
Who Knows Who: A Context-Based Approach to
Network Generation for Social Simulations
Veronika Kurchyna
∗
, Philipp Fl
¨
ugger, Ye Eun Bae, Jan Ole Berndt and Ingo J. Timm
German Research Center for Artificial Intelligence (DFKI),
Cognitive Social Simulation, Behringstr. 21, 54296 Trier, Germany
Keywords:
Synthetic Population, Network Generation, Agent-Based Modelling.
Abstract:
Established network models (small-world, preferential attachment, random, etc.) often fail to capture the full
range of characteristics observed in real social networks, potentially limiting the transferability of model re-
sults. To address this limitation, we propose a Contextual Network Model that is superimposed on a synthetic
population. The model takes into account sociodemographic agent-traits and location data, such as workplaces
and frequent leisure activities, to construct a realistic network. To showcase the effect of network topology
on model dynamics, we investigate a Susceptible-Infectious-Removed (SIR) model with information diffu-
sion by comparing our proposed network model with the aforementioned established network models. The
study identifies an earlier, lower peak of infectious agents, along with a greater number of susceptible agents
remaining at the end of the simulation for the proposed network model. Moreover, the study underscores the
measurable impact of network topology on model behaviour, revealing different expansion rates and patterns
in the information diffusion process. Additionally, this work offers instructions for a customisable implemen-
tation of a contextual network model generator for other agent-based models and populations.
1 INTRODUCTION
Recent phenomena, such as pandemics or opinion
dynamics in social media have driven the develop-
ment of numerous simulation models. These mod-
els are aimed at gaining insight into the function-
ing of social mechanisms, such as the dual causal-
ity between individual and collective actions during
an epidemic (Palomo-Briones et al., 2022), assess-
ing interventions like non-pharmaceutical interven-
tions during the COVID-19 pandemic (Kerr et al.,
2021), and optimizing the allocation of scarce re-
sources, such as water distribution (Khorshidi et al.,
2024). Such models differ, among other aspects,
in their complexity regarding agent behaviour and
the socio-spatial networks of interactions and trans-
missions (Lorig et al., 2021). Ideally, social net-
works generated for agent-based social simulations
should mirror their real-world counterparts by ex-
hibiting observable properties and measurable prop-
erties. However, common approaches often disre-
gard contextual information, such as the nature of
the network, the characteristics of nodes, or the dis-
tribution of edges. In reality, social relations are
∗
Corresponding author
shaped by personal attributes, such as age and edu-
cation, along with common activities like workplaces
or frequent leisure activities (McPherson et al., 2001).
We propose a method for generating a context-based
network model, along with a prototype implementa-
tion, designed to compare against classical social net-
work approaches in agent-based models (ABM). This
method focuses on replicating properties that charac-
terise real-world social networks.
2 BACKGROUND AND RELATED
WORK
We introduce the main observable properties of social
networks and classical approaches to network gener-
ation. Additionally, we investigate how comparable
network model approaches are implemented in the
context of agent-based models.
2.1 Characteristics of Social Networks
Social networks can be represented by graphs, where
agents are depicted as nodes and their social relations
as edges (Marin and Wellman, 2011). Arbitrary sets
342
Kurchyna, V., Flügger, P., Bae, Y. E., Berndt, J. O. and Timm, I. J.
Who Knows Who: A Context-Based Approach to Network Generation for Social Simulations.
DOI: 10.5220/0013141900003890
In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2025) - Volume 1, pages 342-350
ISBN: 978-989-758-737-5; ISSN: 2184-433X
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

of edges (like the Erd
¨
os-R
´
enyi random network) do
not necessarily form a realistic representation of a so-
cial network. Hamill and Gilbert (2009) aggregated
essential structural properties of social networks as
identified by various researchers:
• Low Density. Only a fraction of possible connec-
tions exists in social network graphs.
• Limited Personal Network Size. The number of
social contacts is limited, higher numbers increas-
ingly unlikely, eventually approaching zero.
• Variation in Personal Network Size. The size of
personal networks varies, with some individuals
having large networks while others have smaller
networks.
• Fat-Tail Distribution. Extreme values occur
more often compared to a normal distribution.
• Assortativity. High-degree nodes are more likely
to connect with other high-degree nodes, while
low-degree nodes tend to link with other low-
degree nodes. This results in clusters of agents
with similar connectivity levels.
• High Clustering. A node’s connections tend to
be interconnected, reflecting the transitivity of so-
cial relations (Bruggeman, 2013). This property
can be quantified using the average clustering co-
efficient.
• Communities. Communities are characterized by
a high local clustering coefficient, with most con-
nections concentrated within the community and
relatively few edges extending to nodes outside
the community.
• Short Path Lengths. Nodes are reachable over a
small number of edges from any other node in the
network, leading to a small-world effect.
2.2 Properties of Social Relations
In addition to large-scale effects on the entire net-
work, specific properties of social relations help ex-
plain how those relations between agents are formed.
• Homophily. Individuals seek ties to similar peo-
ple across sociodemographic, behavioural, and in-
trapersonal dimensions. A hierarchical relation-
ship of characteristics has been found - some
traits, such as ethnicity, are stronger associ-
ated with homophilic preference than other at-
tributes (McPherson et al., 2001).
• Reciprocity. Symmetry is favoured over unre-
ciprocated connections in social relations (Hal-
linan, 1978). Asymmetric ties are resolved by
breaking off contact or by transforming into a
mutual relationship (Cook and Emerson, 1987).
As such, friendship is modelled as an undirected
edge (Krackhardt, 2003).
• Transitivity. Individuals tend to be friends with
the friends of their friends, which is a smaller-
scale symptom of the high clustering of networks.
The risk of circularity makes this a non-trivial
issue (Arentze et al., 2012). An iterative ap-
proach is typically used to model transitive rela-
tionships (Arentze et al., 2013).
• Assortativity. People frequently associate with
people of similar connection degrees, meaning
that individuals with large contact networks most
frequently connect to others with similarly large
networks and vice versa for low-connected indi-
viduals (Badham and Stocker, 2010).
2.3 Network Models
Four types of network models are commonly used in
social simulations (Hamill and Gilbert, 2009). These
models only receive basic parameters as input to gen-
erate the edges between nodes. These approaches pro-
vide a valuable benchmark, offering a foundational
framework for novel approaches.
• Regular Lattice. Each node is linked to its
four neighbors in a spatially explicit network.
The result yields a uniform distribution of de-
grees (Hamill and Gilbert, 2009).
• Random Network. Nodes can connect to any
other node. While the degree is not limited, ob-
servations show that most nodes are likely to have
a similar degree. Nodes with significantly fewer
or more edges are rare (Barab
´
asi and Bonabeau,
2003).
• Small-World. By rewiring a few edges in a regu-
lar lattice model, short path lengths and high clus-
tering are achieved (Watts and Strogatz, 1998).
Regarding the characteristics of social networks,
this approach improves upon the previous two
networks in terms of social network characteris-
tics (Dorogovtsev and Mendes, 2003).
• Preferential Attachment. The scale-free model
is characterized by new nodes connecting to ex-
isting nodes with a greater number of links at a
higher probability. The result features highly con-
nected hubs and nodes with significantly different
numbers of edges (Barab
´
asi and Albert, 1999).
Who Knows Who: A Context-Based Approach to Network Generation for Social Simulations
343

2.4 Related Work: Approaches to Social
Network Generation
Other approaches leverage domain-specific knowl-
edge from social sciences and social network analysis
to better represent real-life structures.
Local interactions occurring during agents’ move-
ment in space offer a method for modelling contacts
between agents as they move and cross paths (Caux
et al., 2014). While networks grow organically in this
manner, this approach violates the assortativity cri-
terion typical of social networks. Alternatively, fol-
lowing the proposed ego-network approach of Conti
et al. (2011), networks are initialised based on dif-
ferent types of relationships, resulting in a hierarchi-
cal structure of social groups. This approach demon-
strates the way relationships can be classified, poten-
tially independent of the way these contacts were cho-
sen.
As an in-between approach, social circles map
agents and relationships onto a continuous space,
where proximity indicates closer relationships. The
social reach (radius of social circle) limits the size
of the personal network of an agent. A small social
reach may characterize the network of a family or
close friends, while a large social reach may repre-
sent acquaintances, such as work colleagues (Hamill
and Gilbert, 2009). Moreover, Kapeller et al. (2019)
investigated the impacts of homophilic attribute dis-
tributions on a basic diffusion model by separating
the processes of network generation (structural prox-
imity) and attribute distribution (attribute proximity).
They found that homophilic distribution is essential
for a more accurate analysis of collective behaviour
Talaga and Nowak (2019) and also examined the ex-
tent of homophily necessary to accurately represent
typical social networks by combining it with a ran-
dom edge rewiring. They concluded that homophily
plays a crucial role in generating social networks and
is versatile to be applied across various social struc-
tures.
3 DESCRIPTION OF
CONTEXTUAL NETWORK
MODELS IN THE STUDY
Based on the characteristics of social networks and
related works, we provide a guideline for generating a
context-based network by leveraging individual-level
attributes from a synthetic population.
3.1 Determining Homophilic
Preferences
The model applies the concept of homophily
where similarity positions individuals closer to each
other (Hamill and Gilbert, 2009). Social distance
is explicitly incorporated by computing pairwise dis-
tances between agents. People in proximity are pre-
ferred over remote agents during the initial network
generation process to ensure homophilic preferences
for social relations. Depending on the type of at-
tribute (categorical or metric), appropriate similarity
measures like the Euclidean distance or the Jaccard
index are applied.
Although geographic location may be considered
as the most fundamental form of homophily (McPher-
son et al., 2001), the introduction of new means of
digital communication may have dampened this ef-
fect (Kaufer and Carley, 1984). To incorporate the
increasing relevance of digital interaction patterns,
we exclude location-dependent attributes for one part
(∼10%) of the overall edges in the network.
The average personal network sizes range from
69 to 109 individuals, with large confidence intervals
making it challenging to determine the exact size of
a network (Lindenfors et al., 2021). This information
can be used to parameterize a fat-tailed distribution,
enabling the sampling of personal network sizes for
each agent. By incorporating personal network size
as an individual-level attribute during the similarity
computation, an assortative bias can be integrated into
the network.
3.2 Incorporating Transitivity
To capture the transitive tendency of social relations,
the process begins by adding a subset of edges to the
final graph, referred as the inner circle, which repre-
sents the closest contacts for each agents. This sub-
set can then be used to enhance the similarity for any
node x that is connected to node z through a path with
length = 2 without repeated edges. In other words,
the likelihood of nodes x and z forming a relation in
the following step is increased if they share a common
node y in their neighborhood.
This is done to avoid what Arentze et al. call
“a problem of endogeneity”. Incorporating transitiv-
ity into the network generation process requires in-
formation on mutual connections or common friends.
However, identifying these connections is only possi-
ble after the network has been created (Arentze et al.,
2012, 2013), as they depend on the existing relation-
ships between nodes. A multi-step procedure thus al-
lows the identification of transitivity-enhancing con-
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
344

nections by identifying common connections of two
agents. The remaining contacts, referred to as the
outer circle, are then added based on the updated sim-
ilarities, with edges iteratively added between agents
exhibiting the highest similarity.
3.3 Social Network Constraints
To construct a realistic network, the approach pre-
sented so far has to adhere to the constraints listed
in section 2 (Hamill and Gilbert, 2009). Many of
these constraints can be directly addressed by choos-
ing an appropriate edge distribution (or personal net-
work size distribution). We chose a gamma distribu-
tion, which requires shifting and scaling to align with
typical network sizes (Lindenfors et al., 2021). This
way a low network density can be achieved, though
the exact magnitude of network density is directly in-
fluenced by the examined population size, as the sam-
pled network sizes represent absolute rather than rel-
ative values. However, this effect can be neglected
when working with sufficiently large populations.
The applied parameterized gamma distribution ex-
hibits a fat-tail, while simultaneously limiting the
probability of extraordinary high values. Sampling
from this distribution yields personal networks that
vary in size, exhibit a fat-tail distribution, show a low
density for typical population sizes, and have a practi-
cal size limit due to increasingly unlikely probabilities
for higher values.
Assortativity represents one of the main properties
that differentiates established network models, such
as Preferential Attachment, from models focused on
the representation of social relations. At its core, as-
sortativity describes a homophilic preference of nodes
to connect to other nodes with a similar degree. This
allows us to incorporate the node degree into the sim-
ilarity computation as described in section 3.1. By
adjusting the weight of this attribute when calculating
similarities, the final network can be made more or
less assortative.
As clustering and transitivity represent two
closely related topics in graph theory (Schank and
Wagner, 2005), our iterative implementation of the
inner and outer circle results in an improved global
clustering coefficient compared to approaches with-
out transitivity during the network generation process.
Communities are characterized by a high local
clustering coefficient, while being only loosely con-
nected to the networks remaining nodes. This loose
connection to other nodes primarily depends on the
distribution of the agents attributes. By employing
similarity measures such as the Jaccard index, these
loose connections can be emphasized, in contrast to
the more uniform connections expected by the Eu-
clidean distance. This works because we apply the
Jaccard index as a binary similarity coefficient that
produces polarized similarity values ∈ {0, 1}. Ulti-
mately, the resulting community structure of the fi-
nal network, heavily depends on whether such struc-
tures exist in the provided attribute distribution of the
agents.
Short path lengths are realized by including digi-
tal relations in the similarity computation. These re-
lations, which form independently of location, tend
to connect distant clusters of agents, as they are not
constrained by spatial proximity.
Reciprocity can be simply implemented by adding
the inverse edge for each contact, ensuring that the
relationships are always mutual.
4 USE CASE: INFORMATION
DIFFUSION
To illustrate the impact of network structure on model
behaviour, transmission processes such as informa-
tion diffusion or disease spreads are well suited. We
demonstrate the effects of this network generation ap-
proach with a synthetic population simulating infor-
mation diffusion using a SIR model.
4.1 Synthetic Population Generation
Synthetic populations, simulated to mimic real popu-
lations, are pivotal in research, especially microsimu-
lation, providing substitutes for real data due to cost
and privacy issues. They facilitate detailed individual-
level modeling and analysis when direct data access is
limited or too expensive to obtain (Barthelemy and
Toint, 2013). Commonly generated using Iterative
Proportional Fitting (IPF), synthetic populations align
aggregated data with specific sociodemographic at-
tributes (Frick, 2004) such as age, gender and house-
hold location (Cajka et al., 2010). These attributes
ensure accurate representation but may be limited by
available data.
We use a synthetic population to generate a re-
alistic social network, requiring detailed information
about individuals. Our example population is based
on Kaiserslautern, Germany, with about 100,000 peo-
ple, based on 2011 census data and household grids.
We apply to assign workplaces, schools, and kinder-
gartens to each person. Using synthetic populations
enhances credibility compared to randomly generated
ones and alleviates privacy concerns, as no personal
data is involved. An exemplary excerpt with three
households is shown in Table 1.
Who Knows Who: A Context-Based Approach to Network Generation for Social Simulations
345

4.2 Simulating Information Diffusion
Using Epidemic Models
Information Diffusion (ID) is the flow of informa-
tion between entities in a network (Li et al., 2017),
similarly to disease contagion that involves suscepti-
ble nodes and active spreaders. Infection dynamics
are characterised by state transitions between differ-
ent groups. The most typical model of contagion is
the Susceptible-Infectious-Removed Model (SIR)(Li
et al., 2017), which will be used in this example.
This model class proves to be quite versatile, be-
cause the slight modifications to the groups and tran-
sition processes between them are allowing to adapt
the model to various scenarios. Some models within
this class incorporate additional agent groups, such
as an exposed (E) group (e.g. the SEIR model), pro-
viding a more precise representation of specific pro-
cesses.
4.3 Agent-Based Model for Evaluation
Epidemic models like the SIR model, are easy to ap-
ply to information diffusion use cases (Li et al., 2017).
An initial set of infectious agents start the process by
infecting (informing) each of their immediate neigh-
bors in the network. Each susceptible (uninformed)
neighbor then adopts the information with a global
probability P
i
, or rejects it. If the information is
adopted, the agent becomes infectious (informed) and
spreads the information to all immediate neighbors in
the following simulation step (t +1). Such agents can
switch groups once more by being removed. In this
state, the agent is neither spreading the information
nor is susceptible to it.
We focus on the examination of differences in
model behaviour based on the underlying graph struc-
ture. The main independent variable is the type of
network: the proposed context network, as well as
three classical network models: Erd
˝
os-R
´
enyi (ran-
dom) (Newman et al., 2002), Barab
´
asi–Albert (Pref-
erential Attachment) (Barab
´
asi and Bonabeau, 2003)
and Watts–Strogatz (Small World) (Watts and Stro-
gatz, 1998). Besides that, the influence of the SIR
model parameters will be observed. To avoid parame-
ter configurations obscuring differences between the
network models, each of the SIR parameters is in-
Table 1: Excerpt of synthetic population for Kaiserslautern.
household person
id size location type id age gender workplace
1400 3 7.76 49.46 Couple with child(ren) 2578 33 Female
2579 37 Male 2071
2580 7 Male
3900 1 7.77 49.44 Single Person Household 7224 52 Female 1851
6900 2 7.75 49.43 Couple, no children 12675 43 Female 1808
12676 50 Male 669
Table 2: Levels of independent variables.
Variable Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 Level 4
Network Model Context Random Pref. Attach. Small-World
Initially Infected 0.01% 0.1% 1%
Infection Probability 0.0001 0.001, 0.01
Recovery Probability 0.001 0.01 0.1
cluded as independent variables in the experiment de-
sign: the infection probability, P
i
∈ [0, 1] , recovery
probability P
r
∈ [0, 1], and the amount of initially in-
fected nodes i ∈ [0, 1] at t = 0. The dependent vari-
ables include the temporal evolution of SIR states,
providing insights into the pattern of the infection
spread on different network graphs. The simulation
experiment uses a factorial design documented in Ta-
ble 2, for a total of 324 combinations. Each parameter
configuration was simulated for 10 iterations to mini-
mize the effect of random fluctuations.
5 SIMULATION RESULTS AND
EVALUATION
The first evaluation metric is ensuring the correct
properties of the proposed network model, especially
in comparison to alternative approaches. The results
of the experimental comparison are summarised in
Table 3. The context network model achieves most
of the observed real-world characteristics.
Table 3: Summary of characteristics of examined network
models based on (Hamill and Gilbert, 2009).
Context Random Pref. Attach. Small-World
Low density ! ! ! !
Ego network size limited ! ! # !
Variation in ego network size ! Limited ! Limited
Fat-tail ! # ! #
Assortative ! # # #
High clustering ! # # !
Small-world effect ! ! ! !
The distribution of edges varies drastically be-
tween the different network models. Table 4 refer-
ences the measured properties of node degrees. The
context network model (CNM), in contrast to other
models, can reach a minimum of 4 edges for an agent.
Agents with such a low degree can lead to infections
(information spreading) not reaching all parts of the
graph, thus leading to a higher number of agents re-
maining susceptible (uninformed) at the end of the
simulation.
Figure 1 showcases how the network model im-
pacts diffusion dynamics, in particular regarding the
timing and magnitude of the peak of infections. In
particular, the CNM reaches a lower peak than the
other models, and a slower decline of infections (in-
formation spreading). This figure shows the results
for an infection probability (defined as θ) of 0.001,
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
346
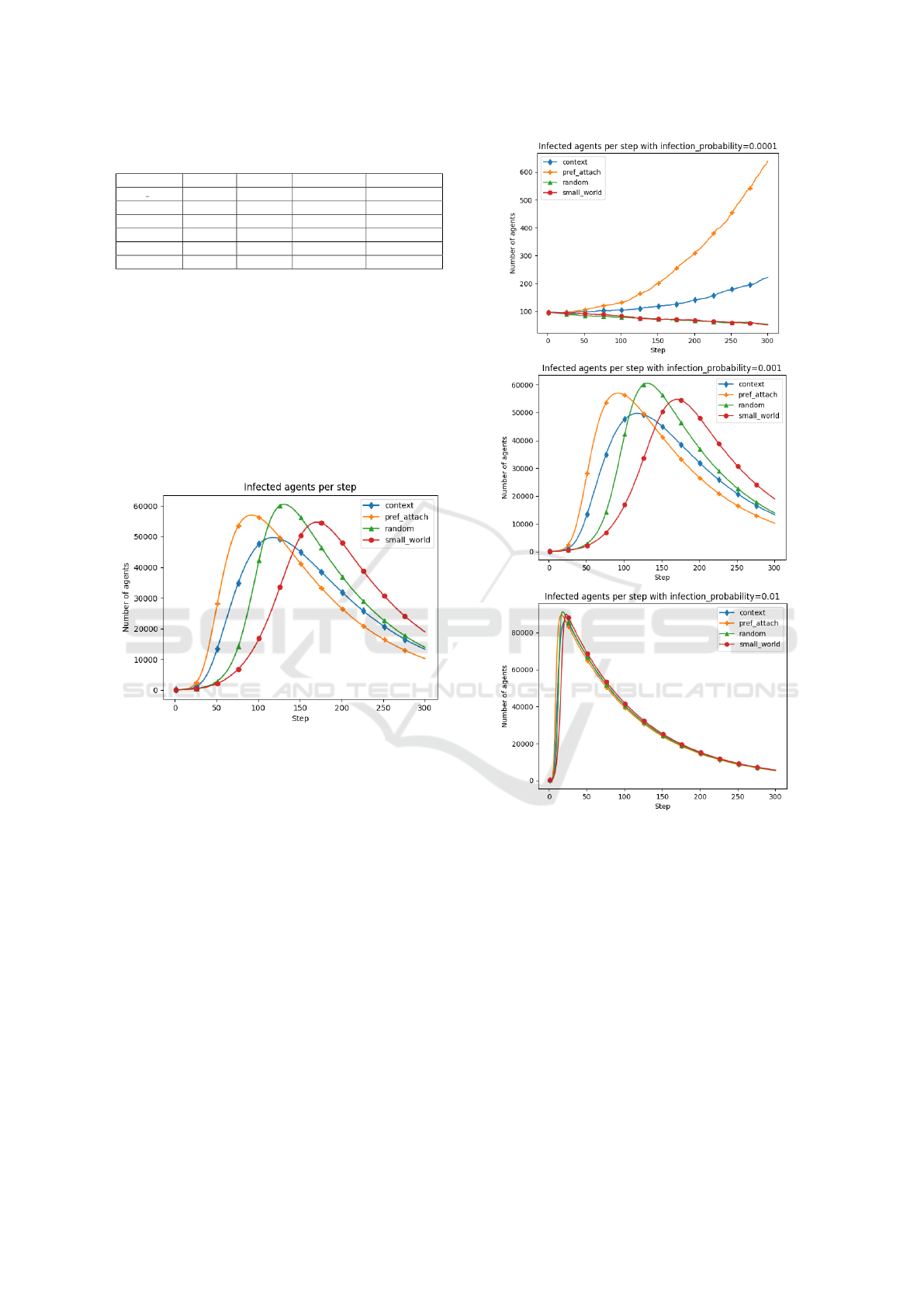
Table 4: Properties of edge distribution.
Context Random Pref. Attach Small-World
num edges 4516587 4516016 4498708 4500824
mean 92 92 92 92
std 41 10 111 2
min 4 55 46 82
max 313 137 3454 102
median 87 92 65 92
and those for other θ values of 0.0001 and 0.01. The
results are summarised in Figure 2. For a low θ, the
major finding is the existence of a critical threshold
θ
min
required for the maintenance of infection dy-
namics. For a high infection probability θ, the dif-
ferences between the networks are visually indistin-
guishable, with a positively right-skewed distribution
mainly determined by the recovery rate. When sim-
ulating with parameter configurations close to those
thresholds, the network structure can significantly in-
fluence the course of the model.
Figure 1: Infected per step for infection probability 0.001.
Further, Figure 3 displays another important prop-
erty of the different network models: altered state
transitions in the SIR model. The context model
retains some agents in the susceptible (uninformed)
state at the end of the simulation - this suggests that
there are clusters of agents that were not reached by
the infections (information), likely due to the exis-
tence of agents with few edges as shown in Table 4.
This is an important observation for different use
cases in which the rate of spread and the connectiv-
ity of all nodes are critical factors. As a particu-
lar example, crisis communications and other time-
sensitive application areas are relevant: on a realis-
tic network model, information cannot spread suffi-
ciently fast across the entire network and peer-to-peer
communication may not be suited to reach all agents
in the network. The initial structure of such a network
could greatly impact the results of emerging com-
munication topologies (Banerjee et al., 2020). Sim-
ilarly, in contexts where interventions on an existing
Figure 2: Side-by-Side comparison of infectious agents for
infection probabilities 0.0001 , 0.001 and 0.01.
network intend to either accelerate or slow down the
spread of a transmission, the network topology im-
pacts the effect of the analysed measures.
6 CONCLUSION AND OUTLOOK
The generation of realistic synthetic populations for
social simulations is a recurrent topic, often inves-
tigated in regards to the properties of resulting net-
works, rather than the impact of different topolo-
gies on model behaviour. This work proposes the
context-based network model, integrating concepts
derived from social sciences. Unlike traditional ap-
Who Knows Who: A Context-Based Approach to Network Generation for Social Simulations
347
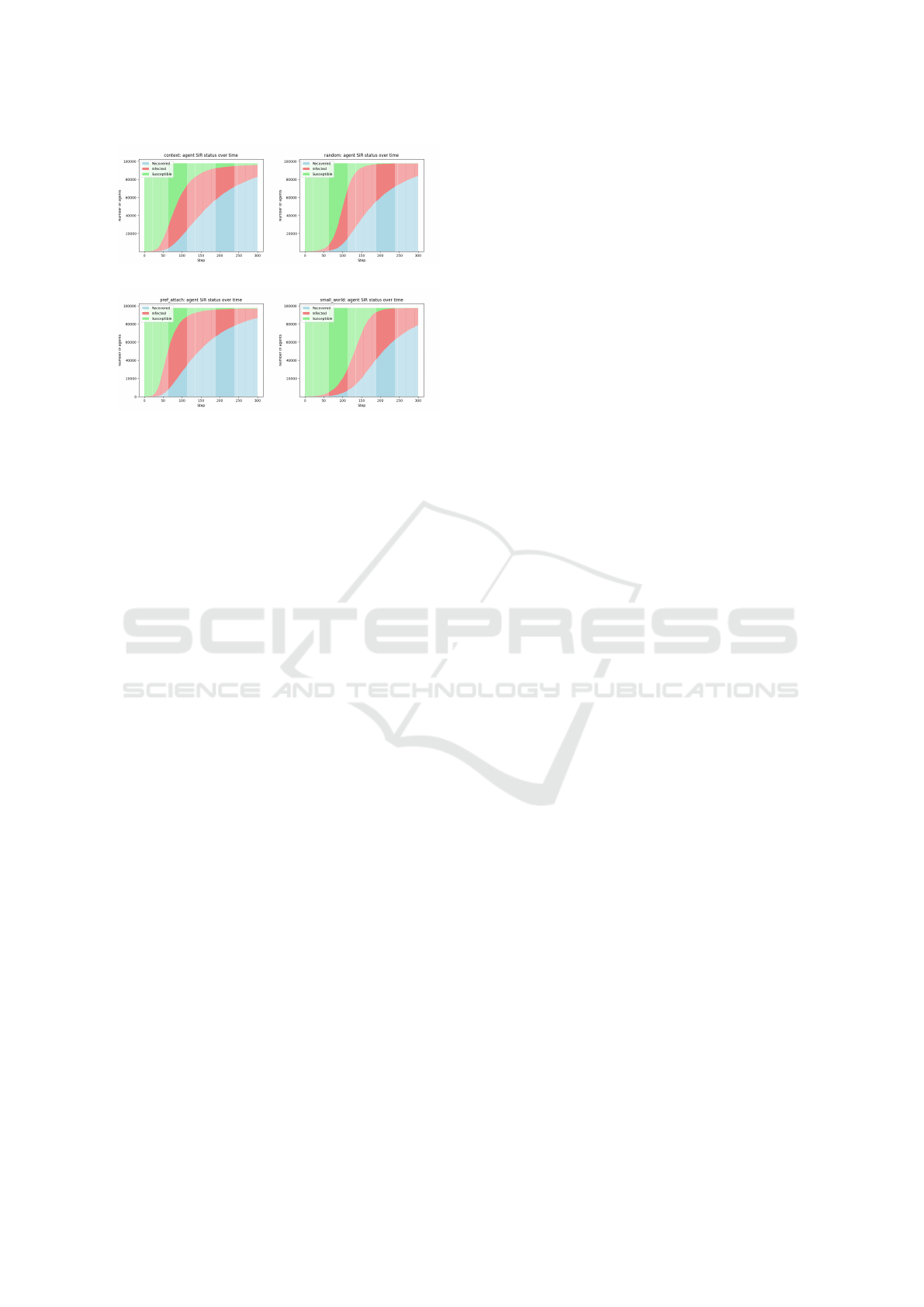
(a) (b)
(c) (d)
Figure 3: Comparison of state transitions in each step for
(a) Context model, (b) Random network, (c) Preferential
Attachment and (d) Small-World.
proaches relying on random or probabilistic deci-
sions, the CNM plausibilizes network generation by
combining applicable concepts, like homophily or
transitivity, with sociodemographic information ob-
tained from a synthetic population. The incorporation
of a CNM, can improve the validity and transferabil-
ity of results generated by simulation studies.
6.1 Summary of Network Generation
To implement a generation procedure which imposes
a realistic network on a given synthetic population,
two major methods were used: based on empirical re-
search, such as Dunbar’s number (Lindenfors et al.,
2021), a shifted and scaled gamma distribution was
found for which sampling the number of edges per
node exhibits a fat right tail, representing individu-
als with very large ego-networks, while the x-axis
of the distribution is limited to positive integer val-
ues. When applying this distribution on a reason-
ably large node population, a network with a low den-
sity is achieved. As the sampled number of edges
falls within the above described range, the number
of nodes directly impacts the resulting density of the
network. For larger networks, the effect is negligible;
however, when sampling for a relatively small node
population, the absolute number of edges can result
in a network with a higher density.
Assortativity, high clustering and the small-
worldness were implemented using a similarity-based
approach. Social relations exhibit homophilic prefer-
ences, which can be applied to different traits, such
as age, sex and the number of social contacts. By
calculating a weighted similarity matrix, agents with
the highest similarity are connected to each other in
a two-phase process: first, a highly clustered, assor-
tative network was formed based on similarity scor-
ing with applicable demographic attributes. Second,
virtual relations were included by removing locations
from the similarity computation to create location-
independent relations taking place in digital spaces.
This two-phase process establishes a small-world ef-
fect in the network.
When dealing with homogeneous anonymous
nodes lacking differentiating factors, applying an ap-
propriate edge distribution can achieve half of the de-
sired social network characteristics. Applying reshuf-
fling algorithms, such as the assortativity tuning al-
gorithm by Xulvi-Brunet and Sokolov (2004), further
refines the network to mirror real-world social net-
work properties. This enables the development of a
more efficient and versatile model, suitable for diverse
social network modeling requirements, without ne-
cessitating in-depth domain-specific knowledge about
social relations.
6.2 Summary of Statistical Properties
While the examination of networks is not entirely
novel, as already explored e.g. by Badham and
Stocker (2010), the comparison of a realistic net-
work against established classics presents a further
contribution towards understanding the impact of net-
work topology on social dynamics in artificial soci-
eties. The evaluation of the CNM was thus compared
against three classic network models: Erd
˝
os-R
´
enyi,
Barab
´
asi–Albert and Watts–Strogatz (random, pref-
erential attachment, small-world, respectively). The
models were compared in the context of an epidemic
spread simulation, using the SIR model to observe the
impact of the network on diffusion dynamics.
The structural comparison between the graphs in-
dicated varying standard deviations regarding edge
distributions, with the CNM ranking in between the
more tightly clustered models (random and small-
world) and the more spread out preferential attach-
ment model. These factors entailed observable dif-
ferences in the simulation results. The higher stan-
dard deviation and assortativity of the CNM led to
an early peak infection (spread) rate with more sus-
ceptible agents at the end of the simulation. The
earlier peaks can be attributed to the higher degree
of some nodes compared to the random and small-
world models, while the remaining susceptible (unin-
formed) agents are due to weakly connected nodes,
with a degree significantly lower than the mean.
When analyzing variations of selected simulation
parameters (specific scenarios for infection, recovery
probability, etc.), the degree distribution proved to
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
348

be more impactful. Due to the higher connectivity
of some nodes, the infection rate of the CNM and
preferential attachment model increases under spe-
cific scenarios (e.g. low infection probability). In
contrast, the infection (information spread) fades out
relatively quickly for the random and small-world
models. These threshold values, drastically impact
the course of the infection and should thus be consid-
ered when developing a simulation model. Other sce-
narios (e.g. high infection probability) minimize the
observable differences between the models, but keep
their ordinal structure regarding the statistical mea-
sures (mean, standard deviation, etc.) intact.
6.3 Challenges and Further Work
The presented CNM, assumes homophily as the dom-
inant force affecting the structure of social relations.
In reality, many more concepts influence relation for-
mation, some of which were considered and inte-
grated during this work (e.g. reciprocity, transitivity),
while others like communities remain unattended.
Identifying and integrating each relevant factor, with-
out them interfering, remains a challenging task. Each
additional concept increases the technical and compu-
tational complexity, and should thus only be included,
if it is inherently relevant for the research task and
does not interfere with already incorporated concepts.
Depending on the size of the network to compute, a
revised similarity calculation approach (less compar-
isons, GPU Cluster, parallelization, etc.) might be
needed to reduce computation time and space con-
straints.
Reciprocity was assumed for this network, yet un-
reciprocated relations can be needed for some use
cases. The proposed CNM can be easily adapted to
support such relations by utilizing a directed graph.
Due to the symmetry of the applied distance mea-
sures, most relations that form within the network are
reciprocated, as both agents initiate an edge connec-
tion. However, some relations form unilateral, as one
of the connected agents is not included in the most
similar agent list of the other. In a directed graph,
this would result in an unreciprocated relation with
a directed edge. The social circles model provides
an example of unreciprocated relations with differ-
ent social reaches among agents(Hamill and Gilbert,
2009). The impact of such unreciprocated relations
offers grounds for further examination.
Finally, the experiment results imply the existence
of isolated nodes in the CNM (see Figure 3. For fur-
ther understanding of these network structures, an in-
depth examination is required to identify if remaining
susceptible agents are evenly spread throughout the
network, or if they are clustered together in commu-
nities. Given the emphasis on the importance of such
isolated graph components for practical use case ap-
plications, it is crucial to not only look at aggregate-
level results, but also at the agent-level dynamics dur-
ing individual simulation runs. This is particularly
important when evaluating the realism of a simula-
tion – while most models can yield a realistic top-level
behaviour after calibration to replicate real world ob-
servations, the underlying causes generating these ef-
fects are not studied closer when validating via pa-
rameter fitting. Assuming that most reasonable mod-
els can be calibrated to produce realistic output, the
aggregated observations alone are not sufficient to
analyse the structural differences and emergent ef-
fects leading to these results.
Instead of comparing different networks based on
their ability to replicate real data, analysis should
rather focus on the process and characteristics of the
approach, such as network resilience in case of node
failures, the impact of particular network generation
steps or the impact of evolving social networks over
the course of the simulation.
Overall, the CNM is an approach using little ac-
tual domain knowledge and expert input, which cre-
ates a social network for a given synthetic population
that mirrors real-life characteristics while maintaining
relevant traits such as shared activities and locations.
The inclusion of further traits for similarity compu-
tation and adjustment of parameters for the distribu-
tion of edges among nodes allows for a high degree
of customization fit for different use cases, types of
networks and available agent data.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work is part of the results of GreenTwin Project,
funded by the Federal Ministry for the Environment,
Nature Conservation, Nuclear Safety and Consumer
Protection (BMUV) (Grant No. 67KI31073C)
REFERENCES
Arentze, T., Berg, P., and Timmermans, H. (2012). Mod-
eling social networks in geographic space: Approach
and empirical application. Environment and Planning
A, 44.
Arentze, T., Kowald, M., and Axhausen, K. W. (2013).
An agent-based random-utility-maximization model
to generate social networks with transitivity in geo-
graphic space. Social Networks, 35(3):451–459.
Badham, J. and Stocker, R. (2010). The impact of network
Who Knows Who: A Context-Based Approach to Network Generation for Social Simulations
349

clustering and assortativity on epidemic behaviour.
Theoretical Population Biology, 77(1):71–75.
Banerjee, I., Warnier, M., and Brazier, F. M. T. (2020).
Self-organizing topology for energy-efficient ad-hoc
communication networks of mobile devices. Complex
Adaptive Systems Modeling, 8(1):7.
Barab
´
asi, A.-L. and Bonabeau, E. (2003). Scale-free net-
works. Scientific american, 288(5):60–69.
Barab
´
asi, A.-L. and Albert, R. (1999). Emergence of scal-
ing in random networks. Science, 286(5439):509–
512.
Barthelemy, J. and Toint, P. L. (2013). Synthetic population
generation without a sample. Transportation Science,
47(2):266–279.
Bruggeman, J. (2013). Social Networks: An Introduction.
Routledge.
Cajka, J. C., Cooley, P. C., and Wheaton, W. D. (2010).
Attribute assignment to a synthetic population in sup-
port of agent-based disease modeling. Methods Rep
RTI Press, 19(1009):1–14.
Caux, R. D., Smith, C., Kniveton, D., Black, R., and Philip-
pides, A. O. (2014). Dynamic, small-world social
network generation through local agent interactions.
Complex., 19:44–53.
Conti, M., Passarella, A., and Pezzoni, F. (2011). A model
for the generation of social network graphs.
Cook, K. S. and Emerson, R. M. (1987). Social exchange
theory.
Dorogovtsev, S. and Mendes, J. (2003). Evolution of
Networks: From Biological Nets to the Internet and
WWW. Oxford University Press.
Frick, M. (2004). Generating synthetic populations using
ipf and monte carlo techniques: Some new results. Ar-
beitsberichte Verkehrs-und Raumplanung, 225.
Hallinan, M. T. (1978). The process of friendship forma-
tion. Social Networks, 1(2):193–210.
Hamill, L. and Gilbert, N. (2009). Social circles: A sim-
ple structure for agent-based social network models.
Journal of Artificial Societies and Social Simulation,
12(2):3.
Kapeller, M. L., J
¨
ager, G., and F
¨
ullsack, M. (2019). Ho-
mophily in networked agent-based models: a method
to generate homophilic attribute distributions to im-
prove upon random distribution approaches. Compu-
tational Social Networks, 6:1–18.
Kaufer, D. S. and Carley, K. M. (1984). Communication at
A Distance: The Influence of Print on Sociocultural
Organization and Change. Routledge, New York, 1st
edition. Subjects: Education, Humanities.
Kerr, C. C., Stuart, R. M., Mistry, D., Abeysuriya, R. G.,
Rosenfeld, K., Hart, G. R., N
´
u
˜
nez, R. C., Cohen,
J. A., Selvaraj, P., Hagedorn, B., et al. (2021). Co-
vasim: an agent-based model of covid-19 dynam-
ics and interventions. PLOS Computational Biology,
17(7):e1009149.
Khorshidi, M. S., Nikoo, M. R., Al-Rawas, G., Bahrami,
N., Al-Wardy, M., Talebbeydokhti, N., and Gan-
domi, A. H. (2024). Integrating agent-based model-
ing and game theory for optimal water resource allo-
cation within complex hierarchical systems. Journal
of Cleaner Production, 482:144164.
Krackhardt, D. (2003). The Strength of Strong Ties: The
Importance of Philos in Organizations. In Networks
in the Knowledge Economy. Oxford University Press.
Li, M., Wang, X., Gao, K., and Zhang, S. (2017). A survey
on information diffusion in online social networks:
Models and methods. Information, 8(4):118.
Lindenfors, P., Wartel, A., and Lind, J. (2021). Dun-
bar’s number deconstructed. Biology Letters,
17(5):20210158. Epub 2021 May 5.
Lorig, F., Johansson, E., and Davidsson, P. (2021). Agent-
based social simulation of the covid-19 pandemic: A
systematic review. Journal of Artificial Societies and
Social Simulation, 24(3):5.
Marin, A. and Wellman, B. (2011). Social network analy-
sis: An introduction. The SAGE handbook of social
network analysis, pages 11–25.
McPherson, M., Smith-Lovin, L., and Cook, J. M. (2001).
Birds of a feather: Homophily in social networks. An-
nual review of sociology, 27(1):415–444.
Newman, M. E. J., Watts, D. J., and Strogatz, S. H.
(2002). Random graph models of social networks.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences,
99(suppl 1):2566–2572.
Palomo-Briones, G. A., Siller, M., and Grignard, A. (2022).
An agent-based model of the dual causality between
individual and collective behaviors in an epidemic.
Computers in biology and medicine, 141:104995.
Schank, T. and Wagner, D. (2005). Approximating clus-
tering coefficient and transitivity. Journal of Graph
Algorithms and Applications, 9(2):265–275.
Talaga, S. and Nowak, A. (2019). Homophily as a
process generating social networks: insights from
social distance attachment model. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1907.07055.
Watts, D. J. and Strogatz, S. H. (1998). Collective dynamics
of ‘small-world’ networks. Nature, 393(6684):440–
442.
Xulvi-Brunet, R. and Sokolov, I. M. (2004). Reshuf-
fling scale-free networks: From random to assortative.
Phys. Rev. E, 70:066102.
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
350
