
Broadband Infrared Imaging for Enhanced Gas Leak Detection
Jianzhi Fan
1
, Jing Zhou
1,2
, Qi Zhao
3
, Dong Luo
1
and Wei Chen
1
1
Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 1068 Xueyuan Avenue,
Shenzhen 518055, China
2
School of Software Engineering, University of Science and Technology of China, 188 RenAi Road, Suzhou 215123, China
3
School of Mechatronical Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, 5th South Zhongguancun Street, Beijing 100081,
China
Keywords:
Optical Gas Imaging, Passive Infrared Detection, Gas Leak Detection.
Abstract:
This paper presents a passive broadband infrared imaging system designed for gas leak detection. The system
utilizes an optical design optimized for the 3–14 µm range, including a wide-spectrum lens and an uncooled
infrared camera. The broadband capability enables the detection of various gases across a wide spectral range.
To identify gas leaks, a novel adaptive gas leakage detection algorithm based on YOLOX and traditional image
processing techniques is developed. The system’s performance is validated through field experiments with SF
6
and CO
2
gases, showcasing its ability to accurately detect and segment gas leakage regions. Furthermore, the
study investigates the potential for gas composition analysis using the system’s broadband imaging. Future
work aims at optimizing the optical design and enhancing detection sensitivity for improved efficiency.
1 INTRODUCTION
Gas leaks in routine applications, industrial produc-
tion, and transportation pose significant risks to public
safety. Therefore, conducting rapid, sensitive, and ac-
curate research on gas leak detection is of critical im-
portance. From a practical perspective, the detection
must locate the source within a large area rapidly and
precisely. It should also measure the size, shape, and
subsequent diffusion patterns of the gas cloud. This
capability enables inspection personnel to promptly
evaluate the severity of the leakage.
Traditional gas leak detection methods, such as
gas chromatography (Moshayedi et al., 2023), elec-
trochemical gas sensing (Tan et al., 2022), and pho-
toacoustic spectroscopy (Zhao et al., 2022), employ
point-measurement techniques. Despite their high
sensitivity, these methods have a limited detection
range that suited only for small-scale, close-range
applications, and are inadequate for larger area as-
sessments (Strahl et al., 2021). Furthermore, even
when gas leaks are identified, due to the dispersion
of leaked gas and varying wind speeds, it is difficult
for personnel to accurately locate the source and com-
prehend current gas diffusion trends.
Many industrial gases have distinct absorption
spectra in the mid- to long-wave infrared. Conse-
quently, gas infrared imaging technology, which op-
erates based on the principle of gas infrared absorp-
tion, enables real-time imaging of scenes and identi-
fication of leaked gases within the imagery. This in-
novative imaging approach can efficiently pinpoints
leak sources and visualizes gas diffusion clouds, and
is therefore increasingly applied in the field of gas de-
tection (Wurst et al., 2017).
Infrared imaging technology for gas leak detec-
tion can be classified into active and passive types,
depending on whether a laser or another active radi-
ation source is utilized (Kulp et al., 1997). In cer-
tain scenarios, the use of a laser radiation source may
enhance the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and thereby
improve the system performance (Strahl et al., 2021).
However, due to the varied infrared absorption char-
acteristics of different gases and the restricted spec-
tral range of radiation sources, the types of detectable
gases are limited (Nutt et al., 2020). Additionally, as
the operational distance increases, the intensity of the
active radiation source diminishes rapidly, complicat-
ing long-range detection efforts. In contrast, passive
infrared imaging technology does not require an ac-
tive radiation source. It covers a broad spectral range,
is capable of detecting a wide variety of gases, and
facilitates long-distance imaging.
Recent advancements in uncooled infrared focal
plane array (IRFPA) detectors have significantly en-
hanced the feasibility of thermal imaging for gas leak
102
Fan, J., Zhou, J., Zhao, Q., Luo, D. and Chen, W.
Broadband Infrared Imaging for Enhanced Gas Leak Detection.
DOI: 10.5220/0013152300003902
In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Photonics, Optics and Laser Technology (PHOTOPTICS 2025), pages 102-108
ISBN: 978-989-758-736-8; ISSN: 2184-4364
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

detection. Regular infrared cameras, however, are
typically limited in either the mid-infrared (3–5 µm)
or the long-infrared (8–14 µm) regions. As a result,
they are unable to detect gases with absorption peaks
in both spectral bands simultaneously (Dong et al.,
2017). For instance, gases such as carbon dioxide
(CO2) has an absorption peak at 4.4 µm in the mid-
infrared band, and sulfur hexafluoride (SF6) has an
absorption peak at 10.6 µm in the long-infrared band,
these two gases cannot be simultaneously detected
by conventional cameras due to their restricted spec-
tral coverage. To overcome this limitation, this pa-
per propose a broadband infrared imaging system op-
timized for the 3–14 µm wavelength range, which can
detect gases across both the mid- and long-infrared
bands, thereby demonstrating the significant advan-
tage of broadband infrared imaging for comprehen-
sive gas leak detection.
2 IMAGING SYSTEM DESIGN
To achieve broadband infrared gas imaging, a passive
imaging system based on a broadband infrared cam-
era is designed. The system’s design is primarily in-
formed by the layer radiative transfer model of pas-
sive infrared imaging and the absorption characteris-
tics of the target gas in the infrared spectrum.
The layer radiative transfer model is commonly
employed in passive infrared gas imaging (Flanigan,
1996). It conceptualizes radiative transfer as a series
of parallel transmission layers, where each layer re-
ceives input radiation from the preceding layer and
emits output radiation to the subsequent layer. As-
suming a uniform atmospheric distribution between
the background and the infrared camera, the multi-
layer radiative transfer model can be simplified into
a three-layer system, as depicted in Figure 1. Here,
I
g
represents the radiation intensity of the gas cloud,
and I
t
indicates the intensity of background radia-
tion after absorption by the gas cloud. In upper path,
when the gas cloud is present, the equivalent temper-
ature detected by the infrared camera is expressed by
T (I
t
+I
g
). The Noise-Equivalent Temperature Differ-
ence (NETD) of the infrared detector should also be
considered. According to the detection principles of
the infrared camera, when the temperature difference
between the target and the background within the ra-
diation system is less than the NETD, the gas cloud
in the foreground cannot be accurately distinguished
from the background. This condition is described by
the following equation (Olbrycht and Kału
˙
za, 2019).
|T (I
B
) − T (I
t
+ I
g
)| > NET D
The background radiation after being absorbed by the
gas cloud is expressed using the basic Lambert-Beer
law of spectral absorption (Claps et al., 2001):
I
T
= I
B
∗ e
−α(λ)LC
Where α(λ) is the absorption cross-section of the
gas at wavelength λ, L is the length of the gas absorp-
tion path, C is the concentration of the target gas.
Therefore, NETD of the infrared camera is a criti-
cal factor in imaging system design. It directly deter-
mines the gas detection system’s performance. Ad-
ditionally, increased gas concentrations and extended
absorption paths result in greater contrast in the back-
ground radiation after passing through the gas cloud,
thereby making the gas trace more detectable.
Figure 1: Principle of passive infrared gas imaging.
The absorption characteristic spectra of gas
molecules are typically concentrated in the mid- to
long-wave infrared regions, specifically in the 3-14
µm range (Meribout, 2021). By imaging a specific gas
within its corresponding spectral band, the gas can be
detected.
Sulfur hexafluoride (SF
6
) and carbon dioxide
(CO
2
) are two gases widely utilized in industrial
production and common infrastructure applications
(Zhou et al., 2018) (Yu et al., 2012). Their absorption
characteristic spectra are available from the HITRAN
database (Gordon et al., 2022). The absorption peaks
of CO
2
and SF
6
located around 4.4 µm and 10.6 µm,
as shown in Figure 2 and 3 respectively, where x axis
is the wavelength in µm, y axis is the corresponding
spectral line intensity, represented by wavenumbers
per column density.
Based on the aforementioned principle of in-
frared broadband gas imaging detection, we have de-
veloped an infrared broadband imaging system for
gas leak detection and gas composition analysis.
The system primarily comprises a broadband lens
and an uncooled infrared focal plane camera(IRAY
RTD611WB). The schematic diagram of the system
is depicted in Figure 4.
The broadband infrared lens is specifically de-
signed and optimized for the 3-14 µm wavelength.
Due to the broadband operating wavelength, two in-
frared materials germanium (Ge) and zinc selenide
Broadband Infrared Imaging for Enhanced Gas Leak Detection
103
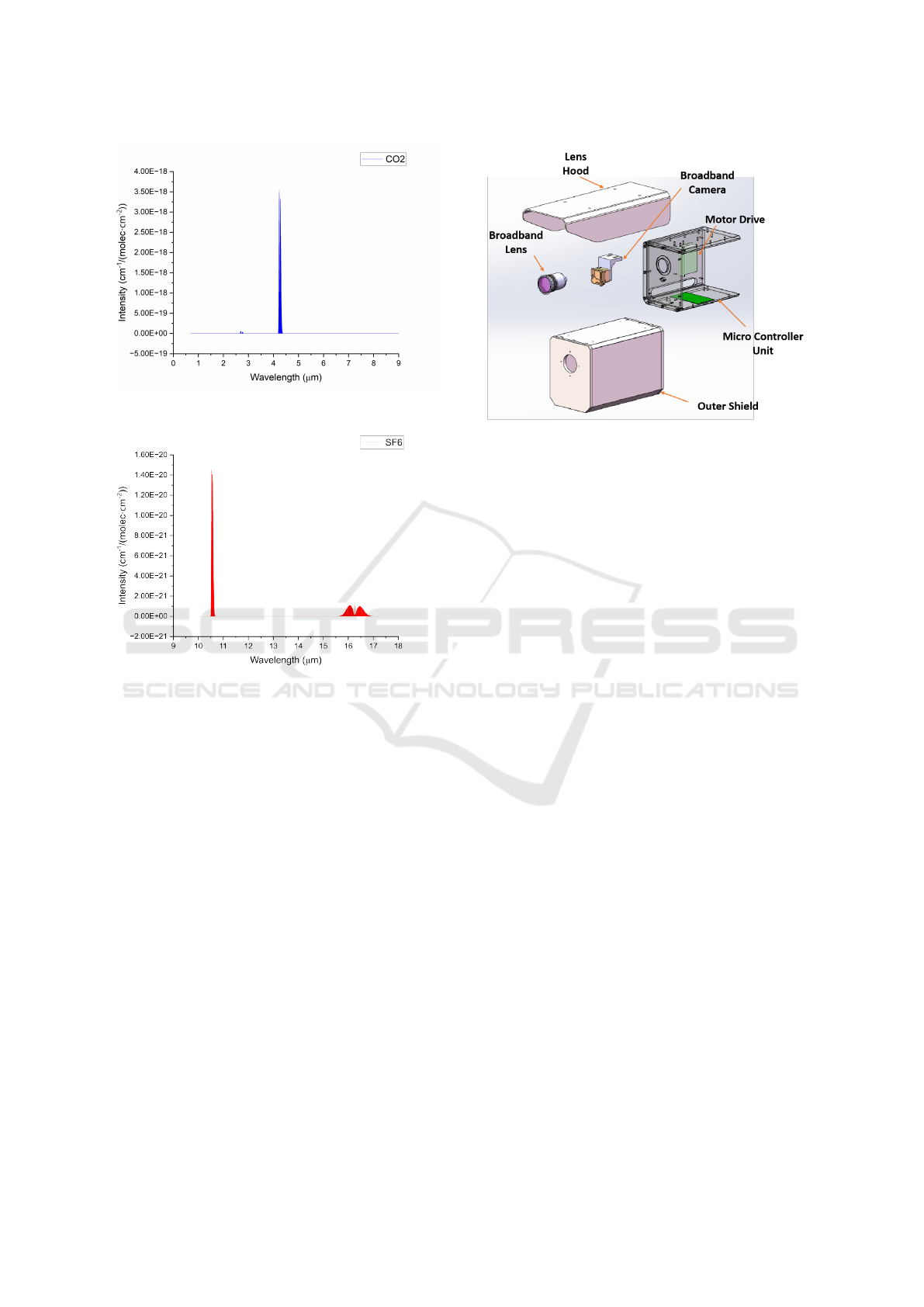
Figure 2: Infrared absorption spectrum of CO
2
.
Figure 3: Infrared absorption spectrum of SF
6
.
(ZnSe) are utilized to minimize potential chromatic
aberration. Additionally, four aspherical surfaces are
integrated to further optimize aberrations, as shown in
Figure 5. The lens has a focal length of 50 mm and an
aperture of 40 mm, resulting in an F-number of 1.25.
Combined with the focal plane camera’s target sur-
face of 10.8 × 8.8 mm, the optical system achieves a
field of view (FOV) of 12.8° × 10°. The average trans-
mittance of the lens across the entire 3-14 µm range is
not less than 80%. Given the detector’s pixel size of
17 µm, the lens resolution must be at least 29.4 lp/mm.
According to the modulation transfer function (MTF)
diagram, the lens contrast ratio at 30 lp/mm is not less
than 0.4, thereby satisfying the design specifications.
3 ALGORITHM DESIGN
Once the gas image is captured through the imaging
system, image processing algorithms should be
applied to segment the region where the gas is
present. For gas leak detection algorithms, both
Figure 4: System diagram.
traditional image processing methods, such as the
image difference algorithm based on OpenCV,
and gas target detection algorithms utilizing deep
learning techniques, have been explored. In this
study, both types of algorithms are evaluated, leading
to the development of a novel adaptive gas leakage
detection algorithm that integrates elements from the
aforementioned methods.
A. Gas Detection Algorithm Based on YOLOX
To identify gas leakage in infrared images, this
study employs a gas target detection model based on
YOLOX. This is a deep learning model belongs to the
YOLO(You Only Look Once) algorithm series (Ge
et al., 2021). It has the feature of enhanced detection
efficiency, which is suitable for the dynamic scenar-
ios of gas detection. Initially, the infrared image size
is adjusted, and downsampling is performed to com-
press the image, thereby reducing the computational
load during the detection process. Subsequently, the
YOLOX gas leak detection model is applied to ad-
just the image channels and extract relevant features.
These features are then input into a feature pyramid
for fusion, enhancing the overall feature extraction
process. Based on the extracted features, the model
predicts the presence of a gas leakage target in the in-
frared image, generating a detection result. This result
not only indicates whether a gas leakage is present but
also identifies the specific region of the leak within the
image.
It is important to note that the gas leak detection
model is a pre-trained deep learning network capable
of identifying gas leaks in infrared images. In
this study, the YOLOX deep learning network is
selected. Compared to traditional target recognition
algorithms, YOLOX demonstrates higher accuracy in
generalization scenarios. YOLOX also have superior
PHOTOPTICS 2025 - 13th International Conference on Photonics, Optics and Laser Technology
104

Figure 5: Lens design diagram.
real-time performance compared to models with large
number of parameters like Vision Transformer. This
is appropriate for deployment in resource-constrained
environments, demonstrating effective performance
even with limited training data.
B. Background Difference Algorithm Based on
OpenCV
For gas trace extraction, this study proposes a gas leak
detection algorithm utilizing traditional OpenCV im-
age processing techniques, specifically designed for
detecting gas leak traces in the 3–14 µm band infrared
images. The implementation steps are as follows:
1) Background Differentiation: A differential im-
age is obtained by subtracting the background image
(without gas leakage) from the target image (with gas
leakage). The resulted differnetial image has the same
pixel dimensions with the original image. To mini-
mize the impact of noise, multiple differential images
are averaged, which is similar to smoothing in time
domain. The differential image is then normalized,
expressed as follows:
I(x, y) =
0
I
max
I(x,y)
× 255
2) Image Filtering: The normalized differential
images are processed using median filtering and bilat-
eral filtering to obtain filtered images. A threshold is
then applied, where pixel values exceeding the thresh-
old are retained, and those below are set to zero, thus
isolating the gas traces within the images.
3) Image Merge: The filtered image is added with
the target image containing the gas leakage, resulting
in the final merged image.
Figure 6: Gas segmentation based on differential and filter-
ing.
C. Adaptive Gas Leakage Comprehensive
Detection Algorithm
The process for the adaptive gas leakage comprehen-
sive detection algorithm proposed in this manuscript
is depicted in Figure 7. Initially, a detection threshold
of the gas leak detection model is set. The infrared
images captured by the imaging system are input into
the YOLOX model for preliminary detection. If no
gas leakage is detected, the detection threshold is
lowered, and the newly acquired infrared images are
subsequently screened until the minimum threshold
value is reached, or a gas leakage target is detected
in any infrared image. If gas leakage is detected,
the image area containing the gas target is identified
by the location of the regression box. Based on the
detection results from each infrared image, images
with detected gas leaks are classified as gas leak
images, whereas those without detected leaks are
considered background images. This enables the
automatic selection and updating of the background,
facilitating future regional background differentiation
based on the classified gas leak and background
images.
Broadband Infrared Imaging for Enhanced Gas Leak Detection
105
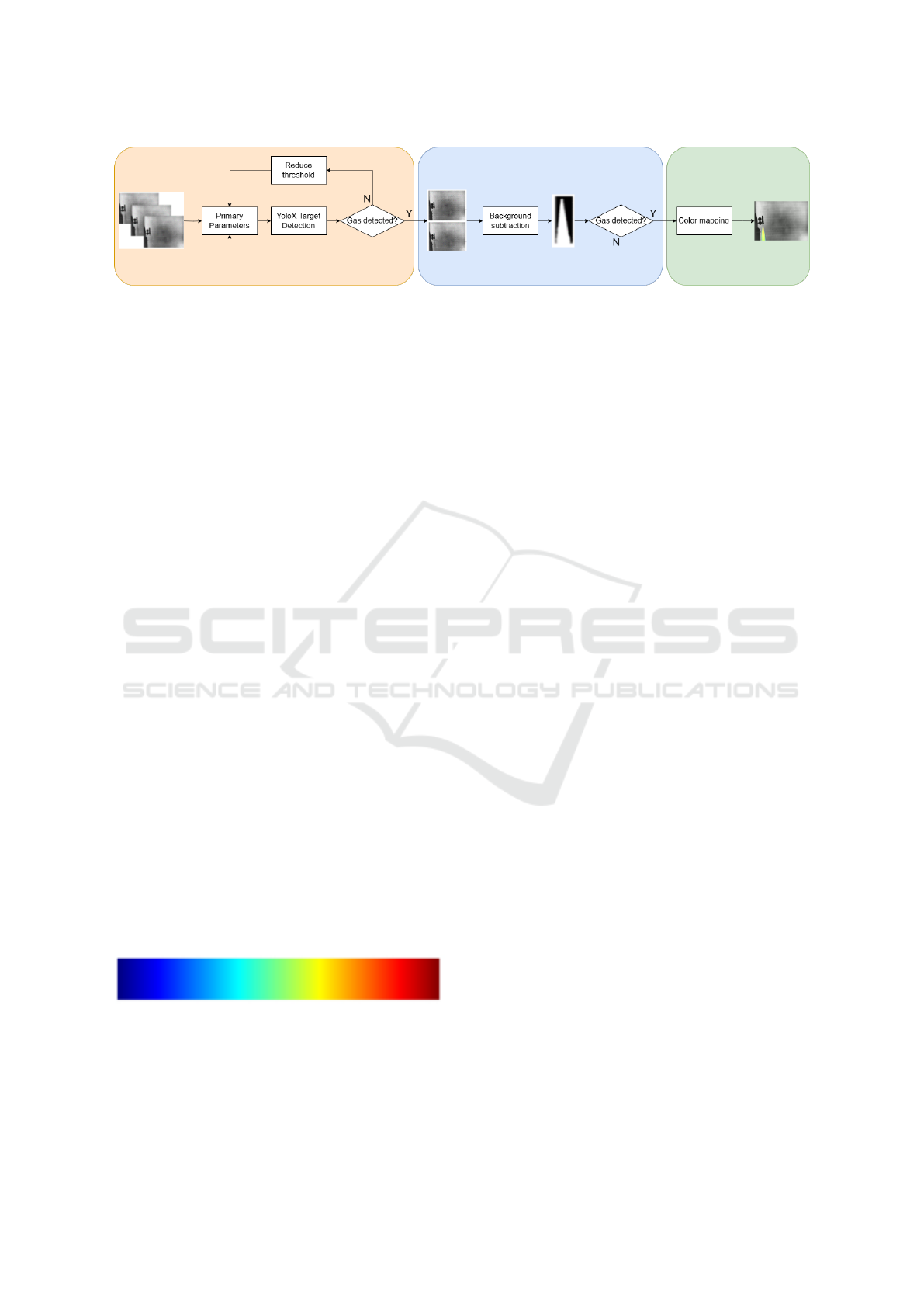
Figure 7: Diagram of adaptive detection algorithm.
After gas leak is detected as previously described,
a background difference algorithm is employed for
detailed examination of the infrared image region
containing the detected leak. This step aims to val-
idate the presence of a gas leak within the regression
box and eliminate any false detection from prelimi-
nary results. If a false detection is identified, the ini-
tial threshold for the gas leak detection model is re-
stored, and the target detection process recommences.
Conversely, if a gas leak is confirmed, the region of
the infrared image containing the leak is enhanced for
display and output.
To further exhibit the gas distribution within the
specific leakage area, jet color mapping is used to
represent the concentration of leaked gases. Jet color
mapping is a visualization technique that assigns col-
ors to data values based on a predefined color gradi-
ent. Typically, the jet color map ranges from red to
green to blue, providing a spectrum that represents
varying data intensities, corresponding color scheme
is shown in Figure 8. In the context of gas leak de-
tection, this mapping method is used to represent the
density of gas in a visually intuitive manner. High-
density regions are colored red, indicating a critical
concentration of gas, while lower-density areas tran-
sition through yellow and ultimately to green, signi-
fying lower gas concentrations.
By mapping gas density to colors, jet color map-
ping allows for an easy and immediate understanding
of gas distribution patterns. This approach is particu-
larly useful in applications such as gas leak detection,
where rapid evaluation is essential. The color-coded
representation enables personnel to identify high-risk
areas effectively, facilitating timely responses to po-
tential hazards.
Figure 8: Color scheme of jet color mapping.
In these application scenarios, continuous detec-
tion of gas leaks is achieved. Through preliminary
and detailed detection, the likelihood of false detec-
tion is minimized while ensuring real-time capabil-
ities. Furthermore, adaptive adjustment to the de-
tection threshold reduces dependency on background
conditions, effectively enhancing the accuracy of gas
leak detection.
4 EXPERIMENT AND RESULT
ANALYSIS
The proposed broadband infrared imaging system
was evaluated through controlled field experiments to
assess its capability in detecting and characterizing
gas leaks. Three scenarios were analyzed involving
the release of SF
6
and CO
2
, and a combination of both
gases. The flow rate for each release was controlled to
approximately 25 L/min using a valve, and the result-
ing plumes were visualized using jet color mapping
to exhibit concentration gradients. The segmented re-
sults are shown in Figure 9a, 9b and 9c.
In the first experiment, SF
6
was released from
a gas cylinder, and the broadband imaging system
effectively recorded and segmented the gas plume
(Figure 9a). The concentration gradient was repre-
sented with colors ranging from red (highest concen-
tration) to blue (lowest concentration), demonstrating
the ability of the system to effectively capture and vi-
sualize the gas distribution.
In the second experiment, CO
2
was released under
the same conditions (Figure 9b). While the concentra-
tion gradient was visualized similarly, the segmented
area of CO
2
appeared smaller compared to SF
6
. This
was attributed to the broadband infrared camera’s
relatively better response in the long-infrared range
(8–14 µm), where SF
6
has a significant absorption
peak at 10.6 µm. Despite the difference in sensitiv-
ity, the system effectively detected and visualized the
CO
2
plume.
The third experiment involved the simultaneous
release of SF
6
and CO
2
from separate sources (Fig-
ure 9c). The broadband imaging system captured
and distinguished both gases in real time, illustrat-
ing their respective concentration gradients using jet
color mapping. The ability to segment and visu-
alize both gases within a single scene demonstrates
PHOTOPTICS 2025 - 13th International Conference on Photonics, Optics and Laser Technology
106

(a) Segmentation results of SF
6
.
(b) Segmentation results of CO
2
.
(c) Segmentation results both CO
2
and
SF
6
.
Figure 9: Segmentation results of three images.
the system’s unique capability for simultaneous de-
tection and differentiation of multiple gases. Con-
ventional infrared cameras, which are typically lim-
ited to either the mid-infrared (3–5 µm) or the long-
infrared (8–14 µm) range, would be unable to simulta-
neously detect gases that absorb in different spectral
bands. The broadband system, by covering the full
3–14 µm range, effectively demonstrated its versatil-
ity and superiority in simultaneously capturing and
analyzing multiple gases with distinct spectral char-
acteristics. This capability is particularly beneficial in
real-world industrial scenarios where multiple gases
may be present.
Overall, the results demonstrated the broadband
infrared imaging system’s robust capability to detect
and visualize different gases simultaneously. The
broadband capability, covering both the mid- and
long-infrared spectral ranges, enabled comprehen-
sive gas detection that conventional infrared cameras
could not achieve. This makes the system particularly
suitable for industrial applications requiring accurate
and simultaneous detection of multiple gases.
5 CONCLUSION
This paper presents a broadband passive infrared
imaging system for the detection of gas leaks. The
system, incorporating a wide-spectrum lens and an
uncooled infrared focal plane array, has been opti-
mized for operation across the 3–14 µm wavelength
range, providing flexibility in detecting a wide vari-
ety of gases. The proposed hybrid gas detection algo-
rithm integrates both deep learning-based (YOLOX)
and traditional image processing methods, thereby
enhancing the system’s sensitivity and reliability in
analyzing gas leaks under realistic field conditions.
Experimental validation using CO2 and SF
6
gases,
with distinct absorption peaks in the mid- and long-
infrared regions, demonstrates the efficacy of the sys-
tem for broadband gas detection.
Unlike conventional infrared cameras, which are
limited to either the mid- or long-infrared range, the
proposed broadband system offers the capability to
detect gases with absorption peaks in both spectral
bands simultaneously. This unique capability is cru-
cial for comprehensive gas detection in diverse indus-
trial and environmental applications. Future research
will focus on the further optimization of the optical
system to enhance sensitivity and the development of
advanced machine learning models for gas detection
applications.
REFERENCES
Claps, R., Englich, F. V., Leleux, D. P., Richter, D., Tittel,
F. K., and Curl, R. F. (2001). Ammonia detection by
use of near-infrared diode-laser-based overtone spec-
troscopy. Applied Optics, 40(24):4387–4394.
Dong, M., Zheng, C., Miao, S., Zhang, Y., Du, Q., Wang,
Y., and Tittel, F. K. (2017). Development and mea-
surements of a mid-infrared multi-gas sensor system
for co, co2 and ch4 detection. Sensors, 17(10):2221.
Flanigan, D. F. (1996). Limits of passive remote detec-
tion of hazardous vapors by computer simulation. In
Electro-Optical Technology for Remote Chemical De-
tection and Identification, volume 2763, pages 117–
127. SPIE.
Ge, Z., Liu, S., Wang, F., Li, Z., and Sun, J. (2021). Yolox:
Exceeding yolo series in 2021.
Gordon, I. E., Rothman, L. S., Hargreaves, e. R., Hashemi,
Broadband Infrared Imaging for Enhanced Gas Leak Detection
107

R., Karlovets, E. V., Skinner, F., Conway, E. K., Hill,
C., Kochanov, R. V., Tan, Y., et al. (2022). The hi-
tran2020 molecular spectroscopic database. Journal
of quantitative spectroscopy and radiative transfer,
277:107949.
Kulp, T. J., Powers, P. E., and Kennedy, R. B. (1997).
Remote imaging of controlled gas releases using ac-
tive and passive infrared imaging systems. In In-
frared technology and applications XXIII, volume
3061, pages 269–278. SPIE.
Meribout, M. (2021). Gas leak-detection and measurement
systems: Prospects and future trends. IEEE Transac-
tions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 70:1–13.
Moshayedi, A. J., Sohail Khan, A., Hu, J., Nawaz, A., and
Zhu, J. (2023). E-nose-driven advancements in am-
monia gas detection: a comprehensive review from
traditional to cutting-edge systems in indoor to out-
door agriculture. Sustainability, 15(15):11601.
Nutt, K. J., Hempler, N., Maker, G. T., Malcolm, G. P., Pad-
gett, M. J., and Gibson, G. M. (2020). Developing
a portable gas imaging camera using highly tunable
active-illumination and computer vision. Optics Ex-
press, 28(13):18566–18576.
Olbrycht, R. and Kału
˙
za, M. (2019). Optical gas imag-
ing with uncooled thermal imaging camera-impact
of warm filters and elevated background tempera-
ture. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics,
67(11):9824–9832.
Strahl, T., Herbst, J., Lambrecht, A., Maier, E., Steinebrun-
ner, J., and W
¨
ollenstein, J. (2021). Methane leak de-
tection by tunable laser spectroscopy and mid-infrared
imaging. Applied Optics, 60(15):C68–C75.
Tan, L., Feng, Z., Zheng, H., Yao, Z., Weng, X., Wang,
F., and Chang, Z. (2022). Development trend of elec-
tronic nose technology in closed cabins gas detection:
a review. Applied Sciences, 12(18):9326.
Wurst, N. P., Meola, J., and Fiorino, S. T. (2017). Im-
proved atmospheric characterization for hyperspectral
exploitation. In Algorithms and Technologies for Mul-
tispectral, Hyperspectral, and Ultraspectral Imagery
XXIII, volume 10198, pages 116–122. SPIE.
Yu, C.-H., Huang, C.-H., Tan, C.-S., et al. (2012). A review
of co2 capture by absorption and adsorption. Aerosol
and air quality research, 12(5):745–769.
Zhao, N., Zhao, D., Ma, L., and Wang, B. (2022). Study
on a photoacoustic spectroscopy trichloromethane gas
detection method based on an arched photoacoustic
cavity. Analytical Methods, 14(15):1507–1514.
Zhou, A., Gao, L., Ji, X., and Zhang, M. (2018). Research
and application of sf6/n2 mixed gas used in gis bus.
Power Syst. Technol, 42(10):3429–3435.
PHOTOPTICS 2025 - 13th International Conference on Photonics, Optics and Laser Technology
108
