
Using Machine Learning to Distinguish Human-Written from
Machine-Generated Creative Fiction
Andrea Cristina McGlinchey
1
and Peter J. Barclay
2 a
1
Lumerate, Canada
2
School of Computing, Engineering & the Built Environment, Edinburgh Napier University, Scotland
Keywords:
Large Language Models, Generative AI, Machine Learning, Classifier Systems, Fake Text Detection.
Abstract:
Following the universal availability of generative AI systems with the release of ChatGPT, automatic detection
of deceptive text created by Large Language Models has focused on domains such as academic plagiarism and
“fake news”. However, generative AI also poses a threat to the livelihood of creative writers, and perhaps
to literary culture in general, through reduction in quality of published material. Training a Large Language
Model on writers’ output to generate “sham books” in a particular style seems to constitute a new form of
plagiarism. This problem has been little researched. In this study, we trained Machine Learning classifier
models to distinguish short samples of human-written from machine-generated creative fiction, focusing on
classic detective novels. Our results show that a Na
¨
ıve Bayes and a Multi-Layer Perceptron classifier achieved
a high degree of success (accuracy > 95%), significantly outperforming human judges (accuracy < 55%).
This approach worked well with short text samples (around 100 words), which previous research has shown
to be difficult to classify. We have deployed an online proof-of-concept classifier tool, AI Detective, as a first
step towards developing lightweight and reliable applications for use by editors and publishers, with the aim
of protecting the economic and cultural contribution of human authors.
1 INTRODUCTION
Generative AI has made remarkable advances in re-
cent years, and is now widely available with the re-
lease of ChatGPT and similar systems. Along with
many beneficial uses, there are diverse concerns for
misuse, including generation of incorrect or harmful
advice (Oviedo-Trespalacios et al., 2023), propaga-
tion of biases (Feng et al., 2023), creation of deepfake
video, fake news and fake product reviews (Botha and
Pieterse, 2020), and various forms of plagiarism, es-
pecially in scientific and other academic fields (Odri
and Yoon, 2023). Previous research has investigated
techniques for identifying artificially generated text in
these domains, with the aim of mitigating the societal
harm from such misuse (see Section 2.3).
Generative AI also presents a threat to the liveli-
hood of writers and other creative artists, and may de-
value their work. Models are often trained on writers’
outputs, without their permission, and then the mod-
els can be used to generate similar content.
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0002-7369-232X
We might characterise this problem as “AI-
mediated plagiarism”: rather than taking or modi-
fying authors’ work directly, a bad actor can create
content using a generative AI trained on the authors’
work. Increasing awareness of the issue is signalled
by developments such as the New York Times’ an-
nouncement in 2023 that it was suing OpenAI and
Microsoft for copyright infringement (Grynbaum and
Mac, 2023).
We note a gap in the literature around develop-
ing detection tools in the area of creative fiction, and
broach this problem by investigating whether Ma-
chine Learning (ML) models can reliably distinguish
between short text samples from human-written nov-
els and similar text automatically generated.
Our early results show a good level of success,
working with text excerpts from classic detective nov-
els, and suggest that relatively simple classifiers can
outperform humans in identifying automatically gen-
erated creative prose. Moreover, the approach works
well with short text samples, which previous studies
found difficult to classify (see Section 7.2).
McGlinchey, A. C. and Barclay, P. J.
Using Machine Learning to Distinguish Human-Written from Machine-Generated Creative Fiction.
DOI: 10.5220/0013110100003890
In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2025) - Volume 2, pages 79-90
ISBN: 978-989-758-737-5; ISSN: 2184-433X
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
79

2 BACKGROUND
2.1 Advances in Text Generation
Recent increases in data availability and computing
power have facilitated approaches to automatic text
generation based on neural network models and deep
learning (Goyal et al., 2023).
A neural network is trained by optimising the
weights and biases based on the observed vs. desired
outputs (Bas et al., 2022). As networks are not re-
stricted to pre-existing patterns, the text generated by
these models can be more “creative” according to the
underlying semantic relationships (Pandey and Roy,
2023).
The introduction of Transformer models in 2017
represented another major advance (Vaswani, 2017).
The architecture of a Transformer consists of an en-
coder and a decoder. The encoder block contains a
multi-head self-attention layer; the decoder block also
has a cross-attention layer, enabling it to use the out-
put of the encoder as context for text generation (Han
et al., 2021). The attention component of Transform-
ers underlies their success in text generation, as it en-
ables a language model to decipher the correct mean-
ing of a word using its context. For example, when
“it” is used in a sentence, the model can better in-
terpret what is being referred to. These types of text
generation models learn from huge amounts of data,
which enables them to generate high quality output.
Increases in scale led to Large Language Models
(LLMs), a notable early example being BERT from
Google, which used the Transformer architecture to
achieve dramatic improvements over earlier models
(Devlin et al., 2019).
OpenAI’s GPT-1 was developed in 2018, and ver-
sion 3.5 was released to the public in 2022 via the
ChatGPT interface, making this technology univer-
sally available. GPT-3 showed its ability to create text
that was seemingly indistinguishable from human-
written text (Pandey and Roy, 2023). The initial ver-
sion of GPT used 110 million learning parameters,
and this number greatly increased with each version.
GPT-2 used 1.5 billion and GPT-3 used 175 billion
(Floridi and Chiriatti, 2020). The number of parame-
ters used for GPT-4 has been speculated to be approx-
imately 100 trillion. Now ChatGPT has the ability to
write human-like essays, news articles, and academic
papers, as well as to complete text summarisation in
multiple languages (Zaitsu and Jin, 2023).
Many other companies have also launched LLMs
with similar capabilities, including GitHub’s and Mi-
crosoft’s Copilot, Meta’s LLama, Anthropic’s Claude,
and Google’s Gemini.
2.2 Text Generation: Concerns for
Misuse
ChatGPT is freely available and widely adopted, rais-
ing the possibility of harm from inaccurate responses,
or deliberate misuse by bad actors generating mis-
leading texts.
One concern regarding text generated by LLMs
is quality. As responses are based on statistical pat-
terns and correlations found in large datasets, they
can at times be irrelevant, nonsensical or offensive
(Wach et al., 2023); different models can vary re-
garding what is considered inaccurate or offensive
(Feng et al., 2023). As LLMs are pre-trained on
large datasets which include opinions and perspec-
tives, there is a risk of the introduction of biases for
downstream models (Barclay and Sami, 2024). More
ominously, ChatGPT can write fake news at scale,
a task which was previously labour-intensive. This
makes it easy to create media supporting or discredit-
ing certain views, political regimes, products or com-
panies (Koplin, 2023).
As awareness of these concerns increased, re-
search has focused on ways to distinguish human-
written from artificially generated text.
There has also been concern in creative industries
that generative AI could be used to replicate artists’
and writers’ work, and possibly replace them. In
2023, members of the Writers Guild of America went
on strike for 148 days seeking an agreement on pro-
tections regarding the use of AI in the television, film,
and online media industries (Salamon, 2024).
2.3 Related Work
Numerous methods have been employed for the cre-
ation of AI-content detectors in other domains, in-
cluding zero-shot classifiers, fine-tuning Neural Lan-
guage Models (NLMs), as well as specialised classi-
fiers trained from scratch (Jawahar et al., 2020).
OpenAI, the creator of ChatGPT, launched its own
AI classifier to identify AI-generated text; however,
they removed availability in July 2023 owing to its
low accuracy (see https://platform.openai.com). A
study which reviewed five AI-content detection tools
(OpenAI, Writer, Copyleaks, GPTZero, and Cross-
Plag) observed high variability across the tools, and
a reduced ability to detect content from a more re-
cent version of GPT. Comparing GPT-4 with GPT-
3.5 content, three of the five tools could find 100% of
GPT-3.5 content, but none achieved this level of de-
tection for GPT-4 – the highest result was 80% by the
OpenAI Classifier; then one detector managed 40%
and the rest only 20%. This suggests that AI detection
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
80

tools will have to evolve in response to the increasing
sophistication of LLMs (Elkhatat et al., 2023).
The majority of zero-shot detectors evaluate the
average per-token log probability of the generated
text. A commercially available tool which uses zero-
shot classification, GPTZero, has been found, in a
study using medical texts, to have an accuracy of 80%
in identifying AI-generated texts (Habibzadeh, 2023).
Another example of a zero-shot detector is
“DetectGPT”, which uses minor rewrites of text and
then plots log probability of the original vs. the
rewrites. The “Perturbation Discrepancy” created re-
sults in the log probability for human text tending
towards zero, whereas the AI text was expected to
give relatively larger values (Mitchell et al., 2023).
DetectGPT was found to perform better than other
existing zero-shot methods at detecting AI-generated
fake news articles (Mitchell et al., 2023). However,
a more recent study reports having outperformed De-
tectGPT by leveraging the log rank information (Su
et al., 2023).
Detectors using RoBERTa, which is based on the
pre-trained model BERT, have been referred to as be-
ing “state-of-the-art” for AI text detection (Crothers
et al., 2023). The success of this approach is re-
ported in a study which used a supervised Multi-
Layer Perceptron (MLP) algorithm to train RoBERTa,
achieving an accuracy of over 97% on the test dataset.
The dataset was created using URLs shared on Red-
dit, which were passed through GPT-3.5 Turbo for
rephrasing. This study also achieved similar results
using the Text-to-Text Transfer Transformer model
(T5) as a starting point (Chen et al., 2023). Another
study based on an Amazon reviews dataset also found
the RoBERTa model gave a 97% accuracy, the highest
result among those tested (Puttarattanamanee et al.,
2023).
An alternative approach for detecting whether text
has been created by a human or an AI is by train-
ing a purpose-built Machine Learning model. One
study looked at medical abstracts and radiology re-
ports using several different ML techniques, includ-
ing text perplexity, and singular and multiple decision
trees. Perplexity is defined as the exponentiation of
the entropy of the text, giving an intuitive measure of
the uncertainty in word choice. This study also used
one LLM, a pre-trained BERT model. Their results
showed that ChatGPT created text which had a rela-
tively lower perplexity (was more predictable) com-
pared with human-written text. Nonetheless, perplex-
ity gave the worst results compared with the other
methods in this study, (with similar poor results for
the singular decision tree). The multiple decision tree
achieved a percentage F1 score of nearly 90% for
both datasets. The pre-trained BERT model still out-
performed all other approaches with F1 scores above
95% for both datasets (Liao et al., 2023).
Another study by Islam et al tested eleven differ-
ent Machine Learning models, with a multiple tree
model performing best with an accuracy of 77%. The
dataset for this study used a combination of news ar-
ticles from CNN and data scraped from the question-
and-answer website Quora (Islam et al., 2023).
Support Vector Machine (SVM) models have
demonstrated success in distinguishing between
human-written and AI-generated text. A study which
looked at identifying fake news on social media
achieved 98% accuracy, the highest result for all mod-
els tested within the experiments, using SVM algo-
rithms (Sudhakar and Kaliyamurthie, 2024). An-
other study, investigating SVM models to detect fake
news, also achieved an accuracy of approximately
98% when the title and first 1000 characters of the
article were used in testing (Altman et al., 2021).
An experiment comparing logistic regression with
a Na
¨
ıve Bayes algorithm, where the dataset fo-
cused on identifying fake news, found the logistic
regression algorithm performed better with an accu-
racy of 98.7% (Sudhakar and Kaliyamurthie, 2022).
The use of statistical-based techniques has also been
shown as a promising approach, such as “GPT-Who”,
which uses a logistic regression classifier to map
extracted Uniform Information Density (UID) fea-
tures. The hypothesis of UID is that humans prefer
evenly spreading information without sudden peaks
and troughs. This detector performed better than
other statistical based detectors, and at the same level
as fine-tuned transformer-based methods (Venkatra-
man et al., 2023).
2.4 Detection of Automatically
Generated Creative Fiction
Prior studies addressed various domains includ-
ing: medical-related text (Hamed and Wu, 2023;
Habibzadeh, 2023), student submissions (Orenstrakh
et al., 2023; Walters, 2023; Elkhatat et al., 2023),
and news articles (Islam et al., 2023; Mitchell et al.,
2023), as well as popular websites with user contribu-
tions (Islam et al., 2023; Chen et al., 2023).
Despite concerns about the misuse of AI in the
creative community, we note a considerable lack of
research on detecting artificially generated creative
fiction
1
. A number of studies have investigated use of
1
We will use the term “creative fiction” as we do not
distinguish “genre” fiction from “literary” fiction, but here
we do not consider other forms of creative writing such as
lyrics, screenplays, and poetry.
Using Machine Learning to Distinguish Human-Written from Machine-Generated Creative Fiction
81

generative AI to assist writers (Ippolito et al., 2022;
Landa-Blanco et al., 2023; Guo et al., 2024; Gero,
2023; Stojanovic et al., 2023). While this may raise
literary questions regarding quality of writing, and
philosophical considerations of the nature of human
creativity, it does not directly threaten the livelihood
of creative writers. Wholesale generation of entire
novels is another matter. In 2024, the Authors’ Guild
noted the prevalence of “sham books” for sale on
Amazon (The Authors Guild, 2024), and some high-
profile stars signed an open letter requesting technol-
ogy companies to pledge protection for human artists’
work (Robins-Early, 2024).
We do not expect that detectors trained on other
domains will work well with creative fiction; indeed,
one study demonstrated a 20% reduction in effective-
ness across different sources within a single domain
(fake news) (Janicka et al., 2019).
The only study found in the literature address-
ing the detection of artificially generated creative fic-
tion was the Ghostbuster study (which also included
two other domains) (Verma et al., 2023). However,
this study did not use published novels. The creative
writing dataset was created from writing prompts and
their associated stories from Reddit. When there was
no prompt available for a story, first ChatGPT was
given the story and asked to create a prompt, then that
prompt was used to re-create the story.
Ghostbuster is a sophisticated and effective model,
created in three steps: each document was first fed
into weaker language models to retrieve word proba-
bilities, which were then combined into a set of fea-
tures by searching over vector and scalar functions.
The resulting features were used in a linear classi-
fier. In the full Ghostbuster trial, the creative writing
dataset performed well, but worse (F1 = 98.4%) than
two other more commonly used types of datasets, fake
news and student essays (both F1 = 99.5%). This sug-
gests that it may be more difficult to distinguish AI-
generated creative writing compared with other con-
tent types, underlining the need for further research in
this area.
Additionally, this study attempted to address brit-
tleness seen in other detectors’ inability to generalise
across different LLMs. Ghostbuster outperformed
other models tested, but still showed a 6.8% F1 de-
crease when analysing text from another LLM com-
pared to ChatGPT.
2.5 Aims of this Research
Having noted the concerns of the creative community,
and the lack of research on detecting artificially gen-
erated creative fiction, we investigate the use of ML
classifiers for this task, using only short samples of
text. We take this approach as:
• Earlier research has shown that ML models can be
effective in detecting other types of AI-generated
content.
• As LLMs are rapidly evolving, and often propri-
etary, we do not wish to depend on the technology
we are trying to detect.
• A useful detector should be able to run indepen-
dently with relatively low resources, so it could
be deployed easily in the workflow of reviewers,
editors, and publishers.
Additionally, we make a first comparison of the
effectiveness of a ML-based classifier versus human
judgment in identifying artificially generated prose.
3 EXPERIMENTAL METHOD
Our broad approach is to chop human-written detec-
tive novels into a sequence of excerpts, then to gen-
erate similar texts using ChatGPT-3.5 Turbo, both by
rewriting existing excerpts and by using a customised
prompt only (with no excerpt provided as an exam-
ple). The generated texts undergo just enough data
preparation to ensure there are no obvious “tells” flag-
ging their provenance. We then attempt to train ML
classifier systems to distinguish the human-written
from the machine-generated texts. We also compare
the accuracy of the best classifiers with samples taken
from two unseen novels, one by a different author, for
insight into how well the models can generalise. We
further compare the classifiers’ success with that of 19
human judges who had attempted to make the same
determination for a small selection of text samples in
an online quiz.
We focus on short text samples, as these have
proved difficult to detect in prior studies, and with
a view to eventually creating a lightweight tool that
could spot-check individual sections of text during the
editing/publishing process.
3.1 Datasets and Data Preparation
For the human-written prose, we used out-of-
copyright novels by Agatha Christie from Project
Gutenberg (https://www.gutenberg.org), as these are
well-known, and the language is not too old-
fashioned. Three novels
2
were used in the base
(human-written) dataset, creating 1424 excerpts,
2
“The Murder on the Links”, “Poirot Investigates” &
“The Man in the Brown Suit”.
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
82

adding three more
3
in the extended base dataset (2713
excerpts). Furthermore, one unseen Agatha Christie
novel and one novel by another writer, Dorothy L
Sayers
4
, were used to investigate the ability of the
classifier to generalise to unseen but broadly similar
text.
A Python script was used to create our base data
set, by chopping the novels into a sequence of ex-
cerpts of the desired length, always terminating on a
full stop
5
, and removing extraneous text such as page
numbers. In these experiments, all excerpts were of
length “approximately 100 words”, as described be-
low. The texts were vectorised without pre-processing
using Scitkit-Learn’s CountVectorizer.
The AI-generated texts were produced in two
ways: (1) by asking ChatGPT to rewrite a sample
from the base dataset of novel excerpts, and (2) by
asking it to write a similar text based on a prompt,
with no sample text provided. Using a Python script,
all requests were sent to OpenAI’s API in a ran-
domised order; one text excerpt was generated or
rewritten per API request. We expect more robust re-
sults from the rewrites datasets, where we were able
to generate many more texts than in the prompt-only
datasets, but we are still able to compare the two
approaches. For detection experiments, the gener-
ated texts in each dataset were mixed with the same
number of human-written excerpts randomly selected
from a base dataset.
To enable a fair comparison of the models, 80%
of the base dataset was used as the training / test set –
this was split as 70% training and 30% test – and the
other 20% was held back as an unseen validation set.
The generated datasets used are summarised in Table
1.
3.2 OpenAI API Settings
The temperature setting and prompt wording used for
the AI-generated text were derived by extensive trial-
and-error over many iterations, arriving at a prompt
which produced text with no obvious tells that it had
been artificially generated. We noted that too long or
specific a prompt sometimes resulted in some require-
ments being ignored. Lower temperatures generated
less varied text; in particular, rewritten excerpts often
just had a few word substitutions. Too high a temper-
ature resulted in text too unlike the target material.
The final OpenAI API settings are shown below:
3
“The Mysterious Affair at Styles”, “The Big Four” &
“The Secret Adversary”.
4
“The Secret of the Chimneys” & “Whose Body?”
5
Terminating on other symbols such as ? and ! did not
give reliable results.
• model=“gpt-3.5-turbo-0125”
• temperature=0.7
• prompt = “You will take the role of an author of
crime novels. A text excerpt will be provided, you
have to review it for number of space characters
and key details. Create a new text excerpt which
contains the same key details but appears struc-
turally different to the original. The new text must
have approximately the same number of spaces as
the original. Only return the new text passage. Do
not include place holders, line breaks or any other
text except the new passage. Text excerpt:”
3.3 Text Excerpt Length Distribution
The lengths of excerpts in the base datasets vary
somewhat due to the requirement of separating
chunks at a full stop. The OpenAI API did not prove
accurate in generating texts of a required length, al-
though there was some modest improvement by re-
questing a particular number of spaces, rather than
number of words. Moreover, the API showed a pref-
erence towards generating shorter texts rather than
longer. Figure 1 shows how the distribution of char-
acter length is significantly different between the base
and generated datasets when the expectation was to
target approximately 600 characters (100 words).
With a difference in mean length of 42 characters,
and a large jump in standard deviation (68 vs. 120),
the length distribution raised a problem as it could
bias the classification. This issue was addressed in
two steps. For the human-written text preparation,
the text was cut (at the nearest full stop) to a ran-
domly selected length within a defined range; and for
all datasets, outliers were removed to reduce the varia-
tions in length. The resultant “balanced” datasets had
excerpts of the same mean length (563 characters) and
much closer standard deviations (61 vs. 81). All ex-
periments reported here were run on these balanced
datasets.
3.4 Models Tested
We tested six ML models from Scikit Learn
(https://scikit-learn.org), based on their earlier use in
detecting generated text in other domains. These
were: Support Vector Machine, Logistic Regression,
Random Forest, MLP Classifier, Decision Tree and
Na
¨
ıve Bayes. The inclusion of a single decision tree
is to allow comparison with the Random Forest (mul-
tiple decision trees), and the decision to include Na
¨
ıve
Bayes was based on its known ability in text classifi-
cation tasks, where it is computationally efficient and
Using Machine Learning to Distinguish Human-Written from Machine-Generated Creative Fiction
83
Table 1: Description of generated data sets.
Data Set
Reference
Description Type of AI
generation
Total No.
examples
AC3Train Training data separated out from a base data set created using 3
Agatha Christie books where human text was excerpts split out
from the novels at approx. 100 word excerpts and the AI text was
created using rewrites of the human text via the OpenAI API.
Rewrites 1595
AC3Test Test data separated out from a base data set created using 3
Agatha Christie books where human text was excerpts split out
from the novels at approx. 100 word excerpts and the AI text was
created using rewrites of the human text via the OpenAI API.
Rewrites 683
AC3Unseen Unseen data separated out from a base data set created using 3
Agatha Christie books where human text was excerpts split out
from the novels at approx. 100 word excerpts and the AI text was
created using rewrites of the human text via the OpenAI API.
Rewrites 570
AC6Train Training data separated out from a base data set created using 6
Agatha Christie books where human text was excerpts split out
from the novels at approx. 100 word excerpts and the AI text was
created using rewrites of the human text via the OpenAI API.
Rewrites 3038
AC6Test Test data separated out from a base data set created using 6
Agatha Christie books where human text was excerpts split out
from the novels at approx. 100 word excerpts and the AI text was
created using rewrites of the human text via the OpenAI API.
Rewrites 1302
AC6Unseen Unseen data separated out from a base data set created using 6
Agatha Christie books where human text was excerpts split out
from the novels at approx. 100 word excerpts and the AI text was
created using rewrites of the human text via the OpenAI API.
Rewrites 1086
ChatGPTAC1 ChatGPT was used with the prompt “please write a story about
a detective in the style of agatha christie”, after each response
from ChatGPT, another prompt would be sent to ask for another
story until there was enough text to create 10 text excerpts of
approx. 100 words. For this dataset 10 text excerpts from the
AC3 Data set were used as human text samples.
Prompt-Only
(no text
provided)
20
ChatGPTGC1 ChatGPT was used here to request a generic crime novel from
the same time period (1920s) to be written. This time it was writ-
ten in chapters and prompts were used to encourage ChatGPT to
keep writing until enough text was available. This dataset has
12 approx. 100 word text excerpts from AI generation and again
human text from another dataset (DLS1) was used to provide 12
human written samples.
Prompt-Only
(no text
provided)
24
DAC1 Created using a different Agatha Christie Novel “The Secret of
Chimneys” – This dataset was created in the same way as the
other datasets for this project.
The text was split into approx. 100 word chunks to the closest
full sentence and the text excerpts were sent through the OpenAI
API to be re-written. 100 random samples were extracted from
the original human set and from the results from the API.
Rewrites 200
DLS1 Whose Body? A Lord Peter Wimsey Novel by Dorothy L. Say-
ers (1923) – This is a novel from a crime author which was writ-
ten around the same time as the Agatha Christie novels. Again
100 samples from the original human text were used along with
100 results from the OpenAI API, completely randomised.
Rewrites 200
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
84
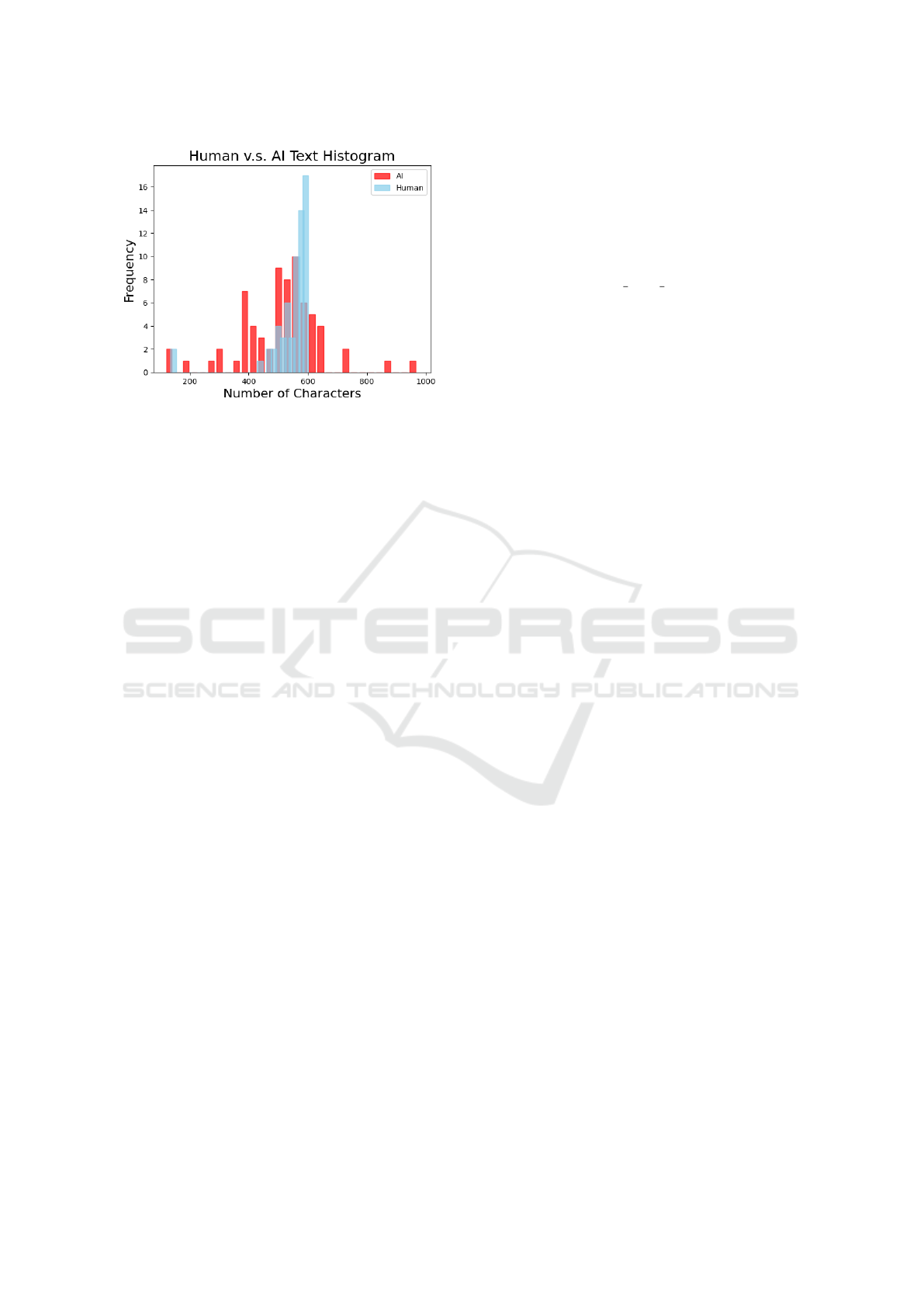
Figure 1: Distribution of character lengths for Human-
written and AI-generated text.
often exhibits a good predictive performance (Chen
et al., 2009).
3.5 Experimental Runs
An initial experiment on all six models with the
three-novel datasets identified the MLP and the Na
¨
ıve
Bayes models as the best performing. These two
models were then optimised and carried forward for
testing against all the AI-generated datasets, with a
follow-on run for these two models where the training
data was increased to six novels. Lastly, to investi-
gate generalisability of the classifiers, we tested them
against excerpts from two previously unseen novels,
one by Agatha Christie, and one of similar style from
a different author, Dorothy L Sayers.
4 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
4.1 Model Comparison
Table 2 summarises results comparing the models
trained on the AC3Train dataset and tested using the
AC3Test and AC3Unseen datasets.
The MLP Classifier and Na
¨
ıve Bayes models per-
formed best overall, while the SVM and Logistic Re-
gression models also gave good results. As expected,
the decision tree model performed the worst with all
results lower than 80%; the random forest model per-
formed better, but still significantly below the other
models.
Based on the results for the AC3Test dataset, it
would be expected that the MLP Classifier would per-
form better than the Na
¨
ıve Bayes for the AC3Unseen
dataset. The results, however, were the same for both
models. On inspection, it was found that generally the
same samples in the AC3Unseen set were mislabelled
by both models.
The MLP Classifier and Na
¨
ıve Bayes models were
tuned and carried forward for further experimenta-
tion. Of the many tunable hyper-parameters of the
MLP model, the only change that improved accuracy
was setting the hidden layer sizes to one layer with
155 units: this enabled the accuracy to exceed the
95% mark and the F1 score was slightly improved
also. For the Na
¨
ıve Bayes model, the highest accuracy
for the AC3Test data set was achieved by the multino-
mial algorithm using an alpha value of 0.7.
The results of the tuned models are shown in Table
3. Both classifiers show similar results on the rewrites
datasets AC3Test and AC3Unseen, with more varia-
tion in the results for the prompt-only datasets Chat-
GPTGC1 and ChatGPTAC1. We note that for rewrit-
ten texts, precision exceeds recall, while the inverse
obtains for the the prompt-only datasets. This im-
plies some qualitative difference resulting from the
two methods used for generating the texts with GPT.
4.2 Six-Novel Data Experiments
The results of the experiments using increased train-
ing data with the optimised models are shown in Ta-
ble 4. For the Na
¨
ıve Bayes model, all but one test set
saw an increase in scores with the six-novel dataset
AC6train, and for the MLP Classifier model, an im-
provement in several tests was also observed.
The larger training dataset significantly improved
the discrimination of both models. The average
accuracy across all tests for the MLP Classifier is
now 96.09% (previously 92.76%) compared with the
Na
¨
ıve Bayes which now has an average accuracy of
96.05% (previously 94.34%). Looking at the per-
centage F1 scores, the MLP Classifier achieved an
average of 96.02% (previously 92.74%) compared
with the Na
¨
ıve Bayes which now has an average F1
score of 95.94% (previously 94.11%). Both classi-
fiers achieved 100% accuracy for the ChatGPTAC1
dataset, rising from 85% and 95% previously. Al-
though this is still a small test dataset, reaching the
100% score as a result of doubling the training data
gives some confidence in the result.
However, two datasets did show minor reductions
in accuracy. The only model whose score was reduced
by more then 1% was Na
¨
ıve Bayes, falling to 95.83%
on the prompted “generic crime novel” dataset Chat-
GPTGC1. This may be a result of overfitting on the
previous smaller dataset. However, the overall im-
provements with the larger training dataset show it is
clearly beneficial overall.
Using Machine Learning to Distinguish Human-Written from Machine-Generated Creative Fiction
85
Table 2: Model comparison using six models and three-novel datasets.
Model AC3Test Accuracy AC3Unseen Accuracy AC3Test F1 Score AC3Unseen F1 Score
Na
¨
ıve Bayes Multinomial 93.42% 92.98% 92.63% 92.39%
SVM 92.84% 92.52% 91.75% 91.77%
Logistic Regression 92.98% 92.73% 91.40% 91.54%
Decision Tree 71.93% 71.00% 76.49% 77.59%
MLP Classifier 94.74% 94.50% 92.81% 92.67%
Random Forest 88.01% 86.90% 90.00% 89.84%
Table 3: Results from the two top-performing models following optimisation and trained using data from three novels.
Dataset Model Accuracy Precision Recall F1
AC3Test MLP Classifier 95.03% 96.89% 92.86% 94.83%
AC3Test Na
¨
ıve Bayes 93.86% 97.12% 90.18% 93.52%
AC3Unseen MLP Classifier 92.28% 94.14% 90.18% 92.11%
AC3Unseen Na
¨
ıve Bayes 92.28% 94.80% 89.47% 92.06%
ChatGPTGC1 MLP Classifier 95.83% 92.31% 100.00% 96.00%
ChatGPTGC1 Na
¨
ıve Bayes 100.00% 100.00% 100.00% 100.00%
ChatGPTAC1 MLP Classifier 85.00% 81.82% 90.00% 85.71%
ChatGPTAC1 Na
¨
ıve Bayes 95.00% 90.91% 100.00% 95.24%
4.3 Generalisation Experiments
Testing against previously unseen novels gave encour-
aging results, shown in Table 5. For the DAC1 dataset
(an unseen novel by the same author), accuracy was
over 90% on all runs; the MLP Classifier performed
better than Na
¨
ıve Bayes, with recall being the main is-
sue for both models. For the DLS1 dataset (an unseen
novel by a different author), the results were compa-
rable or better for both models compared with seen
novels. For the MLP Classifier, the accuracy of the
DLS1 dataset at 95.41% is extremely close to that of
the AC6Unseen set (95.67%). For the Na
¨
ıve Bayes
model, the DLS1 dataset at 95.92% accuracy actually
performs better than the AC6Unseen set (95.03%).
Although this higher score on an unseen novel may
not be significant, it is clear that the models can gen-
eralise well, at least over the same genre of creative
fiction.
4.4 Model Runtimes
The time for completion for the Na
¨
ıve Bayes model
was 5 seconds for the original training/test/validation
set and 8 seconds for the increased training dataset.
However, the MLP Classifier took considerably
longer with 38 seconds for the original set and 61 sec-
onds for the larger set.
As the results of the two optimised classifiers were
close in terms of accuracy and F1 scores, the much
faster run time for the Na
¨
ıve Bayes model recom-
mends this as the better selection for the classification
tool described in Section 6.
4.5 ChatGPT-4o
Since our original experiments, ChatGPT-4 has been
released. We conducted a mini-experiment, using an
unchanged training set and new test sets of randomly
selected novel excerpts. There was a slight drop in
performance when using “gpt-4o-mini” (average ac-
curacy 94.25% compared with the original 95.03%).
A larger drop was observed using “GPT-4o” (average
accuracy 89.25%). We will conduct more extensive
experiments, but we note the drop in performance is
modest given the huge number of parameters in GPT
version 4.
5 DETECTION BY HUMAN
JUDGES
To determine whether the excerpts generated by
ChatGPT could easily be detected upon read-
ing, a small quiz was set up in Google Doc-
uments. This displayed 10 text excerpts that
were either taken from the human-written nov-
els or the AI-rewritten text. A total of 19 peo-
ple completed the quiz, which is available here:
https://forms.gle/JhApKWkC9CAHXRmo8. Only 10
examples were included, to encourage completion, as
the main purpose of the quiz was just to ensure no
obvious tells had been overlooked during data prepa-
ration, allowing too-easy classification of the texts. A
larger survey would be required for robust analysis;
nonetheless, we see some interesting results.
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
86
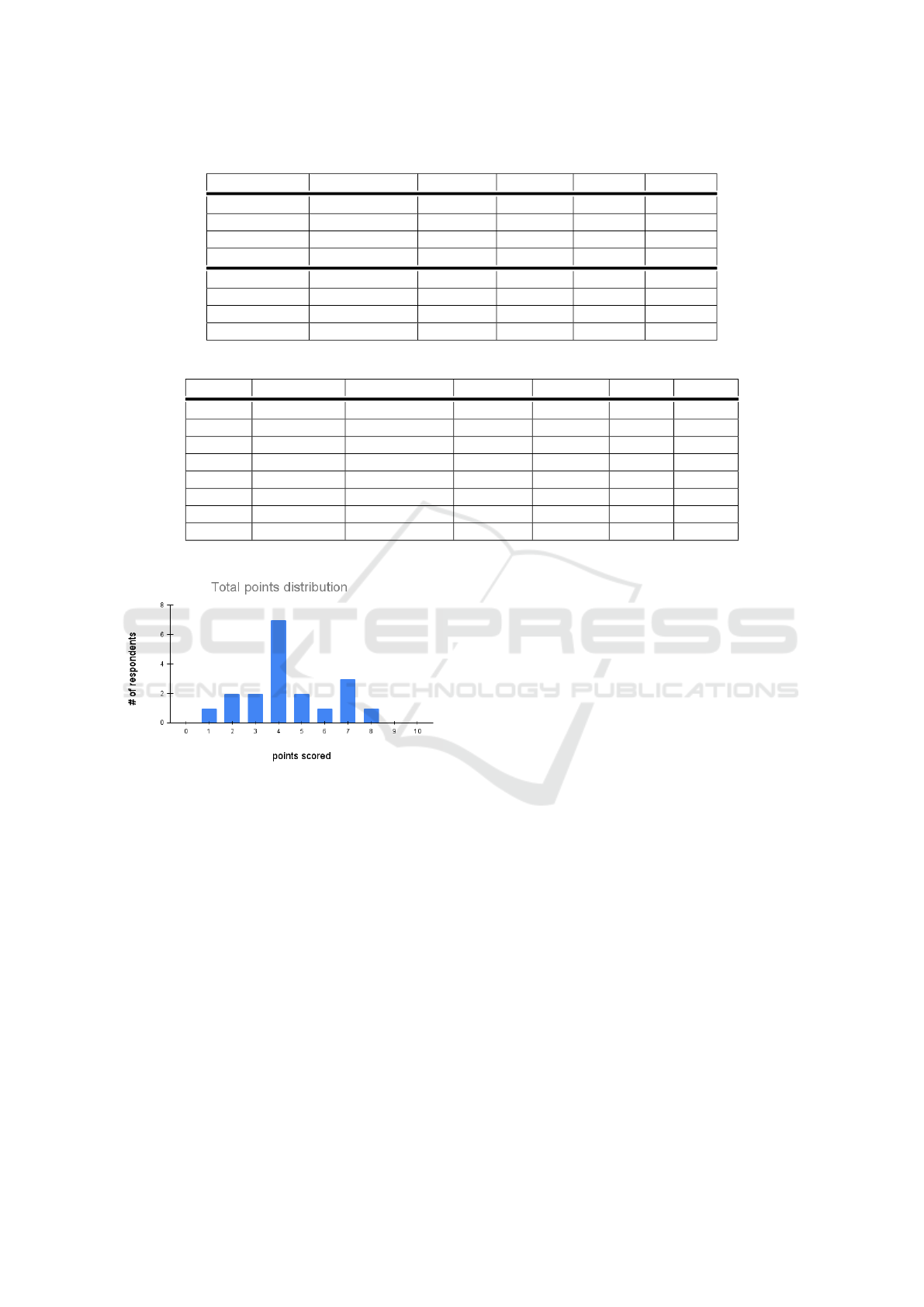
Table 4: Results from the two top-performing models trained using data created from six novels (increased training data).
Dataset Model Accuracy Precision Recall F1
AC6Test MLP Classifier 94.62% 95.97% 92.98% 94.45%
AC6Test Na
¨
ıve Bayes 95.01% 98.48% 91.26% 94.74%
AC6Unseen MLP Classifier 95.67% 97.51% 93.74% 95.59%
AC6Unseen Na
¨
ıve Bayes 95.03% 97.48% 92.45% 94.90%
ChatGPTGC1 MLP Classifier 95.83% 92.31% 100.00% 96.00%
ChatGPTGC1 Na
¨
ıve Bayes 95.83% 92.31% 100.00% 96.00%
ChatGPTAC1 MLP Classifier 100.00% 100.00% 100.00% 100.00%
ChatGPTAC1 Na
¨
ıve Bayes 100.00% 100.00% 100.00% 100.00%
Table 5: Experimental results from the two top performing models on unseen novels.
Dataset TrainingSet Model Accuracy Precision Recall F1
DAC1 AC3Train MLP Classifier 92.50% 98.85% 86.00% 91.98%
DAC1 AC3Train Na
¨
ıve Bayes 90.50% 98.80% 82.00% 89.62%
DLS1 AC3Train MLP Classifier 95.92% 98.91% 92.86% 95.79%
DLS1 AC3Train Na
¨
ıve Bayes 94.39% 96.77% 91.84% 94.24%
DAC1 AC6Train Na
¨
ıve Bayes 94.50% 100.00% 89.00% 94.18%
DAC1 AC6Train MLP Classifier 95.00% 98.91% 91.00% 94.79%
DLS1 AC6Train Na
¨
ıve Bayes 95.92% 97.87% 93.88% 95.83%
DLS1 AC6Train MLP Classifier 95.41% 97.85% 92.86% 95.29%
Figure 2: Distribution of points scored on a Human vs. AI
quiz.
The judges’ scores were normally distributed with
a median score of 4 and a mean of 4.42, as shown in
Figure 2. Thus, the humans showed little ability to
identify the AI-generated texts.
With only 19 judges, we do not have sufficient
data to determine if the results are no better than
chance, but a one-tailed t-test provides good evidence
that the respondents’ ability to distinguish between
the text samples is under 55% in accuracy (t(18) =
−2.5, p-value = 0.01, 95% percent confidence inter-
val: −∞ : 52%), and it is certainly far below the ability
of the ML classifiers.
These results are in line with the literature: for ex-
ample, Clark et al report that untrained human evalua-
tors score no better than chance trying to identify text
from ChatGPT-3 in other domains, with results rising
to 55% with practice (Clark et al., 2021).
6 CLASSIFIER TOOL
The Na
¨
ıve Bayes model was used to create an online
classifier tool, AI Detective, for general experimenta-
tion. The tool is available at: https://tinyurl.com/ai-
detective. This tool used the AC6Train data for train-
ing, and can accept unseen test data and attempt to
classify the input as human-written vs. AI-generated.
The tool can also be used to experiment with different
training and/or test sets: instructions for use are pro-
vided within the Google Colab script. All our code
and data are available for replication and experimen-
tation from the links at this URL.
7 DISCUSSION
7.1 Summary and Review of Findings
Of the six Machine Learning models tested, four gave
promising results with the top two models optimised
and evaluated with multiple test sets. The results
from the best performing models, Na
¨
ıve Bayes and
MLP Classifier, show that it is possible to detect AI-
generated creative writing with high accuracy using
only short text samples. The accuracy scores for
the Na
¨
ıve Bayes model ranged from 94.5% to 100%,
with an average of 96.05%. The MLP Classifier per-
formed with similar accuracy, ranging from 94.62%
to 100% with an average of 96.09%. However, the
Using Machine Learning to Distinguish Human-Written from Machine-Generated Creative Fiction
87

Na
¨
ıve Bayes model was much more efficient, running
in 8 seconds compared with over 1 minute. The av-
erage percentage F1 score across all test sets for the
Na
¨
ıve Bayes model was 95.94% with a range of F1
scores from 94.18% to 100%.
The larger reduction in scores for the MLP Clas-
sifier on the ChatGPTAC1 dataset was unexpected as
this model had been performing well. This suggests
that the training data may be more tightly fitted on the
MLP Classifier model, and therefore it cannot gener-
alise as well as the Na
¨
ıve Bayes model.
Looking at the recall results, the Na
¨
ıve Bayes
model was able to identify all instances of AI text
generated directly from prompts (i.e. not rewritten),
and the MLP Classifier only missed one sample over-
all. For both Na
¨
ıve Bayes and MLP Classifier algo-
rithms, it was more common for AI-generated text to
be incorrectly predicted as human text than vice versa.
Comparing the metrics for the rewritten versus the
prompt-only test datasets, precision and recall show
opposite trends. For text generated from scratch, the
models have higher recall and are therefore identify-
ing more instances of AI text; however, in the rewrites
datasets, the precision is higher. We speculate that
the rewrites may still mirror elements of human text,
making them harder to identify.
The results from both top models show that they
can generalise well to other novels from the same time
period and genre. For the MLP Classifier, the ac-
curacy of the DLS1 dataset, based on the Dorothy
L Sayers novel, was 95.41%, very close to that of
the AC6Unseen set at 95.67%. For the Na
¨
ıve Bayes
model, the DLS1 dataset at 95.92% outperforms the
AC6Unseen set at 95.03% accuracy. How well this
generalisation can extend to other styles of writing re-
mains to be investigated.
7.2 Comparison with Other Work
One study utilising a Na
¨
ıve Bayes model achieved
an accuracy of 94.85% using fake political news data
(Sudhakar and Kaliyamurthie, 2022), somewhat bet-
ter than our AC3 datasets, but outperformed by our
AC6 datasets. Moreover, our results for the MLP
classifier are superior to a previous study which only
achieved 72% (Liao et al., 2023), where the dataset
was created from news and social media content. It
would be interesting to investigate whether differ-
ent classifiers perform better with particular styles of
writing.
Ghostbuster, the only other study to include
datasets derived from creative fiction, achieved an F1
score of 98.4% in this domain (Verma et al., 2023).
While this is higher than the F1 scores reported here,
Ghostbuster’s score is over texts of all lengths. Their
in-domain F1 score drops to around 85% for texts of
100 tokens, and the authors state that performance
“may be unreliable for documents with ≤ 100 to-
kens”. We note also that OpenAI recommended that
AI detectors should use a minimum of 1000 charac-
ters for reliability (see https://platform.openai.com).
Our results suggest therefore that our ML classifier
models may perform better on short text samples, at
least within one style of creative fiction.
Moreover, the Ghostbuster study did not use pub-
lished novels, and their approach was more similar
to the prompt-only datasets tested here. Our average
F1 score for the prompt-only datasets, shown in Ta-
ble 4, reached 98% and therefore is almost as high as
Ghostbuster, despite their using texts of greater aver-
age length.
7.3 Limitations of this Study
In this pilot study, the ML classifiers have been
trained on only one author, and mostly tested on the
same author, with limited testing on one other author
from the same genre and time period.
Moreover, although many LLMs are now avail-
able, only ChatGPT has been used for the AI-
generated texts.
Experiments with more data would increase the
robustness of our results, especially for the prompt-
only datasets. Furthermore, achieving an effective
prompt was harder than expected, and further prompt
engineering may be required to improve the quality of
the AI-generated texts.
Owing to the difficulties in generating texts of a
stipulated length, there is still some difference in the
variance of text length in the datasets used, and other
data-preparation artefacts may remain which could
aid the classifiers. For example, as ChatGPT was re-
quested to review the details of each text passage and
use it to create a new one, the AI-generated rewrites
may appear more “self-contained” compared with the
chunked off parts of a novel appearing in the base
datasets.
We noted also that the AI-generated rewrites
sometimes introduced named entities that were not
present in the original text. Such artefacts of the data
preparation process may have assisted the classifiers
in identifying the automatically generated texts.
At present we have limited evidence that the clas-
sifiers will generalise to other, similar styles of writ-
ing, but it is unclear how far a classifier can generalise
before retraining would be required. These issues will
be addressed in future work.
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
88

8 FUTURE WORK AND
CONCLUSION
Here we present only preliminary results. It remains
to run further tests with more systematically gen-
erated ChatGPT prompts, with larger prompt-only
datasets, with texts of different lengths, and with fur-
ther tuning of the models. We intend especially to
investigate the effect of gradually generalising our un-
seen test data sets to creative fiction increasingly dif-
ferent in style from the training data.
Both the MLP and Na
¨
ıve Bayes classifiers
achieved better accuracy with the prompt-only test
data, compared with the rewritten AC6Unseen
dataset. While this may be an artefact of the differ-
ing sizes of the datasets, the implication is that it may
be easier for the classifiers to identify wholly gener-
ated rather than rewritten text, which we may expect
to mirror the human-authored excerpts more closely.
This is worthy of further investigation.
Expanded experiments with human judges are
also warranted, collecting more data to establish sig-
nificance, and with attention to what characterises ex-
cerpts that are particularly easy/hard to detect, and
to whether particular individuals (perhaps avid read-
ers) have a higher than average ability to distinguish
human-written from AI-generated text. A more devel-
oped version of the classifier tool may support train-
ing humans in this skill.
Nonetheless, our early results indicate that it is
possible for a low-resource classifier to detect artifi-
cially generated creative fiction with a high degree of
accuracy, based only on a short sample of the text.
This opens the door to the construction and deploy-
ment of easily used tools for editors and publishers,
helping to protect the economic and cultural contri-
bution of human writers in the age of generative AI.
REFERENCES
Altman, B., Kim, R., Spear, R., and Spychalski, J. (2021).
Detecting Fake News Using Support Vector Ma-
chines. https://tinyurl.com/altman-2021.
Barclay, P. and Sami, A. (2024). Investigating Mark-
ers and Drivers of Gender Bias in Machine Transla-
tions. In Proceedings of SANER24, pages 455 – 464,
Rovaniemi, Finland. IEEE.
Bas, A., Topal, M. O., Duman, C., and van Heerden, I.
(2022). A brief history of deep learning-based text
generation. In 2022 International Conference on
Computer and Applications (ICCA), pages 1–4.
Botha, J. and Pieterse, H. (2020). Fake news and deepfakes:
A dangerous threat for 21st century information secu-
rity. In ICCWS 2020 15th International Conference on
Cyber Warfare and Security. Academic Conferences
and publishing limited, page 57.
Chen, J., Huang, H., Tian, S., and Qu, Y. (2009). Feature
selection for text classification with Na
¨
ıve Bayes. Ex-
pert Systems with Applications, 36(3):5432–5435.
Chen, Y., Kang, H., Zhai, V., Li, L., Singh, R.,
and Raj, B. (2023). GPT-sentinel: Distin-
guishing human and ChatGPT generated content.
http://arxiv.org/abs/2305.07969.
Clark, E., August, T., Serrano, S., Haduong, N., Gururan-
gan, S., and Smith, N. A. (2021). All That’s ’Human’
Is Not Gold: Evaluating Human Evaluation of Gener-
ated Text. http://arxiv.org/abs/2107.00061.
Crothers, E. N., Japkowicz, N., and Viktor, H. L. (2023).
Machine-generated text: A comprehensive survey of
threat models and detection methods. IEEE Access,
11:70977–71002.
Devlin, J., Chang, M.-W., Lee, K., and Toutanova,
K. (2019). BERT: Pre-training of deep bidi-
rectional transformers for language understanding.
http://arxiv.org/abs/1810.04805.
Elkhatat, A. M., Elsaid, K., and Almeer, S. (2023). Evaluat-
ing the efficacy of AI content detection tools in differ-
entiating between human and AI-generated text. Inter-
national Journal for Educational Integrity, 19(1):1–
16. Number: 1 Publisher: BioMed Central.
Feng, S., Park, C. Y., Liu, Y., and Tsvetkov, Y. (2023). From
pretraining data to language models to downstream
tasks: Tracking the trails of political biases leading
to unfair NLP models. In Proceedings of the 61st
Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational
Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers), pages 11737–
11762. Association for Computational Linguistics.
Floridi, L. and Chiriatti, M. (2020). GPT-3: Its nature,
scope, limits, and consequences. Minds and Ma-
chines, 30(4):681–694.
Gero, K. I. (2023). AI and the Writer: How Language Mod-
els Support Creative Writers. Columbia University.
Goyal, R., Kumar, P., and Singh, V. P. (2023). A systematic
survey on automated text generation tools and tech-
niques: application, evaluation, and challenges. Mul-
timedia Tools and Applications, 82(28):43089–43144.
Grynbaum, M. M. and Mac, R. (2023). The times sues
OpenAI and microsoft over A.I. use of copyrighted
work. The New York Times.
Guo, A., Pataranutaporn, P., and Maes, P. (2024). Explor-
ing the Impact of AI Value Alignment in Collaborative
Ideation: Effects on Perception, Ownership, and Out-
put. http://arxiv.org/abs/2402.12814.
Habibzadeh, F. (2023). GPTZero performance in identify-
ing artificial intelligence-generated medical texts: A
preliminary study. Journal of Korean Medical Sci-
ence, 38(38):e319.
Hamed, A. A. and Wu, X. (2023). Improving de-
tection of ChatGPT-generated fake science
using real publication text: Introducing xFake-
Bibs a supervised-learning network algorithm.
http://arxiv.org/abs/2308.11767.
Han, X., Zhang, Z., Ding, N., Gu, Y., Liu, X., Huo, Y., Qiu,
J., Yao, Y., Zhang, A., Zhang, L., Han, W., Huang,
Using Machine Learning to Distinguish Human-Written from Machine-Generated Creative Fiction
89

M., Jin, Q., Lan, Y., Liu, Y., Liu, Z., Lu, Z., Qiu, X.,
Song, R., Tang, J., Wen, J.-R., Yuan, J., Zhao, W. X.,
and Zhu, J. (2021). Pre-trained models: Past, present
and future. AI Open, 2:225–250.
Ippolito, D., Yuan, A., Coenen, A., and Burnam, S.
(2022). Creative Writing with an AI-Powered Writ-
ing Assistant: Perspectives from Professional Writers.
http://arxiv.org/abs/2211.05030.
Islam, N., Sutradhar, D., Noor, H., Raya, J. T., Maisha,
M. T., and Farid, D. M. (2023). Distinguishing human
generated text from ChatGPT generated text using
machine learning. http://arxiv.org/abs/2306.01761.
Janicka, M., Pszona, M., and Wawer, A. (2019). Cross-
domain failures of fake news detection. Computaci
´
on
y Sistemas, 23(3):1089–1097. Publisher: Insti-
tuto Polit
´
ecnico Nacional, Centro de Investigaci
´
on en
Computaci
´
on.
Jawahar, G., Abdul-Mageed, M., and Lakshmanan,
L. V. S. (2020). Automatic detection of
machine generated text: A critical survey.
http://arxiv.org/abs/2011.01314.
Koplin, J. J. (2023). Dual-use implications of AI text gen-
eration. Ethics and Information Technology, 25(2):32.
Landa-Blanco, M., Flores, M. A., and Mercado, M. (2023).
Human vs. AI Authorship: Does it Matter in Evaluat-
ing Creative Writing? A Pilot Study Using ChatGPT.
https://tinyurl.com/landa-2023.
Liao, W., Liu, Z., Dai, H., Xu, S., Wu, Z., Zhang, Y., Huang,
X., Zhu, D., Cai, H., Liu, T., and Li, X. (2023). Differ-
entiate ChatGPT-generated and human-written medi-
cal texts. http://arxiv.org/abs/2304.11567.
Mitchell, E., Lee, Y., Khazatsky, A., Manning, C. D., and
Finn, C. (2023). DetectGPT: Zero-shot machine-
generated text detection using probability curvature.
http://arxiv.org/abs/2301.11305.
Odri, G.-A. and Yoon, D. J. Y. (2023). Detecting genera-
tive artificial intelligence in scientific articles: evasion
techniques and implications for scientific integrity.
Orthopaedics & Traumatology: Surgery & Research,
109(8):103706.
Orenstrakh, M. S., Karnalim, O., Suarez, C. A., and Liut,
M. (2023). Detecting LLM-generated text in com-
puting education: A comparative study for ChatGPT
cases. http://arxiv.org/abs/2307.07411.
Oviedo-Trespalacios, O., Peden, A. E., Cole-Hunter, T.,
Costantini, A., Haghani, M., Rod, J. E., Kelly, S.,
Torkamaan, H., Tariq, A., and Newton, J. D. A.
(2023). The risks of using ChatGPT to obtain common
safety-related information and advice. Safety science,
167:106244. Publisher: Elsevier.
Pandey, A. K. and Roy, S. S. (2023). Natural language gen-
eration using sequential models: A survey. Neural
Processing Letters, 55(6):7709–7742.
Puttarattanamanee, M., Boongasame, L., and Thammarak,
K. (2023). A comparative study of sentiment analy-
sis methods for detecting fake reviews in e-commerce.
HighTech and Innovation Journal, 4(2):349–363.
Number: 2.
Robins-Early, N. (2024). Billie Eilish, Nicki Minaj, Ste-
vie Wonder and more musicians demand protection
against AI. https://tinyurl.com/robins-2024.
Salamon, E. (2024). Negotiating Technological Change:
How Media Unions Navigate Artificial Intelligence
in Journalism. Journalism & Communication Mono-
graphs, 26(2):159–163.
Stojanovic, L., Radojcic, V., Savic, S., Sandro, A., and
Cvetkovic, D. S. (2023). The Influence of Artificial
Intelligence on Creative Writing: Exploring the Syn-
ergy between AI and Creative Authorship. Interna-
tional Journal of Engineering Inventions.
Su, J., Zhuo, T. Y., Wang, D., and Nakov, P.
(2023). DetectLLM: Leveraging log rank informa-
tion for zero-shot detection of machine-generated text.
http://arxiv.org/abs/2306.05540.
Sudhakar, M. and Kaliyamurthie, K. P. (2022). Effective
prediction of fake news using two machine learning
algorithms. Measurement: Sensors, 24:100495.
Sudhakar, M. and Kaliyamurthie, K. P. (2024). Detection
of fake news from social media using support vector
machine learning algorithms. Measurement: Sensors,
32:101028.
The Authors Guild (2024). AI Is Driving a New Surge of
Sham “Books” on Amazon. https://tinyurl.com/sham-
2024.
Vaswani, A. (2017). Attention is all you need. Advances in
Neural Information Processing Systems.
Venkatraman, S., Uchendu, A., and Lee, D.
(2023). GPT-who: An information density-
based machine-generated text detector.
http://arxiv.org/abs/2310.06202.
Verma, V., Fleisig, E., Tomlin, N., and Klein, D. (2023).
Ghostbuster: Detecting text ghostwritten by large lan-
guage models. In Proceedings of the 2024 Conference
of the North American Chapter of the Association for
Computational Linguistics: Human Language Tech-
nologies (Volume 1: Long Papers), pages 1702–1717.
Association for Computational Linguistics.
Wach, K., Doanh Duong, C., Ejdys, J., Kazlauskait
˙
e, R.,
Korzynski, P., Mazurek, G., Paliszkiewicz, J., and
Ziemba, E. (2023). The dark side of generative arti-
ficial intelligence: A critical analysis of controversies
and risks of ChatGPT. Entrepreneurial Business and
Economics Review, pages 7–30. Num Pages: 7-30
Publisher: Cracow University of Economics.
Walters, W. H. (2023). The effectiveness of software de-
signed to detect AI-generated writing: A comparison
of 16 AI text detectors. Open Information Science,
7(1). Publisher: De Gruyter Open Access.
Zaitsu, W. and Jin, M. (2023). Distinguishing
ChatGPT(-3.5, -4)-generated and human-written pa-
pers through Japanese stylometric analysis. PLoS
One, 18(8):e0288453.
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
90
