
Developing a Research Framework Model for Assessing the Impact of
Social Media Marketing Activities on Brand Loyalty
Meng Xin, Kyriakos Christofi
a
, Lycourgos Hadjiphanis, Pieris Chourides
b
and Nikolaos Boukas
c
Department of Management and Marketing, School of Business Administration,
European University Cyprus, Nicosia, Cyprus
Keywords: Social Media Marketing Activities, Consumer-Brand Relationship, Brand Loyalty, Hospitality, Research
Framework.
Abstract: The rapid growth of internet of things has driven a shift in consumer behaviour, prompting businesses to adopt
social media as a vital communication channel. In the hospitality sector, social media marketing activities
(SMMA)is the cornerstone in business management, marketing research and brand promotion, however,
there is a scarcity of research on the comparative effectiveness of social media strategies within this industry.
This study seeks to fill this gap by establishing a research framework that examine the connections among
SMMA, the consumer-brand relationship (CBR), and brand loyalty (BL) in a systemic way. Specifically, the
research model, draws on the Stimulus-Organism-Response (SOR) framework, proposed that factors like
entertainment, interaction, customization, trendiness, and word of mouth (WOM) can bolster the CBR and
subsequently boost brand loyalty. Moreover, the study considers the mediating and moderating roles of CBR,
gender and age in the relationship to social media stimuli and user behaviour. The study’s outcomes can be
utilized as a solid foundation to host future empirical investigations aiding in the optimization of marketing
strategies and the preservation of a competitive advantage in the digital landscape.
1 INTRODUCTION
The development of digital economy has brought
significant changes in consumer behaviour of internet
users. This global shift is rapidly making the use of
social media as a new tool of communication, both
possible as well as necessary for companies.
Under this prism, the application of the internet
and social media alters consumer behavior, hence
challenging the overall way of conducting business
(Dwivedi et al., 2021). As of April 2024, there were
5.44 billion internet users worldwide, representing
67.1 percent of the global population. Of this number,
5.07 billion, or 62.6 percent of the world’s
population, were social media users. Asia had the
largest number of online users globally, with over
2.93 billion, followed by Europe with around 750
million internet users. China, India, and the United
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2277-5283
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0650-1944
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6498-2291
States lead the world in the number of internet users
(Petrosyan, 2024).
In the hospitality industry, social media serve as a
critical strategic tool of marketing research and brand
promotion (Leung et al., 2013). They are essential for
enhancing customer engagement through attractive,
high-quality, and interactive content (Yoong and
Lian, 2019), as well as for improving customer
experience and building relationships (Verissimo and
Menezes, 2015). Additionally, social media
marketing (SMM) plays a pivotal role in the
hospitality industry by engaging existing and
potential consumers with the ultimate objective being
gaining their loyalty (Beqiri. and Qenaj, 2022). Social
media marketing activities (SMMA) can be defined
as the specific actions that implement the social
media marketing strategy (F. Li et al., 2021). These
154
Xin, M., Christofi, K., Hadjiphanis, L., Chourides, P. and Boukas, N.
Developing a Research Framework Model for Assessing the Impact of Social Media Marketing Activities on Brand Loyalty.
DOI: 10.5220/0013141600003956
In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Finance, Economics, Management and IT Business (FEMIB 2025), pages 154-160
ISBN: 978-989-758-748-1; ISSN: 2184-5891
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
activities include sales, advertising as well as
costumer service(Baines et al., 2021).
While studies on Hallyu tourism (Chung and
Jeong, 2024) and customer engagement in social
media (de Oliveira Santini et al., 2020) offer insights,
they neglected the specific nuances of SMMA in the
hospitality industry. This study, grounded in the
Stimulus- Organism-Response (SOR)model, targets a
unique aspect of SMMA not addressed by existing
theories or meta-analyses, aiming to understand the
impact of SMMA on brand loyalty within the
industry. Specifically, previous research in tourism (J.
Liu et al., 2022), retailing (Safeer, 2024), and airlines
(Ibrahim, 2021b; Khan et al., 2024) has primarily
focused on examining the relationship between social
media marketing activities and their direct outcomes,
such as brand trust, satisfaction, and loyalty.
However, dimensions of the consumer-brand
relationship (CBR), such as brand love and brand
attachment, have not been systematically examined in
the hospitality industry (Ibrahim et al., 2021a, Kumar
and Hsieh, 2024). Hence, little empirical work has
been conducted to understand how SMMA influence
brand loyalty through CBR.
Based on this literature gap, this research aims to
establish a research agenda that sets the directions
towards in-depth investigation on the relationships
among SMMA, CBR, and brand loyalty, holistically,
responding in this way to the calls of Kumar (S.
Kumar and Hsieh, 2024) and Anas (Anas et al., 2023),
which point out the need for investations that examine
the impact of SMMA on brand loyalty.
2 THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
As technology is advancing constantly, the Internet
has evolved from a purely broadcast medium to a
participatory platform that allows people to become
the “media” themselves, since it provides the
functionalities for freely information sharing (X. Li
and Wang, 2011). As a result, through the
development of social media, single individuals can
now share their experiences with products and
companies to hundreds or thousands of others.
In recent years, social media have sparked a
revolution and emerged as an essential marketing tool
across all sectors, due to their substantial growth rate
(Islam, 2021). From a marketing perspective, social
media have transformed traditional practices by
facilitating two-way information exchange (J. Park
and Oh, 2012). Appel et al. (2020) suggested that
social media have become a vital marketing weapon
and communications channel for businesses,
organizations, and institutions, as well as consumers.
As stated in the introduction, social media
marketing activities (SMMA) are the specific actions
that implement the social media marketing strategy.
Different scholars have presented different social
media marketing activities that vary based on the
industry. The main conceptualizations are presented
in Table 1.
Table 1: Main Conceptualizations of SMMA across
Various Industries.
SMMA Industr
y
Sector Scholar
Entertainment
Interaction
Customization
Trendiness
Word of mouth
Luxury Fashion
Kim and
Ko (2012)
Interaction
Trendiness
Customization
Perceived ris
k
Insurance Services
Sano
(2015)
Informativeness
Trendiness
Interactivity
Personalization
Word of mouth
E-commerce
Yadav
and
Rahman
(2017)
Entertainment
Interaction
Trendiness
Customization
Perceived ris
k
Airline industry
Seo and
Park
(2018)
In the rapidly evolving landscape of hospitality,
social media marketing has become a pivotal tool to
engage with customers, build brand loyalty, and drive
revenue. The effectiveness of these marketing
activities is crucial for the success of hospitality in a
highly competitive market. To assess and enhance
the impact of social media marketing in the
hospitality industry, this research proposes to apply
Kim and Ko’s (2012) five-dimension framework
(entertainment, ccustomization, interaction, WOM,
and trendiness), which has been successfully adapted
and utilized in various industries, showcasing its
versatility and applicability (Godey et al., 2016; Zollo
et al., 2020). The hospitality industry, characterized
by its emphasis on customer experience and service
quality (Ali et al., 2021; Hemmington, 2007), aligns
well with the dimensions of the proposed model. The
dimension of entertainment is vital for generating
content that captivates guests and nurtures a brand
community (Bazi et al., 2023). Social media
interaction encompasses a two-way communication
process, which is essential for establishing strong
customer relationships (Lacap et al., 2024).
Developing a Research Framework Model for Assessing the Impact of Social Media Marketing Activities on Brand Loyalty
155

Trendiness allows hotels to stay current with the latest
industry trends and consumer preferences, ensuring
that their offerings remain appealing (Anita et al.,
2023).Customization, facilitated by AI in the
hospitality industry, allows for the alignment of
products and services with guest preferences, thereby
enhancing customer satisfaction and market
competitiveness (Manoharan et al., 2024). Lastly,
Word of mouth (WOM) is particularly potent in the
hospitality industry, where positive reviews and
recommendations can significantly influence booking
decisions (Gellerstedt and Arvemo, 2019). This
integrated approach to social media marketing, as
outlined by the framework, is poised to enhance the
strategic positioning and performance of hospitality.
Social media platforms enhance customer
relationship management by enabling real-time
interactions between firms and consumers and allow
aggressive advertising in target markets. Ample studies
have previously examined the impact of social media
on consumer relationships. For instance, Sultan and
Khan (2022) noted that social media significantly
impact branding by encouraging users to share
personal stories and brand-related details within their
social networks. Consumer-brand relationships (CBR),
as defined by Blackston (1992) and Chang and Chieng
(2006), are characterized as bonds that form either
spontaneously through consumer initiative or through
mutually dependent interactions. According to Ashley
and Tuten (2015), CBR are integral part not only to a
brand’s communication strategy and marketing
activities, but also to its ability to forge enduring
emotional connections with consumers through digital
platforms, including social media.
Fournier (1998) proposed a Brand Relationship
Quality (BRQ) model consisting of six dimensions:
love and passion, self-connection, interdependence,
commitment, intimacy, and partner quality. The BRQ
model offers a framework for understanding the
quality of relationships between consumers and
brands, as well as assessing the strength and durability
of these relationships. Over the years, scholars tend to
enrich this initial conceptualization by providing
additional constructs on the model such as: brand
attachment (Y. Liu et al., 2020; C. W. Park et al.,
2010), brand love (Palusuk et al., 2019), self-brand
connection (Escalas and Bettman, 2003; Hamzah et al.,
2021), brand identification (V. Kumar and Kaushik,
2018), and brand trust (Chaudhuri and Holbrook, 2001;
Jain et al., 2018; Khamitov et al., 2019). Existing
research consistently identifies these constructs as
predictors of loyalty, forming the foundation of CBR
(Albert and Thomson, 2018; Khamitov et al., 2019).
The highly competitive hospitality industry, which
relies heavily on guest loyalty, stands to gain
significantly from understanding how CBR influences
brand loyalty in its context (Alizadeh and Nazarpour
Kashani, 2022). Therefore, this study aims to
investigate the impact of the five constructs of CBR on
brand loyalty within the hospitality industry,
identifying key factors in the formation of brand
loyalty and aligning with the theoretical framework
and practical application of CBR.
One of the strategic objectives of marketing
activities is to create loyalty through branding.
Initially, scholars generally refer to brand loyalty as
consumers’ repeated purchase behaviour for a specific
brand (Guest, 1944; Harary and Lipstein, 1962;
Tucker, 1964). While this initial definition is still
relevant and valuable, in the recent years the definition
of brand loyalty has developed into a multi-
dimensional concept, including also the dimensions of
trust as well as preference. Scholars have increasingly
focused on the mechanisms behind brand loyalty,
examining how factors such as consumer satisfaction
(Ha et al., 2009; Oliver, 1999; Punniyamoorthy and
Prasanna Mohan Raj, 2007), service quality
(Alexandris et al., 2008; Reich et al., 2006; Zehir et al.,
2011) and brand image (Alić et al., 2020; Keller, 2001)
affect consumers’ loyalty behaviour.
The Stimulus-Organism-Response (SOR)model,
grounded in environmental psychology and initially
proposed by Mehrabian and Russell in 1974, is
utilized to illustrate how external environmental
stimuli (S) influence an individual’s internal state
(O), leading to particular behavioural responses (R)
(Mehrabian and Russell, 1974). It is a prominent
model in consumer behaviour research, particularly in
the field of social media marketing. This model plays
a vital role in discussing the relationships among
SMMA, brand equity (Peng et al., 2024), brand
experience (S. Kumar and Hsieh, 2024),brand loyalty
(Changani and Kumar, 2023), purchase intention (Ho
et al., 2024) and E-WOM(Seo and Park, 2018).This
research employs the SOR model for three reasons.
First, it provides a theoretical framework that facilitates
a systematic analysis of SMMA as external stimuli (S)
impacting CBR as the organism (O). Second, the
model elucidates the transformation of these internal
states into behavioural responses (R), specifically
brand loyalty. Finally, the SOR model’s extensive
application and recognition in the domain of consumer
behaviour research, ensure its reliability as a proven
framework for examining and interpreting consumer
behaviours within the social media contexts.
Conclusively, the proposed theoretical framework
synthesises the SOR model with Kim and Ko’s five-
dimensional framework, providing a comprehensive
FEMIB 2025 - 7th International Conference on Finance, Economics, Management and IT Business
156
examination of the effects of SMMA on brand loyalty
within the hospitality industry. It delineates the
pivotal dimensions of CBR and elucidates their
potential to influence loyalty, thereby offering a
robust analytical tool for understanding and
predicting consumer behaviour in this context.
3 A FRAMEWORK MODEL FOR
ASSESSING THE IMPACT OF
SOCIAL MEDIA MARKETING
ACTIVITIES ON BRAND
LOYALTY
3.1 The Need for the Model
Previous studies on SMMA have mostly focused on
the fashion retail brands(Safeer, 2024), property(Ho
et al., 2024) and airlines industries (Khan et al.,
2024),with limited empirical research on how SMMA
affects brand loyalty via the mediating role of CBR in
the hospitality industry. The complex interplay
between SMMA, CBR, and brand loyalty remains
underexplored in the literature, highlighting a critical
research need for both conceptual and empirical
investigations into these interactions.
Addressing this gap, the study aims to develop a
comprehensive model that outlines a clear research
agenda, focusing on the elements that drive customer
behaviour with an emphasis on brand loyalty. This
model is essential for deciphering the mechanisms
through which SMMA can strengthen brand loyalty
by leveraging CBR, and it provides a strategic
blueprint for the hospitality industry to enhance its
marketing efforts.
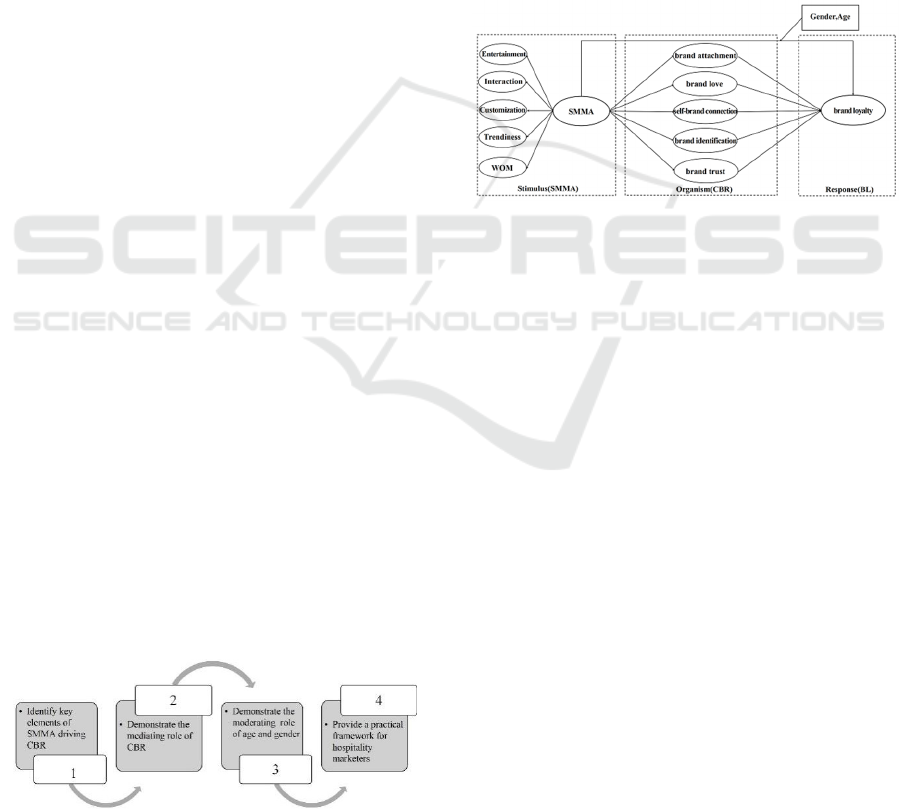
As illustrated in Figure 1, the proposed model
serves a quadruple purpose: (1) identifying the critical
components of SMMA that drive CBR, (2)
demonstrating the mediating effect of CBR on the
relationship between SMMA and brand loyalty, (3)
examining the moderating influence of gender and
age in the SMMA-brand loyalty relationship, and (4)
providing a practical guide for hospitality marketers.
Figure 1: Proposed Framework Model Objectives.
3.2 The Proposed Model
This model, has its intellectual roots on SOR
framework, that aims to examine the impact of
SMMA, including entertainment, interaction,
customization, trendiness, and WOM, as external
stimuli on the CBR. By doing so, the research seeks
to enhance our understanding of how these activities
can foster brand loyalty.
Building on the findings of previous research
(Bushara et al., 2023; Ibrahim and Aljarah, 2021;
Khan et al., 2024; Sohaib et al., 2024), this study
adopts the SOR model to investigate the intrinsic
relationships among SMMA, CBR, and BL within the
hospitality industry. The proposed model is depicted
in Figure 2.
Figure 2: The Proposed Framework Model.
As it is proposed to the model, SMMA are used as
external stimuli (S), CBR is used as a regulatory
mechanism (O), and brand loyalty, represent the
response (R) as the ultimate outcome. Specifically,
SMMA provide hotel information, customer reviews,
promotional activities and other content to form an
initial stimulus to consumers (S). After receiving this
information, consumers will evaluate the service
quality and brand image of the hotel, based on their
own knowledge framework, needs, and expectations.
In this process, CBR plays a vital role (O), which can
not only enhance consumers’ trust in the hotel, but
also improve consumers’ satisfaction through
personalized service and care. BL is the final
behavioural response (R), which reflects consumers’
continued preference for hotel brands and willingness
to repurchase. The effective use of social media and
high-quality customer relationship management work
together to form and enhance brand loyalty.
By applying this proposed model, scholars and
practitioners will be able to answer the following
research questions:
RQ 1 What is the impact of SMMA on CBR, and
which dimension of SMMA has the greatest
influence?
Developing a Research Framework Model for Assessing the Impact of Social Media Marketing Activities on Brand Loyalty
157

RQ2 How do CBR influence BL, and which
dimension of CBR has the greatest impact on BL?
RQ3 What is the mediating role of CBR in the
relationship between SMMA and BL?
RQ4 What is the moderating role of gender and
age in the relationship between SMMA and BL?
4 CONCLUSIONS
The purpose of this study is to establish research
agenda that captures the interactions among social
media marketing activities, customer brand
relationship, and brand loyalty in a systemic manner.
As a result, a conceptual framework is proposed. The
framework makes a substantial contribution to both
the academic literature and the practical strategies of
the hospitality industry. Specifically, it proposed the
application of the SOR model in the context of
hospitality sector, offering a novel approach of
integrating social media marketing activities with the
dimensions of the consumer-brand relationship. This
integration deepens the understanding of the
dynamics between brands and consumers in the
digital economy, and offers both theoretical insights
and practical implications for enhancing brand
loyalty through social media specific activities.
Furthermore, the study acknowledges the
importance of quantitative research in establishing
causal relationships. While the current research lays
the conceptual groundwork, it also highlights the
necessity for empirical investigation to quantify the
effects of social media marketing activities on CBR
and brand loyalty. Subsequent research will involve a
quantitative study to determine the precise
relationships among the variables in the proposed
framework. This quantitative approach will be key to
measuring the impact of social media stimuli on user
behavior, considering the moderating effects of
gender and age. This nuanced understanding will
facilitate a more informed approach to social media
marketing strategies, tailored to the diverse needs and
preferences of different demographic segments.
In summary, this research presents a robust and
applicable framework that seeks to elucidate the
critical role of social media marketing in the
hospitality industry. The findings aim to set the
foundation for future empirical research. The
recommendations provided will be further refined
through quantitative analysis, offering practitioners
evidence-based strategies to optimize their marketing
efforts and maintain a competitive edge in the digital
marketplace.
REFERENCES
Albert, N., & Thomson, M. (2018). A synthesis of the
consumer-brand relationship domain: using text mining
to track research streams, describe their emotional
associations, and identify future research priorities.
Journal of the Association for Consumer Research, 3(2),
130-146.
Alexandris, K., Douka, S., Papadopoulos, P., & Kaltsatou, A.
(2008). Testing the role of service quality on the
development of brand associations and brand loyalty.
Managing Service Quality: An International Journal,
18(3), 239-254.
Ali, B. J., Gardi, B., Othman, B. J., Ahmed, S. A., Ismael, N.
B., Hamza, P. A., Aziz, H. M., Sabir, B. Y., Sorguli, S.,
& Anwar, G. (2021). Hotel service quality: The impact
of service quality on customer satisfaction in hospitality.
International Journal of Engineering, Business
Management and Marketing, 5(3), 14-28.
Alić, A., Činjarević, M., & Agić, E. (2020). The role of brand
image in consumer-brand relationships: similarities and
differences between national and private label brands.
Management Marketing, 15(1), 1-16.
Alizadeh, H., & Nazarpour Kashani, H. (2022). Effect of
brand-consumer relationships on brand loyalty mediated
by brand value creation and moderated by brand
community characteristics in the hospitality industry.
Revista Brasileira de Gestao de Negocios, 24, 594-616.
Anas, A. M., Abdou, A. H., Hassan, T. H., Alrefae, W. M.
M., Daradkeh, F. M., El-Amin, M. A.-M. M., Kegour, A.
B. A., & Alboray, H. M. M. (2023). Satisfaction on the
Driving Seat: Exploring the Influence of Social Media
Marketing Activities on Followers’ Purchase Intention in
the Restaurant Industry Context. Sustainability, 15(9).
doi:10.3390/su15097207
Anita, T. L., Muslikhin, M., Zulkarnain, A., & Wiyana, T.
(2023). Enhancing Customer Satisfaction in Hotel
Industry Through Chatbot as E-Services Agent and
Communication Credibility. Paper presented at the 6th
International Seminar on Research of Information
Technology and Intelligent Systems, ISRITI 2023 -
Proceeding.
Appel, G., Grewal, L., Hadi, R., & Stephen, A. T. (2020). The
future of social media in marketing. Journal of the
Academy of Marketing Science, 48(1), 79-95.
Ashley, C., & Tuten, T. (2015). Creative strategies in social
media marketing: An exploratory study of branded social
content and consumer engagement. Psychology
marketing, 32(1), 15-27.
Baines, P., Whitehouse, S., Rosengren, S., & Antonetti, P.
(2021). Fundamentals of Marketing, Oxford University
Press. New York, 2
nd
edition.
Bazi, S., Filieri, R., & Gorton, M. (2023). Social media
content aesthetic quality and customer engagement: The
mediating role of entertainment and impacts on brand
love and loyalty. Journal of Business Research, 160,
113778.
Beqiri., G., & Qenaj, M. (2022). Social media marketing in
hospitality industry and its effect on consumer behavior
in Kosovo. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 55(39), 66-69.
FEMIB 2025 - 7th International Conference on Finance, Economics, Management and IT Business
158

Blackston, M. (1992). Observations: Building brand equity
by managing the brand's relationships. Journal of
Advertising Research, 32(3), 79-83.
Bushara, M. A., Abdou, A. H., Hassan, T. H., Sobaih, A. E.
E., Albohnayh, A. S. M., Alshammari, W. G., Aldoreeb,
M., Elsaed, A. A., & Elsaied, M. A. (2023). Power of
Social Media Marketing: How Perceived Value Mediates
the Impact on Restaurant Followers’ Purchase Intention,
Willingness to Pay a Premium Price, and E-WoM?
Sustainability, 15(6). doi:10.3390/su15065331
Chang, P. L., & Chieng, M. H. (2006). Building consumer–
brand relationship: A cross‐cultural experiential view.
Psychology marketing, 23(11), 927-959.
Changani, S., & Kumar, R. (2023). How Social Media
Marketing Enhances Brand Communities Engagement:
Developing an Integrated Model Using SOR Paradigm.
Paper presented at the International Working Conference
on Transfer and Diffusion of IT.
Chaudhuri, A., & Holbrook, M. B. (2001). The chain of
effects from brand trust and brand affect to brand
performance: the role of brand loyalty. Journal of
marketing, 65(2), 81-93.
Chung, W. J., & Jeong, C. (2024). The role of social media
engagement in the purchase intention of South Korea's
popular media (Hallyu) tourism package: based on uses
and gratifications theory. Asia Pacific Journal of Tourism
Research, 29(1), 17-30.
de Oliveira Santini, F., Ladeira, W. J., Pinto, D. C., Herter,
M. M., Sampaio, C. H., & Babin, B. J. (2020). Customer
engagement in social media: a framework and meta-
analysis. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science,
48, 1211-1228.
Dwivedi, Y. K., Ismagilova, E., Hughes, D. L., Carlson, J.,
Filieri, R., Jacobson, J., Jain, V., Karjaluoto, H., Kefi, H.,
& Krishen, A. S. (2021). Setting the future of digital and
social media marketing research: Perspectives and
research propositions. International journal of
information management, 59, 102168.
Escalas, J. E., & Bettman, J. R. (2003). You are what they
eat: The influence of reference groups on consumers’
connections to brands. Journal of Consumer Psychology,
13(3), 339-348.
Fournier, S. (1998). Consumers and their brands: Developing
relationship theory in consumer research. Journal of
Consumer Research, 24(4), 343-373.
Gellerstedt, M., & Arvemo, T. (2019). The impact of word of
mouth when booking a hotel: could a good friend’s
opinion outweigh the online majority? Information
Technology & Tourism, 21(3), 289-311.
Godey, B., Manthiou, A., Pederzoli, D., Rokka, J., Aiello, G.,
Donvito, R., & Singh, R. (2016). Social media marketing
efforts of luxury brands: Influence on brand equity and
consumer behavior. Journal of Business Research,
69(12), 5833-5841. doi:10.1016/j.jbusres.2016.04.181
Guest, L. (1944). A study of brand loyalty. Journal of Applied
Psychology, 28(1), 16.
Ha, H. Y., Janda, S., & Park, S. K. (2009). Role of satisfaction
in an integrative model of brand loyalty: Evidence from
China and South Korea. International Marketing Review,
26(2), 198-220.
Hamzah, Z. L., Abdul Wahab, H., & Waqas, M. (2021).
Unveiling drivers and brand relationship implications of
consumer engagement with social media brand posts.
Journal of Research in Interactive Marketing, 15(2), 336-
358.
Harary, F., & Lipstein, B. (1962). The dynamics of brand
loyalty: A Markovian approach. Operations Research,
10(1), 19-40.
Hemmington, N. (2007). From service to experience:
Understanding and defining the hospitality business. The
Service Industries Journal, 27(6), 747-755.
Ho, L. S., Zakaria, N. B., & Foo, S. M. (2024). The impact of
social media marketing activities on customer purchase
intention: a study of the property industry in Malaysia.
Property Management. doi:10.1108/pm-07-2023-0066
Ibrahim, B. (2021b). The nexus between social media
marketing activities and brand loyalty in hotel facebook
pages: A multi-group analysis of hotel ratings. Tourism,
69(2), 228-245. doi:10.37741/t.69.2.5
Ibrahim, B., & Aljarah, A. (2021). The era of Instagram
expansion: matching social media marketing activities
and brand loyalty through customer relationship quality.
Journal of Marketing Communications, 29(1), 1-25.
doi:10.1080/13527266.2021.1984279
Islam, M. T. J. S. J. o. M. (2021). Applications of social
media in the tourism industry: A review. 4(1), 59-68.
Jain, N. K., Kamboj, S., Kumar, V., & Rahman, Z. (2018).
Examining consumer-brand relationships on social
media platforms. Marketing Intelligence & Planning,
36(1), 63-78. doi:10.1108/mip-05-2017-0088
Keller, K. L. (2001). Building customer-based brand equity:
A blueprint for creating strong brands.
Khamitov, M., Wang, X., Thomson, M., Morwitz, V. G.,
Inman, J. J., & Hoegg, J. (2019). How Well Do
Consumer-Brand Relationships Drive Customer Brand
Loyalty? Generalizations from a Meta-Analysis of Brand
Relationship Elasticities. Journal of Consumer Research,
46(3), 435-459. doi:10.1093/jcr/ucz006
Khan, M. F., Amin, F., Jan, A., & Hakak, I. A. (2024). Social
media marketing activities in the Indian airlines: Brand
equity and electronic word of mouth. Tourism and
Hospitality Research. doi:10.1177/14673584241237436
Kim, A. J., & Ko, E. (2012). Do social media marketing
activities enhance customer equity? An empirical study
of luxury fashion brand. Journal of Business Research,
65(10), 1480-1486. doi:10.1016/j.jbusres.2011.10.014
Kumar, S., & Hsieh, J.-K. (2024). How social media
marketing activities affect brand loyalty? Mediating role
of brand experience. Asia Pacific Journal of Marketing
and Logistics. doi:10.1108/apjml-09-2023-0900
Kumar, V., & Kaushik, A. K. (2018). Building consumer–
brand relationships through brand experience and brand
identification. Journal of Strategic Marketing, 28(1), 39-
59. doi:10.1080/0965254x.2018.1482945
Lacap, J. P. G., Cruz, M. R. M., Bayson, A. J., Molano, R.,
& Garcia, J. G. (2024). Parasocial relationships and
social media interactions: building brand credibility and
loyalty. Spanish Journal of Marketing-ESIC, 28(1), 77-
97.
Developing a Research Framework Model for Assessing the Impact of Social Media Marketing Activities on Brand Loyalty
159

Leung, D., Law, R., van Hoof, H., & Buhalis, D. (2013).
Social Media in Tourism and Hospitality: A Literature
Review. Journal of Travel & Tourism Marketing, 30(1-
2), 3-22. doi:10.1080/10548408.2013.750919
Li, F., Larimo, J., & Leonidou, L. C. (2021). Social media
marketing strategy: definition, conceptualization,
taxonomy, validation, and future agenda. Journal of the
Academy of Marketing Science, 49, 51-70.
Li, X., & Wang, Y. (2011). China in the eyes of western
travelers as represented in travel blogs. Journal of Travel
Tourism Marketing, 28(7), 689-719.
Liu, J., Wang, C., Zhang, T., & Qiao, H. (2022). Delineating
the Effects of Social Media Marketing Activities on
Generation Z Travel Behaviors. Journal of Travel
Research, 62(5), 1140-1158. doi:10.1177/004728752
21106394
Liu, Y., Kou, Y., Guan, Z., Hu, J., & Pu, B. (2020). Exploring
hotel brand attachment: The mediating role of
sentimental value. Journal of Retailing and Consumer
Services, 55. doi:10.1016/j.jretconser.2020.102143
Manoharan, G., Ashtikar, S. P., & Kumar, S. (2024).
Delineation of artificial intelligence in the hospitality and
tourism industries. In Impact of AI and Tech-Driven
Solutions in Hospitality and Tourism (pp. 20-42): IGI
Global.
Mehrabian, A., & Russell, J. A. (1974). An approach to
environmental psychology, the MIT Press.
Oliver, R. L. (1999). Whence consumer loyalty? Journal of
marketing, 63(4_suppl1), 33-44.
Palusuk, N., Koles, B., & Hasan, R. (2019). ‘All you need is
brand love’: a critical review and comprehensive
conceptual framework for brand love. Journal of
Marketing Management, 35(1-2), 97-129.
Park, C. W., MacInnis, D. J., Priester, J., Eisingerich, A. B.,
& Iacobucci, D. (2010). Brand attachment and brand
attitude strength: Conceptual and empirical
differentiation of two critical brand equity drivers.
Journal of Marketing Communications, 74(6), 1-17.
Park, J., & Oh, I.-K. (2012). A case study of social media
marketing by travel agency: The salience of social media
marketing in the tourism industry. International Journal
of Tourism Sciences, 12(1), 93-106.
Peng, L., Adeel, I., Ayub, A., & Rasool, Z. (2024).
Investigating the Roles of Word of Mouth and Brand
Image Between Social Media Marketing Activities and
Brand Equity. SAGE Open, 14(1). doi:10.1177/
21582440231220113
Petrosyan, A. (2024, 20240522). Number of internet and
social media users worldwide as of April 2024. Retrieved
from https://www.statista.com/statistics/617136/digital-
population-worldwide/
Punniyamoorthy, M., & Prasanna Mohan Raj, M. (2007). An
empirical model for brand loyalty measurement. Journal
of Targeting, Measurement and Analysis for Marketing,
15(4), 222-233. doi:10.1057/palgrave.jt.5750044
Reich, A. Z., McCleary, K. W., Tepanon, Y., & Weaver, P.
A. (2006). The impact of product and service quality on
brand loyalty: An exploratory investigation of quick-
service restaurants. Journal of Foodservice Business
Research, 8(3), 35-53.
Safeer, A. A. (2024). Harnessing the power of brand social
media marketing on consumer online impulse buying
intentions: a stimulus-organism-response framework.
Journal of Product & Brand Management.
doi:10.1108/jpbm-07-2023-4619
Sano, K. (2015). An empirical study the effect of social
media marketing activities upon customer satisfaction,
positive word-of-mouth and commitment in indemnity
insurance service. Paper presented at the Proceedings
International Marketing Trends Conference.
Seo, E.-J., & Park, J.-W. (2018). A study on the effects of
social media marketing activities on brand equity and
customer response in the airline industry. Journal of Air
Transport Management, 66, 36-41.
Sohaib, M., Safeer, A. A., & Majeed, A. (2024). Does firm-
created social media communication develop brand
evangelists? Role of perceived values and customer
experience. Marketing Intelligence and Planning.
doi:10.1108/MIP-09-2023-0465
Sultan, A.-M., & Khan, Z. A. (2022). Impact of advantageous
campaigns on customer-brand relationship building
through social media marketing. Journal of Business
Management Studies, 4(1), 34-41.
Tucker, W. T. (1964). The development of brand loyalty.
Journal of Marketing Research, 1(3), 32-35.
Verissimo, M., & Menezes, N. (2015). Social media as a tool
to enhance customer experience in hospitality industry.
Portuguese Journal of Marketing/Revista Portuguesa de
Marketing(34).
Yadav, M., & Rahman, Z. (2017). Measuring consumer
perception of social media marketing activities in e-
commerce industry: Scale development & validation.
Telematics and Informatics, 34(7), 1294-1307.
Yoong, L. C., & Lian, S. B. (2019). Customer engagement in
social media and purchase intentions in the hotel
industry. International Journal of academic research in
business social sciences, 9(1), 54-68.
Zehir, C., Şahin, A., Kitapçı, H., & Özşahin, M. (2011). The
effects of brand communication and service quality in
building brand loyalty through brand trust; the empirical
research on global brands. Procedia-Social behavioral
sciences, 24, 1218-1231.
Zollo, L., Filieri, R., Rialti, R., & Yoon, S. (2020). Unpacking
the relationship between social media marketing and
brand equity: The mediating role of consumers’ benefits
and experience. Journal of Business Research, 117, 256-
267.
FEMIB 2025 - 7th International Conference on Finance, Economics, Management and IT Business
160
