
Effect of Phase Mismatch on the Dynamics of Bragg Solitons in a
Semilinear Coupled Bragg Grating System with Cubic-Quintic
Nonlinearity
Etu Podder and Javid Atai
School of Electrical and Computer Engineering, The University of Sydney, NSW 2006, Australia
Keywords:
Gap Soliton, Fiber Bragg Grating, Cubic-Quintic Nonlinearity, Phase Mismatch.
Abstract:
We investigate the dynamics of quiescent Bragg solitons in a dual-core fiber Bragg grating system with a
phase shift between the gratings where one core has cubic-quintic nonlinearity, and the other is a linear core.
Since cubic-quintic nonlinearity is present in one core, our system demonstrates the existence of two distinct
and disjoint families of quiescent Bragg solitons within the specified bandgap, classified as Type 1 and Type 2
solitons. Both types of quiescent solitons have been analyzed numerically to assess their stability. The stability
analysis reveals that the presence of the phase mismatch between Bragg gratings enhances the overall stability
for Type 1 solitons and leads to the formation of stable Type 2 solitons.
1 INTRODUCTION
Fiber Bragg gratings (FBGs) are optical devices
where the refractive index of the core varies periodi-
cally (or aperiodically) along the optical fiber (Sankey
et al., 1992; Kashyap, 2009). FBGs have been the
subject of intense research over the past few decades
due to their applications in optical filtering, sensing,
and optical signal processing (Krug et al., 1995; Loh
et al., 1996; Litchinitser et al., 1997). FBGs can be
utilized for switching as well as pulse compression
when they are operated in the nonlinear regime (Win-
ful et al., 1979; Radic et al., 1995; Sankey et al.,
1992). A fascinating characteristic of FBGs is the ex-
istence of a bandgap which prevents the propagation
of any linear waves (Kashyap, 2009). Another inter-
esting feature of FBGs is that they exhibit a strong dis-
persion which is the result of cross-coupling between
forward and backward- propagating waves (Russell,
1991; De Sterke and Sipe, 1994). When the intensity
is high enough, the grating-induced dispersion can be
counterbalanced by the nonlinearity resulting in the
generation of Bragg grating (BG) solitons (De Sterke
and Sipe, 1994).
In recent decades, Bragg solitons have been
the subject of significant research both theoretically
(Sipe and Winful, 1988; Christodoulides and Joseph,
1989; Aceves and Wabnitz, 1989) and experimentally
(Eggleton et al., 1996; De Sterke et al., 1997; Tav-
erner et al., 1998). In particular, the dynamics and
stability of BG solitons have been investigated in dif-
ferent types of nonlinearities such as Kerr nonlinear-
ity (Aceves and Wabnitz, 1989; Eggleton et al., 1996),
quadratic nonlinearity (Conti et al., 1997; Mak et al.,
1998b), and cubic-quintic nonlinearity (Atai and Mal-
omed, 2001; Islam and Atai, 2014; Islam and Atai,
2018; Atai, 2004; Dasanayaka and Atai, 2010). The
study of gap solitons in cubic-quintic nonlinear me-
dia has become compelling due to their added com-
plexity and control, along with the enriched diversity
of soliton dynamics. Moreover, Bragg solitons dy-
namics have been explored in various optical struc-
tures including waveguide arrays (Mandelik et al.,
2004), grating-assisted single core (Atai and Mal-
omed, 2001) and dual core system (Mak et al., 1998a;
Atai and Malomed, 2000; Mak et al., 2004).
It has been shown that a broad spectrum of soli-
tons can be supported by semilinear coupled sys-
tems, which also have excellent switching features
(Atai and Malomed, 2000; Shnaiderman et al., 2011;
Chowdhury and Atai, 2016; Chowdhury and Atai,
2017). Furthermore, introducing a phase shift be-
tween the gratings has drawn significant attention for
designing optical sensor and multiplexer (Srivastava
et al., 2018). It has been shown that in coupled
Bragg gratings with a phase shift where both cores
have Kerr nonlinearity, asymmetric and quasisym-
metric solitons can exist (Tsofe and Malomed, 2007).
Podder, E. and Atai, J.
Effect of Phase Mismatch on the Dynamics of Bragg Solitons in a Semilinear Coupled Bragg Grating System with Cubic-Quintic Nonlinearity.
DOI: 10.5220/0013106700003902
In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Photonics, Optics and Laser Technology (PHOTOPTICS 2025), pages 59-63
ISBN: 978-989-758-736-8; ISSN: 2184-4364
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
59
In this work, we investigate the existence and stability
of quiescent BG solitons in a system of coupled FBGs
where one core has cubic-quintic nonlinearity and the
other core is linear and there is a phase mismatch be-
tween the gratings.
2 THE MODEL
The model describing the propagation of light in a
semilinear coupled Bragg gratings with a phase mis-
match where cubic-quintic nonlinearity is present in
one core and the other core is linear can be written as:
iu
t
+ iu
x
+
|v|
2
+
1
2
|u|
2
u − η
1
4
|u|
4
+
3
2
|u|
2
|v|
2
+
3
4
|v|
4
u + v + κφ = 0,
iv
t
− iv
x
+
|u|
2
+
1
2
|v|
2
v − η
1
4
|v|
4
+
3
2
|v|
2
|u|
2
+
3
4
|u|
4
v + u + κψ = 0,
iφ
t
+ icφ
x
+ ψe
i
θ
2
+ κu = 0,
iψ
t
− icψ
x
+ φe
−i
θ
2
+ κv = 0,
(1)
where u and v stand for the forward and backward-
propagating waves in the nonlinear core and φ and ψ
are their counterparts in the linear core respectively.
κ > 0 is the linear coupling coefficient between two
cores and c ≤ 1 denotes the relative group velocity
in linear core and the group velocity in the nonlinear
core has been set to one. η > 0 governs the strength
of quintic nonlinearity and 0 ≤ θ ≤ 2π represents the
phase mismatch between the gratings. From the ex-
perimental measurements in Ref. (Boudebs et al.,
2003; Chen et al., 2006; Zhan et al., 2002), it is found
that η can vary between the values of 0.05 and 0.62.
Therefore, our investigation is limited to the range
0 ≤ η ≤ 1.
To define the spectral bandgap within which soli-
ton solutions may exist, it is crucial to analyze the
linear spectrum of the model. Eqs. 1 give rise to the
following dispersion relation:
ω
4
= 2κ
2
2cos
2
θ
4
− 1
− c
2
k
2
+ 1
k
2
+ω
2
c
2
+ 1
k
2
+ 2κ
2
+ 2
− κ
4
+k
2
2cκ
2
− 1
− 1,
(2)
where k represents the wave-number. Analysis of
Eq. 2 demonstrates that the linear spectrum contains
three bandgaps namely, the upper, the central, and the
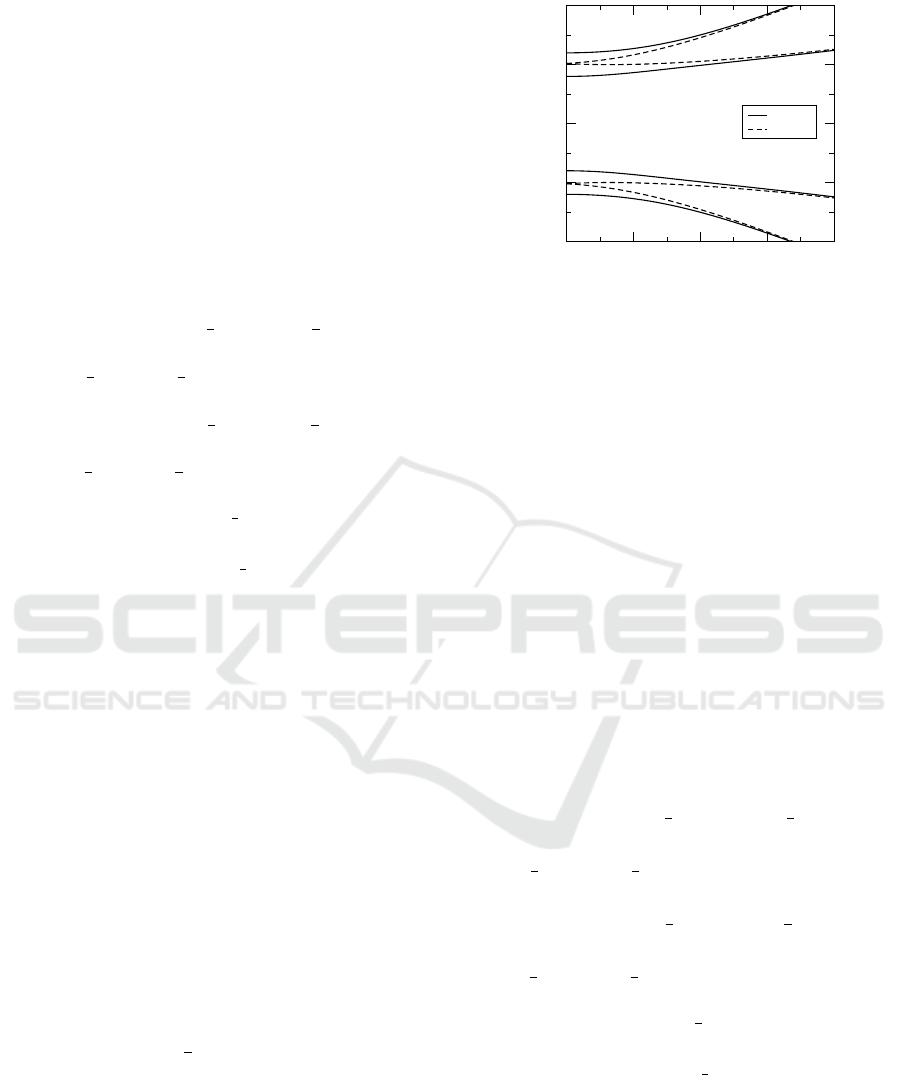
lower bandgaps. The bandgap spectrum is illustrated
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
k
-2
-1
0
1
2
ω
θ = 0
θ = 2π
Figure 1: Linear spectrum at c = 0.4, κ = 0.2 and different
values of θ.
in Figure 1. When θ = 0, the width of the central
bandgap can be defined by |ω| ≤ (1 − κ). It is found
that the central gap widens as θ is increased. Specif-
ically, under the highest phase mismatch condition
(i.e. θ = 2π), the central gap merges with the upper
and lower gaps, forming a single bandgap at k = 0.
3 SOLITON SOLUTIONS
Since no exact analytical solution exists for the model
Eqs. 1, the quiescent soliton solutions have to be
obtained numerically. To this end, we first substi-
tute
{
u(x,t),v (x,t)
}
=
{
U (x),V (x)
}
exp(−iωt), and
{
φ(x, t), ψ(x, t)
}
=
{
Φ(x) , Ψ (x)
}
exp(−iωt) into the
Eqs. 1 and upon simplification we arrive at the follow-
ing system of ordinary differential equations which is
then solved using the relaxation method for different
system parameters:
ωU + iU
x
+
|
V
|
2
+
1
2
|
U
|
2
U −η
1
4
|U|
4
+
3
2
|U|
2
|V |
2
+
3
4
|V |
4
U +V + κΦ = 0,
ωV − iV
x
+
|
U
|
2
+
1
2
|
V
|
2
V − η
1
4
|V |
4
+
3
2
|V |
2
|U|
2
+
3
4
|U|
4
V +U + κΨ = 0,
ωΦ + icΦ
x
+ Ψe
i
θ
2
+ κU = 0,
ωΨ − icΨ
x
+ Φe
−i
θ
2
+ κV = 0.
(3)
In the case of c = 0, our numerical analysis in-
dicates that the quiescent solitons completely fill all
three bandgaps. However, when c ̸= 0, quiescent soli-
ton solutions are found only in the central bandgap.
Moreover, due to the presence of cubic-quintic non-
linearity in one core, it is found that the model sup-
ports two different and disjoint families of solitons,
PHOTOPTICS 2025 - 13th International Conference on Photonics, Optics and Laser Technology
60
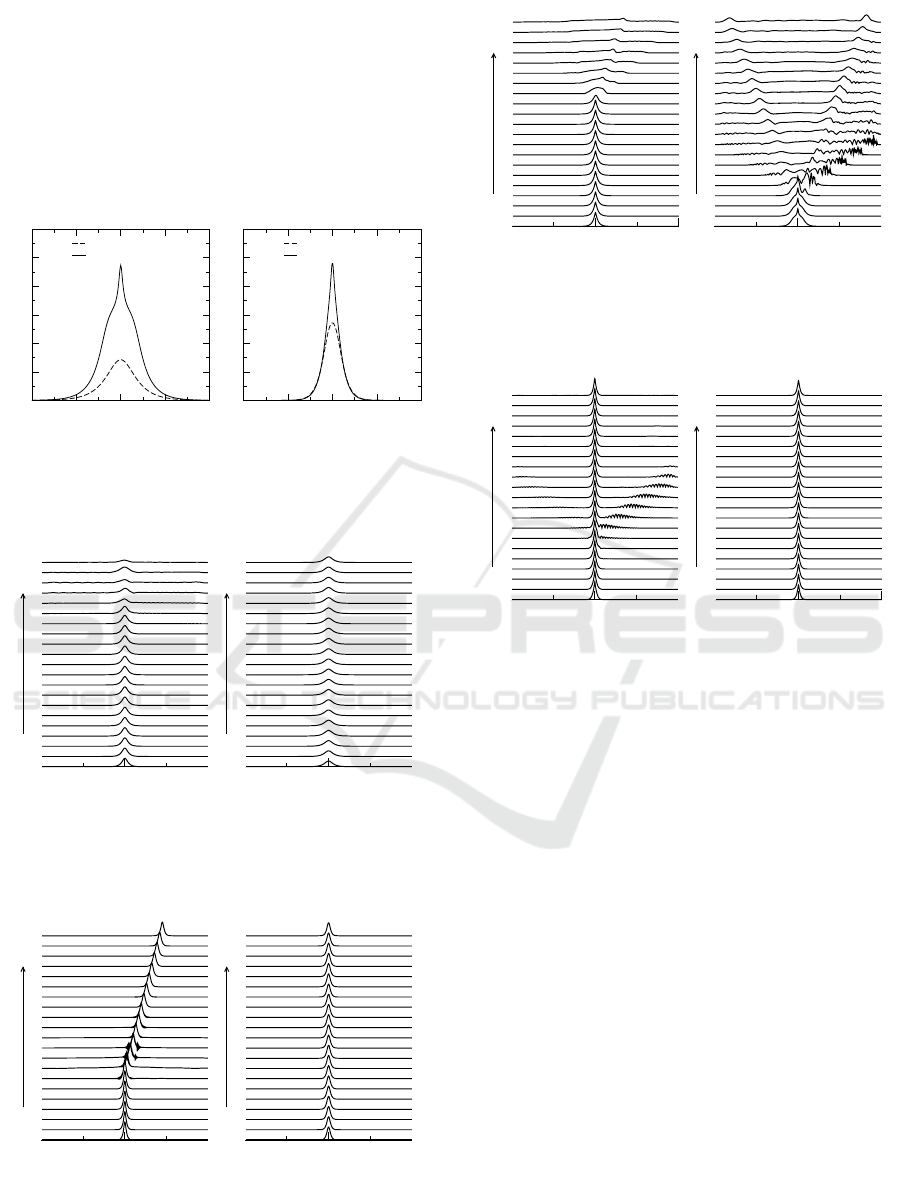
namely Type 1 and Type 2 solitons. These soliton
families are separated by a border which can be deter-
mined numerically. It is noteworthy that Type 1 and
Type 2 solitons differ in their shapes, phases, and par-
ities of their real and imaginary parts. In particular,
near the border, the Type 2 solitons may have a non-
singular and sharp peak, featuring a distinctive two-
tier profile. Figure 2 shows the examples of soliton
profiles for Type 1 and Type 2.
-10
-5
0
5
10
x
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
2.5
3
|u|
Type 1
Type 2
(a)
(ω = 0.30)
(ω = − 0.18)
-10
-5
0
5
10
x
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
2.5
3
|u|
Type 1
Type 2
(b)(b)
(ω = 0.30)
(ω = − 0.18)
Figure 2: Type 1 and Type 2 soliton profiles for (a) c = 0.4,
κ = 0.5, η = 0.18, θ = 0; and (b) c = 0.4, κ = 0.5, η = 0.18,
θ = 2π.
-40 0 40
x
t
2000
t
(a)
0
2000
-40 0 40
x
t
2000
t
(b)
0
2000
Figure 3: Propagation of Type 1 quiescent solitons with c =
0.4, κ = 0.5, θ = 0. (a) η = 0.12, ω = 0.22 (Unstable); and
(b) η = 0.14, ω = 0.38 (Stable).
-40 0 40
x
t
2000
t
(a)
0
2000
-40 0 40
x
t
2000
t
(b)
0
2000
Figure 4: Propagation of Type 1 quiescent solitons with c =
0.4, κ = 0.5, θ = 2π. (a) η = 0.06, ω = −0.48 (Unstable);
and (b) η = 0.12, ω = 0.22 (Stable).
-40 0 40
x
t
100
t
(a)
0
-40 0 40
x
t
150
t
(b)
0
Figure 5: Propagation of Type 2 quiescent solitons with c =
0.4, κ = 0.5, θ = 0. (a) η = 0.72, ω = −0.06 (Unstable);
and (b) η = 0.44, ω = 0.26 (Unstable).
-40 0 40
x
t
150
t
(a)
0
-40 0 40
x
t
2000
t
(b)
0
2000
Figure 6: Propagation of Type 2 quiescent solitons with c =
0.4, κ = 0.5, θ = 2π. (a) η = 0.48, ω = 0.38 (Unstable);
and (b) η = 0.72, ω = −0.06 (Stable).
4 STABILITY ANALYSIS
To investigate the stability of the quiescent soli-
tons, we have utilized the split-step Fourier transform
method. Our analysis reveals the presence of both sta-
ble and unstable Type 1 and Type 2 solitons in our
model depending on the values of system parameters.
Figures 3 and 4 present the examples of stable and
unstable Type 1 solitons propagation for θ = 0 and
θ = 2π respectively. It is apparent that the unstable
Type 1 solitons typically lose some energies as radi-
ation or may evolve into moving solitons after prop-
agating a certain distance. Likewise, Figures 5 and
6 illustrate the evolution of Type 2 solitons for θ = 0
and θ = 2π respectively. A notable observation is that
Type 2 solitons exhibit strong instability and quickly
decay into radiation especially when θ = 0. On the
other hand, in the case of θ = 2π, stable Type 2 soli-
tons are also observed. This demonstrates that the
presence of phase mismatch has a stabilizing effect.
The interplay of θ and other parameters on the stabil-
Effect of Phase Mismatch on the Dynamics of Bragg Solitons in a Semilinear Coupled Bragg Grating System with Cubic-Quintic
Nonlinearity
61

ity of solitons is currently under investigation.
5 CONCLUSIONS
We have investigated the existence and stability of
quiescent gap solitons within a system of coupled
Bragg gratings where one core has cubic-quintic non-
linearity and the other core is linear. In addition, we
have considered a phase shift between the gratings to
explore the dynamics of BG solitons in the system.
By examining the linear spectrum of the system, we
have identified the bandgap region where the station-
ary gap solitons exist. Numerical methods have been
employed to determine the soliton solutions which re-
veals the existence of two distinct families of Bragg
solitons, categorized as Type 1 and Type 2. We have
performed numerical analysis to assess the stability
within each family of solitons and observed stable and
unstable propagation for both types. In the absence
of the phase shift, Type 2 solitons are generally un-
stable. Our findings indicate that the presence of a
higher phase shift between the gratings expands the
overall stability for Type 1 solitons and leads to the
formation of stable Type 2 solitons.
REFERENCES
Aceves, A. and Wabnitz, S. (1989). Self-induced trans-
parency solitons in nonlinear refractive periodic me-
dia. Physics Letters A, 141(1-2):37–42.
Atai, J. (2004). Interaction of bragg grating solitons in a
cubic–quintic medium. Journal of Optics B: Quantum
and Semiclassical Optics, 6(5):S177.
Atai, J. and Malomed, B. A. (2000). Bragg-grating solitons
in a semilinear dual-core system. Physical Review E,
62(6):8713.
Atai, J. and Malomed, B. A. (2001). Families of bragg-
grating solitons in a cubic–quintic medium. Physics
Letters A, 284(6):247–252.
Boudebs, G., Cherukulappurath, S., Leblond, H., Troles, J.,
Smektala, F., and Sanchez, F. (2003). Experimental
and theoretical study of higher-order nonlinearities in
chalcogenide glasses. Optics Communications, 219(1-
6):427–433.
Chen, Y.-F., Beckwitt, K., Wise, F. W., Aitken, B. G.,
Sanghera, J. S., and Aggarwal, I. D. (2006). Mea-
surement of fifth-and seventh-order nonlinearities of
glasses. JOSA B, 23(2):347–352.
Chowdhury, S. S. and Atai, J. (2016). Interaction dynam-
ics of bragg grating solitons in a semilinear dual-core
system with dispersive reflectivity. Journal of Modern
Optics, 63(21):2238–2245.
Chowdhury, S. S. and Atai, J. (2017). Moving bragg grating
solitons in a semilinear dual-core system with disper-
sive reflectivity. Scientific reports, 7(1):4021.
Christodoulides, D. and Joseph, R. (1989). Slow bragg soli-
tons in nonlinear periodic structures. Physical Review
Letters, 62(15):1746.
Conti, C., Trillo, S., and Assanto, G. (1997). Doubly reso-
nant bragg simultons via second-harmonic generation.
Physical review letters, 78(12):2341.
Dasanayaka, S. and Atai, J. (2010). Stability of bragg grat-
ing solitons in a cubic–quintic nonlinear medium with
dispersive reflectivity. Physics Letters A, 375(2):225–
229.
De Sterke, C. and Sipe, J. (1994). Gap solitons progress in
optics. North-Holland, 33:203–260.
De Sterke, C. M., Eggleton, B. J., and Krug, P. A. (1997).
High-intensity pulse propagation in uniform gratings
and grating superstructures. Journal of lightwave
technology, 15(8):1494–1502.
Eggleton, B. J., Slusher, R., De Sterke, C. M., Krug, P. A.,
and Sipe, J. (1996). Bragg grating solitons. Physical
Review Letters, 76(10):1627.
Islam, M. J. and Atai, J. (2014). Stability of gap solitons
in dual-core bragg gratings with cubic-quintic nonlin-
earity. Laser Physics Letters, 12(1):015401.
Islam, M. J. and Atai, J. (2018). Stability of mov-
ing gap solitons in linearly coupled bragg gratings
with cubic–quintic nonlinearity. Nonlinear Dynamics,
91(4):2725–2733.
Kashyap, R. (2009). Fiber bragg gratings. Academic press.
Krug, P., Stephens, T., Yoffe, G., Ouellette, F., Hill, P., and
Dhosi, G. (1995). Dispersion compensation over 270
km at 10 gbit/s using an offset-core chirped fibre bragg
grating. Electronics Letters, 31(13):1091–1093.
Litchinitser, N. M., Eggleton, B. J., and Patterson, D. B.
(1997). Fiber bragg gratings for dispersion compen-
sation in transmission: theoretical model and design
criteria for nearly ideal pulse recompression. Journal
of Lightwave Technology, 15(8):1303–1313.
Loh, W., Laming, R. I., Robinson, N., Cavaciuti, A., Va-
ninetti, F., Anderson, C., Zervas, M., and Cole, M.
(1996). Dispersion compensation over distances in
excess of 500 km for 10-gb/s systems using chirped
fiber gratings. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters,
8(7):944–946.
Mak, W. C., Chu, P., and Malomed, B. A. (1998a). Solitary
waves in coupled nonlinear waveguides with bragg
gratings. JOSA B, 15(6):1685–1692.
Mak, W. C., Malomed, B. A., and Chu, P. (1998b). Three-
wave gap solitons in waveguides with quadratic non-
linearity. Physical Review E, 58(5):6708.
Mak, W. C., Malomed, B. A., and Chu, P. L. (2004). Sym-
metric and asymmetric solitons in linearly coupled
bragg gratings. Physical Review E, 69(6):066610.
Mandelik, D., Morandotti, R., Aitchison, J., and Silberberg,
Y. (2004). Gap solitons in waveguide arrays. Physical
review letters, 92(9):093904.
Radic, S., George, N., and Agrawal, G. P. (1995). Theory
of low-threshold optical switching in nonlinear phase-
shifted periodic structures. JOSA B, 12(4):671–680.
Russell, P. S. J. (1991). Bloch wave analysis of dispersion
and pulse propagation in pure distributed feedback
PHOTOPTICS 2025 - 13th International Conference on Photonics, Optics and Laser Technology
62

structures. Journal of Modern Optics, 38(8):1599–
1619.
Sankey, N., Prelewitz, D., and Brown, T. (1992). All-optical
switching in a nonlinear periodic-waveguide structure.
Applied physics letters, 60(12):1427–1429.
Shnaiderman, R., Tasgal, R. S., and Band, Y. B. (2011).
Creating very slow optical gap solitons with a grating-
assisted coupler. Opt. Lett., 36:2438–2440.
Sipe, J. E. and Winful, H. G. (1988). Nonlinear schr
¨
odinger
solitons in a periodic structure. Optics letters,
13(2):132–133.
Srivastava, D., Tiwari, U., and Das, B. (2018). Interferomet-
ric interrogation of π-phase shifted fiber bragg grating
sensors. Optics Communications, 410:88–93.
Taverner, D., Broderick, N., Richardson, D., Laming, R.,
and Ibsen, M. (1998). Nonlinear self-switching and
multiple gap-soliton formation in a fiber bragg grat-
ing. Optics letters, 23(5):328–330.
Tsofe, Y. J. and Malomed, B. A. (2007). Quasisymmet-
ric and asymmetric gap solitons in linearly coupled
bragg gratings with a phase shift. Physical Review E,
75(5):056603.
Winful, H. G., Marburger, J., and Garmire, E. (1979). The-
ory of bistability in nonlinear distributed feedback
structures. Applied Physics Letters, 35(5):379–381.
Zhan, C., Zhang, D., Zhu, D., Wang, D., Li, Y., Li, D., Lu,
Z., Zhao, L., and Nie, Y. (2002). Third-and fifth-order
optical nonlinearities in a new stilbazolium derivative.
JOSA B, 19(3):369–375.
Effect of Phase Mismatch on the Dynamics of Bragg Solitons in a Semilinear Coupled Bragg Grating System with Cubic-Quintic
Nonlinearity
63
