
Equivariant and SE(2)-Invariant Neural Network Leveraging
Fourier-Based Descriptors for 2D Image Classification
Emna Ghorbel
1,2 a
, Achraf Ghorbel
1
and Faouzi Ghorbel
1
1
CRISTAL Laboratory, GRIFT Research Group ENSI, La Manouba University, 2010, La Manouba, Tunisia
2
Medtech, South Mediterranean University, Tunis, Tunisia
Keywords:
Equivariance, Invariance, Fourier based-Descriptors, Neural Networks, CNNs.
Abstract:
This paper introduces a novel deep learning framework for 2D shape classification that emphasizes equivari-
ance and invariance through Generalized Finite Fourier-based Descriptors (GFID). Instead of relying on raw
images, we extract contours from 2D shapes and compute equivariant, invariant, and stable descriptors, which
represent shapes as column vectors in complex space. This approach achieves invariance to parameteriza-
tion and rigid transformations, while reducing the number of network parameters. We evaluate the proposed
lightweight neural network framework by testing it against a simple CNN and a pre-trained InceptionV3, first
using the original test set and then with rotated and translated images from well-known benchmarks. Ex-
perimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of our method under rigid transformations, showcasing the
benefits of Fourier-based invariants for robust classification.
1 INTRODUCTION
Deep Learning (DL) has recently gained widespread
popularity in the fields of computer vision and ma-
chine learning due to its remarkable performance in
a variety of tasks including image classification and
object detection (Guo et al., 2016; Li et al., 2015).
Despite these advancements, challenges remain, par-
ticularly in managing variability introduced by trans-
formations such as rotation, shifting, and noise, which
can significantly affect model accuracy (Lyle et al.,
2020; Quiroga et al., 2023; Ruderman et al., 2018).
Many existing deep learning models, especially
convolutional neural networks (CNNs), typically rely
heavily on raw image data, rendering them vulnerable
to these transformations. While these models aim to
create effective representations, they often fall short
in achieving the necessary invariance and stability,
which are crucial for robust performance across di-
verse scenarios. As a result, their effectiveness can be
compromised when faced with even minor alterations
in input data.
To address these limitations, recent research has
shifted its focus toward the use of descriptors that
inherently offer invariance to transformations (Mau-
rya et al., 2024; Wang et al., 2024; Shi et al., 2024;
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6179-1358
Quiroga et al., 2023; Li et al., 2024; Delchevalerie
et al., 2021). However, many existing approaches still
rely on raw pixel data, which can undermine the po-
tential of descriptors. Furthermore, these methods of-
ten fail to ensure both equivariance and invariance,
resulting in decreased stability when faced with trans-
formed data. The descriptors used in such approaches
typically lack the ability to fully verify both proper-
ties.
In that context, we propose a novel deep learning
framework that leverages Generalized Finite Fourier-
based Invariant Descriptors (GFID) (Ghorbel et al.,
2022) for image classification. Our approach involves
extracting shapes from images, applying arc-length
parameterization on the resulting contours, and com-
puting invariant descriptors represented as column
vectors in complex space. This representation ensures
the model’s equivariance and invariance to rigid trans-
formations (rotation and translation), while also en-
abling a lightweight architecture that allows for faster
computations and seamless integration into existing
systems. We rigorously evaluate the performance of
our framework against a traditional CNN and the pre-
trained InceptionV3 on well-established datasets, in-
cluding MNIST (LeCun et al., 1998), Fashion MNIST
(Research, 2017), and Hand Gesture Recognition
(rishabh arya, 2021). The results highlight the effec-
tiveness of GFID-based Neural Network, offering a
210
Ghorbel, E., Ghorbel, A. and Ghorbel, F.
Equivariant and SE(2)-Invariant Neural Network Leveraging Fourier-Based Descriptors for 2D Image Classification.
DOI: 10.5220/0013143300003890
In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2025) - Volume 2, pages 210-215
ISBN: 978-989-758-737-5; ISSN: 2184-433X
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

robust and efficient solution for image classification
when dealing with transformed data.
This paper is organized as follows: In Section
2, we present our proposed approach, including the
GFID neural network framework. Section 3 describes
our experimental setup and results, while Section 4
concludes the paper and discusses avenues for future
research.
2 PROPOSED APPROACH
In this section, a novel equivariant, invariant and sta-
ble neural network framework designed for image
classification leveraging Generalized Finite Fourier-
based Invariant Descriptors (GFID) (Ghorbel et al.,
2022; Ghorbel and Ghorbel, 2024) is proposed.
2.1 Generalized Finite Fourier-Based
Invariant Descriptor
Here, we recall the the Generalized Finite Fourier In-
variant Descriptor (GFID) methematical formulation
and its inverse function.
From (Ghorbel and Ghorbel, 2024), F
n
(γ) is cal-
culated as the Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) of N
samples extracted uniformly from a normalized arc
length parameterization (n.a.l.p.) of a given curve γ.
We select a positive integer n
0
such that 1 < n
0
< N,
along with two strictly positive real numbers p and
q. Therefore, the GFID descriptor corresponding to
the complex vector (I
n
) residing in the finite com-
plex vector space C
N−1
is computed as follows for
all 1 ≤ n ≤ N − 1,
I
n
=
F
n
F
n
0
−n−1
n
0
F
n−n
0
n
0
−1
|F
n
0
|
n
0
−n−p−1
|F
n
0
−1
|
n−n
0
−q
if F
n
0
and F
n
0
−1
̸= 0
0 if F
n
0
= 0
Where |·| denotes the modulus operator. The GFID
exhibits crucial invariance properties with respect
to curve parametrization, Euclidean transformations,
and the choice of starting point on the curve. It has
been demonstrated that these descriptors are stable
against subtle curve deformations and are invertible,
allowing for the unique reconstruction of the original
curve from its GFID up to a Euclidean transformation.
Importantly, small modifications to the GFID result in
reconstructed curves that closely resemble the origi-
nal shape, which enhances the model’s robustness.
The analytical inverse formula for the GFID can
be expressed as,
F
n
= I
1
n
I
−p
∆
n
0
I
−q
∆
n
1
e
i(nθ
0
+θ
1
)
Figure 1: Modulus of GFID descriptors demonstrating in-
variance to rigid transformations and robustness to minor
shape changes. (a) Original shape, (b) Transformed shape,
(c) Minor changes. (1) Shapes, (2) GFID modulus.
where ∆ = p + q + 1. The Inverse Fast Fourier Trans-
form (IFFT) of (F
n
) enables reconstruction of the
original curve up to a translation defined by F
0
, a rota-
tion determined by θ
0
, and a starting point represented
by θ
1
where the variables θ
0
and θ
1
correspond to the
arguments of F
n
0
and F
n
0
−1
, respectively.
Figure 1 illustrates the invariance and stability
properties of the GFID descriptors. The first row dis-
plays the GFID modulus of the original shapes. The
second row illustrates the transformed (rotation+shift)
shapes along with their corresponding GFID modu-
lus, demonstrating invariance under euclidean trans-
formations. The third row presents a different shape
belonging to the original’s class and its GFID modu-
lus, highlighting the stability of the descriptors under
shape variations. Overall, these observations confirm
that the GFID descriptors maintain robustness against
both rigid transformations and subtle shape changes.
Given these properties, the GFID is integrated into our
neural network framework, making the model equiv-
ariant, invariant, and stable.
2.2 Neural Network Framework Using
GFID Descriptors
Here, the neural network architecture using GFID de-
scriptors for shape classification is presented.
At the first stage, the image dataset is converted
into binary images, from which contours are ex-
tracted. These contours are then resampled using arc-
length parameterization. GFID descriptors are sub-
sequently computed on the resampled contours, pre-
serving essential shape information while ensuring
equivariance and robustness to geometric transforma-
tions. After that, the GFID vectors are divided into
Equivariant and SE(2)-Invariant Neural Network Leveraging Fourier-Based Descriptors for 2D Image Classification
211
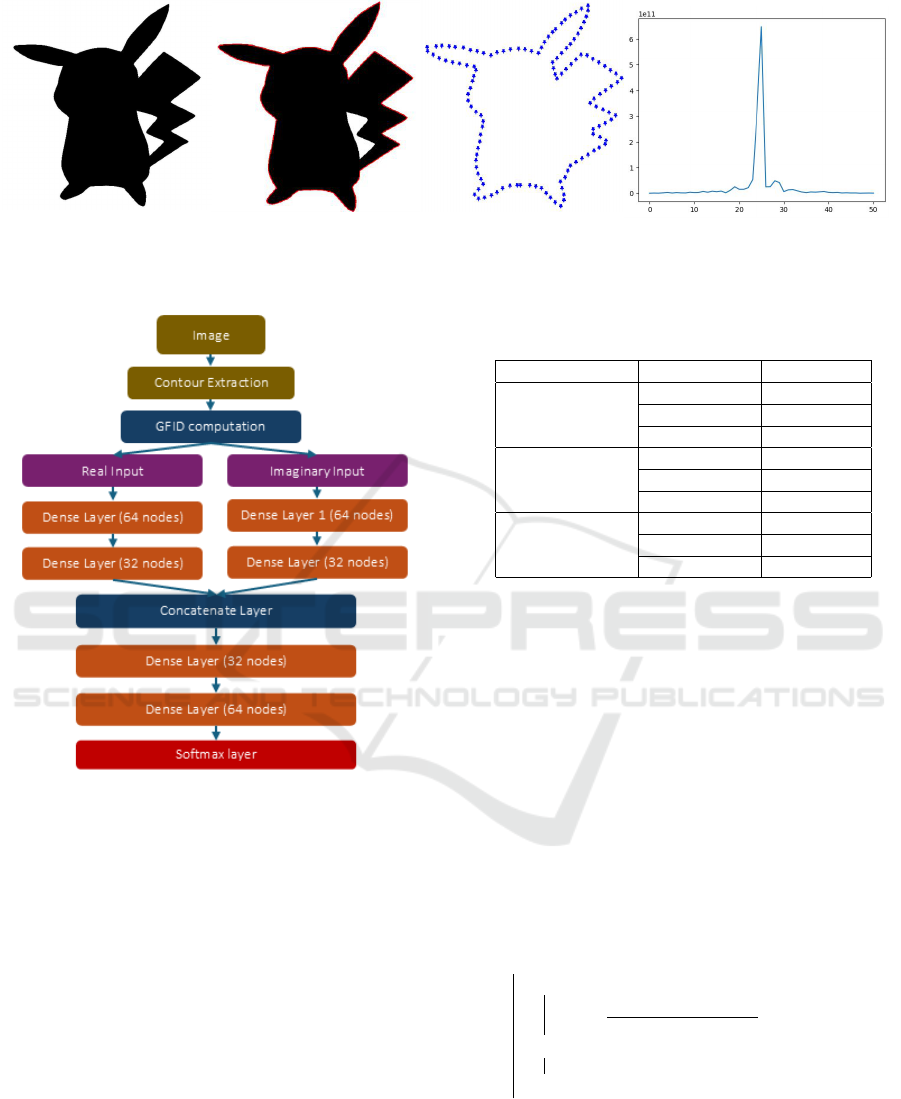
(a) (b) (c) (d)
Figure 2: The GFID computation pipeline: (a) Original image, (b) Contour detection and extraction (the red line), (c) Contour
reparameterization based on arc-length, (d) GFID modulus.
Figure 3: GFID-NN : The Neural Network Framework us-
ing GFID descriptors.
real and imaginary components and normalized for
consistent scaling. We implement a dual-input model
architecture: one input layer processes the real part,
while the other handles the imaginary part. Each path-
way includes dense layers with ReLU activation func-
tions. The outputs from the real and imaginary path-
ways are concatenated to create a unified representa-
tion, which undergoes additional processing through
dense layers before being classified via a softmax out-
put layer. Figure 2 illustrates the GFID computation
pipeline going from the original image to the GFID
description.
Figure 3 presents the Neural Network Framework
using GFID descriptors namely GFID-NN. Note that
the inverse function of the GFID enables reconstruc-
tion at each layer of the proposed neural network.
However, this aspect will be addressed in future work.
Table 1: Comparison of parameters Models Across
Datasets.
Dataset Model Param.
MNIST
GFID-NN 15,648
Simple-CNN 53,322
InceptionV3 22,020,490
FashionMNIST
GFID-NN 15,648
Simple-CNN 53,322
InceptionV3 22,020,490
HandGesture
GFID-NN 16,608
Simple-CNN 84,712
InceptionV3 22,040,980
2.3 Algorithm for GFID Computation
The detailed steps for computing GFID descriptors
are outlined in Algorithm 1. These steps ensure ro-
bust extraction of invariant features.
Input: Curve γ, number of resampling points
N, parameters n
0
, p, q
Output: GFID vector I
n
∈ C
N−1
Step 1: Curve reparameterization
Resample uniformly γ to N points:
{γ
1
, γ
2
, . . . , γ
N
}.
Step 2: Compute Fast Fourier Transform
Compute {F
n
}
N−1
n=1
, the FFT coefficients of the
resampled curve.
Step 3: Compute GFID Invariants
for n = 1 to N − 1 do
if F
n
0
̸= 0 and F
n
0
−1
̸= 0 then
I
n
←
F
n
·F
n
0
−n−1
n
0
·F
n−n
0
n
0
−1
|F
n
0
|
n
0
−n−p−1
·|F
n
0
−1
|
n−n
0
−q
;
else
I
n
← 0;
end
end
Step 4: Return GFID Vector
return I
n
= {I
n
}
N−1
n=1
.
Algorithm 1: Generalized Finite Fourier-based Invariant
Descriptor (GFID) Algorithm.
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
212

Figure 4: Samples from each of the three datasets: (a)
MNIST (b) Hand Gesture Recognition (c) Fashion MNIST.
3 EXPERIMENTS
In this part, we present results to validate the proposed
method for allowing invariance in 2D image classifi-
cation.
3.1 Datasets
The MNIST dataset (LeCun et al., 1998) is a well-
known benchmark in the field of machine learning
and computer vision, consisting of 70,000 grayscale
images of handwritten digits from 0 to 9. Each im-
age is 28x28 pixels, providing a standardized format
for training and testing classification algorithms. The
dataset is divided into 60,000 training samples and
10,000 test samples, enabling robust evaluation of
model performance. MNIST serves as a foundational
dataset for assessing the effectiveness of various clas-
sification techniques, making it a popular choice for
initial experiments in digit recognition tasks.
The Fashion MNIST dataset (Research, 2017)
serves as a more challenging alternative to the orig-
inal MNIST, comprising 70,000 grayscale images of
clothing items from 10 different categories, including
T-shirts, trousers, dresses, and shoes. Like MNIST,
each image in Fashion MNIST is also 28x28 pix-
els, allowing for direct comparisons between models
trained on both datasets. The dataset is structured into
60,000 training images and 10,000 test images.
Hand Gesture Recognition Dataset (rishabh arya,
2021) contains total 24000 images of 20 different
gestures. This dataset primarily use for hand ges-
ture recognition task. Figure 4 displays representative
samples from each of the three datasets.
3.2 Implementation Settings
The GFID-NN model is developed using the Tensor-
Flow and Keras frameworks. For the implementation
of the GFID module, we set the hyperparameters (
n
0
= 2, p = 1, q = 1, N = 100) following the param-
eter studies conducted in (Ghorbel et al., 2022; Ghor-
bel and Ghorbel, 2024). The first layer of the neu-
ral network processes 50 × 2 features derived from
the GFID descriptors. Besides, we implemented a
simplified Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) ar-
chitecture for image classification tasks, specifically
designed for comparison with the GFID-NN model.
The CNN processes grayscale images of size 28×28
with a single channel and consists of two convolu-
tional layers, featuring 32 and 64 filters, respectively.
The output from the last pooling layer is flattened and
passed through a fully connected output layer with
softmax activation. In the same way, we employed the
pre-trained InceptionV3 architecture (Szegedy et al.,
2015) imported from Keras where input images are
resized to 299×299 pixels. Also, we used the Data
Augmentation framework from keras of rotation and
translation that we called Rigid-aug. All training
is conducted over 30 epochs with a batch size of
32 on a single T4 GPU. During the training phase,
we configure the following settings: (1) Loss Func-
tion: Sparse Categorical Cross-Entropy, (2) Opti-
mizer: Adam with a learning rate of 10
−3
, and (3)
Metric: Accuracy.
3.3 Model Complexities
In terms of computational complexity, the Simple-
CNN model has a complexity of O(n
2
), where n is
the input size (28×28 for grayscale images). This is
mainly due to the convolution operations and fully
connected layers. The complexity increases quadrat-
ically with the size of the image as the model applies
convolutions and then processes the features through
dense layers. The InceptionV3 model is more com-
plex, with convolutional layers contributing a com-
plexity of O(n
2
), but the fully connected layers result
in a higher complexity of O(n
3
). This is due to the
deeper architecture and larger number of parameters
in the model, especially when working with larger
input images (224×224). The additional layers and
computations required for the inception modules lead
to significantly higher computational costs. In com-
parison, the GFID-NN model benefits from a more
efficient feature extraction process. By converting im-
ages into contours and applying Fast Fourier Trans-
form (FFT) to extract GFID descriptors, the feature
extraction step has a complexity of O(n logn), where
n represents the number of contour points (typically
50 or fewer for smaller images). This efficient pro-
cess reduces the dimensionality of the input, making
it computationally lighter. After the feature extrac-
tion, the model processes the data through dense lay-
ers, where the complexity scales with the number of
neurons. However, the overall complexity remains
lower compared to other models due to the smaller
input size and compact feature representation.
Equivariant and SE(2)-Invariant Neural Network Leveraging Fourier-Based Descriptors for 2D Image Classification
213
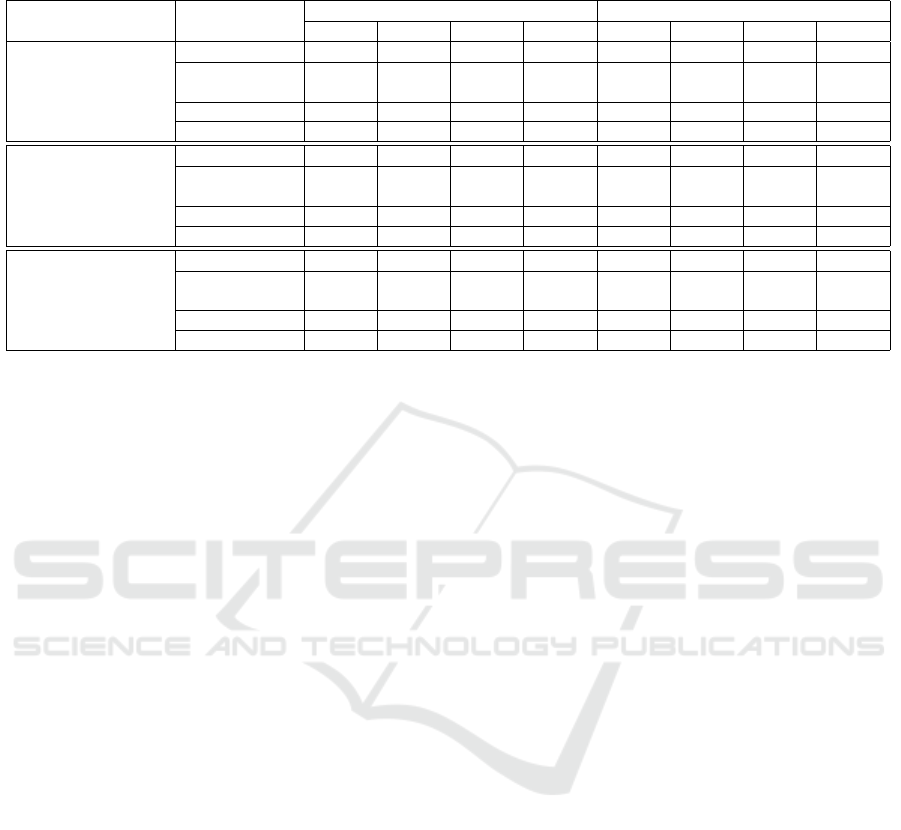
Table 2: Performance Metrics for Different Models on Original and Transformed Tests for MNIST, Fashion MNIST, and
Hand Gesture Recognition.
Dataset Model Original Test Transformed Test
Acc. Pr. Rec. F1Sc. Acc. Pr. Rec. F1Sc.
MNIST
(LeCun et al., 1998)
InceptionV3 0.9926 0.9927 0.9927 0.9927 0.3289 0.4068 0.3289 0.3404
InceptionV3
(+Rigid-aug)
0.9934 0.9935 0.9935 0.9935 0.3806 0.4475 0.3806 0.3715
CNN (Simple) 0.8395 0.8426 0.8395 0.8346 0.7886 0.8167 0.7886 0.7907
GFID-NN 0.8561 0.8553 0.8546 0.8543 0.8431 0.8435 0.8422 0.8434
Fashion
MNIST
(Research, 2017)
InceptionV3 0.9151 0.9149 0.9152 0.9149 0.1641 0.3064 0.1642 0.1521
InceptionV3
(+Rigid-aug)
0.8853 0.8877 0.8854 0.8859 0.2784 0.3490 0.2785 0.2470
CNN (Simple) 0.8597 0.7212 0.7125 0.7106 0.5213 0.5864 0.5214 0.4905
GFID-NN 0.6947 0.6924 0.6945 0.6928 0.6893 0.6824 0.6893 0.6828
Hand Gesture
Recognition
(rishabh arya, 2021)
InceptionV3 1 1 1 1 0.0766 0.2212 0.0766 0.0473
InceptionV3
(+Rigid-aug)
1 1 1 1 0.2722 0.3799 0.2722 0.2159
CNN (Simple) 1 1 1 1 0.1155 0.2306 0.1155 0.1078
GFID-NN 0.9863 0.9863 0.9862 0.9862 0.9712 0.9712 0.9711 0.9711
3.4 Model Parameters Across Datasets
In this section, we analyze the number of trainable pa-
rameters across various architectures to gain insights
into their structure and impact on performance.
The GFID-NN model presents an innovative ap-
proach in its initial layers by transforming input im-
ages into reparameterized contours. This transforma-
tion reduces the dimensionality from a 28 × 28 ma-
trix to 100 complex elements, significantly decreasing
the number of trainable parameters compared to tra-
ditional models. Additionally, the number of points
(N) can be reduced to 50 while preserving the overall
structure, especially for smaller images. Therefore,
by utilizing the compact and efficient GFID descrip-
tors, the GFID-NN model minimizes computational
complexity while maintaining high accuracy, making
it an ideal choice for resource-constrained environ-
ments.
As illustrated in Table 1, the GFID-NN model fea-
tures a lightweight architecture with approximately
16,000 parameters. In contrast, the Simple-CNN
model, designed for the Fashion MNIST dataset, has
over 50,000 parameters due to its convolutional lay-
ers and dense output layer. The InceptionV3 model,
known for its complex architecture, significantly sur-
passes these counts, containing over 22 million pa-
rameters.
3.5 Outcomes
In this section, we propose to analyze invariance mod-
els using performance metrics such as weighted av-
erage (w.a) Accuracy (Acc.), Precision (Pr.), Recall
(Rec.), and F1 Score (F1Sc.) across three datasets:
MNIST, Fashion MNIST, and Hand Gesture Recog-
nition. These metrics are well-suited for this multi-
ple classification task as they provide a comprehen-
sive evaluation of model performance, particularly in
the context of imbalanced datasets.
The results are categorized into two groups: Orig-
inal Test and Transformed Test where transformations
included rotation within a range of 2π and translation
of 10 pixels. According to Table 2, InceptionV3 as
well as InceptionV3 + Rigid-aug show high accuracy
on the Original Test for MNIST (0.9926 & 0.9934)
but drop drastically (0.3289 & 0.3806) under transfor-
mations, indicating a lack of invariance. Similarly, the
models achieve respectively 0.9151 and 0.8853 accu-
racy on Fashion MNIST, with performance plummet-
ing to 0.1641 and 0.2784 post-transformation. The
simple-CNN starts with 0.8395 accuracy on MNIST
but also experiences a significant decline to 0.7886
after transformations. For Fashion MNIST, it per-
forms slightly better with an accuracy of 0.8597 on
the Original Test, but drops to 0.5213 when trans-
formed. GFID-NN, while starting lower at 0.8561 for
MNIST, maintains better performance with 0.8431 af-
ter transformations, demonstrating its invariance. In
the Hand Gesture dataset, all models except GFID-
NN achieve 100% accuracy on the Original Test but
drop when tested with transformed data, while GFID-
NN shows 0.9863 and a robust 0.9712 under the same
conditions, highlighting its invariance effectiveness.
Therefore, results suggest that while InceptionV3 ex-
cel on unaltered data, GFID-NN offers a more reliable
performance when subjected to rigid transformations.
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
214

4 CONCLUSION
This paper introduced a novel deep learning frame-
work for 2D shape classification based on General-
ized Finite Fourier-based Invariant Descriptors. By
extracting contours and computing invariant and sta-
ble descriptors, our model demonstrates robust per-
formance against rigid transformations, ensuring in-
variance under rotations and translations while ex-
hibiting equivariance. Experimental results on the
MNIST, Fashion MNIST, and Hand Gesture Recogni-
tion datasets show that GFID-NN outperforms tradi-
tional convolutional networks when faced with trans-
formed images. Future works will concern integrating
other invariant and stable descriptors for improving
robustness and classification accuracy.
REFERENCES
Delchevalerie, V., Bibal, A., Fr
´
enay, B., and Mayer, A.
(2021). Achieving rotational invariance with bessel-
convolutional neural networks. Advances in Neural
Information Processing Systems, 34:28772–28783.
Ghorbel, E. and Ghorbel, F. (2024). Data augmenta-
tion based on shape space exploration for low-size
datasets: application to 2d shape classification. Neural
Computing and Applications, pages 1–24.
Ghorbel, E., Ghorbel, F., and M’Hiri, S. (2022). A fast
and efficient shape blending by stable and analytically
invertible finite descriptors. IEEE Transactions on Im-
age Processing, 31:5788–5800.
Guo, Y., Liu, Y., Oerlemans, A., Lao, S., Wu, S., and Lew,
M. S. (2016). Deep learning for visual understanding:
A review. Neurocomputing, 187:27–48.
LeCun, Y., Bottou, L., Bengio, Y., and Haffner, P. (1998).
Gradient-based learning applied to document recogni-
tion. Proceedings of the IEEE, 86(11):2278–2324.
Li, Y., Qiu, Y., Chen, Y., He, L., and Lin, Z. (2024). Affine
equivariant networks based on differential invariants.
In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Com-
puter Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 5546–
5556.
Li, Y., Wang, S., Tian, Q., and Ding, X. (2015). Feature
representation for statistical-learning-based object de-
tection: A review. Pattern Recognition, 48(11):3542–
3559.
Lyle, C., van der Wilk, M., Kwiatkowska, M., Gal,
Y., and Bloem-Reddy, B. (2020). On the benefits
of invariance in neural networks. arXiv preprint
arXiv:2005.00178.
Maurya, R., Pradhan, A., Thirumoorthy, G., Saravanan,
P., Sahu, G., and Karnati, M. (2024). Fouriercnn:
Skin cancer classification using convolution neural
network fortified with fast fourier transform. In 2024
IEEE International Conference on Interdisciplinary
Approaches in Technology and Management for So-
cial Innovation (IATMSI), volume 2, pages 1–4. IEEE.
Quiroga, F. M., Torrents-Barrena, J., Lanzarini, L. C., and
Puig-Valls, D. (2023). Invariance measures for neural
networks. Applied Soft Computing, 132:109817.
Research, Z. (2017). Fashion mnist. https://github.com/
zalandoresearch/fashion-mnist. Accessed: 2024-9-
01.
rishabh arya (2021). Hand gesture. https://github.com/
rishabh-arya/Gesture-controlled-opencv-calculator.
Accessed: 2024-8-21.
Ruderman, A., Rabinowitz, N. C., Morcos, A. S., and Zo-
ran, D. (2018). Pooling is neither necessary nor suf-
ficient for appropriate deformation stability in cnns.
arXiv preprint arXiv:1804.04438.
Shi, K., Zhou, X., and Gu, S. (2024). Improved im-
plicit neural representation with fourier reparameter-
ized training. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Con-
ference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition,
pages 25985–25994.
Szegedy, C., Liu, W., Jia, Y., Sermanet, P., Reed, S.,
Anguelov, D., Erhan, D., Vanhoucke, V., and Rabi-
novich, A. (2015). Going deeper with convolutions. In
2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pat-
tern Recognition (CVPR), pages 1–9.
Wang, J., Wu, Q., Liu, T., Wang, Y., Li, P., Yuan, T., and Ji,
Z. (2024). Fourier domain adaptation for the iden-
tification of grape leaf diseases. Applied Sciences,
14(9):3727.
Equivariant and SE(2)-Invariant Neural Network Leveraging Fourier-Based Descriptors for 2D Image Classification
215
