
Impact of Balancing and Regularization on the Semantic Segmentation
of Gleason Patterns
Eduardo Henrique S. Paraíso
1 a
and Alexei M. C. Machado
1,2 b
1
PPGInf - Graduate Program on Informatics, Pontifical Catholic University of Minas Gerais,
Dom José Gaspar 500, Belo Horizonte, Brazil
2
Department of Anatomy and Imaging, Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais,
Alfredo Balena 190, Belo Horizonte, Brazil
Keywords:
Image Segmentation, Deep Learning, Class Balancing, Regularization, Prostate Cancer.
Abstract:
This study investigates the impact of class balancing and regularization on improving the diagnostic agreement
in prostate histological images. The U-Net models applied to the Prostate Cancer Grade Assessment dataset
reveal that class balancing combined with traditional loss functions contributes to an increase of up to 6
percentage points in image agreement. Combining balancing and Focal Loss can increase image classification
agreement by an average of 13 percentage points compared to using an imbalanced dataset with traditional
loss functions. Notably, distinguishing between Gleason patterns 3 and 4 in medical image analysis is crucial,
as this distinction not only directly influences clinical decisions and the prognosis of prostate cancer patients
but also emphasizes the need for careful interpretation of the data.
1 INTRODUCTION
Prostate adenocarcinoma (PA) is the most common
cancer among men worldwide, accounting for 10.2%
of male cancer diagnoses in Brazil, with 72,000 new
cases projected for 2023–2025 (INCA, 2023). Di-
agnosis relies on prostate biopsy and the Gleason
grading system (Gleason and Mellinger, 1974), which
evaluates tumor cell differentiation on a scale of 1 to
5 (Figure 1), with patterns 3 and 4 indicating moder-
ate and high malignancy. However, distinguishing be-
tween these patterns is challenging due to subtle mor-
phological differences, leading to diagnostic discrep-
ancies of 30–53% (Ozkan et al., 2016). These inac-
curacies affect treatment decisions, such as prostate-
ctomy, which can cause severe side effects. Accurate
differentiation is essential to avoid overtreatment and
improve patient outcomes.
Artificial intelligence (AI), especially deep learn-
ing (DL), is increasingly used in medical decision-
making, providing diagnostic results comparable to
specialists (Raciti et al., 2020). Convolutional Neural
Networks (CNNs), including U-Net-based architec-
tures like Residual U-Net (Kalapahar et al., 2020) and
Residual Attention U-Net (Damkliang et al., 2023),
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0004-9236-8300
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8077-3377
Figure 1: Gleason Pattern scale: GP1 - Regular, uniform,
and small cells; GP2 - Uniform cells, loosely grouped, and
irregular borders; GP3 - Very small, uniform cells, angu-
lar or elongated; GP4 - Many cells fused into large amor-
phous masses; GP5 - Large masses with invasion of neigh-
boring organs and tissues, minimal glandular differentia-
tion. Adapted from: University of Pittsburgh Medical Cen-
ter (UPMC) Cancer Centers, Pittsburgh, PA, USA.
are commonly applied for Gleason pattern (GP) seg-
mentation. However, distinguishing between GP 3
and 4 remains challenging due to low agreement in
results, limiting DL’s clinical use. Additionally, class
imbalance in training data introduces bias, reduc-
ing the models’ effectiveness in detecting minority
classes (Dablain et al., 2024).
382
Paraíso, E. H. S. and Machado, A. M. C.
Impact of Balancing and Regularization on the Semantic Segmentation of Gleason Patterns.
DOI: 10.5220/0013105500003911
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 18th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2025) - Volume 2: HEALTHINF, pages 382-389
ISBN: 978-989-758-731-3; ISSN: 2184-4305
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

This article
1
investigates, through an ablative
study (Meyes et al., 2019), the impact of class bal-
ancing in DL models applied to the semantic segmen-
tation of histological images of the prostate and the
effect of regularization for the prevention of overfit-
ting, when applying a loss function designed to handle
class imbalance in classification problems. The study
is specifically directed to the evaluation of the U-Net
models. Ultimately, we aim to increase the accuracy
and agreement metrics of GP 3 and 4 to increase the
patient’s chances of cure and treatment effectiveness.
This structure: Section 2 reviews studies on se-
mantic segmentation in prostate image datasets, high-
lighting the use and importance of balancing in these
datasets. Section 3 explores the fundamental concepts
necessary for a deeper understanding of this work.
Section 4 presents the methodology adopted in this
study. Section 5 explores the results achieved during
the experiments. Finally, Section 6 offers the conclud-
ing remarks and outlines future work.
2 RELATED WORKS
Bulten et al. (2022) conducted a comparative analysis
between CNNs and pathologists using the Quadratic
Weighted Kappa (QWK) metric, showing that CNNs
often outperformed pathologists in accuracy, sensitiv-
ity, and specificity. However, their study did not fo-
cus on CNN performance for Gleason patterns 3 and
4. Similarly, Silva-Rodríguez et al. (2020) achieved a
QWK of 77% when evaluating prostate cancer diag-
nosis on the SICAPv2 dataset, which shares charac-
teristics with the dataset used in this work.
Ikromjanov et al. (2022) achieved F1-scores of
78% and 67% for classifying GP3 and GP4 on the
Prostate Cancer Grade Assessment (PANDA) dataset,
using 256×256 pixel patches without reporting addi-
tional preprocessing techniques. This suggests that
further exploration of preprocessing methods could
lead to improved and more competitive results.
Guerrero et al. (2024) explored data augmentation
techniques to address data imbalance in histopatho-
logical datasets, focusing on classifier-level and data-
level solutions to improve CNN performance. Anal-
ogously, Falahkheirkhah et al. (2023) investigated the
use of deepfake technologies, particularly Generative
Adversarial Networks (GANs), to synthesize realistic
histological images for medical image analysis, clas-
sification tasks, and data augmentation.
1
The repository of the work can be accessed at https:
//www.drive.google.com/drive/folders/1k9AEAkq9X\\4B9
QcjOziEq2Bjw6xwKfNUD
Hancer et al. (2023) focused on addressing the
class imbalance in nucleus segmentation in hema-
toxylin and eosin (H&E) stained histopathological
images using the U-Net architecture. Similarly,
(Haghofer et al., 2023) and Chen (2023) demonstrated
the high performance of U-Net and its variants in
medical image segmentation tasks, including cell and
nucleus segmentation, emphasizing its effectiveness
in histological image analysis.
The study discussed in this work is specifically re-
lated to two previous research efforts: Guerrero et al.
(2024), which uses a Mask Region-Based Convolu-
tional Neural Networks (R-CNN) model enhanced by
a modified copy-paste data augmentation technique to
improve the training process and help class balancing,
and Chen (2023), which employs a U-Net model for
prostate image analysis. This study distinguishes it-
self by using an ablative methodology to analyze the
impact of class balancing and regularization, enhanc-
ing understanding of their roles in semantic tissue seg-
mentation and their effect on classifying Gleason pat-
terns 3 and 4.
3 BACKGROUND
Selecting suitable metrics is vital for accurately as-
sessing a model’s performance in the given context.
The loss functions play a key role in guiding training,
enabling the model to distinguish between patterns ef-
fectively. This ensures precise and clinically mean-
ingful segmentation of Gleason patterns, leading to
improved diagnosis and more appropriate treatments.
3.1 Segmentation Models
The U-Net architecture introduced by Ronneberger
et al. (2015)is a leading semantic segmentation model
known for its efficiency and robust performance. De-
signed for biomedical tasks, it uses a contracting path
to capture spatial context and an expansive path for
precise localization. Its U-shaped structure enables
accurate segmentation even with limited data, making
it widely used in medical and computer vision appli-
cations.
The loss function is pivotal in optimizing semantic
segmentation models, ensuring the network’s output
is appropriately compared to ground truth labels. The
most common loss function combines cross-entropy
(CEL), which evaluates the similarity between the
predicted segmented mask and the ground truth mask,
with regularization terms to prevent overfitting. The
CEL function is defined as:
CEL = −
∑
N
i=1
y
i
log( ˆy
i
), (1)
Impact of Balancing and Regularization on the Semantic Segmentation of Gleason Patterns
383

where N is the total number of classes, y
i
represents a
vector with the true class, and ˆy
i
represents the prob-
ability of the predicted class. This encourages precise
learning of the discriminative characteristics of each
class (R ˛aczkowska et al., 2019).
Focal loss (FL), proposed by Lin et al. (2018),
was explored as an alternative to cross entropy (CEL)
to handle class imbalance in classification problems.
It adds a modulating term, (1 − ˆy
i
)
γ
, to CEL, where
γ > 0 reduces the loss for well-classified examples.
An optional balancing factor, α
i
, can also be used to
address class imbalances:
FL = −α
i
(1− ˆy
i
)
γ
log ˆy
i
. (2)
This approach is beneficial in datasets with minority
classes, improving network performance as demon-
strated by Nguyen et al. (2024).
3.2 Metrics
The performance of the models were assessed based
on a set of well-known metrics:
1. Sensitivity (recall) shows the proportion of true
positives relative to total positive cases, including
false negatives (FN) (Powers, 2015).
2. Specificity is the proportion of genuinely nega-
tive observations in the dataset (Monaghan et al.,
2021). This indicates the model’s ability to avoid
false positives.
3. The F1-Score is a key metric for evaluating classi-
fication models, particularly in cases of class im-
balance. It is the harmonic mean of precision and
recall. It is useful when a balance between the two
is needed, especially when one type of error (false
positives or false negatives) has a greater impact
(Hicks et al., 2022).
4. Quadratic Weighted Kappa (QWK) is a statisti-
cal measure that assesses agreement among raters
when discrepancies between their classifications
have different weights, considering the distance
between categories. The difference between
classes is weighted using a quadratic factor. The
weight for the cell in row i and column j of the
matrix is given by
W (i, j) = (i − j)
2
/(N − 1)
2
, (3)
where N is the total number of categories.
The QWK is calculated by comparing the
weighted confusion matrix with the weighted ex-
pectation matrix:
QWK = 1 −
∑
W (i, j)O(i, j)
∑
W (i, j)E(i, j)
, (4)
where O
i j
is the observed frequency of agreement
among raters in the category and E
i j
is the ex-
pected frequency of agreement in the category.
The quadratic weighting assigns larger weights to
more distant discrepancies on the ordinal scale.
By applying these weights, QWK gives more
importance to severe disagreements, resulting in
smaller values than simple Kappa, thus, QWK is
useful for assessing the reproducibility of diag-
nostic methods with ordinal variables (Silva et al.,
2016). However, QWK evaluates overall agree-
ment across classifications. It provides an aggre-
gate view, reflecting the general level of agree-
ment across all classes.
4 MATERIALS AND METHODS
The PANDA dataset
2
was developed jointly by the
computational pathology group at Radboud Univer-
sity Medical Center (RUMC) and the Department
of Medical Epidemiology and Biostatistics at the
Karolinska Institute (DEMBIK) (Bulten et al., 2022).
The dataset comes from needle core biopsies per-
formed between 2012 and 2017. Due to the subjec-
tive nature of GPs, classification divergences arise, as
noted by Corte (2023), who highlights that the im-
age labels contain significant noise from inconclu-
sive records, annotation errors, diagnostic inaccura-
cies, and pathologist discrepancies.
The dataset comprises 10,616 high-resolution im-
ages stained with H&E pigments and stored in TIFF
(Tagged Image File Format) format. These images
were obtained through optical microscopy and digi-
tized to create high-resolution digital versions with an
objective lens magnification of 20x. An essential fea-
ture of WSIs is their ability to provide multiple mag-
nification levels (see Figure 2a), where the original
image is subdivided into various resolutions.
The specimens provided by DEMBIK were la-
beled by regions (see Figure 2b) into background, be-
nign tissue, and cancerous tissue. In contrast, RUMK
performed a more detailed classification (see Figure
2b) by individually labeling the cytoarchitecture into
background, stroma, GP2, GP3, GP4, and GP5.
In order to investigate the impact of balancing and
regularization through the ablative approach, the U-
Net models were trained using combinations of im-
balanced and balanced image datasets, along with var-
ious pixel normalization and loss functions, resulting
in a total of 24 trained models. All models were
2
https://www.kaggle.com/competitions/prostate-cance
r-grade-assessment
HEALTHINF 2025 - 18th International Conference on Health Informatics
384
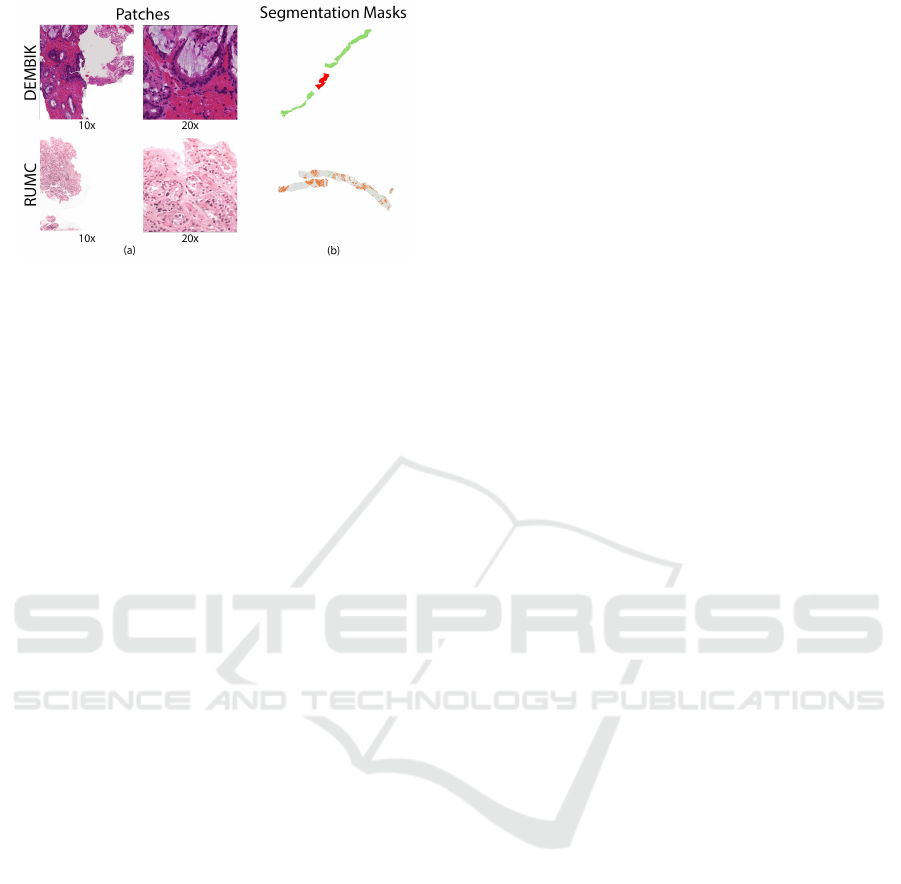
Figure 2: (a) Multiple levels of magnification provided by
the pyramidal structure of a WSI. (b) Full segmentation
mask of a WSI.
trained using 10-fold cross-validation (using a T4
GPU and 28GB of RAM), and a 95% confidence in-
terval was calculated. The ablative approach is help-
ful for better understanding how different components
of the training process affect the model’s final perfor-
mance. In this case, ablating data balancing allows for
evaluating how the imbalance between data classes
influences segmentation metrics, especially between
GP3 and GP4.
4.1 Image Selection and Preprocessing
A total of 5,160 images from the PANDA dataset orig-
inating from RUMC were selected due to their in-
dividualized glandular annotations (Figure 3a). For
training, 330 WSIs were selected, and 80 WSIs for
testing through stratified random sampling (Figure
3b). Stratification was based on the Gleason Score,
a histological classification system consisting of two
numerical scores ranging from 3 to 5, representing the
two predominant tumor patterns in the tissue. Adopt-
ing the ablative approach involves a wide range of
combinations; thus, time constraints and hardware
limitations justified the design of this investigation.
4.2 Patch Generation
The use of patches is crucial for training models
on histological images, as it allows for diversifica-
tion and captures localized details, improving the
model’s ability to recognize intricate features and nu-
ances (Dablain et al., 2024).
During patch generation, the alpha channel was
excluded because transparency is irrelevant for seg-
mentation tasks Alsayat et al. (2023), while the blue
and green channels, from masks, were omitted as
pixel classification data is stored only in the red chan-
nel. Patches were created (Figure. 3c) with dimen-
sions of 224×224×3 for images and 224×224×1 for
masks. This size balances computational efficiency
with deep learning capabilities for high-dimensional
data (Ciga et al., 2021) and ensures compatibility with
widely used architectures, such as those trained on
ImageNet (Russakovsky and et al., 2015).
A sliding window approach was implemented
with a 10% overlap of the patch size, allowing for the
generation of patches with overlapping boundaries.
Among the generated patches, selecting images with
the highest representativeness was based on minimiz-
ing the pixels labeled as background. Patches with
a background proportion exceeding 10% of the to-
tal image area were excluded from the dataset, en-
suring a greater concentration of relevant pixels for
histopathological analysis.
After completing the described processing, 9,442
patches were obtained for the training set and 2,174
patches for the test set (Figure 3c).
Due to the images’ nature, the proportion of each
label was calculated, with the difference between the
majority class (stroma) and the minority class (GP3)
being 68%. Balancing was performed in four steps:
1. Images containing GP3 or GP4 were selected.
2. Patches with a composition of pixels classified as
stroma greater than 80% were removed.
3. Patches composed of more than 50% GP3 or GP4
were selected for artificial augmentation.
4. Transformations were applied to 512 GP3 and
937 GP4 patches, generating four new images per
original GP3 patch and one new image per origi-
nal GP4 patch.
The following transformations were used for the
data augmentation:
a. Random contrast and brightness;
b. Rotation, limited to 35º;
c. Horizontal and/or Vertical flipping;
After the balancing step of the training set (see
Figure 5d), a final set of 6,700 patches was obtained,
with a class imbalance difference between the major-
ity and minority class of less than 30% (Figure 4).
4.3 Normalization
Both balanced and imbalanced image sets were an-
alyzed without any initial normalization. Then, two
different normalization techniques were applied: nor-
malization by maximum pixel value and normaliza-
tion by mean and standard deviation of the training
set. Each of these created sets was used to train 24
distinct models, employing different loss functions as
depicted in Figure 5.
Impact of Balancing and Regularization on the Semantic Segmentation of Gleason Patterns
385
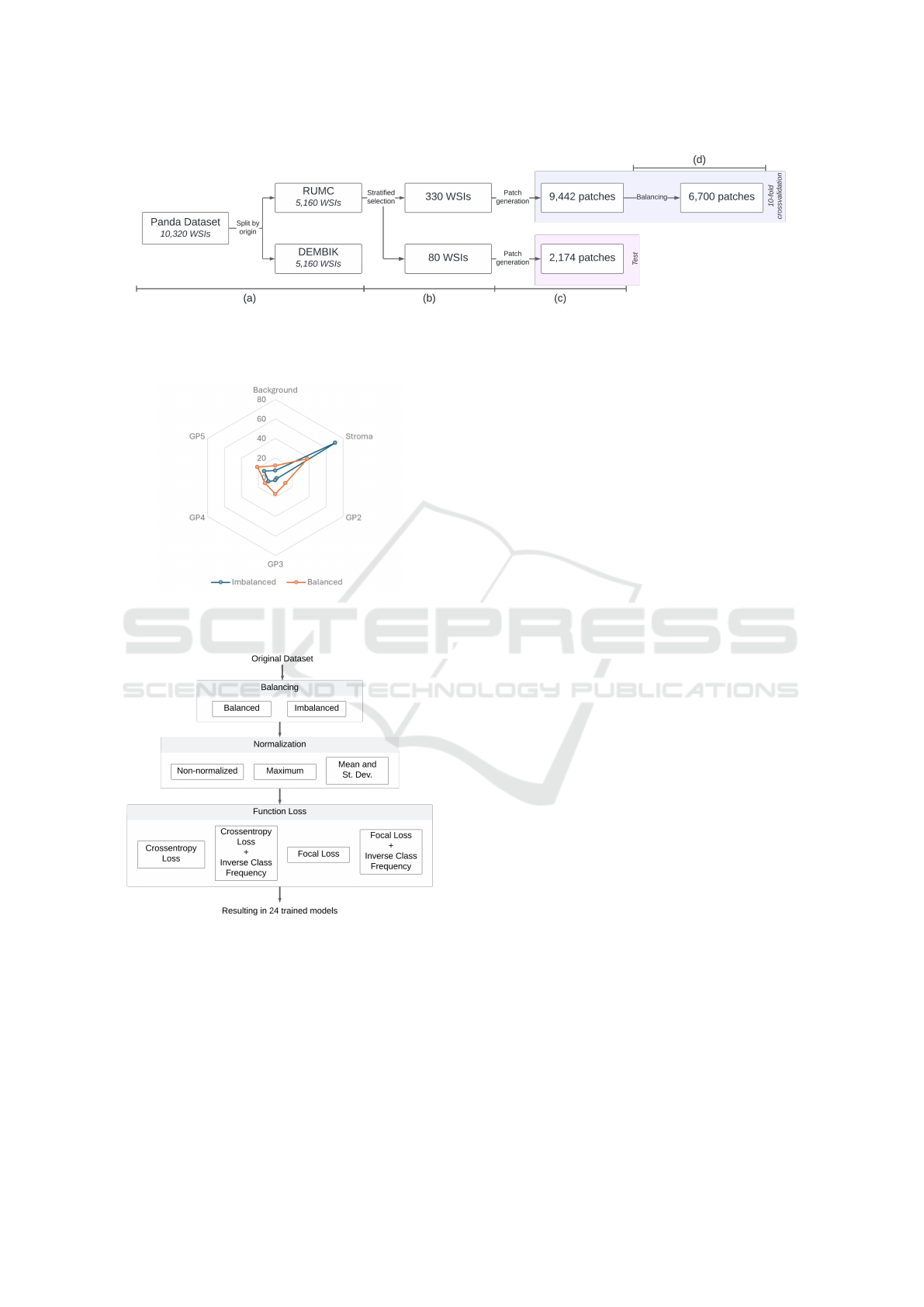
Figure 3: (a) Separation of the image set according to its source. (b) The training and testing sets are created through stratified
random selection from the RUMC dataset. (c) Selected set of patches with at least 90% relevant area for classification. (d)
The final set of patches resulted from class balancing.
Figure 4: Distribution of classes in the original dataset
(blue) and balanced dataset (orange).
Figure 5: The ablative scheme proposed in this study com-
prises 24 distinct models, each resulting from the combina-
tion of three different steps: balancing or not balancing the
dataset, using a specific type of pixel normalization, and ap-
plying a loss function during training.
4.4 Loss Function
In addition to Cross Entropy Loss, this study uti-
lized Focal Loss, designed to handle scenarios with
extreme class imbalances. Additionally, CEL and
FL variations were employed, incorporating weights
based on inverse class frequency. This adjust-
ment mitigates potential biases and facilitates equi-
table model learning, promoting better generalization
and performance, particularly for underrepresented
classes. All models were based on a standard U-Net
architecture, following the implementation by Ron-
neberger et al. (2015).
5 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The FL demonstrates superior stability in cross-
validation results compared to CE and a more con-
sistent and steady reduction in loss values. This high-
lights the regularization capability of FL in mitigat-
ing the disparity between the model’s predictions and
the true data labels throughout the training process,
as illustrated in Figure 6a and 6b, which compare the
performance of these functions on an imbalanced and
non-normalized dataset.
The simultaneous application of FL with the bal-
ancing of the image set (Figure 6c) leads to a reduc-
tion in the distance between the training and valida-
tion loss curves. In DL models, this approximation
indicates a generalization capability, implying better
adaptation of the model to training data and, in turn,
a greater ability to predict new datasets accurately.
Such models are less prone to overfitting, ensuring
greater reliability and robustness in real world.
The Table 1 demonstrates the ability of Focal Loss
to mitigate the impact of majority classes in the clas-
sification of GPs 3 and 4 within a highly imbalanced
dataset, resulting in better model performance in bal-
ancing sensitivity and specificity. This indicates the
regularization potential of FL through class balanc-
ing, supported by the increased stability observed in
Figure 6b. Focal Loss stands out in F1-score met-
rics, showing a slight advantage compared to other
loss functions. However, it is not possible to deter-
mine which normalization is superior, as the results
HEALTHINF 2025 - 18th International Conference on Health Informatics
386
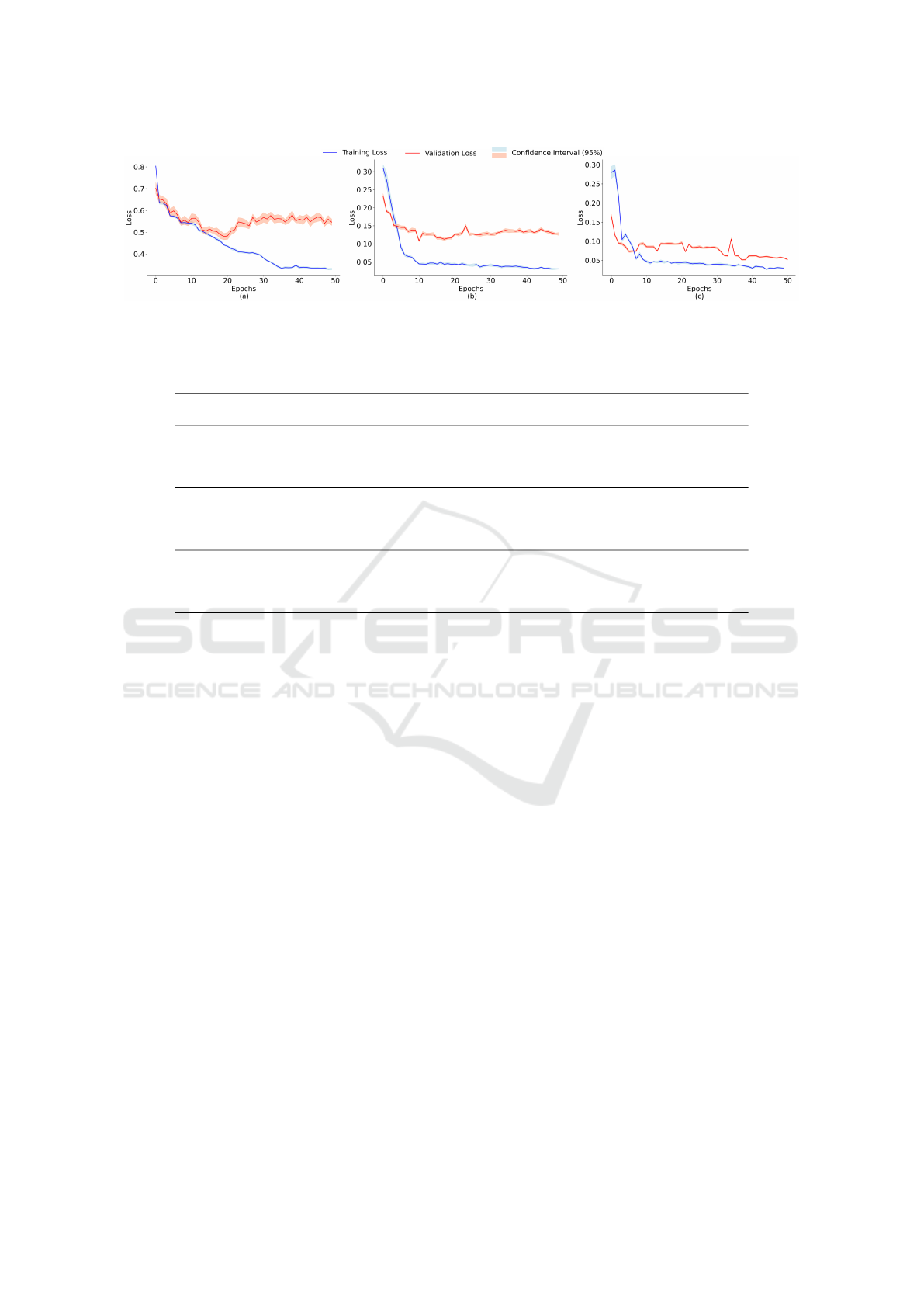
Figure 6: Loss functions resulting from 10-fold cross-validation for an imbalanced dataset using Cross-Entropy Loss (a), for
an imbalanced dataset using Focal Loss (b), and for a balanced dataset using Focal Loss (c) simultaneously.
Table 1: Results of 10-fold cross-validation and their respective 95% confidence intervals for training on an imbalanced
dataset.
Normalization Loss
Gleason Pattern 3 Gleason Pattern 4
Sensitivity Specificity F1-Score Sensitivity Specificity F1-Score
Non-normalized
CEL 0.66 ± 0.02 0.97 ± 0.03 0.61 ± 0.02 0.37 ± 0.02 0.95 ± 0.01 0.46 ± 0.03
CEL+ICF 0.58 ± 0.06 0.82 ± 0.08 0.57 ± 0.04 0.30 ± 0.07 0.88 ± 0.02 0.35 ± 0.07
FL 0.72 ± 0.02 0.95 ± 0.01 0.66 ± 0.03 0.40 ± 0.01 0.97 ± 0.01 0.52 ± 0.02
FL+ICF 0.64 ± 0.04 0.90 ± 0.04 0.59 ± 0.03 0.34 ± 0.03 0.93 ± 0.03 0.40 ± 0.04
Maximum
CEL 0.73 ± 0.01 0.95 ± 0.02 0.63 ± 0.02 0.39 ± 0.02 0.96 ± 0.03 0.46 ± 0.01
CEL+ICF 0.57 ± 0.04 0.94 ± 0.03 0.52 ± 0.05 0.37 ± 0.02 0.91 ± 0.08 0.39 ± 0.02
FL 0.76 ± 0.03 0.96 ± 0.01 0.68 ± 0.01 0.41 ± 0.03 0.95 ± 0.02 0.50 ± 0.01
FL+ICF 0.65 ± 0.04 0.90 ± 0.02 0.58 ± 0.03 0.37 ± 0.03 0.88 ± 0.03 0.42 ± 0.03
Mean/St. Dev.
CEL 0.69 ± 0.02 0.95 ± 0.03 0.64 ± 0.02 0.34 ± 0.03 0.97 ± 0.02 0.47 ± 0.02
CEL+ICF 0.59 ± 0.04 0.90 ± 0.05 0.57 ± 0.02 0.40 ± 0.05 0.88 ± 0.09 0.40 ± 0.03
FL 0.78 ± 0.02 0.95 ± 0.03 0.69 ± 0.01 0.43 - 0.01 0.98 ± 0.02 0.53 ± 0.01
FL+ICF 0.63 ± 0.03 0.87 ± 0.02 0.59 ± 0.01 0.35 ± 0.03 0.91 ± 0.01 0.41 ± 0.02
of this metric overlap within the confidence intervals.
The results highlighted in Table 2 highlight the
importance of dataset balancing, emphasizing the cru-
cial role of balance and regularization. The analysis
of the F1-score reveals a more significant improve-
ment compared to models trained on an imbalanced
dataset, with approximately an increase of eight per-
centage points for GP3 and around 14 percentage
points for GP4, averaged across the three normaliza-
tions when trained using Focal Loss. However, de-
termining the best normalization is again not directly
possible, as the obtained values overlap when consid-
ering the confidence intervals.
Analyzing the global image classification results
through the QWK metric, it is observed that, on av-
erage, models trained on balanced image sets using
CEL achieved levels of agreement similar to those
obtained by models trained on imbalanced sets using
FL. Regardless of the normalization applied, FL could
return an average gain of 7 percentage points over
CEL for imbalanced datasets. When comparing this
metric for balanced datasets, FL showed an average
gain of 6 percentage points. Therefore, when compar-
ing the agreement between an imbalanced set trained
with CEL and a balanced set trained with FL, an ap-
proximate average gain of 13 percentage points is ob-
served. These results align with those obtained by
Silva-Rodríguez et al. (2020), despite being derived
from different image sets, both datasets share similar-
ities regarding objective lens magnification and his-
tochemical staining. Additionally, it is important to
note that in the competition organized on the Kaggle
platform, winning works achieved concordance val-
ues of approximately 90%. However, label denoising
techniques were employed to eliminate images with
discrepancies between the results obtained by CNNs
and segmentation masks. While effective in remov-
ing erroneously labeled images that hinder training,
this technique is also responsible for discarding im-
ages that are challenging to classify. Given the subjec-
tive nature and difficulty distinguishing between GP
3 and 4, such information may have been eliminated,
contributing to the high concordance values obtained.
Therefore, the results obtained in this study remain
competitive and highlight the importance of balanc-
ing and regularization in future research endeavors.
However, the application of a specific pixel nor-
malization technique did not significantly improve
agreement (see Table 3), highlighting that normaliza-
tion’s impact varies by context. This underscores the
complexity of optimizing segmentation models, re-
quiring careful consideration of factors like data bal-
ancing and preprocessing techniques. While weight-
ing strategies can aid balancing, weights defined by
Impact of Balancing and Regularization on the Semantic Segmentation of Gleason Patterns
387

Table 2: Results of 10-fold cross-validation and their respective 95% confidence intervals for training on an balanced dataset.
Normalization Loss
Gleason Pattern 3 Gleason Pattern 4
Sensitivity Specificity F1-Score Sensitivity Specificity F1-Score
Non-normalized
CEL 0.77 ± 0.04 0.94 ± 0.02 0.71 ± 0.04 0.81 ± 0.02 0.95 ± 0.02 0.61 ± 0.04
CEL+ICF 0.65 ± 0.06 0.84 ± 0.3 0.60 ± 0.03 0.60 ± 0.05 0.80 ± 0.04 0.48 ± 0.09
FL 0.80 ± 0.01 0.94 ± 0.04 0.73 ± 0.02 0.80 ± 0.03 0.95 ± 0.04 0.66 ± 0.02
FL+ICF 0.72 ± 0.03 0.96 ± 0.02 0.66 ± 0.03 0.80 ± 0.02 0.90 ± 0.03 0.51 ± 0.06
Maximum
CEL 0.76 ± 0.01 0.95 ± 0.03 0.66 ± 0.03 0.82 ± 0.02 0.92 ± 0.01 0.60 ± 0.01
CEL+ICF 0.69 ± 0.03 0.85 ± 0.02 0.61 ± 0.05 0.60 ± 0.07 0.85 ± 0.02 0.58 ± 0.04
FL 0.78 ± 0.03 0.96 ± 0.02 0.75 ± 0.03 0.82 ± 0.03 0.96 ± 0.02 0.66 ± 0.03
FL+ICF 0.73 ± 0.02 0.93 ± 0.04 0.66 ± 0.04 0.73 ± 0.03 0.97 ± 0.01 0.60 ± 0.03
Mean/St. Dev.
CEL 0.78 ± 0.02 0.91 ± 0.02 0.73 ± 0.02 0.81 ± 0.04 0.95 ± 0.02 0.59 ± 0.02
CEL+ICF 0.70 ± 0.03 0.86 ± 0.01 0.59 ± 0.04 0.61 ± 0.02 0.84 ± 0.04 0.54 ± 0.05
FL 0.85 ± 0.02 0.97 ± 0.02 0.77 ± 0.01 0.81 ± 0.01 0.97 ± 0.01 0.65 ± 0.02
FL+ICF 0.75 ± 0.04 0.92 ± 0.03 0.66 ± 0.02 0.77 ± 0.01 0.96 ± 0.01 0.59 ± 0.04
Table 3: Results of 10-fold cross-validation and their respective 95% confidence intervals for QWK metric for all models.
CEL CEL+ICF FL FL+ICF
Imbalanced
Non-normalized 0.57 ± 0.05 0.20 ± 0.14 0.65 ± 0.03 0.34 ± 0.04
Maximum 0.61 ± 0.03 0.23 ± 0.06 0.67 ± 0.02 0.40 ± 0.02
Mean/St. Dev 0.55 ± 0.02 0.21 ± 0.03 0.64 ± 0.02 0.51 ± 0.03
Balanced
Non-normalized 0.66 ± 0.02 0.25 ± 0.09 0.64 ± 0.06 0.60 ± 0.05
Maximum 0.65 ± 0.01 0.27 ± 0.07 0.70 ± 0.02 0.66 ± 0.02
Mean/St. Dev 0.62 ± 0.03 0.28 ± 0.02 0.73 ± 0.01 0.64 ± 0.02
ICF proved challenging for model convergence.
The use of inverse class frequency, combined
with the adopted loss functions, failed to improve
model performance and worsened the classification
of GP3 and GP4, reducing agreement compared to
other methods. This may be due to overemphasis on
underrepresented classes, exacerbating class imbal-
ance and impairing generalization, especially when
the loss functions cannot handle such weighting ef-
fectively.
6 CONCLUSION
This study demonstrates that image balancing is cru-
cial for accurately diagnosing histological PA im-
ages and is an effective regularization strategy dur-
ing model training. It also emphasizes caution when
using moderating weights in loss functions, as im-
proper application can destabilize models or slow
convergence without improving accuracy. The study
achieved competitive results with minimal prepro-
cessing, highlighting the importance of balancing and
regularization techniques.
Efforts should focus on reducing dataset noise,
particularly in annotations, as it compromises pre-
diction quality. Addressing histological anomalies or
distortions from tissue preparation is also essential to
prevent analysis distortions. Implementing ensemble
techniques could improve the classification of Glea-
son patterns 3 and 4, addressing a key challenge in the
field. Additionally, exploring new architectures and
evaluating their specific behaviors is crucial, given the
limited research on this topic. These strategies could
significantly enhance the understanding and analysis
of prostate adenocarcinoma.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors thank the Pontifícia Universidade
Católica de Minas Gerais – PUC-Minas and
Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal
de Nível Superior - CAPES - (Grant PROAP
88887.842889/2023-00 - PUC/MG, Grant PDPG
88887.708960/2022-00 - PUC/MG - INFOR-
MÁTICA and Finance Code 001). Conselho Nacional
de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico do
Brasil (CNPq – Código:311573/2022-3). Scholarship
FAPEMIG/CNPq - Brazil (Grant BPQ-06556-24).
Grant FAPEMIG - Brazil APQ-02753-24.
REFERENCES
Alsayat, A., Elmezain, M., Alanazi, S., Alruily, M.,
Mostafa, A. M., and Said, W. (2023). Multi-Layer
Preprocessing and U-Net with Residual Attention
Block for Retinal Blood Vessel Segmentation. Diag-
nostics, 13(21):3364.
Bulten, W., Kartasalo, K., Chen, P. C., Ström, P., Pinckaers,
HEALTHINF 2025 - 18th International Conference on Health Informatics
388

H., and Nagpal, K. (2022). Artificial intelligence for
diagnosis and Gleason grading of prostate cancer: the
PANDA challenge. Nat Med, 28(1):154–163.
Chen, Z. (2023). Medical Image Segmentation Based on
U-Net. J. Phys.: Conf. Ser., 2547(1):012010.
Ciga, O., Xu, T., Nofech-Mozes, S., Noy, S., Lu, F.-I., and
Martel, A. L. (2021). Overcoming the limitations of
patch-based learning to detect cancer in whole slide
images. Sci Rep, 11(1):8894.
Corte, D. D. (2023). Towards a Clinically Useful AI
Tool for Prostate Cancer Detection: Recommenda-
tions from a PANDA Dataset Analysis. JCRMHS,
5(3).
Dablain, D., Krawczyk, B., and Chawla, N. (2024). To-
wards a holistic view of bias in machine learning:
bridging algorithmic fairness and imbalanced learn-
ing. Discov Data, 2(1):4.
Damkliang, K., Thongsuksai, P., Kayasut, K., Wongsiri-
chot, T., Jitsuwan, C., and Boonpipat, T. (2023). Bi-
nary semantic segmentation for detection of prostate
adenocarcinoma using an ensemble with attention and
residual U-Net architectures. PeerJ Computer Sci-
ence, page e1767.
Falahkheirkhah, K., Tiwari, S., Yeh, K., Gupta, S., Herrera-
Hernandez, L., McCarthy, M. R., Jimenez, R. E.,
Cheville, J. C., and Bhargava, R. (2023). Deepfake
Histologic Images for Enhancing Digital Pathology.
Laboratory Investigation, 103(1):100006.
Gleason, D. F. and Mellinger, G. T. (1974). Predic-
tion of Prognosis for Prostatic Adenocarcinoma by
Combined Histological Grading and Clinical Staging.
Journal of Urology, 111(1):58–64.
Guerrero, E. D., Lina, R., Lina, R., Bocklitz, T., Popp,
J., and Oliveira, J. L. (2024). A Data Augmenta-
tion Methodology to Reduce the Class Imbalance in
Histopathology Images. J Digit Imaging. Inform. med.
Haghofer, A., Fuchs-Baumgartinger, A., Lipnik, K.,
Klopfleisch, R., Aubreville, M., Scharinger, J., Weis-
senböck, H., Winkler, S. M., and Bertram, C. A.
(2023). Histological classification of canine and fe-
line lymphoma using a modular approach based on
deep learning and advanced image processing. Sci
Rep, 13:19436.
Hancer, E., Traoré, M., Samet, R., Yıldırım, Z., and Ne-
mati, N. (2023). An imbalance-aware nuclei segmen-
tation methodology for H&E stained histopathology
images. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control,
83:104720.
Hicks, S. A., Strümke, I., Thambawita, V., Hammou, M.,
Riegler, M. A., Halvorsen, P., and Parasa, S. (2022).
On evaluation metrics for medical applications of ar-
tificial intelligence. Scientific Reports, 12(1):5979.
Ikromjanov, K., Bhattacharjee, S., Hwang, Y.-B., Sumon,
R. I., Kim, H.-C., and Choi, H.-K. (2022). Whole
Slide Image Analysis and Detection of Prostate Can-
cer using Vision Transformers. In 2022 ICAIIC, pages
399–402, Jeju Island, Korea, Republic of.
INCA, I. N. D. C. (2023). Estimativa 2023: incidência de
câncer no Brasil. Instituto Nacional De Câncer, Rio
de Janeiro, RJ.
Kalapahar, A., Silva-Rodríguez, and et al. (2020). Gleason
Grading of Histology Prostate Images through Seman-
tic Segmentation via Residual U-Net.
Lin, T.-Y., Goyal, P., Girshick, R., He, K., and Dollár, P.
(2018). Focal Loss for Dense Object Detection.
Meyes, R., Lu, M., de Puiseau, C. W., and Meisen, T.
(2019). Ablation Studies in Artificial Neural Net-
works.
Monaghan, T. F., Rahman, S. N., Agudelo, C. W., Wein,
A. J., Lazar, J. M., Everaert, K., and Dmochowski,
R. R. (2021). Foundational Statistical Principles
in Medical Research: Sensitivity, Specificity, Posi-
tive Predictive Value, and Negative Predictive Value.
Medicina, 57(5):503.
Nguyen, T. T. U., Nguyen, A.-T., Kim, H., Jung, Y. J.,
Park, W., and Kim, Kyoung Min, e. a. (2024). Deep-
learning model for evaluating histopathology of acute
renal tubular injury. Sci Rep, 14(1):9010.
Ozkan, T. A., Eruyar, A., Cebeci, O., Memik, O., Ozcan,
L., and Kuskonmaz, I. (2016). Interobserver variabil-
ity in Gleason histological grading of prostate cancer.
Scandinavian Journal of Urology, 50(6):420–424.
Powers, D. M. W. (2015). Evaluation Evaluation a Monte
Carlo study.
Raciti, P., Sue, J., Ceballos, R., Godrich, R., Kunz, J. D.,
Kapur, S., Reuter, V., Grady, L., Kanan, C., Klim-
stra, D. S., and Fuchs, T. J. (2020). Novel artificial
intelligence system increases the detection of prostate
cancer in whole slide images of core needle biopsies.
Modern Pathology, 33(10):2058–2066.
Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., and Brox, T. (2015). U-Net:
Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Seg-
mentation. In MICCAI 2015, volume 9351, pages
234–241.
Russakovsky, O. and et al. (2015). ImageNet Large Scale
Visual Recognition Challenge. Int J Comput Vis,
115(3):211–252.
R ˛aczkowska, A., Mo
˙
zejko, M., Zambonelli, J., and
Szczurek, E. (2019). ARA: accurate, reliable and ac-
tive histopathological image classification framework
with Bayesian deep learning. Sci Rep, 9(1):14347.
Silva, A. F. D., Velo, M. M. D. A. C., and Pereira, A. C.
(2016). Importância da reprodutibilidade dos méto-
dos para diagnóstico em odontologia. Rev. da Fac. de
Odontologia, UPF, 21(1).
Silva-Rodríguez, J., Colomer, A., Sales, M. A., Molina, R.,
and Naranjo, V. (2020). Going deeper through the
Gleason scoring scale: An automatic end-to-end sys-
tem for histology prostate grading and cribriform pat-
tern detection. Computer Methods and Programs in
Biomedicine, 195:105637.
Impact of Balancing and Regularization on the Semantic Segmentation of Gleason Patterns
389
