
A Parallel Implementation of the Clarke-Wright Algorithm on GPUs
Francesca Guerriero
a
and Francesco Paolo Saccomanno
b
Department of Mechanical, Energy and Management Engineering,
University of Calabria, Ponte Pietro Bucci, 87036 Rende, Italy
Keywords:
Capacitated Vehicle Routing Problem, CVRP, Clarke-Wright Algorithm, GPU Computing, CUDA, Heuristics.
Abstract:
The Clark & Wright (CW) algorithm is a greedy approach, aimed at finding good-quality solutions for the
capacitated vehicle routing problem (CVRP). It is the most widely applied heuristic algorithm to solve CVRP
due to its simple implementation and effectiveness. In this work, we propose a parallel implementation of the
CW algorithm well suited to be executed on GPUs. In order to evaluate the performance of the developed
approach, an extensive computational phase has been carried out, by considering a large set of test problems.
The results are very encouraging, showing a significant reduction in computational time compared to the
sequential version, especially for large-scale networks.
1 INTRODUCTION
The Capacitated Vehicle Routing Problem (CVRP)
is a NP-Hard combinatorial optimization problem
(Laporte, 1992), which seeks to determine an opti-
mal set of routes for a fleet of vehicles, with lim-
ited capacity to deliver goods to customers, while
minimizing the total transportation cost. Due to its
NP-hard nature, finding exact solutions for large-
scale instances is computationally intractable, there-
fore, optimal solutions can be found only when a
limited number of nodes (customers and depot) are
considered. For more complex scenarios, heuris-
tics and meta-heuristics have been developed to find
approximate optimal solutions, (Accorsi and Vigo,
2021), (Liu et al., 2023). Among these, the Clarke-
Wright algorithm (CW) is a greedy approach widely
used for its efficiency and effectiveness in address-
ing the CVRP through a simple approach, (Clarke and
Wright, 1964), (Augerat et al., 1995). In particular, it
relies on building a list of possible savings, obtained
when two routes are merged, followed by iterative
merging of routes if the constraints of the problem
are satisfied. Despite its simplicity, the CW approach,
based on savings, can achieve results within 7% of
the optimal value, especially for large instances. In
the scientific literature, several authors have proposed
improvements to the CW algorithm to enhance its ef-
fectiveness or address other variants of the CVRP,
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3887-1317
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8807-8659
(Bor
ˇ
cinov
´
a, 2022), (Nurcahyo et al., 2023), (Tun-
nisaki and Sutarman, 2023). Parallel computing sys-
tems also offer a viable approach for developing solu-
tion methods capable of solving large-scale CVRPs.
In this work, we propose a parallel implementation of
the basic CW algorithm on GPU.
In what follows, a concise overview of the lit-
erature related to the development of parallel ap-
proaches to solve the CVRP is provided. Attention
is focused on the scientific contributions most rele-
vant to our study. Previous studies have primarily
focused on parallelizing existing metaheuristics us-
ing GPUs to enhance execution speed. These works
used graphics processors to handle specific portions
of the code. For example, (Benaini and Berrajaa,
2018) proposed a GPU-accelerated evolutionary ge-
netic algorithm for dynamic vehicle routing prob-
lems (DVRP), in which requests can occur later. The
proposed approach is able to find good-quality solu-
tions for up to 3,000 nodes. Similarly, (Abdelatti and
Sodhi, 2020) parallelized a genetic algorithm with lo-
cal search strategies. Other works used ant colony
optimization (Diego et al., 2012), which determines
the solution to the problem by imitating the behavior
of certain insects in nature, and local search methods
(Luong et al., 2013), which iteratively move from one
solution to another in a given neighborhood. Simi-
larly, the local search approach is used in (Schulz,
2013). In particular, the two classical heuristics 2-
opt and 3-opt were implemented in parallel on GPUs.
The instances considered include CVRP and DVRP
100
Guerriero, F. and Saccomanno, F. P.
A Parallel Implementation of the Clarke-Wright Algorithm on GPUs.
DOI: 10.5220/0013138100003893
In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Operations Research and Enterprise Systems (ICORES 2025), pages 100-111
ISBN: 978-989-758-732-0; ISSN: 2184-4372
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

problems, ranging from 57 to 2400 nodes.
In (Jin et al., 2014), a tabu search approach is con-
sidered, in which the threads work in parallel for the
intensification and diversification phase. The authors
have achieved effective results in instances with up to
1,200 nodes.
In (Boschetti et al., 2017), the authors used
dynamic programming and a relaxation approach,
namely state-space relaxation, to compute the bounds.
Since these methods are time-consuming, they devel-
oped a GPU computing approach and proved that it
is capable of achieving up to 40 times time reduction
compared to the sequential version, when solving an
instance with 2,000 nodes.
(Benaini et al., 2016) presented a GPU-based
heuristic for single and multi-depot VRPs, generat-
ing initial solutions in parallel and progressively re-
fining them. Unlike our approach, which directly op-
timizes the CW algorithm’s steps, their method uses
GPUs to generate multiple initial solutions and re-
lies on the standard CW algorithm. In subsequent
works, (Benaini and Berrajaa, 2016), (Benaini et al.,
2017) developed GPU implementations for dynamic
request insertion and multi-capacity VRPs, respec-
tively. More recent studies, such as (Yelmewad and
Talawar, 2021), have focused on improving the per-
formance of local search heuristics using GPUs.
To the best of our knowledge, the only CUDA-
based approach aimed at implementing the basic CW
algorithm on GPUs has been presented in (Guerriero
and Saccomanno, 2024). This early research ad-
dresses the merging of tasks sequentially and focuses
on cases with a relatively small number of nodes, pri-
marily due to memory constraints. The present paper
addresses these limitations and provides a more effi-
cient parallel version of the CW algorithm.
Contribution and Organization of the Paper.
This work focuses on developing the CW heuristic
on GPUs to enhance performance. A comparison be-
tween the GPU implementation and its CPU coun-
terpart reveals significant speed-ups achieved by the
GPU, especially for large-scale instances.
The main contributions of this paper are the fol-
lowing:
• development and testing of a parallel version of
CW steps, by exploiting GPU capability;
• design and implementation of CUDA Kernel ad-
hoc for the calculation of Distance/Cost Matrix
and relative savings;
• implementation of a benchmark system to analyse
each step of CW algorithm;
• definition of an approach for reducing in parallel
the number of operations to be executed sequen-
tially on the CPU.
The structure of the paper is as follows. Sec-
tion 2 provides a summary of the steps involved in
the CW method, illustrating the process on a toy ex-
ample. Section 3 outlines the proposed parallel ap-
proach. Section 4 focuses on the analysis of the com-
putational results, collected in an extensive experi-
mental phase. The paper concludes with final obser-
vations in Section 5.
2 THE CW ALGORITHM
The CW approach can be viewed as divided into four
main phases: calculating the distance/cost matrix, cal-
culating the savings list, sorting, and finally merging
the routes. The cost calculation is typically based
on the Euclidean distance between nodes, but other
metrics can be used. Furthermore, distances are usu-
ally rounded to the nearest integer in experiments, as
floating-point calculations are much slower.
Figure 1: Saving with node i and j.
The list of savings is calculated as the cost reduc-
tions that can be achieved when a vehicle transports
goods to node i starting from another node j, instead
of starting again from the depot d (see Fig. 1):
Saving(i, j) = d(D, i) + d(D, j) − d(i, j). (1)
In practice, even though it adds a trip and there-
fore a cost between the nodes i and j, it allows the
elimination of two other trips: one between the depot
and the nodes i and another between the depot and the
node j. Subsequently, before starting route merging,
this list of savings is reordered according to decreas-
ing values, allowing the largest savings values to be
considered first.
There are two versions of route merging: sequen-
tial and parallel. However, these terms do not refer
A Parallel Implementation of the Clarke-Wright Algorithm on GPUs
101
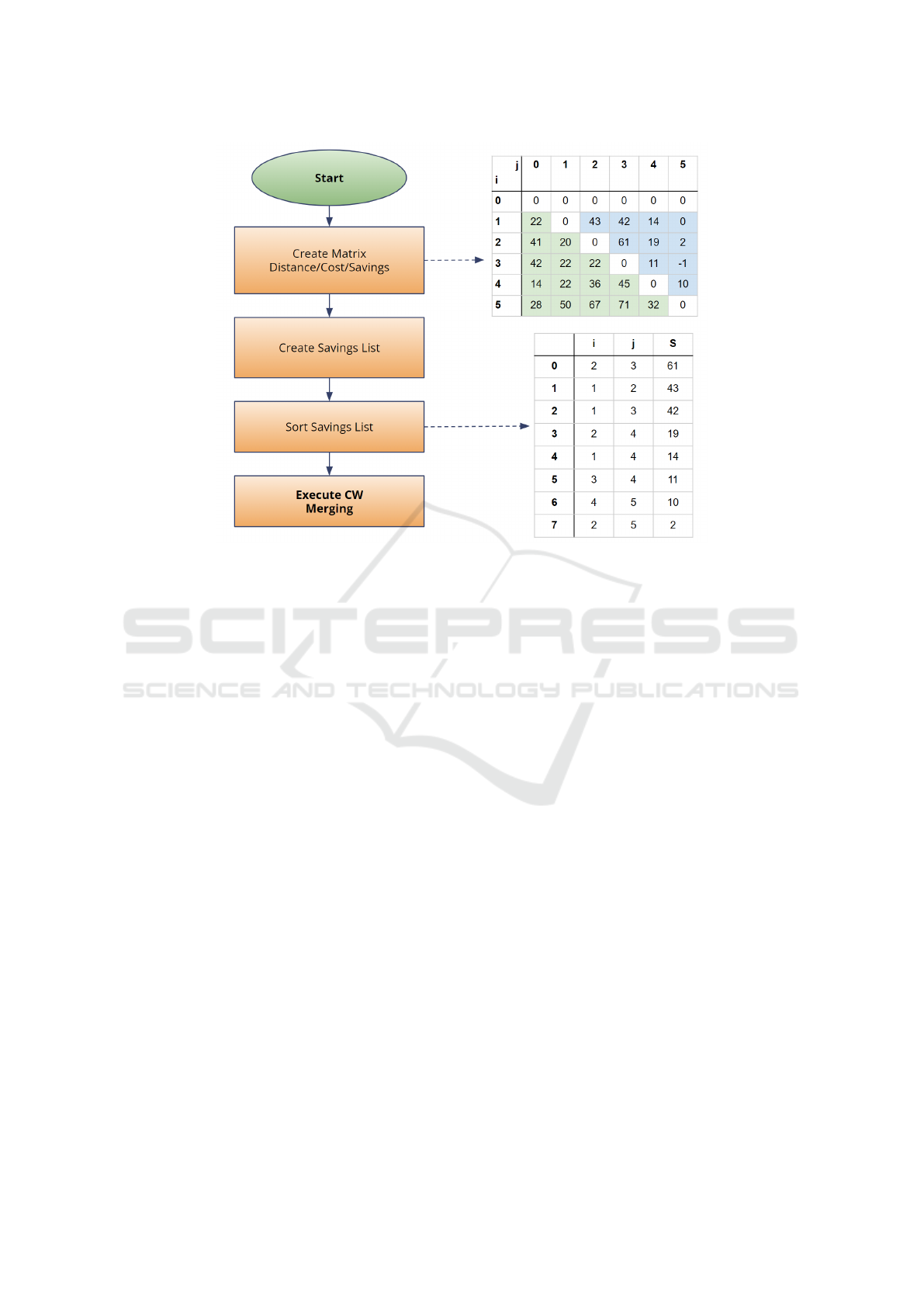
Figure 2: Schematization of the CW algorithm.
to execution on specific hardware, but rather they de-
scribe how the elements of the savings list are pro-
cessed. In the former, the sequential, one route at
a time, is completed by sequentially considering the
items in the savings list and inserting the nodes that
do not violate the constraints. The next route is con-
sidered when it is no longer possible to insert further
savings into the current one. In the parallel case, in-
stead, an element of the saving list is extracted in se-
quence and the two indicated routes are merged, al-
ways taking into account the constraints. In this case,
therefore, during iterations, multiple routes are con-
sidered “in parallel”.
The performance of the sequential approach
presents an average gain compared to the optimal so-
lution of 18%, while in the parallel case, it improves
to 7% (Caccetta et al., 2013). For this reason, we will
use only the parallel variant of CW in both the CPU
and GPU implementations.
In detail, in the parallel case, the merging steps are
as follows:
1. The next element of the savings list sorted in de-
scending order is extracted.
2. The constraints are verified: in this work, only the
vehicle capacity restrictions are considered, even
though it is possible to easily modify the approach
to consider time windows or incompatibilities be-
tween goods constraints.
3. If the constraints are satisfied, if neither of the two
nodes i, j is assigned, a new route is created.
4. Otherwise, the unassigned node is added to the
route or the two routes are merged.
To explain how the CW algorithm works, it is use-
ful to consider a toy example made up of six nodes
with the following coordinates in the Euclidean space:
[10, 20], [10, 40], [30, 30], [-10, 10], [-20, -20] and
the depot on [0,0]. The costs, i.e., the distances, are
then calculated based on these coordinates (as de-
picted in Fig. 2). Suppose that the corresponding de-
mand vector is [50, 50, 50, 25, 25] and the vehicle
capacity is 100. The first operations to be performed
involve calculating the Cost Matrix and the creation
and ordering of the Savings List (Fig. 2). Then each
link in the savings list is considered: the first one
(2,3), since both nodes are unassigned, involves creat-
ing a new tour {2,3} with a load 50 +50 = 100, equal
to the maximum capacity of the vehicles. After, the
links (1,2) and (1,3) are discarded, since nodes 2 and
3 are already present in the tour {0,2,3,0}, but the ve-
hicle is already full. The iteration proceeds with dis-
carding (2,4), and with the creation of a new tour for
the link (1,4) (i.e., {0,1,4,0}), which reaches a load of
75. Then the link (3,4) is discarded, since the nodes
3 and 4 are already assigned to two different routes.
Finally, the link (4,5) is added to obtain from the sec-
ond tour the new tour {0, 1, 4, 5, 0}. Obviously, the
remaining links (2,5) and (3,5) will be discarded. Af-
ter processing all the elements of the savings list, the
ICORES 2025 - 14th International Conference on Operations Research and Enterprise Systems
102
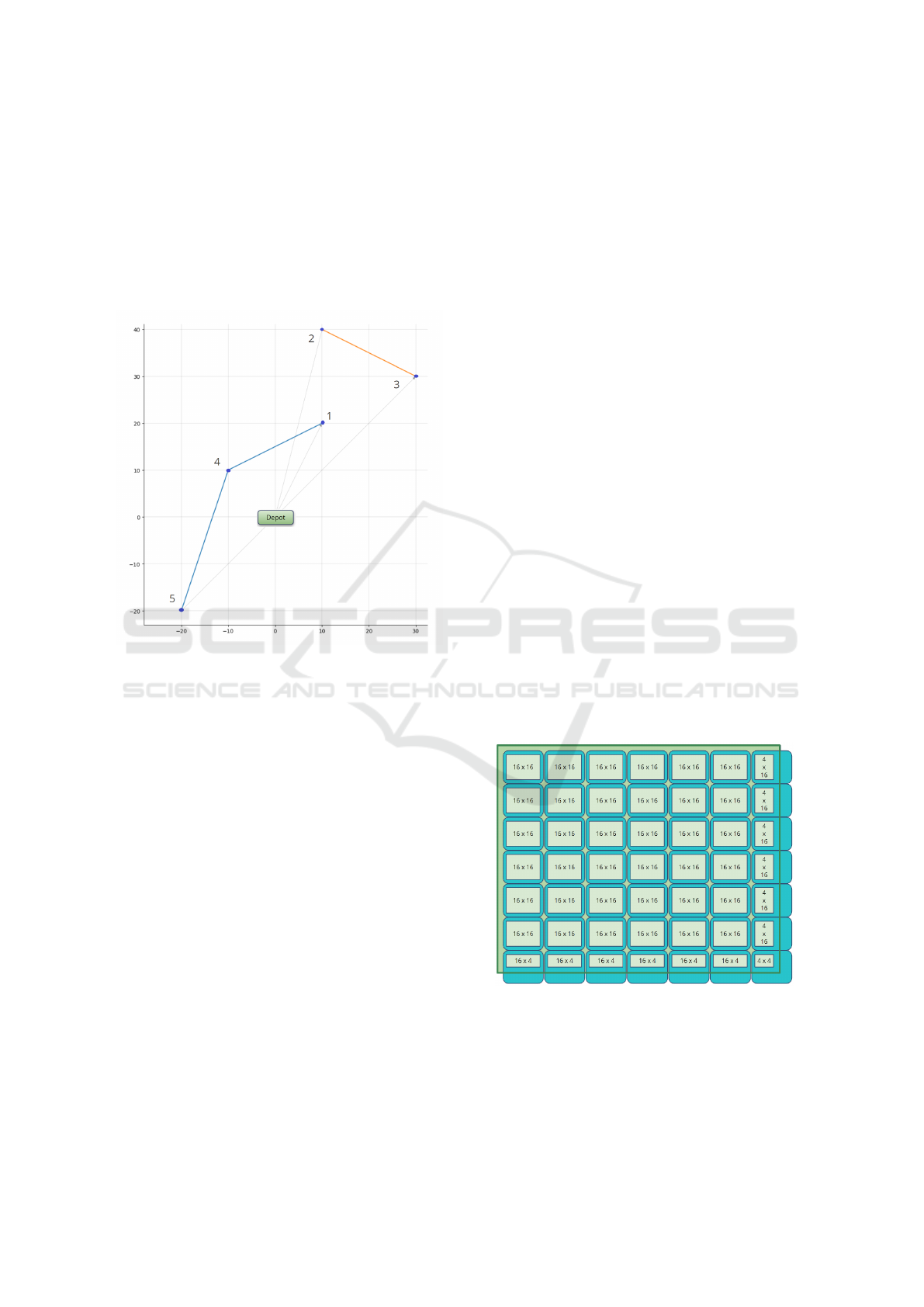
obtained solution (Fig. 3) will consist of only two
routes: {0, 2,3,0},{0,1,4, 5, 0}. It is worth noting
that, after processing saving (4,5), node 4 becomes
internal to the route, allowing us to ignore any sub-
sequent links in the list, where node 4 appears. This
key idea will be used in our approach to reduce the
remaining items belonging to the savings list, and, in
our approach, this reduction will be performed con-
currently on GPU.
Figure 3: Example with six nodes.
The description provided highlights that although
the elements of the savings list require sequential pro-
cessing, both the computation of the distance/cost ma-
trix and the generation of the savings list can be opti-
mized using parallelization. Consequently, this study
aims to implement these steps in parallel by exploiting
GPU capabilities and analyzing the potential speed-
up over traditional CPU-based processing. As illus-
trated in the toy example, an alternative technique for
the merging phase will also be developed to effec-
tively use the GPU: the list is handled sequentially,
but reduced through a parallel method. In the sub-
sequent section, the details of this approach will be
clarified.
3 THE CW ALGORITHM ON GPU
(CWG)
The purpose of this work is to improve the ef-
ficiency of the basic CW approach, by using a
GPU. GPUs were created to improve graphics perfor-
mance, but were later used for mathematical model-
ing and solving optimization problems. Unlike CPUs,
which have a few highly performant cores, GPUs are
equipped with thousands of cores capable of perform-
ing simpler computations. Among the various usage
paradigms, NVidia, one of the GPU brands, intro-
duced the CUDA framework, which allows for ab-
straction from the physical structure of the graphics
card: the functions to be executed in the threads are
called kernels, identical for all threads but operating
on different data. The various threads are logically
grouped into blocks and the blocks are grouped into a
grid. The size of the blocks depends on the problem
at hand and the resources needed. Each thread uses
a private local memory and a shared memory with all
other threads in the same block. These memories are
fast, but limited, and restrict the maximum number of
threads that can be executed in a block. There is also
a global memory, which is accessible to all threads in
the grid, slower than the previous ones, but generally
with capacities reaching up to tens of gigabytes.
CUDA requires the division of processing capac-
ity into blocks made up of t x t threads. A common
choice is to use blocks of 32 x 32 or 16 x 16 threads, as
these configurations provide a good balance between
computational efficiency and compatibility across dif-
ferent GPU architectures. Currently, the maximum
number of threads per block in CUDA is 32 x 32 =
1,024. While using a high number of threads might
seem advantageous, it can often result in some threads
remaining unused. The optimal number of threads per
block depends on several factors: the actual number
of threads needed for the computation, the available
local memory resources per block, and the perfor-
mance achieved with different block sizes.
Figure 4: Covering a 100 x 100 matrix using 7 x 7 blocks
of 16 x 16 threads.
To better explain the first point, that is, the need
to determine the right number of threads to be used,
it is useful to consider the example of a matrix with
100 nodes (see Fig. 4), for which the number of op-
A Parallel Implementation of the Clarke-Wright Algorithm on GPUs
103

erations to be executed (i.e. the cells of the matrix) is
100 x 100 = 10,000. If a block of 16 x 16 threads is
chosen, a minimum number of 7 x 7 blocks is needed,
for a total of 12,544 threads, therefore the 20.28% of
threads remain unused. As illustrated in the figure,
the final blocks of threads are only partially utilized,
leading to some threads being left idle.
Table 1: Unused threads for different thread block configu-
ration.
Nodes Num. Block Size Min Block Numbers Unused
100 32 x 32 4 x 4 38.96%
300 32 x 32 10 x 10 12.11%
500 32 x 32 16 x 16 4.63%
1000 32 x 32 32 x 32 4.63%
3000 32 x 32 94 x 94 0.53%
5000 32 x 32 157 x 157 0.95%
6000 32 x 32 188 x 188 0.53%
10000 32 x 32 313 x 313 0.32%
20000 32 x 32 626 x 626 0.32%
50000 32 x 32 1563 x 1563 0.06%
100 16 x 16 7 x 7 20.28%
300 16 x 16 19 x 19 2.61%
500 16 x 16 32 x 32 4.63%
1000 16 x 16 63 x 63 1.58%
3000 16 x 16 188 x 188 0.53%
5000 16 x 16 313 x 313 0.32%
6000 16 x 16 376 x 376 0.53%
10000 16 x 16 626 x 626 0.32%
20000 16 x 16 1251 x 1251 0.16%
50000 16 x 16 3126 x 3126 0.06%
100 8 x 8 13 x 13 7.54%
300 8 x 8 38 x 38 2.61%
500 8 x 8 63 x 63 1.58%
1000 8 x 8 126 x 126 1.58%
3000 8 x 8 376 x 376 0.53%
5000 8 x 8 626 x 626 0.32%
6000 8 x 8 751 x 751 0.27%
10000 8 x 8 1251 x 1251 0.16%
20000 8 x 8 2501 x 2501 0.08%
50000 8 x 8 6251 x 6251 0.03%
Tab. 1 shows the amount of unused threads as a
function of the number of nodes N and block size.
The column “Min Block Numbers” represents the
minimum block size of threads to cover the matrix.
The last column indicates the percentage of unused
threads: this drops below 5% in the case of problems
with more than 500 nodes, which are the problems
considered in this paper.
The CW algorithm was profiled to identify which
specific steps to be implemented in parallel, by us-
ing CUDA. Furthermore, this initial analysis allowed
us to optimize the various steps of the CPU ap-
proach, avoiding the various bottlenecks, including
those related to the use of the specific programming
language used in the computational phase (that is,
Python). This empowers the CPU version efficiently
even on medium/large instances, and additionally en-
ables a more effective evaluation of the performance
improvement using GPU. As expected, most of the
time is spent calculating the distance/cost matrix, cre-
ating the savings list, and merging processing in the
main loop. For this reason, we have built an ad-
hoc CUDA kernel that allows the first two phases of
the algorithm to be completed in parallel. Instead,
for the sorting phase we relied on the cupy library
(https://cupy.dev/) which already offers efficient sort-
ing algorithms based on CUDA. For the last merging
phase, we provided a reduction approach that aims to
filter the number of savings to analyze, the procedure
of which will be described in the next paragraph.
Fig. 5 illustrates the distance/cost matrix to be
computed. Each element below the diagonal repre-
sents the distance between the nodes, while the ele-
ments above the diagonal indicate the possible sav-
ings obtained by joining the two nodes i and j. The
calculation performed by a thread in a given cell is
represented in the figure and reflects the explanations
presented in the previous section. From this matrix,
the elements above the diagonal are extracted in order
to form the savings list (see the lower part of the same
figure).
The matrix is computed using a CUDA kernel,
which takes care of calculating each of the elements in
parallel, therefore, if the number of nodes is N, NxN
threads are launched in parallel to compute this ma-
trix: half of these threads are responsible for comput-
ing the distances/costs (below the diagonal), and the
other half the savings between two nodes.
In practice, in parallel, each created thread takes
care of calculating a given element of the matrix using
formulas (2) and (1).
C =
q
(x
i
− x
j
)
2
+ (y
i
− y
j
)
2
(2)
Then, the savings list is extracted in the same
CUDA kernel which, in a simple way, retrieves the
elements above the diagonal and copies them into a
contiguous array of savings. The number of threads
is equal to the number of possible links between the
nodes. Therefore, excluding the links to the depot, it
is given by:
Link
i, j
= N ∗ (N − 1)/2. (3)
Look Ahead Parallel Reduction (LAPR). In the
last stage, the iterations of the CW algorithm cannot
be executed in parallel, because the analysis of subse-
quent savings requires waiting for the previous ones
to be processed. A different approach has been devel-
oped to utilize the GPU: once a node x is inserted into
ICORES 2025 - 14th International Conference on Operations Research and Enterprise Systems
104

Figure 5: Representation of operations performed in the CUDA kernel.
a route r, if the node becomes internal to the same
route r, or if the route r has reached the maximum
capacity C of the vehicle, the node x cannot be con-
sidered any more; therefore, we can create a tabu list
which contains all nodes that cannot longer be con-
sidered. The key idea is to process in parallel the re-
maining elements of the savings list, on the basis of
a “looking ahead” strategy, and to remove all of them
that contain nodes belonging to the tabu list, i.e. node
that cannot be further inserted or merged in a route.
The performance improvements are particularly sig-
nificant in the case of large-scale instances. In Sec-
tion 4, the benefits related to the application of this
technique, in terms of reduction of the length of the
saving list at each iteration, will be highlighted.
Since the merging phase is executed on the CPU,
every time the reduction approach is executed on the
GPU, a certain overhead is experienced. This lim-
its the possibility of calling the procedure after each
node, as the overhead time would exceed the bene-
fit of list reduction. To address this issue, the nodes
are inserted into a tabu list and only when a certain
number is reached, the parallel reduction procedure is
activated. This hyperparameter has been empirically
determined, as shown in Section 4.
4 COMPUTATIONAL RESULTS
In order to assess the performance of the proposed ap-
proach, computational experiments have been carried
out considering X instances from (Uchoa et al., 2017)
and the Belgium sets (Arnold et al., 2019). The choice
was made because the first ones are the ones currently
most used in evaluating the performance of solution
approaches for the CVRP and because they include
easy-to-solve instances (starting from 100 nodes, but
we have selected those starting from 500), for assess-
ing the overhead of the parallel algorithm, as well as
more complicated cases (up to 1,000 nodes). The sec-
ond dataset (i.e., Belgium dataset) contains test net-
works with a number of nodes ranging from 3,000 to
30,000. However, due to memory constraints to in-
stantiate matrices and lists, we were able to consider
instances of up to 16,000 nodes on CPU. The compu-
tational experiments have been carried out by imple-
menting and comparing the following algorithms:
• CWG: the GPU-based parallel implementation of
the CW algorithm;
• CWG
f
: the first version of CWG introduced in
(Guerriero and Saccomanno, 2024). This method
is similar to CWG. However, the primary differ-
ence lies in its approach of analyzing all items in
the savings list, due to the absence of the LAPR
procedure;
• CWC: the CPU-based implementation of the CW
algorithm;
• PyVRP: the state-of-art algorithm proposed in
(Wouda et al., 2024), based on an hybrid ge-
netic search algorithm that combines the global
search capabilities of genetic algorithms with lo-
cal search methods.
The code was developed in Python for both the
CPU and the GPU versions, whereas the CUDA ker-
nels were implemented using the NUMBA library.
The development environment used is COLAB, an
online platform offered by Google for the rapid devel-
opment of Python-based software. The environment
A Parallel Implementation of the Clarke-Wright Algorithm on GPUs
105

was linked to a local computing system to take advan-
tage of the PC in use equipped of an Intel i9-14900HX
2.2Ghz processor with 24 cores and 64GB of Ram,
and a RTX4090 laptop GPU with 16Gb GDDR5 fea-
turing 9728 CUDA cores.
In the subsequent sections, we will investigate
the influence of the dimensions of the thread blocks
on the performance, the solution quality achieved
through the CW method versus the best known so-
lution (BKS), the time comparison against the CWC
version, and how the LAPR method affects the num-
ber of savings. In addition, a comparison with the
state-of-art approach proposed in (Guerriero and Sac-
comanno, 2024) is also presented.
Impact of Thread Block Size on Performance.
The analysis performed in the previous section
showed that all threads per block configurations can
effectively exploit the number of active threads (see
Tab. 1), for the considered instances above 500 nodes,
as less than 5% of threads remain inactive.
In the Tab. 2, we report the execution times re-
quired by the initial two phases of the CWG algo-
rithm for instances belonging to the Belgium set, with
a number of nodes ranging from 3001 to 30001. The
columns indicate in order: the instance name, num-
ber of nodes, number of threads in a block (TxB),
and time of execution as min time (T
min
), max time
(T
max
) and average time (T
avg
). The computational
results are averaged over 10 runs. This allowed us to
determine the minimum, maximum, and average exe-
cution times using thread blocks of sizes 8x8, 16x16,
and 32x32: although the average value does not differ
much, there is a slight advantage for the 16x16 block
configuration.
The one with 16x16 threads per block is chosen as
it has proved to be the most effective.
Solution Quality Evaluation. In order to evalu-
ate the quality of the solutions determined by the
CWG approach, we compared the obtained results
with the BKS and with those found by the state-of-
the-art PyVRP algorithm, for which a time-limit of
60 seconds has been imposed for instances up to 1001
nodes, and 600 seconds for other instances. In partic-
ular, for each test problem, the solution quality gap is
evaluated as
δ
alg2
alg1
% =
(c
alg1
− c
alg2
)
c
alg2
× 100,
where c represents the cost, and alg1 and alg2 re-
fer to the approaches under comparison (i.e., CWG,
PyVRP, or the BKS).
Table 2: Executions time for different number of threads per
block.
Instance Nodes TxB T
min
T
max
T
avg
Leuven1 3001 (8, 8) 0.03 0.12 0.0450
Leuven2 4001 (8, 8) 0.05 0.14 0.0710
Antwerp1 6001 (8, 8) 0.10 0.23 0.1559
Ghent1 10001 (8, 8) 0.33 0.48 0.3990
Ghent2 11001 (8, 8) 0.40 0.56 0.4730
Brussels1 15001 (8, 8) 0.76 0.99 0.9010
Brussels2 16001 (8, 8) 0.92 1.12 1.0290
Flanders1 20001 (8, 8) 1.34 1.56 1.4113
Flanders2 30001 (8, 8) 3.09 3.51 3.2363
Avg 0.8579
Leuven1 3001 (16, 16) 0.03 0.1 0.0426
Leuven2 4001 (16, 16) 0.05 0.13 0.0705
Antwerp1 6001 (16, 16) 0.10 0.22 0.1499
Ghent1 10001 (16, 16) 0.34 0.48 0.3990
Ghent2 11001 (16, 16) 0.39 0.62 0.4870
Brussels1 15001 (16, 16) 0.77 1.01 0.8600
Brussels2 16001 (16, 16) 0.83 1.09 0.9770
Flanders1 20001 (16, 16) 1.35 1.77 1.4763
Flanders2 30001 (16, 16) 3.00 3.18 3.1188
Avg 0.8423
Leuven1 3001 (32, 32) 0.03 0.11 0.0466
Leuven2 4001 (32, 32) 0.05 0.13 0.0718
Antwerp1 6001 (32, 32) 0.13 0.25 0.1610
Ghent1 10001 (32, 32) 0.36 0.53 0.4360
Ghent2 11001 (32, 32) 0.45 0.58 0.4980
Brussels1 15001 (32, 32) 0.81 0.97 0.8910
Brussels2 16001 (32, 32) 0.91 1.25 1.0310
Flanders1 20001 (32, 32) 1.38 1.66 1.4350
Flanders2 30001 (32, 32) 3.14 3.31 3.2125
Avg 0.8648
Tab. 3 gives the results for each instance. The first
column lists the name of the test problem, followed
by the number of nodes in the second column, and the
BKS in the third column. The next two columns are
related to the PyVRP approach, displaying the solu-
tion cost c
PyV RP
and the solution quality gap δ
BKS
PyV RP
%
with the respect to the BKS. The final columns sum-
marize the results for the CWG approach, including
the cost c
CWG
, the execution time t
CWG
and the so-
lution quality gap δ
BKS
CWG
% with respect to BKS and
δ
PyV RP
CWG
% with respect to PyVRP.
For the small-size instances, CWG shows an aver-
age GAP of δ
BKS
CWG
% = 5.12% when compared to BKS,
and δ
PyV RP
CWG
% = 2.51% in comparison to PyVRP. For
larger instances from the Belgium Dataset, CWG in-
creases its performance, with δ
PyV RP
CWG
% being 1.60%,
0.53%, and 0.22% for different groups. CWG, on
the other hand, has significantly reduced execution
times, requiring a maximum of t
CWG
= 183 seconds
for the largest scenario considered, which includes
ICORES 2025 - 14th International Conference on Operations Research and Enterprise Systems
106

Table 3: Benchmarking Solution Quality.
Instance Name Nodes BKS PyVRP CWG
c
PyVRP
δ
BKS
Py
% c
CWG
t
CWG
δ
BKS
CWG
% δ
Py
CWG
%
X-n502-k39 502 69226 69740 0.74% 71388 0.53 3.12% 2.36%
X-n513-k21 513 24201 24562 1.49% 26805 0.41 10.76% 9.13%
X-n524-k153 524 154593 155531 0.61% 163352 0.42 5.67% 5.03%
X-n536-k96 536 94846 96514 1.76% 99872 0.46 5.30% 3.48%
X-n548-k50 548 86700 88390 1.95% 89574 0.45 3.31% 1.34%
X-n561-k42 561 42717 43721 2.35% 45557 0.45 6.65% 4.20%
X-n573-k30 573 50673 51780 2.18% 52565 0.46 3.73% 1.52%
X-n586-k159 586 190316 193405 1.62% 199817 0.54 4.99% 3.32%
X-n599-k92 599 108451 111045 2.39% 113296 0.53 4.47% 2.03%
X-n613-k62 613 59535 60837 2.19% 62829 0.49 5.53% 3.27%
X-n627-k43 627 62164 63523 2.19% 65218 0.52 4.91% 2.67%
X-n641-k35 641 63682 66233 4.01% 67550 0.64 6.07% 1.99%
X-n655-k131 655 106780 107480 0.66% 108353 0.61 1.47% 0.81%
X-n670-k130 670 146332 148413 1.42% 158154 0.63 8.08% 6.56%
X-n685-k75 685 68205 69940 2.54% 71685 0.64 5.10% 2.49%
X-n701-k44 701 81923 84959 3.71% 85589 0.61 4.47% 0.74%
X-n716-k35 716 43373 45238 4.30% 45744 0.53 5.47% 1.12%
X-n733-k159 733 136187 140627 3.26% 139997 0.81 2.80% -0.45%
X-n749-k98 749 77269 79838 3.32% 79462 0.69 2.84% -0.47%
X-n766-k71 766 114417 117711 2.88% 119262 0.77 4.23% 1.32%
X-n783-k48 783 72386 75598 4.44% 76566 0.91 5.77% 1.28%
X-n801-k40 801 73305 76321 4.11% 76700 0.86 4.63% 0.50%
X-n819-k171 819 158121 161054 1.85% 166287 0.9 5.16% 3.25%
X-n837-k142 837 193737 198166 2.29% 200443 1.03 3.46% 1.15%
X-n856-k95 856 88965 90453 1.67% 92368 1.05 3.83% 2.12%
X-n876-k59 876 99299 102140 2.86% 102306 0.98 3.03% 0.16%
X-n895-k37 895 53860 56052 4.07% 58614 1.04 8.83% 4.57%
X-n916-k207 916 329179 334298 1.56% 343501 0.97 4.35% 2.75%
X-n936-k151 936 132715 137082 3.29% 146523 1.23 10.40% 6.89%
X-n957-k87 957 85465 87608 2.51% 89212 1.09 4.38% 1.83%
X-n979-k58 979 118976 121788 2.36% 123690 1.27 3.96% 1.56%
X-n1001-k43 1001 72355 75955 4.98% 77377 1.52 6.94% 1.87%
2.55% 5.12% 2.51%
Leuven1 3001 192848 200297 3.86% 200790 3.75 4.12% 0.25%
Leuven2 4001 111391 118483 6.37% 124194 3.49 11.49% 4.82%
Antwerp1 6001 477277 497588 4.26% 497009 4.83 4.13% -0.12%
Antwerp2 7001 291350 312371 7.22% 316878 7.57 8.76% 1.44%
5.43% 7.13% 1.60%
Ghent1 10001 469,531 491610 4.70% 488056 14.18 3.95% -0.72%
Ghent2 11001 257,748 277372 7.61% 283202 15.87 9.88% 2.10%
Brussels1 15001 501,719 533768 6.39% 529846 35.69 5.61% -0.73%
Brussels2 16001 345,468 373996 8.26% 379516 29.95 9.86% 1.48%
6.74% 7.32% 0.53%
Flanders1 20001 7240118 7542347 4.17% 7497837 54.74 3.56% -0.59%
Flanders2 30001 4373244 4716145 7.84% 4764789 182.57 8.95% 1.03%
6.01% 6.26% 0.22%
30K nodes.
The results indicate that the proposed CWG ap-
proach is capable of producing solutions of a quality
comparable to PyVRP, while offering substantial im-
provements in terms of computational time.
Time Analysis Against CWC Version. Table 4
presents the results obtained with CWC. In particu-
lar, the first column displays the name of the instance,
whereas the second gives the number of nodes. The
subsequent columns display the total execution time
of the CWC approach (T
CWC
), the time spent creat-
A Parallel Implementation of the Clarke-Wright Algorithm on GPUs
107

Table 4: Time Analysis against CWC version.
Instance Nodes T
CWC
T
1
CWC
T
2
CWC
T
3
CWC
T
4
CWC
T
CWG
T
1
CWG
T
2
CWG
T
3
CWG
T
4
CWG
Speed-UP
X-n502-k39 502 1.40 0.77 0.45 0.01 0.17 0.53 0.01 0.00 0.01 0.51 3
X-n513-k21 513 1.58 0.98 0.35 0.01 0.24 0.41 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.40 4
X-n524-k153 524 1.37 0.68 0.41 0.02 0.26 0.42 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.41 3
X-n536-k96 536 1.23 0.69 0.35 0.01 0.18 0.46 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.45 3
X-n548-k50 548 1.36 0.75 0.41 0.01 0.19 0.45 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.44 3
X-n561-k42 561 1.65 0.97 0.46 0.01 0.21 0.45 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.44 4
X-n573-k30 573 1.59 0.84 0.48 0.01 0.26 0.46 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.45 3
X-n586-k159 586 1.61 0.94 0.40 0.01 0.26 0.54 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.53 3
X-n599-k92 599 1.66 0.90 0.47 0.01 0.28 0.53 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.52 3
X-n613-k62 613 1.66 1.00 0.42 0.01 0.23 0.49 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.48 3
X-n627-k43 627 1.77 1.02 0.49 0.01 0.25 0.52 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.51 3
X-n641-k35 641 1.92 1.14 0.52 0.01 0.25 0.64 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.63 3
X-n655-k131 655 2.06 1.15 0.55 0.02 0.34 0.61 0.01 0.00 0.01 0.59 3
X-n670-k130 670 1.91 1.08 0.51 0.01 0.31 0.63 0.01 0.00 0.01 0.61 3
X-n685-k75 685 2.23 1.22 0.60 0.04 0.37 0.64 0.01 0.00 0.01 0.62 3
X-n701-k44 701 2.35 1.42 0.62 0.02 0.29 0.61 0.01 0.00 0.01 0.59 4
X-n716-k35 716 2.77 1.51 0.77 0.04 0.45 0.53 0.01 0.00 0.01 0.51 5
X-n733-k159 733 2.51 1.42 0.68 0.02 0.39 0.81 0.01 0.00 0.01 0.79 3
X-n749-k98 749 2.44 1.44 0.66 0.01 0.33 0.69 0.01 0.00 0.01 0.67 4
X-n766-k71 766 2.45 1.48 0.62 0.02 0.33 0.77 0.01 0.00 0.01 0.75 3
X-n783-k48 783 2.64 1.53 0.71 0.02 0.38 0.91 0.01 0.00 0.01 0.89 3
X-n801-k40 801 2.84 1.55 0.81 0.03 0.45 0.86 0.01 0.00 0.01 0.84 3
X-n819-k171 819 2.88 1.60 0.83 0.02 0.43 0.90 0.01 0.00 0.01 0.88 3
X-n837-k142 837 3.01 1.74 0.79 0.02 0.46 1.03 0.01 0.00 0.01 1.01 3
X-n856-k95 856 3.14 1.74 0.87 0.03 0.50 1.05 0.02 0.00 0.01 1.02 3
X-n876-k59 876 3.53 1.99 0.99 0.03 0.52 0.98 0.01 0.00 0.01 0.96 4
X-n895-k37 895 3.32 1.87 0.92 0.03 0.50 1.04 0.01 0.00 0.01 1.02 3
X-n916-k207 916 3.83 2.14 1.05 0.03 0.61 0.97 0.01 0.00 0.01 0.95 4
X-n936-k151 936 4.17 2.29 1.15 0.03 0.70 1.23 0.01 0.00 0.01 1.21 3
X-n957-k87 957 4.09 2.28 1.17 0.06 0.58 1.09 0.01 0.00 0.01 1.07 4
X-n979-k58 979 4.15 2.42 0.97 0.04 0.72 1.27 0.01 0.00 0.01 1.25 3
X-n1001-k43 1001 4.47 2.62 1.20 0.03 0.62 1.52 0.02 0.00 0.01 1.49 3
Leuven1 3001 47.15 27.00 13.01 0.64 6.50 3.75 0.12 0.00 0.07 3.56 13
Leuven2 4001 84.70 46.48 24.33 1.29 12.60 3.49 0.21 0.00 0.03 3.25 24
Antwerp1 6001 186.33 114.14 46.20 2.87 23.12 4.83 0.34 0.00 0.08 4.41 39
Antwerp2 7001 207.33 120.09 53.91 3.98 29.35 7.57 1.09 0.00 0.12 6.36 27
Ghent1 10001 543.66 305.96 137.03 10.63 90.04 14.18 0.57 0.00 0.20 13.41 38
Ghent2 11001 657.45 370.74 181.01 11.95 93.75 15.87 0.74 0.00 0.57 14.56 41
Brussels1 15001 1073.02 570.40 275.92 25.19 201.51 35.69 1.06 0.00 0.61 34.02 30
Brussels2 16001 1393.93 777.41 373.63 30.97 211.92 29.95 1.11 0.00 0.55 28.29 47
Average 106.83 3.48 9.10
ing the distance/cost matrix (T
1
CWC
), generating the
savings list (T
2
CWC
), ordering (T
3
CWC
), and executing
merge iterations (T
4
CWC
). Similarly, times for CWG
operations on GPU are given (i.e., T
CWG
, T
1
CWG
, T
2
CWG
,
T
3
CWG
, T
4
CWG
). The last column displays the speed-up
achieved by the CWG compared to the CWC, calcu-
lated as
T
CWC
T
CWG
.
The results show the ability of the CWG approach
to scale in the calculation of the cost matrix and
the savings list. In particular, the higher the num-
ber of nodes, the higher the speed-up achieved. For
example, for the Brussels2 instance it reduces from
1151.04 seconds (i.e., 777.41 + 373.63 seconds) to
1.11 seconds.
It should be noted that in the case of the CWG
approach, the savings list creation time is equal to 0
since this, as we saw in the previous section, is calcu-
lated in parallel together with the cost matrix. As ex-
pected, the first three phases, being entirely processed
on the GPU, benefit from the maximum speed-up. Al-
though the final route merging phase is performed on
the CPU, it still achieves significant time improve-
ment due to the reductions provided by the LAPR pro-
cedure. For instance, in the Brussels2 case, the total
time decreases from 211.92 to 28.29 seconds.
Clearly, the performance improvements of the
CWG implementation compared to the CWC version
ICORES 2025 - 14th International Conference on Operations Research and Enterprise Systems
108
become more significant for the latest set of test prob-
lems under consideration. In effect, the real potential
of the CWG becomes more evident in these latter in-
stances, characterized by a high number of nodes.
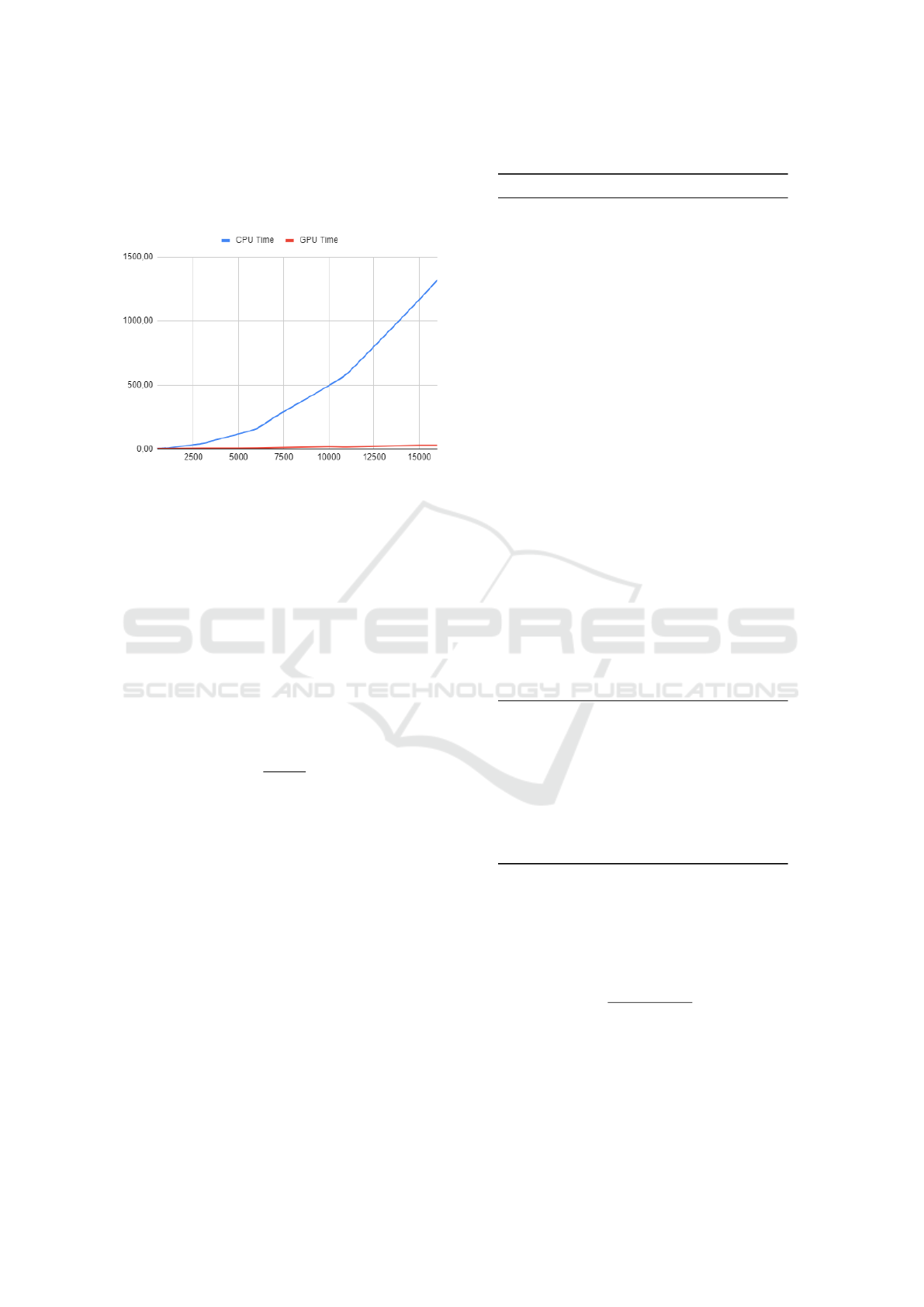
Figure 6: Execution time of CWC (blue) and CWG (red).
Figure 6 shows the execution times as a function
of the number of nodes for the CWC (blue), where the
trend is exponential, and for the CWG (red), which
remains essentially linear.
Impact of LAPR. The table 5 shows the results ob-
tained by applying the LAPR approach. The first two
columns indicate the instance name and the number of
nodes, respectively. The next two columns are related
to the number of entries in the original savings list
Len
Ori
and those belonging to the reduced list Len
Red
.
The last column displays the reduction achieved, de-
termined as
δ
RA
% =
Len
Red
Len
Ori
× 100.
The computational results underline a substantial re-
duction. In fact, considering that each node is con-
nected with all other nodes to obtain the savings list,
each time a node is excluded, on average, entries
equal to the number of nodes are removed from the
savings list. This approach required adjusting a hy-
perparameter that defines how often nodes, present in
the tabu list, should activate the reduction procedure.
Since the merging is done on the CPU and reduction
on the GPU, each time reduction is invoked, neces-
sary overhead must be considered. Empirically, we
found that the best result is obtained by filtering the
list when the tabu list contains 1,000 nodes.
Comparison with Previous Approach. Lastly, the
Tab. 6 presents a comparative analysis of perfor-
mance with the algorithm in (Guerriero and Sacco-
manno, 2024), in eight different instances, selected
Table 5: LAPR reduction of savings list.
Instance Nodes Len
Ori
Len
Red
δ
RA
%
X-n502-k39 502 125250 23696 19%
X-n513-k21 513 130816 11593 9%
X-n524-k153 524 136503 70336 52%
X-n536-k96 536 142845 46667 33%
X-n548-k50 548 149331 32120 22%
X-n561-k42 561 156520 18518 12%
X-n573-k30 573 163306 27272 17%
X-n586-k159 586 170820 102870 60%
X-n599-k92 599 178503 57547 32%
X-n613-k62 613 186966 27913 15%
X-n627-k43 627 195625 39735 20%
X-n641-k35 641 204480 25929 13%
X-n655-k131 655 213531 76920 36%
X-n670-k130 670 223446 79827 36%
X-n685-k75 685 233586 30928 13%
X-n701-k44 701 244650 37951 16%
X-n716-k35 716 255255 33764 13%
X-n733-k159 733 267546 90159 34%
X-n749-k98 749 279378 58502 21%
X-n766-k71 766 292230 49023 17%
X-n783-k48 783 305371 38183 13%
X-n801-k40 801 319600 35025 11%
X-n819-k171 819 334153 108502 32%
X-n837-k142 837 349030 105944 30%
X-n856-k95 856 365085 46315 13%
X-n876-k59 876 382375 50136 13%
X-n895-k37 895 399171 28040 7%
X-n916-k207 916 418155 176281 42%
X-n936-k151 936 436645 84975 19%
X-n957-k87 957 456490 59367 13%
X-n979-k58 979 477753 66164 14%
X-n1001-k43 1001 499500 39275 8%
Leuven1 3001 4498500 974232 22%
Leuven2 4001 7998000 1092037 14%
Antwerp1 6001 17997000 1187458 7%
Antwerp2 7001 24496500 1498080 6%
Ghent1 10001 49995000 2826278 6%
Ghent2 11001 60494500 1878885 3%
Brussels1 15001 112492500 3336386 3%
Brussels2 16001 127992000 2287755 2%
Flanders1 20001 199990000 5018038 3%
Flanders2 30001 449985000 5022633 1%
due to their large number of nodes. The columns rep-
resent the instance, the computational time in seconds
for both algorithms (T
f
CWG
and T
CWG
), and the per-
centage reduction in computational time when using
T
f
CWG
compared to T
CWG
, calculated as
δ
T R
% =
T
f
CWG
− T
CWG
T
f
CWG
!
× 100.
CWG demonstrates a decrease in time ranging from
at least 75% to as much as 93%. Furthermore, as
the number of nodes increases, the time reduction be-
comes more significant, highlighting the impact of the
LAPR procedure that is absent in T
f
CWG
. In effect,
A Parallel Implementation of the Clarke-Wright Algorithm on GPUs
109

previous research focused on assessing the viability
of running the CW algorithm on GPUs and analyz-
ing the execution times of various steps on both the
CPU and GPU. However, that study did not include
the development of the LAPR reduction method, thus
the route merging phase was quite costly due to the
large number of savings to process when dealing with
instances that have a high number of nodes.
Table 6: Comparison with (Guerriero and Saccomanno,
2024).
Instance T
f
CWG
T
CWG
δ
T R
%
L1 15.21 3.75 75.35%
L2 23.40 3.49 85.09%
A1 46.78 4.83 89.68%
A2 72.30 7.57 89.53%
G1 155.66 14.18 90.89%
G2 203.80 15.87 92.21%
B1 393.24 35.69 90.92%
B2 451.05 29.95 93.36%
Average 170.18 14.42 88.38%
5 CONCLUSIONS
In this work, a CWG implementation on GPU of the
CW algorithm was proposed. The computational re-
sults collected clearly highlight that it is significantly
faster than the CWC implementation, especially for
large instances. This is due to the parallel process-
ing capabilities of GPUs, which enable efficient ex-
ecution of the computational steps of the algorithm,
leading to substantial speedups.
Comparison with a state-of-the-art PyVRP algo-
rithm, which uses the same initial data structures, in-
dicates that the GPU implementation could signif-
icantly improve the performance and scalability of
such a solver, particularly in the early stages, there-
fore suggesting a possible integration of the two ap-
proaches. Moreover, by enabling substantial accelera-
tion in the search for an initial solution, albeit not nec-
essarily optimal, this approach can be integrated into
other heuristics to quickly provide an initial solution.
It can also serve as the basis for an iterative method,
aimed at quickly exploring the solution space.
Future research could focus on extending the
applicability of GPU-accelerated CW algorithms to
more complex VRP variants and exploring their
potential for solving related optimization problems
across various domains.
For instance, it provides an effective approach for
real-time applications needing rapid, nearly optimal
vehicle routing solutions. Our findings indicate that
the algorithm consistently achieves results within a
7% gap from optimal, thus making it ideal for sce-
narios where timely decisions are essential. By utiliz-
ing the parallel processing power of GPUs, we have
accomplished notable speed enhancements, allowing
the algorithm to produce high-quality solutions in
much less time than standard CPU-based methods.
These results underscore the promise of GPU acceler-
ation in addressing complex optimization challenges
in dynamic and time-sensitive settings.
REFERENCES
Abdelatti, M. F. and Sodhi, M. S. (2020). An improved
gpu-accelerated heuristic technique applied to the ca-
pacitated vehicle routing problem. In Proceedings of
the 2020 Genetic and Evolutionary Computation Con-
ference, GECCO ’20, page 663–671, New York, NY,
USA. Association for Computing Machinery.
Accorsi, L. and Vigo, D. (2021). A fast and scalable heuris-
tic for the solution of large-scale capacitated vehicle
routing problems. Transportation Science, 55(4):832–
856.
Arnold, F., Gendreau, M., and S
¨
orensen, K. (2019). Ef-
ficiently solving very large-scale routing problems.
Computers & Operations Research, 107:32–42.
Augerat, P., Belenguer, J. M., Benavent, E., Corberan, A.,
Naddef, D., and Rinaldi, G. (1995). Computational
results with a branch and cut code for the capacitated
vehicle routing problem. Computer Science, Mathe-
matics.
Benaini, A. and Berrajaa, A. (2016). Solving the dynamic
vehicle routing problem on gpu. In 2016 3rd Interna-
tional Conference on Logistics Operations Manage-
ment (GOL), pages 1–6.
Benaini, A. and Berrajaa, A. (2018). Genetic algorithm for
large dynamic vehicle routing problem on gpu. In
2018 4th International Conference on Logistics Op-
erations Management (GOL), pages 1–9.
Benaini, A., Berrajaa, A., and Daoudi, E. M. (2016).
Solving the vehicle routing problem on gpu. In
El Oualkadi, A., Choubani, F., and El Moussati, A.,
editors, Proceedings of the Mediterranean Conference
on Information & Communication Technologies 2015,
pages 239–248, Cham. Springer International Pub-
lishing.
Benaini, A., Berrajaa, A., and Daoudi, E. M. (2017). Par-
allel implementation of the multi capacity vrp on gpu.
In Rocha,
´
A., Serrhini, M., and Felgueiras, C., editors,
Europe and MENA Cooperation Advances in Infor-
mation and Communication Technologies, pages 353–
364, Cham. Springer International Publishing.
Bor
ˇ
cinov
´
a, Z. (2022). Kernel search for the capacitated ve-
hicle routing problem. Applied Sciences, 12(22).
Boschetti, M. A., Maniezzo, V., and Strappaveccia, F.
(2017). Route relaxations on gpu for vehicle rout-
ing problems. European Journal of Operational Re-
search, 258(2):456–466.
ICORES 2025 - 14th International Conference on Operations Research and Enterprise Systems
110

Caccetta, L., Alameen, M., and Abdul-Niby, M. (2013). An
improved clarke and wright algorithm to solve the ca-
pacitated vehicle routing problem. Engineering, Tech-
nology & Applied Science Research, 3(2):413–415.
Clarke, G. and Wright, J. W. (1964). Scheduling of vehicles
from a central depot to a number of delivery points.
Operations research, 12(4):568–581.
Diego, F. J., G
´
omez, E. M., Ortega-Mier, M., and Garc
´
ıa-
S
´
anchez,
´
A. (2012). Parallel cuda architecture for
solving de vrp with aco. In Sethi, S. P., Bogataj, M.,
and Ros-McDonnell, L., editors, Industrial Engineer-
ing: Innovative Networks, pages 385–393, London.
Springer London.
Guerriero, F. and Saccomanno, F. (2024). Accelerating
the clarke-wright algorithm for the capacitated vehicle
routing problem using gpus. In Proceedings of BOS /
SOR 2024, Polish Operational and Systems Research
Society Conference, Warsaw.
Jin, J., Crainic, T. G., and Løkketangen, A. (2014). A co-
operative parallel metaheuristic for the capacitated ve-
hicle routing problem. Computers & Operations Re-
search, 44:33–41.
Laporte, G. (1992). The vehicle routing problem: An
overview of exact and approximate algorithms. Eu-
ropean Journal of Operational Research, 59(3):345–
358.
Liu, F., Lu, C., Gui, L., Zhang, Q., Tong, X., and Yuan,
M. (2023). Heuristics for vehicle routing problem: A
survey and recent advances.
Luong, T. V., Melab, N., and Talbi, E.-G. (2013). Gpu com-
puting for parallel local search metaheuristic algo-
rithms. IEEE Transactions on Computers, 62(1):173–
185.
Nurcahyo, R., Irawan, D. A., and Kristanti, F. (2023). The
effectiveness of the clarke & wright savings algorithm
in determining logistics distribution routes (case study
pt.xyz). E3S Web of Conferences, 426.
Schulz, C. (2013). Efficient local search on the
gpu—investigations on the vehicle routing prob-
lem. Journal of Parallel and Distributed Computing,
73(1):14–31. Metaheuristics on GPUs.
Tunnisaki, F. and Sutarman (2023). Clarke and wright sav-
ings algorithm as solutions vehicle routing problem
with simultaneous pickup delivery (vrpspd). Journal
of Physics: Conference Series, 2421(1):012045.
Uchoa, E., Pecin, D., Pessoa, A., Poggi, M., Vidal, T., and
Subramanian, A. (2017). New benchmark instances
for the capacitated vehicle routing problem. European
Journal of Operational Research, 257(3):845–858.
Wouda, N. A., Lan, L., and Kool, W. (2024). PyVRP: a
high-performance VRP solver package. INFORMS
Journal on Computing.
Yelmewad, P. and Talawar, B. (2021). Parallel version
of local search heuristic algorithm to solve capaci-
tated vehicle routing problem. Cluster Computing,
24(4):3671–3692.
A Parallel Implementation of the Clarke-Wright Algorithm on GPUs
111
