
PenQuestEnv: A Reinforcement Learning Environment for Cyber
Security
Sebastian Eresheim
1,2 a
, Simon Gmeiner
2 b
, Alexander Piglmann
2
, Thomas Petelin
1
,
Robert Luh
2 c
, Paul Tavolato
1 d
and Sebastian Schrittwieser
1,3 e
1
University of Vienna, Faculty of Computer Science, Austria
2
St. Poelten UAS, Institute for IT-Security Research, Austria
3
Christian Doppler Laboratory for Assurance and Transparency in Software Protection, Austria
Keywords:
Reinforcement Learning, Machine Learning, Cyber Security.
Abstract:
We present PenQuestEnv, a reinforcement learning environment for the digital board game PenQuest. Pen-
Quest is a cyber security strategic attack and defense simulation game that enables players to carry out cyber
attacks and defenses in specific scenarios, without the need for technical know-how. Its two-player setup is
highly customizable and allows to model a versatile set of scenarios in which players need to find optimal
strategies to achieve their goals. This environment enables the training of reinforcement learning agents for
finding optimal attack and defense strategies in a variety of different scenarios and multiple different game
options. With this work we intend to ignite future research on multipurpose cyber security strategies, where a
single agent is capable of finding optimal strategies against a versatile set of opponents in different scenarios.
1 INTRODUCTION
Navigating the complex world of IT risk management
poses demanding challenges. Identifying and prior-
itizing potential risks, necessitates a nuanced under-
standing of evolving threats and vulnerabilities. Com-
pound this difficulty with the inherent uncertainty
surrounding cyber threats, as adversaries continually
adapt their tactics in response to defensive measures.
Moreover, communicating these risks to higher man-
agement stakeholders can present substantial hurdles,
particularly when conveying technical intricacies in a
digestible manner.
PenQuest (Luh et al., 2022; Luh et al., 2020), a
high level cyber attack - defense simulation game,
is one approach to close this gap where complex
situations intermixed with complicated measures are
clearly displayed. PenQuest is built upon cyber se-
curity frameworks like MITRE ATT&CK
®1
, MITRE
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7620-8391
b
https://orcid.org/0009-0007-2880-5547
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6536-6706
d
https://orcid.org/0009-0004-4641-8653
e
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2115-2022
1
https://attack.mitre.org/
D3FEND
®2
and NIST SP 800-53 (NIST, 2020) for
close to realistic game mechanics. Finding optimal
strategic decisions in every situation, however, is a
non-trivial task that requires a deep understanding of
the game and its dynamics.
In response to these challenges, there arises a
pressing demand for innovative methodologies in IT
security, risk assessment and strategic modelling.
Traditional approaches often struggle to capture the
dynamic and adversarial nature of cyber-attacks, lead-
ing to suboptimal resource allocation and vulnerabil-
ity management. In recent years the advent of rein-
forcement learning (RL) (Sutton and Barto, 2018) has
opened promising avenues for addressing these de-
ficiencies. By harnessing the principles of machine
learning, RL empowers the development of adaptive
strategies that can learn and evolve amidst evolving
environments and adversaries. Indeed, the application
of RL techniques to specific domains has created sub-
stantial research progress, spanning from autonomous
vehicle navigation (Dosovitskiy et al., 2017), over
computer games (Bellemare et al., 2013; OpenAI
et al., 2019; Vinyals et al., 2017; Vinyals et al., 2019)
to financial trading (Liu et al., 2020).
Recognizing the potential of RL in the domain
2
https://d3fend.mitre.org/
Eresheim, S., Gmeiner, S., Piglmann, A., Petelin, T., Luh, R., Tavolato, P. and Schrittwieser, S.
PenQuestEnv: A Reinforcement Learning Environment for Cyber Security.
DOI: 10.5220/0013122700003899
In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy (ICISSP 2025) - Volume 1, pages 217-224
ISBN: 978-989-758-735-1; ISSN: 2184-4356
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
217

of IT security, in this paper, we introduce Pen-
QuestEnv, an open-source extension to the adversar-
ial security game PenQuest
3
. It provides a reinforce-
ment learning environment for PenQuest and enables
agents to learn to attack and defend assets in the
cyber domain. Based on multiple information se-
curity standards combined with well-known industry
frameworks and vocabularies, PenQuestEnv provides
attack-defense simulations that focus on the strategic
components of cyber security. Offensive agents must
progress through the cyber kill chain, gaining con-
trol of the defender’s assets to enable lateral move-
ment or achieve a specific malicious objective. De-
fensive agents must balance preventive, detective and
counter-active measures to protect their network. The
setting poses a complex RL challenge due to par-
tial state observation, aligning short-term actions with
long-term strategies, and uncertain infrastructure hi-
erarchies.
As our key contributions, we:
• provide PenQuestEnv consisting of an open-
source extension to the existing game,
• provide an API to choose from a versatile col-
lection of information security scenarios as well
as several game options that customize the game-
play,
• provide two rule-based, opponent bots, which are
able to play both roles, attack and defense, and
• showcase several promising research avenues
made possible by this environment.
The remainder of this work is structured as fol-
lows: section 2 discusses previous work, related to
PenQuestEnv and why it fills a previously empty
niche, section 3 explains the main concepts of the
game PenQuest, section 4 dives deeper into the en-
vironment around the game, section 5 highlights the
potential research directions that we hope to address
with this environment, before section 6 concludes the
paper.
2 MOTIVATION AND RELATED
WORK
CyberBattleSim (Microsoft-Defender-Research-
Team., 2021) explores the use of autonomous agents
in a simulated enterprise environment to study the
application of reinforcement learning in cybersecu-
rity. It focuses on lateral movement within a cyber
network in a post-breach scenario from an attacker’s
3
https://www.pen.quest
point of view. Kunz et al. (2022) extend the Cy-
berBattleSim framework by incorporating defensive
agents and Walter et al. (2021) explore the integration
of deceptive elements such as decoys and honeypots.
In contrast, PenQuestEnv incorporates actions and
equipment for both attackers and defenders and it
includes more advanced cyber security concepts like
information gathering and lateral movement.
Hammar and Stadler (2020) present a model that
simulates interactions between attackers and defend-
ers as a Markov game. The authors utilizie reinforce-
ment learning and self-play to autonomously evolve
strategies on a small, static, simulated infrastructure.
It highlights the ongoing challenge of achieving con-
sistent policy convergence even on a small infrastruc-
ture. PenQuestEnv on the other hand includes a ver-
satile set of scenarios that include network infrastruc-
tures of differing shapes and sizes.
Besides these simulation environments, a few spe-
cialised agents have been developed using RL, for ex-
ample for cross side scripting (Caturano et al., 2021)
or Denail-of-Service attacks (Sahu et al., 2023). How-
ever, they operate for their particular setting only,
lacking more advanced concepts of cyber security,
like reconnaissance or lateral movement.
To the best of our knowledge, there is no rein-
forcement learning environment, that may be used to
train agents for cyber attack-defence battles that:
• leverages the full cyber kill chain, and therefore
contains at least actions for reconnaissance, ini-
tial foot holding, elevating privileges and lateral
movement,
• incorporates different scenarios as well as differ-
ent infrastructure networks of different sizes and
shapes,
• includes customisable roles for attackers and de-
fenders
• is based on existing cyber security frameworks
(e.g. MITRE ATT&CK) and industry conventions
and
• contains bots for baseline evaluation.
3 PenQuest
PenQuest (Luh et al., 2020; Luh et al., 2022), is a
digital, turn-based attacker–defender board game in
the field of information security. It was built with
cyber security frameworks (e.g. MITRE ATT&CK,
MITRE D3FEND and NIST SP 800-53 (NIST, 2020))
in mind for real-world resembling game mechanics.
Its game board consists of interconnected digital as-
ICISSP 2025 - 11th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy
218

sets (depicted in Figure 1) that can form complex in-
terdependencies. Each turn, both players use action
cards to interact with and manipulate these assets. Ac-
tions model certain activities associated with the cor-
responding role. The success and visibility of each
action is probabilistically evaluated, where any event
of the previous game history may influence the evalu-
ation outcome. The attacker’s goal in the game varies
by scenario and may range from gaining knowledge
about potential future targets, to stealing confidential
industry secrets from a database, or taking multiple
application servers offline. The defender’s goal in the
game is always to prevent the attacker from reaching
their specific goal and thus successfully defending the
network as a whole.
Note that PenQuest’s underlying framework has
been previously published (Luh et al., 2022), which
may still serve as a reference for the more detailed and
theoretical aspects of PenQuest’s meta model. The
game is still regularly updated, therefore more recent
publications might be available.
Gameplay. PenQuest is a turn-based game where
both players play action cards in sequence. Each
turn is separated into two distinct phases: attack, and
defense, where each player plays during their corre-
sponding phase while the other waits for their turn.
Actors. Each game contains two actors, an attacker
and a defender, both are defined by mostly the same
attributes. These attributes model different capabili-
ties and influence the game-play as well as the out-
come of the game:
• Skill (1-5) - capabilities of the actor; determines
which and how many actions in the deck can be
used.
• Determination (1-5) - motivation and drive of the
actor; determines how many action cards a player
can choose from every turn.
• Wealth (1-5) - financial means of the actor; influ-
ences the actor’s overall budget.
• Insight (0-15) - level of knowledge about the op-
ponent actor; influences the success of future ac-
tions.
• Initiative (0-15) - financial and mental endurance
of the attacker; if it is 0, the defender wins.
Assets. Assets are the core component of the game
board. They model any desired IT component, rang-
ing from physical computers to docker containers, or
individual services. The state of each asset is tracked
via a three dimensional damage scale where each di-
Figure 1: An asset of the game board. On the lower level
the attacker’s progress within our simplified cyber kill chain
(Reconnaissance - eye, Initial Access - key, Execution -
gear) is depicted - currently only the Reconnaissance phase
is unlocked. Right next to it is the indicator whether the at-
tacker has gained administrator privileges (crown). On the
right side the 3 dimensional damage scale is visible, C for
confidentiality, I for integrity and A for availability.
mension corresponds to one edge of the infamous CIA
triad, confidentiality, integrity and availability. Each
scale ranges from 0 to 3, where 3 damage points de-
pict the maximum damage achievable. The effect – in
gameplay terms – depends on the type of impact:
• Confidentiality: the attacker has retrieved all
relevant information or data from the asset (e.g.
passwords, files, configuration, etc.), which gets
them additional Insight.
• Integrity: the attacker managed to modify data,
configuration, settings, etc. on the asset, thereby
gaining full control. As an effect, the actor can
now use this asset for lateral movement and attack
assets that where previously unreachable.
• Availability: the attacker has successfully taken
services (or the asset a whole) offline, making it
unavailable to legitimate users. Since the asset is
offline, the attacker can no longer utilize actions
targeting this asset. The defender, however, still
may attempt recovery.
Next to damage, the progress of the attacker along
an asset’s cyber kill chain is of key importance. Suc-
cessfully playing an action of a preceding phase un-
locks the next phase in the sequence, progressing the
overall attack. For accessibility’s sake, PenQuest sim-
plifies known models to 3 primary stages:
• Reconnaissance: the attacker gathers informa-
tion about the target(s). More information lead to
likelier future successes.
• Initial Access: the attacker establishes an initial
foothold on the system.
• Execution: the attacker has access to the asset
and is free to wreak havoc.
Assets come with three additional properties:
privilege level, operating system, and category. Some
actions require elevated privileges in order to be exe-
cuted, while others grant them. Operating system and
asset category serve as constraint and need to match
the action used on the asset.
PenQuestEnv: A Reinforcement Learning Environment for Cyber Security
219

(a) Asset (b) Action (c) Equipment
Figure 2: Detailed views of examples of (a) assets, (b) actions and (c) equipment.
Actions. Actions
4
are the means by which players
interact with assets. Each action represents an of-
fensive or defensive activity the player exhibits. This
e.g., includes system scans, code injection attacks, or
account remediation measures. While attack actions
progress the cyber kill chain as well as inflict dam-
age points, defense actions remove damage points,
apply supporting effects, or shield assets. Each action
has both a base success chance as well as detection
chance, which are influenced by a multitude of factors
during the game (e.g. actors’ Skill ratings, Insight).
Optimising the own chance of success while staying
covert and decreasing the opponent’s success chance
is a main strategic goal of PenQuest (similar to real-
world cyber security actions/measures). Actions are
additionally constrained by compatible operating sys-
tems and the aforementioned asset categories. They
also may have effects that impact the game in different
ways such as providing elevated privileges, shielding
future potential damage or granting equipment to the
player.
Equipment. Equipment typically provides bonuses
in regard to success and detection chances, although
an equipment can also be a prerequisite to play an ac-
tion. Attack equipment is split into Attack Tools, Cre-
dentials, Exploits and Malware, where Attack Tools
are permanent lasting equipment that provide passive
buffs. Other equipment types must be used alongside
an action card. Similarly, defense equipment is dis-
tinguished into Security Systems, Policies, Fixes and
Analysis Tools, where Security Systems provide per-
manent passive buffs.
4
A full list of actions is accessible at https://www.pen.
quest/wp-content/uploads/2024/07/Actionlists.pdf
Scenarios. PenQuest allows game administrators to
build different scenarios, where nearly all compo-
nents (assets, actions, etc.) are independently con-
figurable. This includes attacker goals, an overarch-
ing narrative, and a multitude of game options to tune
most of the game’s inherent mechanics.
4 PenQuestEnv
4.1 Main Components
PenQuestEnv
5
is built on top of the Farama Gym-
nasium (Towers et al., 2023) framework, which it-
self builds on top of the widely used OpenAI Gym
framwork (Brockman et al., 2016). Therefore,
observation- and action-spaces build upon spaces
contained in these frameworks.
State & Observations. A state in PenQuestEnv
contains the full game information. This includes all
role attributes of both players, all assets, all previ-
ously played actions and their outcomes, effects and
damage dealt, all purchased equipment of both play-
ers, all action cards on the players hands and com-
mon turn information. However, an observation only
includes public information such as the current turn
and game phase, or player-owned specific informa-
tion, like the players action cards, detected assets or
purchased equipment. It does not include opponent
information like the opponent’s action cards. The ob-
servation space of the environment is a multi-level,
dictionary space that resembles the logical model of
5
https://github.com/seresheim/penquest-env
ICISSP 2025 - 11th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy
220

the game, where keys are strings and the values again
different gymnasium spaces depending on the prop-
erty they model. The following snippet shows the
highest level observation space:
{
"turn": Discrete(1e10),
"phase": Discrete(6),
"actor_id": Discrete(64),
"actor_connection_id": Discrete(64),
"roles": Sequence(...),
"hand": Sequence(...),
"equipment": Sequence(...),
"board": Sequence(...),
"shop": Sequence(...),
"selection_choices": Sequence(...),
"selection_amount": Discrete(20)
}
Each value of the dictionary space either consists of
a discrete space containing a number of different dis-
crete values provided, or a sequence space, containing
variable size lists where each element is also again a
dictionary space. For more information, please visit
the documentation.
Actions. The action space is a sequence space of
discrete values, where the sequence length of the
action depends on the currently required interaction
type: buy equipment, redraw action cards and play
action cards. For a buy equipment action, each ele-
ment of the sequence is an index to the position an
equipment currently holds in the shop. For example
the action
a = (5, 17, 3) # buy equipment
indicates to buy the 3rd, 5th and 17th equipment in the
shop. An empty sequence indicates to buy no equip-
ment this turn. Redraw action cards actions have the
same structure, except the indices are entries into a
list of (pre-selected) offered actions. The specific set
of action cards for redrawing is configuarble via game
options. Play action cards actions always contain six
integers. Table 1 lists the exact meanings for each po-
sition of the play action card action. For example the
action
a = (1, 22, 1, 4, 2, 0) # play action card
means: ’Play the second action on the hand onto the
asset with ID 22 with confidentiality damage sup-
ported by the fourth action on the hand and provided
with the second equipment in hand’.
Rewards. Rewards are provided sparsely at the end
of the game, +1 for winning or -1 for losing. On all
intermediate steps the reward is 0.
Table 1: ’play action card’ actions always consists of an
integer sequence of length six. Each position has it’s own
meaning. Apart from the first position all other fields may
be 0, indicating that this position is not required for this
action. Because of this use of the value 0, integers at the
positions 1-5 which indicate indices, start indexing from 1.
Position Meaning
0 Index of action card that is played
1 ID of the asset the action targets
2 Index of damage scale
3 Index of support action card
4 Index of an equipment card
5 ID of a previously played action card,
the current one tries to mitigate
Scenarios. Currently, PenQuestEnv encompasses
nine scenarios, where each scenario contains a differ-
ent infrastructure setup. Out of brefity we provide the
following statistics about the number of assets across
all scenarios: maximum: 34, average: 12.77, median:
10 and minimum: 6.
4.2 Playing the Game
Game Dynamics. The game is a non-cooperative,
two-player game and non-deterministic, as each
player can in most situations choose between a num-
ber of possible actions non-deterministically. Ad-
ditionally, it also contains stochastic dynamics, as
the success and detection of action cards depends on
probabilities. PenQuestEnv is an imperfect and in-
complete information game, due to invisible opponent
actions as well as unknown opponent objectives and
strategies. Only a very restricted set of information
about the current game state is observed by the play-
ers; during the game, more parts of this information
may become unveiled. This aspect of partial observ-
ability is most notable when both players are initially
presented with their own view of the game board. At-
tackers do not know the full details of the network and
defenders do not know the attacker’s goal. Addition-
ally, both players per default do not know the action
cards the other player played, however both have the
opportunity to detect some opponent actions during
the game.
Game Options. Because it might be challenging for
an agent to learn all game mechanics at once, game
options introduce the possibility to customise aspects
of the dynamics individually and allow to simplify the
game across multiple dimensions. Besides others, this
includes scenarios, attacker goals, seeds, making suc-
cess and detection chances (individually) determinis-
tic and turning on/off support actions and equipment.
PenQuestEnv: A Reinforcement Learning Environment for Cyber Security
221
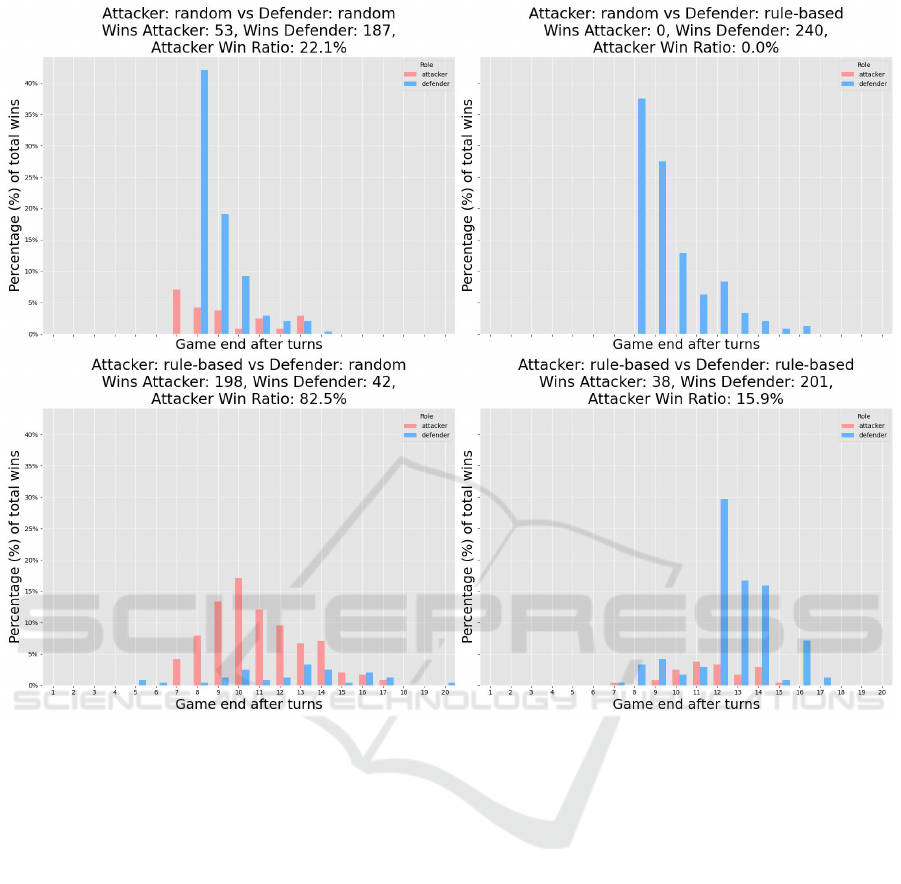
Figure 3: Shows the amount of turns it took a type of bot (rule-based or random) to achieve it’s goal when matched against
other specific bot types. Each plot shows the outcomes of 240 games, evaluated on scenario ’Medium 1’. A bar indicates
the amount of games that were won at each turn by the player (red: attacker, blue: defender). The amount of games won,
displayed as a fraction of total games played is shown on the y-axis, the final game turn on the x-axis. In total, the games
were won by the attacker in 30.1% of games, and 69.9% by the defender. The performance difference between attacker and
defender greatly depends on the complexity and depth of the chosen scenario. We have chosen a scenario with a slight bias
towards favoring the defensive side, which appears more pronounced when looking at longer game-durations or the pairing of
rule-based against rule-based bot, where the rule-based attacker only came out on top in 15.9% of games against the rule-based
defender’s reactive strategy. Note that both axes have the same scale for all plots.
4.3 Built-In Opponent Bots
The environment also currently controls opponent
bots that can be used to challenge or evaluate RL
agents. There are currently two kinds of opponent
bots, a random bot, and a rule-based bot.
• Random Bot - selects actions randomly from a
pool of valid options.
• Rule-based Bot The rule-based bot has separate
strategy sets for attack and defense. Its attack-
ing strategy revolves around discovering the tar-
get asset(s) as quickly as possible by probing un-
explored attack vectors (integrity attacks) and fo-
cusing the target directly once it is exposed. The
defending rules focuses primarily on immediately
responding to all harm done (response actions)
and secondly pre-emptively securing assets from
receiving damage (prevention actions).
To showcase the performance of the bots as well
as typical game lengths (measured in game turns) we
conducted multiple matches between the bot types.
Figure 3 depicts the outcomes of 240 games for each
pairing of bot type, with rule-based and random bot
taking the role of attacker or defender. Note that the
game lengths may increase if an attacking agent pays
much care on it’s intrusion attempts not being de-
tected. These opponent bots can be used to evaluate
RL agents or strategies.
ICISSP 2025 - 11th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy
222

5 PROMISING RESEARCH
DIRECTIONS
5.1 Multiplayer Experiments
PenQuestEnv enables to train an agent against differ-
ent opponents, one at a time. This style of training
bears the potential to overfit on a specific opponent
strategy where a specific weakness is exploited. This
can result in winning against one specific (advanced)
strategy but due to a lack of generalization at the same
time loosing against a rather simple opponent. Such
behaviour was already observed in other games where
no single best strategy exists, like football (Kurach
et al., 2020), or StarCraft2 (Vinyals et al., 2019). This
non-transitivity of strategies is also characteristic for
real-world cyber incidents, where an ever evolving
arms race between attackers and defenders, constantly
adapting to the opponents strategy, takes place. We
therefore think that PenQuestEnv is a fitting opportu-
nity to inspire research in this area, as little similar
work currently exists in IT security in this manner.
5.2 Risk Assessment Experiments
Risk assessment in computer systems is a non-trivial
task. By finding strategies in given scenarios that are
most likely to succeed, trained agents can also be used
to support decisions for risk assessment. Such agents
may provide additional information for security man-
agement decisions on where to put resources like per-
sonnel attention or money. The insights gathered by
these agents, adaptable to different risk-tolerances can
be invaluable resources to decision makers. We be-
lieve PenQuestEnv provides a unique setting to enable
future research into this area.
6 CONCLUSION
In this paper we introduced PenQuestEnv, a novel
open source reinforcement learning environment ex-
tension to the partial-information, turn-based, digi-
tal, cyber security board game PenQuest. It is non-
symmetric in its action choices, highly diverse and
challenging to win against a wide variety of oppo-
nents. PenQuestEnv comes with a diverse set of dif-
ferent scenarios making it a fitting environment for
training multipurpose cyber agents, as well as two
baseline bots that help evaluating new RL agents. We
expect that this environment will be useful to AI and
security researchers alike to investigate current scien-
tific challenges.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research was primarily funded by the Austrian
Science Fund (FWF) [P 33656-N]. Additionally the
financial support by the Austrian Federal Ministry
of Labour and Economy, the National Foundation
for Research, Technology and Development and the
Christian Doppler Research Association is gratefully
acknowledged. For the purpose of open access, the
author has applied a CC BY public copyright licence
to any Author Accepted Manuscript version arising
from this submission.
REFERENCES
Bellemare, M. G., Naddaf, Y., Veness, J., and Bowling, M.
(2013). The arcade learning environment: An evalua-
tion platform for general agents. Journal of Artificial
Intelligence Research, 47:253–279.
Brockman, G., Cheung, V., Pettersson, L., Schneider, J.,
Schulman, J., Tang, J., and Zaremba, W. (2016). Ope-
nai gym.
Caturano, F., Perrone, G., and Romano, S. P. (2021). Dis-
covering reflected cross-site scripting vulnerabilities
using a multiobjective reinforcement learning envi-
ronment. Computers & Security, 103:102204.
Dosovitskiy, A., Ros, G., Codevilla, F., Lopez, A., and
Koltun, V. (2017). CARLA: An open urban driving
simulator. In Proceedings of the 1st Annual Confer-
ence on Robot Learning, pages 1–16.
Hammar, K. and Stadler, R. (2020). Finding effective se-
curity strategies through reinforcement learning and
self-play. In 2020 16th International Conference on
Network and Service Management (CNSM), pages 1–
9. IEEE.
Kunz, T., Fisher, C., La Novara-Gsell, J., Nguyen, C., and
Li, L. (2022). A multiagent cyberbattlesim for rl cyber
operation agents. In 2022 International Conference
on Computational Science and Computational Intelli-
gence (CSCI), pages 897–903. IEEE.
Kurach, K., Raichuk, A., Sta
´
nczyk, P., Zaj ˛ac, M., Bachem,
O., Espeholt, L., Riquelme, C., Vincent, D., Michal-
ski, M., Bousquet, O., et al. (2020). Google re-
search football: A novel reinforcement learning en-
vironment. In Proceedings of the AAAI conference on
artificial intelligence, volume 34, pages 4501–4510.
Liu, X.-Y., Yang, H., Chen, Q., Zhang, R., Yang, L., Xiao,
B., and Wang, C. D. (2020). Finrl: A deep rein-
forcement learning library for automated stock trad-
ing in quantitative finance. In Proceedings of the 34th
Conference on Neural Information Processing Sys-
tems (NeurIPS 2020.
Luh, R., Eresheim, S., Größbacher, S., Petelin, T., Mayr, F.,
Tavolato, P., and Schrittwieser, S. (2022). Penquest
reloaded: A digital cyber defense game for technical
education. In 2022 IEEE Global Engineering Educa-
tion Conference (EDUCON), pages 906–914. IEEE.
PenQuestEnv: A Reinforcement Learning Environment for Cyber Security
223

Luh, R., Temper, M., Tjoa, S., Schrittwieser, S., and
Janicke, H. (2020). Penquest: a gamified at-
tacker/defender meta model for cyber security assess-
ment and education. Journal of Computer Virology
and Hacking Techniques, 16:19–61.
Microsoft-Defender-Research-Team. (2021). Cyberbat-
tlesim. https://github.com/microsoft/cyberbattlesim.
Created by Christian Seifert, Michael Betser, William
Blum, James Bono, Kate Farris, Emily Goren, Justin
Grana, Kristian Holsheimer, Brandon Marken, Joshua
Neil, Nicole Nichols, Jugal Parikh, Haoran Wei.
NIST (2020). Security and privacy controls for information
systems and organizations. Technical Report Federal
Information Processing Standards Publications (FIPS
PUBS) 140-2, Change Notice 5 December 10, 2020,
U.S. Department of Commerce, Washington, D.C.
OpenAI, Berner, C., Brockman, G., Chan, B., Cheung,
V., D˛ebiak, P., Dennison, C., Farhi, D., Fischer, Q.,
Hashme, S., Hesse, C., Józefowicz, R., Gray, S., Ols-
son, C., Pachocki, J., Petrov, M., de Oliveira Pinto,
H. P., Raiman, J., Salimans, T., Schlatter, J., Schnei-
der, J., Sidor, S., Sutskever, I., Tang, J., Wolski, F.,
and Zhang, S. (2019). Dota 2 with large scale deep
reinforcement learning.
Sahu, A., Venkatraman, V., and Macwan, R. (2023). Re-
inforcement learning environment for cyber-resilient
power distribution system. IEEE Access.
Sutton, R. S. and Barto, A. G. (2018). Reinforcement learn-
ing: An introduction. MIT press.
Towers, M., Terry, J. K., Kwiatkowski, A., Balis, J. U.,
Cola, G. d., Deleu, T., Goulão, M., Kallinteris, A.,
KG, A., Krimmel, M., Perez-Vicente, R., Pierré, A.,
Schulhoff, S., Tai, J. J., Shen, A. T. J., and Younis,
O. G. (2023). Gymnasium.
Vinyals, O., Babuschkin, I., Czarnecki, W. M., Mathieu,
M., Dudzik, A., Chung, J., Choi, D. H., Powell, R.,
Ewalds, T., Georgiev, P., et al. (2019). Grandmas-
ter level in starcraft ii using multi-agent reinforcement
learning. Nature, 575(7782):350–354.
Vinyals, O., Ewalds, T., Bartunov, S., Georgiev, P., Vezhn-
evets, A. S., Yeo, M., Makhzani, A., Küttler, H., Aga-
piou, J., Schrittwieser, J., et al. (2017). Starcraft ii:
A new challenge for reinforcement learning. arXiv
preprint arXiv:1708.04782.
Walter, E., Ferguson-Walter, K., and Ridley, A. (2021).
Incorporating deception into cyberbattlesim for au-
tonomous defense. arXiv preprint arXiv:2108.13980.
ICISSP 2025 - 11th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy
224
