
A Systematic Review of Sustainable Supplier Selection Using Advanced
Artificial Intelligence Methods
Hanen Neji
1
, Mouna Rekik
2
, Lotfi Souifi
1
and Ismail Bouassida Rodriguez
1
1
ReDCAD, ENIS, University of Sfax, Tunisia
2
MIRACL, ISIMS, University of Sfax, Tunisia
fi fi
Keywords:
Sustainable Supplier Selection, Sentiment Analysis, Text Analytics, Multi-Criteria Decision-Making
(MCDM).
Abstract:
Artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms have significantly advanced various fields, driving innovation in domains
such as healthcare, finance, and sustainability. In the realm of sustainable development, selecting suppliers
is crucial for promoting environmental responsibility and safeguarding the well-being of future generations.
This complex decision-making process requires evaluating suppliers across numerous criteria. Multi-Criteria
Decision-Making (MCDM) and AI techniques, including Natural Language Processing (NLP), Deep Learn-
ing (DL), and Machine Learning (ML), have emerged as powerful tools to address these challenges. However,
these methods often face transparency issues and the risk of greenwashing, which can erode trust in sustain-
ability assessments. To address this, we conducted a systematic literature review (SLR) of 44 papers published
between 2019 and 2024, sourced from databases such as Springer (12 papers), IEEE Xplore Digital Library
(11 papers), and Science Direct (21 papers). This review offers an equitable analysis of MCDM and AI mod-
els (NLP, DL, ML) for evaluating both supplier sustainability and the risk of greenwashing. Additionally,
sentiment analysis techniques are integrated to enhance transparency and provide insights into stakeholder
perceptions.
1 INTRODUCTION
In the rapidly evolving landscape of sustainability,
the ability to effectively analyze and interpret vast
amounts of data has become crucial. With the increas-
ing complexity of sustainability assessments, leverag-
ing advanced technologies and methodologies is es-
sential for making informed decisions. Cutting-edge
approaches in data analysis and artificial intelligence
are pivotal in enhancing our understanding of sustain-
ability practices, particularly in evaluating supplier
performance across various dimensions.
In the current global context, heightened environ-
mental concerns have propelled the selection of sus-
tainable suppliers to the forefront of corporate pri-
orities. Yet, evaluating these suppliers solely based
on sustainable criteria reveals inherent imperfections,
emphasizing the pressing need for a comprehen-
sive assessment of their sustainability. This imper-
ative stems from the timeless definition outlined by
the United Nations Brundtland Commission in 1978,
which advocates for meeting present needs without
compromising the ability of future generations to
meet their own.
Currently, evaluating supplier sustainability based
on (Environmental, Social, Governance) ESG crite-
ria and the Triple Bottom Line (TBL)—encompassing
economic, social, and environmental dimensions—is
gaining momentum as the gold standard. This ap-
proach offers a comprehensive perspective on sup-
plier performance, including environmental steward-
ship, social responsibility, and transparent governance
practices.
However, the multifaceted nature of these crite-
ria presents a complex decision-making landscape,
prompting the adoption of Multi-Criteria Decision-
Making (MCDM) methods to facilitate the selection
of sustainable suppliers. MCDM methods system-
atically evaluate multiple, often conflicting, criteria
such as environmental impact, social responsibility,
and economic performance. By using quantitative
and qualitative data, MCDM helps prioritize suppliers
who best align with sustainability goals, minimizing
subjective biases through a structured framework.
Machine Learning (ML) and Deep Learning (DL)
techniques further enhance the objectivity of this se-
Neji, H., Rekik, M., Souifi, L. and Rodriguez, I. B.
A Systematic Review of Sustainable Supplier Selection Using Advanced Artificial Intelligence Methods.
DOI: 10.5220/0013149900003890
In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2025) - Volume 3, pages 451-460
ISBN: 978-989-758-737-5; ISSN: 2184-433X
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
451

lection process by analyzing vast amounts of data
from social media and sustainability reports with high
precision and consistency. These technologies iden-
tify patterns and insights that might be missed by
human evaluators, enhancing the objectivity and ef-
ficiency of ESG criteria analysis in supplier evalua-
tions.
Nevertheless, reliance solely on objective evalua-
tion methods poses risks, such as greenwashing and
opacity. Greenwashing refers to the practice where
companies misleadingly present their sustainability
initiatives to maintain a positive image while maxi-
mizing profits, often at the expense of transparency
and genuine environmental impact (Vinella et al.,
2023).
Herein lies the significance of sentiment anal-
ysis as a complementary method, augmenting the
credibility and transparency of supplier evaluations.
By providing insights into stakeholders’ perceptions
and sentiments, sentiment analysis enriches evalua-
tion processes, fostering a more balanced and trans-
parent approach to supplier sustainability assessment.
Moving forward, in Section 2, we outline the plan-
ning of our Systematic Literature Review, followed by
the presentation of Results and discussion in Section
3. Finally, we conclude with overarching highlights
and propose avenues for further research in Section 4.
2 SYSTEMATIC LITERATURE
REVIEW PLANNING
2.1 Research Questions
Aiming to explore the application of web-based and
data-driven methodologies in sustainable supplier se-
lection and greenwashing detection, the following re-
search questions (RQ) were established:
• RQ1. What criteria and web-based data sources
are essential for evaluating sustainable supplier?
• RQ2. What advanced methods and data science
approaches for sustainable supplier selection?
• RQ3. How can web-driven sentiment analysis and
text analytics contribute to detecting greenwash-
ing?
Subsequently, we determined the initial research in
the research databases. In relation to the keywords,
three groups were formed:
• Group1: (”sustainable supplier selection”,”ESG”,
”sustainability evaluation”,”assessment criteria”,)
• Group2: (”MCDM”,”sentiment analysis”, ”text
analytics”,”Artificial Intelligence”)
• Group3: (”greenwashing detection”, ”greenwash-
ing”, ”detection of eco-washing”)
2.2 Search Strategy
The search strategy combines the key concepts of our
research questions in order to retrieve accurate re-
sults. It is an organized structure of keywords, in-
cluding ”sustainable supplier selection”, ”MCDM”,
”sentiment analysis”, and ”greenwashing” as well as
ESG criteria (environmental, social, and governance)
, all related to our research questions. We then added
synonyms, variations, and related terms for each key-
word, including ESG criteria, triple bottom line cri-
teria (environmental, social, and economic) . The
use of Boolean operators (AND and OR) allows us
to explore different combinations of search terms to
improve the relevance and comprehensiveness of the
results obtained. The final search string is (Green-
washing OR ”sustainable supplier” OR ”responsible
supplier” OR ”ESG”) AND (”sentiment analysis” OR
”MCDM” OR ”artificial intelligence” OR ”text ana-
lytics”)
2.3 Selection Criteria
After obtaining the search results from different
sources, a set of inclusion and exclusion criteria
was applied to help identify relevant primary studies.
Therefore, Inclusion Criteria (IC) are used to select
primary studies that indicate web-based analytical ap-
proaches and methods used for sustainable supplier
selection, such as MCDM , Artificial Intelligence (AI)
and sentiment analysis, or methods such as MCDM
and sentiment analysis contributing to greenwashing
detection. As for the Exclusion Criteria (EC), they
are used to eliminate those primary studies that do
not address the main topics searched in this System-
atic Literature Review (SLR), are not available, or are
directly related to an included primary study by the
same author.
• Inclusion Criteria (IC):
— Publications published in peer-reviewed jour-
nals (articles and conference papers)
— Publications published in English
— Publications published between 2019 and 2024
— Publications that are related to the research
questions
— Publications that match one of the search items
— Publications that have examples of best prac-
tices
— Publications that are related to higher education
institutions/universities
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
452
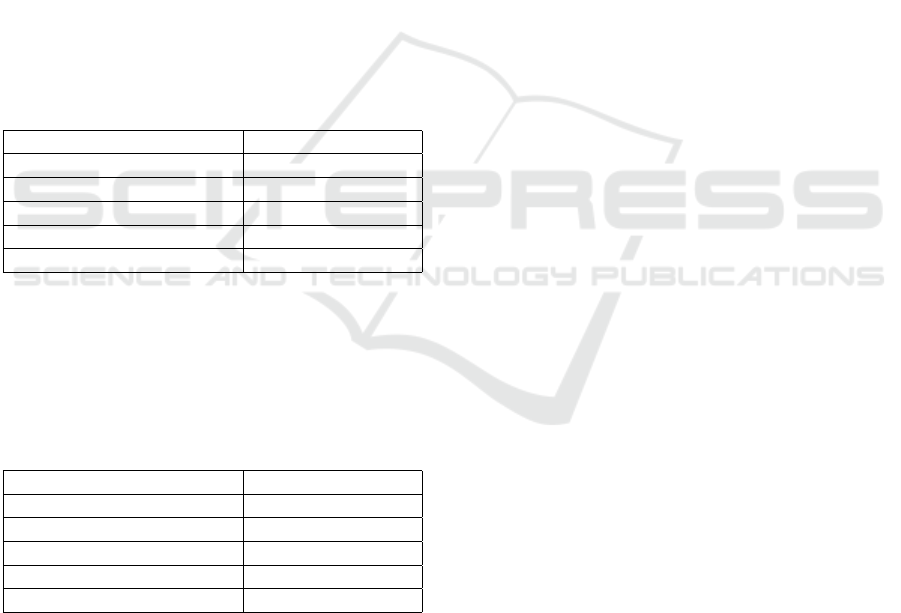
• Exclusion Criteria (EC):
— Publications not published in peer-reviewed
journals (books and chapters)
— Publications not published in English
— Publications not published between 2019 and
2024
— Publications that are not related to the research
questions
— Publications that do not match any of the search
items
— Publications that do not have examples of best
practices
— Publications that are not related to higher edu-
cation institutions/universities
2.4 Data Collection
The search process integrates the main concepts of
our research questions to obtain precise results. The
chosen sources are listed in the table 1, along with the
associated number of papers.
Table 1: Search results by Resource.
Resource Number of papers
springer 778
IEE Xplore Digital Library 35
ACMDigital library 103
Science Direct 123
Total 1039
After filtering the papers by excluding those based
on reading the abstracts, excluding more based on
reading the introductions, removing duplicate papers,
and excluding those with file not found errors, we
adopted 44 papers for this SLR. Table 2 presents the
filtered search results by resources.
Table 2: Filtered search results by resources.
Resource Number of papers
springer 12
IEE Xplore Digital Library 11
ACMDigital library 0
Science Direct 21
Total reading 44
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Criteria Enumeration for
Sustainable Supplier Evaluation
To accurately evaluate sustainable suppliers, iden-
tifying comprehensive sustainability criteria is es-
sential. These criteria, encompassing environmen-
tal, social, governance (ESG), and economic factors,
form the foundation for data collection and analy-
sis. In the context of sustainable supplier evalua-
tion, the enumeration of criteria plays a crucial role
in both the Multi-Criteria Decision-Making (MCDM)
process and in Natural Language Processing (NLP)-
based sentiment analysis.
In MCDM, criteria such as carbon footprint, re-
source efficiency, ethical labor practices, and sup-
ply chain transparency are carefully defined. Com-
mon MCDM techniques like the Analytic Hierarchy
Process (AHP) or Technique for Order of Preference
by Similarity to Ideal Solution (TOPSIS) can be em-
ployed to weigh and rank suppliers based on these cri-
teria. The effectiveness of MCDM hinges on a robust,
well-defined set of criteria, as it directly influences the
decision model’s accuracy and relevance.
During the sentiment analysis phase, these sus-
tainability criteria guide the process of extracting
meaningful information from large amounts of un-
structured textual data, such as user reviews, social
media posts, or reports. Various NLP techniques can
be employed to capture stakeholder perceptions and
detect potential greenwashing.
Aspect-Based Sentiment Analysis (ABSA) allows
for granular sentiment analysis by associating specific
criteria (e.g., environmental impact, working condi-
tions) with corresponding opinions. For example,
user reviews can be parsed to identify opinions tied
to specific sustainability aspects (e.g., “The supplier
uses renewable energy, but their labor conditions are
questionable”). ABSA helps determine how stake-
holders feel about each criterion, providing insights
into the supplier’s performance on multiple fronts.
Named Entity Recognition (NER) can be used to
identify and classify named entities (e.g., organiza-
tions, materials, processes) mentioned in textual data.
In sustainable supplier selection, NER could be em-
ployed to highlight references to specific criteria such
as ”carbon emissions,” ”fair trade,” or ”energy effi-
ciency,” ensuring that the analysis focuses on relevant
sustainability aspects.
Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA), a topic model-
ing technique, can uncover hidden topics and themes
related to sustainability in large text corpora. This
could help identify emerging sustainability concerns,
such as environmental degradation or unethical sourc-
ing practices, that may not have been previously con-
sidered in the criteria set.
Machine learning models like Support Vector Ma-
chines (SVM), Random Forests, or deep learning
models such as BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Rep-
resentations from Transformers) can classify text ac-
A Systematic Review of Sustainable Supplier Selection Using Advanced Artificial Intelligence Methods
453

cording to positive, negative, or neutral sentiments to-
ward sustainability criteria. These models are highly
effective when applied to large datasets of stakeholder
feedback, allowing the identification of trends in per-
ception.
One of the key challenges is identifying green-
washing, where companies make exaggerated or false
claims about their sustainability efforts. Textual en-
tailment or stance detection methods can be applied
to detect inconsistencies between what companies say
(e.g., in reports or press releases) and actual stake-
holder experiences (e.g., in reviews). These tech-
niques help cross-verify the authenticity of sustain-
ability claims, flagging companies that may be engag-
ing in deceptive practices.
Combining MCDM with NLP methods enhances
supplier evaluation by ensuring both quantitative
and qualitative assessments are taken into account.
MCDM methods can assign weights to different sus-
tainability criteria based on their importance, which
can then be applied in sentiment analysis to priori-
tize feedback on higher-weighted criteria (e.g., giving
more importance to environmental impact over cost).
Additionally, NLP-derived insights from stakeholder
reviews or social media can complement quantita-
tive metrics (e.g., carbon emissions, energy usage),
adding a layer of sentiment-driven decision-making
that captures public perception and trust.
The combined use of MCDM and advanced NLP
techniques allows for a thorough evaluation of sus-
tainable suppliers, ensuring transparency and reduc-
ing the risk of greenwashing. By leveraging methods
like ABSA, NER, LDA, and sentiment classification,
organizations can extract critical insights from vast
amounts of unstructured data, aligning the evaluation
process with core sustainability criteria and improv-
ing decision-making accuracy.
Conducting a comprehensive evaluation of sus-
tainable suppliers requires more than just assessing
environmental criteria. Critical studies have under-
scored this limitation, driving many organizations to
integrate additional dimensions such as social, eco-
nomic, and governance criteria into their supplier
evaluation processes (Khan et al., 2021; Ahmadi
et al., 2020). As a result, companies increasingly
use frameworks like the Triple Bottom Line (TBL),
which encompasses economic, social, and environ-
mental dimensions (Omair et al., 2021; Rani et al.,
2020; Hoseini et al., 2020; Cheng et al., 2023; Konys,
2019; Gidiagba et al., 2023; Wang et al., 2024; Menon
and Ravi, 2022; Tavana et al., 2023), or ESG (Envi-
ronmental, Social, and Governance) criteria to ensure
a well-rounded assessment of sustainability (Khan
et al., 2021; Fischbach et al., 2024; Gupta et al., 2024;
Daying and Zi’Ao, 2023).
Incorporating Industry 4.0 criteria has become
increasingly important, aligning modern technolog-
ical advancements with sustainability goals (Tavana
et al., 2023; Fallahpour et al., 2021). Addition-
ally, resilience criteria—evaluating suppliers’ ability
to withstand and recover from disruptions such as nat-
ural disasters or economic crises—are vital. These
criteria focus on risk management, supply chain trans-
parency, and flexibility, ensuring suppliers can nav-
igate unforeseen challenges while maintaining busi-
ness continuity (Ghamari et al., 2022; G
¨
okler and Bo-
ran, 2023; Mohammed et al., 2019).
Therefore, a supplier’s sustainability should be
evaluated holistically rather than solely through eco-
logical metrics, emphasizing the need for comprehen-
sive sustainability practices. Integrating diverse cri-
teria into text analytics and data science methodolo-
gies is essential for a thorough assessment of suppli-
ers. This approach includes evaluating environmental
impacts, social responsibility, and governance prac-
tices, ensuring alignment with corporate social re-
sponsibility and ethical business standards. Adopting
such a multi-faceted evaluation approach is crucial for
leveraging information retrieval and text analytics, so-
cial analysis, and web mining to enhance the accu-
racy and transparency of sustainability assessments.
This alignment with advanced data-driven techniques
not only supports more robust supplier evaluations
but also addresses potential greenwashing, thus pro-
moting long-term business success and sustainability
goals.
The Table 3 illustrates some examples of criteria
for evaluating sustainable suppliers.
3.2 Web-Based Data Sources for
Evaluating Sustainable Suppliers
To effectively evaluate supplier sustainability, lever-
aging web-based data sources is essential for a thor-
ough and accurate assessment. Key data sources in-
clude company reports, which provide detailed in-
sights into ESG practices through annual and inte-
grated reports, adhering to international regulations
such as the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Direc-
tive (CSRD) (Twinamatsiko and Kumar, 2022). In ad-
dition, web-based data from social media platforms,
including tweets, news articles, and press releases,
offer valuable perspectives on public sentiment and
expert opinions regarding a company’s ESG perfor-
mance (Biju et al., 2023; Fischbach et al., 2024). Fur-
ther, academic and industry studies on global supply
chain risks provide context and additional informa-
tion on supplier practices at various levels (Chu et al.,
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
454
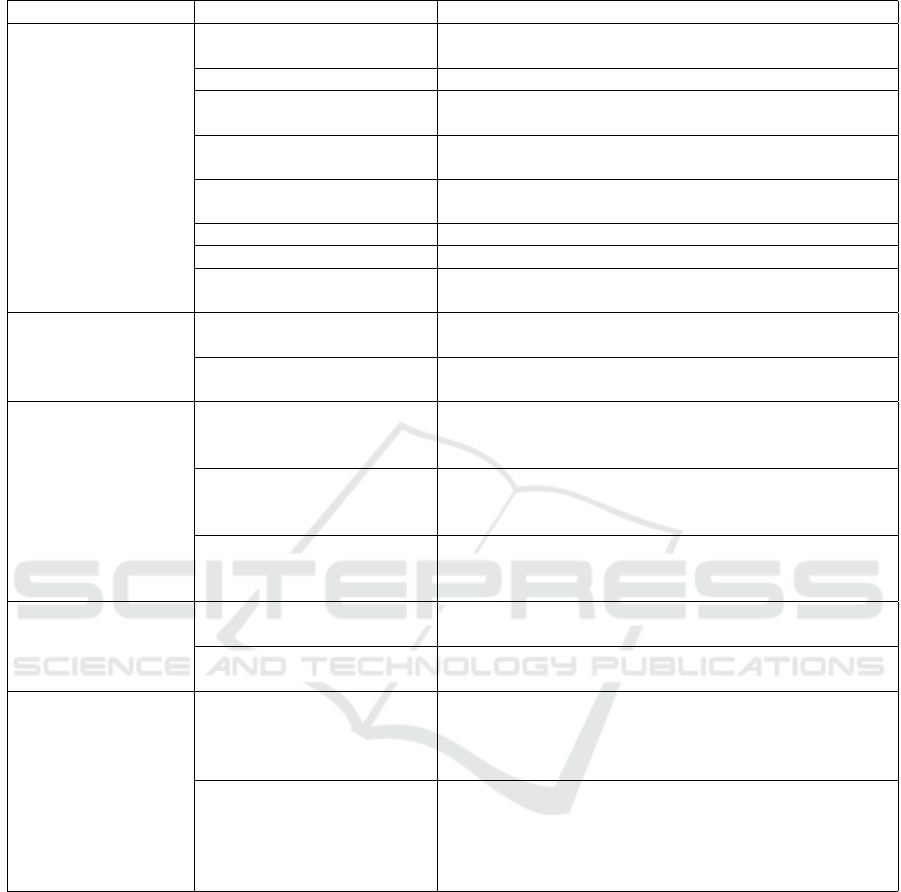
Table 3: Criteria for evaluating sustainable suppliers.
Dimension Criteria Definition
Environmental
Wastewater Suppliers should manage wastewater to minimize pollu-
tion.
Air emissions Suppliers should reduce emissions to improve air quality.
Friendly materials Suppliers should use sustainable materials to reduce en-
vironmental impact.
Resource consumption Suppliers should conserve resources throughout produc-
tion.
Carbon emissions reduction Suppliers should strive to minimize their carbon emis-
sions to mitigate climate change impacts.
Eco-friendly packaging Suppliers should use sustainable packaging materials.
Pollution control Suppliers should prevent pollution to protect ecosystems.
Renewable electricity and
energy
Suppliers should use clean energy sources for sustainabil-
ity.
Social
Work contract Suppliers should provide stable work contracts to their
employees.
Health insurance at work Suppliers should ensure that their employees are pro-
tected by health insurance.
Economic
Quality Suppliers should strive to provide products or services
meeting agreed-upon quality standards to ensure cus-
tomer satisfaction and product sustainability.
Flexibility Suppliers should be able to adapt quickly to changes in
demand, design, or other requirements to ensure an agile
and efficient supply chain.
Service Suppliers should provide responsive and quality cus-
tomer service, delivering support and appropriate solu-
tions throughout the business relationship.
Governance
Compliance Sustainable suppliers should demonstrate compliance
with relevant laws, regulations, and industry standards.
Transparency Sustainable suppliers should uphold transparency in their
operations, providing clear and accessible information.
Industry 4.0
Industry 4.0 Training and
Awareness
Suppliers should offer Industry 4.0 training and aware-
ness programs to their employees to enhance their skills,
which can contribute to better utilization of sustainable
technologies and reduced environmental impact.
Information technology (IT)
facilities
Suppliers should have adequate IT facilities, computers,
and high-speed internet access to support the adoption
and effective use of Industry 4.0 technologies, which can
promote more efficient and environmentally friendly pro-
duction.
2019). By integrating these diverse web-based data
sources, organizations can achieve a more compre-
hensive and nuanced evaluation of suppliers’ sustain-
ability practices.
3.3 MCDM Methods for Evaluating
Supplier Sustainability
The evaluation of sustainable suppliers is based on a
multitude of criteria. This diversity of criteria cre-
ates a MCDM challenge, requiring a holistic evalu-
ation that considers all these dimensions. Compa-
nies are faced with the complexity of weighing and
comparing these often conflicting criteria to select the
most sustainable suppliers. For example, prioritizing
criteria such as environmental impact may conflict
with economic considerations such as cost. Corpo-
rate governance, including transparency and business
ethics, as well as corporate governance practices, are
also crucial but often difficult to quantify elements.
Thus, companies must use advanced MCDM meth-
ods to integrate these criteria in a balanced way and
make informed decisions regarding the selection of
sustainable suppliers. A series of articles focuses on
the application of MCDM methods for selecting sus-
tainable suppliers (Hoseini et al., 2020; Wang et al.,
A Systematic Review of Sustainable Supplier Selection Using Advanced Artificial Intelligence Methods
455

2024; Menon and Ravi, 2022; Fallahpour et al., 2021;
G
¨
okler and Boran, 2023; Yildizbasi and Arioz, 2022;
Gidiagba et al., 2023; Zhang et al., 2021; Pu
ˇ
ska et al.,
2022; Khan and Ali, 2021; Masoomi et al., 2022; Liu
et al., 2019b; Chang et al., 2023; Liu et al., 2019a;
Varriale et al., 2024). Authors in (Omair et al., 2021)
introduce a decision support framework for supplier
prioritization using a MCDM approach. This frame-
work combines the Analytical Hierarchical Process
(AHP) and the Fuzzy Inference System (FIS). AHP
is employed to determine key sustainability criteria,
while FIS assesses the sustainability index of each
supplier based on these criteria. Expert opinions are
incorporated linguistically to account for the subjec-
tivity in decision-making, and fuzzy logic is used to
manage uncertainties. (Rani et al., 2020) proposes a
Pythagorean fuzzy sets (PFSs), an extension of intu-
itionistic fuzzy sets (IFSs), to manage uncertainty and
ambiguity. This study develops an approach using
PFSs and the Technique for Order Preference by Sim-
ilarity to Ideal Solution (TOPSIS) method to address
sustainable recycling partner selection problems with
unknown decision experts and criteria weights. The
study in (Tavana et al., 2023) introduces a decision
support system for evaluating and prioritizing suppli-
ers in public–private partnership projects. The ap-
proach involves two stages: first, assessing six poten-
tial suppliers using economic, circular, social, and In-
dustry 4.0 criteria with a novel group BWM method;
and second, using fuzzy inference rules and a FIS
structure to map non-linear relationships between the
criteria and the final score. The FIS includes 625
rules. The approach was validated using data from an
offshore wind farm project and the expertise of four
specialists. Sensitivity analysis revealed that the FIS
output is most sensitive to Industry 4.0 criteria.
The discussed works present robust methodolo-
gies for evaluating and prioritizing sustainable sup-
pliers, utilizing advanced MCDM techniques such as
AHP, FIS, and Pythagorean fuzzy sets. However,
a notable limitation across these studies is the lim-
ited consideration of user feedback in the evalua-
tion process. While these frameworks meticulously
assess suppliers based on a comprehensive set of
criteria—including environmental, social, economic,
and Industry 4.0 dimensions—they often overlook the
critical perspective provided by end-users and stake-
holders.
The MCDM approach is one of the most com-
monly used methods. However, a limitation of cur-
rent multi-criteria models for supplier selection and
performance evaluation lies in the models themselves.
Methods like the Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP),
the Analytic Network Process (ANP), and the Fuzzy
Analytic Hierarchy Process (Fuzzy AHP) are widely
applied in most studies. These methods require
decision-makers to make judgments based on com-
parisons. While they are effective for handling vague
or qualitative information, they often restrict the num-
ber of factors and suppliers that can be analyzed si-
multaneously.
3.4 Exploring Artificial Intelligence
Approaches for Supplier
Sustainability Evaluation
The use of artificial intelligence in the evaluation of
sustainable suppliers enhances companies’ ability to
effectively implement ESG criteria in their procure-
ment processes.
AI methods excels in processing large volumes of
data (Zekhnini et al., 2023), making it particularly
suitable for analyzing vast datasets such as those re-
lated to ESG performance. Its ability to efficiently
process large amounts of information and identify
patterns and trends within the data significantly en-
hances its effectiveness in evaluating supplier sus-
tainability. This capability to handle big data sets
AI apart as a powerful tool for sustainability assess-
ment and decision-making in procurement processes.
In the context of supplier evaluation, artificial intelli-
gence methods are divided into three categories: Ma-
chine Learning (ML), Deep Learning (DL), and Nat-
ural Language Processing (NLP). Each category has
distinct applications.
3.4.1 Machine Learning Approaches
ML has recently attracted more attention as a result of
its effectiveness in a variety of applications ranging
from image categorization to a variety of decision-
making challenges. The applications of ML ap-
proaches have increased dramatically in recent years
due to the explosion of data. In a predictive setting,
methods such as data envelopment analysis super-
vised learning, and unsupervised learning has shown
very outstanding performance. Furthermore, machine
learning can tolerate inaccuracies, uncertainty, and
imprecise information to achieve robustness when
replicating human decision-making behavior. These
functions not only solve the problem of scalability and
rapidity, but they also reduce the drawbacks of ear-
lier approaches and meet the demands of ever more
difficult supplier networks (Jagyasi and Raut, 2023).
In (Kulkarni et al., 2023; Baqi et al., 2022), authors
emphasize using AI to optimize the analysis of sup-
pliers’ ESG data, thereby facilitating ESG perfor-
mance monitoring and measurement. Additionally,
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
456

(Ahmad et al., 2023) proposes using ML to analyze
ESG data in the context of sustainability, with a fo-
cus on auto mating data collection and analysis. Fur-
thermore, in the context of evaluating sustainable sup-
pliers, employing ML techniques, particularly regres-
sion analysis, could be considered to analyze ESG
data and identify correlations with company perfor-
mance, thereby contributing to more responsible in-
vestment decisions (Twinamatsiko and Kumar, 2022).
Concurrently, AI can also play a vital role in re-
ducing greenhouse gas emissions by enabling precise
data analysis and identifying areas where companies
can enhance their environmental sustainability (Gaur
et al., 2023).
These various approaches illustrate the diversity
of methods and applications of AI in assessing sus-
tainable suppliers, offering unique perspectives on
how this technology can promote sustainability within
businesses.
The results of the experiment demonstrated the
effectiveness of this approach, with most classifica-
tion algorithms achieving an accuracy of over 90%.
Specifically, models such as LGBM, extra tree, gradi-
ent boosting, and decision tree exceeded expectations
by achieving an accuracy of over 99%.
(Abdulla et al., 2019) proposes a hybrid model for
supplier selection by integrating AHP with a machine
learning model. They utilized a decision tree classifier
to distinguish between good and bad suppliers.
ML methods are used for predicting financial per-
formance from ESG data, as well as for calculat-
ing ESG scores from financial data, where experi-
ments have shown that ML algorithms, particularly
gradient boosting and XGB, yielded accurate predic-
tions. Furthermore, anomaly detection techniques
based on ML, particularly the Local Outlier Factors
(LOF) model, can be deployed to identify outliers
or unusual values in ESG datasets, thus providing a
robust methodology for detecting any noise or mali-
cious data manipulation that could compromise their
integrity and reliability (Lee et al., 2022)
3.4.2 Deep Learning Approaches
In recent years, various deep learning methods have
been applied to the field of sustainable supplier se-
lection, leveraging their ability to handle complex,
high-dimensional data and capture intricate patterns
(Nicherala et al., 2022).. Techniques such as Convo-
lutional Neural Networks (CNNs) have been used for
their strength in feature extraction and pattern recog-
nition, especially when dealing with large datasets
that include images or spatial data. Recurrent Neural
Networks (RNNs) and their variants, like Long Short-
Term Memory (LSTM) networks, are employed to
analyze sequential data, such as time-series informa-
tion related to supplier performance. Autoencoders
have been utilized for dimensionality reduction and
anomaly detection, helping to identify outliers and
inconsistencies in supplier data. Furthermore, hy-
brid models combining deep learning with traditional
methods, like Decision Trees or the Analytic Hier-
archy Process (AHP), have been developed to en-
hance decision-making by integrating structured de-
cision frameworks with the powerful data processing
capabilities of deep learning.
Another recent study in the realm of sustainabil-
ity and ESG data utilizes advanced DL techniques to
analyze ESG data. In this experiment, deep learn-
ing techniques were employed to classify news arti-
cles into ESG labels. Specifically, embedding and
Bi-LSTM (Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory)
models were utilized for this multi-class classification
task. The results indicated significant performance
improvements when employing these deep learning
techniques, achieving a maximum prediction score of
0.8582 without processing Stop Words and 0.8936 af-
ter processing Stop Words. This demonstrates the
effectiveness of deep learning in accurately catego-
rizing news articles based on their ESG attributes.
Additionally, the experiment highlighted the impor-
tance for institutions to promptly address ESG is-
sues to safeguard their reputation and value, given
the rapid dissemination of company-related informa-
tion through the media. Therefore, the utilization of
deep learning models like Bi-LSTM showcases their
capability to efficiently analyze and categorize news
articles, providing valuable insights into companies’
ESG activities and facilitating timely responses to
emerging issues.(Lee et al., 2022)
3.4.3 NLP and Web-Driven Sentiment Analysis
Approaches
Natural Language Processing (NLP) is a branch of ar-
tificial intelligence that deals with language process-
ing and knowledge extraction. There are multiple ap-
plications of NLP, from sentiment analysis to key-
word extraction, text classification, and text summa-
rization. Since NLP plays a crucial role in text anal-
ysis, advanced techniques such as BERT and YAKE
are used to explore and understand sustainability re-
ports, particularly focusing on ESG aspects. BERT is
a pre-trained language model that supports tokeniza-
tion. It uses a tokenization technique called ”Word-
Piece,” which breaks down words into smaller sub-
units called ”subwords” for a more efficient and flex-
ible representation of language. However YAKE ex-
cels at keyword extraction by automatically analyz-
ing a text to identify the most important terms espe-
A Systematic Review of Sustainable Supplier Selection Using Advanced Artificial Intelligence Methods
457

cially related to sustainability criteria and values. A
data preprocessing phase is prominent after data col-
lection, where BERT tokenization can be employed.
This involved subdividing the data into keywords,
with ESG subcategories associated with the extracted
keywords and identified sustainability criteria (Gupta
et al., 2024). The ESG-Miner is a sophisticated tool
designed to evaluate companies’ ESG performance
through the analysis of news headlines. It begins
by automatically detecting specific companies men-
tioned in headlines using named entity recognition
and string matching with TF-IDF and cosine similar-
ity. Then, it classifies these headlines in two steps:
first, by determining their ESG relevance using ML
and DL models such as BERT, TF-IDF, and SVM;
second, by assigning relevant headlines to one of the
three ESG categories. For sentiment analysis, the
tool identifies whether the company’s behavior men-
tioned is perceived as neutral, positive, or negative,
using a classifier trained on a manually annotated
corpus (Fischbach et al., 2024). An other study fo-
cuses on the selection of regions in the global supply
chain, taking regional differences into account. While
the global supply chain offers advantages such as in-
creased flexibility and cost reduction, it also presents
various risks depending on the regions. The objec-
tive of this research is to identify these regional risks
through an analysis based on text mining. To achieve
this, a corpus of 11 well-cited and relevant academic
articles on global supply chain risk management was
compiled. These articles were imported into RStudio
for text data preprocessing using the tm and tidytext
packages. Additionally, the words were transformed
into their stems using the SnowballC package. Au-
thors in (Chu et al., 2019) focus on measuring the
ESG impacts in African cities using topic-based sen-
timent analysis methodologies applied to datasets col-
lected from social media platforms. The aim is to un-
derstand the population’s perception of ESG impacts,
given their significant influence on society. The pro-
cess begins with Data Collection: The study utilizes
basic keywords from the 40 Cities framework, cover-
ing themes aligned with the Sustainable Development
Goals (SDGs). Data is collected from social media
platforms like Twitter using Snscrape, and from web
pages via Google Search using Selenium and Trafi-
latura. Then, in the Data Filtering phase: Tweets con-
taining both city names and keywords are considered
relevant.
3.5 Greenwashing Avoidance Using
Sentiment Analysis
Despite the effectiveness of mentioned methods and
approaches instead of objective evaluation methods
based on criteria for sustainable suppliers, these eval-
uations remain insufficient as it does not account for
the risk of greenwashing. Greenwashing is ”the dis-
semination of false or deceptive information regard-
ing an organization’s environmental strategies, goals,
motivations, and actions”(Aronczyk et al., 2024),re-
ferring to the practice of misleadingly or exaggerat-
edly presenting a company’s practices or products as
environmentally friendly when they may not neces-
sarily be so.
Sentiment analysis plays a crucial role in detect-
ing and avoiding greenwashing by enabling a critical
evaluation of corporate communications. In the case
of Pathways Alliance, this method helps identify indi-
cators of greenwashing by analyzing the tone and per-
ception of public messages, thereby revealing poten-
tial discrepancies between sustainability promises and
actual actions. (Aronczyk et al., 2024). Another study
shows that sentiment analysis is conducted using a
qualitative approach, particularly analyzing Twitter
data related to ”ESG” and ”greenwashing”. The
methodology relies on the use of MAXQDA software,
which provides a reliable solution for analyzing qual-
itative data, including sentiments expressed in tweets.
To perform this analysis, researchers extracted tweets
containing the keywords ”ESG” and ”greenwashing”
separately. Subsequently, they utilized MAXQDA
software to analyze this data and assess the sentiments
expressed in the tweets. MAXQDA evaluates senti-
ments by assigning a sentiment score to each word in
the lexicon used, categorizing words in terms of pos-
itive, neutral, or negative connotations. Tweets are
then automatically coded with sentiment labels, en-
abling rapid capture of public sentiment on a specific
research topic. The results of this sentiment analy-
sis revealed a positive correlation between sentiments
toward ESG and greenwashing. This indicates that
concerns regarding greenwashing have increased pro-
portionally with interest in ESG-related issues (Biju
et al., 2023).
4 CONCLUSIONS
In this SLR, we have explored the growing trend
of sustainable supplier evaluation in today’s business
landscape, where sustainability has become a ma-
jor concern. However, evaluating the sustainability
of suppliers poses a complex challenge that requires
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
458

a holistic approach, considering various criteria and
data sources. Furthermore, we have discussed various
evaluation methods available, including multi-criteria
decision-making (MCDM) and artificial intelligence
approaches such as machine learning and deep learn-
ing. These methods enable a comprehensive analy-
sis of supplier performance across a diverse range of
criteria, thereby facilitating informed and data-driven
decision-making.
While many traditional methods such as multi-
criteria decision-making (MCDM), machine learning,
and deep learning are used for this evaluation, they
present potential risks of greenwashing and lack of
transparency. It is important to note that most existing
studies primarily focus on evaluating sustainable sup-
pliers based on expert opinions in the field. However,
this approach may be limited as it does not always
consider the opinions and sentiments of end-users and
public feedback, which can offer important perspec-
tives on the actual sustainability of suppliers.
With this in mind, a promising future approach
would be to integrate user feedback analysis into the
process of evaluating sustainable suppliers. By ex-
amining user feedback on supplier services, valuable
insights could be obtained into their performance in
terms of sustainability perceived by consumers. This
approach would complement traditional evaluations
based on expert opinions with data from direct and au-
thentic sources, thus providing a more comprehensive
and balanced perspective on supplier sustainability.
REFERENCES
Abdulla, A., Baryannis, G., and Badi, I. (2019). Weight-
ing the key features affecting supplier selection using
machine learning techniques.
Ahmad, V., Goyal, L., Arora, M., Kumar, R., Chythanya,
K. R., and Chaudhary, S. (2023). The impact of ai
on sustainability reporting in accounting. In 2023 6th
International Conference on Contemporary Comput-
ing and Informatics (IC3I), volume 6, pages 643–648.
IEEE.
Ahmadi, H. B., Lo, H.-W., Gupta, H., Kusi-Sarpong, S.,
and Liou, J. J. (2020). An integrated model for select-
ing suppliers on the basis of sustainability innovation.
Journal of Cleaner Production, 277:123261.
Aronczyk, M., McCurdy, P., and Russill, C. (2024). Green-
washing, net-zero, and the oil sands in canada: The
case of pathways alliance. Energy Research and So-
cial Science, 112:103502.
Baqi, A., Abdeldayem, M. M., and Aldulaimi, S. H. (2022).
Embedding artificial intelligence and green ideology
in formulating corporate and marketing strategies.
In 2022 ASU International Conference in Emerging
Technologies for Sustainability and Intelligent Sys-
tems (ICETSIS), pages 1–4.
Biju, A., Kodiyatt, S., and Krishna, P. e. a. (2023). Esg sen-
timents and divergent esg scores: suggesting a frame-
work for esg rating. In SN Business and Economics,
volume 3, page 209.
Chang, J.-P., Chen, Z.-S., Wang, X.-J., Mart
´
ınez,
L., Pedrycz, W., and Skibniewski, M. J. (2023).
Requirement-driven sustainable supplier selection:
Creating an integrated perspective with stakeholders’
interests and the wisdom of expert crowds. Computers
and Industrial Engineering, 175:108903.
Cheng, C., Wang, X., and Ren, X. (2023). Selection of
outsourcing logistics providers in the context of low-
carbon strategies. Environmental Science and Pollu-
tion Research, 30(7):18701–18717.
Chu, C.-Y., Park, K., and Kremer, G. E. (2019). Apply-
ing text-mining techniques to global supply chain re-
gion selection: Considering regional differences. Pro-
cedia Manufacturing, 39:1691–1698. 25th Interna-
tional Conference on Production Research Manufac-
turing Innovation: Cyber Physical Manufacturing Au-
gust 9-14, 2019 — Chicago, Illinois (USA).
Daying, Y. and Zi’Ao, Y. (2023). Discovering variation fi-
nancial performance of esg scoring through big data
analytics. In 2023 Asia-Europe Conference on Elec-
tronics, Data Processing and Informatics (ACEDPI),
pages 141–150.
Fallahpour, A., Wong, K. Y., Rajoo, S., Fathollahi-Fard,
A. M., Antucheviciene, J., and Nayeri, S. (2021). An
integrated approach for a sustainable supplier selec-
tion based on industry 4.0 concept. Environmental
science and pollution research, pages 1–19.
Fischbach, J., Adam, M., Dzhagatspanyan, V., Mendez, D.,
Frattini, J., Kosenkov, O., and Elahidoost, P. (2024).
Automatic esg assessment of companies by mining
and evaluating media coverage data: Nlp approach
and tool.
Gaur, L., Afaq, A., Arora, G. K., and Khan, N. (2023). Ar-
tificial intelligence for carbon emissions using system
of systems theory. Ecological Informatics, 76:102165.
Ghamari, R., Mahdavi-Mazdeh, M., and Ghannadpour, S. F.
(2022). Resilient and sustainable supplier selection
via a new framework: a case study from the steel in-
dustry. Environment, development and sustainability,
pages 1–39.
Gidiagba, J., Tartibu, L., and Okwu, M. (2023). Sustainable
supplier selection in the oil and gas industry: An inte-
grated multi-criteria decision making approach. Pro-
cedia Computer Science, 217:1243–1255. 4th Inter-
national Conference on Industry 4.0 and Smart Man-
ufacturing.
Gupta, A., Chadha, A., and Tewari, V. (2024). A natural
language processing model on bert and yake technique
for keyword extraction on sustainability reports. IEEE
Access, 12:7942–7951.
G
¨
okler, S. H. and Boran, S. (2023). A novel resilient and
sustainable supplier selection model based on d-ahp
and dematel methods. Journal of Engineering Re-
search.
Hoseini, A. R., Ghannadpour, S. F., and Ghamari, R.
(2020). Sustainable supplier selection by a new
A Systematic Review of Sustainable Supplier Selection Using Advanced Artificial Intelligence Methods
459

possibilistic hierarchical model in the context of z-
information. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Hu-
manized Computing, 11:4827–4853.
Jagyasi, D. and Raut, A. R. (2023). Implementation of esg
index on long-term value and performance of ogani-
zations using ai and ml. In 2022 OPJU International
Technology Conference on Emerging Technologies for
Sustainable Development (OTCON), pages 1–5.
Khan, A. U. and Ali, Y. (2021). Sustainable supplier selec-
tion for the cold supply chain (csc) in the context of
a developing country. Environment, development and
sustainability, pages 1–30.
Khan, S. A. R., Yu, Z., Golpira, H., Sharif, A., and Mardani,
A. (2021). A state-of-the-art review and meta-analysis
on sustainable supply chain management: Future re-
search directions. Journal of Cleaner Production,
278:123357.
Konys, A. (2019). Methods supporting supplier selec-
tion processes – knowledge-based approach. Proce-
dia Computer Science, 159:1629–1641. Knowledge-
Based and Intelligent Information and Engineering
Systems: Proceedings of the 23rd International Con-
ference KES2019.
Kulkarni, A., Joseph, S., and Patil, K. (2023). Role of artifi-
cial intelligence in sustainability reporting by leverag-
ing esg theory into action. In 2023 International Con-
ference on Advancement in Computation and Com-
puter Technologies (InCACCT), pages 795–800.
Lee, O., Joo, H., Choi, H., and Cheon, M. (2022). Propos-
ing an integrated approach to analyzing esg data via
machine learning and deep learning algorithms. Sus-
tainability, 14(14).
Liu, A., Xiao, Y., Lu, H., Tsai, S.-B., and Song, W. (2019a).
A fuzzy three-stage multi-attribute decision-making
approach based on customer needs for sustainable
supplier selection. Journal of Cleaner Production,
239:118043.
Liu, H.-C., Quan, M.-Y., Li, Z., and Wang, Z.-L. (2019b).
A new integrated mcdm model for sustainable sup-
plier selection under interval-valued intuitionistic un-
certain linguistic environment. Information Sciences,
486:254–270.
Masoomi, B., Sahebi, I. G., Fathi, M., Yıldırım, F., and
Ghorbani, S. (2022). Strategic supplier selection for
renewable energy supply chain under green capabil-
ities (fuzzy bwm-waspas-copras approach). Energy
Strategy Reviews, 40:100815.
Menon, R. R. and Ravi, V. (2022). Using ahp-topsis
methodologies in the selection of sustainable suppli-
ers in an electronics supply chain. Cleaner Materials,
5:100130.
Mohammed, A., Harris, I., Soroka, A., and Nujoom, R.
(2019). A hybrid mcdm-fuzzy multi-objective pro-
gramming approach for a g-resilient supply chain net-
work design. Computers and Industrial Engineering,
127:297–312.
Nicherala, Y. K., Sadula, S., and Shrinivas, V. P. (2022).
Deep learning based sustainable material attribution
for apparels. In 2022 IEEE 18th International Confer-
ence on Automation Science and Engineering (CASE),
pages 1352–1357.
Omair, M., Noor, S., Tayyab, M., Maqsood, S., Ahmed,
W., Sarkar, B., and Habib, M. (2021). The selection
of the sustainable suppliers by the development of a
decision support framework based on analytical hier-
archical process and fuzzy inference system. Inter-
national Journal of Fuzzy Systems, 23(7):1986–2003.
Publisher Copyright: © 2021, Taiwan Fuzzy Systems
Association.
Pu
ˇ
ska, A., Beganovi
´
c, A., Stojanovi
´
c, I., and Murti
ˇ
c, S.
(2022). Green supplier’s selection using economic and
environmental criteria in medical industry. Environ-
ment, Development and Sustainability, pages 1–22.
Rani, P., Mishra, A. R., Rezaei, G., Liao, H., and Mardani,
A. (2020). Extended pythagorean fuzzy topsis method
based on similarity measure for sustainable recycling
partner selection. International Journal of Fuzzy Sys-
tems, 22:735–747.
Tavana, M., Sorooshian, S., and Mina, H. (2023). An inte-
grated group fuzzy inference and best–worst method
for supplier selection in intelligent circular supply
chains. Annals of Operations Research, pages 1–42.
Twinamatsiko, E. and Kumar, D. (2022). Incorporating esg
in decision making for responsible and sustainable in-
vestments using machine learning. In 2022 Interna-
tional Conference on Electronics and Renewable Sys-
tems (ICEARS), pages 1328–1334.
Varriale, V., Cammarano, A., Michelino, F., and Caputo,
M. (2024). The role of digital technologies in pro-
duction systems for achieving sustainable develop-
ment goals. Sustainable Production and Consump-
tion, 47:87–104.
Vinella, A., Capetz, M., Pattichis, R., Chance, C., and
Ghosh, R. (2023). Leveraging language models to de-
tect greenwashing.
Wang, Y., Wang, W., Wang, Z., Deveci, M., Roy, S. K., and
Kadry, S. (2024). Selection of sustainable food suppli-
ers using the pythagorean fuzzy critic-marcos method.
Information Sciences, 664:120326.
Yildizbasi, A. and Arioz, Y. (2022). Green supplier
selection in new era for sustainability: A novel
method for integrating big data analytics and a hybrid
fuzzy multi-criteria decision making. Soft Comput.,
26(1):253–270.
Zekhnini, K., Chaouni Benabdellah, A., and Cherrafi, A.
(2023). A multi-agent based big data analytics sys-
tem for viable supplier selection. Journal of Intelli-
gent Manufacturing, pages 1–21.
Zhang, J., Li, L., Zhang, J., Chen, L., and Chen, G. (2021).
Private-label sustainable supplier selection using a
fuzzy entropy-vikor-based approach. Complex and In-
telligent Systems, pages 1–18.
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
460
