Evaluation of Body Parts Representations in Motion Reconstruction
Philippe de Clermont Gallerande
1,2 a
, Quentin Avril
2 b
, Philippe Henri Gosselin
2 c
,
Ferran Argelaguet
1 d
and Ludovic Hoyet
1 e
1
Inria, Univ. Rennes, CNRS, IRISA, France
2
InterDigital, Rennes, France
{philippe.de-clermont-gallerande, ferran.argelaguet, ludovic.hoyet}@inria.fr,
Keywords:
Animation, Neural Networks, Human Motion, Body Parts.
Abstract:
Acquiring, encoding, transmitting, decoding, and displaying motion signals is an essential challenge in our
new world of interconnected immersive applications (XR, online games etc.). In addition to being potentially
disturbed by multiple factors (e.g., signal noise, latency, packet loss), this motion data should be modifiable and
customizable to fit the needs of specific applications. Simultaneously, several approaches have successfully
proposed to explicitly integrate the semantics of the human body in a deep learning framework by separating
it into smaller parts. We propose to use such an approach to obtain a robust streamed animation data. Specif-
ically, we create and train several neural networks on the motion of different body parts independently from
each other. We further compare the performances of several body decompositions using multiple objective
reconstruction metrics. Eventually, we show that this Body Parts approach brings new opportunities compared
to a compact one, such as a perfectly partitioned and more interpretable motion data, while obtaining compa-
rable reconstruction results.
1 INTRODUCTION
In an increasingly digital and connected world, ap-
plications showcasing virtual humans for video calls
and multi-users immersive applications are rapidly
spreading. Such programs will typically require in a
foreseeable future to represent users with customiz-
able and realistic virtual avatars driven in real-time by
their own movements. Similarly to current require-
ments for video streams, novel constraints will then
be introduced on the reliability and quality of the mo-
tion data transmitted, in addition to traditional human
motion modeling needs (e.g., Character Animation).
In particular, a number of errors can be introduced in
the motion data, e.g., due to missing or drifting sen-
sors, user occlusions, as well as packet losses (i.e.
transmission disturbances). As current approaches
rely on a holistic representation of the human body
motion, such errors have typically an impact on the
complete reconstructed body motion, which can be
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0002-2151-8135
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0101-3351
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0973-4030
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6160-8015
e
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7373-6049
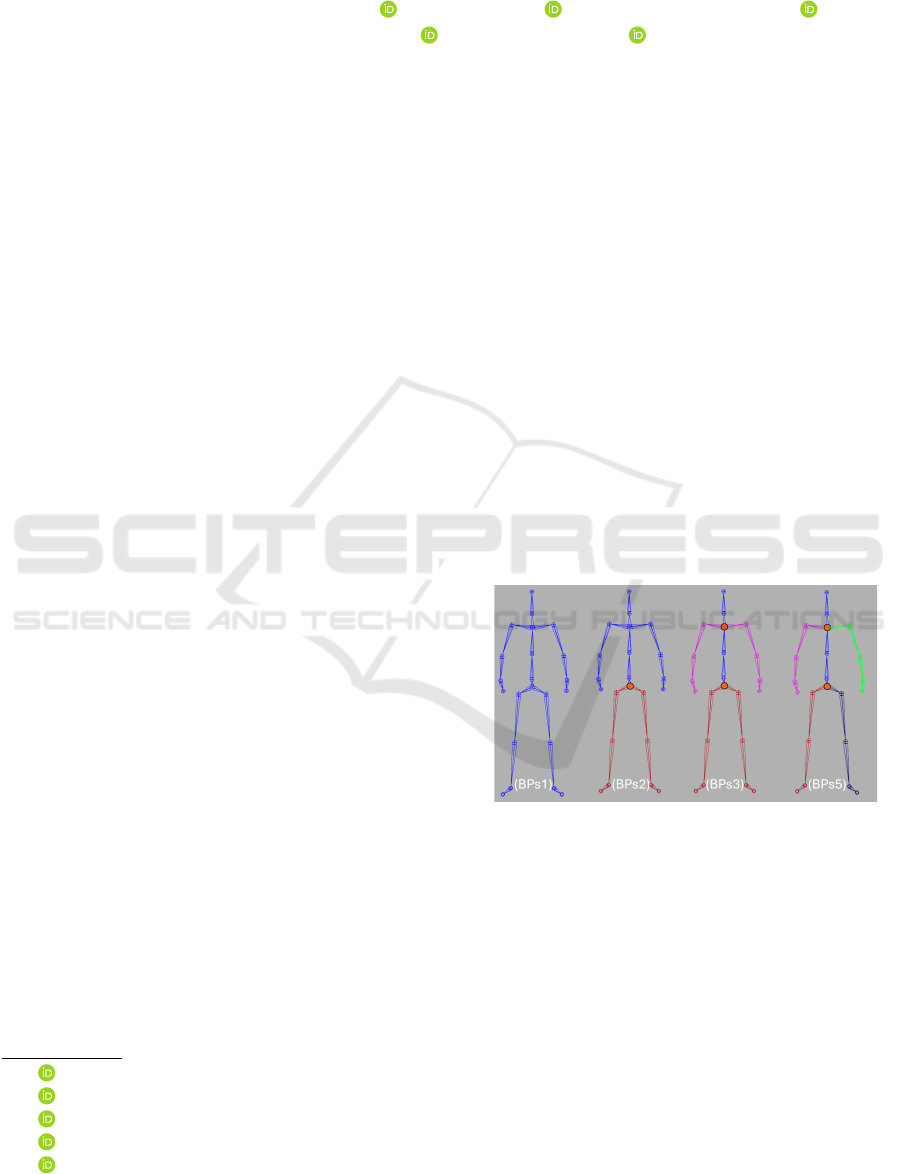
Figure 1: The different body decompositions evaluated in
this work. A Body Parts (BPs) model is a wrapper of one,
or several, neural networks reconstructing a body part mo-
tion. They are linked together by overlapping joints: the
BPs Connectors (orange circles). From left to right: BPs1
(whole-body), BPs2 (upper/lower body), BPs3 (spine, arms
and legs) and BPs5 (spine, right/left arm, right/left leg).
detrimental for the user experience. To illustrate this
problem, let us take as an example a situation where
only the upper body of the user is visible (e.g., facing
a webcam): in this scenario, any erroneous informa-
tion about the lower body pose would be incorporated
in the entangled representation, and result in an incor-
rect reconstruction of the whole body animation on
the remote client side.
To tackle these challenges, we propose in this pa-
de Clermont Gallerande, P., Avril, Q., Gosselin, P. H., Argelaguet, F. and Hoyet, L.
Evaluation of Body Parts Representations in Motion Reconstruction.
DOI: 10.5220/0013138200003912
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 20th International Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications (VISIGRAPP 2025) - Volume 1: GRAPP, HUCAPP
and IVAPP, pages 53-64
ISBN: 978-989-758-728-3; ISSN: 2184-4321
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
53

per to explore the value of a semantically partitioned
representation of the motion data (i.e., a body parts-
based representation). Such representations have al-
ready been successfully leveraged for various motion
modeling tasks. Specifically, their common key inter-
est was to precisely model and act on the local motion
data, thus driving changes at a global scale.
Taking inspiration from this idea, we explore the
potential benefits of an independent body parts-based
representations in the context of motion data stream-
ing. More precisely, we propose a novel human mo-
tion modeling framework enabling the creation of dis-
tinct body parts models, which we evaluate on a mo-
tion reconstruction task through several experiments.
We believe that such an approach can provide: a) a ro-
bust and semantically partitioned representation to re-
strain local degradation (e.g., noise or errors) of the
whole-body (global) animation to specific body parts
motion; b) an efficient solution to update specific
body parts information at a time, which could be valu-
able in situations where they might not be available
or relevant (e.g. an occluded arm motion, or a lower-
body pose sequence in a seated meeting context); c) a
novel and intuitive solution to animate complex non-
humanoid characters based on body semantics, for in-
stance to accommodate applications where users are
not necessarily represented by anthropomorphic char-
acters (e.g., (Cheymol et al., 2023)).
Although such an approach comes with poten-
tial limitations in some use cases (e.g. motion syn-
thesis), results of our experiments on a pure mo-
tion reconstruction task suggest that independent sub-
models lead to similar performances than a whole-
body model. Such results could imply that modeling
every body motion correlations might not be relevant
in all applications, in contrast to recent works in deep-
based character animation, which tend to involve the
creation of complex and holistic neural networks.
The key contributions of this paper are therefore:
• A novel and highly modular human motion mod-
eling framework to explicitly create semantic rep-
resentations.
• A first comparative study of the impact of the
body decomposition granularity in a reconstruc-
tion task involving several noisy scenarios.
2 RELATED WORK
In this section, we present related research on deep-
based human motion processing with whole-body
(Section 2.1) and body parts approaches (Section 2.2).
2.1 Whole Body Motion Modeling
Over the years, many approaches have been proposed
to edit (Aristidou and Lasenby, 2011), organize (Ko-
var et al., 2002), or synthesize skeletal animations (Ko
and Badler, 1996) based on a variety of heuristics or
paradigms. As their limits became apparent on in-
creasingly challenging poses, data-based approaches
that can model stochastic processes gained interest.
The spread of deep neural networks to model non-
linear manifolds (Mourot et al., 2022; Chen, 2023)
further increased their performances. For instance,
the pioneering work from Holden et al. (2015) lever-
ages a convolutional network to learn a motion mani-
fold, which can then be used to denoise human anima-
tions. Increasingly complex architectures were later
proposed to model the spatiotemporal correlations of
the human body, such as graph convolutions to exploit
the topological information of the human body at var-
ious scales (Dang et al., 2021). Along improvements
in the deep learning literature such as attention layers
and Transformers, performances increased (Shu et al.,
2022; Mao et al., 2020) but they were still focused
on a specific skeleton. This issue was then addressed
through retargeting tasks (Aberman et al., 2020), cul-
minating in the use of transformers to learn motion
semantics (Lee et al., 2023a; Zhang et al., 2024).
In the context of motion synthesis, Generative
Adversarial Networks (Liu et al., 2021; Malek-
Podjaski and Deligianni, 2023) and Variational Auto-
Encoders (Yan et al., 2018) have been widely used.
These architectures produce coherent latent spaces
that can be used to interpolate between learned sam-
ples and generate new ones that respect the data dis-
tribution constraints. Various strategies have been de-
signed to ease the training without losing interesting
features, such as using multi-task learning (Li et al.,
2022a; Butepage et al., 2017). Others have lever-
aged prior knowledge (e.g., motion periodicity) to dy-
namically change the approximated manifold (Holden
et al., 2017; Zhang et al., 2018). Starke et al. (2022)
extended this approach to learn the motion phase
manifold by creating approximated sinusoidals in the
latent space. Finally, other recent approaches explore
reconstructing skeleton motions from sparse signals,
which is a severely ill-defined problem, particularly
when the pelvis transformation is not available (Yang
et al., 2021). To compensate for the lack of input
signals to condition the network, deep reinforcement
learning (Ye et al., 2022) and physic simulation were
leveraged (Jiang et al., 2022; Lee et al., 2023b). Reda
et al. (2023) extended these approaches to solve a
combination of the previous challenges by retargeting
motions on other topologies using such sparse signals.
GRAPP 2025 - 20th International Conference on Computer Graphics Theory and Applications
54

2.2 Body Parts-Based Representations
Separating the body into parts is a well-established
idea for its modeling, used by Hanavan (1964) to
obtain a mathematical model and later leveraged
by Zhou et al. (2014) to design a multivariate Gaus-
sian process model based on inter-joints correlations.
It was first exploited in a Deep Learning context
by Wang and Neff (2015) in their multi-channel auto-
encoder and shortly after to evaluate a structural
RNN (Jain et al., 2016). Since then, it has been
widely used either by imitating the hierarchical struc-
ture over the depth of the network (Shao et al., 2019;
Li et al., 2019) or by progressively incorporating each
body parts features (Li et al., 2022b). Wang et al.
(2022) used multiple hierarchical decompositions of
the body and the different intrinsic relationships prop-
erties between each node, merged together by a dedi-
cated information fusion network, to perform a robust
human semantic parsing of challenging images.
Other recent works used body parts as basic units
for various tasks. E.g., Hu et al. (2024) used them
for skeletal motion retargeting, feeding body part fea-
tures to attention layers to obtain a fixed-size vector,
independent of the number of input joints. These la-
tent vectors were then stacked, added to the features
of the same dimension from the targeted skeleton, and
decoded. To some extent, this approach is reminiscent
of the “primal skeleton” proposed by Aberman et al.
(2020). Body decompositions were also used to have
a finer control of the local motion style of each body
part (Jang et al., 2022), e.g., enabling the addition of
different style features on the legs and arms. Interest-
ingly, this approach leveraged retargeting principles,
although used to transfer motion styles and not skele-
tons, providing flexibility for modifying the global
motion style by acting locally. Zou et al. (2025) used
such an approach to train independent generators for
each body part motion, coupled with a part coordina-
tion module for global coherency, that were then used
to obtain more details in text to motion results.
Another advantage is that each body part can act
as a building block that can be added, removed, or
swapped. Lee et al. (2022) leveraged this modular-
ity to create and animate chimera characters, where
the different body parts animations came from prede-
fined virtual source characters equipped with simple
motions such as walking, running, jumping, or punch-
ing. Deep Reinforcement Learning was then used to
assemble body parts and synthesize synchronized and
realistic motions, in combination with energy-aware
rewards and editing techniques (similar to Dynamic
Time Warping).
These works demonstrate the value of body part
approaches on a number of topics related to human
motion modeling. First, it allows to focus the learning
on local, high-frequency features, and prevents exces-
sive averaging at the global level. Second, it often
leads to models with greater flexibility and versatility.
However, even though various body parts decompo-
sitions have been used in the past, no evaluation has
been conducted yet on their relative performances.
3 BODY PARTS MODELING
We describe here our human motion modeling frame-
work for creating independent body parts sub-models.
First, Section 3.1 defines the different Body Parts
(BPs) models corresponding to different body decom-
positions. Then, Section 3.2 describes the connectors
articulating different sub-models. Finally, Section 3.3
elaborates on the combination of the body parts mo-
tions to produce the final result.
3.1 Body Parts Definition
To evaluate several body parts approaches, we first
create a common structure. We start by splitting an
animation skeleton into one or several sub-graphs at
various granularity. Each of these set of trees corre-
sponds to a specific hierarchy of body parts and forms
a Body Parts (BPs) model. A BPs model is thus a
wrapper around one or several neural networks, each
tasked with the motion modeling of a body part (i.e.
a semantic sub-graph). In other words, a BPsn model
uses n neural networks trained independently on n dis-
tinct body parts motion.
Formally, for animation data X ∈ R
T ×J×F
, with T
frames, an entire skeleton of J joints and F features, a
body part bp sub-model will be trained on the tensor
X
bp
∈ R
T ×J
bp
×F
with J
bp
≤ J the number of joints.
Conveniently, the particular case of a single-body
part model, BPs1, is our baseline: a whole-body ap-
proach (Holden et al., 2015). Then, we progressively
increase the number of body parts while keeping a se-
mantic decomposition. Based on previous works in
the literature, we design some BPs models (Figure 1):
• BPs1 wraps one body part: Whole-Body
• BPs2 wraps two body parts: Upper-Body and
Lower-Body (Yang et al., 2021)
• BPs3 wraps three body parts: Both-Arms, Spine,
and Lower-Body (Jang et al., 2022)
• BPs5 wraps five body parts: Right-/Left-Arm,
Right-/Left-Leg, and Spine (Hu et al., 2024)
Evaluation of Body Parts Representations in Motion Reconstruction
55
3.2 Body Parts Connectors
The literature highlights diverse methods to effec-
tively aggregate the information from different body
parts, e.g., using graph-based approaches with seman-
tic edges (Wang et al., 2022) or skeleton-based pool-
ing (Aberman et al., 2020; Jang et al., 2022). How-
ever, these approaches lead to interdependence be-
tween the body parts, which can impair flexibility and
generalization (either to topologies, morphologies or
motions). With the goal of proposing a versatile, par-
titioned, and semantic human motion model, we in-
stead chose to use a simpler approach to connect the
sub-models. Specifically, we reduce the overlap be-
tween different body parts to a single joint, which we
call the BPs Connector. This joint thus links two con-
nected body parts (as illustrated in Figure 1). Early
results suggested that keeping this joint (at the cost
of managing the overlap) was important to create the
local manifolds as it often acts as the root of the tree
and thus impacts the whole kinematic chain.
Although this choice introduces a number of
strong constraints in some contexts, as we explic-
itly discard long-range correlations, it also presents
a number of benefits that are further explored in Sec-
tion 5. First, as the body parts motions are not con-
ditioned on each other, we obtain independent sub-
models. It means that bending the right arm (Right-
Arm model) will have no incidence on the knee ori-
entation (Right-Leg model). Even though it prevents
an easier solving of some motion ambiguities, e.g., in
locomotion (no upper/lower body coordination), such
a model could be less biased in handling other simi-
lar motions (e.g. walking while carrying an object).
In other words, it will less suffer from overfitting
and generalize more easily to diverse motion datasets.
Second, this separation of the BPs sub-models en-
ables a fully independent (and parallel) training. It
also provides an unexpected benefit, as different sub-
models can thus be trained or fine-tuned on specific
datasets (cf. Section 5). Finally, this separation into
independent sub-models enables to work (generate,
reconstruct, edit) on the animation of a body part
without impacting anything else. E.g., we can gen-
erate the animation of an arm moving alone, or attach
it to an arbitrary kinematic chain.
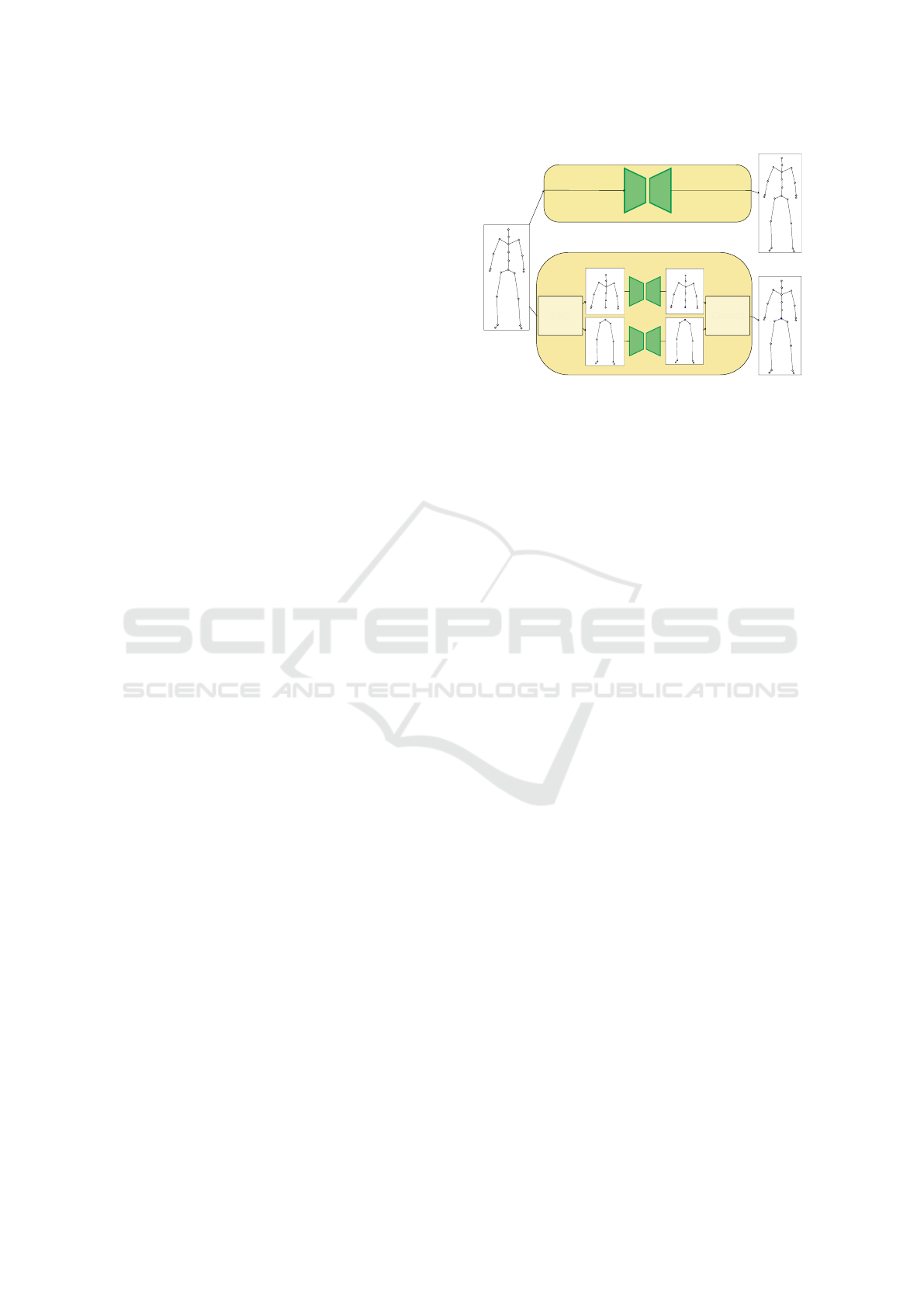
3.3 Body Parts Combination
To obtain an end-to-end skeleton reconstruction re-
gardless of the body decomposition, we designed a
generic strategy to concatenate the sub-graphs mo-
tions. For anatomical reasons, we make the assump-
tion that the sub-model corresponding to the motion
BPs1
Input
Animation
Output
Animations
BPs2
Split
Concat
Figure 2: Inference of two Body Parts models with differ-
ent body decompositions. (Top) a single body part model
(BPs1) and (bottom) a multiple body parts one (BPs2).
of the axial skeleton (i.e., the spine) is the most im-
portant for the global animation. This body part sub-
model is framed in blue in Figure 1, i.e., Upper-Body
for BPs2, and Spine for BPs3 and BPs5. This prior-
itization choice is also motivated by a) the compara-
tively easier task of predicting the spine movements
compared to the limbs and b) the intuitiveness of hav-
ing the torso and hips lead the overall motion.
Indeed, combining the different sub-models
through their common joint leads to two practical im-
plementations: a) overwriting the child BPs Connec-
tor rotation or b) interpolating them with specific hy-
perparameters as weights. In practice, we restricted
ourselves to scenario (a) because of its faster infer-
ence time, comparatively good results and explicit
separation of the body parts in line with the rest of
our work. The pipeline also includes a splitting opera-
tion (cf. Figure 2), which is a straightforward process
leveraging masks along the joints’ dimension.
In the end, we thus work at a level of abstraction
helpful to track the networks performances and com-
pare the different body decomposition.
4 EXPERIMENT
In this section, we detail the experiments conducted to
evaluate the BPs models. Section 4.1 provides train-
ing details (i.e., datasets, architectures and losses),
while Section 4.2 describes our experimental results.
4.1 Training
4.1.1 Dataset & Implementation Details
For our experiments, we rely on several motion cap-
ture datasets processed by Holden et al. (2016). We
GRAPP 2025 - 20th International Conference on Computer Graphics Theory and Applications
56

particularly rely on the CMU part, a choice moti-
vated by its size, its widespread use, and the extensive
range of covered motions. 60% of the CMU dataset
is used for training, 20% for validation and hyperpa-
rameters tuning, while the rest of the sequences and
other datasets are kept for evaluation.
Since the skeleton is normalized across the
datasets, we base our definition of a motion sequence
on the joint rotations. A motion sequence is therefore
a vector X ∈ R
T ×J
BP
×F
with T the number of frames,
J
BP
the number of joints in the body part, and F the
dimension of our rotation representation. In our ex-
periment, T = 61, which corresponds to ∼ 0.5 s at
120 Hz, J
BP
= 31 when considering the entire skele-
ton, and F = 6 as suggested by Zhou et al. (2019).
To mitigate overfitting, we use a random sampling
strategy with a fixed number of sequences per anima-
tion for training, and we switch to a sequential sam-
pling during evaluation. We manually fix the seed
of the random generators to enable a fair and repro-
ducible comparison between each model. We use the
AdamW optimizer with a learning rate of 1e
−4
and a
weight decay of 1e
−2
; together with a learning rate
scheduler at epoch (decay) and step (cyclical triangu-
lar) scales. The batch size is fixed at 16.
4.1.2 Architectures
Since one of our objectives is to create and compare
robust, efficient, and effective representation of our
data, we use simple Auto-Encoder-like architectures.
We take inspiration from siMLPe for the encoder and
decoder layers (Guo et al., 2023) to benefit from its
good performances, its small number of trainable pa-
rameters and its reduced time complexity. In the fol-
lowing, we describe our main architectures:
The first is an Auto-Encoder (AE). Let φ be the
encoder and ψ the decoder. The architecture is thus
described as: φ : R
T ×J
BP
×F
→ R
d
and ψ : R
d
→
R
T ×J
BP
×6
with (here) d < T · J
BP
· F.
The second is a Periodic Auto-Encoder
(PAE) (Starke et al., 2022). It exploits the in-
herent periodicity of the motion by constraining the
network to produce a latent phase manifold.
The third is a Variational Auto-Encoder (VAE).
It enables the automatic creation of a continuous la-
tent space, which is extensively used in generation
and leads to a strong regularization. It takes root in
Bayesian inference and assumes that its optimized la-
tent representation will approximate the real data dis-
tribution, implicitly capturing the hidden causes be-
hind it. The initial prior distribution and subsequent
parameterization are Gaussians in the VAE original
and widespread form.
Finally, there is the Hyperspherical Variational
Auto-Encoder (S-VAE) (Davidson et al., 2018). This
VAE takes a von Mises-Fischer (vMF) distribution as
prior instead of a Gaussian to better fit hyperspherical
structures such as rotations. As originally reported,
the vMF collapses in higher dimensionality, which led
us to use several low dimension latent channels.
Specifically, in our experiments, one sub-model
latent code has a size d
BP
= ⌊
100
n
BP
⌋ to obtain a compa-
rable dimension of d ≈ 100 for all BPs models. Since,
early results on tuning the latent vectors size did not
significantly change the results, we chose to divide its
size equally between each body part depending on the
addressed granularity, which would also generalize to
other decompositions in the future.
4.1.3 Models Complexity
In this Section, we report the models complexity as
number of trainable parameters and inference time.
We report the mean and standard deviation of the
number of parameters in several BPs models based on
different sub-model architectures (cf. Section 4.1.2).
Overall, BPs1 is bigger with 184,221 ± 378 pa-
rameters, BPs2 and BPs3 are smaller with respec-
tively 146, 423 ±362 and 145, 304 ± 361, and BPs5
is medium with 171, 968 ± 374 parameters.
In terms of inference times, all our models are
below 0.08s, with variations depending on the ar-
chitecture of the sub-models (e.g. AE-based mod-
els ≈ 0.005 s, VAE-based models ≈ 0.012 s). In par-
ticular, BPs2, BPs3 and BPs5 necessarily need the
forward pass of several models to produce a whole
skeleton. Such a process could be parallelized, but
we decided to leave it sequential in our experiment
to prevent the need for several GPUs. However, this
choice leads to a steady increase in the time complex-
ity with the number of sub-models (e.g. an AE-based
BPs1 is 4 times faster than an AE-based BPs5).
4.1.4 Loss
We train our models with a total loss described in this
Section, which includes some reconstruction losses
and regularization terms. Note that we also use some
of the following as pure evaluation metrics, up to a
scaling factor.
• Mean Squared Error (MSE) compares term-wise
the ground-truth and predicted matrices.
• Mean Per Joints Angular Error (MPJAE) is a
geodesic distance on SO(3). We first estimate the
difference rotation between R
gt
and R
pred
(global
scale) before computing its angle. Formally:
R
di f f
= R
gt
R
T
pred
and θ
di f f
= arccos(
(tr(R
di f f
)−1)
2
).
Evaluation of Body Parts Representations in Motion Reconstruction
57

• Mean Per Joints Local Angular Error (MPJLAE)
is like the MPJAE, but computed at the local scale.
• The Angular Velocity (AV) is estimated by keep-
ing the geodesic distance results over several sub-
sequent frames. We then approximate the angu-
lar velocity by observing the angle variations over
multiple frames. In practice, we average the an-
gular difference every 10 frames to prevent an ex-
plosion of the metric in initial steps.
• The Angular Acceleration (AA) is estimated us-
ing the results of the angular velocity.
• Mean Per Joints Positional Error (MPJPE), which
computes the distance of the global position of the
joints between ground-truth and prediction.
• Jerk, which compares the 3rd order time deriva-
tive of the global positions between ground-truth
and prediction.
The complete loss used for training is then:
L
recon
= w
MSE
· L
MSE
+ w
MPJPE
· L
MPJPE
+ w
MPJAE
· L
MPJAE
+ w
MPJLAE
· L
MPJLAE
+ w
AV
· L
AV
+ w
AA
· L
AA
+ w
Jerk
· L
Jerk
(1)
If a sub-model is an instance of a VAE, we further
add the corresponding Kullback-Leibler Divergence
with its own weight (w
KL
), and a cyclical KL anneal-
ing (Fu et al., 2019) to mitigate KL vanishing. In the
experiments described in the next section, we used
w
MSE
= 1, w
MPJAE
= 1, w
MPJLAE
= 0.1, w
AV
= 0.001,
w
AA
= 0.01, w
MPJPE
= 0.1, w
Jerk
= 0.001 and w
KL
=
0.005, and we further added a L1-norm on the weights
as regularization to complement the weight decay.
4.2 Results
In this section, we present our different evaluation
steps. The first focuses on the objective robustness,
which includes the reconstruction accuracy in perfect
(Section 4.2.1) and noisy (Section 4.2.2) conditions.
Then we observe the interpretability (Section 4.2.3)
and controllability (Section 4.2.4) of this partitioned
latent representation. In the following, the reported
means and standard deviations are computed based on
the performance of the BPs models on the test anima-
tions of the corresponding dataset(s) for seven gener-
ation seeds.
4.2.1 Reconstruction Accuracy
This section first reports the reconstruction metrics
computed on the original dataset (CMU) test sub-
set (Table 1, top). As introduced previously, CMU
is a very large dataset involving numerous motions
(4, 164, 000 frames), ranging from walking and run-
ning to dancing via boxing and digging. The re-
sults show that BPs1 achieves the best results on the
MPJPE overall, which is easily explained by the ad-
ditional information provided by long-range depen-
dencies. However, the other BPs models still provide
interesting results: in particular, all three decomposi-
tions have similar performances, although worse than
BPs1, which suggests that the upper/lower body co-
ordination was particularly relevant to model in this
dataset (e.g. many locomotion animation). It is also
relevant to note that the MPJAE results are more am-
biguous, with BPs 3 and 5 producing overall better
results on this metric.
To assert the generalization capacities of the mod-
els, we then exhibit the results of the reconstruction
metrics computed on three unseen datasets: MHAD,
Edin locomotion and Edin fight. MHAD includes
several general motions (601, 000 frames), mostly
involving the upper body: e.g. clapping, waving
arms, bending, throwing, or a long-lasting T-pose.
Edin locomotion is focused on mostly unstructured
locomotion tasks (81, 000 frames), i.e. walking, jog-
ging, running forward and backward, but also side-
stepping. Edin fight contains boxing and kicking mo-
tions (90, 000 frames), with an ever present and quite
specific “en garde” posture.
In Table 1 (bottom) we describe the distribution
of errors on a concatenation of the datasets (thus
weighted by their number of animation frames), while
Table 2 details the metrics per dataset. The results of
the Mean in Table 1 is thus closer to the results of
MHAD in Table 2 because this dataset has four times
more animations that the other two. On these unseen
datasets, we observe that BPs1 is still better than the
others on Edin locomotion, which is linked to the up-
per/lower body coordination addressed earlier. How-
ever, the gap is closer on Edin fight, on which BPs5
has comparable performances to BPs1 and better ones
than BPs2 and BPs3. It suggests that for some specific
datasets, having a biased coordination between body
parts might hurt generalizability. Furthermore, BPs1
performs the worst out of all BPs models on MHAD,
which suggests good overall generalization capacities
for perfectly independent body parts sub-models.
4.2.2 Noise Robustness
In numerous applications, such as immersive video-
conferencing, motion models robust to various kinds
of noise are necessary to preserve user experience.
In our application context, such detrimental perturba-
tions can typically come from noisy input (e.g., track-
ing errors), or corruption during transmission. Tra-
ditionally, a more resilient model is obtained through
GRAPP 2025 - 20th International Conference on Computer Graphics Theory and Applications
58

Table 1: MPJPE and MPJAE results on the CMU test (top) and other (Bottom) datasets. MPJPE was normalized to correspond
to the error (in cm) on a 1.80m skeleton. The metrics reported for the distinct datasets are weighted by the number of
animations per dataset. Results in bold are the best overall BPs model for this metric, and those underlined are the second
one.
CMU test subset
MPJPE [cm] MPJAE [deg]
BPs1 BPs2 BPs3 BPs5 BPs1 BPs2 BPs3 BPs5
AE 4.98 ± 6.69 6.18 ± 8.09 6.24 ± 8.07 6.62 ± 8.51 16.8 ± 22.7 16.2 ± 21.4 15.0 ± 19.8 15.3 ± 19.9
PAE 4.92 ± 6.46 7.00 ± 8.99 7.17 ± 9.14 6.91 ± 8.98 16.0 ± 21.1 18.8 ± 24.6 17.3 ± 22.5 16.0 ± 21.0
VAE 5.58 ± 7.30 6.43 ± 8.24 6.35 ± 8.05 7.16 ± 9.01 17.5 ± 23.3 17.1 ± 22.5 15.4 ± 20.1 16.5 ± 20.9
S-VAE 6.54 ± 8.64 7.40 ± 9.55 8.60 ± 11.07 8.42 ± 10.72 19.9 ± 26.8 20.6 ± 27.1 21.0 ± 27.4 20.8 ± 26.5
Mean 5.50 ± 0.65 6.75 ± 0.48 7.09 ± 0.94 7.28 ± 0.69 17.6 ±1.5 18.2 ±1.7 17.2 ± 2.4 17.2 ± 2.1
MHAD, Edin locomotion, Edin fight
MPJPE [cm] MPJAE [deg]
BPs1 BPs2 BPs3 BPs5 BPs1 BPs2 BPs3 BPs5
AE 12.00 ± 13.18 12.03 ± 12.60 11.16 ± 11.71 11.46 ± 12.30 30.3 ± 31.5 29.7 ± 30.9 28.4 ± 29.0 27.3 ± 28.1
PAE 12.03 ± 12.98 12.65 ± 13.20 11.95 ± 12.77 11.85 ± 12.74 30.4 ± 31.7 31.2 ± 32.3 29.3 ± 30.2 27.9 ± 28.8
VAE 12.91 ± 13.74 12.22 ± 12.72 11.30 ± 12.14 11.52 ± 12.38 31.2 ± 31.8 30.4 ± 31.4 28.6 ± 29.2 28.0 ± 29.0
VAE-S 13.47 ± 14.23 13.13 ± 13.86 13.08 ± 13.92 12.75 ± 13.95 32.6 ± 32.8 32.4 ± 33.1 32.0 ± 32.5 31.0 ± 32.2
Mean 12.60 ± 0.62 12.51 ± 0.42 11.87 ± 0.76 11.90 ± 0.52 31.1±0.9 30.9 ±1.0 29.6 ± 1.4 28.5 ± 1.4
Table 2: Mean reconstruction Metrics MPJPE and MPJAE on distinct datasets. Results in bold are the best overall Body Parts
model for this metric, and those underlined are the second one.
MPJPE [cm] MPJAE [deg]
BPs1 BPs2 BPs3 BPs5 BPs1 BPs2 BPs3 BPs5
MHAD 13.43 ± 0.60 12.84 ± 0.44 12.09 ± 0.73 12.19 ± 0.47 30.9 ± 0.9 30.3 ± 0.9 29.0 ± 1.3 28.0 ± 1.2
Edin loco 8.13 ± 0.62 9.96 ± 0.44 9.78 ± 0.70 10.00 ± 0.61 26.3 ± 1.0 27.8 ± 1.1 25.7 ± 1.4 24.5±1.9
Edin fight 11.25 ± 0.81 12.74 ± 0.51 12.39 ± 1.00 11.72 ± 0.83 37.1 ±1.4 38.3 ± 1.4 36.8 ± 2.4 35.9 ± 2.5
data augmentation (e.g. incorporating noise to train-
ing samples), however such a curriculum could miss
on unexpected noise distributions or impair the main
task learning. An inherently robust model could
therefore be interesting, and we evaluate the different
BPs models in this prospect on three noisy situations:
1. “Input Noise”: add random SO(3) noise (i.e. unit
quaternions with small angles) on each input sam-
ple. It simulates tracking errors or occlusions.
2. “Latent Noise”: remove (i.e. set at 0) a random
part of the latent vector (10%). This typically cor-
responds to data corruption during transmission.
3. “Input+Latent Noise”: combination of the above.
In each situation, we compute the metrics by com-
paring with the noise-free animation. The results are
reported on all the test datasets and averaged over the
various architectures (Table 3) and seeds.
First of all, most results appear to be the same than
in the noise-free evaluation (previous section), i.e.,
BPs3 performs better than BPs1 on MHAD and BPs5
is still second on half of the datasets. We can also note
that the BPs models perform overall better on the la-
tent noise scenario than on the input noise one, which
suggests that it is an easier task to solve here. How-
ever, BPs1 provides an exception on the Edin fight
dataset where it is slightly worse in the latent noise
case and, we can observe the same tendency for BPs5
with virtually the same results in both scenarios. In
other words, on certain datasets, having an error on
the latent vector might be particularly difficult to re-
cover. It seems however interesting to note that BPs2,
BPs3 and BPs5 seem to provide a relevant alternative
to BPs1 without losing excessive reconstruction accu-
racy.
4.2.3 Partitioned Latent Representation
Complementary to the traditional evaluation of noise
on latent representations, we provide in this section
visual examples of animations where noise is applied
to strategic parts of the motion data. Such errors could
be representative of local tracking errors such as a
drifting sensor. Even in a case where the noise was
not properly eliminated, we would reasonably expect
the noise to still be localized on the same body part.
In other words, we would expect some interpretability
of the model.
Specifically, we present examples where we add
noise on specific parts of the latent vectors and visu-
ally compare the results between all the BPs models
(Figure 3). In this scenario, we a) tamper the latent
vector produced by one or several sub-models of ei-
ther BPs2, BPs3 or BPs5, b) tamper an arbitrary part
of the latent vector produced by BPs1, and c) compare
Evaluation of Body Parts Representations in Motion Reconstruction
59
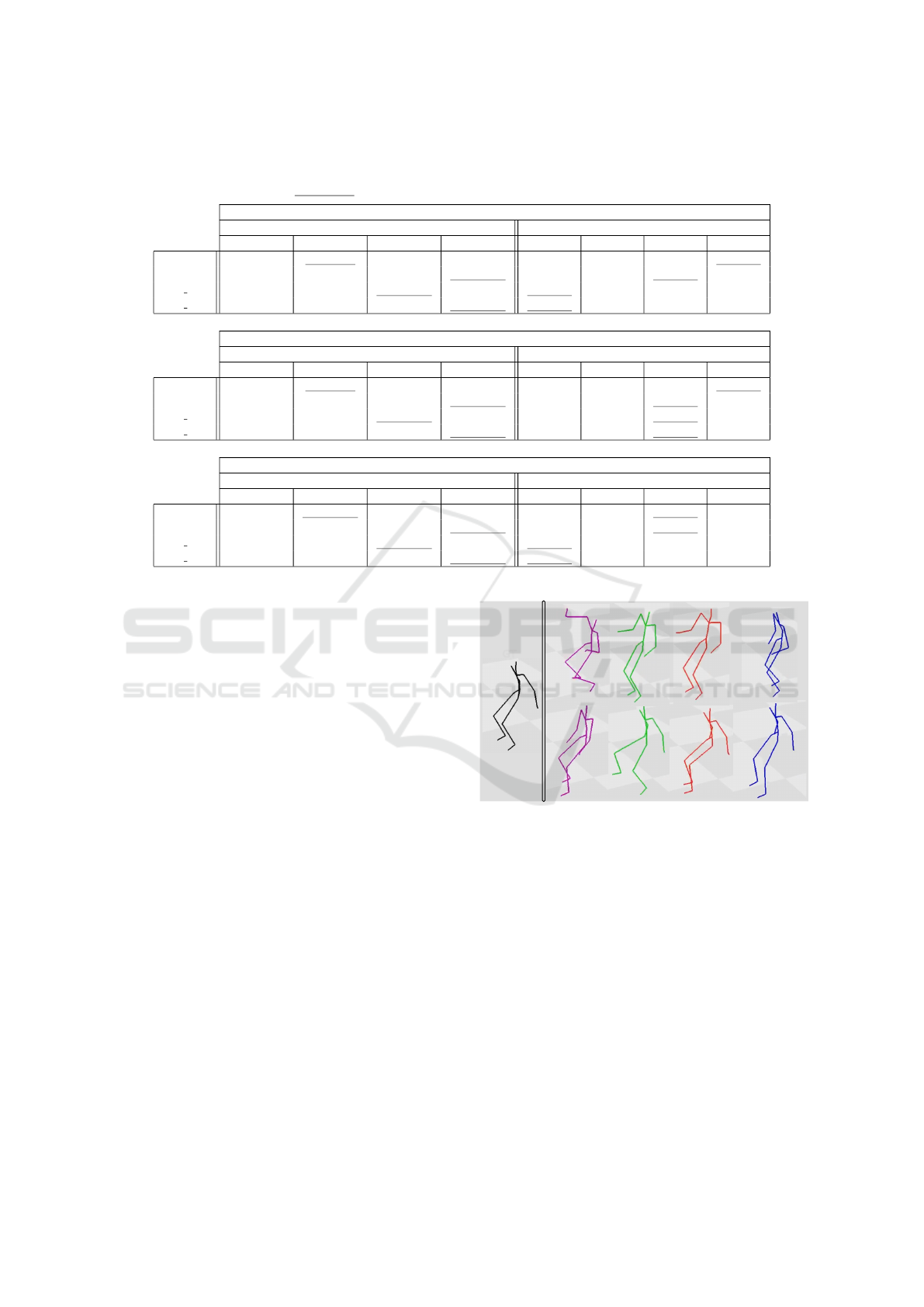
Table 3: MPJPE and MPJAE results on the different datasets after applying input, latent, or input+latent noise. MPJPE was
normalized to correspond to the error in centimeters on a 1.80m skeleton. Results in bold are the best overall Body Parts
model for this metric, and those underlined are the second one.
Input noise
MPJPE [cm] MPJAE [deg]
BPs1 BPs2 BPs3 BPs5 BPs1 BPs2 BPs3 BPs5
CMU 8.05 ± 0.32 9.47 ± 0.28 9.63 ± 0.61 10.08 ± 0.26 21.0 ± 1.1 22.4 ± 1.2 21.8 ± 1.6 21.7±1.2
MHAD 16.27 ± 0.50 15.74 ± 0.48 15.15 ± 0.63 15.24 ± 0.35 32.9 ±0.5 32.7±0.7 32.5 ±0.8 31.2 ± 0.6
Edin loco 10.38 ± 0.40 12.44 ± 0.36 12.18 ± 0.55 12.57 ± 0.33 28.4 ± 0.8 30.5 ± 1.0 29.0 ± 1.2 27.6 ± 1.6
Edin fight 13.14 ± 0.70 14.67 ± 0.56 14.41 ± 0.88 13.63 ± 0.65 39.4 ±1.3 41.3 ± 1.4 40.3 ± 2.1 39.3 ± 2.0
Latent noise
MPJPE [cm] MPJAE [deg]
BPs1 BPs2 BPs3 BPs5 BPs1 BPs2 BPs3 BPs5
CMU 8.02 ± 1.28 8.51 ± 1.08 8.82 ± 1.39 9.15 ± 1.17 21.3 ± 2.1 21.3 ± 2.6 20.6 ± 3.2 21.1 ±3.0
MHAD 15.28 ± 0.97 14.40 ± 0.84 13.87 ± 1.10 14.13 ± 0.79 33.1 ±1.4 32.4±1.6 31.6 ±2.0 31.0 ± 1.8
Edin loco 9.72 ± 1.20 10.95 ±0.96 10.82 ± 1.20 11.22 ± 1.02 28.4 ± 1.6 29.3 ± 1.9 27.6 ± 2.3 27.1 ± 2.7
Edin fight 13.28 ± 1.22 14.30 ± 1.02 14.07 ± 1.41 13.62 ± 1.20 39.8 ±1.8 40.7 ± 2.1 39.5 ± 3.0 38.8 ± 3.0
Input + Latent noise
MPJPE [cm] MPJAE [deg]
BPs1 BPs2 BPs3 BPs5 BPs1 BPs2 BPs3 BPs5
CMU 9.77 ± 0.99 10.57 ±0.80 10.74 ± 1.05 11.28 ± 0.75 23.9 ± 1.7 24.6 ± 2.0 24.1 ± 2.5 24.5 ± 2.1
MHAD 17.63 ± 0.82 16.82 ± 0.77 16.36 ± 0.89 16.64 ± 0.55 34.8 ±1.1 34.4±1.3 34.4 ±1.5 33.6 ± 1.2
Edin loco 11.44 ± 0.93 12.98 ± 0.73 12.82 ± 1.04 13.30 ± 0.69 30.1 ± 1.4 31.6 ± 1.7 30.4 ± 2.2 29.7 ± 2.2
Edin fight 14.75 ± 1.08 15.89 ± 0.95 15.66 ± 1.22 15.11 ± 0.98 41.8 ±1.7 43.3 ± 2.1 42.4 ± 2.7 41.6 ± 2.5
and analyze the results. Since we use distinct latent
spaces to reconstruct our animation, it is natural that
adding noise to a specific latent vector will not impact
the others. Indeed, we observe on Figure 3 (bottom)
that tampering the lower-body latent vector modifies
the entire BPs1 animation, i.e., all the joint positions
are visibly different from the ground-truth. However,
for BPs2, BPs3 or BPs5 the upper-body pose is al-
most exactly the same as the ground-truth one. In
other words, a partitioned approach will constrain the
noise to be localized in contrast to BPs1, which suf-
fers from its entangled representation. Interestingly,
we can note in Figure 3 (top) that all the models suffer
from tampering the upper-body latent vectors, i.e, the
lower-body joints’ positions are disturbed compared
to the ground-truth. Non-BPs1 models still seem to
produce closer poses overall and we can observe that
the lower-body pose is locally similar to the ground-
truth (i.e. the knees are bent, but not as much as
in BPs1 reconstruction and the legs are less spread
out). In traditional Character Animation, disturbing
the root rotation produces overall bad animation, and
we observe a similar behavior in our framework. In-
deed, the root rotation is managed by the axial skele-
ton (e.g. Spine or Upper-Body sub-models), which
might explain worse overall performances when it is
disturbed, highlighting its importance.
Upper body latent noise
Lower body latent noise
BPs1 BPs2 BPs3 BPs5
GT
Figure 3: Reconstruction results after adding noise to spe-
cific parts of the latent vector. The left skeleton is the orig-
inal animation (black), then each column displays the re-
construction from BPs1 (purple), BPs2 (green), BPs3 (or-
ange) and BPs5 (blue). In the case of BPs2, BPs3 and
BPs5, we tamper the latent vectors of the upper (top row)
or lower body (bottom row) sub-models. We can notice that
the whole animation produced by BPs1 is noisy, whereas
the other BPs models produce coherent animations for the
unperturbed part.
4.2.4 Modular Body Parts Models
Finally, we illustrate an additional benefit of a modu-
lar motion modeling approach. Indeed, its high flexi-
bility enables its use for other scenarios than the orig-
inal one and turns it into a reliable and controllable
framework. For instance, it provides an easy way of
GRAPP 2025 - 20th International Conference on Computer Graphics Theory and Applications
60

Figure 4: Animation of a novel topology with several sub-
models. Here, we simultaneously reconstruct the humanoid
skeleton motion with several Auto Encoder-based body
parts sub-models (blue) and generate an animation for an-
other pair of arms with two Variational Auto Encoder-based
sub-models (cyan).
creating coarse animation of novel character topolo-
gies, e.g., as often seen in applications where users
can choose to embody non-anthropomorphic charac-
ters. For instance, we can easily copy, remove, or re-
place a specific sub-model by another one with only
minor modifications to the original BPs model. This
process enables the use of the sub-models as building
blocks too reconstruct or create local animations. To
illustrate this modularity, we showcase (cf. Figure 4)
the use of an AE-based BPs5 model to perform the re-
construction of the original skeleton and of two VAEs,
trained respectively on the right and left arms motion.
By slightly altering the latent code produced by the
VAE encoders, we effectively generate the new arms
animations. Eventually, the motions can then be con-
catenated following a novel topology to obtain a new
animation. The whole process is close to a straightfor-
ward manipulation of the animation skeleton in tra-
ditional Character Animation, but would usually be
difficult to handle using a BPs1 model.
5 DISCUSSION
The experiments presented in this paper, evaluating
the benefits of body parts-based representations on
human motion reconstruction tasks, brought many in-
teresting results, which we discuss in this section.
Although BPs1 achieves the best results overall on
the objective reconstruction metrics, the other models
show comparable, and sometimes better, results, de-
spite discarding the upper/lower coordination crucial
in locomotion tasks. However, on datasets that have
many motions involving mostly the coordination of
both arms together (such as MHAD), BPs3 performs
better. This result could be explained by the rela-
tively good modeling of the arms coordination (one
sub-model in this 3-parts decomposition) and the re-
moval of the upper/lower body communication that
might bring spurious motions. We observe similar ob-
jective performances on Edin
fight, which also relies
heavily on the upper-body; although there are a) some
boxing motions in CMU that could explain BPs1 suc-
cess and b) some kicks and steps that might be eas-
ier to model with prior locomotion knowledge. Over-
all and counter-intuitively, BPs5 achieves the second
place in terms of reconstruction performance on half
the studied scenarios. In other words, the trade-off
between global coherency and local modeling could
be interesting to explore in some reconstruction task,
using appropriated metrics.
The results presented in this paper rely on several
objective metrics, some of them with a certain level
of correlation, that were chosen due to their wide us-
age in the literature. In particular, we focused on re-
porting the MPJPE and MPJAE that are extensively
used in skeletal motion modeling (i.e., human pose
estimation, motion prediction, or reconstruction) and,
although strongly correlated, can be complementary.
As introduced previously, the MPJPE is an objective,
interpretable and differentiable metric, and as such
our main evaluation criterion. In a kinematic repre-
sentation, it is linked to the MPJAE, which itself suf-
fers from a) relying only on global angular informa-
tion (and thus ignoring potential local errors, hence
the need for other metrics such as MPJLAE), and
b) a lack of interpretability. However, the MPJAE
more strongly penalizes incorrect global rotations that
might still produce correct joint positions (e.g. wrist
rotation around the wrist-elbow axis), and thus a low
MPJPE.
Furthermore, we chose to evaluate the reconstruc-
tion results using metrics applied on the whole skele-
ton, which provided three benefits: a) a fair compari-
son between the various models, b) a coherency with
our main use case, and c) accounting for joint accu-
mulation errors by including the most proximal joints
in the skeletal chains. Indeed, since the MPJPE and
MPJAE are computed at the global scale (i.e. after a
forward kinematics pass), they tend to accumulate the
errors along the kinematic chain (i.e. the whole skele-
ton). While they are not specifically tailored for eval-
uating discrepancies at the junction between body part
models, such errors are then necessarily accounted
by the metrics. However, exploring metrics describ-
ing more precisely the error distributions across joints
would be valuable, and would provide insights on the
difficulty of modeling the connectors, which are key
joints from an anatomical standpoint. Situational met-
rics, such as the MPJPE computed on specific body
part chains (here used as training losses) could also
be evaluated, for instance in scenarios similar to the
one described in Section 4.2.3. Finally, multiple other
metrics would be interesting to consider in the fu-
ture for human motion modeling, e.g., ranging from
Evaluation of Body Parts Representations in Motion Reconstruction
61

metrics based on time derivatives (in particular jerk),
which would penalize bad temporal coherency and
jerkiness, to metrics closer of the human perception.
While time derivatives metrics were indeed computed
for this work, reliable perceptive metrics that would
not necessitate subjective evaluations is still an issue
in deep-based animation, as is the data availability for
creating them.
We believe that the above results highlight the dif-
ficulty of obtaining a comprehensive human motion
representation. In fact, in terms of motion diversity,
structured motion capture dataset are sparse, priori-
tizing widespread and generic motions that might not
be relevant for specific applications. To obtain such
motions, we thus rely on often approximated meth-
ods (e.g. latent, or linear, interpolations) to man-
age transitions or generalization, or on unstructured
datasets. Nevertheless, expensive and cumbersome
motion capture setups, actors and plenty of time are
required, which prevent the creation of large-scales
datasets comparable in size to what can be found
in the image community. Furthermore, some mo-
tions are inherently challenging to capture and thus
under-represented, either because they are special-
ized (e.g. the “en garde” posture or making pot-
tery) or because they occur in challenging conditions
(e.g., swimming implies water, refraction, reflection
and waterproof equipment). As such, creating mod-
els complex enough to learn all the correlations at
the gesture and body scales on a dataset might lead
to overfitting its motion distribution and thus hurt the
model generalizability. In contrast, small independent
models could learn to reconstruct a set of local mo-
tions, that would together form a complex gesture and
an action by specifying a number of objectives, e.g.,
having some models learn body parts motion distri-
butions and an autonomous agent sampling them to
perform specific, goal-driven tasks.
Another major advantage of a body parts-based
approach is its modularity, which produces a struc-
tured latent vector while providing several benefits
that apply at different levels of the animation pipeline.
E.g., body parts approaches enable the edition or syn-
thesis of local animations independently from an-
other, which can be used for instance to denoise or
update them selectively. As illustrated in the results,
it could prevent spatially located noise from tamper-
ing the whole signal (e.g. motion capture method
with trackers drift), while also providing novel editing
capabilities for characters with novel topologies. It
would further increase the controllability of the deep-
based pipeline, for instance by adapting the body
parts latent vectors depending on other control sig-
nals. E.g., in case of high streaming latency, we could
keep the reconstruction fidelity of the axial skeleton
while sacrificing the other body parts updates or high-
frequencies. In short, we obtain a flexible and adapt-
able representation that can address a wide variety of
exotic scenarios ranging from an interactive tool for
artistic creation at the body part level to a reduction in
the quantity and quality of transmitted information in
a streaming setting (i.e., reconstructing relevant body
parts and generating the others, or having a coarse to
fine approach on the server side).
Finally, separating the human body into parts also
provides an increased flexibility to train human mo-
tion models. As introduced previously and illustrated
in Figures 2 and 5 (top), the evaluation process di-
rected our framework towards several BPs wrappers
designed to train different sub-models with the same
pipeline than for a whole-body model, in a transpar-
ent “Centralized” manner. Such a method could be
extended in the future to better consider the body
parts relationships, e.g., to train a network in charge
of the synchronization between sub-models. How-
ever, our framework also enables to train the different
sub-models separately (as illustrated in Figure 5, bot-
tom). The training could then be fully parallelized, or
performed on entirely different data sources similarly
to a Federated Learning process. Hybrid schemes,
e.g., first training sub-models in a “Centralized” fash-
ion, before fine-tuning them using the “Federated” ap-
proach on dedicated datasets (e.g. expert motions)
would also be interesting to explore. As another ex-
ample, we could also consider use cases where rel-
evant body part models would be tuned on datasets
of people with missing limbs, to model their motions
without the artifacts that a traditional post-processing
of the skeleton could produce. However, we leave
such novel learning mechanisms for future work.
6 CONCLUSION
This paper proposes a new human motion modeling
framework for creating independent body parts mod-
els and a simple technique for combining them to ad-
dress several use cases. Additionally, we evaluate dif-
ferent body decompositions used in the literature by
testing them on various use case simulations. Our re-
sults suggest that even though we explicitly discard
long-range dependencies across the body, our inde-
pendent body parts models can produce results com-
parable to a whole-body model in a reconstruction
task. Moreover, results suggest that their denoising
(especially at the local scale) and generalization ca-
pacities are relevant, and their modularity provides
other interesting features. For instance, they semanti-
GRAPP 2025 - 20th International Conference on Computer Graphics Theory and Applications
62
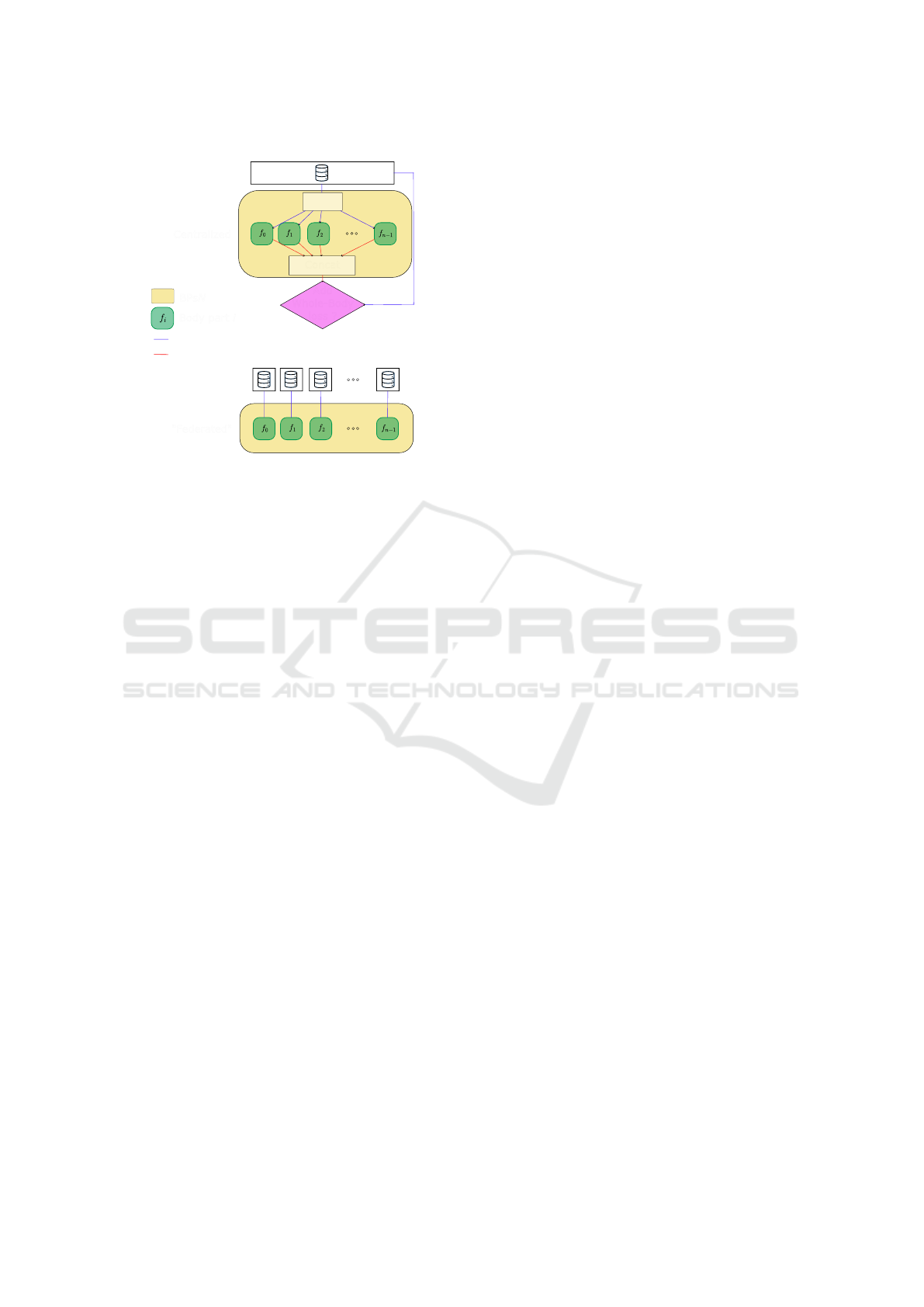
N sources of data
"Federated"
Centralized
Output
Training signal
Body part i
BPsN
1 source of data
Split
Concat
Add
Whole-Body
loss ?
Figure 5: Possible generic training processes for a Body
Parts model with N sub-models. In the “Federated” case
(bottom), we make the assumption that the sources of data
would provide the data corresponding to each body part. In
other words, if we use one or several whole-body datasets,
the masking would be done at the sources of data level.
cally partition the animation data, enabling a more in-
terpretable and controllable representation, which is a
desirable property in unsupervised and unpredictable
contexts. This property includes the modification of
the latent vector in a scenario of real-time anima-
tion transmission (UDP-based) over the Internet. Fi-
nally, this semantic representation could further lead
to novel semantic-based animation techniques of non-
humanoid avatars, novel training schemes for large or
privacy-aware models, or even to different compres-
sion methods.
In future works, we aim to address some limita-
tions of the current approach and further exploit its
advantages. In particular, our work aimed at explor-
ing the benefits of an alternative approach compared
to the current state-of-the-art techniques that involve
highly specialized and engineered architectures. As
such, this study should be perceived as complemen-
tary to other body parts works, to encourage the ex-
ploitation of more modular motion representations,
and to serve as a possible milestone in the correspond-
ing open discussion. The future steps would thus in-
volve more in-depth exploration and analysis of in-
dependent body parts motion modeling, and compar-
isons with state-of-the-art models on specialized top-
ics. We believe that creatively leveraging local motion
distributions, that are fast to model, tune, or modify,
could prove valuable in numerous scenarios that do
not necessarily need an explicit and holistic model-
ing of every joints correlations (e.g. learning expert
motions or managing occlusions and trackers issues).
REFERENCES
Aberman, K., Li, P., Lischinski, D., Sorkine-Hornung, O.,
Cohen-Or, D., and Chen, B. (2020). Skeleton-aware
networks for deep motion retargeting. ACM Trans. on
Graph., 39(4).
Aristidou, A. and Lasenby, J. (2011). Fabrik: A fast, itera-
tive solver for the inverse kinematics problem. Graph-
ical Models, 73(5):243–260.
Butepage, J., Black, M. J., Kragic, D., and Kjellstrom, H.
(2017). Deep representation learning for human mo-
tion prediction and classification. In IEEE/CVF Conf.
on Comp. Vision and Pattern Recognition.
Chen, A. (2023). Character motion synthesis based on deep
learning: A survey. Highlights in Science, Engineer-
ing and Technology, 76:705–724.
Cheymol, A., Fribourg, R., L
´
ecuyer, A., Normand, J.-
M., and Argelaguet, F. (2023). Beyond my real
body: Characterization, impacts, applications and
perspectives of “dissimilar” avatars in virtual real-
ity. IEEE Trans. on Visualization and Comp. Graph.,
29(11):4426–4437.
Dang, L., Nie, Y., Long, C., Zhang, Q., and Li, G. (2021).
Msr-gcn: Multi-scale residual graph convolution net-
works for human motion prediction. In IEEE/CVF Int.
Conf. on Comp. Vision, pages 11467–11476.
Davidson, T. R., Falorsi, L., De Cao, N., Kipf, T., and Tom-
czak, J. M. (2018). Hyperspherical variational auto-
encoders. Conf. on Uncertainty in Artificial Intelli-
gence.
Fu, H., Li, C., Liu, X., Gao, J., Celikyilmaz, A., and Carin,
L. (2019). Cyclical annealing schedule: A simple ap-
proach to mitigating kl vanishing. In North American
Chapter of the Ass. for Computational Linguistics.
Guo, W., Du, Y., Shen, X., Lepetit, V., Alameda-Pineda,
X., and Moreno-Noguer, F. (2023). Back to mlp:
A simple baseline for human motion prediction. In
IEEE/CVF Conf. on Comp. Vision and Pattern Recog-
nition, pages 4809–4819.
Hanavan, E. P. (1964). A mathematical model of the human
body, volume 32. Aerospace Medical Research Lab.,
Aerospace Medical Div., Air Force Systems Com-
mand.
Holden, D., Komura, T., and Saito, J. (2017). Phase-
functioned neural networks for character control.
ACM Trans. on Graph., 36(4):1–13.
Holden, D., Saito, J., and Komura, T. (2016). A deep learn-
ing framework for character motion synthesis and
editing. ACM Trans. on Graph., 35(4):1–11.
Holden, D., Saito, J., Komura, T., and Joyce, T. (2015).
Learning motion manifolds with convolutional au-
toencoders. In ACM SIGGRAPH Asia Technical
Briefs.
Hu, L., Zhang, Z., Zhong, C., Jiang, B., and Xia, S. (2024).
Pose-aware attention network for flexible motion re-
targeting by body part. IEEE Trans. on Visualization
and Comp. Graph., 30(8):4792–4808.
Jain, A., Zamir, A. R., Savarese, S., and Saxena, A.
(2016). Structural-rnn: Deep learning on spatio-
Evaluation of Body Parts Representations in Motion Reconstruction
63

temporal graphs. In IEEE/CVF Conf. on Comp. Vision
and Pattern Recognition, pages 5308–5317.
Jang, D.-K., Park, S., and Lee, S.-H. (2022). Motion puzzle:
Arbitrary motion style transfer by body part. ACM
Trans. on Graph., 41(3).
Jiang, J., Streli, P., Qiu, H., Fender, A., Laich, L., Snape,
P., and Holz, C. (2022). Avatarposer: Articulated full-
body pose tracking from sparse motion sensing. In
Comp. Vision – ECCV 2022, pages 443–460. Springer
Nature.
Ko, H. and Badler, N. (1996). Animating human locomo-
tion with inverse dynamics. IEEE Comp. Graph. and
Applications, 16(2):50–59.
Kovar, L., Gleicher, M., and Pighin, F. (2002). Motion
graphs. ACM Trans. on Graph., 21(3):473–482.
Lee, S., Kang, T., Park, J., Lee, J., and Won, J. (2023a).
Same: Skeleton-agnostic motion embedding for char-
acter animation. In ACM SIGGRAPH Asia Conf. Proc.
Lee, S., Lee, J., and Lee, J. (2022). Learning virtual
chimeras by dynamic motion reassembly. ACM Trans.
on Graph., 41(6):1–13.
Lee, S., Starke, S., Ye, Y., Won, J., and Winkler, A. (2023b).
Questenvsim: Environment-aware simulated motion
tracking from sparse sensors. In ACM SIGGRAPH
Conf. Proc.
Li, M., Chen, S., Chen, X., Zhang, Y., Wang, Y., and Tian,
Q. (2022a). Symbiotic graph neural networks for 3d
skeleton-based human action recognition and motion
prediction. IEEE Trans. on Pattern Analysis and Ma-
chine Intelligence, 44(6).
Li, M., Chen, S., Zhang, Z., Xie, L., Tian, Q., and Zhang,
Y. (2022b). Skeleton-parted graph scattering networks
for 3d human motion prediction. In Comp. Vision –
ECCV 2022, page 18–36.
Li, Y., Wang, Z., Yang, X., Wang, M., Poiana, S. I.,
Chaudhry, E., and Zhang, J. (2019). Efficient con-
volutional hierarchical autoencoder for human motion
prediction. The Visual Computer, 35(6):1143–1156.
Liu, Z., Lyu, K., Wu, S., Chen, H., Hao, Y., and Ji, S.
(2021). Aggregated multi-gans for controlled 3d hu-
man motion prediction. AAAI Conf. on Artificial In-
telligence Proc., 35(3):2225–2232.
Malek-Podjaski, M. and Deligianni, F. (2023). Adversarial
attention for human motion synthesis. In IEEE Sym-
posium Series on Computational Intelligence, pages
69–74.
Mao, W., Liu, M., and Salzmann, M. (2020). History re-
peats itself: Human motion prediction via motion at-
tention. In Comp. Vision – ECCV 2020, pages 474–
489.
Mourot, L., Hoyet, L., Le Clerc, F., Schnitzler, F., and
Hellier, P. (2022). A survey on deep learning for
skeleton-based human animation. Comp. Graph. Fo-
rum, 41:122–157.
Reda, D., Won, J., Ye, Y., van de Panne, M., and Winkler,
A. W. (2023). Physics-based motion retargeting from
sparse inputs. Proc. ACM Comput. Graph. Interact.
Tech., 6.
Shao, Z., Li, Y., Guo, Y., Zhou, X., and Chen, S. (2019). A
hierarchical model for human action recognition from
body-parts. IEEE Trans. on Circuits and Systems for
Video Technology, 29(10):2986–3000.
Shu, X., Zhang, L., Qi, G.-J., Liu, W., and Tang, J. (2022).
Spatiotemporal co-attention recurrent neural networks
for human-skeleton motion prediction. IEEE Trans.
on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 44(6).
Starke, S., Mason, I., and Komura, T. (2022). Deepphase:
periodic autoencoders for learning motion phase man-
ifolds. ACM Trans. on Graph., 41(4):1–13.
Wang, W., Zhou, T., Qi, S., Shen, J., and Zhu, S.-C. (2022).
Hierarchical human semantic parsing with compre-
hensive part-relation modeling. IEEE Trans. on Pat-
tern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 44(7):3508–
3522.
Wang, Y. and Neff, M. (2015). Deep signatures for index-
ing and retrieval in large motion databases. In ACM
SIGGRAPH Conf. on Motion in Games, page 37–45.
Yan, X., Rastogi, A., Villegas, R., Sunkavalli, K., Shecht-
man, E., Hadap, S., Yumer, E., and Lee, H. (2018).
Mt-vae: Learning motion transformations to gener-
ate multimodal human dynamics. In Comp. Vision –
ECCV 2018.
Yang, D., Kim, D., and Lee, S.-H. (2021). Lobstr:
Real-time lower-body pose prediction from sparse
upper-body tracking signals. Comp. Graph. Forum,
40(2):265–275.
Ye, Y., Liu, L., Hu, L., and Xia, S. (2022). Neural3points:
Learning to generate physically realistic full-body
motion for virtual reality users. Comp. Graph. Forum,
41(8):183–194.
Zhang, H., Starke, S., Komura, T., and Saito, J. (2018).
Mode-adaptive neural networks for quadruped motion
control. ACM Trans. on Graph., 37(4):1–11.
Zhang, J., Tu, Z., Weng, J., Yuan, J., and Du, B. (2024). A
modular neural motion retargeting system decoupling
skeleton and shape perception. IEEE Trans. on Pattern
Analysis and Machine Intelligence.
Zhou, L., Shang, L., Shum, H. P., and Leung, H. (2014).
Human motion variation synthesis with multivariate
gaussian processes. Comp. Animation and Virtual
Worlds, 25(3-4):301–309.
Zhou, Y., Barnes, C., Lu, J., Yang, J., and Li, H. (2019). On
the Continuity of Rotation Representations in Neural
Networks. In IEEE/CVF Conf. on Comp. Vision and
Pattern Recognition, pages 5738–5746.
Zou, Q., Yuan, S., Du, S., Wang, Y., Liu, C., Xu, Y., Chen,
J., and Ji, X. (2025). Parco: Part-coordinating text-to-
motion synthesis. In Comp. Vision – ECCV 2024.
GRAPP 2025 - 20th International Conference on Computer Graphics Theory and Applications
64
