
A Serious Game for Early Detection and Assessment of Social Apathy: A
Pilot Study
Cristina D
´
ıez Bort
1,2 a
, Razeen Hussain
1 b
, Valeria Manera
3 c
, Manuela Chessa
1 d
and Fabio Solari
1 e
1
DIBRIS, University of Genoa, Genoa, Italy
2
School of Aerospace Engineering and Industrial Design, Universitat Polit
`
ecnica de Val
`
encia, Valencia, Spain
3
CoBTeK Laboratory, Universit
´
e C
ˆ
ote d’Azur, Nice, France
Keywords:
Apathy, Serious Games, Mild Cognitive Impairment, Human Computer Interaction.
Abstract:
With increasing life expectancy, the prevalence of age-related disorders such as dementia, often preceded by
mild cognitive impairment (MCI), has risen significantly. Among the early signs of cognitive decline, social
apathy stands out as a key indicator, associated with an increased risk of progression to dementia. In this
context, we present ApathySEED, a serious game developed to assess social apathy in individuals with MCI.
The game uses decision-making in social scenarios to evaluate apathy across initiative, interest, and emotion
subdomains. A pilot study involving 33 healthy participants was conducted to validate the game’s usability and
effectiveness as a tool for assessing social apathy. Standardized questionnaires, including SUS, NASA-TLX,
and AMI, were used to measure game performance, cognitive load, and apathy levels. Results suggest that
ApathySEED is a promising tool for apathy assessment, with low cognitive load and high usability, making it
suitable for future clinical utilization.
1 INTRODUCTION
Mild cognitive impairment (MCI) is a common con-
dition among the elderly, bridging normal aging and
more severe cognitive decline, such as Alzheimer’s
disease (AD). It involves memory and attention
deficits without major impact on daily life. With no
cure for AD or dementia, early detection is vital (Et-
gen et al., 2011). Social apathy, marked by reduced
interest and engagement in interactions, is a key MCI
indicator and linked to a higher risk of progression
to AD (Kazui et al., 2017). Early detection of social
apathy could help delay or prevent severe cognitive
decline.
Traditional methods for assessing apathy, like
clinical interviews and paper-based questionnaires,
often struggle to capture real-life social engagement
and can introduce bias through subjective reporting.
Digital and gamified approaches offer a more inter-
active and objective alternative, allowing for scalable,
user-driven assessments without needing trained per-
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3631-3458
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7579-5069
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4490-4485
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3098-5894
e
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8111-0409
sonnel. This improves accessibility and engagement,
leading to more accurate and ecologically valid re-
sults compared to traditional methods (Tong et al.,
2014).
In this work, we introduce ApathySEED (SErious
game for Early Detection), a novel serious game de-
veloped to assess social apathy in patients with MCI.
Serious games, designed for purposes beyond enter-
tainment, have gained traction in healthcare for diag-
nosis, rehabilitation, and cognitive training (Chessa
et al., 2024). Effective serious games in health-
care must integrate more than just biomedical con-
tent—they must also prioritize usability, accessibil-
ity, and aesthetic appeal to engage users, particularly
older adults (Khalili-Mahani et al., 2019).
The contributions of our study are multi-faceted.
First, ApathySEED provides an innovative alterna-
tive to paper-based assessments for social apathy in
MCI, with a design tailored for elderly users. A pi-
lot study demonstrated its effectiveness and correla-
tion with traditional tools, showcasing its potential
for reliable, complementary data. The game also en-
ables early detection, supporting timely interventions
to prevent further cognitive decline. Finally, its intu-
itive design and visually appealing elements enhance
user engagement, improving both the user experience
and the efficacy of cognitive evaluations in healthcare.
Bort, C. D., Hussain, R., Manera, V., Chessa, M. and Solar i, F.
A Serious Game for Early Detection and Assessment of Social Apathy: A Pilot Study.
DOI: 10.5220/0013119700003912
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 20th International Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications (VISIGRAPP 2025) - Volume 1: GRAPP, HUCAPP
and IVAPP, pages 543-550
ISBN: 978-989-758-728-3; ISSN: 2184-4321
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
543

2 RELATED WORKS
Currently, there are several tests available for screen-
ing MCI (Tsoi et al., 2015), with the choice of test
largely depending on various factors such as the ad-
ministering expert’s familiarity with the tool, time
constraints, or the test’s perceived accuracy. Despite
this variety, there is a notable lack of standardization
in terms of accepted tests and scoring criteria, which
can affect the reliability of the results.
Several tests specifically designed for MCI diag-
nosis, such as the Memory Alteration Test (M@T)
(Rami et al., 2007) and Montreal Cognitive Assess-
ment (MoCA) (Nasreddine et al., 2005), are widely
used in psycho-geriatric settings for initial cognitive
evaluations (Chen et al., 2021b). While they as-
sess broad cognitive domains, they require profes-
sional administration and may not fully capture spe-
cific deficits like social apathy.
Apathy often coexists with other clinical syn-
dromes, such as depression, fatigue, and anhedonia.
Recently, the diagnostic criteria for apathy in brain
disorders have been updated (Robert et al., 2018;
Miller et al., 2021). These new criteria refine the do-
mains of apathy, indicating that a reduction in goal-
directed activity can manifest in behavioral, cognitive,
emotional, or social dimensions. Furthermore, apathy
is also observed to varying degrees in healthy individ-
uals (Ang et al., 2017), making its assessment impor-
tant for early identification and prevention of future
cognitive decline.
Integrating information and communication tech-
nologies into medical evaluation can offer valuable
diagnostic insights (Zeghari et al., 2020). However,
developing serious games for users with cognitive
impairments is challenging, as it requires addressing
their needs, emotional responses, and overall com-
fort. Since most affected individuals are elderly and
may have limited technological familiarity, usability
adaptations and a well-designed interface are crucial
for maintaining focus and immersion (Chen et al.,
2021a).
Several serious games for MCI assessment have
been developed. Kitchen and Cooking (Manera et al.,
2015) evaluates planning, attention, and object recog-
nition through cooking tasks, tracking performance
over time to monitor cognitive decline. In (Chessa
et al., 2019), a non-immersive exergame and an im-
mersive VR environment were tested, showing strong
correlation with standard clinical tests. SynapseTo-
Life (Costa et al., 2017) assesses problem-solving
skills through virtual real-life scenarios, while Skil-
lLab (Pedersen et al., 2023) uses six mini-games to
assess cognitive abilities like reaction time and mem-
ory. Despite these advancements, there remains a sig-
nificant gap in games designed specifically to assess
apathy in MCI populations.
3 THE PROPOSED SERIOUS
GAME
The ApathySEED serious game for social apathy as-
sessment has been designed in alignment with the di-
agnostic criteria for apathy outlined by (Robert et al.,
2018), ensuring the game’s relevance for clinical eval-
uation. The game’s narrative centers on decision-
making within social contexts. Participants are scored
based on their choices, which are mapped to the ap-
athy dimensions specified in the updated diagnostic
criteria. Figure 1 illustrates the various elements of
the developed game, including the avatars, 3D envi-
ronments, and user interface.
3.1 Narrative/Storytelling
The development of the narrative was closely super-
vised by an expert in the field, who is among the
authors, ensuring that both the storyline and deci-
sion points are clinically relevant and effectively con-
tribute to the evaluation of apathy. The storyline was
designed as a linear structure to enhance immersion
and to provide a smooth and continuous progression.
This seamless flow supports accurate assessments by
reflecting the patient’s social engagement or detach-
ment through their decision-making. To accommo-
date older adults’ limited tech experience, a brief tu-
torial was incorporated at the beginning of the game
to introduce the game mechanics.
The narrative unfolds across three distinct scenar-
ios (see below) and involves three characters: the
protagonist, representing the player; the protagonist’s
neighbor; and the protagonist’s daughter. User deci-
sions guide the player through various narrative paths
that intertwine and diverge throughout the game, en-
suring a coherent evaluation regardless of the chosen
route.
3.1.1 First Scenario: Living Room
The narrative begins with the player relaxing at home
when the doorbell rings amidst heavy rainfall. Upon
opening the door, the player encounters their neigh-
bor, who is soaked and distressed. The neighbor ex-
plains they’ve forgotten their keys and asks to stay un-
til the storm passes or their spouse arrives. The evalu-
ation in this scene focuses on the player’s willingness
to let the neighbor in and engage in conversation.
HUCAPP 2025 - 9th International Conference on Human Computer Interaction Theory and Applications
544

Figure 1: Various elements of the ApathySEED game.
3.1.2 Second Scenario: Neighbor’s Garden
After the storm subsides, the neighbor, express-
ing gratitude for the hospitality extended, offers the
player fresh vegetables from their garden. This of-
fer leads to two potential narrative pathways: accept-
ing or declining the offer, which assesses the player’s
willingness to leave the house.
• Accepting the Offer. The scene transitions to the
neighbor’s garden, where a conversation ensues.
The player’s responses to the neighbor’s emotions
and life events are assessed, alongside their initia-
tive to participate in activities like helping with the
vegetable harvest. Afterwards, the player returns
home and receives a phone call from their daugh-
ter, who reminds them of a dinner reservation at
a restaurant. The decisions made during this call
set the stage for the third part of the narrative.
• Declining the Offer. The player remains in the
living room, resting, and receives a phone call
from their daughter, reminding them of the din-
ner reservation at the restaurant. On the way to
the restaurant, the player encounters the neigh-
bor again in their garden, leading to a conversa-
tion that follows a similar pattern to that of the
“accepting the offer” narrative pathway, providing
another opportunity for assessing social engage-
ment.
3.1.3 Third Scenario: Restaurant
The final scene takes place in a restaurant where the
daughter had made a reservation for dinner. In this
setting, the player and their daughter reconnect after a
period of separation. This conversation serves to eval-
uate the player’s interest in their daughter’s life and
concerns, as well as their willingness to discuss per-
sonal matters. This scene is used to assess emotional
engagement and social apathy, as it involves intimate
family interaction.
To conclude the narrative, the player returns home
and is presented with a final decision that summarizes
their overall experience and engagement throughout
the game.
3.2 Scoring System
The final narrative framework encompasses twenty
key decisions, each offering three distinct options.
Depending on the player’s choice, a scoring sys-
tem is applied, awarding 0, 1, or 2 points per deci-
sion, resulting in a maximum achievable score of 40
points. These decisions are structured within social
dimension of apathy outlined in the diagnostic crite-
ria (Robert et al., 2018). In particular, 6 decisions cor-
respond to the emotion subdomain, 6 to the initiative
subdomain, and 6 to the interest subdomain, while the
remaining 2 decisions are intentionally left ambigu-
ous. To ensure a focused and reliable evaluation, the
five most definitive decisions from each subdomain
were selected for scoring, with each subdomain car-
rying a maximum potential score of 10 points. Higher
scores indicate lower levels of social apathy, reflect-
ing greater emotional engagement, initiative, and in-
terest in social interactions, while lower scores sug-
gest higher levels of apathy.
A Serious Game for Early Detection and Assessment of Social Apathy: A Pilot Study
545

3.3 Game Design
The game’s style and interface were designed to en-
sure accessibility for older users while meeting the
game’s needs. A stylized approach was chosen,
blending cartoonish and realistic elements to leverage
the benefits of both styles (Korre, 2023) while user-
centered guidelines informed the creation of simpli-
fied, high-contrast interface elements for intuitive and
accessible navigation (Gerling et al., 2012).
Character design was developed using the Ready-
PlayerMe
1
platform. Each character was crafted with
specific aesthetic and color criteria in mind, ensur-
ing alignment with the narrative requirements of the
characters. Simultaneously, Blender
2
was utilized for
the development of various 3D scenarios, combin-
ing internally created materials and models with pre-
existing elements sourced from BlenderKit
3
, Sketch-
fab
4
, and the Unity Asset Store
5
.
The user interface design was inspired by visual
concepts commonly found in existing video games,
aiming to create an engaging 3D background. To en-
hance immersion and narrative flow, dialogue boxes
featuring character portraits were integrated. Graphic
elements were developed using Illustrator
6
and Pho-
toshop
7
, while Figma
8
facilitated the integration and
overall design of the user interfaces. The design pro-
cess involved selecting a color palette and typography
that aligned with established design guidelines.
The game was developed using the Unity
9
game
engine. Three distinct scenes were created, utilizing
Blender models imported in FBX format with textures
and UV maps. A lighting system combining real-time
and pre-computed techniques was implemented, us-
ing directional, spot, and point lights, along with sky-
boxes, to create an immersive atmosphere.
Game mechanics were managed with custom
scripts and the Fungus
10
tool to streamline interactive
storytelling. Cameras were strategically positioned to
support the narrative, and characters were animated
using Mixamo
11
animations and custom ones from
Blender. Sound, visual effects, and post-processing
techniques were added to enhance immersion.
1
https://readyplayer.me/
2
https://www.blender.org/
3
https://www.blenderkit.com/
4
https://sketchfab.com/
5
https://assetstore.unity.com/
6
https://www.adobe.com/products/illustrator.html
7
https://www.adobe.com/products/photoshop.html
8
https://www.figma.com/
9
https://unity.com/
10
https://fungusgames.com/
11
https://www.mixamo.com/
Figure 2 shows gameplay screenshots high-
lighting key user interactions, including dialogues,
decision-making, and the user interface. These im-
ages illustrate how players engage with the narrative
and make choices that assess social apathy by simu-
lating real-life interactions, reflecting their social ini-
tiative and emotional connection.
4 GAME VALIDATION
To prepare for clinical use, it was essential to eval-
uate the game’s effectiveness, usability, and overall
feasibility as a tool for assessing social apathy. This
validation process was necessary to ensure the game
not only aligns with clinical diagnostic standards but
also remains functional, engaging, and accessible for
diverse user groups.
Therefore, a pilot study was conducted aimed to
gather data on technical performance and user inter-
action, focusing on ease of use, narrative immersion,
and clarity in decision-making. The study also pro-
vided preliminary insights into the game’s potential
for detecting social apathy by simulating real-world
interactions. The user study was conducted after ap-
proval from the university ethics research committee
of the University of Genoa (n. 2024/59).
4.1 Study Participants
A total of 33 participants were recruited from the stu-
dents and researchers community. The overall demo-
graphics of the participants can be found in Table 1.
All participants were volunteers and received no com-
pensation.
Table 1: Demographics of the participants. Gaming and
serious games experience is self-rated out of 10.
Total Participants 33
Male Participants 18
Female Participants 15
Age 26 ± 8.2
Video Gaming Experience 6.4 ± 2.6
Serious Games Experience 4.2 ± 2.7
All participants were presumed to be healthy, as
the primary objective of this pilot study was to evalu-
ate the game’s usability, user experience, and general
acceptance, rather than to assess its diagnostic accu-
racy in clinical populations. This approach allowed
the study to focus on refining the game mechanics and
interface, ensuring that the design would be intuitive
and engaging for a broader audience, including indi-
viduals with cognitive impairments in future studies.
HUCAPP 2025 - 9th International Conference on Human Computer Interaction Theory and Applications
546

Figure 2: Examples of various dialogues and decision making scenarios from the game.
4.2 Experimental Procedure
The game was installed on an Android tablet, specifi-
cally the Samsung Galaxy Tab S7 FE, which features
a 12.4-inch display with a resolution of 2560x1600
and runs on Android 13. This device was selected for
its large screen and high resolution, which facilitated
a more immersive and accessible gaming experience.
The experiments were conducted in a controlled
room at our institute, designed to provide a neutral,
distraction-free environment conducive to consistent
testing conditions for all participants. Each session
lasted approximately 20 minutes.
Prior to commencing the study, participants re-
ceived a thorough briefing on the project’s objectives,
including the ethical handling and confidentiality of
their personal data. After reviewing this information,
participants voluntarily signed a consent form, con-
firming their willingness to take part in the study. The
participants were further informed of their right to
withdraw from the study at any time without prej-
udice. A thorough explanation of the experimental
tasks and procedures was also provided to them.
At the start of each session, participants com-
pleted a brief demographic questionnaire, which in-
cluded questions about their prior experience with
video games and serious games. They then engaged
with the ApathySEED game, navigating the narrative
and making decisions independently. Upon complet-
ing the game, participants were asked to complete
several post-interaction questionnaires, which served
to assess their experience and evaluate key aspects of
the game’s usability, workload, and alignment with
its apathy detection objectives. These questionnaires
included:
• System Usability Scale (SUS). The SUS
(Brooke, 1996) consists of 10 items, each rated
on a five-point Likert scale. It provides a global
usability score out of 100, reflecting the game’s
user-friendliness.
• NASA Task Load Index (NASA-TLX). The
NASA-TLX (Hart and Staveland, 1988) measures
perceived workload across six dimensions: men-
tal demand, physical demand, temporal demand,
performance, effort, and frustration. Participants
rated each dimension on a scale from 0 to 20. The
raw version of the questionnaire was used and the
scores are scaled out of 100.
• Apathy Motivation Index (AMI). The AMI
(Ang et al., 2017) evaluates apathy across three di-
mensions (behavioral, social, and emotional) us-
ing 18 items, rated from 0 to 4. A standardized
range from 0 to 4 is used, where 0 represents no
apathy, and 4 indicates high apathy levels for each
dimension as well as the total score.
Throughout the process, participants were encour-
aged to respond honestly and were given the oppor-
tunity to ask questions for clarification at any point,
ensuring they fully understood the tasks and question-
naires.
4.3 Data Analysis
A boxplot for the mean game scores can be seen in
the left image in Figure 3. The mean scores (General:
32.58; Initiative: 7.55; Interest: 7.45; Emotion: 9.18)
suggest that participants displayed low levels of social
apathy, which aligns with expectations given that all
participants were presumably healthy individuals.
A Serious Game for Early Detection and Assessment of Social Apathy: A Pilot Study
547

Figure 3: Questionnaire responses. (left) ApathySEED game scores. (middle) User experience questionnaires, i.e., NASA
Task Load Index and System Usability Scale (rightmost column). (right) Apathy Motivation Index.
Among the subdomains, the emotion subdomain
exhibited both a higher mean score and a lower stan-
dard deviation compared to the interest and initia-
tive subdomains. This could imply that participants
demonstrated greater emotional responsiveness. Al-
ternatively, this result may reflect limitations in how
the emotional content of the game is currently framed,
as the narrative and decision-making process might be
influenced by socially acceptable norms rather than
authentic emotional engagement.
The middle image in Figure 3 illustrates partic-
ipants’ responses to the user experience question-
naires. In terms of system usability, low variability
was observed in participant responses, indicating a
general consensus regarding the ease of use and func-
tionality of the game. Users found the system in-
tuitive, accessible, and easy to learn, even without
prior experience, reflecting well on the design’s ef-
fectiveness. Most participants felt confident in using
the game, and the overall SUS score of 88.64 reflects
a strong perception of the system’s usability, though
some variation in individual user experiences was ob-
served.
Cognitive load responses showed low to moderate
variability, with the performance sub-scale exhibiting
the highest variability, indicating mixed perceptions
of success. The physical demand, effort, and frustra-
tion sub-scales were rated consistently low, suggest-
ing minimal strain. Mental and temporal demands
were seen as low to moderate, indicating some cog-
nitive challenge and time pressure, but not excessive.
The highest perceived workload was related to per-
formance, reflecting differing views on success. The
average NASA-TLX score of 26.16 suggests moder-
ate cognitive engagement without significant burden.
The right image in Figure 3 presents the scores for
the apathy questionnaire. The average scores across
the various dimensions (Behavioural: 1.49; Social:
1.53, Emotional: 1.39; Total: 1.47) are notably simi-
lar, suggesting that participants exhibited a generally
low level of apathy across all dimensions. This find-
ing aligns with expectations, given the healthy status
of the participants. Furthermore, the standard devia-
tions for each dimension demonstrate moderate vari-
ability in participants’ responses, which reinforces the
overall perception of low levels of apathy.
An analysis was conducted to explore the rela-
tionship between participants’ scores in the game
and their scores in the social dimension of the
AMI. The Shapiro-Wilk test revealed non-normal
data distribution(p < 0.05). Consequently, Spearman
correlation coefficients were computed to examine the
associations (see Figure 4). The results showed a neg-
ative trend due to inverse scoring scales. The initiative
dimension had the strongest correlation, highlighting
its reliability as an indicator of social apathy, while
the interest dimension showed the weakest correla-
tion. In general, the consistent trend across the AMI
scores mirrors the game scores, providing additional
validation for the effectiveness of the serious game in
assessing social apathy.
Figure 4: Spearman correlation coefficients between game
scores and AMI scores.
To further investigate this relationship, partici-
pants were divided into two groups based on their so-
HUCAPP 2025 - 9th International Conference on Human Computer Interaction Theory and Applications
548
cial apathy levels: low social apathy and high social
apathy. This classification facilitated a comparative
analysis of game performance in relation to the par-
ticipants’ social apathy levels. A cutoff of 1.5, corre-
sponding to the median AMI social dimension score,
was used, i.e., scores below 1.5 were categorized as
low, and scores above 1.5 as high. A Mann-Whitney
U-test assessed statistical differences between groups,
with results summarized in Table 2.
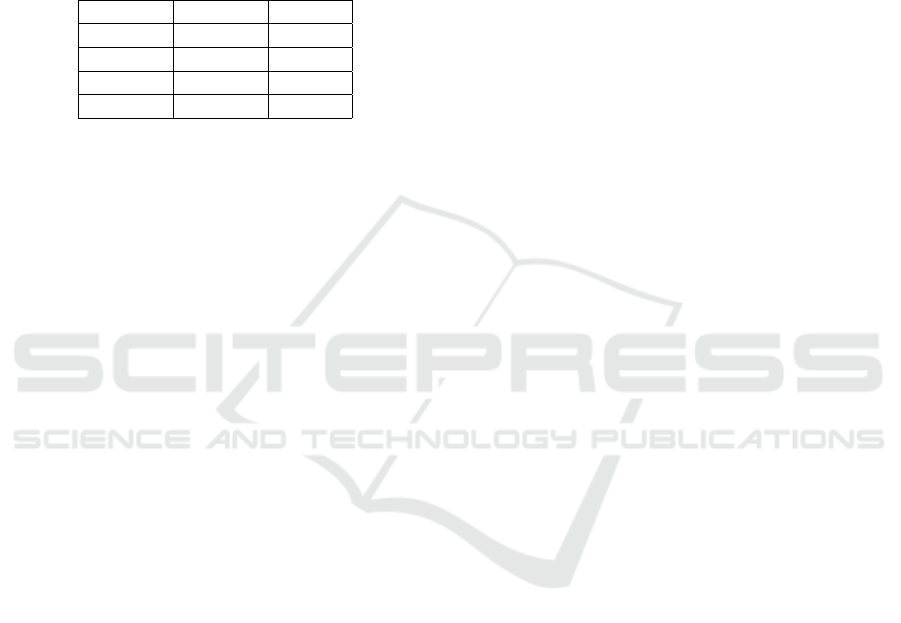
Table 2: Mann-Whitney U-test.
Statistics p-value
Initiative 76.5 0.038
Interest 110.0 0.405
Emotion 86.5 0.070
General 93.5 0.153
The comparison between the low and high social
apathy groups revealed no statistically significant dif-
ferences in the general score or in the dimension of
interest, indicating a lack of clear distinction between
the groups in these areas. Although the dimension of
emotion did not achieve statistical significance, the p-
value was close to the conventional threshold of 0.05,
suggesting a potential trend towards a difference be-
tween the groups. Notably, the dimension of initiative
displayed statistically significant differences between
the groups. This suggests that variations in partici-
pants’ willingness to take initiative in social situations
are closely associated with their levels of social apa-
thy, making this dimension a valuable focus for future
assessments and interventions.
4.4 Discussion
This pilot study aimed to evaluate the usability and
effectiveness of the ApathySEED serious game in as-
sessing social apathy. The high SUS score suggests
that participants found the game user-friendly and in-
tuitive, meeting the design goal of easy adoption for a
wide audience, including potential clinical users. The
NASA-TLX results reflected a low to moderate cog-
nitive load, indicating the game was challenging yet
manageable for participants, with minimal frustration
or physical demand.
The game scores were consistent with AMI
scores, reflecting similar patterns across self-reported
and game-based measures. The game scores indi-
cated low levels of apathy among healthy partici-
pants, reinforcing the game’s validity as an apathy as-
sessment tool. The initiative subdomain, in particu-
lar, demonstrated the strongest correlation with AMI
scores, suggesting that this aspect of the game aligns
well with traditional measures of social apathy. This
dimension also revealed statistically significant differ-
ences between participants with low and high social
apathy, underscoring its sensitivity in detecting vary-
ing levels of initiative in social contexts.
Although the study yielded promising results, sev-
eral limitations should be acknowledged. First, the
sample consisted exclusively of healthy participants,
limiting the generalizability of the findings to clini-
cal populations with cognitive impairments or apathy-
related disorders. Future studies will involve patients
with known apathy or cognitive impairment to evalu-
ate the game’s effectiveness in a more clinically rele-
vant context.
Moreover, the emotional domain of the developed
game showed potential for improvement, as the cur-
rent narrative may not fully engage or evaluate emo-
tional apathy as intended. Revisiting the design and
content of the emotional scenarios could enhance the
game’s ability to assess this dimension more accu-
rately.
5 CONCLUSIONS
This work introduced ApathySEED, a serious game
designed for the assessment of social apathy, particu-
larly targeting individuals with cognitive impairment.
The game design focused on simulating decision-
making in social contexts to evaluate apathy across
various dimensions by paying attention to the effec-
tiveness and easiness of interactions. A pilot user
study was conducted with 33 healthy participants to
evaluate the game’s validity, usability, and cognitive
demand using standardized tools such as the SUS,
NASA-TLX, and AMI questionnaires. The findings
show the game’s potential as an effective tool for as-
sessing apathy, with promising usability and low cog-
nitive load. Future work will expand the study to clin-
ical environments, involving patients with mild cog-
nitive impairment to further validate the game’s effec-
tiveness in clinical settings.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The work was supported by the Interreg Alcotra
project INTEVIDI (n. 20178). The authors would
like to thank all the volunteers who took part in the
user study.
A Serious Game for Early Detection and Assessment of Social Apathy: A Pilot Study
549

REFERENCES
Ang, Y.-S., Lockwood, P., Apps, M. A., Muhammed, K.,
and Husain, M. (2017). Distinct subtypes of apathy
revealed by the apathy motivation index. PloS one,
12(1):e0169938.
Brooke, J. (1996). SUS - a quick and dirty usability scale.
Usability evaluation in industry, 189(194):4–7.
Chen, Y.-T., Hou, C.-J., Derek, N., Huang, S.-B., Huang,
M.-W., and Wang, Y.-Y. (2021a). Evaluation of the re-
action time and accuracy rate in normal subjects, mci,
and dementia using serious games. Applied Sciences,
11(2):628.
Chen, Y.-X., Liang, N., Li, X.-L., Yang, S.-H., Wang, Y.-
P., and Shi, N.-N. (2021b). Diagnosis and treatment
for mild cognitive impairment: a systematic review of
clinical practice guidelines and consensus statements.
Frontiers in Neurology, 12:719849.
Chessa, M., Bassano, C., Gusai, E., Martis, A. E., and
Solari, F. (2019). Human-computer interaction ap-
proaches for the assessment and the practice of the
cognitive capabilities of elderly people. In Leal-Taix
´
e,
L. and Roth, S., editors, Computer Vision – ECCV
2018 Workshops, pages 66–81, Cham. Springer Inter-
national Publishing.
Chessa, M., Gerini, L., Hussain, R., Martini, M., Pizzo,
M., Solari, F., and Viola, E. (2024). Extended reality
and artificial intelligence for exergaming: Opportuni-
ties and open challenges for rehabilitation and cogni-
tive training. In 2024 IEEE 8th Forum on Research
and Technologies for Society and Industry Innovation
(RTSI), pages 357–362.
Costa, J., Neto, J., Alves, R., Escudeiro, P., and Escudeiro,
N. (2017). Neurocognitive stimulation game: Seri-
ous game for neurocognitive stimulation and assess-
ment. In Serious Games, Interaction and Simulation:
6th International Conference, SGAMES 2016, Porto,
Portugal, June 16-17, 2016, Revised Selected Papers
6, pages 74–81. Springer.
Etgen, T., Sander, D., Bickel, H., and F
¨
orstl, H. (2011).
Mild cognitive impairment and dementia: the impor-
tance of modifiable risk factors. Deutsches
¨
Arzteblatt
International, 108(44):743.
Gerling, K. M., Schulte, F. P., Smeddinck, J., and Ma-
such, M. (2012). Game design for older adults: ef-
fects of age-related changes on structural elements
of digital games. In 11th International Conference
on Entertainment Computing (ICEC), pages 235–242.
Springer.
Hart, S. G. and Staveland, L. E. (1988). Development
of NASA-TLX (task load index): Results of empiri-
cal and theoretical research. In Hancock, P. A. and
Meshkati, N., editors, Human Mental Workload, vol-
ume 52 of Advances in Psychology, pages 139–183.
North-Holland.
Kazui, H., Takahashi, R., Yamamoto, Y., Yoshiyama, K.,
Kanemoto, H., Suzuki, Y., Sato, S., Azuma, S., Sue-
hiro, T., Shimosegawa, E., et al. (2017). Neural
basis of apathy in patients with amnestic mild cog-
nitive impairment. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease,
55(4):1403–1416.
Khalili-Mahani, N., De Schutter, B., et al. (2019). Affec-
tive game planning for health applications: quanti-
tative extension of gerontoludic design based on the
appraisal theory of stress and coping. JMIR serious
games, 7(2):e13303.
Korre, D. (2023). Comparing photorealistic and animated
embodied conversational agents in serious games: An
empirical study on user experience. In International
Conference on Human-Computer Interaction, pages
317–335. Springer.
Manera, V., Petit, P.-D., Derreumaux, A., Orvieto, I., Ro-
magnoli, M., Lyttle, G., David, R., and Robert, P. H.
(2015). ‘kitchen and cooking,’a serious game for mild
cognitive impairment and alzheimer’s disease: a pilot
study. Frontiers in aging neuroscience, 7:24.
Miller, D. S., Robert, P., Ereshefsky, L., Adler, L., Bateman,
D., Cummings, J., DeKosky, S. T., Fischer, C. E., Hu-
sain, M., Ismail, Z., et al. (2021). Diagnostic criteria
for apathy in neurocognitive disorders. Alzheimer’s &
Dementia, 17(12):1892–1904.
Nasreddine, Z. S., Phillips, N. A., B
´
edirian, V., Charbon-
neau, S., Whitehead, V., Collin, I., Cummings, J. L.,
and Chertkow, H. (2005). The montreal cognitive as-
sessment, moca: a brief screening tool for mild cogni-
tive impairment. Journal of the American Geriatrics
Society, 53(4):695–699.
Pedersen, M. K., D
´
ıaz, C. M. C., Wang, Q. J., Alba-
Marrugo, M. A., Amidi, A., Basaiawmoit, R. V.,
Bergenholtz, C., Christiansen, M. H., Gajdacz, M.,
Hertwig, R., et al. (2023). Measuring cognitive
abilities in the wild: Validating a population-scale
game-based cognitive assessment. Cognitive Science,
47(6):e13308.
Rami, L., Molinuevo, J. L., Sanchez-Valle, R., Bosch, B.,
and Villar, A. (2007). Screening for amnestic mild
cognitive impairment and early alzheimer’s disease
with m@ t (memory alteration test) in the primary care
population. International Journal of Geriatric Psychi-
atry: A journal of the psychiatry of late life and allied
sciences, 22(4):294–304.
Robert, P., Lanct
ˆ
ot, K., Ag
¨
uera-Ortiz, L., Aalten, P., Bre-
mond, F., Defrancesco, M., Hanon, C., David, R.,
Dubois, B., Dujardin, K., et al. (2018). Is it time to
revise the diagnostic criteria for apathy in brain disor-
ders? the 2018 international consensus group. Euro-
pean Psychiatry, 54:71–76.
Tong, T., Chignell, M., Lam, P., Tierney, M. C., and Lee,
J. (2014). Designing serious games for cognitive as-
sessment of the elderly. In Proceedings of the Interna-
tional Symposium on Human Factors and Ergonomics
in Health Care, volume 3, pages 28–35. Sage Publi-
cations Sage CA: Los Angeles, CA.
Tsoi, K. K., Chan, J. Y., Hirai, H. W., Wong, S. Y., and
Kwok, T. C. (2015). Cognitive tests to detect demen-
tia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA in-
ternal medicine, 175(9):1450–1458.
Zeghari, R., Manera, V., Fabre, R., Guerchouche, R., K
¨
onig,
A., Phan Tran, M. K., and Robert, P. (2020). The “in-
terest game”: A ludic application to improve apathy
assessment in patients with neurocognitive disorders.
Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease, 74(2):669–677.
HUCAPP 2025 - 9th International Conference on Human Computer Interaction Theory and Applications
550
