
Noisemaker 3D: Comprehensive Framework for Mesh Noise Generation
Vladimir Mashurov
1,2,∗ a
, Vasilii Latonov
1,∗ b
, Anastasia Martynova
1,3 c
and Natalia Semenova
1,4 d
1
Sberbank PJSC, 19 Vavilova St., Moscow 117312, Russia
2
ITMO University, Kronverkskiy Lane 49, Saint-Petersburg, 197101, Russia
3
HSE University, 20 Myasnitskaya St., Moscow 101000, Russia
4
AIRI, Kutuzovsky prospect 32 bld 1, Moscow 121170, Russia
Keywords:
Mesh Denoising, 3D Noise Generation, Synthetic Dataset, Topological and Node Noise.
Abstract:
In this article, we present a comprehensive library for generating node and topological noise in meshes. The
library provides a versatile tool for creating corrupted mesh datasets, which are essential for learning-based
denoising algorithms. Our main contributions include cluster and patch noise generation techniques for mesh
topology corruption. Cluster generation supports two modes: separated and merged clusters. We also compare
the node noise generated by the library to real noise from a scanned object dataset. Finally, we create a noisy
object dataset using the library and test it with filter-based and machine learning-based denoising methods.
1 INTRODUCTION
The 3D scene reconstruction problem is a common
challenge in various fields (Ma Z., 2018). Solving this
problem often requires specialized technical support
and complex software for data processing. Advanced
3D reconstruction algorithms use input data from
various sensors, such as cameras, RGB-D cameras,
and infrared cameras, to generate a reconstructed 3D
model of the scene. The 3D figure is represented in
various ways, including polygon meshes and voxel
grids. However, despite the use of advanced scan-
ning technologies and state-of-the-art signal process-
ing algorithms, the reconstructed scene is still prone
to errors. As a result, the virtual scene may differ
from the original (Kamberova G., 1997) real-world
one, making it unsuitable for immediate use in subse-
quent graphics pipelines.
In this article, we discuss various types of errors
that can occur in triangle meshes generated by 3D
scene reconstruction algorithms. These errors are re-
ferred to as noise. The process of eliminating noise
from a triangle mesh is known as denoising. The aim
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0000-1148-8425
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7810-8033
c
https://orcid.org/0009-0007-7003-5822
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4189-5739
∗
These authors contributed equally
of removing noise from a 3D scene is to create a re-
constructed 3D model that is as similar to the original
real-life scene as possible.
Modern research has developed a wide range of
denoising algorithms for triangle meshes. These al-
gorithms can be divided into two main categories.
The first category includes classical methods, which
are represented by filters and do not require train-
ing (Wang P.-S., 2016).
The second group includes learning-based meth-
ods for mesh denoising (Botsch J., 2022), (Zhao W.,
2021) and shape reconstruction (Litany O.,
2018), (Dai A., 2017). These methods require
sufficient number of clear (ground-truth) meshes and
their noised versions. The greater the variety of noise
in the training dataset, the better trained algorithm
can deal with noise.
In this paper, we present a library of noise gener-
ation algorithms that can generate node and topolog-
ical noise for any triangle mesh. We have also pro-
vided our library with probing based on five denois-
ing approaches, and have applied learning- and non-
learning-based methods to the noised datasets gener-
ated by our library.
Our motivation is to provide a comprehensive
toolkit for a variety of noise generation methods
on 3D meshes, to help researchers avoid the time-
consuming process of searching for and configuring
separate approaches. Additionally, we aim to address
Mashurov, V., Latonov, V., Martynova, A. and Semenova, N.
Noisemaker 3D: Comprehensive Framewor k for Mesh Noise Generation.
DOI: 10.5220/0013155800003912
In Proceedings of the 20th Inter national Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications (VISIGRAPP 2025) - Volume 2: VISAPP, pages
667-674
ISBN: 978-989-758-728-3; ISSN: 2184-4321
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
667

the issue of the non-reproducibility of open-source
implementations.
Our main contribution can be summarized as fol-
lows:
• We introduce a new library of algorithms for gen-
erating mesh noise. This library provides an effi-
cient way to create a large-scale dataset, with high
computational speed. Additionally, we have gen-
erated a dataset using our algorithmic approach..
• We provide a probing of our dataset and a com-
parison with other relevant dataset.
2 MESH NOISE OVERVIEW
We consider two types of noise that researchers usu-
ally face in triangle meshes. The first type is called
node noise (I., 2013). The most common cause of
this type of noise is low precision of the sensors used
for 3D scene capture.
The second type is topological noise or holes.
This causes the absence of small or significant frag-
ments of the mesh. The most common cause of these
holes is occlusion. Another reason is the inability to
capture the figure from all necessary angles. More-
over, holes can appear in the reconstructed model due
to low reflectivity (Davis J., 2002). Removing this
type of noise is called hole filling (Zhong M., 2016)
or shape completion.
3 NOISE GENERATION
FRAMEWORK
In this section, the noise generation algorithms imple-
mented in our library are presented. These algorithms
are divided into node noise and topological noise gen-
eration.
3.1 Node Noise
3.1.1 Random Noise
Node random noise is modeled with probability distri-
butions (Nguyen C. V., 2012). By varying the distri-
bution parameters, any required noisy surface can be
achieved. The probability distribution function (PDF)
defines the distance of each node’s shift.
We provide the following PDF for node noise
generation: Gaussian, Laplace, Exponential, Ex-
treme value, Gamma, Log normal, Uniform, Weibull,
Cauchy, Fisher, Student and Chi squared distribu-
tions.
The second part of the node noise is the direction
of the shift. This can be defined randomly or as the
normal of a vertex.
3.1.2 Impulsive Noise
The Impulsive noise
1
supposes that a specified range
of vertices is shifted. The Gaussian distribution is
used to calculate vertices offsets. The number of ver-
tices to generate noise can be specified (the number
must be less or equal than range size).
Some examples of node noise generated with the
algorithms developed are depicted on Figure 1.
3.2 Topological Noise
We provide the following topological noise genera-
tion algorithms:
• Random vertex removing algorithm
• Cluster algorithm with random removing center
• Cluster algorithm with specified removing center
• Set of clusters removing algorithm
• Patch noise
Let us denote the graph that represents the mesh
we are considering with G = (V,E,F), where V is the
set of vertices, E the set of edges, which are pairs
of vertices, and F the set of faces, each of which is
bounded by three edges. Each face is in the shape of
a triangle.
3.2.1 Random Noise
The Random algorithm is quite simple: it removes
each mesh vertex with a specified probability.
3.2.2 Cluster Noise
The Cluster noise algorithm allows to remove a set
of vertices in the vicinity of a specified vertex which
is called removing center. Let us give the descrip-
tion of a cluster. The vertex c is the center vertex that
is removed. Let us denote by d(v,c) the number of
edges in the shortest path between vertex v ∈ V and
the cluster center c. We define by R the cluster radius.
If d(v,c) ≥ R than vertex v is not removed. The ver-
tices with d(v,c) < R are deleted with a probability
P(v) that is calculated with the following method.
Consider the Gaussian distribution with mean µ =
0 and standard deviation σ. We denote the corre-
sponding probability density function by 1:
1
We used a part of implementation of Impulsive noise
from GCN-Denoiser
VISAPP 2025 - 20th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
668
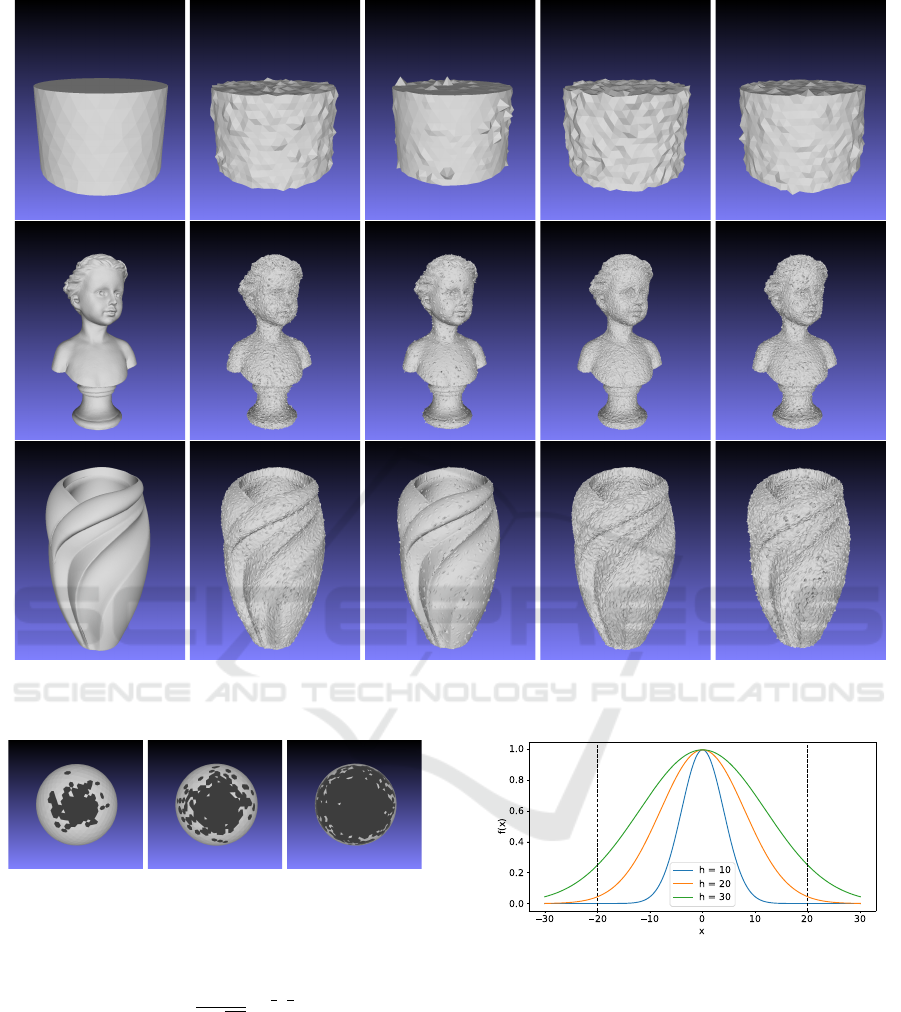
(a) GT (b) Exponential (c) Gamma (d) Gaussian (e) Weibull
Figure 1: Results of node noise generation applied to cylinder, bust and vase100K.
(a) (b) (c)
Figure 2: Topological noise clusters generated on the sphere
with σ = 0.5 and different h parameters: h = 10 (b), h = 20
(c), and h = 30 (d).
f (x, σ) =
1
σ
√
2π
e
−
1
2
(
x
σ
)
2
. (1)
Zero mean is required to make the highest proba-
bility of removing of vertices that are the closest to c.
We calculate d
v
= d(v, c) for a vertex v. The probabil-
ity to remove vertex v equals f (d
v
/h,σ), where h is a
special divider that determines how close to the peak
of the normal distribution the probabilities should be
chosen. The examples of cluster noise depending on
h is displayed on the Figures 2 and 3.
Figure 3: The Gaussian distributions with different h di-
viders, µ = 0 and σ = 0.5. The dashed vertical lines define
the interval [−20,20] that is used for clusters generation on
Figure 2. The bigger h the higher probability of faces re-
moving near the border of cluster.
Thus, the topological noise cluster C is defined as
C = C(c,σ,h,R). The d(v, c) calculation is performed
via Breadth First Search (BFS) algorithm with the
start point at c vertex which can be specified by vertex
index or selected randomly.
Noisemaker 3D: Comprehensive Framework for Mesh Noise Generation
669

(a) (b)
(c)
(d)
Figure 4: Consider R = 2 and D = 4. The clusters are gen-
erated in the following way: a) The first cluster is generated
randomly. b) The second cluster is generated so the distance
between centers equals D. c) The distance between third
cluster centers and the others centers is maximal if strat-
egy S(c
k+1
) → max is used. d) The distance between fourth
cluster centers and the others centers is minimal if strategy
S(c
k+1
) → min is used.
3.2.3 Set of Clusters Noise
The Set of Clusters algorithm generates the specified
number K of noise clusters C, where each cluster is
defined as described above. The clusters are gener-
ated sequentially one by one. Each cluster is defined
as C
i
= C(c
i
,σ,h,R); i = 1,.. . ,K. This algorithm re-
quires two additional parameters in comparison with
the previous one. The first parameter which is labeled
by D is a desired distance between centers of each
pair of clusters. The second one is a variable that de-
scribes a strategy of clusters centers selection. We de-
fine a function of sum distance between a new i + 1-th
center point and all previous ones with 2:
S(c
k+1
) =
k
∑
i=0
d(c
i
,v
c+1
). (2)
There are two strategies of c
k+1
selection:
S(c
k+1
) → max and S(c
k+1
) → min.
The following algorithm was implemented. Let us
denote as isMax a boolean variable that defines if max
S(c
k+1
) is required. The idea of the algorithm consists
of BFS modification. We start BFS K times. In the
end of i-th BFS the c
i+1
vertex is obtained. The first
BFS is started from randomly selected vertex which
is set as c
0
. We introduce a priority queue structure
which is labeled as prQueue. This queue contains
pairs (v, S(v)). The comparison operator is adjusted
to make highest priority either pair with the smallest
S(v) if minimization is required or the pair with the
biggest S(v) if maximization is required. The c
i+1
is
selected randomly from the candidates with the best
S(v).
Input: C = (V,E,F),c
0
Parameter: K, R, D,σ,h
Output: verticesToDelete Let k = 0,c
k
= c
0
;
Let verticesToDelete =
/
0;
while k < K do
prQueue.clear();
totalDistMap.clear();
queue.push(c
k
);
while !queue.empty() do
vCurr = queue. f ront();
Calculate d(c
k
,v) for vertices v
adjacent to vCurr;
if d(c
k
,v) > K ·R then
continue;
end
Let totalDistMap[v]+ = d(c
k
,v);
if d(c
k
,v) == D then
prQueue.push(v,totalDistMap[v]);
end
queue.push(v);
if d(c
k
,v) < R then
Calculate p = f (d
v
/h,σ);
isDelete =
GenerateBernoulli(p);
if d(c
k
,v) < R then
verticesToDelete.insert(v);
end
end
end
k + +;
c
k
= prQueue.top();
end
return verticesToDelete;
Algorithm 1: Set of clusters generation.
The strategies for selecting c
k+1
provide a specific
sequence for generating clusters. These strategies are
illustrated in Figure 4. The output of the algorithm is
a list of vertices that need to be removed. Figure 5
shows an example of the result.
VISAPP 2025 - 20th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
670

3.2.4 Patch Noise
The Patch noise algorithm enables faces removing de-
pending on theirs position in relation to neighboring
faces. The small convex and concave fragments are
often missed. We introduce the specific noise model
to search such difficult faces. we use the normal vot-
ing tensor (Yadav S.K., 2018) approach.
A patch p
i
that refers to the face f
i
∈F is a face f
i
and a set of faces in
ˆ
R-ring neighborhood. The
ˆ
R is a
radius that determines a size of patch.
Consider an arbitrary face and its patch. We de-
note the face’s normal as ¯n and the radius-vector of
the face center’s as ¯c. Let us introduce a vector
¯c
′
j
= ¯c
j
− ¯c, where ¯c
j
is a radius-vector of j-th face
in neighborhood of considered face. Here we label all
neighboring faces with j = 1,.. . ,N.
For each j-th face in neighborhood we denote by
a
j
the area of the face. We introduce the following
notions:
a
max
= max
j=1,...,N
a
j
, µ
j
=
a
j
a
max
exp(−||¯c
′
j
||/σ), (3)
where σ defines an importance of faces depending on
theirs distance from central face. Besides it we intro-
duce n
′
j
= 2( ¯n
j
· ¯w
j
) ¯w
j
− ¯n
j
, where ¯w
j
= [ ¯c
′
j
× ¯n
j
]× ¯c
′
j
.
The normal voting tensor is defined by the formula 4:
T =
N
∑
j=1
µ
j
n
′
j
n
′
T
j
. (4)
The eigenvalues of this tensor (λ
1
,λ
2
,λ
3
) are nor-
malized and sorted in the decreasing order: λ
1
≥λ
2
≥
λ
3
. The face can be classified according to its patch
eigenvalues. The special restricting constants are used
to classify faces: ˆc
k
,k = 1,. ..,5. The faces are clas-
sified as follows (Shen Y., 2022):
• If λ
2
< ˆc
1
and λ
3
< ˆc
2
then face classified as Plane
• If λ
2
> ˆc
3
and λ
3
< ˆc
4
then face classified as Edge
• If λ
3
> ˆc
5
then face classified as Corner
• In all other cases face is classified as Transitional
The Patch noise algorithm selects randomly the
specified portion of all faces from specified classes
and deletes them with neighboring faces. The number
of rings of neighboring faces to delete is also speci-
fied.
Some examples of topological noise generated
with the algorithms developed are shown on Figure
5.
More examples of node and topological noise are
provided in supplementary materials in our GitHub
repository.
The time consuming report is provided in supple-
mentary materials in our GitHub repository. A per-
sonal computer with Intel(R) Core(TM) i5-4670 CPU
3.40 GHz was used for library testing.
4 GENERATED DATASET
OVERVIEW
We used a dataset from (Wang P.-S., 2016) for our
tests
2
. This dataset was chosen because it is open-
source and contains both small and large meshes with
various geometric features. The Synthetic subset was
used to create examples of noisy meshes. We selected
three groups of meshes for testing:
• Complicated geometry models: armadillo, Chi-
nese lion and gargoyle;
• CAD models: block, joint and turbine Lp;
• Models with smooth surface: bumpy torus, fertil-
ity and kitten;
These models are selected to diversify the geome-
try as much as possible.
We choose three types of noise for testing. Each
type is used with three different parameters, resulting
in 9 noisy models from each ground truth. The types
of noise used for generation can be found in Table 1:
Table 1: Noise types and parameters used for examples gen-
eration.
Noise PDF Parameters
Exp. λe
−λx
λ = 4,7,10
Gamma
e
−x/β
β
α
Γ(α)
·x
α−1
α = 0.1,
β = 0.2,0.3,0.4
Weibull
k
λ
(
x
λ
)
k−1
exp−(
x
λ
)
k
λ = 1,
k = 0.1, 0.2, 0.3
The code of our library with dataset examples are
presented via the link NoiseMaker3D.
5 NOISE VERIFICATION FOR
MICROSOFT KINECT V1
In this section, we demonstrate that our library’s tools
can generate noise that is similar to real-world noise.
We use the Kinect Fusion dataset from (Wang P.-
S., 2016), which contains 7 meshes. Each figure is
presented in two formats: the ground truth and the
noisy version. The natural noise is generated from the
scanning process using Microsoft Kinect v1 and the
2
wang-ps.github.io/denoising
Noisemaker 3D: Comprehensive Framework for Mesh Noise Generation
671

(a) Random (b) Cluster (c) Clusters set sepa-
rately
(d) Clusters set merged (e) Patch
Figure 5: Here, we present the results of topological noise generation applied to the armadillo, gargoyle, and Merlion meshes.
Each type of noise affects a different part of the mesh, as shown in the images. Random noise evenly covers the mesh with
holes. The cluster noise generates a single hole in the mesh, or a cascade of merged or separate holes. The patch noise
generates tiny holes at the bending points of the surface.
Kinect Fusion technique (Izadi et al., 2011). We eval-
uate the natural noise distribution by collecting shifts
of each node along its corresponding normal vector.
We use our library to generate artificial noise with
a Student distribution, with parameters n = 5 and
scale = 0.6. We collect the shift values of our arti-
ficial noise for all meshes and calculate the KL diver-
gence and Chi-squared distance between the artificial
distribution and the Microsoft Kinect v1 distribution.
The results are 0.007 and 0.006, respectively. We also
calculate the KL divergence and Chi-squared distance
between each individual mesh’s natural noise and the
total natural noise, for comparison. The total natu-
ral and total artificial noise distributions are shown
in Figure 6. We calculate the distances between the
natural noise distributions of the mesh and the mean
artificial/natural distribution. The mean is calculated
over all figures considered. The results are presented
in Table 2.
Table 2: Each column contains the distance from specified
mesh natural noise distribution and average artificial or av-
erage natural distributions. KL divergence and Chi-squared
distance are used as measures.
Mesh
KL nat.
×10
−3
KL art.
×10
−3
Chi sq.
nat.
Chi sq.
art.
big girl 132 167 113 135
boy01 22 36 18 30
boy02 63 81 41 46
cone 100 100 95 94
david 58 56 22 21
girl 23 36 24 36
pyramid 56 59 47 49
The total distribution histogram is close to the Stu-
dent distribution. Each mesh natural noise distribu-
tion separately differs from the artificial distribution
approximately the same. The total natural noise dis-
tribution differs significantly from the artificial one
VISAPP 2025 - 20th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
672
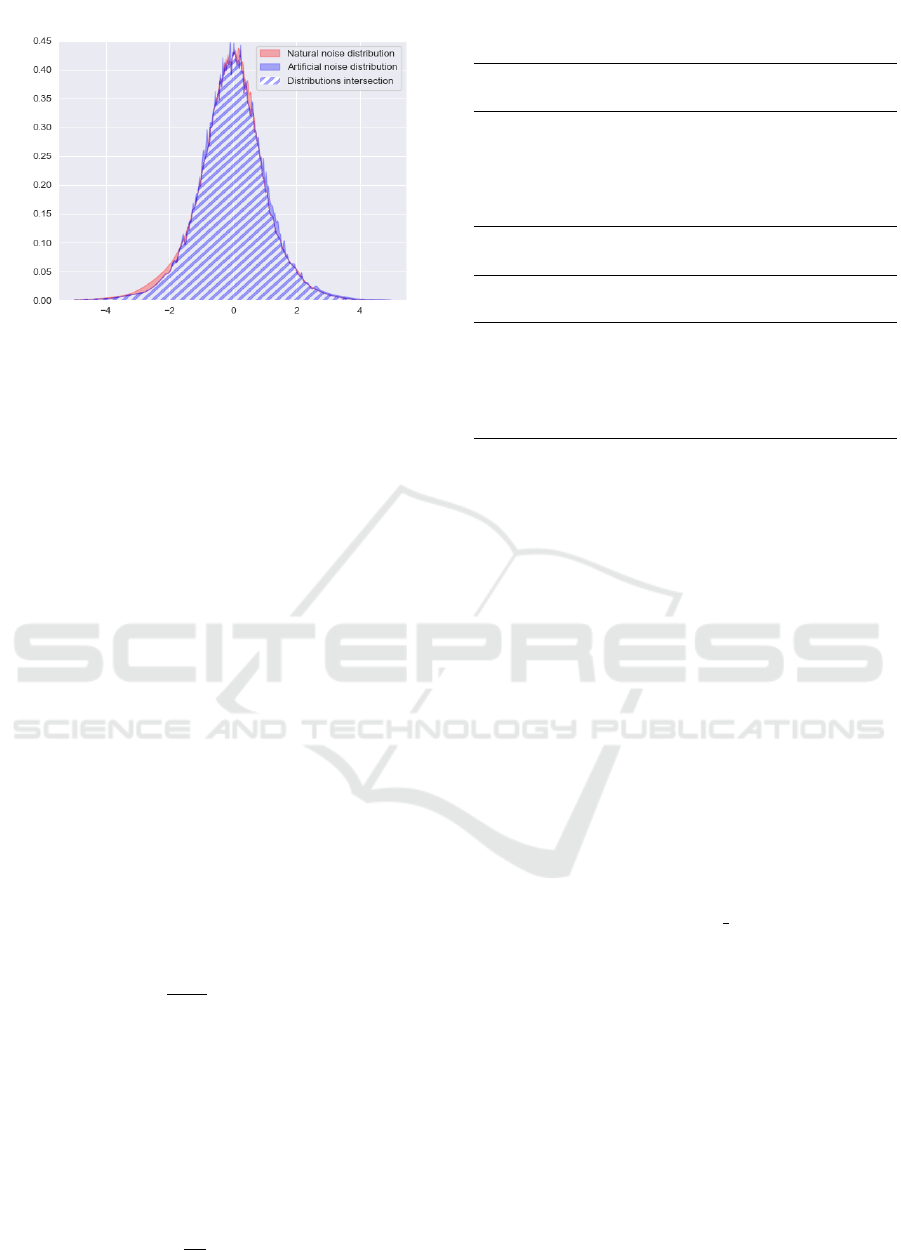
Figure 6: Comparison of artificial Student distribution (n =
5) noise with natural noise of Microsoft Kinect v1. The
distributions are close.
compared to any separate natural distribution from the
total natural noise distribution.
6 MESH DENOISING PROBING
In this section, we demonstrate the denoising meth-
ods applied to dataset generated by our library. Some
learning-based denoising algorithms were also trained
on this dataset.
The following methods are used for noise re-
moval: Bilateral normal filtering (C.-L., 2011),
Guided bilateral normal filtering (Zhang W., 2015),
Fast and effective feature preserving mesh denois-
ing (Sun X, 2007), GeoBi-GNN (Zhang Y., 2022),
Cascaded normal regression (Wang P.-S., 2016).
Learning-based methods were trained on the Syn-
thetic data of dataset from (Wang P.-S., 2016).
For the evaluation of selected methods on gener-
ated node noise data, we choose the following met-
rics:
• Average weighted Hausdorff distance:
Err
HD
=
1
N
v
L
d
∑
v
i
∈V
min
v
j
∈
e
V
(||v
i
−v
j
||), (5)
where N
v
is the number of vertices in the ground
truth mesh, L
d
is the length of the noisy mesh min-
imal oriented bounding box diagonal, V and
e
V are
an original and noisy mesh vertices’ sets respec-
tively.
• Average normal angular difference between
ground truth and denoised meshes:
Err
Ang
=
1
N
f
∑
f
i
∈F
arccos(n
i
·
e
n
i
), (6)
Table 3: Complicated geometry models denoising metrics.
Method
Hausdorff
×10
−3
Angle
CD
×10
−4
Bilateral 0.67 8.79 2.96
Guided mesh 0.70 10.09 3.19
Fast and Effective 1.28 13.99 10.8
GeoBi-GNN 0.55 5.04 1.93
Cascaded 0.55 6.86 2.06
Table 4: CAD models denoising metrics.
Method
Hausdorff
×10
−3
Angle
CD
×10
−4
Bilateral 1.20 2.29 1.73
Guided mesh 1.21 2.53 1.79
Fast and Effective 1.28 2.64 2.0
GeoBi-GNN 1.17 2.56 1.77
Cascaded 1.16 2.12 1.66
where F is a set of mesh faces, N
f
is F cardinality,
n
i
and
e
n
i
are normals of the same face of ground
truth and noisy mesh respectively.
• Average Chamfer Distance:
Err
CD
=
|V |
−1
∑
v
i
∈V
∥v
i
−argmin
v
j
∈
e
V
∥v
i
−v
j
∥)∥
2
+
∑
v
j
∈
e
V
∥v
j
−argmin
v
i
∈V
∥v
j
−v
i
∥)∥
2
#
.
(7)
These metrics are borrowed from (Shen Y.,
2022), (Zhang W., 2015). The result metrics of de-
noising probing are presented in tables 3, 4 and 5. The
detailed table is provided in supplementary materials
in our GitHub repository.
Each metric is obtained by averaging over all de-
noised meshes, regardless of the type of noise. These
denoising metrics are comparable to those that can be
achieved in tests using Kinect Fusion. The normal
angular difference ranges from approximately 0.5 to
3.6 degrees, depending on the figure, and the Chamfer
distance ranges from 0.1 to 0.3 ×10
−4
. These values
are quoted from (Mashurov and Semenova, 2024).
7 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
WORK
In this paper, we present a new library for generating
mesh noise. The library includes node and topologi-
cal noise generation methods, with a total of 15 meth-
ods implemented. Each algorithm can be adjusted us-
ing a set of input parameters, depending on the user’s
requirements.
Noisemaker 3D: Comprehensive Framework for Mesh Noise Generation
673

Table 5: Smooth surface models denoising metrics.
Method
Hausdorff
×10
−3
Angle
CD
×10
−4
Bilateral 1.24 3.9 6.94
Guided mesh 1.31 5.27 7.93
Fast and Effective 2.09 6.3 17.6
GeoBi-GNN 1.16 2.7 5.67
Cascaded 1.12 3.17 5.67
The algorithms have been tested on a synthetic
dataset, using five non-learning and learning-based
denoising methods. Tables with the resulting met-
rics are provided. The experiments demonstrate that
meshes with artificial noise generated using our tool
can be effectively denoised. The denoising metrics
achieved in our tests are of the same order, and some-
times almost equal, as those in Kinect Fusion tests.
Currently, the parameters for topological noise
generation are not automatically adjusted. In future
work, these algorithms will automatically select input
parameters based on model size and specific require-
ments. Moreover, we will examine the meshes gen-
erated with topological noise on existing hole-filling
algorithms. We will perform an objective comparison
with the noise from real 3D sensors. For this purpose,
we will use Kinect to collect a dataset.
REFERENCES
Botsch J., Jain H., H. O. (2022). Imd-net: A deep learning-
based icosahedral mesh denoising network. IEEE Ac-
cess, 10:38635–38649.
C.-L., Z. Y. F. H. A. O. K.-C. T. (2011). Bilateral normal
filtering for mesh denoising. IEEE Transactions on
Visualization and Computer Graphics, 17(10):1521–
1530.
Dai A., Qi C.R., N. M. (2017). Shape Completion Using
3D-Encoder-Predictor CNNs and Shape Synthesis. In
Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vi-
sion and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pages 5868–
5877, Honolulu, Hawaii, USA. IEEE.
Davis J., Marschner S.R., G. M. L. M. (2002). Fill-
ing holes in complex surfaces using volumetric diffu-
sion. In Proceedings. First International Symposium
on 3D Data Processing Visualization and Transmis-
sion, pages 428–441, Padua, Italy. IEEE.
I., Y. Y. P. N. I. (2013). Linear correlations between
spatial and normal noise in triangle meshes. IEEE
Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graph-
ics, 19(1):45–55.
Izadi, S., Kim, D., Hilliges, O., Molyneaux, D., Newcombe,
R., Kohli, P., Shotton, J., Hodges, S., Freeman, D.,
Davison, A., et al. (2011). Kinectfusion: real-time 3d
reconstruction and interaction using a moving depth
camera. In Proceedings of the 24th annual ACM sym-
posium on User interface software and technology,
pages 559–568.
Kamberova G., B. R. (1997). Precision of 3D points recon-
structed from stereo. Technical Report . MS-CIS-97-
20, Dept. of Computer & Information Science, Univ.
of Pennsylvania.
Litany O., Bronstein A., B. M. M. A. (2018). Deformable
Shape Completion With Graph Convolutional Au-
toencoders. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference
on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR),
pages 1886–1895, Salt Lake City, Utah, USA. IEEE.
Ma Z., L. S. (2018). A review of 3d reconstruction tech-
niques in civil engineering and their applications. Ad-
vanced Engineering Informatics, 37:163–174.
Mashurov, V. and Semenova, N. (2024). Topological and
node noise filtering on 3d meshes using graph neu-
ral networks (student abstract). In Proceedings of
the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol-
ume 38, pages 23582–23584.
Nguyen C. V., Izadi S., L. D. (2012). Modeling Kinect
Sensor Noise for Improved 3D Reconstruction and
Tracking. In 2012 Second International Conference
on 3D Imaging, Modeling, Processing, Visualization
& Transmission, pages 524–530, Zurich, Switzerland.
IEEE.
Shen Y., Fu H., D. Z. C. X. B. E.-Z. D. Z. K. Z. Y. (2022).
Gcn-denoiser: Mesh denoising with graph convolu-
tional networks. ACM Transactions on Graphics,
41(1):1—-14.
Sun X, Rosin P. L., M. R. L. F. (2007). Fast and ef-
fective feature-preserving mesh denoising. IEEE
Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graph-
ics, 13(5):925–938.
Wang P.-S., Liu Y., T. X. (2016). Mesh denoising via
cascaded normal regression. ACM Transactions on
Graphics, 35(6):1–12.
Yadav S.K., Reitebuch U., S. M. Z. E. P. K. (2018).
Constraint-based point set denoising using normal
voting tensor and restricted quadratic error metrics.
Computers & Graphics, 74:234—-243.
Zhang W., Deng B., Z. J. B. S. L. L. (2015). Guided mesh
normal filtering. Comput. Graph. Forum., 34(7):23–
–34.
Zhang Y., Shen G., W. Q. Q. Y. W. M.-Q. J. (2022).
Geobi-gnn: Geometry-aware bi-domain mesh denois-
ing via graph neural networks. Computer-Aided De-
sign, 144:103154.
Zhao W., Liu X., Z. Y. F. X. Z. D. (2021). Normal-
net: Learning-based mesh normal denoising via local
partition normalization. IEEE Transactions on Cir-
cuits and Systems for Video Technology, 31(12):4697–
4710.
Zhong M., Q. H. (2016). Surface inpainting with spar-
sity constraints. Computer Aided Geometric Design,
41:23–35.
VISAPP 2025 - 20th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
674
