
Highly Interpretable Prediction Models for SNP Data
Robin Nunkesser
Hamm-Lippstadt University of Applied Sciences, Marker Allee 76–78, 59063 Hamm, Germany
Keywords:
Interpretable Machine Learning, SNP Data, Genetic Programming, Simulation Study.
Abstract:
Binary prediction models for SNP data are often used in genetic association studies. The models should
be highly interpretable to help understand possible underlying biological mechanisms. logicFS, GPAS, and
logicDT can yield highly interpretable prediction models. The automatic prevention of overfitting requires
improvement, however. We propose using GPAS as a black box and applying an external method for automatic
model selection. We present an approach using the GPAS algorithm as a black box and show initial results
on simulated data. The simulation is designed to motivate research to extend GPAS with automatic model
selection. Additionally, we give an outlook on further extensions of GPAS.
1 INTRODUCTION
Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) are the
most common type of genetic variation in humans.
Each SNP represents a difference in a single DNA
building block (nucleotide). For example, a SNP
may replace the nucleotide cytosine (C) with the nu-
cleotide thymine (T) in a certain stretch of DNA. The
human genome consists of approximately 3.2 billion
base pairs, however (International Human Genome
Sequencing Consortium, 2001). Typically, only the
variants occurring with a frequency of at least one
percent are considered. It is widely known that, in
the analysis of disease risks, it is important to not
only consider the effect of single SNPs, but that of in-
teractions with demographic and environmental data
or other genetic variables such as other SNPs (Garte,
2001; Che and Motsinger-Reif, 2013).
A high degree of interpretability in prediction
models is especially desirable, as such models may
also help to understand possible underlying biolog-
ical mechanisms. High interpretability is achieved,
for example, by logicFS (Schwender and Ickstadt,
2007) and GPAS (Nunkesser et al., 2007) (according
to Chen et al., 2011). In addition, newer approaches
such as logicDT (Lau et al., 2024) are specifically de-
signed to yield highly interpretable prediction mod-
els, while maintaining a high predictive ability. All
of the aforementioned approaches yield very good re-
sults on simulated and real data. However, the auto-
matic prevention of overfitting requires improvement.
Additionally, it is shown, that the approaches are ca-
pable of surpassing specific and more general state-
of-the-art algorithms chosen by Microsoft’s AutoML
for the considered problem. It is therefore of inter-
est to extend them to multi-valued responses or other
categorical predictors besides SNPs and to compare
these extensions to more general algorithms.
This position paper argues that the above men-
tioned possible improvements offer important oppor-
tunities for research and presents work in progress
on the automatic prevention of overfitting in GPAS
and an outlook on possible further extensions. In a
first step, the relevance of the research is shown by a
short comparison of the methods logicFS, GPAS, and
logicDT with state-of-the-art machine learning algo-
rithms chosen by Microsoft’s AutoML on simulated
data. The simulation is intended to motivate research
to extend GPAS with automatic model selection. In a
second step, we present an approach using the GPAS
algorithm as a black box to extend GPAS with auto-
matic model selection. The approach is evaluated on
the same data as the comparison. In a third step, we
give an outlook on further extensions of GPAS.
The paper is structured as follows: Section 2 gives
an overview of related work. The following Section
3 gives a brief overview of SNP data and highly in-
terpretable prediction models. In Section 4, we will
provide a brief comparison of the methods logicFS,
GPAS, logicDT, and Microsoft’s AutoML by showing
results on simulated data. In Section 5, we present an
approach to extend GPAS with automatic model se-
lection, finishing in Sections 6 and 7 with future work
and conclusions.
Nunkesser, R.
Highly Interpretable Prediction Models for SNP Data.
DOI: 10.5220/0013137600003911
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 18th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2025) - Volume 1, pages 555-562
ISBN: 978-989-758-731-3; ISSN: 2184-4305
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
555

2 RELATED WORK
With regard to the main topics of this paper (highly
interpretable prediction models for SNP data and au-
tomatic model selection for such models), the fol-
lowing related work must be mentioned: Lau et al.
(2024) proposes logicDT as designed to yield highly
interpretable prediction models with a high degree
of predictive ability. Nunkesser (2008) describes ap-
proaches for automatic model size selection in GPAS
which were not integrated into the available algo-
rithm. The work of Chen et al. (2011) offers a review
of methods for identifying SNP interactions which
also compares interpretability.
An overview of more general methods for SNP
data is given in Lau et al. (2024). These include
the following, as yet unmentioned, methods: tree-
based statistical learning methods such as decision
trees, random forests, or logic regression applied in
Bureau et al. (2005); Winham et al. (2012); Ruczinski
et al. (2004), for example. Tong et al. (2021) give an
overview of further methods for SNP data.
For an overview of principles in interpretable ma-
chine learning, we refer to Rudin et al. (2022).
3 BACKGROUND
In the following, we will give a brief overview of SNP
data and highly interpretable prediction models.
3.1 Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms
Less than 1% of human DNA differs between indi-
viduals. In absolute terms, these are still millions of
base pair positions at which different bases can occur.
Each of the forms a DNA segment can take is called
an allele. Alleles occurring in more than 1% of the
population are called polymorphisms. Looking at a
fixed base pair position or locus, a polymorphism at
this specified locus is called a single nucleotide poly-
morphism. In an analysis concerning the genotype
of individuals, we consider the chromosome pairs of
an individual. A SNP typically has two alleles, the
major allele occurring in the majority of the popu-
lation and the minor allele (often denoted by A and
a). We consider diploid organisms with chromosome
pairs, therefore a SNP in our analysis can take three
forms: AA (homozygous reference), Aa/aA (heterozy-
gous variant), and aa (homozygous variant). In the
following, the SNP values are frequently encoded as
AA = 1,Aa/aA = 2,aa = 3 (another more popular en-
coding is AA = 0,Aa/aA = 1, aa = 2 which may also
be interpreted as the number of minor alleles).
3.2 Highly Interpretable Prediction
Models for SNP Data
Interpretability depends on the domain, but in general,
a model is interpretable if the reasoning processes are
more understandable to humans (Rudin et al., 2022).
The methods considered operate on genetic risk
factors given by SNPs and are an attempt to predict a
binary disease status. More precisely, in case-control
genetic association studies on SNP data, we intend
to understand a procedure that produces output in
{case,control} (encoded by B = {0,1}) from inputs
in {AA,aA/Aa,aa}
n
(encoded by P
n
= {1,2, 3}
n
or
P
n
= {0,1,2}
n
) where cases are individuals with the
considered disease and controls are individuals with-
out the considered disease.
logicFS and GPAS return boolean models repre-
senting a function
f : P
n
→ B
while logicDT and AutoML provide risk estimates
representing
f : P
n
→ [0,1] .
The models returned by logicFS, GPAS, and logicDT
are highly interpretable, as they are given in a form
that is easily understandable by humans. In addition,
they resemble the models in Garte (2001).
Garte (2001) states that it is "to be expected that no
single metabolic gene variant should ever be observed
to have a large role in cancer susceptibility for any
general cancer type" and that in "some cases, effects
were only observed in the presence of two or more
risk alleles." The presented studies in Garte (2001)
suggest models such as
a woman with alleles of GSTM1 and GSTT1
that is premenopausal and frequently drinks
alcohol or an african-american woman with an
allele of CYP1A1 or a woman with an allele
of NAT1*11 that frequently smokes
for an increased breast cancer risk. The methods con-
sidered rely on subgroups with similar demographic
and environmental data and therefore only consider
the SNPs. The methods are not restricted to SNPs,
however. logicFS, GPAS, and logicDT can also op-
erate on dichotomized data. According to Nunkesser
(2008) GPAS is extendable to general ordinal data.
From the results of preceding studies it seems rea-
sonable to assume that the models should not be very
large. Highly interpretable prediction models should
be similar to the models in Garte (2001). This would
also help to understand possible underlying biological
mechanisms.
BIOINFORMATICS 2025 - 16th International Conference on Bioinformatics Models, Methods and Algorithms
556

4 SHORT COMPARISON OF
RELEVANT METHODS
scrime (Schwender and Fritsch, 2018) is a popular R
package that is capable of simulating SNP data. With
standard parameters, the function simulateSNPglm
simulates case control data where the case risk is in-
creased by either SNP6 not being AA and SNP7 being
AA or SNP3, SNP9, and SNP10 all being AA. Alter-
natively, we can denote this with boolean operators as
follows (∧ may be omitted in monomials):
(SNP6 ̸= AA)(SNP7 = AA)
∨ (SNP3 = AA)(SNP9 = AA)(SNP10 = AA)
This data simulation corresponds to the observations
of Garte (2001) for subgroups with similar demo-
graphic and environmental data.
Please note that the following analysis may not be
as rigorous and fair as it should be. The main purpose
is to introduce the methods considered and to show
their relevance and potential for extensions. One
might think that the simulation from scrime may be
outdated by now, so we will also look briefly at what
an analysis with state-of-the-art machine learning al-
gorithms chosen by Microsoft’s AutoML reveals. For
a future deeper analysis with simulated data, it it also
possible to use the more sophisticated simulations
based on scrime used in Lau et al. (2022).
4.1 Software Used
As mentioned above, we use the R package scrime
for data simulation. We use version 1.3.5 available
from CRAN. logicDT is also available from CRAN
and we use version 1.0.4. logicFS is available from
Bioconductor and we use version 2.24.0. GPAS is
part of the R package RFreak available from GitHub
and we use version 0.3-1. Microsoft’s AutoML is
part of ML.Net and we use version 16.18.2.
4.2 Microsoft AutoML
Figure 1 shows the accuracy (ratio of correctly pre-
dicted instances to the total number of instances) on
test data of the underlying model and the model cho-
sen by AutoML in 100 runs with standard parame-
ters for simulateSNPglm and AutoML. It is appar-
ent that the standard data simulated by scrime is still
complex enough for the comparison of different al-
gorithms. In addition, many of the machine learning
algorithms chosen by AutoML do not have compara-
ble interpretability to logicFS, GPAS, and logicDT.
Figure 1: Accuracy on test data of the underlying model and
the model chosen by AutoML.
!X5 & !X17 & !X95
!X5 & X57 & !X58
!X17 & !X19 & !X92
!X17 & !X19 & !X46
!X17 & !X19 & !X88 & !X92
X21 & X31 & !X59
X13 & !X47 & !X94
X13 & !X47
!X52 & X57 & X61
!X2 & X57 & X61
X57 & !X58 & X61
X57 & X61
!X5 & !X17 & !X19
X57 & X61 & !X92
X11 & !X13
0 2 4 6 8 10 12
Single Tree Measure
Importance
Figure 2: logicFS importance measures of interactions.
4.3 logicFS
For the purpose of demonstration, let us assume that
GPAS and logicDT are capable of automatically com-
puting the best model size. logicFS does not require
this assumption.
Figure 2 shows the importance measures of inter-
actions for an exemplary run of logicFS on the stan-
dard simulated data of scrime.
logicFS requires a recoding of the SNPs to be able
to handle the data. The five most important interac-
tions in Figure 2 are:
• (SNP6 ̸= AA)(SNP7 = AA)
• (SNP29 ̸= AA)(SNP31 ̸= AA)(SNP46 ̸= aa)
• (SNP3 = AA)(SNP9 = AA)(SNP10 = AA)
• (SNP29 ̸= AA)(SNP31 ̸= AA)
• (SNP29 ̸= AA)(SNP29 ̸= aa)(SNP31 ̸= AA)
Highly Interpretable Prediction Models for SNP Data
557
(SNP6!=1)
(255,142)
399 (45.54%)
(SNP9==1)
(336,227)
231 (26.36%)
(SNP7==1)
(177,56)
387 (96.99%)
(SNP10==1)
(214,104)
228 (98.7%)
(SNP3==1)
(144,41)
222 (97.36%)
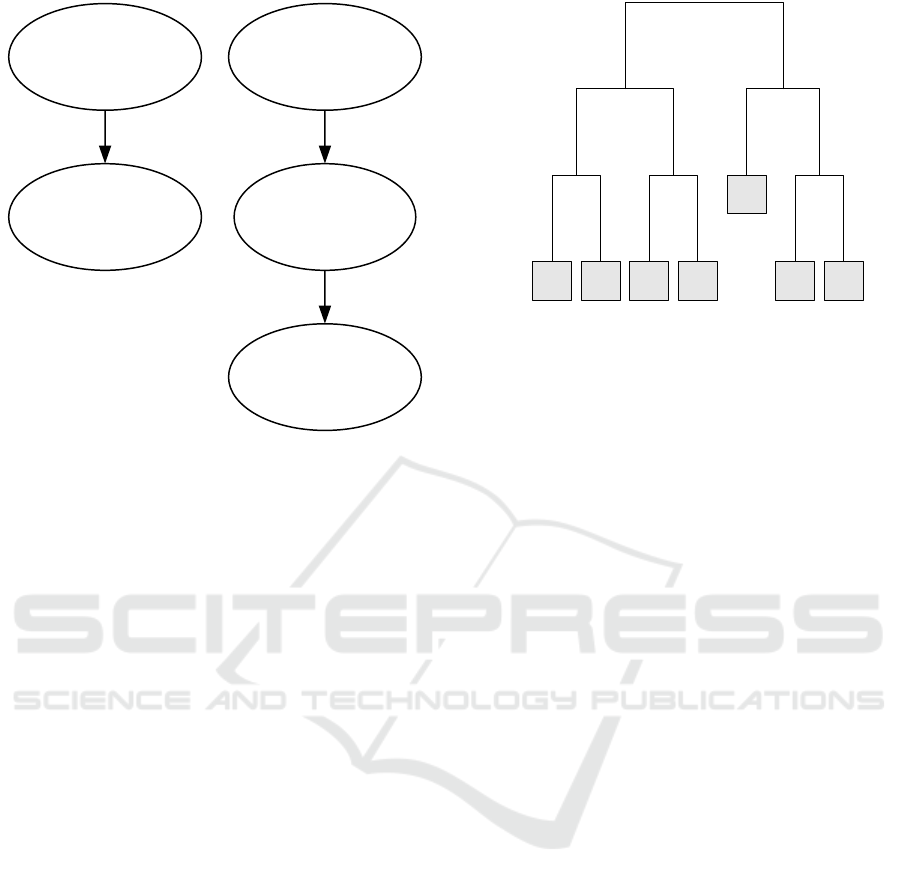
Figure 3: Exemplary returned interaction graph of GPAS-
Interactions.
The interactions of the underlying model are
found by logicFS. The model is highly interpretable,
but the interactions are provided in an isolated state
and there seems to be no way to distinguish
(SNP3 = AA)(SNP9 = AA)(SNP10 = AA)
from similarly important interactions.
4.4 GPAS
GPAS offers two different modes for the in-
tended purpose: GPASDiscrimination and
GPASInteractions. The former determines
(SNP6 ̸= 1)(SNP7 = 1)
∨ (SNP3 = 1)(SNP9 = 1)(SNP10 = 1)
as the best model with the same size as the true model,
which is in fact GPAS notation of the true model.
The latter returns a graph similar to the one in Figure
3. The graph shows as principal information for im-
portant alleles and interactions of alleles the number
of correct cases and false controls explained by the
corresponding interaction (in brackets; the first value
needs to be maximized, the second minimized). We
have chosen a very strict pruning of subtrees for the
graph, showing only subtrees with frequencies above
75%.
With regard to the interpretability and precision
of the models, we can see that there cannot be a better
solution than the result of GPASDiscrimination for
simulated data, because the true model is found and
given in the biologically meaningful way described by
0.70 0.40 0.35 0.50
0.88
0.62 0.79
SNP10D
c
AND SNP9D
c
AND SNP3D
c
SNP31R
c
AND SNP6D
c
SNP3R
c
AND SNP7D SNP3R
c
AND SNP7D
SNP31R
c
AND SNP6D
c
SNP3R
c
AND SNP7D
0 =
= 1
0 =
= 1
0 =
= 1
0 =
= 1
0 =
= 1
0 =
= 1
Figure 4: Exemplary returned model of logicDT.
Garte (2001). The result of GPASInteractions is an
interesting and highly interpretable model which, in
this case, also shows the underlying model. We may
see more interactions with lower values for pruning,
however, making it an interesting alternative for real
data. An obvious extension would be to add to the
method strategies to prevent overfitting if no pruning
is applied.
4.5 logicDT
Figure 4 shows an exemplary returned model of log-
icDT. If we assign a case to probabilities > 0.5
and apply transformation rules, we get the following
model:
(SNP3 = AA)(SNP9 = AA)(SNP10 = AA)
∨ (SNP6 ̸= AA)(SNP7 = AA)
∨ (SNP3 = aa)(SNP31 = aa)
∨ (SNP6 ̸= AA)(SNP3 = aa)
∨ (SNP7 = AA)(SNP31 = aa)
The model is highly interpretable, as with logicFS,
but there does not seem to be a straightforward way
to distinguish (SNP6 ̸= AA)(SNP7 = AA) from simi-
larly important interactions.
4.6 Conclusion
If we assume that GPAS and logicDT are capable
of automatically computing the best model size, all
methods apart from AutoML are capable of finding
the underlying model (in the case of logicFS and log-
icDT with additional interactions). GPAS is capable
of finding the true model in the most interpretable
way. logicFS and logicDT are capable of finding the
true model, but in the cases considered here there
BIOINFORMATICS 2025 - 16th International Conference on Bioinformatics Models, Methods and Algorithms
558
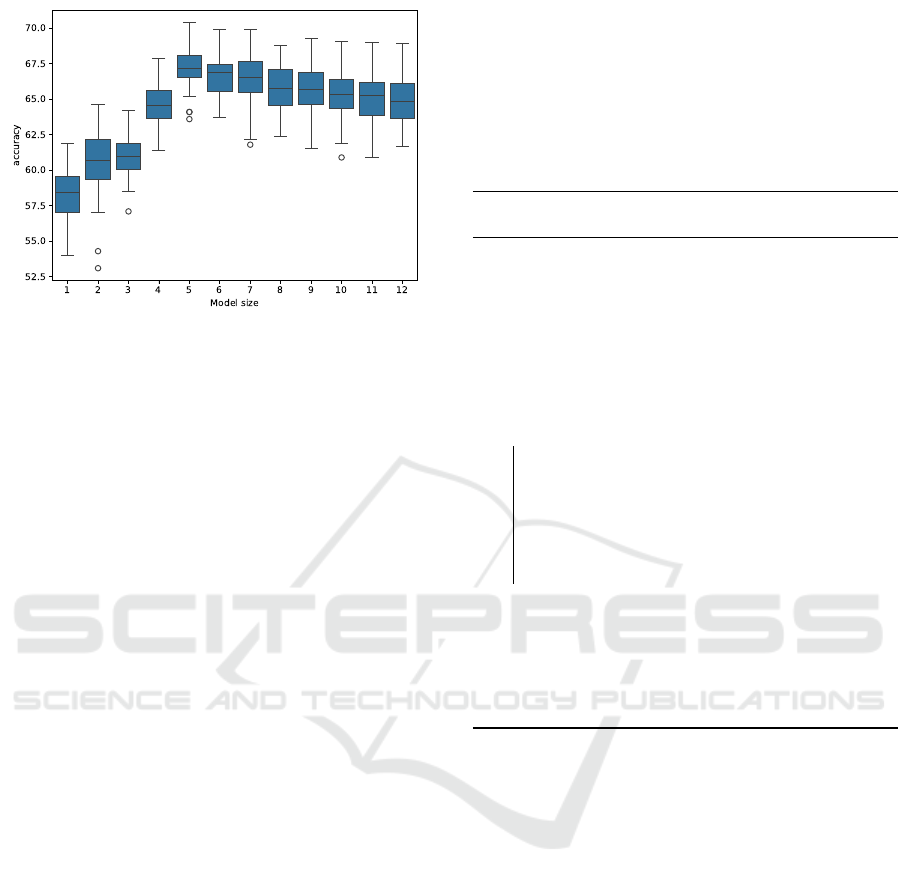
Figure 5: Accuracy on test data of models of different sizes
returned by GPASDiscrimination (originally published in
Nunkesser (2008)).
seems to be no way to distinguish between the un-
derlying interactions and similarly important interac-
tions. It is therefore desirable to extend GPAS with a
method to select the best model size automatically.
5 AUTOMATIC MODEL
SELECTION FOR GPAS
GPAS is available as an open source R package from
GitHub. However, a direct extension of GPAS on a
source code basis is not advisable as the sources have
heterogenous dependencies and the best model size
selection algorithm should be chosen first to justify
the effort to change the code.
We therefore propose using GPAS as a black
box and applying an external method for automatic
model selection. For the black box algorithm, we can
use GPASDiscrimination and GPASInteractions
as described above.
5.1 GPASDiscrimination
The simulation results from Section 4.4 suggest that
GPASDiscrimination is capable of finding the true
model if the model size is automatically chosen
correctly. In a typical run on the simulated data,
GPASDiscrimination proposes models with sizes
between 1 and 12 literals.
Nunkesser (2008) gives more detailed insight into
the challenges in automatic model size selection for
GPAS. Figure 5 shows the accuracy on test data of
models of different sizes returned by GPASDiscrimi-
nation.
As mentioned before, Nunkesser (2008) describes
approaches for automatic model size selection in
GPAS which were not integrated into the available
algorithm. In this paper, we propose using a cross-
validation approach instead to automatically select
the best model size. Cross-validation is a standard
method to prevent overfitting not attempted in GPAS
before. We propose the approach described by Algo-
rithm 1 to automatically select the best model size.
Algorithm 1: Automatic Model Selection in
GPASDiscrimination.
Input: Data set, Cross-validation strategy,
Consolidation strategy, Selection
strategy
Output: Chosen polynomial
1 Use the cross-validation strategy to split the
data set into a set of training and validation
data pairs;
2 foreach Pair of training and validation data
do
3 Call GPASDiscrimination with the
training data set;
4 Compute the accuracies of the returned
models on the validation data set;
5 Add the returned models to a list of
candidate models;
6 end
7 Consolidate the list of candidate models with
the consolidation strategy;
8 Select a model from the candidate list with
the selection strategy;
9 return The chosen model
Initial experiments on the data from Section 4.4
suggest, that the following choices offer a very
promising automatic model selection: For cross vali-
dation, 5-fold cross validation is chosen. The consol-
idation strategy works as follows:
1. Discard all models that do not appear in all of the
5 runs on the folds.
2. Discard all models where a model of the same size
with a better average accuracy on the validation
data exists.
Lastly, as a selection strategy, the accuracy gain with
regard to larger model sizes is considered. Large
models that do not at least offer 1% more accuracy
than all smaller models are discarded. Afterwards,
the model with the greatest accuracy is chosen.
In a simulation with the data used in Section 4.2,
the algorithm has chosen the real underlying model in
71 out of 100 runs. Figure 6 shows a summary.
The mean accuracy of the models chosen by
GPAS is 0.666 with a standard deviation of 0.019
(while the true model would result in an accuracy
Highly Interpretable Prediction Models for SNP Data
559
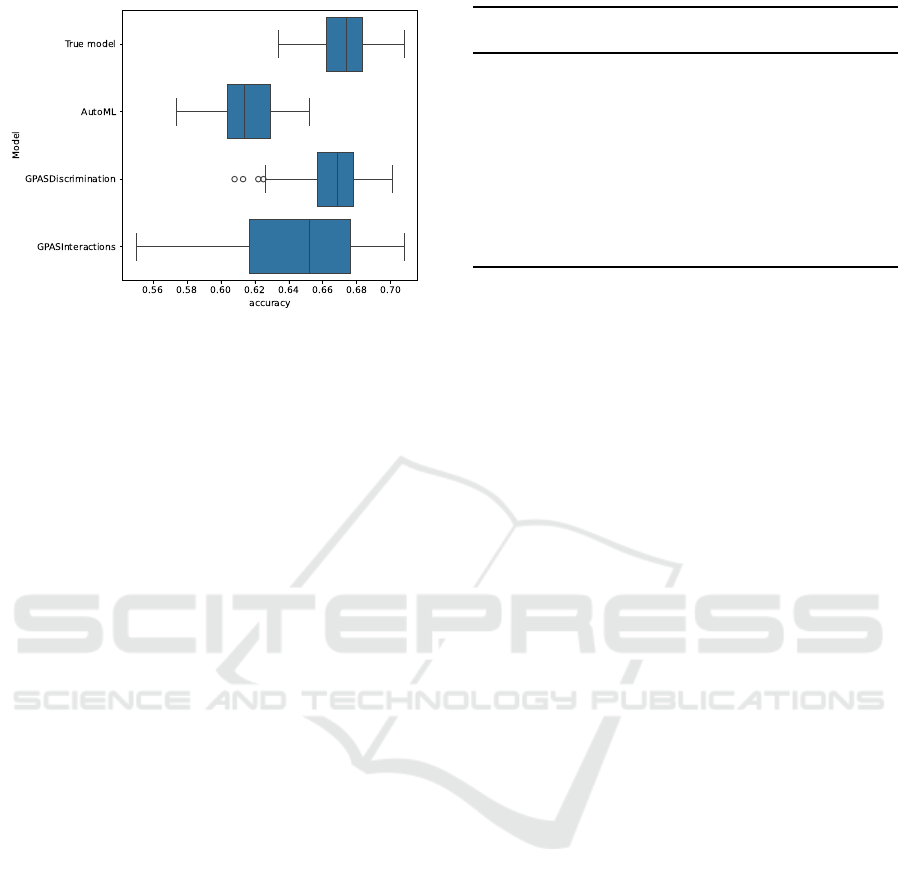
Figure 6: Accuracy on test data of the underlying model and
the model chosen by AutoML and GPAS.
of 0.673 with a standard deviation of 0.015). This
is comparable to the results achieved by Nunkesser
(2008). However, the method proposed here is more
general and easier to parameterize. The results are
promising, but the approach is not yet fully devel-
oped. Future research must show if the choice of dif-
ferent parameters may yield better results and how the
concept performs on further simulated data.
5.2 GPASInteractions
It is possible to extend Algorithm 1 to
GPASInteractions in a straightforward way.
Only the most frequent interactions are kept in
the interaction tree. This approach will not be
investigated further here, as it appears sensible to
investigate further and optimize the approach for
GPASDiscrimination first.
Apart from cross-validation, in the case of
GPASInteractions, we can also use a pruning
method for the interaction tree. The simula-
tion results from Section 4.4 already suggest that
GPASInteractions is capable of finding the true
model if the pruning method for the interaction tree
is chosen correctly. We propose using Algorithm 2 to
automatically prune the interaction tree.
In an initial simulation with the data used in Sec-
tion 4.4 and t
r
= 0.2,t
s
= 0.75 the algorithm has cho-
sen the real underlying model in 56 out of 100 runs.
Figure 6 shows a summary of the runs. As men-
tioned above, GPASInteractions is intended as an
interesting alternative for real data, as it may show
more interactions than GPASDiscrimination. With-
out pruning, the results tend to be very large and less
interpretable. The pruning approach proposed here is
a first step to making the method more interpretable
and preventing overfitting while still maintaining the
greater variety of results.
Algorithm 2: Automatic Tree Pruning in GPAS-
Interactions.
Input: Data set, Root frequency threshhold
t
r
, Subtree frequency threshold t
s
Output: Pruned interaction tree
1 Call GPASInteractions with the data set;
2 Prune all subtrees with a root frequency
below t
r
;
3 Prune all subtrees with a frequency of a
non-root-node below t
s
;
4 return The pruned interaction tree
6 FUTURE WORK
The approach proposed here is a first step in extend-
ing GPAS with automatic model selection. Further
research is needed before integrating the selection
method into the existing algorithm.
6.1 Application to Further Data
Future research must show whether the choice of dif-
ferent parameters yields better results and how the
concept performs on further data. The parameteriza-
tion encompasses the choice of the cross-validation
strategy, the consolidation strategy, and the selection
strategy. In order to further substantiate these results,
further studies on different data are necessary. The
next obvious data sets are:
1. More sophisticated simulations based on scrime
such as the ones used in Lau et al. (2022).
2. More general dichotomized data such as that used
in Lau et al. (2024).
3. Ordinal data with the extension to GPAS proposed
in Nunkesser (2008)
After the results on these data sets are available,
the next steps should be the application of the ap-
proach to real data and the integration of the selection
method into the existing algorithm.
6.2 Generalization of the Method
The comparisons with the state-of-the-art algorithms
chosen by AutoML should be extended to the new
data sets. If it is confirmed that an algorithm based
on Genetic Programming is capable of achieving or
even outperforming state-of-the-art results, the next
step should be the further extension of the method to
multi-valued responses or other categorical predictors
besides SNPs.
BIOINFORMATICS 2025 - 16th International Conference on Bioinformatics Models, Methods and Algorithms
560

This may be the most challenging part of the re-
search, as the methods are currently only designed for
binary responses and SNP data. At the moment two
alternatives seem sensible: generalizing the used dis-
junctive normal forms or extending the methods to de-
cision diagrams.
6.2.1 Generalizing Disjunctive Normal Forms
A possible extension of the used literals
• SNP
x
= AA
• SNP
x
̸= AA
• SNP
x
= Aa/aA
• SNP
x
̸= Aa/aA
• SNP
x
= aa
• SNP
x
̸= aa
to general nominal data is to use the generalizable lit-
erals
• SNP
x
∈ {AA}
• SNP
x
∈ {Aa/aA,aa}
• SNP
x
∈ {Aa/aA}
• SNP
x
∈ {AA,aa}
• SNP
x
∈ {aa}
• SNP
x
∈ {AA,Aa/aA}
instead. A challenge is of course to deal with the ex-
ponentially growing search space.
A possible extension for multi-valued responses
is to abandon boolean algebra and exchange it for a
more general algebra. If we replace ∧ by × and ∨ by
+ and introduce weight vectors, a model like
(SNP6 ̸= AA)(SNP7 = AA)
∨ (SNP3 = AA)(SNP9 = AA)(SNP10 = AA)
could be expressed as:
0
0
+
0
1
SNP6 ∈ {Aa/aA, aa}SNP7 ∈ {AA}
+
0
1
SNP3 ∈ {AA}SNP9 ∈ {AA}SNP10 ∈ {AA}
After an application of the softmax function, the
model could yield probabilities for different classes
and is generalizable to multi-valued responses.
6.2.2 Extending the Method to Decision
Diagrams
If the approach of using disjunctive normal forms
or a generalization of them as a model is no longer
sufficient, an extension to decision diagrams is con-
ceivable. There are already investigations being con-
ducted here in the context of Genetic Programming
(see e.g. Droste, 1997; Wegener, 2000). In recent re-
sults, Florio et al. (2023) propose to use Decision Di-
agrams trained by MILP while Hu et al. (2022) use
MaxSAT. However, as Florio et al. (2023) state:
Most likely, the biggest obstacle towards the
effective use of decision diagrams remains the
ability to learn them efficiently.
It is an interesting question how an approach
based on Genetic Programming would perform in
comparison.
7 CONCLUSION
In this paper, we have shown that highly interpretable
prediction models for SNP data are important for
understanding possible underlying biological mech-
anisms. We have also shown that logicFS, GPAS, and
logicDT are capable of yielding highly interpretable
prediction models. The automatic prevention of over-
fitting requires improvement, however. We have pro-
posed using GPAS as a black box and applying an ex-
ternal method for automatic model selection. We have
presented an approach using the GPAS algorithm as
a black box and shown initial results on simulated
data. The initial results are comparable to the results
achieved by Nunkesser (2008). The approach offers
an easier parameterization and is more general, how-
ever. Future research must demonstrate whether the
choice of different parameters yields better results and
how the concept performs on other simulated data. As
this paper presents work in progress, the outlook on
future work is of great interest.
REFERENCES
Bureau, A., Dupuis, J., Falls, K., Lunetta, K. L., Hayward,
B., Keith, T. P., and Van Eerdewegh, P. (2005). Iden-
tifying snps predictive of phenotype using random
forests. Genetic Epidemiology, 28(2):171–182.
Che, R. and Motsinger-Reif, A. (2013). Evaluation of ge-
netic risk score models in the presence of interaction
and linkage disequilibrium. Frontiers in Genetics, 4.
Chen, C. C., Schwender, H., Keith, J., Nunkesser, R.,
Mengersen, K., and Macrossan, P. (2011). Methods
for identifying snp interactions: A review on varia-
tions of logic regression, random forest and bayesian
logistic regression. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Com-
putational Biology and Bioinformatics, 8(6):1580–
1591.
Highly Interpretable Prediction Models for SNP Data
561

Droste, S. (1997). Efficient genetic programming for find-
ing good generalizing Boolean functions. In Koza,
J. R., Deb, K., Dorigo, M., Fogel, D. B., Garzo, M.,
Iba, H., and Riolo, R. L., editors, Proceedings of the
Second Annual Conference on Genetic Programming,
pages 82–87, San Francisco, Calif. Morgan Kaufmann
Publishers, Inc.
Florio, A., Martins, P., Schiffer, M., Serra, T., and Vidal,
T. (2023). Optimal decision diagrams for classifi-
cation. In Williams, B., Chen, Y., and Neville, J.,
editors, AAAI-23 Technical Tracks 6, Proceedings of
the 37th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence,
AAAI 2023, pages 7577–7585. AAAI Press.
Garte, S. (2001). Metabolic Susceptibility Genes As Cancer
Risk Factors: Time for a Reassessment? Cancer Epi-
demiology, Biomarkers & Prevention, 10(12):1233–
1237.
Hu, H., Huguet, M.-J., and Siala, M. (2022). Optimizing bi-
nary decision diagrams with maxsat for classification.
Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial In-
telligence, 36:3767–3775.
International Human Genome Sequencing Consortium
(2001). Initial sequencing and analysis of the human
genome. Nature, 409(6822):860–921.
Lau, M., Schikowski, T., and Schwender, H. (2024). log-
icDT: a procedure for identifying response-associated
interactions between binary predictors. Machine
Learning, 113(2):933–992.
Lau, M., Wigmann, C., Kress, S., Schikowski, T., and
Schwender, H. (2022). Evaluation of tree-based sta-
tistical learning methods for constructing genetic risk
scores. BMC Bioinformatics, 23(1):97.
Nunkesser, R. (2008). Analysis of a genetic program-
ming algorithm for association studies. In GECCO
’08: Proceedings of the 10th Annual Conference on
Genetic and Evolutionary Computation, pages 1259–
1266, New York. ACM.
Nunkesser, R., Bernholt, T., Schwender, H., Ickstadt, K.,
and Wegener, I. (2007). Detecting high-order in-
teractions of single nucleotide polymorphisms using
genetic programming. Bioinformatics, 23(24):3280–
3288.
Ruczinski, I., Kooperberg, C., and L. LeBlanc, M. (2004).
Exploring interactions in high-dimensional genomic
data: an overview of logic regression, with applica-
tions. Journal of Multivariate Analysis, 90(1):178–
195.
Rudin, C., Chen, C., Chen, Z., Huang, H., Semenova, L.,
and Zhong, C. (2022). Interpretable machine learn-
ing: Fundamental principles and 10 grand challenges.
Statistics Surveys, 16:1 – 85.
Schwender, H. and Fritsch, A. (2018). scrime: Analysis
of High-Dimensional Categorical Data such as SNP
Data. R package version 1.3.5.
Schwender, H. and Ickstadt, K. (2007). Identification of
SNP interactions using logic regression. Biostatistics,
9(1):187–198.
Tong, H., Küken, A., Razaghi-Moghadam, Z., and
Nikoloski, Z. (2021). Characterization of effects
of genetic variants via genome-scale metabolic mod-
elling. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences,
78(12):5123–5138.
Wegener, I. (2000). Branching Programs and Binary Deci-
sion Diagrams. SIAM, Philadelphia.
Winham, S. J., Colby, C. L., Freimuth, R. R., Wang,
X., de Andrade, M., Huebner, M., and Biernacka,
J. M. (2012). SNP interaction detection with Random
Forests in high-dimensional genetic data. BMC Bioin-
formatics, 13(1):164.
BIOINFORMATICS 2025 - 16th International Conference on Bioinformatics Models, Methods and Algorithms
562
