
Interactive Wind Simulation in Settlement Areas
Michael Burch
a
, Raphael Brunold
b
and Ralf-Peter Mundani
c
University of Applied Sciences, Chur, Switzerland
{firstname.lastname}@fhgr.ch
Keywords:
Flow Visualization, Wind Simulation, Geographic Information Systems.
Abstract:
We investigate the research problem of simulating interactive wind flows in settlement areas containing build-
ings of arbitrary shapes. To reach this goal we generate two-dimensional wind flow simulations based on
geographic data from areas in Switzerland. In modern cities it is crucial to explore wind flows that might
have effects on the fresh air circulation, urban heat islands, or transport and flow directions of polluted or
contaminated air. In our work, we create a pipeline to define and implement the steps and techniques to gen-
erate a wind flow simulation with which we can monitor the flow around buildings while also allowing user
interactions during and after the wind flow computation. To achieve our results we focus on data accessed
from public geographic information systems (GIS) in Switzerland that are available in different geo-spatial
granularities. The visualizations can combine several wind flow metrics like wind directions, wind intensities
and velocities, as well as air pressure, either in separate visual depictions or as overlays in geographic maps.
Finally, we discuss limitations and scalability issues and provide an outlook based on future directions.
1 INTRODUCTION
Figure 1: The steps in this research and how they build
on each other. Data is accessed, processed, simulations are
computed, visualized, and explored on users’ demands.
Wind can have a crucial impact on natural and
unnatural environments (Yan et al., 2022) including
agricultural areas, forests, as well as buildings in set-
tlement areas. In particular for the people living
in such settlement areas (Meinel, 2008) the conse-
quences can come in various forms. For example,
wind flows are responsible for the air circulation, the
reduction of the number and size of urban heat is-
lands (Seebacher et al., 2019), as well as natural ef-
fects coming in the form of erosion or soil dehydra-
tion. Even contaminated or polluted air (Papalexiou
and Moussiopoulos, 2006) or controlling the flow of
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4756-5335
b
https://orcid.org/0009-0006-7981-5596
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6248-714X
fire and smoke (Forney et al., 2003) can be impacted
by wind flows and their directions and intensities. Not
only direction but even more the obstacles in the way
in form of trees, mountains, or man-made buildings
have an impact on how the aforementioned aspects
have to be taken into account in certain geographic
areas, in particular in wind simulation algorithms to
compute reliable and realistic results.
In this paper, we describe a model for wind flow
simulation taking into account buildings in settlement
areas that have an influence on how the wind affects
certain subregions or not. Such a simulation can be
useful for experts or (political) decision makers in
various application fields to monitor or predict heat
islands, air pollution, or erosion and dehydration ef-
fects. Apart from generating static wind flow visu-
alizations we integrate interactive simulations. This
interactivity allows to modify several parameters like
wind directions or building shapes to explore the im-
pact of wind on certain user-defined situations. More-
over, the interactive visualizations can be a combina-
tion of overlaid views depicting streamlines for the
wind direction as well as color coded contour lines
for the geo-spatial pressure. Many more features are
included in the visualization tool focusing on the task
to identify wind effects in settlement areas.
We investigate the following research question:
• Which steps, techniques, and technologies are
Burch, M., Brunold, R. and Mundani, R.-P.
Interactive Wind Simulation in Settlement Areas.
DOI: 10.5220/0013107600003912
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 20th International Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications (VISIGRAPP 2025) - Volume 1: GRAPP, HUCAPP
and IVAPP, pages 823-830
ISBN: 978-989-758-728-3; ISSN: 2184-4321
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
823

required to design, create, and run an interac-
tive flow visualization for this kind of application
based on GIS models (see Figure 1)?
To illustrate our approach we apply it to data from
geographic information systems (GIS) focusing on
Switzerland, allowing us to simulate wind in local
regions of the country. The novelty of the approach
is its interactivity to allow region selections and to
generate a wind simulation on users’ demands. As
a proof-of-concept we simulate the data in the two-
dimensional space, but we can also extend our work
to three-dimensional data since the data is accessible
in 3D. However, the 3D data is more coarse-grained
at the moment compared to the 2D counterpart.
2 RELATED WORK
Our work is a composition of several subfields, in par-
ticular simulation, computer graphics, wind flow, and
geographic information systems.
2.1 Simulations
We make use of numerical computations of wind
flows (Kirkil and Lin, 2020; Yan et al., 2022) and
focus on the simulation pipeline (Bader et al., 2011)
that we adapt for our research purposes (see Figure 1)
starting with the data acquisition and ending at the
visual depictions of the computed simulations. Such
a pipeline is important since it describes the stages
from the data to the final output: Modeling, numeri-
cal treatment, implementation, visualization, and the
embedding into a tool like in our case for example,
in which we also integrate user interactions (Yi et al.,
2007). Those can directly impact the visual depic-
tion of the wind flow in the visual embedding. They
also allow adaptations to involved parameters that im-
pact the flow simulation like wind direction changes
or modifications of the buildings in the scene, typ-
ically with the goal to detect patterns in the wind
flows (Wang et al., 2022).
2.2 Computer Graphics Perspective
The modeling and technical processing of the coor-
dinates is based on a grid that is used to maintain
the pixel properties in the resulting image, also al-
lowing to interactively draw lines, build and cut out
shapes, or transform resolutions. On the grid we com-
pute the simulation steps while we take into account
each building and its outlines as obstacles for the flow
and the flow directions. This is somewhat different to
original work in flow visualization, for example based
on surface particles (van Wijk, 1993) or taking into
account virtual and augmented reality to create wind
flow (Bryson and Levit, 1992). From a visualization
perspective there are various options to depict the flow
but we use a standard way of visualizing it given by
streamlines (Schlemmer et al., 2007).
2.3 Flow Around Buildings
Modern city planning (Burch et al., 2020) has to take
into account crucial aspects like heat (Seebacher et al.,
2019) or air pollution (Papalexiou and Moussiopou-
los, 2006), even special wind situations like torna-
dos for example (Yang et al., 2010). Those are typi-
cally impacted by wind and wind flows around build-
ings (Li and Zhao, 2023; Zu and Lam, 2018), hence
generating models that compute them and integrate
the results into the city planning is of great impor-
tance. An efficient simulation model can reduce costs
before they even occur (Paterson and Apelt, 1989).
This means they can serve as pure monitoring tool but
might even be used to predict (Mayo et al., 2018) sit-
uations to prevent human catastrophies or just reduce
the costs during planning cities. Constructing aerody-
namic buildings depends on many parameters as well
as boundary conditions and mean a challenge for to-
day’s architects and the construction industry.
2.4 GIS-Related Concepts
Geographic information systems (GIS) are important
to provide data of cities or city parts (Yin et al., 2014)
for generating simulation models. Those can be pro-
vided in several resolutions and users should be able
to extend them by adding extra buildings or parts of
buildings that have a direct impact on the wind flow in
the surrounding environment. The results of the sim-
ulations are datasets which are graphically depicted,
for example using 3D vectorization (Ridzuan et al.,
2023) or based on 3D city models (Deininger et al.,
2020), but in most cases, interactions are not sup-
ported (Yi et al., 2007).
3 DATA
Before we can start simulating wind flows we need
to access data from geographic information systems
to integrate the buildings and their outlines into the
model generation. We transformed the data to make
it usable by our simulation tool.
IVAPP 2025 - 16th International Conference on Information Visualization Theory and Applications
824

3.1 Data Acquisition
The data source we base our work on is provided by
the Ministerial Measurement of Switzerland which
incorporates measurements from the whole coun-
try on different levels of geographic granularities.
The data can be accessed by the federal office for
ground topography and its Swisstopo’s interface (Ei-
dgenossenschaft, 2024). They also support 3D maps
in addition to the more standard two-dimensional data
measurements. The tool provides an easy way to ac-
cess parts of the data and to enrich the current visual
simulation by additional data, for example to interac-
tively add surrounding buildings that were omitted in
the first step of a simulation.
3.2 Data Processing and Further Steps
Once the original data is accessed it will be processed
in several steps (see Figure 1). We use the program-
ming language Python and several libraries to read
and parse the data, preprocess it in a way to create a
flag field, compute a wind flow simulation, and finally
visualize the generated results while we also support
user interactions. The data processing is important
since on its basis we will compute the wind flow sim-
ulation, including additional parameters like wind di-
rections as well as building extensions.
Due to the fact that we can access GIS data of
the whole country of Switzerland (Eidgenossenschaft,
2024) we can simulate wind flows for any local re-
gion in the country, on different levels of geographic
granularity which is one of the novelties in our work,
i.e. interactions are possible that support the spatial
navigation in the data as well as replacing buildings
or changing wind directions on demand for example.
The corresponding data parts are then processed to
make these interactions a crucial component in our
tool. Users of the tool decide which parameters to
adapt and which visual variables are used to depict
the simulation data (Wu et al., 2023).
4 FLOW SIMULATION
To compute wind flow we use block-structured Carte-
sian grids for the spatial discretization of geographic
regions. The smaller the grid sizes are, the better we
can capture geographic details, but the more expen-
sive the computations will be due to growing num-
bers of grid cells. Hence, there exists some kind
of trade-off between the accuracy of the results and
the runtime performance given by the number of grid
cells. In particular, for a real-time or live computation
(important for interactive responsiveness of the tool)
we should not exhibit too many grid cells since those
would tremendously reduce the interactivity.
4.1 Algorithmic Concepts
We use an iterative computation approach for the tran-
sient wind flow simulation by numerically solving the
Navier-Stokes equations (see Algorithm 1). We base
our work on a relatively simple model that applies a
finite differences method for spatial and temporal dis-
cretization of the derivatives. Applying Chorin’s pro-
jection method (Chorin, 1967), we end up with a Pois-
son equation for the pressure computation which con-
tributes as most complex part of the entire calculation.
For each grid cell we compute the wind speed and the
pressure by using a just-in-time (JIT) compiler based
on the Python package called numba which compiles
Python functions into machine code.
The integration of buildings or obstacles are in-
corporated by means of so called flag fields. A simple
geometry is shown in Figure 2 used in a first test of
the approach. It shows visualizations for the wind and
pressure as a 2D scene (a) and a more 3D representa-
tion (b).
Algorithm 1 consists of five major subroutines
for the initialization of the parameters, grids, and in-
volved fields, the main simulation loop, the pressure
calculation loop, the check for convergence, and the
final plotting of the results.
(a) (b)
Figure 2: Wind flow and pressure: (a) A 2D scene with a
few buildings. (b) The same scene augmented by a more 3D
representation, a so-called quasi 3D visualization that adds
3D polygonal shapes on the buildings of the 2D representa-
tion to make it more understandable for the users.
(a) (b)
Figure 3: The 2D outline of a building (a) gets placed into
a grid consisting of equally sized grid cells (b).
Interactive Wind Simulation in Settlement Areas
825
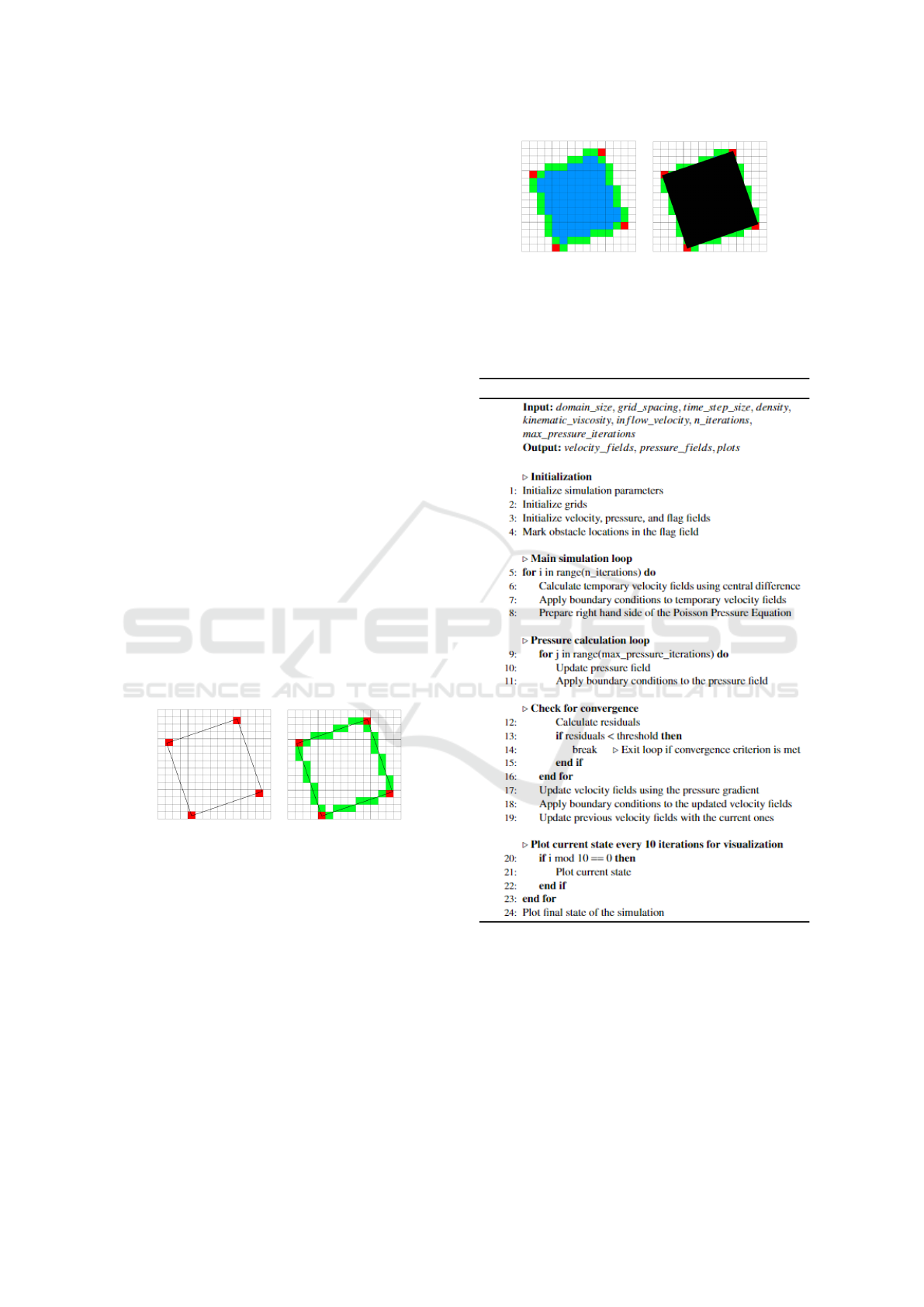
4.2 Integrating Outlines into a Grid
In a first step, we describe how an outline gets mapped
to a grid which requires an exact matching from the
building geometry to a corresponding grid of a cer-
tain resolution. Figure 3 illustrates a 2D model of a
building depicted as black square (a) that is placed
into a uniform grid of equally sized grid cells (b). It
may be noted that the resolution of the grid cannot
be infinitely high due to the fact that each grid cell
will be treated as a separate variable in the physical
computation, i.e. more of them would cause more
complex computations resulting in a higher runtime
performance. For this reason, we need an adequate
resolution to allow live computations and hence, inter-
active responsiveness during the simulation process.
Each grid cell can only have one out of two states:
Either it belongs to a building or not, requiring a pre-
step before the simulation computation that checks
each grid cell for this property. To get a quick so-
lution to this problem we apply the Bresenham algo-
rithm (Angel and Morrison, 1991) that is able to draw
lines between the corners of the polygon modeling the
building outlines. Negatively, we soon get effects that
are well-known as pixel staircases in low resolution
images (see Figure 4).
Finally, we obtain a geometry that is compatible
with the simulation algorithm, i.e. we generate a so-
called flag field that we take into account in the com-
putation to judge whether a grid cell corresponds to a
piece of a building or not (see Figure 5).
(a) (b)
Figure 4: Computing the corners (red squares) of the 2D
outline (a) and identifying the grid cells that are hit by the
corner-connecting lines (green squares) (b). This may result
in some kind of staircase effect.
4.3 Invalid Geometry
The computation of the simulation is problematic at
the walls and corners around an obstacle. We must
apply boundary conditions to follow physical laws
correctly. Otherwise, the wind might flow through
walls or the pressure is incorrectly computed. Most
of the computation methods have such problems with
obstacle grid cells that have more than 2 free, direct
neighbors or that have free neighbors above and be-
low (which is a wall consisting of just one grid cell).
(a) (b)
Figure 5: An identified outline of a building depicted as
corners (red squares), outline connecting the corners (green
squares), and the inside (blue squares) (a). Overplotting
with the original 2D building shows the final result in the
grid with the original shape (b).
Algorithm 1: The windy flow simulation algorithm.
For this reason, we have to re-inspect all situ-
ations after the geometries have been computed to
avoid such negative and error-prone cases. Actually,
we have three options to avoid such cases:
• Grid Refinement. We refine the grid. If we split
the involved grid cell into 2 × 2 grid cells we
get rid of the problematic cell due to the fact that
it does not have 3 free neighbor cells anymore.
However, a new problem might be the increased
number of cells that can cause a more complex
IVAPP 2025 - 16th International Conference on Information Visualization Theory and Applications
826

(a) (b)
Figure 6: Refining the grid due to the fact that there are
free neighbors causing problems in the physical correctness:
(a) One grid cell has 3 free neighbors. (b) Grid refinement
avoids this situation.
(a) (b)
Figure 7: Two more options to get rid of the problematic
situation: (a) Local adaptation of the grid. (b) Removal of
the problematic grid cell.
and longer running computation (see Figure 6).
• Adaptive Grid. We adapt the grid by refining it
only at locations in which invalid geometries ex-
ist. The benefit of this approach is that we do not
need much more storage as in the general grid re-
finement, however as a drawback the storing pro-
cess would get much more complex due to the fact
that our data structures have to handle such special
situations (see Figure 7 (a)).
• Grid Cell Removal. Just removing the problem-
atic grid cell might be the simplest solution, how-
ever, the simulation will get less exact due to the
missing geo-spatial information. In most cases
such scenarios just occur for tiny pieces of houses
or obstacles, hence this solution might be the best
one, also because we have tested it in experiments
(see Figure 7 (b)).
It may be noted that the grid is discretized, ac-
tually allowing to make it infinitesimally small but
due to the fact that we have to solve equation sys-
tems whose complexity depends on the number of in-
volved grid cells, we should avoid such a situation.
This means the buildings have to be downscaled to
make the simulation efficiently computable.
4.4 Algorithmic Performance
We tested our approach by applying it to a scenario
containing 150 × 150 grid cells, in total 22,500 cells.
The used hardware is a laptop with a CPU, a Mi-
crosoft Surface Laptop Studio processor Intel Core
i7-11370H, 4 core, 3 GHz and 16 GB RAM.
The visualizations will be shown as animation
which means they can be regarded as some kind of gif,
overplotting each image in the sequence by the next
one. The initialization lasts 2.4 to 3.5 seconds, but
this is independent from the final performance. The
concrete measurements for the running program and
for 1,270 iterations and 127 visualizations are 2.7031
seconds for the initialization, 0.8409 seconds for the
mean time between visualizations, 0.0022 seconds
variance, 0.0468 seconds standard deviation, 1.0005
seconds maximum, and 0.7501 seconds minimum.
5 VISUALIZATION TOOL
To explore the results of the simulation algorithm we
created a visualization tool that can depict the results
in different visual encodings and views. Moreover, in-
teractions are supported to let users adapt parameters
or navigate in the visual results. Before implementing
the tool we started with a design phase including visu-
alization techniques and interactions as well as algo-
rithmic concepts. All of them are integrated and laid
out in a user interface.
We focus on the most prominent visualization
techniques for this kind of data. The visualizations
can be shown separately or as overlay on users’ de-
mands.
• Wind Flow. The wind flow will be displayed
by streamlines, also showing the wind directions,
densities, and speed by arrow heads, proximity,
and frequency of arrow heads.
• Pressure. The pressure is visually depicted by a
contour plot using color coding to show the pres-
sure values in certain regions. We use a categori-
cal color scale here instead of a continuous one.
• Geography and Buildings. A geographic map
containing abstractions for the buildings provides
an overview about the geo-spatial data.
• 3D Augmentation: Quasi 3D depictions are use-
ful to better illustrate the geographical scene with
wind flows and pressures and look more natural
and more aesthetically pleasing.
We integrate user interactions for modifying simu-
lation parameters and for directly impacting the visual
output (Yi et al., 2007).
Interactive Wind Simulation in Settlement Areas
827

(a) (b) (c) (d)
Figure 8: Visualizing the outcomes of the simulation for two scenarios: (a) shows streamlines for the wind direction overlaid
on a contour map depicting the pressure with a color coding. (b) We modified one building (top left) to compare the impact
on wind flows and pressure. (c) Same scenario as in (a) but this time the wind comes from East and not from West as in (a).
In (d) we see again the modification of one building and its impact on the wind flow result.
(a) (b) (c) (d)
Figure 9: Visualizing the velocities of the wind flows for different wind directions as well as different building outlines:
(a) Wind from West and standard buildings. (b) Wind from West and building extension. (c) Wind from East and standard
buildings. (d) Wind from East and building extension.
6 APPLICATION EXAMPLE AND
RESULTS
As some kind of stress test we applied our approach
to GIS data from Zurich in Switzerland with 50,750
buildings.
6.1 Simple Scenarios
Figure 8 shows before-after scenes for the results of
the simulation algorithm. The visualizations are com-
posed of streamlines (for wind directions and inten-
sities) and contour maps (for pressure values). Fig-
ures 8 (a) and (c) show the simulation result for dif-
ferent wind directions while the computation in Fig-
ures 8 (b) and (d) also show different wind directions
but this time the scenario was modified by extend-
ing one building (top left) with an additional build-
ing. Figures 8 (a) and (b) show the wind coming from
West while Figures 8 (c) and (d) show the simulation
computation for wind coming from East.
For the variants without building extension in Fig-
ures 8 (a) and (c), we can see that the wind is mov-
ing more smoothly in the upper left corner without
turbulent or eddy currents compared to Figures 8 (b)
and (d), apart from the fact that in Figure 8 (a) the
wind is moving in a diagonal (West-North) direction
but in Figure 8 (c) this is not the case. For the sce-
nario in Figure 8 (b) with the modified building we
see that the wind from West is moving around the new
building part while in Figure 8 (d) the wind from East
creates turbulent and eddy currents and swirls in the
upper left corner. For the pressure (the color coded
contours) we can also see some differences between
the scenarios. Comparing Figures 8 (a) and (b) for
the wind from West we find stronger pressure regions
in the corner of the modified building. For the situ-
ations in Figures 8 (c) and (d) with the wind coming
from East we see that the pressure in the corner of the
extended building got much lower which might be a
hint for a quiet place in the garden to relax in cases the
wind comes from the East direction. It may be noted
that we are able to interactively modify those situa-
tions to explore the best shapes for new built houses,
for example to create wind-free zones. Such a sim-
ulation might be of particular interest for architects
who plan a new house based on the house owners’
demands.
Figure 9 depicts the same building situation as in
Figure 8 but in this case we focus on the wind speed
instead of the wind pressure. The color of the con-
tour plot indicates the strength of the wind in terms
of wind speed. We can see that the wind speed is ac-
tually the highest around the corners of the building
close to the direction from where the wind is coming.
Also in a wind channel between two buildings we can
see a higher wind speed than in the open environment
which is due to physical laws related to wind speed
and wind pressure.
Figure 10 shows another example with three
buildings while one building is a bit smaller than the
IVAPP 2025 - 16th International Conference on Information Visualization Theory and Applications
828

Figure 10: Three buildings while one is smaller than the
two others. The wind is coming from West. We can clearly
see the effect of the buildings on the wind.
(a) (b)
(c) (d)
Figure 11: Buildings from Zurich and the impact of wind
flows and the fact that buildings are removed: (a) A part
from Zurich while the wind is coming from East. (b) One
building is removed and the wind is coming from the West.
(c) Industriequartier in Zurich. (d) Sihlporte in Zurich.
other two ones. The wind is coming from West and
we can directly spot the largest pressure right before
the buildings closer to the West. In general, the pres-
sure is always largest at the side of the building facing
the wind directly and lowest behind the building.
6.2 More Complex Scenarios
Figure 11 shows examples including more buildings
than the scenes before. Also some real-world build-
ings from areas in Zurich are taken into consideration
for this kind of wind simulation. Also different wind
settings were applied resulting in different flows while
buildings are removed to get an impression about the
impact of new building environments.
In Figures 11 (a) and (b) we can easily detect that
the wind direction has an impact on the wind flows
around the buildings as well as the pressure. In (c) we
detect that there are just some strong pressure regions
while the center area of this environment seems to be
a quiet place with not much wind and low pressure
(blue color). In (d) it seems as if the wind is strongest
when it is leaving the building environment (yellow
and red colors to the right hand side).
6.3 Open Challenges and Perspectives
We are aware of the fact that there are also limitations
of our approach, however we developed a solution to
this problem at hand and will further develop more
scalable and user-friendly versions of the tool. For
example, more interaction techniques should be inte-
grated in the future, also letting users modify more pa-
rameters to change algorithmic computations on-the-
fly. There are also still some limitations with respect
to scalability issues regarding visual, perceptual, and
algorithmic issues. We are still experimenting with
the tool and the algorithms that we use as well as the
hardware could be enhanced in the future to get even
faster and even more interactive results.
7 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
WORK
In this work, we investigated the research problem
of computing wind flows in settlement areas with the
goal to create a model to understand such wind situ-
ations, for example before a new building is planned,
built, or just extended. We show the results of the sim-
ulations visually and let the users interactively change
wind directions or add, remove, replace buildings as
well as other obstacles while the simulation adapts
immediately to the new situation. To illustrate the
usefulness of our approach we applied it to GIS data
from Switzerland and showed some visual results of
the simulations under different conditions. For fu-
ture work we plan to extend our work by using bet-
ter hardware and more efficient algorithms and paral-
lelization, in particular with a focus on interactive re-
sponsiveness. This means we might install the tool on
some kind of large high-resolution display to let sev-
eral experts explore the data in a collaborative manner
(LHRD). We also plan to conduct an expert user study
with city planners and architects, maybe also tracking
eye movements (Burch, 2022) of the users with the
goal to analyze their visual attention behavior.
Interactive Wind Simulation in Settlement Areas
829

REFERENCES
Angel, E. and Morrison, D. (1991). Speeding up bresen-
ham’s algorithm. IEEE Computer Graphics and Ap-
plications, 11(6):16–17.
Bader, M., Mehl, M., R
¨
ude, U., and Wellein, G. (2011).
Simulation software for supercomputers. Journal of
Computational Science, 2(2):93–94.
Bryson, S. and Levit, C. (1992). The virtual wind tun-
nel. IEEE Computer Graphics and Applications,
12(4):25–34.
Burch, M. (2022). Eye Tracking and Visual Analytics. River
Publishers.
Burch, M., Wallner, G., Arends, S. T. T., and Beri, P.
(2020). Procedural city modeling for AR applications.
In et al., E. B., editor, Proceedings of the 24th Inter-
national Conference on Information Visualisation, IV,
pages 581–586. IEEE.
Chorin, A. J. (1967). Numerical solution of the navier-
stokes equations. Mathematics of Computation,
22:745–762.
Deininger, M. E., von der Gr
¨
un, M., Piepereit, R., Schnei-
der, S., Santhanavanich, T., Coors, V., and Voß, U.
(2020). A continuous, semi-automated workflow:
From 3d city models with geometric optimization and
CFD simulations to visualization of wind in an urban
environment. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-
Information, 9(11):657.
Eidgenossenschaft, S. (2024). Bundesamt f
¨
ur Landesto-
pografie swisstopo.
Forney, G. P., Madrzykowski, D., McGrattan, K. B., and
Sheppard, L. (2003). Understanding fire and smoke
flow through modeling and visualization. IEEE Com-
puter Graphics and Applications, 23(4):6–13.
Kirkil, G. and Lin, C. (2020). Large eddy simulation of
wind flow over A realistic urban area. Computation,
8(2):47.
Li, Y. and Zhao, H. (2023). Spatial wind flow load and
shape optimization for folding grid shell buildings.
IEEE Access, 11:135304–135322.
Mayo, M., Wakes, S., and Anderson, C. (2018). Neural net-
works for predicting the output of wind flow simula-
tions over complex topographies. In Wu, X., Ong, Y.,
Aggarwal, C. C., and Chen, H., editors, Proceedings
of the IEEE International Conference on Big Knowl-
edge, ICBK, pages 184–191. IEEE Computer Society.
Meinel, G. (2008). High resolution analysis of settlement
structure on base of topographic raster maps - method
and implementation. In Gervasi, O., Murgante, B., La-
gan
`
a, A., Taniar, D., Mun, Y., and Gavrilova, M. L.,
editors, Computational Science and Its Applications
- ICCSA 2008, International Conference, Perugia,
Italy, June 30 - July 3, 2008, Proceedings, Part I,
volume 5072 of Lecture Notes in Computer Science,
pages 16–25. Springer.
Papalexiou, S. and Moussiopoulos, N. (2006). Wind
flow and photochemical air pollution in thessaloniki,
greece. part II: statistical evaluation of european
zooming model’s simulation results. Environmental
Modelling and Software, 21(12):1752–1758.
Paterson, D. and Apelt, C. (1989). Simulation of wind flow
around three-dimensional buildings. Building and En-
vironment, 24(1):39–50.
Ridzuan, N., Ujang, U., and Azri, S. (2023). 3d vector-
ization and rasterization of citygml standard in wind
simulation. Earth Science Informatics, 16(3):2635–
2647.
Schlemmer, M., Hotz, I., Hamann, B., Morr, F., and Hagen,
H. (2007). Priority streamlines: A context-based visu-
alization of flow fields. In Museth, K., M
¨
oller, T., and
Ynnerman, A., editors, Proceedings of the 9th Joint
Eurographics - IEEE VGTC Symposium on Visualiza-
tion, EuroVis, pages 227–234. Eurographics Associa-
tion.
Seebacher, D., Miller, M., Polk, T., Fuchs, J., and Keim,
D. A. (2019). Visual analytics of volunteered geo-
graphic information: Detection and investigation of
urban heat islands. IEEE Computer Graphics and Ap-
plications, 39(5):83–95.
van Wijk, J. J. (1993). Flow visualization with surface par-
ticles. IEEE Computer Graphics and Applications,
13(4):18–24.
Wang, T., Wang, B., Matekole, E. S., and Atif, M. (2022).
Finding hidden patterns in high resolution wind flow
model simulations. In Kothe, D. B., Geist, A.,
Pophale, S., Liu, H., and Parete-Koon, S., editors,
Proceedings of the Accelerating Science and Engi-
neering Discoveries Through Integrated Research In-
frastructure for Experiment, Big Data, Modeling and
Simulation - 22nd Smoky Mountains Computational
Sciences and Engineering Conference, SMC, Revised
Selected Papers, volume 1690 of Communications in
Computer and Information Science, pages 345–365.
Springer.
Wu, A., Deng, D., Chen, M., Liu, S., Keim, D. A., Ma-
ciejewski, R., Miksch, S., Strobelt, H., Vi
´
egas, F. B.,
and Wattenberg, M. (2023). Grand challenges in vi-
sual analytics applications. IEEE Computer Graphics
and Applications, 43(5):83–90.
Yan, Z., Chen, R., and Cai, X. (2022). Large eddy simu-
lation of the wind flow in a realistic full-scale urban
community with a scalable parallel algorithm. Com-
puter Physics Communications, 270:108170.
Yang, Z., Sarkar, P., and Hu, H. (2010). Visualiza-
tion of flow structures around a gable-roofed building
model in tornado-like winds. Journal of Visualization,
13(4):285–288.
Yi, J. S., ah Kang, Y., Stasko, J. T., and Jacko, J. A.
(2007). Toward a deeper understanding of the role
of interaction in information visualization. IEEE
Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graph-
ics, 13(6):1224–1231.
Yin, J., Zhan, Q., Xiao, Y., Wang, T., Che, E., Meng, F.,
and Qian, Y. (2014). Correlation between urban mor-
phology and wind environment in digital city using
GIS and CFD simulations. International Journal of
Online Engineering, 10(3):42–48.
Zu, G. and Lam, K. M. (2018). LES and wind tunnel test
of flow around two tall buildings in staggered arrange-
ment. Computation, 6(2):28.
IVAPP 2025 - 16th International Conference on Information Visualization Theory and Applications
830
