
Trust-Based Multi-Agent Authentication Decision Process for the
Internet of Things
Marc Saideh
1 a
, Jean-Paul Jamont
2 b
and Laurent Vercouter
1 c
1
INSA Rouen Normandie, Normandie Universit
´
e, LITIS UR 4108, 76000 Rouen, France
2
Universit
´
e Grenoble Alpes, LCIS, 26000 Valence, France
Keywords:
Multi-Agent Systems, Internet of Things, Authentication, Trust, Security.
Abstract:
In the Internet of Things (IoT), systems often operate in open and dynamic environments composed of het-
erogeneous objects. Deploying a multi-agent system in such environments requires agents to interact with
new agents and use their information and services. These interactions and resulting dependencies create vul-
nerabilities to malicious behaviors, highlighting the need for a robust trust management system. Multi-agent
trust management models rely on observations of the behavior of other agents who must be authenticated.
However, traditional authentication systems face significant limitations in adapting to diverse contexts and
addressing the hardware constraints of the IoT. This paper proposes a novel trust-based multi-agent adaptive
decision-making process for authentication in the IoT. Our approach dynamically adjusts authentication de-
cisions based on the context and trustworthiness of the agent being authenticated, thereby balancing resource
use for authentication with security needs and ensuring a more adaptable authentication process. We evaluate
our model in a multi-agent navigation simulation, demonstrating its effectiveness for security and resource
efficiency.
1 INTRODUCTION
The deployment of Multi-Agent Systems (MAS) in
the context of the Internet of Things (IoT) requires
agents to be able to act autonomously despite limited
resources and partial knowledge of their environment.
These constraints necessarily lead to dependence on
the services and resources offered by other agents to
achieve their goals. The uncertainty regarding the re-
liability of other agents, who may not follow the same
set of rules and guidelines or act dishonestly, compli-
cates the decision-making of an agent in a situation
of dependence. This emphasizes the importance of
assessing trust and taking into account the risks in-
volved in interacting with other agents.
A trust relationship involves two roles: a truster,
the agent who depends on another agent for a service
or information, and a trustee, the agent providing the
service to the truster. Trust in itself then corresponds
to the belief that the truster has in the trustee’s abil-
ity, competence or intention to act in a way that ben-
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0007-5406-8149
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0268-8182
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0918-8033
efits the truster (Sabater-Mir and Vercouter, 2013; Yu
et al., 2013). Agents benefiting from trust manage-
ment systems prioritize interactions with those they
trust, enabling them to detect and isolate any exhibit-
ing malicious behavior. In our study context, these
systems are essential components for ensuring coop-
eration, information sharing, and effective decision-
making.
When a truster agent has to make a decision based
on information provided by a trustee agent, it relies on
the trust it estimates in the latter’s claimed identity.
As a result, the trust relationship established is vul-
nerable to authentication attacks, especially if a ma-
licious agent manages to impersonate the identity of
a trusted one. The potential risk to the truster is sig-
nificant when they communicate with a compromised
trusted agent, as they will rely on the false informa-
tion or malicious services provided by the imperson-
ated identity. Authentication ensures that communi-
cation occurs between agents with verified identities,
and that only authorized agents access services and
data, maintaining the integrity and confidentiality of
the system.
While authentication ensures the identity of inter-
acting agents, it encounters several major challenges
Saideh, M., Jamont, J.-P. and Vercouter, L.
Trust-Based Multi-Agent Authentication Decision Process for the Internet of Things.
DOI: 10.5220/0013125900003890
In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2025) - Volume 1, pages 45-55
ISBN: 978-989-758-737-5; ISSN: 2184-433X
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
45

when applied in IoT environments. IoT interactions
involve devices with highly heterogeneous character-
istics, ranging from high-powered computing devices
to low-powered sensors operating under strict energy,
cost, and time constraints. The system must be able
to manage and adapt communication between a wide
variety of objects with varying capabilities and ensure
efficient scalability (Sobin, 2020). Traditional authen-
tication schemes often rely on static approaches, al-
ways using the same authentication factors without
considering the dynamic nature of IoT environments
(El-Hajj et al., 2019). This restricts their ability to
adapt to the specific requirements of the heteroge-
neous agents involved in each interaction, as well as
to estimate and adjust the level of security needed for
authentication.
This paper proposes a new multi-agent Adap-
tive Authentication decision process based on Trust
(AAT) for information exchange in the IoT. While
trust helps assess agent reliability, we recognize that
authentication strengthens the certainty of that trust.
However, authentication comes with costs, especially
in resource-constrained IoT environments. In AAT,
we exploit trust both to assess agent reliability and
to determine the authentication factors to be used
for each authentication, dynamically adapting secu-
rity measures based on the trust level of agents. This
dynamic selection of authentication factors ensures
that the level of security is directly proportional to
the trustworthiness of the agents involved. Given the
limited resources in IoT environments, the objective
of AAT is to ensure that resources for authentication
are used only when necessary. We validate our model
through a multi-agent navigation scenario, demon-
strating its efficacy and efficiency in terms of both se-
curity and energy consumption.
Section 2 provides an overview of existing adap-
tive authentication methods in IoT and trust manage-
ment systems for security. Section 3 offers a com-
prehensive and detailed explanation of AAT, which is
used in the simulations presented in section 4. Fi-
nally, we conclude in section 5 on the advantages of
the proposed model and present our avenues for future
research.
2 BACKGROUND
The aim of this section is to present existing tech-
niques for authentication in the IoT and trust manage-
ment systems in order to highlight the limitations of
current solutions as well as the essential features for
the development of a trust-based authentication pro-
cess.
2.1 Authentication in IoT
The rapid expansion of the IoT has presented sig-
nificant security challenges, particularly in the area
of authentication. As billions of devices become in-
terconnected, ensuring secure and reliable authenti-
cation methods becomes paramount to protect sensi-
tive data and prevent unauthorized access. Much re-
search has focused on identifying these security issues
and finding ways to protect against attacks (Jahangeer
et al., 2023; Kaur et al., 2023; Babun et al., 2021;
Meneghello et al., 2019).
One of the primary methods explored is Multi-
Factor Authentication (MFA), which combines two
or more independent credentials typically categorized
into three main groups: what the entity knows (pass-
word), what the entity has (security token), and what
the entity is (biometric verification) (Ometov et al.,
2018). Recent advancements in MFA mechanisms
emphasize the integration of adaptive and context-
aware approaches to enhance the security of IoT envi-
ronments (Ometov et al., 2018; Arias-Cabarcos et al.,
2019; Miettinen et al., 2018). For instance, adaptive
MFA systems can adjust the required authentication
factors based on the risk level of the access attempt.
Context-aware models have been largely used to se-
cure authentication mechanisms, adding an additional
layer of security by evaluating variables such as con-
text of interaction, time, location, and behavior pat-
terns (Khanpara et al., 2023; Ryu et al., 2023; Ar-
faoui et al., 2019). For example, location-based au-
thentication involves using the entity’s geographical
location, verified through GPS coordinates, to authen-
ticate their identity (Zhang et al., 2012). Addition-
ally, innovative techniques like Physically Unclon-
able Functions (PUFs) leverage the unique physical
properties of hardware components to generate cryp-
tographic keys, providing a robust solution against
cloning attacks (Mall et al., 2022).
2.2 Trust Management for Security
Trust management is a critical aspect of security in
IoT, where agents often operate with limited compu-
tational and energy resources. Trust can be assessed
from direct or indirect feedback based on interactions.
Direct trust is the trust that a truster has in a trustee
based on their direct interactions, while indirect trust
is built by feedback that the truster receives from
third parties about the trustee (Pinyol and Sabater-
Mir, 2013).
The literature reveals a growing interest in trust
management as a fundamental aspect of IoT security.
Studies (Koohang et al., 2022; Sharma et al., 2020;
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
46

Pourghebleh et al., 2019) highlight the critical role
of trust in managing the complexity and vulnerabil-
ities inherent in IoT networks. These works demon-
strate the need to move beyond static security models
towards more adaptive, context-informed frameworks
capable of responding dynamically to changing con-
ditions and threats. Adaptive trust management sys-
tems can adjust their trust assessments based on real-
time information, ensuring a more resilient and flex-
ible security posture (Pham and Yeo, 2018). Simi-
larly, (Feng et al., 2023) incorporate trust and repu-
tation mechanisms in their authentication scheme for
the Internet of Vehicles, highlighting the importance
of these elements in ensuring secure and reliable com-
munications.
Embedded MAS face particular challenges such
as managing limited energy resources and maintain-
ing robust trust and security properties (Sahoo et al.,
2019; Jamont and Occello, 2015). These systems re-
quire efficient and lightweight trust management and
authentication protocols that do not overly burden
their limited resources. The importance of having a
reliable authentication process that relies on a trust
management system was highlighted by (Vercouter
and Jamont, 2012), specifically in an embedded MAS
context. This work proposed attaching a measure of
trust to an identifier rather than to the agent it is sup-
posed to represent, circumventing the difficulty of di-
rectly assessing an agent’s trustworthiness.
In addition to trust management, adaptive selec-
tion of authentication factors has been explored as a
means to enhance security. For example, (Dasgupta
et al., 2016) proposed an adaptive strategy for se-
lecting authentication factors based on the selection
of devices, media, and surrounding contexts. This
approach dynamically adjusts the factors used, such
as passwords or biometric data, according to perfor-
mance metrics and contextual information gathered
during the authentication process. Such strategies aim
to optimize security while accommodating the vary-
ing capabilities of devices and the specific require-
ments of different environments.
While existing studies lay a foundation for trust-
based security and adaptive selection of authentica-
tion factors, they generally overlook how trust rela-
tionships between agents can inform decision-making
during authentication processes. Although trust met-
rics are used to evaluate the reliability of agents, there
is a need for frameworks that dynamically adjust au-
thentication requirements based on these trust lev-
els. Our proposed adaptive authentication decision
process introduces trust as a two-faceted concept: it
serves both as a measure of belief in the reliability
of information and as a determinant of the authenti-
cation strategy employed. This dual-role of trust en-
ables a more nuanced and context-sensitive approach
to security, allowing authentication protocols to be
dynamically adjusted based on the trustworthiness of
the agents involved.
3 ADAPTIVE TRUST-BASED
AUTHENTICATION
In this section, we present the decision-making pro-
cess used to select the agents to be authenticated, and
to determine the level of security required for each au-
thentication by selecting the factors to be used. The
IoT offers a diversity of authentication factors; for in-
stance, IoT sensors can collect real-time data from
their environment and other objects where agents are
deployed, providing valuable information that can be
leveraged for authentication. (Saideh et al., 2024)
have illustrated the relevance of opportunistic use of
sensors deployed in related systems to make authen-
tication based on a single RFID tag more reliable in
the context of access control to a parking lot. Data
collected by sensors can thus represent authentication
factors. We propose to develop a strategy for selecting
the most appropriate authentication factors according
to specific criteria.
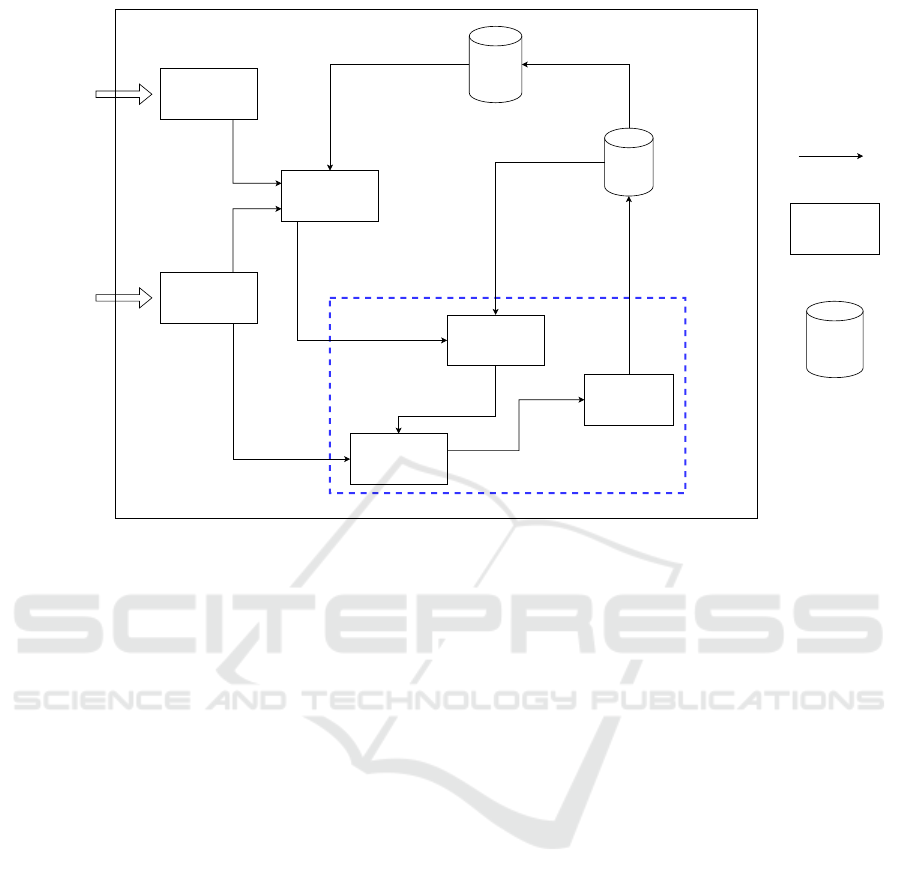
3.1 General Architecture
We introduce specific components for trust-based au-
thentication, designed to be integrated into applica-
tion agents within an embedded MAS, as shown in
Figure 1. Each agent is equipped with sensors and/or
actuators, enabling it to perceive its environment, per-
form actions and communicate with others. Agents
vary in terms of computing power, storage capacity
and energy resources, reflecting the diversity of IoT
environments.
The environment in which agents evolve is char-
acterized by its dynamic nature and the occurrence
of unpredictable events. We focus on the types of
environment where agents can be led to simultane-
ously receive the same type of information from sev-
eral agents. However, the veracity of this information
is sometimes variable and may indicate malicious be-
havior or an attack attempt by one or more agents.
A trust management system enables agents to
evaluate and update the trust values they assign to
other agents, based on past interactions and the qual-
ity of shared information. Although the choice of trust
management system is not the main focus of our pa-
per, it does represent an important decision to be made
when implementing the application agent.
Trust-Based Multi-Agent Authentication Decision Process for the Internet of Things
47
Perception
Communication
Trust
model
Agents
Selection of
authentication factors
Trust-based decision
making on who to
authenticate
Preliminary
assessment
Authenticate
Update the authenticated
agent's trust level
<ID, Trust>
<ID, timestamp,
information>
Contextual information
Historical context
<ID, information, criticality>
Contextual information
to use for authentication
<ID, information, criticality>
Begin authentication
with selected factors
Knowledge
base
Update historical
context
Authentication decision making
Data flows / Actions
Functional step
Data
repository
Environment
Figure 1: Components related to authentication and trust management.
The decision-making process proposed in this
article enables agents to evaluate the trustworthi-
ness of messages based on the trust assigned to the
sender’s identity, dynamically adjusting the authenti-
cation rigor accordingly. By considering the risk and
resource requirements, the process ensures that agents
are authenticated only when necessary, balancing se-
curity with the need to optimize energy, computation,
and communication resources. This approach is de-
signed to meet the specific constraints of IoT environ-
ments, providing an efficient solution that maintains
security while minimizing resource consumption.
In this model, authentication specifically aims to
verify the identity of the agent sending the message.
Each message sent by an agent includes essential in-
formation such as the agent’s unique identifier (a de-
clared identifier), a timestamp indicating when the
message was sent, and the data content, which varies
according to the agent’s purpose and the nature of the
information being shared.
3.2 Attack Model
In our study, we focus on impersonation attacks, a
critical security concern in multi-agent systems and
IoT environments. An impersonation attack occurs
when a malicious agent pretends to be a legitimate
agent by claiming its identity. This type of attack un-
dermines the trust model by allowing the attacker to
exploit the trusted identity of another agent. The con-
sequences of successful impersonation attacks are se-
vere:
• Data manipulation: the attacker can alter or inject
false information, leading to incorrect data being
propagated through the system.
• Communication disruption: by pretending to be
a legitimate agent, the attacker can interfere with
or disrupt ongoing communications and transac-
tions.
• Reputation damage: the trustworthiness of legiti-
mate agents can be compromised, damaging their
reputation and the overall integrity of the system.
To counter impersonation attacks, IoT systems
must implement robust authentication mechanisms
capable of detecting and mitigating identity theft and
the abuse of multiple identities.
3.3 Trust-Based Authentication
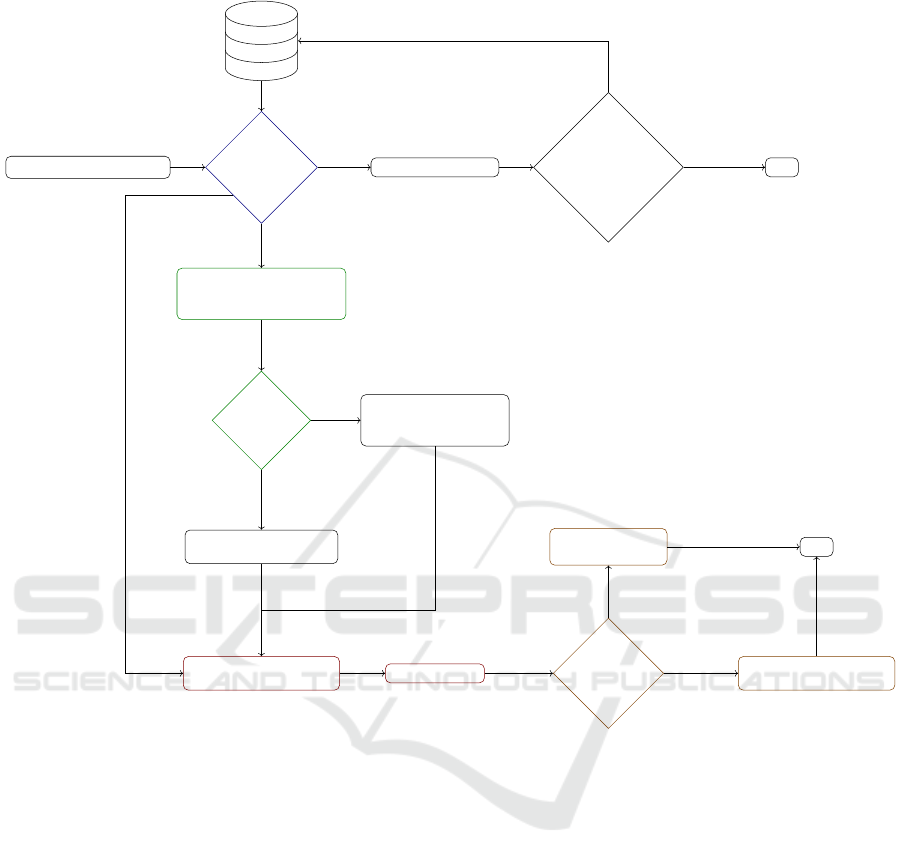
Decision-Making Process
The purpose of the decision-making process pre-
sented here is for an agent to perform authentication,
thereby assuming the role of the truster to confirm or
deny the identity of another agent. All parameters and
functions used in the AAT model are summarized in
Table 1. This process unfolds in five steps, each of
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
48

which may contain several sub-stages, as detailed be-
low. Figure 2 illustrates this decision-making process,
which comprises the following stages:
1. Receiving Messages. The process starts when a
truster agent receives messages from other agents.
These messages can be pre-processed by the
truster agent before authenticating their senders.
This pre-processing can be justified, for example,
when latency is a critical constraint and immedi-
ate verification could delay urgent responses re-
quired for system operation. In our study, this pre-
processing is mainly used to assess the criticality
level of shared information.
2. Trust Evaluation. We define two trust thresh-
olds: a minimum trust threshold, Θ
min
, at which
the truster agent accepts to deploy resources for
authentication, and a high trust threshold, Θ
high
,
at which we consider the agent to be trustwor-
thy. For each message received, three scenarios
are considered based on the level of trust placed
in the claimed identity:
• If the claimed identity is that of a trustworthy
agent (trust level greater than Θ
high
), the truster
agent performs a preliminary assessment of the
criticality of the information received. It then
compares this information, where appropriate,
with other messages received in the same con-
text from other agents claiming trustworthy
identities. This comparison of information is
intrinsically linked to the specific application in
which the agents are deployed, underlining the
importance of an adapted methodological ap-
proach.
• If the claimed identity is that of an agent the
truster does not trust (trust level below Θ
min
),
the authentication process can be bypassed.
This is because the truster agent would not
consider the shared information reliable regard-
less, due to the insufficient trust in the sender’s
claimed identity.
• If the level of trust attached to the claimed iden-
tity is uncertain (trust level between Θ
min
and
Θ
high
) due to a lack of direct interactions or
third-party feedback, a medium security level is
applied for identity verification. Alternatively,
authentication can be disregarded if other mes-
sages on the same information from trustwor-
thy identities are available.
3. Consistency Check. This step is essential when
the truster agent receives multiple messages about
the same information from agents claiming trust-
worthy identities, and is particularly relevant to
the specific application. For example, consider re-
Table 1: Overview of parameters and functions in the au-
thentication decision process.
Parameter/Function Description
Θ
min
Minimum trust threshold to justify an au-
thentication.
Θ
high
High trust threshold indicating a trustwor-
thy agent.
τ
min
Minimum criticality threshold to justify an
authentication.
Trust Trust value in the claimed identity of the
sender.
Crit Criticality level of shared information.
w
FAR
Weight for False Acceptance Rate (FAR).
w
EC
Weight for Energy Cost (EC).
M
FAR
Maximum allowable weight for w
FAR
.
a, b Coefficients balancing the impact of Trust
and Crit.
Score
FAR
Weighted average FAR across utilized fac-
tors.
Score
EC
Sum of energy costs of all utilized factors.
Score
Global
Overall score for the selected set of factors.
ceiving several messages indicating the tempera-
ture at a specific location. If the information is
inconsistent, there is a suspicion of a possible at-
tack, leading to the authentication of all agents. If
the information is consistent, the truster agent se-
lects a subgroup of agents for thorough authenti-
cation. We assume that it is highly unlikely that
all agents in the initial group are compromised
simultaneously while sharing consistent informa-
tion, thus reducing the number of agents needed
for authentication without significantly impacting
security.
4. Authentication. For each agent in the selected
group, following the trust evaluation and consis-
tency check phases, an appropriate security level
is determined for authentication. This level is de-
termined based on several key criteria, including
the level of trust associated with the claimed iden-
tity and the criticality of the shared information.
We assume the availability of a diverse set of au-
thentication factors, each offering specific trade-
offs between energy cost, security robustness, and
False Acceptance Rate (FAR). The objective here
is to select the optimal combination of factors ac-
cording to these criteria. To achieve this, we de-
fine :
• Trust: Trust value in the claimed identity by
the agent seeking authentication, Trust : id →
[Θ
min
, 1], where Θ
min
is the minimum trust
threshold to justify authentication, and 1 rep-
resents the maximum trust level.
• Crit: The criticality level of the shared infor-
mation, Crit : in f o → [τ
min
, 1], where τ
min
is the
minimum criticality threshold to justify authen-
tication, and 1 is the maximum criticality level.
• w
FAR
and w
EC
: Weights for FAR and Energy
Trust-Based Multi-Agent Authentication Decision Process for the Internet of Things
49
1. Reception of messages Trustworthy?
2. Trust evaluation
Do not authenticate
Evaluate
trust without
authentication?
End
Trust model
verification of consistency
with other trustworthy
agents
3. Consistency check
Consistent?
Selection of a subgroup
for authentication
Selection of the security
level for authentication
4. Authentication
Might be an alert
for an eventual attack.
Authenticate all agents
Authentication
Confirmed
identity?
5. Authentication evaluation
Consider received infor-
mation for evaluation
Learn and adjust
security measures
End
For each
agent
No No
Yes
Yes
No
For each
agent
Yes
For all
factors
No
Yes
Incertain
Figure 2: Diagram of authentication decision-making process.
Cost (EC), calculated as follows:
w
FAR
= min(M
FAR
, a × Trust + b ×Crit) (1)
w
EC
= 1 − w
FAR
(2)
where, a + b = 1, M
FAR
denotes the maximum al-
lowable weight for w
FAR
, while a and b serve as
adjustable coefficients aimed at balancing the im-
pact of Trust and Crit on both security and cost
considerations.
• Score
FAR
: Calculated as the weighted average
FAR across all utilized factors.
Score
FAR
=
n
∑
i=1
w
i
× FAR
i
(3)
where
∑
n
i=1
w
i
= 1, FAR
i
is the FAR of the i-th
authentication factor in the combination, and w
i
are the weights assigned to each factor, which
may be equal or vary according to other criteria.
• Score
EC
: Calculated as the sum of the energy
costs of all utilized factors.
Score
EC
=
n
∑
i=1
cost
i
(4)
where cost
i
represents the energy cost of the
i-th authentication factor in the combination.
These scores must be normalized to ensure that
all components contribute in a balanced way to
the overall evaluation.
• Score
Global
: The overall score assigned to the
selected set of factors.
Score
Global
= w
FAR
× Score
FAR
+ w
EC
× Score
EC
(5)
The objective is to minimize the global score
Score
Global
. A low Score
Global
indicates an effec-
tive combination of low FAR and low energy cost,
demonstrating optimal performance of the authen-
tication system in terms of security and energy ef-
ficiency.
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
50

5. Authentication Evaluation. In this phase, after
selecting the authentication factors to verify the
agent’s identity, we assess whether the agent has
successfully responded to all chosen factors. If
the agent meets the authentication requirements,
the truster accepts the claimed identity sent at the
beginning of the interaction as authentic. Conse-
quently, the information shared in the message is
considered valid and is used for further evaluation
and updates to the trust level. If the agent fails to
respond to the required authentication factors, the
identity is deemed unverified, and the received in-
formation is disregarded. This ensures that only
authenticated agents can influence the decision-
making process and trust assessments.
4 IMPLEMENTATION AND
EVALUATION
To validate our AAT model, we implemented a simu-
lation of an IoT environment that represents a multi-
agent navigation scenario. This scenario is ideal for
evaluating our mechanism due to the dynamic nature
of the environment, where agents rely on information
from other agents to navigate efficiently. The sim-
ulation was developed using the MESA agent-based
framework (Kazil et al., 2020). AAT, which includes
a trust evaluation model and an adaptive authentica-
tion process, has been fully integrated into this sim-
ulation. Each IoT device is represented as an au-
tonomous agent capable of dynamically evaluating
trust levels and making authentication decisions based
on the criteria in our model.
4.1 Multi-Agent Navigation Scenario
4.1.1 Environment
The navigation space is represented as a 2D grid that
serves as a map, providing a spatial framework for
the agents’ movements. Obstacles are strategically or
randomly placed on the map, marking positions that
agents cannot cross. The environment is character-
ized by dynamic events, including shifts in obstacle
positions or the introduction of new obstacles, which
contribute to its inherent uncertainty.
4.1.2 Agents
The MAS is open, allowing dynamic entry and exit
of agents. We distinguish two types of agent in our
simulation:
1. Navigators. A navigator agent is an autonomous
agent randomly placed on the map and endowed
with navigation capabilities. Its objective is to
reach a specific, unknown destination while min-
imizing the navigation distance. It has limited
knowledge of the map, being able to detect only
its immediate surroundings, which includes all the
cells adjacent to the one where it is located on the
map.
2. Guides. A guide agent is an autonomous agent
that has no physical presence on the map, but has
global knowledge of the map, including the posi-
tion of obstacles and the destinations of the navi-
gators. The guides communicate with navigators,
transmitting essential information such as the lo-
cations of obstacles and the designated destina-
tions, helping them navigate the map more effi-
ciently and safely.
4.2 Interaction and Collaboration
The guides communicate the location of obstacles on
the map and the destinations to be reached to each
navigator. The navigators, relying on this interaction
to obtain the necessary information for navigation,
evaluate the information received based on their trust
in the guides to make decisions about their route on
the map. Consequently, information about the same
object (map and destinations) is received from differ-
ent guides.
4.2.1 Trust
In our simulation, navigators use the Beta Reputation
System (BRS) (Josang and Ismail, 2002) to evaluate
the trustworthiness of guides based on their past ac-
tions. Other trust management models can be used,
as the choice of trust model is not the central contri-
bution of our article. BRS uses the positive and neg-
ative results of previous interactions to calculate the
probability that an agent will act reliably in the fu-
ture. Mathematically, the trust value of an agent in
BRS is calculated using the following formula:
Trust =
α
α + β
(6)
α = r + 1 and β = s + 1 (7)
where r and s respectively represent the num-
ber of positive and negative interactions an agent
truster has had with the trustee in question. This
formula provides an estimate of the probability
that the agent will behave honestly in a future
Trust-Based Multi-Agent Authentication Decision Process for the Internet of Things
51

Table 2: Artificial authentication factors.
Factor Energy cost (mJ) Security level TNR FAR
1 0.2 Low 0.85 0.15
2 3.0 High 0.98 0.02
3 1.5 Medium 0.92 0.08
4 2.6 High 0.97 0.03
5 0.8 Medium 0.89 0.11
6 0.6 Low 0.88 0.12
7 2.0 High 0.95 0.05
8 1.2 Medium 0.90 0.10
interaction. A value close to 1 indicates high relia-
bility, while a value close to 0 suggests low reliability.
In our scenario, a negative interaction occurs when
a navigator receives incorrect information about the
map from a guide. For instance, if the map provided
by the guide contains inaccuracies, such as erroneous
obstacle positions or incorrect destinations, this con-
stitutes a negative interaction. Such inaccuracies can
significantly impact the navigator’s ability to navi-
gate effectively, leading to a negative evaluation of the
guide’s trustworthiness.
Conversely, a positive interaction is characterized
by accurate information—where the map reflects the
correct positions of obstacles and destinations, allow-
ing the navigator to proceed. The trust level of a guide
is thus influenced by the quality of the information
they provide.
Given that navigators can detect inaccuracies in
obstacle positions more rapidly than errors in destina-
tion information, we introduce a weight w
β
to the pa-
rameter β to more strongly penalize guides who pro-
vide incorrect destination information. This weight-
ing reflects the greater impact of destination inaccu-
racies on navigation effectiveness and trust. By ap-
plying this penalty, we aim to prevent guides from
maintaining a high trust score if they provide accu-
rate obstacle information but frequently share incor-
rect destination details.
4.2.2 Authentication
Navigator agents use the AAT model proposed in
section 3 to authenticate guide agents. We have de-
fined several artificial authentication factors for the
simulation in Table 2. Each factor is abstractly rep-
resented by its energy cost, the level of security it
provides, and the True Negative Rate (TNR), with
FAR = 1 − T NR. Security levels are classified into
three categories: low, medium, and high. The factors
are defined such that their energy cost increases pro-
portionally with the level of security. Depending on
the adopted strategy, an agent selects authentication
factors in various ways from the available options.
The three authentication strategies used in our simu-
lation are:
• Static Authentication (SA): this method uses the
same two factors for all agents. The selection of
these factors follows a traditional approach, com-
bining a low-security factor with a medium or a
high-security factor.
• Adaptive Authentication based on the Criticality
of Shared Information (AAC): an adaptive method
that selects authentication factors based on the
level of criticality of the shared information, with-
out incorporating trust values.
• Adaptive Authentication based on Trust and crit-
icality (AAT): This method, which represents our
authentication decision-making process, utilizes
trust levels to decide which identities to authen-
ticate and combines trust and criticality values to
select appropriate authentication factors.
4.3 Results and Evaluation
We describe here the results obtained by running our
simulation over 200 episodes. Each episode begins
with the initialization of the environment and the
placement of the navigators on the map, and ends
when all the navigators have reached their destina-
tions. In each episode, the guides provide the naviga-
tors with information about the map. The latter au-
thenticate the messages received and evaluate and up-
date the trust values during navigation. We simulated
3 navigator agents, each adopting a different authen-
tication strategy among the three strategies detailed
previously, and 10 guide agents, 6 of them malicious,
sharing erroneous map information.
4.3.1 Resource Efficiency
Figure 3 illustrates the cumulative energy consump-
tion over 200 episodes using the three authentica-
tion strategies for a navigator communicating with 10
guides per episode.
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
52
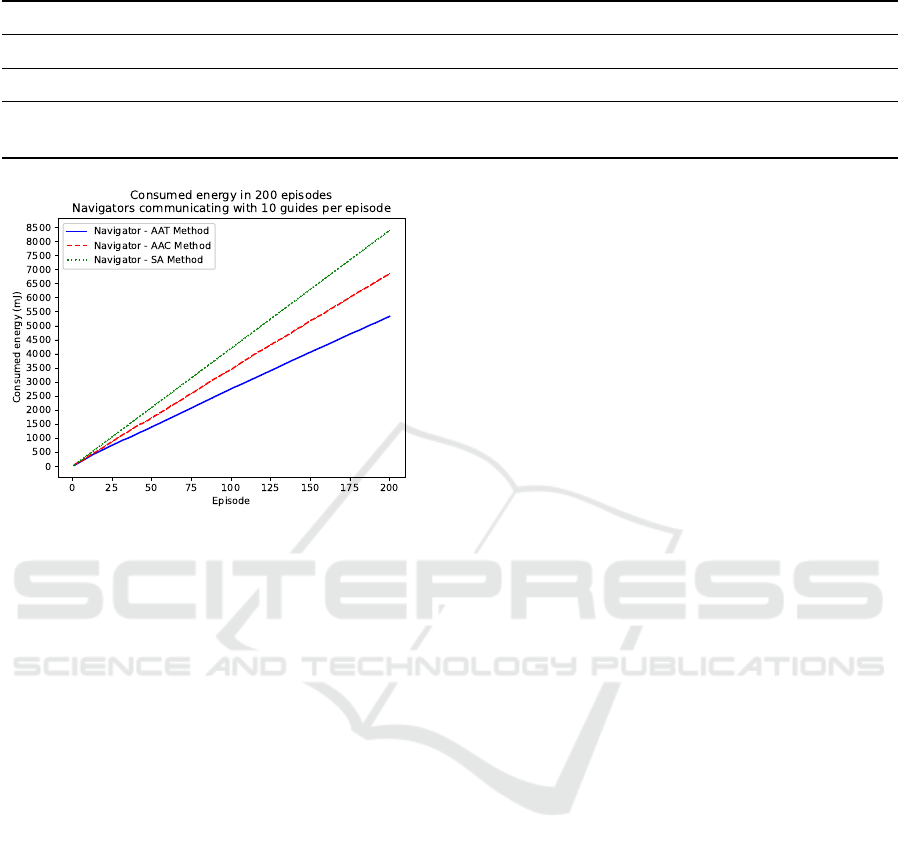
Table 3: Number of successful attacks and average steps per episode over 200 episodes.
AAT AAC SA
Number of successful attacks 9 14 17
Successful attack rate 2.25% 3.5% 4.25%
Average steps per episode
(20 being the optimal) 22 25 27
Figure 3: Energy consumed for authentication in 200
episodes.
Our proposed trust-based authentication decision
process AAT reduces energy consumption by 19%
compared with the AAC method, which does not
consider trust, and by 37% compared with the SA
method, which employs static authentication for all
agents, resulting in linear energy consumption due to
repeated use of the same factors at each authentica-
tion.
By avoiding authentication of agents with whom
previous interactions have provided sufficient but in-
conclusive trust information, and by adapting authen-
tication factors based on established trust and the crit-
icality of exchanged information, we enhance energy
efficiency. Authentication occurs only when the risk
justifies the energy expenditure. This approach allows
resources to be focused where they provide the most
value, directly contributing to observed energy sav-
ings.
4.3.2 Impact on Security
We simulated identity impersonation attacks based
on the FARs of the artificial authentication factors
(Table 2). Over 200 episodes, a total of 2,000 inter-
actions were recorded, including 400 unauthorized
attempts. The simulation was structured to evaluate
attackers’ attempts to impersonate trusted guide
agents. Each successful attack attempt allows the
attacker to transmit erroneous map information to
the navigators, leading to misguided paths. Table
3 summarizes the number of successful attacks and
their corresponding impact on the number of steps
required for navigators to reach their destinations.
Specifically, when a navigator accepts an incorrect
map sent by an attacker, the number of steps required
to reach the destination can increase to over 50.
This impact may not always be apparent in the
average steps per episode, due to the relatively small
number of successful attacks compared to the total
interactions. Overall, AAT performs better in terms
of detecting malicious agent attacks, preventing
97.75% of them, compared with 96.5% and 95.75%
for competing models (Table 3).
The complementary nature of resource efficiency
and security in our proposed AAT framework high-
lights its overall effectiveness. By significantly
reducing energy consumption while maintaining a
high level of security, AAT demonstrates that efficient
resource usage does not come at the expense of secu-
rity integrity. The ability to adaptively authenticate
based on trust not only conserves resources but also
enhances the system’s resilience against imperson-
ation attacks. This dual benefit underscores the value
of our approach, illustrating how optimizing one
aspect can simultaneously bolster another, ultimately
leading to a more robust and sustainable multi-agent
system in IoT environments. Specifically, only
2.25% of malicious agent attacks were successful in
AAT, compared with 3.5% and 4.25% for other less
adaptive models. Furthermore, AAT significantly
reduces energy costs, achieving savings of 19% to
37% compared to less adaptive methods.
To further enhance the effectiveness and appli-
cability of the AAT framework, future experiments
could focus on testing its performance across diverse
contexts and applications. For instance, evaluating
the system in varying IoT environments, such as in-
dustrial, healthcare, and smart home settings, could
provide deeper insights into its adaptability and re-
liability. Additionally, the computational cost of the
decision process algorithm should be rigorously ana-
Trust-Based Multi-Agent Authentication Decision Process for the Internet of Things
53

lyzed to ensure that the benefits of resource efficiency
do not come at the expense of scalability or real-time
responsiveness. Another critical avenue for improve-
ment involves developing and simulating strategic at-
tack methods, such as coordinated multi-agent imper-
sonation or evolving adversarial strategies, to test the
resilience of the framework. These refinements would
not only validate the robustness of the AAT model but
also identify potential areas for optimization, allow-
ing more comprehensive and future-proof solutions.
5 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, we presented a novel trust-based adap-
tive authentication decision process designed for the
dynamic and heterogeneous environments of the In-
ternet of Things. Specifically developed for informa-
tion exchange within embedded MAS, this process
dynamically adjusts the required security level for au-
thentication based on both the trustworthiness of the
claimed identity by the sender and the criticality of
the transmitted information. By evaluating trust lev-
els and criticality, the process selects which identities
to authenticate and employs the most effective combi-
nation of authentication factors. This approach opti-
mizes resource allocation while minimizing the false
positive rate.
The effectiveness of our model is demonstrated
by the results obtained in the multi-agent navigation
simulations, which showed a significant reduction in
the success rate of malicious agent attacks compared
to other, less adaptive models. Additionally, our ap-
proach demonstrates a marked improvement in re-
source efficiency, allowing for the intelligent use of
energy and computational resources. This highlights
that our adaptive authentication strategy not only en-
hances security by foiling more attacks — particu-
larly by strengthening authentication for trustworthy
agents — but also optimizes resource utilization by
minimizing unnecessary authentications.
The integration of trust management and adap-
tive authentication mechanisms in IoT and embedded
MAS represents a promising direction for enhanc-
ing security. By leveraging the strengths of both ap-
proaches, it is possible to create systems that are more
resilient to attacks and better suited to the dynamic
and resource-constrained environments typical of IoT
and MAS. Our future work will focus on the follow-
ing three main areas: validating our model using real
rather than artificial authentication factors, develop-
ing a trust management system with a more sophis-
ticated strategy for selecting authentication factors,
and expanding our model to address other types of
identity-related attacks. These improvements will en-
hance the model’s robustness and flexibility against a
broader range of threats, while dynamically optimiz-
ing agent authentication processes and trust relation-
ships in IoT environments.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work is supported by the French National Re-
search Agency (ANR) in the framework of the project
MaestrIoT ANR-21-CE23-0016.
REFERENCES
Arfaoui, A., Cherkaoui, S., Kribeche, A., Senouci, S. M.,
and Hamdi, M. (2019). Context-aware adaptive au-
thentication and authorization in internet of things.
In ICC 2019-2019 IEEE International Conference on
Communications (ICC), pages 1–6. IEEE.
Arias-Cabarcos, P., Krupitzer, C., and Becker, C. (2019). A
survey on adaptive authentication. ACM Computing
Surveys (CSUR), 52(4):1–30.
Babun, L., Denney, K., Celik, Z. B., McDaniel, P., and Ulu-
agac, A. S. (2021). A survey on iot platforms: Com-
munication, security, and privacy perspectives. Com-
puter Networks, 192:108040.
Dasgupta, D., Roy, A., and Nag, A. (2016). Toward the
design of adaptive selection strategies for multi-factor
authentication. computers & security, 63:85–116.
El-Hajj, M., Fadlallah, A., Chamoun, M., and Serhrouchni,
A. (2019). A survey of internet of things (iot) authen-
tication schemes. Sensors, 19(5):1141.
Feng, X., Wang, X., Cui, K., Xie, Q., and Wang, L.
(2023). A distributed message authentication scheme
with reputation mechanism for internet of vehicles.
Journal of Systems Architecture, 145:103029.
Jahangeer, A., Bazai, S. U., Aslam, S., Marjan, S., Anas,
M., and Hashemi, S. H. (2023). A review on the se-
curity of iot networks: From network layer’s perspec-
tive. IEEE Access, 11:71073–71087.
Jamont, J.-P. and Occello, M. (2015). Meeting the chal-
lenges of decentralised embedded applications using
multi-agent systems. International Journal of Agent-
Oriented Software Engineering, 5(1):22–68.
Josang, A. and Ismail, R. (2002). The beta reputation sys-
tem. In Proceedings of the 15th Bled Electronic Com-
merce Conference, volume 5, pages 2502–2511.
Kaur, B., Dadkhah, S., Shoeleh, F., Neto, E. C. P., Xiong,
P., Iqbal, S., Lamontagne, P., Ray, S., and Ghorbani,
A. A. (2023). Internet of things (iot) security dataset
evolution: Challenges and future directions. Internet
of Things, 22:100780.
Kazil, J., Masad, D., and Crooks, A. (2020). Utilizing
python for agent-based modeling: The mesa frame-
work. In Social, Cultural, and Behavioral Mod-
eling: 13th International Conference, SBP-BRiMS
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
54

2020, Washington, DC, USA, October 18–21, 2020,
Proceedings 13, pages 308–317. Springer.
Khanpara, P., Lavingia, K., Trivedi, R., Tanwar, S., Verma,
A., and Sharma, R. (2023). A context-aware internet
of things-driven security scheme for smart homes. Se-
curity and Privacy, 6(1):e269.
Koohang, A., Sargent, C. S., Nord, J. H., and Paliszkiewicz,
J. (2022). Internet of things (iot): From awareness to
continued use. International Journal of Information
Management, 62:102442.
Mall, P., Amin, R., Das, A. K., Leung, M. T., and Choo, K.-
K. R. (2022). Puf-based authentication and key agree-
ment protocols for iot, wsns, and smart grids: a com-
prehensive survey. IEEE IoT Journal, 9(11):8205–
8228.
Meneghello, F., Calore, M., Zucchetto, D., Polese, M., and
Zanella, A. (2019). Iot: Internet of threats? a survey
of practical security vulnerabilities in real iot devices.
IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 6(5):8182–8201.
Miettinen, M., Nguyen, T. D., Sadeghi, A.-R., and Asokan,
N. (2018). Revisiting context-based authentication in
iot. In Proceedings of the 55th Annual Design Au-
tomation Conference, pages 1–6.
Ometov, A., Bezzateev, S., M
¨
akitalo, N., Andreev, S.,
Mikkonen, T., and Koucheryavy, Y. (2018). Multi-
factor authentication: A survey. Cryptography, 2(1):1.
Pham, T. N. D. and Yeo, C. K. (2018). Adaptive trust
and privacy management framework for vehicular net-
works. Vehicular Communications, 13:1–12.
Pinyol, I. and Sabater-Mir, J. (2013). Computational trust
and reputation models for open multi-agent systems:
a review. Artificial Intelligence Review, 40(1):1–25.
Pourghebleh, B., Wakil, K., and Navimipour, N. J. (2019).
A comprehensive study on the trust management tech-
niques in the internet of things. IEEE Internet of
Things Journal, 6(6):9326–9337.
Ryu, R., Yeom, S., Herbert, D., and Dermoudy, J. (2023).
A comprehensive survey of context-aware continu-
ous implicit authentication in online learning environ-
ments. IEEE Access, 11:24561–24573.
Sabater-Mir, J. and Vercouter, L. (2013). Trust and Repu-
tation in Multi-Agent Systems, pages 381–419. Num-
ber 9. MIT Press, g. weiss edition.
Sahoo, S. S., Veeravalli, B., and Kumar, A. (2019). A hybrid
agent-based design methodology for dynamic cross-
layer reliability in heterogeneous embedded systems.
In Proceedings of the 56th Annual Design Automation
Conference 2019, pages 1–6.
Saideh, M., Jamont, J.-P., and Vercouter, L. (2024). Oppor-
tunistic sensor-based authentication factors in and for
the internet of things. Sensors, 24(14):4621.
Sharma, A., Pilli, E. S., Mazumdar, A. P., and Gera, P.
(2020). Towards trustworthy internet of things: A sur-
vey on trust management applications and schemes.
Computer Communications, 160:475–493.
Sobin, C. (2020). A survey on architecture, protocols and
challenges in iot. Wireless Personal Communications,
112(3):1383–1429.
Vercouter, L. and Jamont, J.-P. (2012). Lightweight trusted
routing for wireless sensor networks. Progress in Ar-
tificial Intelligence, 1:193–202.
Yu, H., Shen, Z., Leung, C., Miao, C., and Lesser, V. R.
(2013). A survey of multi-agent trust management
systems. IEEE Access, 1:35–50.
Zhang, F., Kondoro, A., and Muftic, S. (2012). Location-
based authentication and authorization using smart
phones. In 2012 IEEE 11th International Confer-
ence on Trust, Security and Privacy in Computing and
Communications, pages 1285–1292. IEEE.
Trust-Based Multi-Agent Authentication Decision Process for the Internet of Things
55
