RNS-
CKKS homomorphic encryption using optimal mini-
max polynomial approximation and inverse sine func-
tion. In Canteaut, A. and Standaert, F.-X., editors,
Advances in Cryptology – EUROCRYPT 2021, pages
618–647, Cham. Springer International Publishing.
Lou, Q. and Jiang, L. (2019). SHE: A fast and accurate
deep neural network for encrypted data. In Wallach,
H., Larochelle, H., Beygelzimer, A., d'Alch
´
e-Buc, F.,
Fox, E., and Garnett, R., editors, Advances in Neural
Information Processing Systems, volume 32. Curran
Associates, Inc.
Meurer, A., Smith, C. P., Paprocki, M.,
ˇ
Cert
´
ık, O., Kir-
pichev, S. B., Rocklin, M., Kumar, A., Ivanov, S.,
Moore, J. K., Singh, S., Rathnayake, T., Vig, S.,
Granger, B. E., Muller, R. P., Bonazzi, F., Gupta, H.,
Vats, S., Johansson, F., Pedregosa, F., Curry, M. J.,
Terrel, A. R., Rou
ˇ
cka, v., Saboo, A., Fernando, I., Ku-
lal, S., Cimrman, R., and Scopatz, A. (2017). SymPy:
symbolic computing in Python. PeerJ Computer Sci-
ence, 3:e103.
Meyre, A., Chevallier-Mames, B., Frery, J., Stoian, A., Bre-
dehoft, R., Montero, L., and Kherfallah, C. (2022).
Concrete ML: a privacy-preserving machine learning
library using fully homomorphic encryption for data
scientists. https://github.com/zama-ai/concrete-ml.
Ng, L. K. L. and Chow, S. S. M. (2023). SoK: Crypto-
graphic neural-network computation. In 2023 IEEE
Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP), pages 497–
514.
Regev, O. (2005). On lattices, learning with errors, random
linear codes, and cryptography. In Proceedings of the
Thirty-Seventh Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of
Computing, STOC ’05, page 84–93, New York, NY,
USA. Association for Computing Machinery.
Remez, E. Y. (1934). Sur la d
´
etermination des polyn
ˆ
omes
d’approximation de degr
´
e donn
´
ee. Comm. Soc. Math.
Kharkov, 10(196):41–63.
Stoian, A., Frery, J., Bredehoft, R., Montero, L., Kherfallah,
C., and Chevallier-Mames, B. (2023). Deep neural
networks for encrypted inference with TFHE. Cryp-
tology ePrint Archive, Paper 2023/257.
Trivedi, D., Boudguiga, A., Kaaniche, N., and Triandopou-
los, N. (2023). Sigml++: Supervised log anomaly
with probabilistic polynomial approximation. Cryp-
tography, 7(4).
ICISSP 2025 - 11th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy
454
