
Powerful & Generalizable, Why not both? VA: Various Attacks
Framework for Robust Adversarial Training
Samer Khamaiseh
1 a
, Deirdre Jost
1
, Abdullah Al-Alaj
2 b
and Ahmed Aleroud
3
1
Department of Computer Science & Software Engineering, Miami University, OH, U.S.A.
2
Department of Computer Science, Virginia Wesleyan University, Virginia Beach, U.S.A.
3
Department of Computer & Cyber Sciences, Augusta University, Augusta, U.S.A.
Keywords:
Adversarial Training, ML Adversarial Attacks, Deep Neural Networks, Adversarial Examples.
Abstract:
Due to its effectiveness, adversarial training (AT) is becoming the first choice to improve the robustness of
deep learning models against adversarial attacks. AT is formulated as a min-max optimization problem. The
performance of AT is essentially reliant on the inner optimization problem (i.e., max optimization), which re-
quires the generation of adversarial examples. Most AT methods rely on a single attack to craft these examples
neglecting the impact of image-class robustness on the adversarial training. This oversight led to shortcomings
such as poor generalization on both perturbed and clean data, unreliable robustness against unseen adversar-
ial attacks, and limited exploration of the perturbation space. Therefore, an investigation and analysis of AT
robustness via adapting various attacks based on image-class robustness is still unaddressed. In this paper, we
propose Various Attacks (VA), a novel framework for a robust and generalizable adversarial training based on
image-class robustness. Our framework introduces two novel components: Advanced Curriculum Training
(ACT), which ensures the diversity of adversarial attacks by gradually increasing attack strength while rotat-
ing through these attacks, and Class-Attack Assignment (CAA), which adaptively determines and assigns the
optimal adversarial attack to each image-class to maximize the loss. The proposed framework trains image
classification neural networks using a variety of adversarial attacks that significantly improve the general-
ization robustness. The results of experiments on two benchmark datasets show the superiority of the VA
framework over state-of-the-art adversarial training methods.
1 INTRODUCTION
Deep neural networks (DNNs) have achieved sig-
nificant success in various domains such as im-
age classification (Khamaiseh et al., 2022b), voice
recognition(Kosuge et al., 2023), and security appli-
cations(Khamaiseh et al., 2022a)(Khamaiseh et al.,
2020)(Alsmadi et al., 2016). However, it is been
found that DNNs are vulnerable to adversarial ex-
amples(Szegedy et al., 2013). Adversarial exam-
ples can be generated by adding small, often imper-
ceptible perturbations to clean images causing even
well-trained image classification models to misclas-
sify them. This vulnerability raises security con-
cerns about adapting DNNs, particularly in criti-
cal applications. To address this issue, researchers
have proposed various defense methods (Goodfellow
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9339-1685
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2640-7007
et al., 2015)(Madry et al., 2019)(Papernot and Mc-
Daniel, 2017)(Kurakin et al., 2016)(Liao et al., 2018).
Among these, adversarial training (AT) stands out as
the most effective method for enhancing the robust-
ness of DNN models against adversarial attacks. Gen-
erally speaking, standard adversarial training involves
incorporating adversarial examples during the train-
ing phase to improve the DNN’s robustness. The AT
framework is formulated as a min-max optimization
problem, where generating effective adversarial ex-
amples (i.e., solving the inner maximization problem)
is the key factor in determining the robustness of the
AT methods.
Previous studies have revealed that discrepancies
between image classes impact natural training (i.e.,
training on clean examples). Specifically, some im-
age classes are harder to learn and require more time
to converge compared to other classes (Tang et al.,
2020)(Wang et al., 2019). In adversarial settings,
a few people investigate the image-class robustness,
228
Khamaiseh, S., Jost, D., Al-Alaj, A. and Aleroud, A.
Powerful & Generalizable, Why not both? VA: Various Attacks Framework for Robust Adversarial Training.
DOI: 10.5220/0013146800003890
In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2025) - Volume 2, pages 228-239
ISBN: 978-989-758-737-5; ISSN: 2184-433X
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

and they reveal that some image classes show lower
robustness than other classes against some adversar-
ial attacks. Furthermore, examples within the same
image class are often vulnerable to similar pertur-
bations, causing them to be misclassified into the
same incorrect class, as other correctly labeled im-
ages (Tian et al., 2021). However, in the adversarial
training community, the majority of proposed AT de-
fense methods (Cui et al., 2023)(Zhang et al., 2021)
(Zhang et al., 2019a)(Addepalli et al., 2022)(Xu et al.,
2023) (Huang et al., 2022) solve the inner maximiza-
tion problem by using a single adversarial attack (e.g.,
PGD attack(Dong et al., 2018)). However, they of-
ten overlook the differences in image classes robust-
ness and their impact on the generalization robustness
of the adversarial training (Tang et al., 2020)(Wang
et al., 2019). This oversight is partly due to the as-
sumption that the benchmark datasets seem to have
balanced robustness across all image classes. As de-
tailed in §2, single-attack AT methods suffer from
multiple shortcomings, with a significant issue be-
ing their poor generalization robustness against un-
seen adversarial attacks. Generalization robustness is
a pivotal property that measures the ability of the AT
defense method to provide robustness against unseen,
newer, stronger, and adaptive adversarial attacks(Lee
et al., 2020). The phenomenon of improving the AT
generalization robustness by leveraging the discrep-
ancies of image class robustness using multiple at-
tacks is still largely unaddressed.
To fill this void, we propose the various attacks
method (VA). VA is a novel framework that applies
multiple adversarial attacks based on the robustness
levels of different image classes leading to improv-
ing the overall model robustness. The VA frame-
work comprises two components as follows: (1) the
advanced curriculum training (ACT) systematically
rotates a variety of adversarial attacks across im-
age classes while gradually increasing the attacks’
strength, thereby improving the model’s generaliza-
tion robustness. (2) The novel Class-Attack Assign-
ment (CAA) algorithm exploits the discrepancies of
image-class robustness to assign adversarial attacks
to image classes at key training points in a way that
maximizes the loss. To evaluate the performance of
our proposed methods, we conduct extensive experi-
ments using the CIFAR-10 and CIFAR-100 datasets.
During our experiments, we tested state-of-the-art AT
defense methods against several adversarial attacks.
The reported results in §6 validate the effectiveness
of our proposed framework in improving the overall
robustness, including the generalization robustness of
the DNN models when compared to other state-of-
the-art AT defense methods.
To summarize, our contributions are as follows:
■ We propose and implement a novel Various At-
tacks (VA)
1
framework that utilizes various adver-
sarial attacks based on image class discrepancies
to improve the overall robustness, including the
generalization robustness, of trained DNN mod-
els against stronger and more adaptive adversarial
attacks.
■ We propose the Advanced Curriculum Training
(ACT) method that can be viewed as an improved
form of curriculum training in addition to the a
new Class-Attack Assignment (CAA) algorithm.
Jointly, these components provide an effective so-
lution to the inner-maximization problem of AT.
This method can be applied to other AT defense
methods to improve the generalization robustness.
■ We conduct extensive comparisons with state-of-
the-art AT defense methods using CIFAR-10 and
CIFAR-100 datasets and six other baseline adver-
sarial attacks. The reported results demonstrate
that the VA framework significantly improves the
robustness of the trained DNN models and outper-
forms other AT defense methods.
The rest of the paper is organized as follows. In
§2, we discuss the motivation of this work by intro-
ducing the shortcomings of the single-attack AT de-
fense methods. In §3, we discuss the preliminary and
the background of this work. An extensive overview
of the related work is explained in §4. In §5, we
present the formulation of the proposed framework.
Experimental settings and results are explained in §6.
Finally, §7 concludes our work.
2 MOTIVATION
Generalization Robustness of Single-Attack AT.
AT methods typically use a single attack throughout
the training process to approximate the inner maxi-
mization problem. This step involves finding the ad-
versarial example that causes the highest loss before
adjusting the model weights through backpropaga-
tion to minimize its impact (outer minimization prob-
lem). However, relying on a single attack limits the
exploration of the space of perturbations (Croce and
Hein, 2020), resulting in a vulnerable trained model
with poor generalization robustness (Lee et al., 2020).
Even single-attack defense methods that utilize vari-
able hyperparameters are optimized to defend only
1
The source code is available:
https://github.com/LAiSR-SK/VariousAttacks.
Powerful & Generalizable, Why not both? VA: Various Attacks Framework for Robust Adversarial Training
229

against the specific types of attacks (e.g., gradient-
based attacks) (Gowal et al., 2021). While such mod-
els can show high robustness against the attack used
during training, they lack generalization robustness,
making them vulnerable to other attacks. This prob-
lem is introduced in (Cai et al., 2018) and demon-
strated in Table 1, which displays the robust accu-
racy of a model trained adversarially using the FGSM
attack against multiple attacks. The FGSM-trained
model achieves a high robust accuracy of 81.55%
against the FGSM attack but fails against stronger at-
tacks like PGD-20 (Madry et al., 2019) and AutoAt-
tack (AA) (Croce and Hein, 2020), with robust ac-
curacies of only 0.04% and 0.0%, respectively. To
address these shortcomings, recent defense methods
have adapted the PGD attack with random initializa-
tion to increase the diversity of perturbations and im-
prove the model’s generalization robustness and over-
all robust accuracy (Croce and Hein, 2020) (Croce
and Hein, 2021). However, such defense methods
have still been defeated by stronger and more adap-
tive attacks (Dong et al., 2020). Another example
of a single-attack training method is Customized-AT
(Cheng et al., 2020), also shown in Table 1. While
it shows a high accuracy against most attacks, it is
defeated by AA with a very low robust accuracy of
21.68%, indicating poor generalizability to more so-
phisticated and adaptive attacks. These examples
demonstrate that models trained with a single attack
lack the defensive capabilities necessary for them to
be considered robust against the wide variety of ad-
versarial attacks, underscoring the need for more di-
verse and robust training methods.
Table 1: The robust accuracy values of two WideResNet-
34 models on the CIFAR-10 dataset. One model is trained
using the FGSM attack and another one is trained using the
Customized-AT defense method. The table compares their
performance against multiple attacks.
Single-Attack Training Accuracy
Attack FGSM Customized-AT
Clean 85.59% 94.04%
PGD-20 0.04% 68.47%
MIM 0.0% 74.13%
FGSM 81.55% 81.29%
AA 0.0% 21.68%
3 PRELIMINARIES
3.1 Adversarial Training (AT)
As depicted in Equation 1, AT is formulated as a min-
max optimization problem:
min
Θ
E
(x,y)∈D
[max L( f
Θ
(x + δ),y)] (1)
where f
Θ
represents the model with parameters Θ, x
is an input image and y its assigned image-class in
dataset D, and L (.) is a loss function that measures
the error between the model’s prediction and the true
class. E
(x,y)∈D
denotes the expected value of the in-
ner maximization problem for a sample (x, y) from
D. The goal of AT is to find the parameter set Θ of
f that minimizes the expected maximum loss L (for
an image (x,y) in dataset D) caused by a perturba-
tion δ. δ is constrained to ensure the imperceptibil-
ity of adversarial images to the human eye and pre-
vent the true class of the targeted image from shift-
ing. In other words, AT optimization problem is of-
ten divided into two subproblems: the outer mini-
mization and inner maximization problems. While the
outer minimization problem is traditionally solved us-
ing gradient descent to find the optimal model param-
eters, a large portion of recent research is focused on
how to approximate the solution for the inner maxi-
mization problem (Madry et al., 2019).
3.2 Class-Wise Properties
Some works (Tang et al., 2020)(Wang et al., 2019) re-
veal that certain classes are inherently harder to learn
than other classes, usually refer these type of class
as hard-classes. In adversarial training, these classes
have a lower image-class robustness (i.e., vulnerable
classes), making them more susceptible to attacks,
even after AT training. The problem is even more
prevalent in adversarial training compared to standard
training, as demonstrated by the class-wise variance
(Tian et al., 2021). Letting |C| represent the number of
classes in a dataset, α
y
denote the accuracy of class y,
and
¯
α denote the average accuracy across all classes,
the CV is defined as:
CV =
1
|C|
|C|
∑
y=1
(α
y
−
¯
α)
2
(2)
In (Tian et al., 2021), authors reported that class-wise
variance of adversarial training is 28 times higher than
in standard training. This increased variance causes
vulnerable image-classes to reduce the efficacy of ad-
versarial training remarkably. Therefore, it becomes
essential to enhance the image-class robustness of the
most vulnerable classes to improve the overall robust-
ness of the model. This can be done by targeting spe-
cific vulnerable classes and improving the robustness
at the weakest points of the dataset. This approach
involves maximizing the loss generated through per-
turbing images within these vulnerable image classes.
This targeted approach not only increases the robust-
ness of the most vulnerable image-classes, but also
contributes to the overall robustness of the model.
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
230

Another significant property of class-wise is class
grouping. Recent research has shown that image-
classes can often be divided into groups called super-
classes (Tian et al., 2021). An image from an image-
class within one superclass is more commonly per-
turbed to be classified as another image-class within
that superclass, and less commonly perturbed to be
classified outside its group. For instance, a “car”
image within the “vehicle” superclass is more likely
to be misclassified as a “truck” within the “vehicle”
group, rather than as a “dog”, which is outside the
group. Images that fall under the same class or super-
class possess similar characteristics that can be lever-
aged in the AT process to enhance the accuracy of the
model (Tian et al., 2021).
4 RELATED WORK
Adversarial Attacks. Many adversarial attack meth-
ods have been proposed to exploit vulnerabilities in
neural networks (Khamaiseh et al., 2022b). The Fast
Gradient Sign Method (FGSM) attack (Goodfellow
et al., 2015) calculates the loss gradient for each im-
age and perturbs the target image in that direction.
Building on FGSM, the Projected Gradient Descent
(PGD) attack iterates FGSM for a set number of steps.
After each perturbation step the attack projects the ad-
versarial image x
adv
back onto the ε-ball around the
clean image, ensuring the perturbation remains small
and imperceptible. Dong et al. (Dong et al., 2018)
enhance this approach with the Momentum Iterative
Method (MIM) attack, which adds a momentum term
and uses previous gradients to update x
adv
at each it-
eration. Carlini and Wagner (CW) (Carlini and Wag-
ner, 2017) propose an attack that creates adversar-
ial images by adjusting the standard objective func-
tion, specifically designed to evaluate defense meth-
ods. The Target-X attack (Khamaiseh et al., 2023)
gradually builds up the least perturbations by calculat-
ing the projection onto a specified decision boundary
and adding a tuning vector to force a misclassifica-
tion. Finally, Croce et al. (Croce and Hein, 2020)
propose AutoAttack (AA), a sequence of up to six
different attacks designed to test models’ robustness.
AA is widely regarded throughout the research com-
munity as a benchmark for evaluating the robustness
of adversarial training (AT) methods.
Adversarial Training. The AT optimization problem
(see Equation 1) is an NP-hard problem. This is due
to the inner maximization problem: the cost function
of neural networks are non-concave (and non-convex)
with respect to the input (Huang et al., 2022) (Madry
et al., 2019). The standard AT approach, proposed in
(Madry et al., 2019), uses a PGD attack to approxi-
mate the inner maximization problem. This approach
has been extended and adjusted in various ways, such
as adjusting the loss function, altering the framework
structure, and adapting strategies to evolve with spe-
cific images or training stages.
Novel Loss Functions. Standard AT training typi-
cally uses a predefined loss function such as Cross-
Entropy (CE) or Kullback-Leibler (KL) divergence to
calculate the distance between the model output and
the correct labels. Cui et al. (Cui et al., 2023) pro-
pose an Improved Kullback-Leibler (ILK) loss, which
addresses asymmetry by enabling gradient propaga-
tion and replaces sample-wise weights with class-
wise weights. Pang et al. (Pang et al., 2022) in-
troduced the SCORE robust error which calculates
the loss as the maximum distance between the data
distribution and the model output for adversarial im-
ages. Zhang et al. (Zhang et al., 2019b) proposed
the TRADES loss function, which adds an additional
hyperparameter to control the balance between clean
accuracy and robustness. These loss functions are
commonly used in conjunction with other methods to
boost robustness (Jia et al., 2022) (Wu et al., 2020)
(Zhang et al., 2021). However, they fail to consider
the class properties we exploit in the Various Attacks
(VA) method. Moreover, these loss functions remain
unchanged throughout the AT process, which means
they neglect the weak areas of training and fail to
adapt to specific images or stages of training (Tian
et al., 2021). Simply adjusting the loss function while
keeping other factors constant throughout reduces the
generalization robustness of the final model. This is
because the training cannot adaptively respond to the
changing capabilities of the model and the properties
of the dataset.
Adaptive Training Strategies. These AT formulations
change the training strategy throughout the process
for a more effective solution. Zhang et al. (Zhang
et al., 2021) propose GAIRAT, which categorizes
samples as “attackable” or “guarded” based on their
vulnerability to attack, adjusting weights accordingly.
Xu et al. (Xu et al., 2023) propose DyART, which
prioritizes the increase of distances between samples
and decision boundaries using the novel Temperature-
PGD attack. Tian et al. (Tian et al., 2021) leverage
class-specific properties of different examples to in-
crease a model’s robustness. Cai et al. (Cai et al.,
2018) propose Curriculum AT (CAT), increasing at-
tack strength as training progresses. Shi et al. (Shi
and Liu, 2024) further analyze curriculum training
and provide a mathematical foundation for the suc-
cess of adaptive training methods. Jia et al. (Jia
et al., 2022) design the LAS-AT framework, utiliz-
Powerful & Generalizable, Why not both? VA: Various Attacks Framework for Robust Adversarial Training
231

ing a secondary model to generate a targeted attack
strategy at each training stage. These methods aim to
increase robustness against a wider variety of adver-
saries. However, they lack the variety of attacks that
the VA method employs to improve generalization
robustness. Additionally, they adapt training based
only on either the stage of training or image-specific
properties, whereas the VA framework adjusts train-
ing strategies based on both aspects. As a result, these
methods produce models with lower robust accuracy
values and less generalization robustness than VA, as
we demonstrate in §6.
5 VARIOUS ATTACKS
FRAMEWORK (VA)
Here, we introduce the VA (Various Attacks) adver-
sarial training method, designed to increase both the
overall model robustness and generalizability robust-
ness. The VA framework takes advantage of the class-
wide differences discussed in §3.2 by assigning spe-
cific attacks to specific classes based on the relative
attack strength. In this context, the term assignment
means that for the image-class y and attack a at epoch
e, attack a is used to perturb the images in class y dur-
ing that specific training epoch. These assignments
are epoch-specific and are adjusted throughout train-
ing to improve the generalization robustness. They
maintain the diversity of generated examples while
still maximizing loss values to effectively approxi-
mate the solution to the inner maximization problem
in AT.
The VA framework consists of two major com-
ponents. First, Advanced Curriculum Training
(ACT) gradually incorporates stronger attacks over
the course of training while maintaining the abil-
ity to pinpoint the most vulnerable classes at each
stage. This approach helps in progressively strength-
ening the model against increasingly powerful adver-
sarial examples. Second, the Class-Attack Assign-
ment (CAA) algorithm assigns the strongest attacks
to the most vulnerable classes at key training stages,
thereby increasing the lowest image-class robustness
(i.e., improving the robustness of the weakest image-
classes) and consequently improving the overall ro-
bustness of the model.
5.1 Advanced Curriculum Training
Curriculum training is an AT technique that gradu-
ally increases the strength of the attacks used to gen-
erate adversarial examples. The rationale behind this
approach is that stronger attacks will yield more ef-
fective solutions to the inner maximization problem
of AT, thereby theoretically leading to a more effec-
tive training process and improving model robustness
(Madry et al., 2019). However, previous work has
highlighted a significant drawback: models trained
exclusively with stronger attacks tend to “forget” how
to defend against weaker attacks. This phenomenon
leads to decreased accuracy against such less effec-
tive attacks, thereby reducing overall model robust-
ness (Cai et al., 2018). Curriculum training works by
adaptively adjusting the training radius to correspond
with the Wasserstein distance between the adversar-
ial distributions of adjacent training iterations. In the
earlier phases of training, a small radius (indicating a
weaker attack) is used to stabilize the model when the
distance between iterations is relatively large. In later
phases and as training progresses, the radius is gradu-
ally increased to incorporate stronger attacks and im-
prove robustness as the distance decreases (Shi and
Liu, 2024).
Despite its success in improving the robustness of
adversarially trained models against certain attacks,
curriculum training still suffers from several problems
similar to traditional AT. First, it relies on a single at-
tack type adjusted to various strength levels to gener-
ate adversarial examples throughout the training pro-
cess. Although this approach helps a model to de-
velop increased robustness against different strength
levels of the attack used during training, it does not
help enhancing the model’s generalization robustness
against attacks not used in training. Moreover, the
existing form of curriculum training does nothing
to specifically target vulnerable image-classes dur-
ing training, the presence of which have been proven
to reduce the overall robustness of a model. To
address these issues we propose Advanced Curricu-
lum Training (ACT), an improved form of curriculum
training framework designed to enhance generaliza-
tion robustness by incorporating multiple attack types
throughout the training phases. ACT employs vari-
ous attacks at each training phase while gradually in-
creasing attack strength throughout the training pro-
cess. This method maintains the benefits of standard
curriculum training while diversifying the types of at-
tacks used, thereby improving the model’s generaliza-
tion robustness. ACT is composed of two key compo-
nents: phase-based curriculum training and class rev-
olution.
Phase-Based Curriculum Training. Phase-based
curriculum training divides training into multiple
phases, or groups of subsequent epochs. During each
phase E, a set of attacks A with similar strengths is as-
signed to generate adversarial examples for different
image classes. To determine the strength of an attack,
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
232

we examine the loss values produced by each attack
when perturbing a set of clean images. Higher av-
erage loss values indicate stronger attacks and lower
loss values indicate weaker attacks. Using a variety
of attack types across successive training iterations
prevents the model from overfitting to a single attack
type. Instead, it forces the model to adapt to various
distributions of adversarial examples. This approach
maintains the benefits of standard curriculum training,
with the relative strength of attacks increases through-
out the training and adjusts according to the Wasser-
stein distances between distributions of consecutive
training iterations. Simultaneously, it raises the gen-
eralization robustness by incorporating a broader di-
versity of attacks during training.
Class Revolution. To maintain the attack diversity,
ACT employs a mechanism called class revolution for
assigning attacks to classes during phase-based cur-
riculum training. Within each training phase E, ev-
ery attack a ∈ A is systematically rotated through all
classes. This ensures that each attack in A is used to
generate adversarial examples for every image class
in the dataset for at least one epoch. The strongest
attack-class pairings, determined using the CAA al-
gorithm are reserved for the final assignment in each
phase.
Class revolution ensures that the generalization
robustness of individual classes remains high. As
discussed in §3.2, image-classes within datasets have
different properties and thus different levels of robust-
ness. Equation 3 defines the class-wise variance of
generalization robustness:
CV
GR
=
1
C
C
∑
c=1
1
|A|
∑
a∈A
(α
c−a
−
¯
α
a
)
2
(3)
where α
c−a
represents the accuracy of class c un-
der attack a, and α denotes the average accuracy
across all classes for attack a. A high class-wise vari-
ance of generalization robustness indicates that the
more vulnerable image classes are significantly re-
ducing the overall image-class robustness. This oc-
curs when each image class is only exposed to cer-
tain attacks, resulting in a lower generalization robust-
ness. Class revolution mitigates this issue by ensur-
ing that each image class is subjected to all available
attacks, thereby enhancing the generalization robust-
ness of each class. A small-scale variation of curricu-
lum training is implemented within each phase as the
strength of class-attack assignments increases until
the strongest pairings have are applied. This compre-
hensive exposure reduces the class-wise variance of
generalization robustness while increasing the overall
generalization robustness of the model.
5.2 Class-Attack Assignment Algorithm
The Class-Attack Assignment (CAA) algorithm de-
termines the strongest class-attack assignments used
in the final pairing of each training phase. Using
loss values calculated prior to training, the CAA it-
eratively assigns the strongest attacks to generate ad-
versarial examples from images in the most vulner-
able image-classes. Once an attack is assigned, it is
removed from consideration to ensure diversity in ad-
versarial examples. Analogous to how the strongest
attacks are set, the most vulnerable image classes are
identified by looking at the average loss values caused
by all attacks. The class with the highest average
loss value is the most vulnerable, while image-classes
with lower average loss values are less vulnerable. By
placing the strongest assignments last in each phase,
the CAA maximizes its impact on increasing the ro-
bustness values of the most vulnerable image classes.
In the final training phase, the model is trained on the
strongest class-attack assignments for the strongest
attacks.
Working Process of CAA. As depicted in Algorithm
1, the CAA starts calculating the average loss
¯
l
y
using
all selected adversarial attacks for each image class y
(lines 1-3) via the formula below:
¯
l
y
=
1
|A|
∑
a∈A
1
|L
y−a
|
|L
y−a
|
∑
i=1
l
y−a
i
(4)
where L
y−a
denotes the set of loss values calculated
by using attack a against class y, and l
y−a
i
represents
a specific loss value within the set. On (line-4), the
image-classes are sorted in descending order based
on
¯
l
y
. On (lines 7-14), the CAA algorithm iterates
through each class, starting with the class y with the
highest
¯
l
y
. it calculates the average loss
¯
l
y−a
of each
attack a against class y as follows:
¯
l
y−a
=
1
|L
y−a
|
|L
y−a
|
∑
i=1
l
y−a
i
(5)
The attack with the highest
¯
l
y−a
is selected and as-
signed to y (line -11):
a
y
← argmax
a
¯
l
y−a
(6)
The selected attack a is then removed from con-
sideration for other classes (line- 12). This process
repeats for the class with the next highest
¯
l
y
, so that
it is assigned to the remaining attack with the high-
est
¯
l
y−a
. This continues until all classes have been
assigned a different attack.
5.3 Theoretical Formulation
In this section, we formally define the loss and objec-
tive functions of the VA method.
Powerful & Generalizable, Why not both? VA: Various Attacks Framework for Robust Adversarial Training
233

Algorithm 1: Class Assignment Algorithm.
Input : L – Loss values for each attack for
every class
C – Classes
A – Attacks
Output: A
f inal
– Unique attack assigned to
each class
1 for class y ∈ C do
2
¯
l
y
=
1
|A|
∑
a∈A
1
|L
y−a
|
∑
|L
y−a
|
i=1
l
y−a
i
3 end
4 C
sorted
← C
5 A
r
← A // Remaining attacks
6 A
f inal
7 for class y ∈ C
sorted
do
8 for attack a ∈ A
r
do
9
¯
l
y−a
=
1
|L
y−a
|
∑
|L
y−a
|
i=1
l
y−a
i
// Calculate average loss for each a left for c
10 end
11 a
y
← argmax
a
¯
l
y−a
// Select remaining attack with highest loss
12 A
r
← A
r
− a
y
13 A
f inal
= A
f inal
+ a
y
14 end
15 Return: A
f inal
Sample-Specific Loss Definition. Each attack a ∈ A
is provided with a separate bound to ensure perturba-
tions remain appropriately small. If perturbations are
unbounded, AT cannot fit all samples and is forced to
sacrifice some, leading to a distorted decision bound-
ary and diminished robustness (Cheng et al., 2020).
We use ε
a
to denote the perturbation limit for attack
a and then define the loss for sample (x,y) ∈ D as the
following:
max
a
y
(x)∈B(x,ε
a
y
)
L( f
Θ
(a
y
(x)),y) (7)
Here, a
y
denotes the attack assigned to image-class y
at the current training stage. B(x, ε
a
) represents the l
p
-
norm ball centered at x with radius ε
a
. This formula
selects the perturbed image a
y
(x) within the ε
a
-ball
around x with the largest loss.
Class-Wise Loss Definition. As described earlier, an
example x is assigned an attack a
y
based on its correct
image-class y. As such, we define the class-wise loss
for an image-class y as:
∑
a∈A
∑
x∈D
y
L( f
Θ
(a
y
(x)),y) (8)
Here, D
y
describes the subset of dataset D with cor-
rect the image-class y. This formula calculates the
loss for all images x with image-class y when per-
turbed by every attack a from the attack set A. (Recall
that by using class revolution in ACT, the VA method
trains samples against each available attack at some
stage of training).
Formal Formulation. Based on the sample-specific
and class-wise loss definitions defined above, along
with the standard AT formulation defined in Equation
1, the VA objective function is defined as:
min
Θ
E
(x,y)∈D
1
|C|
∑
y∈C
[
1
|D
y
|
∑
a∈A
∑
x∈D
y
max
a
y
(x)∈B(x,ε
a
y
)
L( f
Θ
(a
y
(x)),y)] (9)
where C denotes the number of classes in dataset D.
5.4 VA Pipeline
The VA framework is depicted in Algorithm 2. The
attacks assigned to each class at a particular epoch are
determined prior to training using the ACT and CAA
techniques described above. For each batch, the aver-
age image-class is identified and the attack is selected
accordingly (lines 4-5). Then, the images in the batch
are perturbed using the selected attack (line 6). The
loss between the correct image-class and the model
output of the perturbed image is calculated (line-7).
Finally, the calculated loss is used to update the model
parameters (line 8).
Algorithm 2: The Pipeline of Various Attacks.
Input : N – Number of epochs
f
Θ
– model with parameters Θ
η – Learning rate
A
f inal
– Assignments
D – Dataset
1 Initialize Θ
2 for epoch = 1 to N do
3 for batch b ⊂ D do
4 ¯y ← argmax f
Θ
(b)
5 a ← A
f inal− ¯y
// Select attack based on class
6 x
adv
← a(x) // Perturb x with attack a
7 l ← L ( f
Θ
(x
adv
),y)
8 Θ ← Θ − η · ∇l
9 end
10 end
5.5 Attack Selection Criteria
For the VA algorithm to be most effective, it is impor-
tant to select attacks that provide diversity and meet
criteria related to practical feasibility in training.
Attack Diversity. To ensure diversity, the chosen
set of attacks must incorporate distinct elements and
strategies for perturbing an image. This may include
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
234

using different norms for distance calculations, dif-
ferent loss functions, randomness, and/or adding ad-
ditional terms to gradient calculations. The focus here
is on having a set of differences rather than on the na-
ture of the differences themselves. Proper attack di-
versity results in a diverse set of generated adversar-
ial examples (Croce and Hein, 2020). Therefore, the
proper selection of attacks is essential to the success
of the VA method — using attacks that use similar
perturbation methods will not generate the necessary
diversity in adversarial examples, which is necessary
for effective training.
Practical Feasibility. The chosen attacks must be
suitable for practical use in adversarial training set-
tings. This can be determined by three criteria: time,
space, and effectiveness. Each attack should be fast
and require minimal computational resources, as slow
attacks that demand extensive resources such as disk
and GPU space make the training process impracti-
cably long or unfeasible. Additionally, the selected
attacks must be effective in increasing generalization
robustness during AT. Ineffective or weak attacks will
negatively impact the model’s performance. As de-
tailed in §6.5, we only select attacks that are exper-
imentally proven to improve model robustness when
used in AT.
6 EXPERIMENTS
This section details our experimental setup, includ-
ing the adversarial attacks and defense methods used.
Then, we provide an extensive analysis of the results
of VA compared to other AT methods. Finally, we
provide an ablation study of the VA framework.
6.1 Experimental Design
Comparison with Existing Methods. To provide
a comprehensive evaluation, we compared our VA
framework with the baseline as well as a variety of
reputable and highly cited AT defense methods. We
utilized the source code and the recommended train-
ing settings provided by the authors to train mod-
els using the following methods: GAIRAT, ADT,
TRADES, LAS-AT, and FAT (Friendly Adversarial
Training) (Zhang et al., 2020). In addition, we trained
models adversarially using the PGD attack as pro-
posed in (Madry et al., 2019) (labeled as ’Standard
AT’) and trained models only on clean data with no
adversarial training or other defenses applied (labeled
as ’Clean’). We also tested DNR (Kundu et al., 2021)
and YOPO (Zhang et al., 2019a) using the pre-trained
models provided by the authors.
Evaluation Metrics. We evaluated all models against
the AA attack using the standard evaluation set
(APGD-T, APGD-DLR, FAB, and Square Attack)
with ℓ
∞
norm and ε = 8/255. Also, we tested the
models against the ℓ
∞
norm PGD attack with 20 and
40 steps, a step size of 0.01, and ε = 8/255. Addition-
ally, we evaluated the models against the CW, MIM,
and FGSM attacks using 20 steps with ε = 8/255, a
step size of 2/255, and a margin of 50 where appli-
cable. Then, we reported two metrics: clean accu-
racy and robust accuracy. Clean accuracy refers to
the model accuracy when tested against unperturbed
samples from the predefined test subset of the dataset.
Robust accuracy refers to the accuracy of the model
when tested against samples from the same test sub-
set but perturbed with the attack under evaluation.
6.2 Settings
We implemented all experiments using Pytorch 2.01
with CUDA enabled and conducted on NVIDIA
GeForce RTX 4090 GPUs. We used a batch size of
128 for the VA method and trained for 100 epochs
on CIFAR-10 and 110 epochs on CIFAR-100. The
training included a warm-up round of 15 epochs for
CIFAR-10 and 25 epochs for CIFAR-100. We set the
weight decay to 2e−4 and used an initial learning rate
of 0.1 with a 10% decay at the 75th, 90th, and 100th
epochs. All training is conducted using an SGD opti-
mizer with a momentum of 0.9. We trained VA mod-
els using the WideResNet-34 architecture.
6.3 Robustness Comparisons
CIFAR-10 Dataset. As shown in Table 2, the VA
framework achieved higher robust accuracy scores
than the majority of other AT methods. Specif-
ically, VA outperformed Standard-AT, TRADES,
ADT, GAIRAT, LAS-AT, DNR (C), DNR (I), YOPO,
and FAT in terms of robust accuracy across all at-
tacks. (The results of the Curriculum AT and Cus-
tomized AT methods are discussed in §6.4). The VA
method also achieved 91.15% clean accuracy, which
is higher than all methods except Customized AT.
The clean model without any AT training achieves
95.09%. This discrepancy can be attributed to the
accuracy-robustness trade-off, where AT generally
decreases clean accuracy (Lee et al., 2020).
CIFAR-100 Dataset. The results on the CIFAR-100
dataset depicted in Table 3, further support the supe-
riority of the VA method. It achieved a higher ro-
bust accuracy against all attacks compared to Stan-
dard AT, TRADES, ADT, GAIRAT, LAS-AT, YOPO,
and FAT. (The results of the Curriculum AT and Cus-
Powerful & Generalizable, Why not both? VA: Various Attacks Framework for Robust Adversarial Training
235
Table 2: The robustness of AT defense methods on the CIFAR-10 dataset. Bold results with (*) refer to the highest results
among all AT methods. Bold results without (*) refer to the highest results among the majority of other AT methods.
The Experimental Results of CIFAR-10 Dataset
Defense Method Clean FGSM MIM CW PGD-20 PGD-40 AA
Clean (Without AT) 95.09%* 26.08% 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% 0.00%
Standard AT 86.89% 57.78% 51.09% 49.90% 51.68% 51.56% 48.32%
TRADES 84.58% 60.18% 54.97% 52.95% 55.53% 55.40% 52.02%
ADT 83.63% 56.90% 49.93% 48.73% 50.51% 50.29% 45.98%
GAIRAT 85.74% 56.69% 56.81% 44.48% 58.63% 58.67% 42.48%
LAS-AT 87.34% 62.11% 55.81% 54.72% 56.39% 56.23% 53.03%
DNR (C) 87.48% 55.74% 46.65% 44.76% 47.41% 47.00% 42.40%
DNR (I) 87.31% 54.69% 45.80% 43.07% 46.42% 46.18% 40.97%
YOPO 86.34% 55.26% 48.17% 47.71% 48.72% 48.37% 44.93%
FAT 89.06% 58.81% 48.78% 47.29% 48.28% 47.96% 44.42%
Curriculum AT 89.92% 78.55% 3.83% 35.40% 40.27% 26.01% 0.14%
Customized AT 94.04% 81.29%* 74.13%* 58.79%* 68.47% 66.40% 21.68%
Ours (VA) 91.15% 64.98% 61.69% 56.52% 68.71%* 68.58%* 55.74%*
Table 3: The robustness of AT defense methods on the CIFAR-100 dataset. Bold results with (*) refer to the highest results
among all AT methods. Bold results without (*) refer to the highest results among the majority of other AT methods.
The Experimental Results of CIFAR-100 Dataset
Defense Method Clean FGSM MIM CW PGD-20 PGD-40 AA
Clean (Without AT) 78.65%* 8.77% 0.01% 0.00% 0.00% 0.00% 0.00%
Standard AT 60.73% 31.08% 27.47% 26.13% 27.79% 27.64% 24.90%
TRADES 52.06% 27.88% 25.79% 22.75% 26.52% 26.53% 21.93%
ADT 57.72% 30.50% 24.76% 23.88% 25.47% 25.29% 21.53%
GAIRAT 60.06% 28.61% 24.66% 23.11% 25.08% 25.01% 21.28%
LAS-AT 59.22% 32.00% 26.39% 23.21% 25.75% 25.45% 21.96%
YOPO 62.31% 28.51% 24.23% 23.57% 24.48% 24.31% 21.37%
FAT 65.09% 29.18% 23.24% 23.02% 23.25% 23.14% 21.44%
Curriculum AT 64.73% 70.55%* 0.98% 8.92% 20.32% 12.97% 0.03%
Customized AT 73.14% 45.99% 37.23%* 7.23% 34.96%* 33.83%* 11.59%
Ours (VA) 61.90% 32.77% 29.55% 28.13%* 29.92% 30.11% 25.93%*
tomized AT methods are discussed in §6.4). Addi-
tionally, the clean accuracy for VA on CIFAR-100 is
equal to 61.90%, which is higher than many AT meth-
ods including Standard AT, LAS-AT, ADT, GAIRAT,
and TRADES.
6.4 Analysis of Generalization
Robustness
The results reported in Tables 2 and 3 demonstrate
the VA method’s ability to generalize to a variety
of attacks, thereby increasing the robustness of the
trained model against attacks of different types and
strengths. VA provides effective robustness against
weak and strong types of gradient-based attacks such
as FGSM and PGD. It is also able to defend a trained
model against sophisticated and more adaptive at-
tacks such as AA. Meanwhile, other AT methods
show promising results in terms of clean and ro-
bust accuracy against some types of attacks. How-
ever, they fail to defend the trained models against
more adaptive and stronger attacks. For instance,
the Customized-AT defense achieved a higher robust
accuracy on CIFAR-10 than the VA method when
tested against FGSM, MIM, CW, and PGD-7 at-
tacks. It also achieved a higher clean accuracy. How-
ever, when the strength of the attack increased (e.g.,
PGD-20 and PGD-40), Customized-AT failed signif-
icantly and achieved lower robust accuracy than the
VA method. Notably, Customized-AT only achieved
21.68% robust accuracy against AA, significantly
lower than VA (55.74%) and the majority of other
AT methods. The same pattern holds for CIFAR-100,
where Customized-AT achieved high robust accuracy
against weak attacks such as FGSM (45.99%). Mean-
while, it reported very low robust accuracy against
AA (11.59%). This indicates that Customized-AT is
designed to provide robustness against weak gradient-
based attacks and cannot generalize to unseen and
stronger attacks.
This lack of generalization robustness is also
present in Curriculum-AT. On CIFAR-10, it reported
a higher robust accuracy against the FGSM attack
(78.55%) compared to the VA accuracy (64.98%).
However, it achieved lower robust accuracy against
the remaining attacks. Specifically, it reported only
0.14% robust accuracy against AA. This indicates a
major weakness in the training process that leaves the
model vulnerable to unseen attacks — a low gener-
alization robustness. The results were corroborated
on CIFAR-100 where the Curriculum-AT method re-
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
236
ports a higher robust accuracy against the FGSM at-
tack, but a significantly lower robust accuracy against
all other attacks. For instance, against both MIM and
AA, Curriculum-AT reported a robust accuracy of less
than 1%. Meanwhile, VA achieved 29.55% against
MIM and 25.93% against AA.
These results demonstrate examples where cer-
tain AT defense methods fail to generalize to differ-
ent types of attacks. Unlike these methods, the VA
method significantly enhances overall robustness and
specifically generalization robustness. By achieving
the highest robust accuracy against the strong and
adaptive AA attack on both CIFAR-10 and CIFAR-
100 datasets, VA not only demonstrates its superior
capability in defending DNN models against unseen,
strong, and adaptive attacks but also stands out as a
robust baseline AT method for ensuring model pro-
tection.
6.5 Ablation Studies
The parameters discussed in Section 6.2 were cho-
sen using a combination of experimentation and pre-
viously established baselines. The weight decay, ini-
tial learning rate, choice of optimizer, and momentum
were selected as the same training settings as the ma-
jority of the other tested methods in order to provide
a more accurate baseline comparison. In this section,
we describe the experiments we performed to select
the attacks used in training, the appropriate length of
training, and the most effective learning rate schedule.
The Impact of Attack Selection. Numerous tech-
niques have been designed to attack DNN models,
but many of them are not suitable for use in AT. To
identify the most effective attacks for the VA frame-
work, we conducted ablation studies by experiment-
ing with different attacks and analyzed their impact
on model robustness. For each experiment, we trained
two models using the VA framework. All attacks and
other training parameters are kept identical, except
one model is trained using the attack under exami-
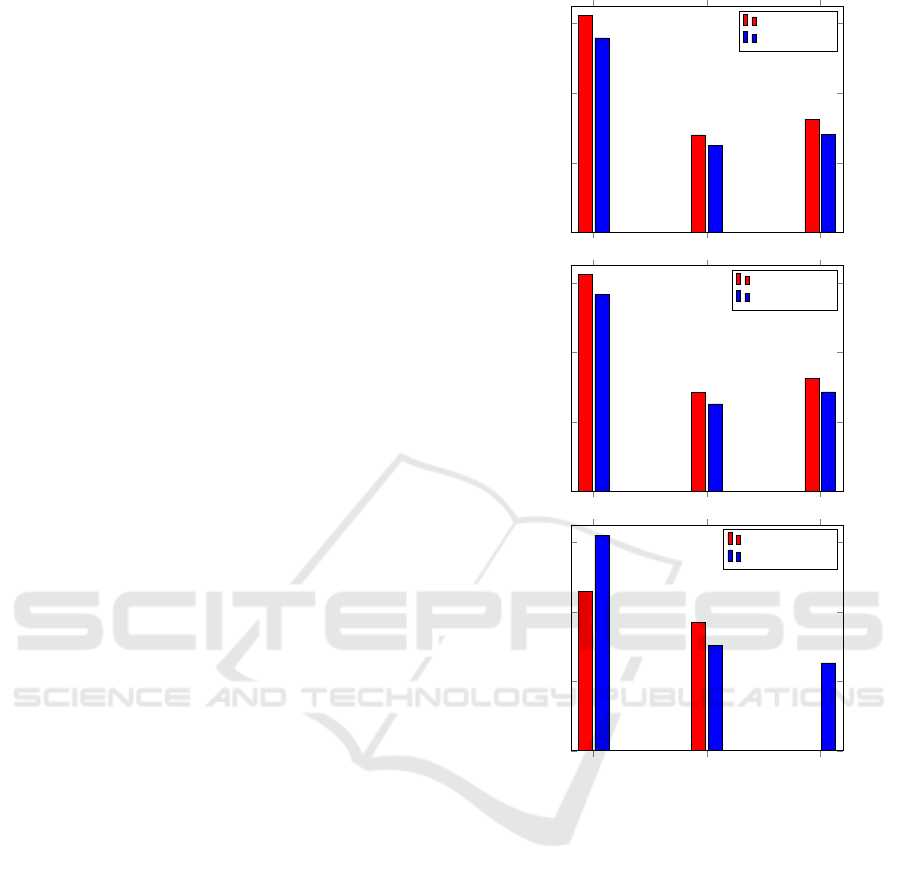
nation and the other is trained without it. Figure 1
demonstrates a sample of attacks and their impact on
the AT robustness. This experiment concluded that
the CW and MIM attacks increase both clean and
robust accuracy, making them suitable for training.
Conversely, the FGSM attack was found to signifi-
cantly decrease both clean and robust accuracy, indi-
cating its unsuitability for AT.
The Impact of Training Duration. We explore
the impact of the number of training epochs on fi-
nal model accuracy and robustness. While other AT
methods can utilize early stopping, where training
concludes after a set accuracy has been reached or
Clean FGSM PGD
0
20
40
60
Robustness %
With CW
Without CW
Clean FGSM PGD
0
20
40
60
Robustness %
With MIM
Without MIM
Clean FGSM PGD
0
20
40
60
Robustness %
With FGSM
Without FGSM
Figure 1: Three ablation studies, each comparing two mod-
els trained with or without a specific attack on the CIFAR-
100 dataset.
progress has slowed to a set rate, the VA method re-
quires all phases to be completed for maximum train-
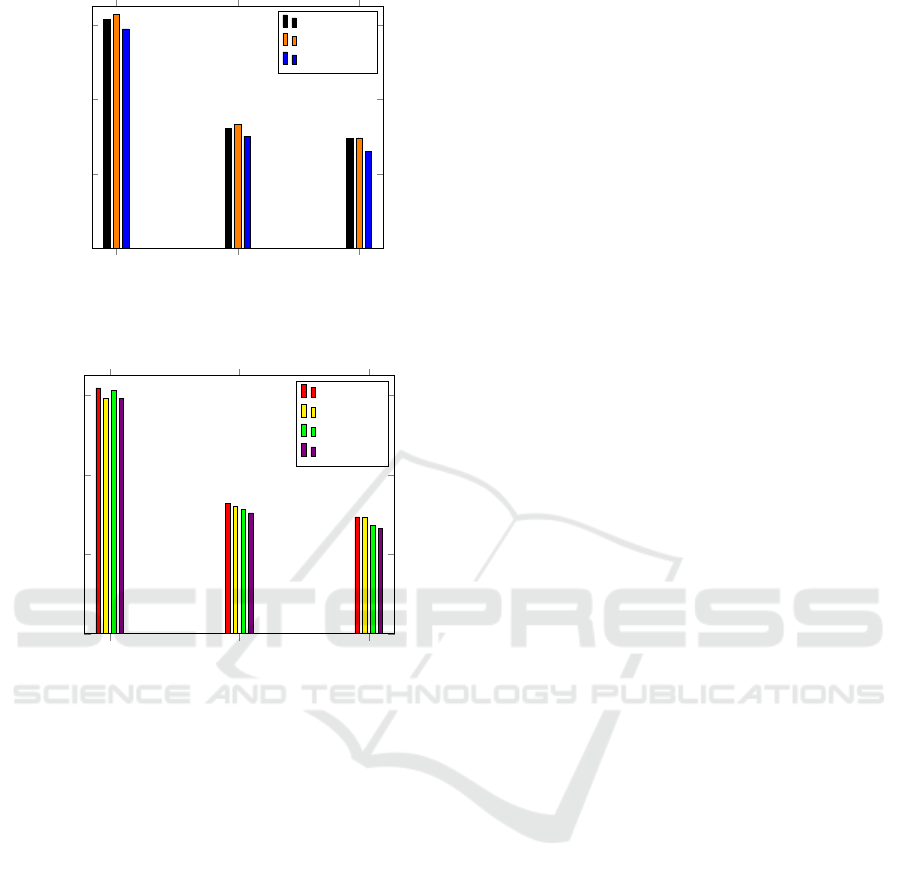
ing success. Fig. 2 shows the best results from three
different models trained on the CIFAR-100 dataset.
One model was trained for 70 total epochs, another
for 110, and the third for 140 epochs. The total num-
ber of epochs is divided into four phases of approx-
imately 17-18, 27-28, and 35 epochs each. The at-
tack choices, schedules, and other experimental set-
tings are otherwise identical.
For all three categories, clean and robust accu-
racy increases when moving from 70 to 110 total
epochs, indicating that a longer length of training
could be useful. However, the clean and robust ac-
curacy dropped when the model was trained for 140
epochs, reporting scores lower than the other two
models in all three categories. This indicates that
Powerful & Generalizable, Why not both? VA: Various Attacks Framework for Robust Adversarial Training
237
Clean FGSM PGD
0
20
40
60
Robustness %
70 Epochs
110 Epochs
140 Epochs
Figure 2: Ablation study comparing three WRN-34 models
trained for differing lengths of training on the CIFAR-100
dataset.
Clean FGSM PGD
0
20
40
60
Robustness %
Cyclic
Cyclic-5
Decaying
Constant
Figure 3: Ablation study comparing three WRN-34 models
trained with different learning rate schedules on the CIFAR-
100 dataset.
longer training does not always correlate with im-
proved AT results. For each dataset, we selected the
training length that resulted in the highest accuracies
and robustness: 110 epochs for CIFAR-100 and 100
epochs for CIFAR-10.
The Impact of Learning Rate Schedule on AT. To
select an effective schedule for adjusting the learning
rate, we conducted ablation studies examining the ef-
fects of different learning rate schedules. Fig. 3 dis-
plays the results of four different learning rates. The
‘Cyclic’ model uses a learning rate that increases and
decreases within each group of subsequent epochs.
The ‘Cyclic-5’ model uses a learning rate that cy-
cles every 5 epochs. The ‘Decaying’ model uses a
learning rate that decays towards the end of train-
ing. The ‘Constant’ model uses a constant learn-
ing rate throughout training. All four models used a
base learning rate of 0.1 and all other training settings
were identical. This experiment demonstrated that the
‘Cyclic’ model achieved the highest clean accuracy
and the highest robust accuracy against both PGD and
FGSM. Thus, we adopted the ‘Cyclic’ learning rate
learning rate for the final training.
7 CONCLUSION
We propose the various attacks Various Attacks (VA)
method, a novel adversarial training (AT) framework
designed to enhance both overall and generalization
robustness of models against unseen attacks. VA uses
Advanced Curriculum Training (ACT) to adjus train-
ing at each stage dynamically, coupled with the Class-
Attack Assignment CAA) algorithm to maximize loss
effectively. By employing a variety of attacks, we the
VA method significantly improves the generalization
robustness of the models and overall performance.
We further provide a theoretical formulation and gen-
eral algorithm for the VA method as well as guidelines
for the effective choice of attacks.
Our extensive experiments on two benchmark
datasets demonstrate the effectiveness and generaliz-
ability of the VA method. The results demonstrate
that VA significantly improves both the overall ro-
bustness and generalization robustness. Notably, it
achieves the highest robust accuracy against AutoAt-
tack (AA), an evaluation method specifically designed
to test robustness against diverse attack types, thereby
underscoring the superior generalization robustness
of the VA method. The success of our method sheds
lights on the limitations of current AT techniques,
which often fail to protect models against unseen and
stronger attacks, and position VA as a robust baseline
for defending deep neural networks.
REFERENCES
Addepalli, S., Jain, S., and Babu, R. V. (2022). Efficient and
effective augmentation strategy for adversarial train-
ing.
Alsmadi, I., Khamaiseh, S., and Xu, D. (2016). Network
parallelization in hpc clusters. In 2016 International
Conference on Computational Science and Computa-
tional Intelligence (CSCI), pages 584–589.
Cai, Q.-Z., Du, M., Liu, C., and Song, D. (2018). Curricu-
lum adversarial training.
Carlini, N. and Wagner, D. (2017). Towards evaluating the
robustness of neural networks.
Cheng, M., Lei, Q., Chen, P.-Y., Dhillon, I., and Hsieh, C.-
J. (2020). Cat: Customized adversarial training for
improved robustness.
Croce, F. and Hein, M. (2020). Reliable evaluation of
adversarial robustness with an ensemble of diverse
parameter-free attacks.
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
238

Croce, F. and Hein, M. (2021). Mind the box: l
1
-apgd
for sparse adversarial attacks on image classifiers. In
ICML.
Cui, J., Tian, Z., Zhong, Z., Qi, X., Yu, B., and Zhang, H.
(2023). Decoupled kullback-leibler divergence loss.
Dong, Y., Deng, Z., Pang, T., Su, H., and Zhu, J. (2020).
Adversarial distributional training for robust deep
learning. In Advances in Neural Information Process-
ing Systems.
Dong, Y., Liao, F., Pang, T., Su, H., Zhu, J., Hu, X., and Li,
J. (2018). Boosting adversarial attacks with momen-
tum.
Goodfellow, I. J., Shlens, J., and Szegedy, C. (2015). Ex-
plaining and harnessing adversarial examples.
Gowal, S., Rebuffi, S.-A., Wiles, O., Stimberg, F., Calian,
D. A., and Mann, T. (2021). Improving robustness
using generated data.
Huang, Z., Fan, Y., Liu, C., Zhang, W., Zhang, Y., Salz-
mann, M., S
¨
usstrunk, S., and Wang, J. (2022). Fast
adversarial training with adaptive step size.
Jia, X., Zhang, Y., Wu, B., Ma, K., Wang, J., and Cao, X.
(2022). Las-at: Adversarial training with learnable
attack strategy.
Khamaiseh, S., Al-Alaj, A., Adnan, M., and Alomari, H. W.
(2022a). The robustness of detecting known and un-
known ddos saturation attacks in sdn via the integra-
tion of supervised and semi-supervised classifiers. Fu-
ture Internet, 14(6).
Khamaiseh, S. Y., Al-Alaj, A., and Warner, A. (2020).
Flooddetector: Detecting unknown dos flooding at-
tacks in sdn. In 2020 International Conference on In-
ternet of Things and Intelligent Applications (ITIA),
pages 1–5.
Khamaiseh, S. Y., Bagagem, D., Al-Alaj, A., Mancino, M.,
Alomari, H., and Aleroud, A. (2023). Target-x: An
efficient algorithm for generating targeted adversarial
images to fool neural networks. In 2023 IEEE 47th
Annual Computers, Software, and Applications Con-
ference (COMPSAC), pages 617–626.
Khamaiseh, S. Y., Bagagem, D., Al-Alaj, A., Mancino,
M., and Alomari, H. W. (2022b). Adversarial deep
learning: A survey on adversarial attacks and defense
mechanisms on image classification. IEEE Access,
10:102266–102291.
Kosuge, A., Sumikawa, R., Hsu, Y.-C., Shiba, K., Hamada,
M., and Kuroda, T. (2023). A 183.4nj/inference
152.8muw single-chip fully synthesizable wired-logic
dnn processor for always-on 35 voice commands
recognition application. In 2023 IEEE Symposium on
VLSI Technology and Circuits (VLSI Technology and
Circuits), pages 1–2.
Kundu, S., Nazemi, M., Beerel, P. A., and Pedram, M.
(2021). Dnr: A tunable robust pruning framework
through dynamic network rewiring of dnns. In Pro-
ceedings of the 26th Asia and South Pacific Design
Automation Conference, pages 344–350.
Kurakin, A., Goodfellow, I., and Bengio, S. (2016). Ad-
versarial machine learning at scale. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1611.01236.
Lee, S., Lee, H., and Yoon, S. (2020). Adversarial vertex
mixup: Toward better adversarially robust generaliza-
tion.
Liao, F., Liang, M., Dong, Y., Pang, T., Hu, X., and Zhu,
J. (2018). Defense against adversarial attacks using
high-level representation guided denoiser. In Proceed-
ings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and
pattern recognition, pages 1778–1787.
Madry, A., Makelov, A., Schmidt, L., Tsipras, D., and
Vladu, A. (2019). Towards deep learning models re-
sistant to adversarial attacks.
Pang, T., Lin, M., Yang, X., Zhu, J., and Yan, S. (2022).
Robustness and accuracy could be reconcilable by
(proper) definition.
Papernot, N. and McDaniel, P. (2017). Extending defensive
distillation.
Shi, L. and Liu, W. (2024). A closer look at curriculum
adversarial training: From an online perspective. In
Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial In-
telligence, volume 38, pages 14973–14981. Associa-
tion for the Advancement of Artificial Intelligence.
Szegedy, C., Zaremba, W., Sutskever, I., Bruna, J., Er-
han, D., Goodfellow, I., and Fergus, R. (2013). In-
triguing properties of neural networks. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1312.6199.
Tang, K., Huang, J., and Zhang, H. (2020). Long-tailed
classification by keeping the good and removing the
bad momentum causal effect. Advances in Neural In-
formation Processing Systems, 33:1513–1524.
Tian, Q., Kuang, K., Jiang, K., Wu, F., and Wang, Y. (2021).
Analysis and applications of class-wise robustness in
adversarial training. KDD ’21, page 1561–1570, New
York, NY, USA. Association for Computing Machin-
ery.
Wang, Y., Ma, X., Chen, Z., Luo, Y., Yi, J., and Bailey, J.
(2019). Symmetric cross entropy for robust learning
with noisy labels. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF
international conference on computer vision, pages
322–330.
Wu, D., tao Xia, S., and Wang, Y. (2020). Adversarial
weight perturbation helps robust generalization.
Xu, Y., Sun, Y., Goldblum, M., Goldstein, T., and Huang, F.
(2023). Exploring and exploiting decision boundary
dynamics for adversarial robustness.
Zhang, D., Zhang, T., Lu, Y., Zhu, Z., and Dong, B.
(2019a). You only propagate once: Accelerating
adversarial training via maximal principle. arXiv
preprint arXiv:1905.00877.
Zhang, H., Yu, Y., Jiao, J., Xing, E. P., Ghaoui, L. E., and
Jordan, M. I. (2019b). Theoretically principled trade-
off between robustness and accuracy. In International
Conference on Machine Learning.
Zhang, J., Xu, X., Han, B., Niu, G., Cui, L., Sugiyama, M.,
and Kankanhalli, M. (2020). Attacks which do not kill
training make adversarial learning stronger.
Zhang, J., Zhu, J., Niu, G., Han, B., Sugiyama, M., and
Kankanhalli, M. (2021). Geometry-aware instance-
reweighted adversarial training. In International Con-
ference on Learning Representations.
Powerful & Generalizable, Why not both? VA: Various Attacks Framework for Robust Adversarial Training
239
