
Sequential Counter Encoding for Staircase At-Most-One Constraints
Hieu Xuan Truong, Tuyen Van Kieu and Khanh Van To
VNU University of Engineering and Technology, Vietnam
Keywords:
CNF Encoding, Sequential Counter Encoding, Sequence Constraints, Anti-Bandwidth.
Abstract:
This paper presents a new SAT encoding to represent Staircase At-Most-One (SCAMO) constraints by
combining similar sub-formulae between At-Most-One (AMO) constraints within constructing blocks. The
SCAMO constraints exhibit a staircase shape due to the structural similarity between consecutive AMO con-
straints. The proposed method utilizes Sequential Counter (SC) encoding to represent each block in a staircase
form, taking advantage of connecting the constraint representation for two consecutive blocks. Compared to
the existing SCAMO representation based on Binary Decision Diagrams (BDD), our method requires fewer
variables and clauses, resulting in improved solving time for SCAMO. Experimental results on real-world
problems, such as Anti-bandwidth problems, demonstrate that the SC encoding representation method for
SCAMO consistently outperforms alternative methods.
1 INTRODUCTION
Sequence constraints are a common type of con-
straint appearing in many combinatorial problems,
such as Car Sequencing, Nurse Rostering, and Em-
ployee Scheduling or Crew Rostering. For exam-
ple, in the Car Sequencing problem (Artigues et al.,
2014) (Siala, 2015), a sequence constraint limits the
at-most number of cars in a sequence that can be as-
sembled with a particular option. In the Nurse Ros-
tering problem (Ceschia et al., 2015) (Kletzander and
Musliu, 2020), a constraint might limit nurses to work
a maximum of 3-night shifts in 7 consecutive work-
ing days. Similarly, the Employee Scheduling prob-
lem (Nieuwenhuis et al., 2021) has a fairness con-
straint to balance morning and afternoon shifts. Se-
quence constraints restrict the number of occurrences
of certain values in a sequence of k variables, denoted
as AmongSeq (Bessiere et al., 2007) and AtMostSeq
(Artigues et al., 2014).
Sequence constraint is also in the anti-bandwidth
problem (Sinnl, 2021), applied for many applications
in scheduling (Leung et al., 1984), radio frequency
assignment (Hale, 1980), obnoxious facility location
(Cappanera, 1999) and map coloring (Hu et al., 2010).
SAT solving is used in many real-life applications
because SAT solvers have significantly improved in
strength. When applying SAT encoding to combi-
natorial problems, a large number of clauses are of-
ten generated. To address this issue, various encod-
ing techniques have been proposed to reduce the sig-
nificant number of clauses (Haberlandt et al., 2023)
(Vasconcellos-Gaete et al., 2020).
In our paper, we focus on addressing the At-
Most-One (AMO) sequence constraints, which means
that in any k consecutive elements, there is at most
1 element with the value TRUE. This constraint is
called the Staircase At Most One (SCAMO) con-
straint (Fazekas et al., 2020). The paper presents a
new SAT encoding for SCAMO by leveraging similar
sub-formulae to encode for a set of AMOs instead of
encoding each AMO separately. Our new encoding is
based on the sequential counter encoding (SC) (Sinz,
2005), instead of applying BDD as in (Fazekas et al.,
2020). The set of AMO constraints is divided into
blocks that share similar sub-formulae among AMO
constraints and then SC encoding is applied to repre-
sent a block and its neighboring blocks. This is done
to reduce the number of clauses required when encod-
ing each AMO constraint separately.
The key contributions of our research are as fol-
lows:
• We propose an efficient SAT encoding for
SCAMO constraints, which significantly reduces
the number of variables and clauses compared to
using BDD and other encodings to represent each
AMO separately.
• We propose an efficient SAT encoding to solve the
anti-bandwidth problems.
164
Truong, H. X., Van Kieu, T. and Van To, K.
Sequential Counter Encoding for Staircase At-Most-One Constraints.
DOI: 10.5220/0013124600003890
In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2025) - Volume 2, pages 164-175
ISBN: 978-989-758-737-5; ISSN: 2184-433X
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

The paper is organized as follows: Section 1 in-
troduces the research problem and summarizes the
new contributions of this study. Section 2 covers the
fundamentals of SCAMO constraints and encodings
using Binary Decision Diagrams (BDD). Section 3
presents our approach to representing SCAMO us-
ing SC. Section 4 discusses the Antibandwidth prob-
lem and its reduction to propositional logic formu-
las. Section 5 details the experiments comparing our
new SCAMO encoding with BDD, as well as the en-
coding techniques for each AMO constraint individ-
ually, including the experimental results for the Anti-
bandwidth problem. Finally, Section 6 concludes the
paper.
2 STAIRCASE AT-MOST-ONE
CONSTRAINTS
2.1 SCAMO Definition
The Staircase At-Most-One (SCAMO) constraint, as
discussed in (Fazekas et al., 2020), is a specialized
variant of the At-Most-One (AMO) constraint. The
SCAMO constraint set is created when a series of
AMO constraints share overlapping variables across
consecutive constraints, forming a “staircase” struc-
ture. This arrangement allows for the reuse of inter-
mediate results among these consecutive constraints,
thereby reducing the number of variables and clauses
required for encoding.
Definition 1. Given a sequence of n Boolean vari-
ables Ω = {x
1
, x
2
, ..., x
n
} and a number w st. 1 < w ≤
n, a SCAMO with a width of w is formulated as fol-
lows:
SCAMO(Ω, w) =
V
n−w
i=0
(
∑
i+w
j=i+1
x
j
≤ 1)
Example 1. Given a sequence of 10 Boolean vari-
ables Ω = {x
1
, x
2
, ..., x
10
}, the SCAMO constraints of
the 4-width staircase can be illustrated as follows:
x
1
+ x
2
+ x
3
+ x
4
≤ 1∧
x
2
+ x
3
+ x
4
+ x
5
≤ 1∧
x
3
+ x
4
+ x
5
+ x
6
≤ 1∧
x
4
+ x
5
+ x
6
+ x
7
≤ 1∧
x
5
+ x
6
+ x
7
+ x
8
≤ 1∧
x
6
+ x
7
+ x
8
+ x
9
≤ 1∧
x
7
+ x
8
+ x
9
+ x
10
≤ 1
The SCAMO constraint, as defined in Definition
1 and illustrated in Example 1, can be decomposed
into a set of overlapping AMO constraints that slide
over the sequence of variables. The key feature of
this “staircase” structure is the overlap between con-
secutive constraints. For instance, in Example 1, the
first and second constraints both include the variables
x
2
, x
3
, x
4
, and the second and third constraints share
the variables x
3
, x
4
, x
5
. This overlap allows reuse of
previous computation to evaluate the first AMO con-
straint as x
1
+ (x
2
+ x
3
+ x
4
), which can just consider
the sub-expression (x
2
+ x
3
+ x
4
) together with x
5
to
evaluate the second AMO constraint. In general, each
successive constraint shares a sum over w −1 vari-
ables with both the previous constraint and the next
constraint, allowing partial reuse of sub-expressions
across constraints, as shown in Definition 1.
2.2 Decomposition of SCAMO
Efficient encoding of SCAMO constraints necessi-
tates their decomposition into smaller, reusable sub-
constraints. This decomposition strategy minimizes
the number of variables and clauses required and
leverages the inherent overlapping nature of SCAMO
constraints to enhance computational efficiency. We
illustrate the decomposition of SCAMO constraints in
Figure 1.
Proposition 1. The constraint x
1
+ x
2
+ . . . + x
n
≤ 1
holds iff for all 1 ≤i < n :
(x
1
+ . . . + x
i
≤ 1) ∧(x
i+1
+ . . . + x
n
≤ 1)∧
(x
1
+ . . . + x
i
≤ 0 ∨x
i+1
+ . . . + x
n
≤ 0)
Encoding SCAMO constraints requires break-
ing down the larger constraints into smaller sub-
constraints that can be reused across consecutive win-
dows of variables. To begin the decomposition, we
first partition the sequence of Boolean variables Ω =
⟨
x
1
, x
2
, . . . , x
n
⟩
into M =
n
w
consecutive “windows”,
where each window contains w variables, except
possibly the last window, which may contain fewer
variables if n mod w ̸= 0. Formally, each window
ω
i
contains the variables ω
1
=
⟨
x
1
, x
2
, . . . , x
w
⟩
, ω
2
=
⟨
x
w+1
, x
w+2
, . . . , x
2w
⟩
, etc.
The encoding process begins with the construction
of individual constraints for each AMO constraint de-
rived from the SCAMO decomposition. Each con-
straint accurately captures the exclusivity condition of
its respective AMO constraint. However, to maintain
the staircase structure, it is imperative to ensure con-
sistency across overlapping variables in consecutive
AMO constraints. This is achieved by introducing At-
Most-Zero (AMZ) constraints, as shown in Proposi-
tion 1. The AMZ constraints ensure that shared vari-
ables do not violate the exclusivity conditions when
transitioning between blocks. Specifically, the AMZ
constraints (x
1
+ . . . + x
i
≤ 0 ∨x
i+1
+ . . . + x
n
≤ 0)
in Proposition 1 guarantee that at least one of the
two sub-expressions must be zero. This, combined
with the individual AMO constraints on each sub-
expression, maintains the overall at-most-one prop-
erty across the entire set of variables. Applying this
Sequential Counter Encoding for Staircase At-Most-One Constraints
165

(x
1
+ (x
2
+ (x
3
+ (x
4
)))) ≤ 1
(x
2
+ (x
3
+ (x
4
))) + (x
5
) ≤ 1
(x
3
+ (x
4
)) + ((x
5
) + x
6
) ≤ 1
(x
4
) + (((x
5
) + x
6
) + x
7
) ≤ 1
((((x
5
) + x
6
) + x
7
) + x
8
) ≤ 1
(x
5
+ (x
6
+ (x
7
+ (x
8
)))) ≤ 1
(x
6
+ (x
7
+ (x
8
+ (x
9
)))) ≤ 1
(x
7
+ (x
8
+ (x
9
+ (x
10
)))) ≤ 1
(x
8
)
Figure 1: Decomposition of SCAMO.
x
1
+ x
2
+ x
3
+ x
4
≤ 1
b
4
x
2
+ x
3
+ x
4
≤ 1 x
3
+ x
4
≤ 1
x
4
≤ 1
b
6
b
5
b
1
x
1
+ x
2
+ x
3
+ x
4
≤ 0 x
2
+ x
3
+ x
4
≤ 0
b
2
x
3
+ x
4
≤ 0
b
3
x
4
≤ 0
⊤
⊥
x
5
+ x
6
+ x
7
+ x
8
≤ 1
b
10
x
6
+ x
7
+ x
8
≤ 1
b
11
x
7
+ x
8
≤ 1
b
12
x
8
≤ 1
x
5
+ x
6
+ x
7
+ x
8
≤ 0 x
6
+ x
7
+ x
8
≤ 0
x
7
+ x
8
≤ 0 x
8
≤ 0
b
9
b
8
b
7
⊥
⊤
¬x
1
¬x
2
¬x
3
¬x
3
¬x
2
¬x
1
¬x
8
¬x
7
¬x
6
¬x
8
¬x
7
¬x
6
x
1
x
2
x
3
x
8
x
7
x
6
x
4
x
5
x
1
x
2
x
3
x
4
x
8
x
7
x
6
x
5
¬x
4
¬x
5
¬x
4
¬x
5
l
1
l
3
l
4
l
2
l
1
l
2
l
3
l
4
Figure 2: Forward and backward BDDs for SCAMO constraints (Fazekas et al., 2020).
proposition to the SCAMO constraint illustrated in
Figure 1, the constraint x
2
+ x
3
+ x
4
+ x
5
≤ 1 can be
decomposed into:
(x
2
≤ 1) ∧(x
3
+ x
4
+ x
5
≤ 1)∧
(x
2
≤ 0 ∨x
3
+ x
4
+ x
5
≤ 0)
2.3 BDD Encoding for SCAMO
To encode AMO and AMZ constraints, we use BDD
encoding (Bryant, 1986), (Akers, 1978) to represent
the constraints in a compact form. The BDD en-
coding consists of two parts: forward and backward
BDDs for each window of variables. Forward BDD
(ω
f
) is constructed using a right-associative variable
ordering, where variables are ordered from x
1
to x
w
. It
captures the AMO and AMZ constraints for the win-
dow, ensuring that At-Most-One variable can be set
to true. Backward BDD (ω
b
) uses a left-associative
ordering, starting from the last variable x
w
and pro-
ceeding backward to x
1
. Figure 2 illustrates two
BDDs of ω
1
, ω
2
with ordering x
1
≺ x
2
≺ x
3
≺ x
4
and
x
5
≺ x
6
≺ x
7
≺ x
8
respectively in Example 1.
To maintain consistency across overlapping AMO
constraints in consecutive windows, the forward BDD
of one window is bonded to the backward BDD of
the subsequent window. Specifically, for each pair
of consecutive windows ω
i
and ω
i+1
, the j
th
layer of
ω
f
i
is connected to the (w − j + 2)
th
layer of ω
b
i+1
,
where 2 ≤ j ≤ w. This bonding is enforced through
binary clauses that synchronize the sub-constraints of
overlapping variables, ensuring that shared variables
adhere to the SCAMO constraints without redundant
encodings. On layers ω
f
1
-BDD and ω
b
2
-BDD, we have
following sub-formulae:
(x
1
+ x
2
+ x
3
+ x
4
≤ 1)
∧(x
2
+ x
3
+ x
4
≤ 1) ∧(x
5
≤ 1)
∧(x
2
+ x
3
+ x
4
≤ 0 ∨x
5
≤ 0)
∧(x
3
+ x
4
≤ 1) ∧(x
5
+ x
6
≤ 1)
∧((x
3
+ x
4
≤ 0) ∨(x
5
+ x
6
≤ 0))
∧(x
4
≤ 1) ∧(x
5
+ x
6
+ x
7
≤ 1)
∧((x
4
≤ 0) ∨(x
5
+ x
6
+ x
7
≤ 0))
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
166

Duplex encoding (Fazekas et al., 2020) lever-
ages BDDs to systematically decompose and en-
code SCAMO constraints, and reduces the number
of clauses compared to naive encoding by reusing
sub-constraints. It introduces additional complexity
in both clause generation and memory usage, lead-
ing to increased clause generation (N(3(w − 2) +
2(w −1) −1) clauses), especially in larger problem
instances (in the worst case it is O
n
2
). The need
for auxiliary variables to bond BDDs across windows
adds to the memory overhead (N(2w − 3)). Each
window requires multiple variables for both AMO
and AMZ constraints, which may cause inefficiencies
when scaling to larger datasets or higher dimensions.
3 THE SC ENCODING FOR
SCAMO CONSTRAINTS
In this section, we will introduce our method for en-
coding SCAMO, called SCL (Sequential Counter en-
coding for Ladder constraints). Our approach takes
advantage of the reusable potential of decomposed
constraints. First, we break down the large SCAMO
into smaller blocks based on related sub-expressions.
These related sub-expressions can then be encoded
into a single Sequential Counter (SC), which gener-
ates some auxiliary register bits. Finally, we connect
these auxiliary bits to reformulate the original con-
straints of the SCAMO.
3.1 SCL Encoding for SCAMO
Given a SCAMO set of width w over n variables,
let Ω = {x
1
, x
2
, . . . , x
n
}, we divide Ω into M =
n
w
subsets, denoted as {ω
1
, . . . , ω
M
}. Each subset con-
tains up to w unique variables, such that ω
i
=
{x
i,1
, . . . , x
i,w
}. For each subset ω
i
, we create two SC
blocks that represent the constraint (x
i,1
+ . . . + x
i,w
≤
1) by using different variable orderings: a left order-
ing starting from x
i,1
to x
i,w
and a right ordering start-
ing from x
i,w
to x
i,1
. The sub-expressions obtained
from the SC construction of adjacent blocks can then
be combined to reconstruct the AMO constraints of
the original SCAMO.
As illustrated in Figure 1, the set of variables in
the example SCAMO is divided into three subsets:
ω
1
= {x
1
, x
2
, x
3
, x
4
}, ω
2
= {x
5
, x
6
, x
7
, x
8
}, and ω
3
=
{x
9
, x
10
}. Constructing ω
1
using SC with right vari-
able ordering yields a block of four sub-expressions:
R
1,1
= {x
4
}, R
1,2
= {x
3
+x
4
}, R
1,3
= {x
2
+x
3
+x
4
}and
R
1,4
= {x
1
+ x
2
+ x
3
+ x
4
}. Similarly, constructing ω
2
using the same method but in reverse order produces
another block of four sub-expressions: R
2,1
= {x
5
},
R
2,2
= {x
5
+ x
6
}, R
2,3
= {x
5
+ x
6
+ x
7
}, and R
2,4
=
{x
5
+x
6
+x
7
+x
8
}. Combining R
1,3
and R
2,1
results in
the expression {x
2
+ x
3
+ x
4
+ x
5
}. Meanwhile, com-
bining R
1,2
and R
2,2
yields {x
3
+ x
4
+ x
5
+ x
6
}, and so
on for other combinations.
We observe that when two blocks represent the
same set of variables but are ordered differently, it is
sufficient to use only one of these blocks to satisfy
the AMO constraint. We refer to the block that satis-
fies the AMO constraint as the AMO block, while the
other block is called the AMZ block.
Note that the first and the last subsets are the spe-
cial cases. They are adjacent to only one subset, ei-
ther on the left or the right side, unlike the other
subsets, which are adjacent to two subsets on both
sides. Therefore, their construction consists of only
one block with the AMO constraint, i.e., the AMO
block.
Let R
i, j
represent the register bit that indicates the
sum of the first j variables. Let x
i, j
denote the j
th
vari-
able of block B
i
according to the variable ordering.
The relationship for R
i, j
is defined as follows:
R
i, j
is true if and only if
j
∑
j
′
=1
x
i, j
′
= 1,
which means that exactly one of the first j variables in
block B
i
is true. Conversely,
R
i, j
is false if and only if
j
∑
j
′
=1
x
i, j
′
≤ 0,
indicating that all of the first j variables in block B
i
are false.
AMO and AMZ blocks are encoded by the follow-
ing four formulas:
(1)
V
w
j=2
x
i, j
→ R
i, j
(2)
V
w
j=2
R
i, j−1
→ R
i, j
(3)
V
w
j=2
¬x
i, j
∧¬R
i, j−1
→ ¬R
i, j
(4)
V
w
j=2
x
i, j
→ ¬R
i, j−1
Formula (1) sets the register bits R
i, j
to true when
x
i, j
is true. Formula (2) sets R
i, j
to true if the previous
register bit R
i, j−1
is true. Formula (3) sets R
i, j
to false
when all the j variables are false. Finally, we include
formula (4) to ensure that at most one variable can be
true.
For example, we indexed four blocks derived from
the decomposition of the SCAMO as illustrated in
Figure 1. The corresponding register bits of their sub-
expressions are shown in Figure 3. Block B
1
repre-
sents the first subset and must therefore be classified
as an AMO block. Its construction utilizes all four
formulas as follows:
Sequential Counter Encoding for Staircase At-Most-One Constraints
167
B
1
(x
1
+ (x
2
+ (x
3
+ (x
4
)))) ≡ R
1,4
(x
2
+ (x
3
+ (x
4
))) ≡ R
1,3
(x
3
+ (x
4
)) ≡ R
1,2
(x
4
) ≡ R
1,1
B
2
(x
5
) ≡ R
2,1
((x
5
) + x
6
) ≡ R
2,2
(((x
5
) + x
6
) + x
7
) ≡ R
2,3
((((x
5
) + x
6
) + x
7
) + x
8
) ≡ R
2,4
B
3
(x
5
+ (x
6
+ (x
7
+ (x
8
)))) ≡ R
3,4
(x
6
+ (x
7
+ (x
8
))) ≡ R
3,3
(x
7
+ (x
8
)) ≡ R
3,2
(x
8
) ≡ R
3,1
B
4
x
9
≡ R
4,1
(((x
9
)) + x
10
) ≡ R
4,2
Figure 3: Register bits constructing of SC blocks.
(1)
V
4
j=2
⇐⇒
x
1,2
→ R
1,2
x
1,3
→ R
1,3
x
1, j
→ R
1, j
x
1,4
→ R
1,4
(2)
V
4
j=2
⇐⇒
R
1,1
→ R
1,2
R
1,2
→ R
1,3
R
1, j−1
→ R
1, j
R
1,3
→ R
1,4
(3)
V
4
j=2
⇐⇒
¬x
1,2
∧¬R
1,1
→ ¬R
1,2
¬x
1,3
∧¬R
1,2
→ ¬R
1,3
¬x
1, j
∧¬R
1, j−1
→ ¬R
1, j
¬x
1,4
∧¬R
1,3
→ ¬R
1,4
(4)
V
4
j=2
⇐⇒
x
1,2
→ ¬R
1,1
x
1,3
→ ¬R
1,2
x
1, j
→ ¬R
1, j−1
x
1,4
→ ¬R
1,3
According to the variable ordering of block B
1
,
we have x
1,1
≡ x
4
, x
1,2
≡ x
3
, x
1,3
≡ x
2
, x
1,4
≡ x
1
, and
x
4
≡ R
1,1
. As a result, the constraints above are now
equivalent to:
x
1,2
→ R
1,2
⇐⇒
x
3
→ R
1,2
x
1,3
→ R
1,3
x
2
→ R
1,3
x
1,4
→ R
1,4
x
1
→ R
1,4
R
1,1
→ R
1,2
⇐⇒
x
4
→ R
1,2
R
1,2
→ R
1,3
R
1,2
→ R
1,3
R
1,3
→ R
1,4
R
1,3
→ R
1,4
¬x
1,2
∧¬R
1,1
→ ¬R
1,2
⇐⇒
¬x
3
∧¬x
4
→ ¬R
1,2
¬x
1,3
∧¬R
1,2
→ ¬R
1,3
¬x
2
∧¬R
1,2
→ ¬R
1,3
¬x
1,4
∧¬R
1,3
→ ¬R
1,4
¬x
1
∧¬R
1,3
→ ¬R
1,4
x
1,2
→ ¬R
1,1
⇐⇒
x
3
→ ¬x
4
x
1,3
→ ¬R
1,2
x
2
→ ¬R
1,2
x
1,4
→ ¬R
1,3
x
1
→ ¬R
1,3
Let block B
2
be an AMO block from the second
subset. The construction of the block B
2
is as follows:
x
6
→ R
2,2
¬x
6
∧¬x
5
→ ¬R
2,2
x
7
→ R
2,3
¬x
7
∧¬R
2,2
→ ¬R
2,3
x
8
→ R
2,4
¬x
8
∧¬R
2,3
→ ¬R
2,4
x
5
→ R
2,2
x
6
→ ¬x
5
R
2,2
→ R
2,3
x
7
→ ¬R
2,2
R
2,3
→ R
2,4
x
8
→ ¬R
2,3
The block B
3
also represents the second subset,
just as block B
2
does. Since block B
2
is an AMO
block, block B
3
is designated as an AMZ block and
is constructed without applying formula (4):
x
7
→ R
3,2
¬x
7
∧¬x
8
→ ¬R
3,2
x
6
→ R
3,3
¬x
6
∧¬R
3,2
→ ¬R
3,3
x
5
→ R
3,4
¬x
5
∧¬R
3,3
→ ¬R
3,4
x
8
→ R
3,2
R
3,2
→ R
3,3
R
3,3
→ R
3,4
The block B
4
represents the final subset and can
be constructed using the same method as the B
1
and
B
2
blocks. The important point is that B
4
is an in-
complete block; its width is only 2. Therefore, rather
than creating a wide SC of length w, we will create an
SC that matches the actual width of the B
4
block by
implementing the following constraints:
x
10
→ R
4,2
¬x
10
∧¬x
9
→ ¬R
4,2
x
9
→ R
4,2
x
10
→ ¬x
9
After breaking down into SC blocks, we need
to connect these blocks to reformulate the original
SCAMO. In this process, we connect each block
from every subset to the corresponding block of the
neighboring subsets.
The connection between blocks B
1
and B
2
is in-
tended to reformulate the following five AMO con-
straints:
(x
1
+ x
2
+ x
3
+ x
4
≤ 1)∧
(x
2
+ x
3
+ x
4
+ x
5
≤ 1)∧
(x
3
+ x
4
+ x
5
+ x
6
≤ 1)∧
(x
4
+ x
5
+ x
6
+ x
7
≤ 1)∧
(x
5
+ x
6
+ x
7
+ x
8
≤ 1)
Proposition 1 is applied to decompose these five
constraints into:
(x
1
+ x
2
+ x
3
+ x
4
≤ 1)∧
(x
2
+ x
3
+ x
4
≤ 1) ∧(x
5
≤ 1) ∧(x
2
+ x
3
+ x
4
≤ 0 ∨x
5
≤ 0)∧
(x
3
+ x
4
≤ 1) ∧(x
5
+ x
6
≤ 1) ∧(x
3
+ x
4
≤ 0 ∨x
5
+ x
6
≤ 0)∧
(x
4
≤ 1) ∧(x
5
+ x
6
+ x
7
≤ 1) ∧(x
4
≤ 0 ∨x
5
+ x
6
+ x
7
≤ 0)∧
(x
5
+ x
6
+ x
7
+ x
8
≤ 1)
The resulting AMZ constraints can then be re-
placed with the corresponding register bits as follows:
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
168
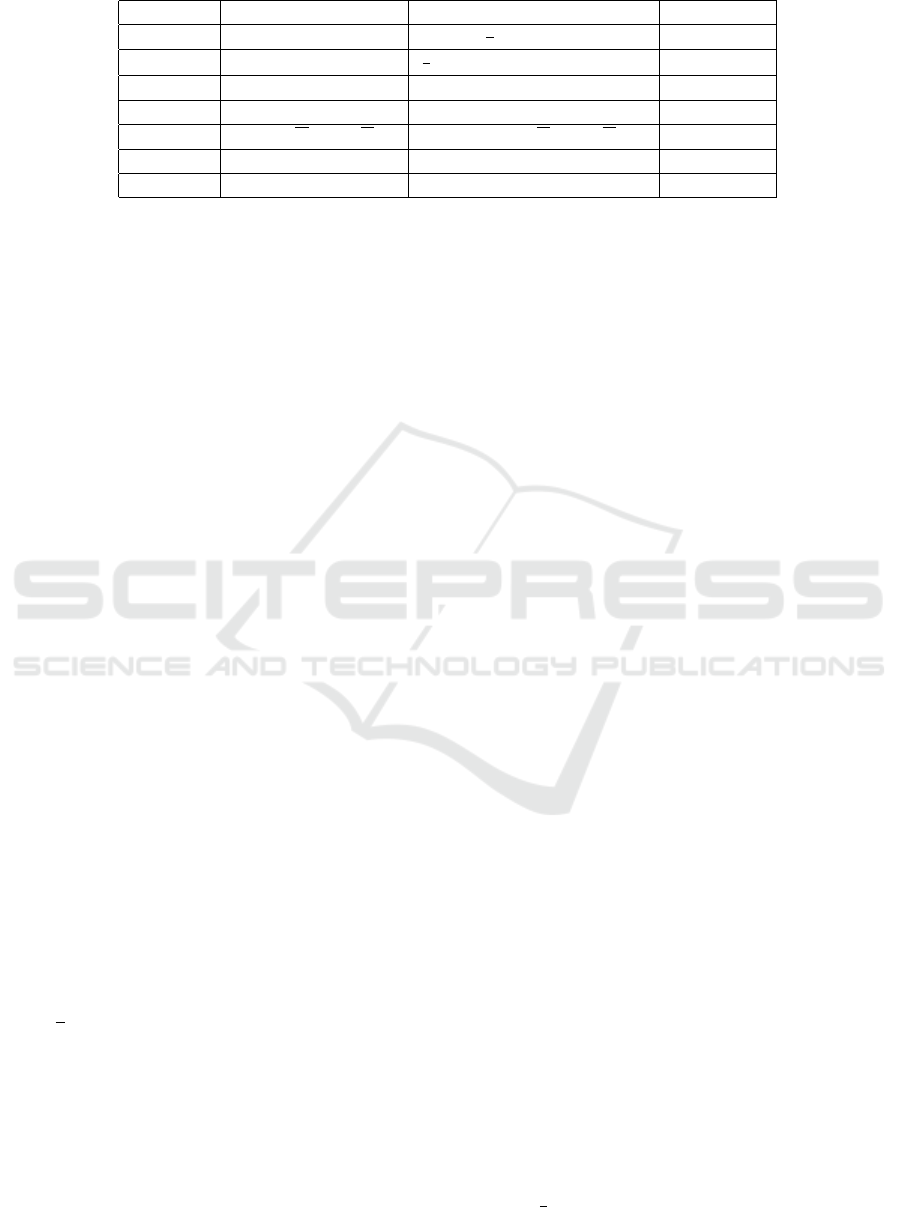
Table 1: Size of SAT encoding for a SCAMO constraint over n variables with width w.
Encoding Auxiliary variables Clauses Complexity
Naive 0
1
2
N(w −1)w O(n
3
)
Reduced 0
1
2
(w −1)w + (N −1)(w −1) O(n
2
)
Seq N(w −2) N(3(w −2) + 1) O(n
2
)
BDD N(2w −3) N(3(w −2) + 2(w −1) −1) O(n
2
)
2-product N(2
√
w + O
4
√
w) N(2w + 4
√
w + O
4
√
w) O(n
2
)
Duplex 4Mw −4M 13Mw −14M −3w + 2 O(n)
SCL 2Mw −3M −2w + 4 8Mw −8M −7w + 7 O(n)
(x
1
+ x
2
+ x
3
+ x
4
≤ 1)∧
(x
2
+ x
3
+ x
4
≤ 1) ∧(x
5
≤ 1) ∧(¬R
1,3
∨¬x
5
)∧
(x
3
+ x
4
≤ 1) ∧(x
5
+ x
6
≤ 1) ∧(¬R
1,2
∨¬R
2,2
)∧
(x
4
≤ 1) ∧(x
5
+ x
6
+ x
7
≤ 1) ∧(¬x
4
∨¬R
2,3
)∧
(x
5
+ x
6
+ x
7
+ x
8
≤ 1)
Likewise, the connection between blocks B
3
and
B
4
is encoded by:
(x
5
+ x
6
+ x
7
+ x
8
≤ 1)∧
(x
6
+ x
7
+ x
8
+ x
9
≤ 1)∧
(x
7
+ x
8
+ x
9
+ x
10
≤ 1)
≡
(x
5
+ x
6
+ x
7
+ x
8
≤ 1)∧
(x
6
+ x
7
+ x
8
≤ 1) ∧(x
9
≤ 1) ∧(¬R
3,3
∨¬x
9
)∧
(x
7
+ x
8
≤ 1) ∧(x
9
+ x
10
≤ 1) ∧(¬R
3,2
∨¬R
4,2
)
All in all, given two blocks that represent two
consecutive windows of width w {x
i
, . . . , x
i+w
} and
{x
i+w+1
, . . . , x
i+w+w
}. Connecting these two blocks re-
quires w −1 clauses:
∑
w
j=2
(
∑
i+w
k=i+ j
x
k
≤ 0 ∨
∑
i+w+ j−1
k
′
=i+w+1
x
k
′
≤ 0)
3.2 Comparison of SCAMO Encodings
In this section, we compare our proposed SCL encod-
ing with Duplex (Fazekas et al., 2020) and several en-
codings for each AMO constraint, including Pairwise,
Sequential Counter (Sinz, 2005), BDD (Ab
´
ıo et al.,
2012), and 2-Product (Chen, 2010).
Table 1 presents the results concerning the number
of new variables and clauses generated for each en-
coding, both from the study by (Fazekas et al., 2020)
and our SCL encoding. The Naive method utilized
Pairwise encoding, while the Reduced method elimi-
nated duplicate binary clauses in the pairwise encod-
ing process. Note that in Table 1, N = (n −w) + 1 and
M =
n
w
.
The Duplex encoding encodes each window sepa-
rately by creating two BDDs, each containing 2(w +
1) nodes. After constructing these diagrams, the lay-
ers of the neighboring BDDs are connected, result-
ing in M −1 bond clauses. According to the esti-
mation in (Fazekas et al., 2020), Duplex encoding re-
quires approximately 13Mw −14M −3w + 2 clauses
and 4Mw −4M auxiliary variables.
When comparing the construction of two BDDs
used in Duplex encoding with our SCL encoding, we
find that SCL requires fewer variables and clauses. To
simplify the calculation, let’s assume that each block
has the same size, although most of the time the last
block is smaller. For the first and last subsets, SCL
creates one AMO block, while for the remaining (M-
2) subsets, SCL creates one AMO block and one AMZ
block each. This results in a total of M AMO blocks
and M −2 AMZ blocks. Additionally, M + M −2 =
2M −2 blocks require M −1 connections. In con-
clusion, the number of clauses in SCL encoding is:
AMO-block-clauses ≤ M(4(w −1))
= 4Mw −4M
AMZ-block-clauses ≤ (M −2)(3(w −1))
= 3Mw −3M −6w + 6
Connect-clauses ≤ (M −1)(w −1)
= Mw −M −w + 1
Total-clauses = AMO-block-clauses +
AMZ-block-clauses +
Connect-clauses +
≤ 8Mw −8M −7w + 7
The total number of auxiliary variables in our en-
coding is at most (w −1) + (M −2)((w −1) + (w −
2) + (w −1)) = 2Mw −3M −2w + 4. In this expres-
sion, the first and last (w −1) variables are used to
encode the AMO block of the first and last subsets.
The remaining (M −2)((w −1) + (w −2)) variables
are used to encode the (M −2) subsets between the
first and last subsets, with each subset using (w −1)
variables for the AMO block and (w−2) variables for
the AMZ block. The AMZ blocks require one variable
less than the AMO blocks because the highest regis-
ter bits of both blocks are the same, allowing AMZ
blocks to reuse them from the AMO blocks instead of
creating new ones. For example, the register bit R
2,4
of
block B
2
and the register bit R
3,4
of block B
3
in Figure
3 both represent {x
5
+x
6
+x
7
+x
8
}, hence R
2,4
≡R
3,4
.
Table 1 shows the number of auxiliary variables,
the number of clauses, and the complexity of differ-
ent SAT encodings in the SCAMO constraint set of n-
variable with AMO constraints of width w. The com-
plexity of each approach is calculated based on the
number of clauses in the worst case (i.e., w is approx-
imately
n
2
).
Sequential Counter Encoding for Staircase At-Most-One Constraints
169
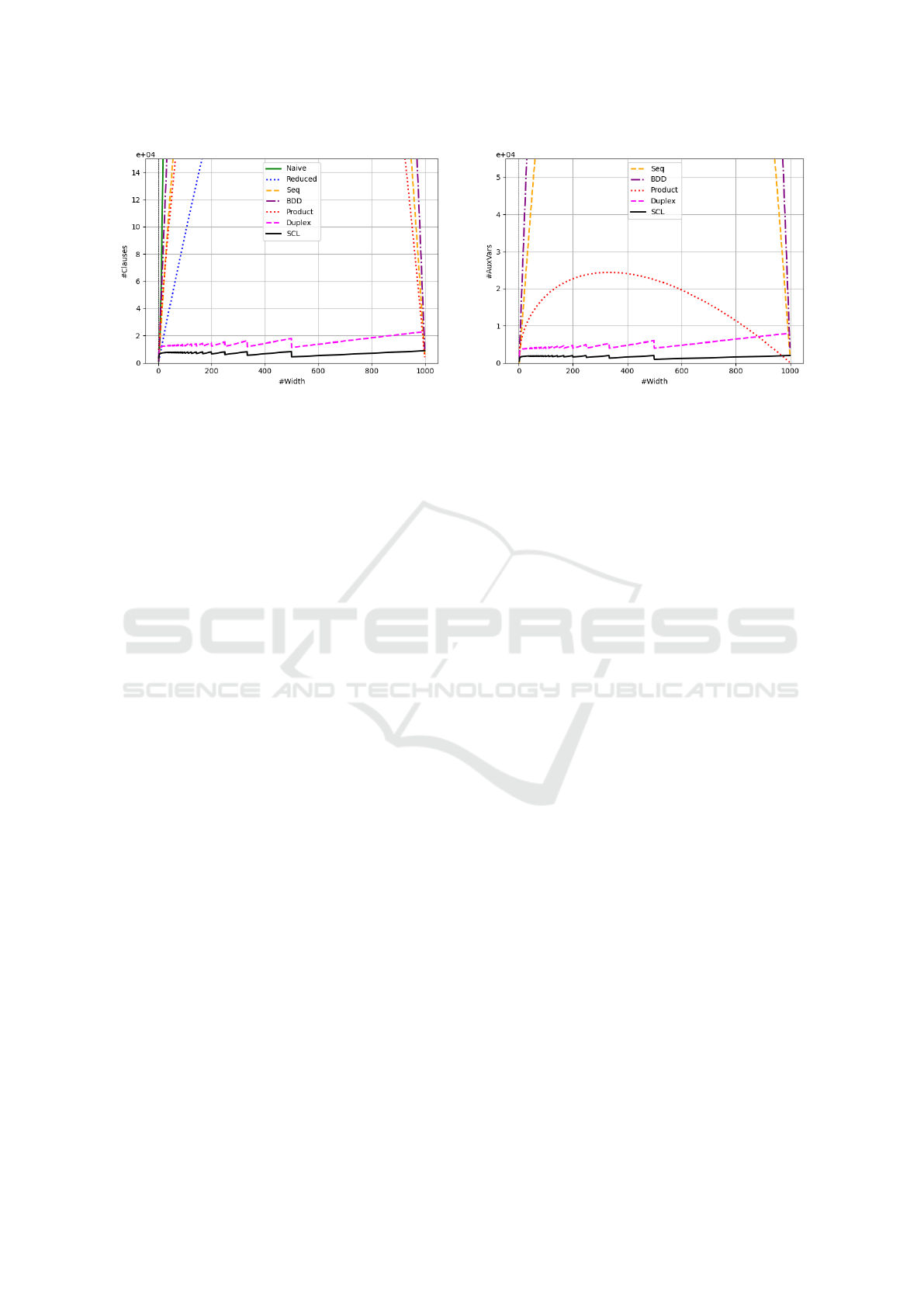
Figure 4: Comparison of the number of clauses of a
SCAMO with parameters set to n = 1000 and w ∈(1, 1000).
The theoretical calculations provided above show
that our proposed encoding demonstrates superior
performance in terms of the number of clauses. It has
linear complexity and uses just over half the number
of variables compared to the Duplex encoding, which
also has linear complexity. Importantly, our SCL en-
coding requires fewer auxiliary variables than the Se-
quential counter, BDD, 2-product, and even Duplex
encodings. The Naive and Reduced encodings are the
only ones that do not use any auxiliary variables; how-
ever, their complexities of O(n
3
) and O(n
2
) cannot be
compared to our complexity of O(n).
Figures 4 and 5 illustrate the number of clauses
and auxiliary variables needed to encode a set of
SCAMO constraints with n = 1000 and w ∈ (1, 1000)
for various SAT encodings, based on calculations
from Table 1.
4 ANTI-BANDWIDTH PROBLEM
We apply our proposed method to the anti-bandwidth
problem (ABP) (Sinnl, 2021), which is an NP-hard
problem with applications in various scheduling sce-
narios, including radio frequency assignment, obnox-
ious facility location, and map coloring.
4.1 Problem Definition
Let G = (V, E) be a graph where V is the set of vertices
and E is the set of edges. Let n = |V| be the number
of vertices, and m = |E| be the number of edges. A la-
beling f of the vertices is a bijection V → {1, ..., n}
such that each vertex i ∈ V receives a unique label
f(i) ∈ {1, ..., n}.
Given graph G and labeling f, AB
f
(i) is the mini-
mum bandwidth of vertex i ∈V and the labeling f:
AB
f
(i) = min{|f (i) − f (i
′
)| : {i, i
′
} ∈ E}
Figure 5: Comparison of the number of auxiliary vari-
ables of a SCAMO with parameters set to n = 1000 and
w ∈(1, 1000).
The bandwidth of G is the minimal value among
the AB
f
(i) values:
AB
f
(G) = min{AB
f
(i) : i ∈V }
Let F(G) denote all labels of G. The anti-
bandwidth problem aims at finding a labeling f
∗
that
maximizes the bandwidth of G. The corresponding
value AB
f
∗
(G) is called anti-bandwidth AB(G) of G,
i.e.,
AB(G) = max
f ∈F
AB
f
(G)
4.2 Constraint Representation
(Duarte et al., 2011) introduced a mixed-integer
programming (MIP) approach to provide a solution
to ABP. Then, based on the MIP approach, (Sinnl,
2021) presented an iterative formulation, which is
a feasibility problem, to answer the question “Does
there exist a solution with AB(G) ≥ k + 1?”. This
iterative approach can be stated as follows:
Let boolean variables x
l
i
take the value true i f f
vertex i gets labels l, i.e. f
i
= l. To make sure that
every vertex gets a unique labeling, the following set
of constraints (V ERT ICES) and (LABELS) are used:
∑
i∈V
x
l
i
= 1 ∀l ∈ {1, . . . ,
|
V
|
} (V ERT ICES)
∑
l∈{1,...,
|
V
|
}
x
l
i
= 1 ∀i ∈V (LABELS)
If k is a feasible bandwidth of the ABP, the con-
straint (OBJ −k), which makes sure that for each edge
{i, i
′
} ∈ E, the difference between the labeling of ver-
tex i and i
′
must not be lower than or equal to k, must
be satisfied; otherwise, it is unsatisfied:
∑
l
2+k
l
′
=l
2
(x
l
′
i
+ x
l
′
i
′
) ≤ 1 ∀{i, i
′
} ∈ E (OBJ −k)
∀1 ≤ l
2
≤
|
V
|
−k
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
170

This iterative approach firstly assigns k ← 1 then
solves the set of three constraints above. After that,
it continues to increase k by one and restart the solv-
ing process until we obtain an unsatisfied result. The
value of k when the solution process yields the value
unsatis f iability is the AB(G) of ABP.
For each edge in E, there should be an OBJ −k
constraint to ensure that the difference between the
two vertices of that edge is at least k. It means encod-
ing all the edges in E results in
|
E
|
different SCAMOs.
In order to reduce the number of SCAMOs, (Fazekas
et al., 2020) uses Proposition 1 to decompose (OBJ −
k) constraints into:
∑
l
2+k
l
′
=l
2
(x
l
′
i
+ x
l
′
i
′
) ≤ 1
Prop. 1
≡
∑
l
2+k
l
′
=l
2
x
l
′
i
≤ 1 ∧
∑
l
2+k
l
′
=l
2
x
l
′
i
′
≤ 1∧
(
∑
l
2+k
l
′
=l
2
x
l
′
i
≤ 0 ∨
∑
l
2+k
l
′
=l
2
x
l
′
i
′
≤ 0)
This decomposition breaks a SCAMO of an edge
into two SCAMOs of a single vertex. Since the num-
ber of edges
|
E
|
is much more than the number of
vertices
|
V
|
in most of the graphs, the number of
SCAMOs obtained from this decomposition after ter-
minating all duplicates is lower than from the origi-
nal OBJ −k constraints. Then, the two SCAMOs are
reconnected using a dis junction of some AMZ con-
straints of width k + 1, which can be formulated by
combining our constructed AMZ sub-expressions in
SCAMOs, as outlined in Proposition 2:
Proposition 2. A constraint x
1
+ x
2
+ . . . + x
n
≤ 0
holds iff for all 1 ≤ i < n :
(x
1
+ . . . + x
i
≤ 0) ∧(x
i+1
+ . . . + x
n
≤ 0)
Let the SCAMO in Figure 1 be the SCAMO of a
single vertex got from decomposing a SCAMO of an
edge. The connect dis junction now contains all the
constraints of the SCAMO in Figure 1 but in AMZ
form, such as (x
2
+ x
3
+ x
4
+ x
5
≤ 0). Proposition 2
then breaks the constraint (x
2
+ x
3
+ x
4
+ x
5
≤ 0) into
(x
2
+ x
3
+ x
4
≤ 0) ∧(x
5
≤ 0), which is equivalent to
¬R
1,3
∧¬R
2,1
(see Figure 3).
Take note that the (LABELS) constraint can be
formulated by merging subsets in corresponding
SCAMO, so instead of creating AMO constraints for
all variables, we focus on creating AMO constraints
for the subsets only. Because every subset also is
an AMO constraint and already constructed in the
(OBJ-k) constraint, this approach not only yields the
same result but also takes advantage of reusing subset
constructions. For example, in the Figure 1, instead
of creating the AMO constraint of all the 10 variables,
we only need to create the AMO constraint of 3
subsets {x
1
, x
2
, x
3
, x
4
}, {x
5
, x
6
, x
7
, x
8
} and {x
9
, x
10
}.
In addition, we can see that for every labeling f
of the n-vertex graph, there exists a corresponding re-
versed labeling f
′
where f
′
= n + 1 − f . Since f
′
is
a linear transformation of f , it ensures that for each
value in f , there is exactly one corresponding value
in f
′
. This means that if f satisfies the conditions
of (V ERT ICES) and (LABELS) then f
′
also satisfies
these conditions. Furthermore, f
′
maintains the same
bandwidth as f :
|
f
′
(i) − f
′
(i
′
)
|
=
|
(n + 1 − f (i)) −(n + 1 − f (i
′
))
|
=
|
f (i
′
) − f (i)
|
Based on this observation, we apply the symme-
try breaking technique (Gent et al., 2006) to reduce
the search space. In our implementation of ABP, we
employ symmetry breaking at one selected node us-
ing two different configurations: the first node and the
highest-degree node.
5 EXPERIMENTAL EVALUATION
5.1 Experimental Setup
We implemented two frameworks to compare state-
of-the-art methods with our proposed encoding, SCL.
The first framework focuses on the SCAMO, while
the second focuses on the ABP.
In the first framework
1
, we compare SCL along-
side five other SAT encodings: Naive, Reduced, Se-
quential counter, 2-product (Product), and Duplex, as
detailed in Section 3.2. These methods were applied
to a SCAMO with parameters set to n = 1000 and w
varying between 1 and 1000.
In the second framework
2
, in addition to our pro-
posed encoding and the other SAT encodings from
the first framework, we also included several Con-
straint Programming (CP) and Mixed Integer Pro-
gramming (MIP) approaches. We benchmarked our
experiments using 24 matrices from the Harwell-
Boeing Sparse Matrix Collection (Rodriguez-Tello
et al., 2015), which consists of 12 relatively small
to medium-sized graphs and 12 significantly larger
graphs. These matrices were tested on a cluster in
Google Cloud Platform
3
with configurations of ma-
chine type e2-highmem-8 (8 vCPUs, 4 cores, 64GB
memory) and Debian GNU/Linux 12 operating sys-
tem. For selected SAT solver, we used version 1.2.1
of the CaDiCal solver (Biere, 2019).
Table 2 presents information on 24 matrices, in-
cluding their names, the number of vertices |V |, and
1
https://github.com/TruongXuanHieu-H/
StaircaseEncoderSCL.git
2
https://github.com/TruongXuanHieu-H/
AntiBandwidthSCL.git
3
https://console.cloud.google.com/compute
Sequential Counter Encoding for Staircase At-Most-One Constraints
171
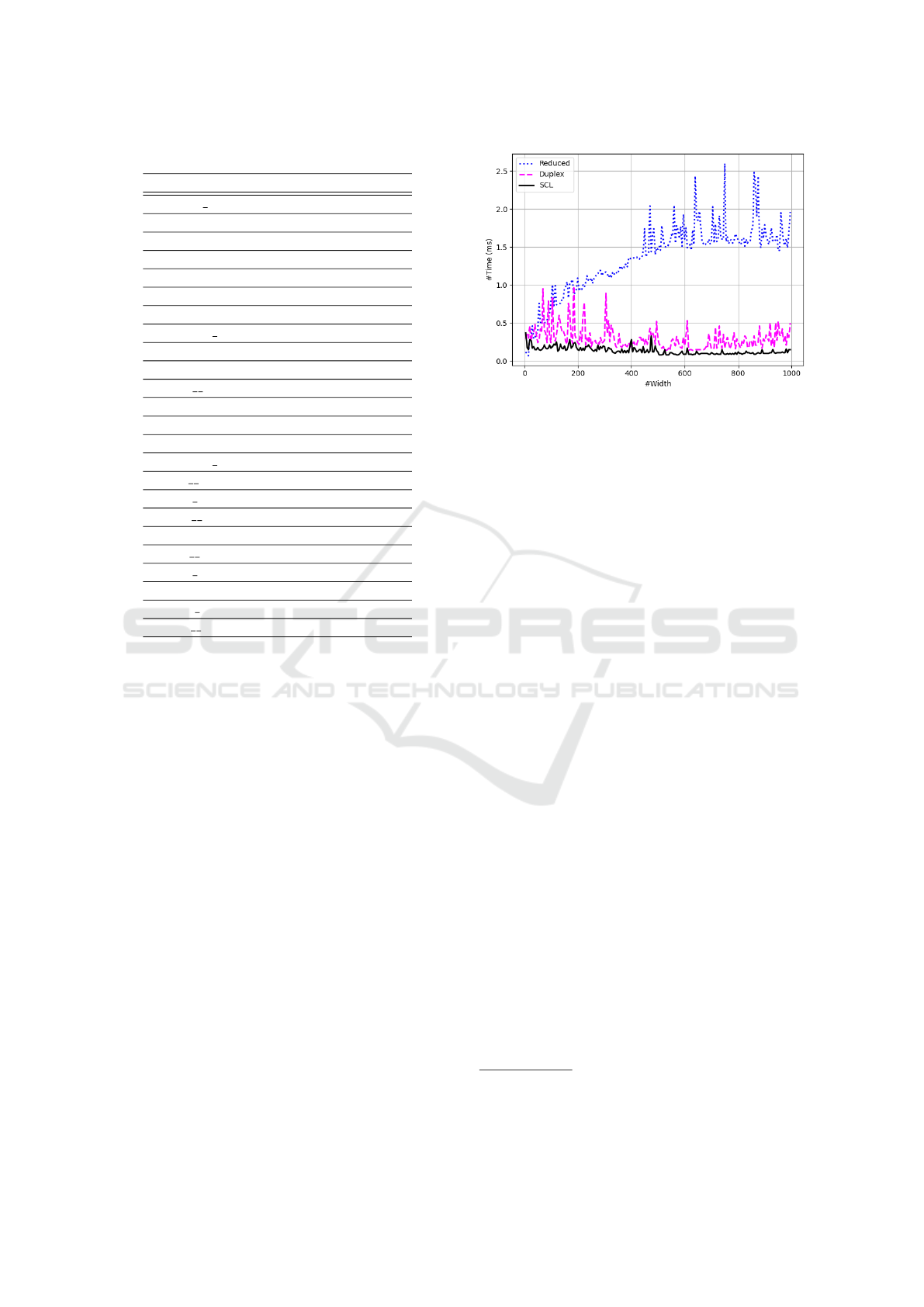
Table 2: Harwell-Boeing Sparse Matrix benchmark.
Instance
|
V
| |
E
|
LB UB
A-pores 1 30 103 6 8
B-ibm32 32 90 9 9
C-bcspwr01 39 46 16 17
D-bcsstk01 48 176 8 9
E-bcspwr02 49 59 21 22
F-curtis54 54 124 12 13
G-will57 57 127 12 14
H-impcol b 59 281 8 8
I-ash85 85 219 19 27
J-nos4 100 247 32 40
K-dwt 234 117 162 46 58
L-bcspwr03 118 179 39 39
M-bcsstk06 420 3720 28 72
N-bcsstk07 420 3720 28 72
O-impcol d 425 1267 91 173
P-can 445 445 1682 78 120
Q-494 bus 494 586 219 246
R-dwt 503 503 2762 46 71
S-sherman4 546 1341 256 272
T-dwt 592 592 2256 103 150
U-662 bus 662 906 219 220
V-nos6 675 1290 326 337
W-685 bus 685 1282 136 136
X-can 715 715 2975 112 142
the number of edges |E|. The corresponding lower
and upper bounds (LB and UB) are provided in
(Fazekas et al., 2020).
5.2 Evaluation for the SCAMO
We have evaluated the performance in terms of solv-
ing time for the given SCAMO with n = 1000 vari-
ables, where the width w was adjusted from 5 to 995
(i.e., 5, 10, 15, . . . , 995), as shown in Figure 6. Among
the three best encodings, SCL emerged as the most
effective, surpassing Duplex, which was previously
found to be the efficient encoding. A detailed com-
parison of all implemented encodings can be found
in Figure 9 in the Appendix. Overall, the results in-
dicate that, in most cases, the SCL encoding signifi-
cantly outperforms all other SAT encodings in terms
of time efficiency. Additionally, the effectiveness of
the generated clauses and the required auxiliary vari-
ables for SCL are discussed earlier in Figure 4 and 5.
5.3 Evaluation for the ABP
In the second framework, we implemented our ap-
proach along with four SAT encodings: Product, Re-
duced, Sequential counter, and Duplex. We followed
the same process throughout. Initially, we consider
Figure 6: Comparison of solving time for three best encod-
ings of a given SCAMO with n = 1000 and w ∈ (1, 1000).
LB as the starting width of SCAMO. If the SAT solver
yields a satisfiable result, we increase the width by 1
and restart the process. If the solver returns unsatisfi-
able or reaches the upper bound (UB), it indicates that
the optimal solution has been found and the iteration
process ends.
If the computation time exceeds 1800 seconds or
the memory usage exceeds 30GB, a termination sig-
nal is raised, causing the process to stop due to a time-
out (TO) or memory overload (MO), respectively. In
these cases, the highest solved width is reported as the
best result of the technique. If the technique fails to
solve the problem with the initial LB value, the result
is marked with a ”-”.
We also explore three approaches based on Con-
straint Programming (CP): F
e
(k), CP-CPLEX, and
CP-MZ-Chuffed. In our experiment, the F
e
(k) en-
coding utilizes the MIP (Mixed Integer Programming)
APIs provided by IBM ILOG CPLEX Optimization
Studio
4
version 20.1. Meanwhile, CP-CPLEX em-
ploys the CP APIs of IBM ILOG CPLEX Optimiza-
tion Studio version 22.1.1 (latest version). CP-MZ-
Chuffed makes use of the MiniZinc language (Nether-
cote et al., 2007) version 2.8.6 and incorporates
Chuffed solver
5
version 0.13.2. While these methods
take advantage of constraint programming techniques,
treating the ABP as a labeling problem and encoding
it straightforwardly still poses a considerable perfor-
mance drawback.
Table 3 presents a summary of our experimental
results on 24 selected matrices, with a time limit of
1800 seconds and a memory limit of 30 GB for the
Duplex, SCL, F
e
(k), CP-CPLEX, and CP-MZ-Chuffed
approaches. The Reduced, Sequential counter, and 2-
product encodings showed poorer performance com-
pared to both Duplex and SCL, therefore these encod-
4
https://www.ibm.com/products/
ilog-cplex-optimization-studio/cplex-optimizer
5
https://github.com/chuffed/chuffed.git
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
172
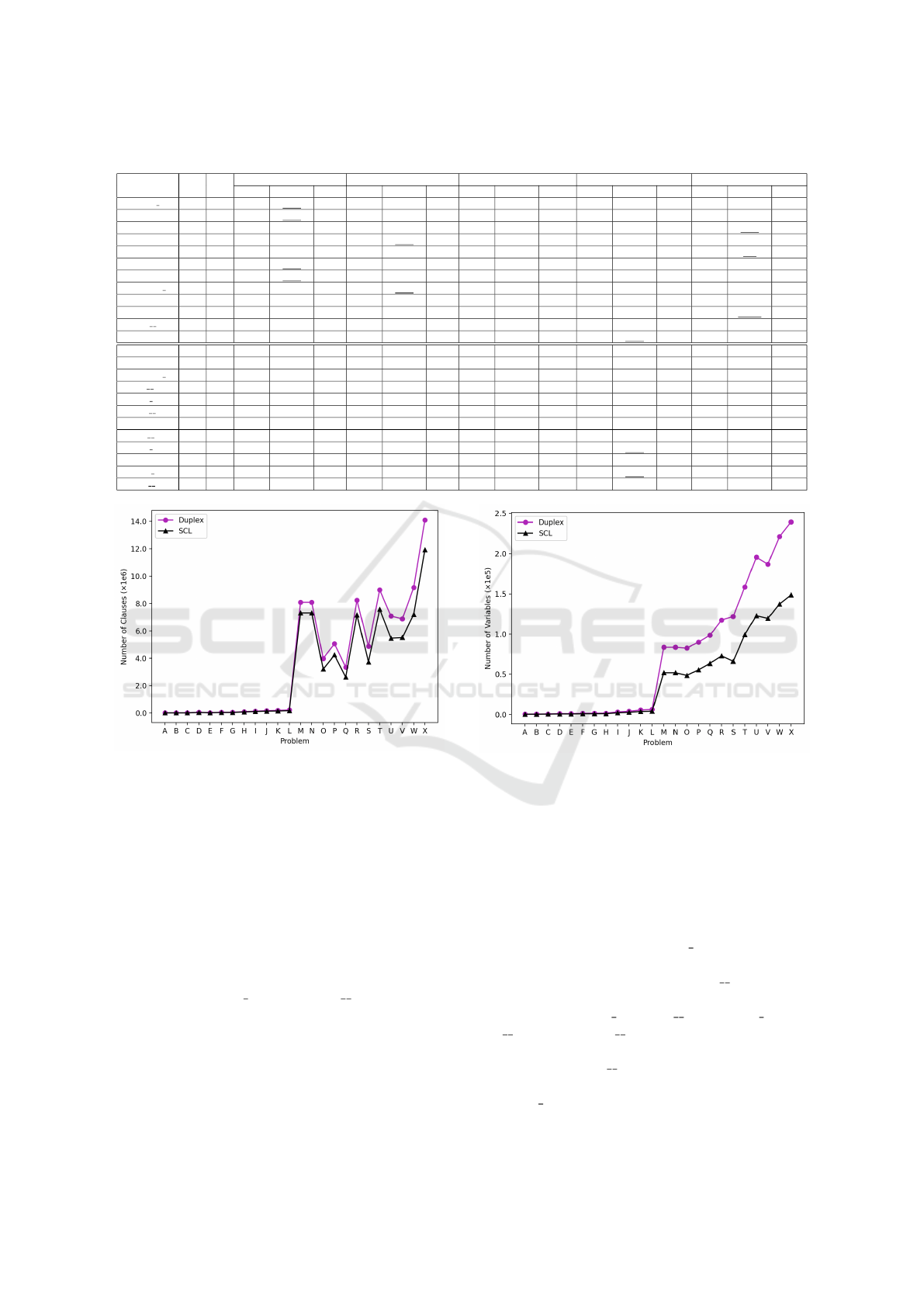
Table 3: ABP solving results with TO = 1800s and MO = 30GB.
Instance LB UB
Duplex SCL F
e
(k) CP-CPLEX CP-MZ-Chuffed
Obj-k Time(s) MB Obj-k Time(s) MB Obj-k Time(s) MB Obj-k Time(s) MB Obj-k Time(s) MB
A-pores 1 6 8 6 3.40 14.1 6 3.48 12.6 6 3.53 74.9 7 TO 579.3 6 4.75 42.3
B-ibm32 9 9 9 0.19 8.8 9 0.3 7.8 9 4.57 106.8 9 0.39 41.3 9 1.06 29.3
C-bcspwr01 16 17 17 1.11 11.2 17 4.19 18.6 17 3.59 97.5 17 0.67 41.0 17 0.43 28.6
D-bcsstk01 8 9 9 0.54 14.9 9 0.19 12.6 9 14.9 147.0 9 2.28 46.8 9 1.12 41.0
E-bcspwr02 21 22 21 2.15 14.9 21 1.52 11 21 17.8 170.2 21 15.83 51.5 21 0.8 31.5
F-curtis54 12 13 13 0.27 14.1 13 0.28 12.3 13 13.3 145.8 13 2.5 47.2 13 1.35 38.8
G-will57 12 14 13 0.29 14.4 13 0.47 13.9 13 18.5 175.6 13 14.18 51.5 13 1.09 39.9
H-impcol b 8 8 8 0.26 21.0 8 0.23 16.8 8 3.12 167.4 8 0.32 44.7 8 0.86 55.5
I-ash85 19 27 24 TO 272 24 TO 381 22 TO 460.3 23 TO 288.2 23 TO 374.8
J-nos4 32 40 35 472 177 35 980 503 - TO 927.0 35 TO 272.7 35 384.4 343.9
K-dwt 234 46 58 51 TO 685 51 TO 530 50 TO 895.3 52 TO 243.8 47 TO 244.6
L-bcspwr03 39 39 39 0.58 53 39 0.69 40.9 39 11.15 559.0 39 0.25 48.2 39 2.34 66.6
M-bcsstk06 28 72 35 TO 1726 35 TO 1398 - TO 12207 30 TO 738.4 - TO 3016
N-bcsstk07 28 72 35 TO 1726 35 TO 1397 - TO 12244 30 TO 737.9 - TO 3016
O-impcol d 91 173 101 TO 1745 102 TO 1802 - - MO 121 TO 491.3 - TO 1410
P-can 445 78 120 - TO 2464 79 TO 2156 - - MO 79 TO 869.2 - TO 1843
Q-494 bus 219 246 - TO 1443 220 TO 1301 - TO 23775 220 TO 701.6 - TO 763.8
R-dwt 503 46 71 64 TO 1634 64 TO 1474 - TO 10633 56 TO 717.6 - TO 1950
S-sherman4 256 272 - TO 1326 - TO 1073 - - MO - TO 689.9 - TO 888.8
T-dwt 592 103 150 - TO 5357 104 TO 2619 - - MO 104 TO 1366 - TO 1905
U-662 bus 219 220 220 471 2498 220 144 1377 - - MO 220 3.15 250.4 - TO 1061
V-nos6 326 337 - TO 1836 - TO 1532 - - MO - TO 967.9 - TO 1168
W-685 bus 136 136 136 10.7 1431 136 7.57 1164 - - MO 136 1.95 332.6 - TO 1325
X-can 715 112 142 - TO 3060 113 TO 4599 - - MO 113 TO 1380 - TO 2442
Figure 7: Comparison of the number of clauses between
Duplex and SCL.
ings are not included in Table 3. For each problem, the
table includes the best solution identified by each ap-
proach, the solving time (in seconds), and the memory
consumption (in MB). The best anti-bandwidth value
is highlighted in bold, while the best solving time is
underlined.
Figures 7 and 8 illustrate the comparison of the
number of clauses and auxiliary variables utilized in
the ABP encoding across 24 problems, evaluated us-
ing both the SCL and Duplex encodings. Each prob-
lem is represented by the first letter of its name (A for
the problem A-pores 1, X for X-can 715). We ana-
lyze the encodings achieved at the maximum width
that both methods can solve within specified time
and memory limits. The results indicate that as the
problem size increases, SCL requires fewer clauses
and auxiliary variables than Duplex. This evidence
demonstrates why SCL can outperform Duplex in
Figure 8: Comparison of the number of variables between
Duplex and SCL.
solving certain ABPs, particularly in challenging sce-
narios characterized by a high number of edges and
vertices in the 12 larger graphs, as well as in terms of
memory usage.
In the 12 relatively small to medium-sized graphs,
both SCL and Duplex demonstrate competitive per-
formance, generally surpassing other methods. Com-
pared to the best CP approach, SCL outperforms CP-
CPLEX in the problems A-pores 1, I-ash85, and J-
nos4. However, CP-CPLEX performs better than
SCL and Duplex in the problem K-dwt 234. Among
the 12 larger graphs, SCL outperforms Duplex in 5
problems: O-impcol d, P-can 445, Q-494 bus, T-
dwt 592, and X-can 715. Additionally, SCL ex-
ceeds CP-CPLEX in 3 problems: M-bcsstk06, N-
bcsstk07, and R-dwt 503. Nonetheless, CP-CPLEX
achieves significantly outperforms SCL in the problem
O-impcol d. When solving UNSAT instances, CP-
Sequential Counter Encoding for Staircase At-Most-One Constraints
173

CPLEX is weaker than both SCL and Duplex in cases
such as A-pores 1 (UNSAT with a width of 17), E-
bcspwr02 (UNSAT with a width of 22), and G-will57
(UNSAT with a width of 14).
5.4 Summary
Our proposed encoding, SCL, offers a valuable solu-
tion for addressing various SCAMO and ABP prob-
lems. In terms of SCAMO encoding, SCL outper-
forms all other SAT encodings regarding the number
of clauses, auxiliary variables, and solving time. For
ABP problems, SCL either matches or exceeds opti-
mal values in many instances, while demonstrating
competitive time efficiency and low memory usage.
Its ability to find valid solutions in complex instances
where other encodings timeout underscores its robust-
ness and scalability. Experimental results show that
SCL surpasses Duplex, which is recognized as an effi-
cient encoding for SCAMO and ABP (Fazekas et al.,
2020). Additionally, SCL outperforms CP-CPLEX, a
well-known commercial tool developed by IBM; SCL
exceeds CP-CPLEX in 6 out of 24 problems, while
CP-CPLEX only surpasses SCL in 2 out of 24 prob-
lems. Overall, SCL effectively balances performance
with resource management, making it a strong option
for tackling SCAMO and ABP challenges.
6 CONCLUSIONS
The paper presents our proposed SAT encoding for
SCAMO constraints, named SCL encoding. It uti-
lizes Sequential Counter Encoding for at-most-one
constraints with a staircase shape. SCL requires fewer
auxiliary variables and generates fewer clauses, mak-
ing it effective for encoding SCAMO constraints. It
yields better results for the anti-bandwidth problem
compared to other SAT encoding techniques as well
as Constraint Programming (CP) and Mixed Integer
Programming (MIP) approaches. Our proposed en-
coding, SCL, provides an efficient encoding for other
combinatorial problems that involve SCAMO con-
straints.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We thank the authors of Duplex encoding (Fazekas
et al., 2020) for publishing the source code of Du-
plex, which allows us to implement the Antiband-
width problem more conveniently. This work has
been supported by VNU University of Engineering
and Technology under project number CN24.10.
REFERENCES
Ab
´
ıo, I., Nieuwenhuis, R., Oliveras, A., Rodr
´
ıguez-
Carbonell, E., and Mayer-Eichberger, V. (2012). A
new look at bdds for pseudo-boolean constraints.
Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research, 45:443–
480.
Akers (1978). Binary decision diagrams. IEEE Transac-
tions on computers, 100(6):509–516.
Artigues, C., Hebrard, E., Mayer-Eichberger, V., Siala, M.,
and Walsh, T. (2014). Sat and hybrid models of the
car sequencing problem. In Integration of AI and OR
Techniques in Constraint Programming: 11th Inter-
national Conference, CPAIOR 2014, Cork, Ireland,
May 19-23, 2014. Proceedings 11, pages 268–283.
Springer.
Bessiere, C., Hebrard, E., Hnich, B., Kiziltan, Z., Quim-
per, C.-G., and Walsh, T. (2007). Reformulating
global constraints: The slide and regular constraints.
In Abstraction, Reformulation, and Approximation:
7th International Symposium, SARA 2007, Whistler,
Canada, July 18-21, 2007. Proceedings 7, pages 80–
92. Springer.
Biere, A. (2019). Cadical at the sat race 2019. In Heule, M.,
J
¨
arvisalo, M., and Suda, M., editors, Proceedings of
SAT Race 2019: Solver and Benchmark Descriptions,
volume B-2019-1 of Department of Computer Science
Series of Publications B, University of Helsinki 2019,
pages 8–9.
Bryant, R. E. (1986). Graph-based algorithms for boolean
function manipulation. Computers, IEEE Transac-
tions on, 100(8):677–691.
Cappanera, P. (1999). A survey on obnoxious facility loca-
tion problems.
Ceschia, S., Dang, N. T. T., De Causmaecker, P., Haspes-
lagh, S., and Schaerf, A. (2015). Second in-
ternational nurse rostering competition (inrc-ii)—
problem description and rules—. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1501.04177.
Chen, J. (2010). A new sat encoding of the at-most-one con-
straint. Proc. constraint modelling and reformulation,
page 8.
Duarte, A., Mart
´
ı, R., Resende, M. G., and Silva, R. M.
(2011). Grasp with path relinking heuristics for the
antibandwidth problem. Networks, 58(3):171–189.
Fazekas, K., Sinnl, M., Biere, A., and Parragh, S. (2020).
Duplex encoding of staircase at-most-one constraints
for the antibandwidth problem. In International
Conference on Integration of Constraint Program-
ming, Artificial Intelligence, and Operations Re-
search, pages 186–204. Springer.
Gent, I. P., Petrie, K. E., and Puget, J.-F. (2006). Symmetry
in constraint programming. Foundations of Artificial
Intelligence, 2:329–376.
Haberlandt, A., Green, H., and Heule, M. J. (2023). Ef-
fective auxiliary variables via structured reencoding.
arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.01904.
Hale, W. K. (1980). Frequency assignment: Theory and
applications. Proceedings of the IEEE, 68(12):1497–
1514.
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
174
Hu, Y., Gansner, E. R., and Kobourov, S. (2010). Visual-
izing graphs and clusters as maps. IEEE Computer
Graphics and Applications, 30(6):54–66.
Kletzander, L. and Musliu, N. (2020). Solving the general
employee scheduling problem. Computers & Opera-
tions Research, 113:104794.
Leung, J. Y., Vornberger, O., and Witthoff, J. D. (1984). On
some variants of the bandwidth minimization prob-
lem. SIAM Journal on Computing, 13(3):650–667.
Nethercote, N., Stuckey, P. J., Becket, R., Brand, S., Duck,
G. J., and Tack, G. (2007). Minizinc: Towards a stan-
dard cp modelling language. In International Con-
ference on Principles and Practice of Constraint Pro-
gramming, pages 529–543. Springer.
Nieuwenhuis, R., Oliveras, A., Rodr
´
ıguez-Carbonell, E.,
and Rollon, E. (2021). Employee scheduling with sat-
based pseudo-boolean constraint solving. IEEE ac-
cess, 9:142095–142104.
Rodriguez-Tello, E., Romero-Monsivais, H., Ram
´
ırez-
Torres, J., and Lardeux, F. (2015). Harwell-boeing
graphs for the cb problem.
Siala, M. (2015). Search, propagation, and learning in se-
quencing and scheduling problems. PhD thesis, INSA
de Toulouse.
Sinnl, M. (2021). A note on computational approaches for
the antibandwidth problem. Central European Jour-
nal of Operations Research, 29(3):1057–1077.
Sinz, C. (2005). Towards an optimal cnf encoding of
boolean cardinality constraints. In International con-
ference on principles and practice of constraint pro-
gramming, pages 827–831. Springer.
Vasconcellos-Gaete, C., Barichard, V., and Lardeux, F.
(2020). Abacus: A new hybrid encoding for sat prob-
lems. In 2020 IEEE 32nd International Conference on
Tools with Artificial Intelligence (ICTAI), pages 145–
152. IEEE.
APPENDIX
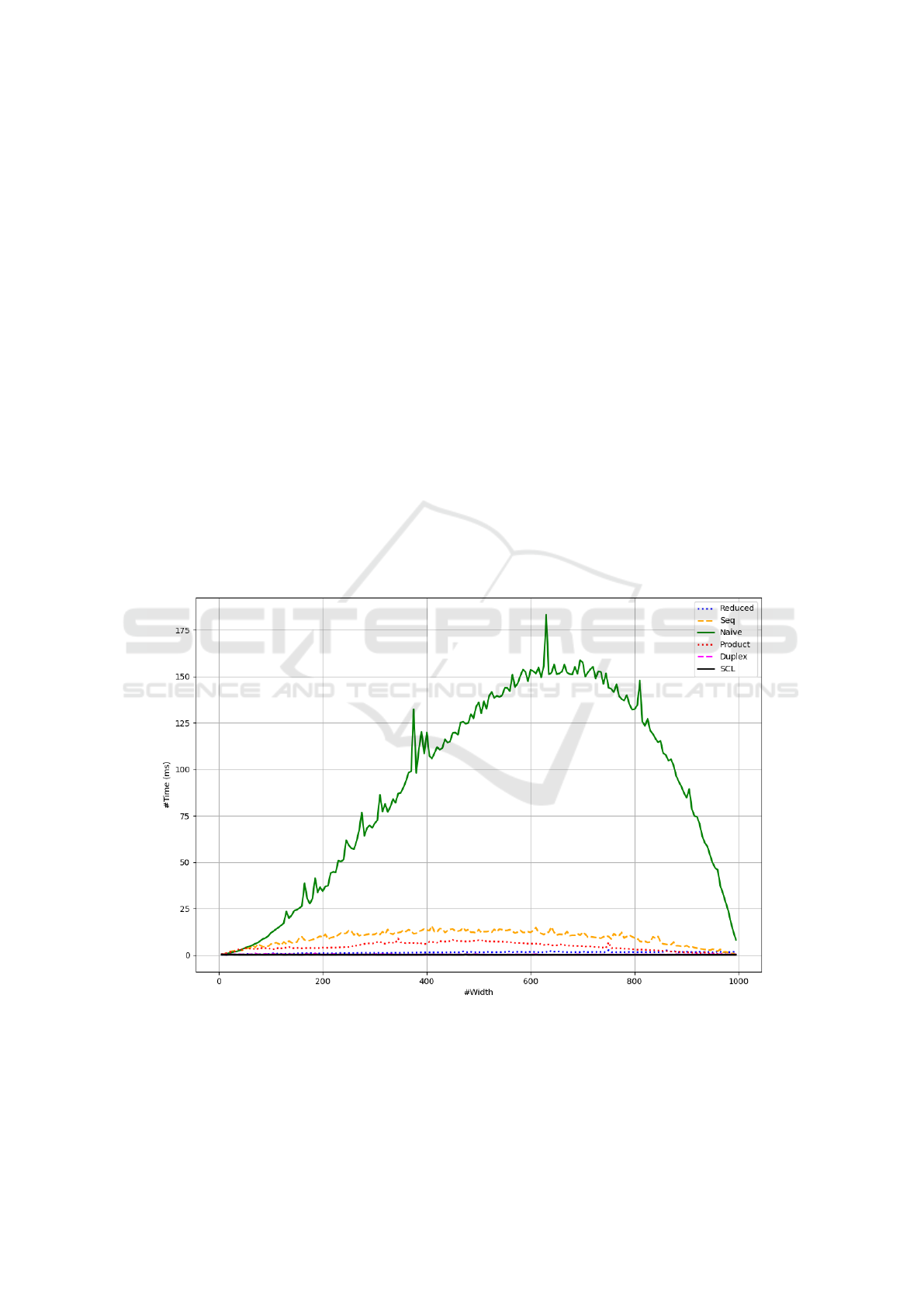
Figure 9 shows the time taken (in milliseconds) by
the Reduced, Seq, Naive, Product, Duplex, and SCL
encodings for the SCAMO problem, where n = 1000
and w ranges from 1 to 1000 in increments of 5.
Figure 9: Comparison of solving time of different encodings in SCAMO with parameters set to n = 1000 and w ∈(1, 1000).
Sequential Counter Encoding for Staircase At-Most-One Constraints
175
