
Sentiment-Enriched AI for Toxic Speech Detection: A Case Study of
Political Discourses in the Valencian Parliament
Antoni Mestre
1 a
, Franccesco Malafarina
2 b
, Joan Fons
1 c
, Manoli Albert
1 d
, Miriam Gil
3 e
and
Vicente Pelechano
1 f
1
VRAIN Institute, Universitat Polit
`
ecnica de Val
`
encia, 46022, Valencia, Spain
2
Universit
`
a degli Studi del Sannio, 82100, Benevento, Italy
3
Departament d’Inform
`
atica, Universitat de Val
`
encia, 46100, Burjassot, Spain
Keywords:
Toxic Speech Detection, Hate Speech, Text Classification, Parliamentary Speeches.
Abstract:
The increasing prevalence of toxic speech across various societal domains has raised significant concerns re-
garding its impact on communication and social interactions. In this context, the analysis of toxicity through
AI techniques has gained prominence as a relevant tool for detecting and combating this phenomenon. This
study proposes a novel approach to toxic speech detection by integrating sentiment analysis into binary clas-
sification models. By establishing a confusion zone for ambiguous probability scores, we direct uncertain
cases to a sentiment analysis module that informs final classification decisions. Applied to political discourses
in the Valencian Parliament, this sentiment-enriched approach significantly improves classification accuracy
and reduces misclassifications compared to traditional methods. These findings underscore the effectiveness
of incorporating sentiment analysis to enhance the robustness of toxic speech detection in complex political
contexts, paving the way for future research in this relevant area.
1 INTRODUCTION
The growing prevalence of toxic speech across di-
verse societal domains has become a significant con-
cern due to its harmful effects on communication, so-
cial cohesion, and trust within communities. Toxic
speech, characterized by offensive, inflammatory, or
demeaning language, not only disrupts civil discourse
but also fosters polarization, harassment, and exclu-
sion (Buitrago L
´
opez et al., ). In an era where digital
platforms amplify such speech and where transcripts
of public interactions are increasingly available, the
urgency of developing robust mechanisms for detect-
ing and mitigating toxic content has escalated.
Artificial intelligence has emerged as a powerful
tool in this context, enabling automated detection and
analysis of toxic speech (Chhabra and Vishwakarma,
2023). Traditional binary classification models have
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8572-2579
b
https://orcid.org/0009-0004-4494-6620
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3718-3096
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3747-400X
e
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2987-1825
f
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1090-230X
been widely used for this task, offering a straightfor-
ward approach to categorizing content as toxic or non-
toxic. However, these models often face limitations
when confronted with ambiguous cases—instances
where the likelihood of toxicity is unclear (Islam
et al., 2021). This ambiguity, which typically occurs
when a speech’s toxicity is contextually or sentimen-
tally nuanced, can lead to misclassification, hindering
efforts to foster healthier communication, especially
in complex environments such as political discourse.
To overcome these challenges, this study presents
a novel framework that enhances toxic speech de-
tection by incorporating sentiment analysis into con-
ventional binary classification models. By defining a
”confusion zone” for ambiguous classification prob-
abilities, our approach directs uncertain cases to a
sentiment analysis module. This added layer of con-
textual understanding helps refine classification deci-
sions, ensuring greater accuracy in identifying toxic
content.
Our methodology is particularly tailored to polit-
ical discourse, where the impact of toxic language
is profound, influencing public perception, societal
norms, and behavior. We apply this approach to
Mestre, A., Malafarina, F., Fons, J., Albert, M., Gil, M. and Pelechano, V.
Sentiment-Enriched AI for Toxic Speech Detection: A Case Study of Political Discourses in the Valencian Parliament.
DOI: 10.5220/0013159600003890
In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2025) - Volume 3, pages 555-561
ISBN: 978-989-758-737-5; ISSN: 2184-433X
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
555

speeches from the Valencian Parliament, a bilingual
legislative body, to evaluate its effectiveness in de-
tecting nuanced toxic speech in a politically charged
environment. By improving accuracy and reducing
misclassification, this research contributes to ongoing
efforts to enhance the detection of toxic speech and
promote more respectful and constructive communi-
cation in complex social contexts.
2 RELATED WORK
The detection of toxic speech—defined as language
that is rude, disrespectful, or likely to disrupt conver-
sations and alienate users (Arab and D
´
ıaz, 2015)—has
become increasingly important in the digital era,
where online discourse is widespread and often
volatile. Toxic speech detection has evolved signifi-
cantly, starting with basic rule-based systems and key-
word filtering approaches. These early methods strug-
gled to capture the nuances of language, often leading
to high rates of false positives and negatives, as they
were unable to understand context or infer meaning
from subtle linguistic cues (Bonetti et al., 2023).
The introduction of machine learning represented
a major leap forward, with models like Support Vec-
tor Machines and Naive Bayes improving detection
accuracy by leveraging features extracted from text,
such as word frequencies and n-grams (Subramanian
et al., 2023). While these models offered better gen-
eralization than rule-based approaches, they still en-
countered difficulties when dealing with more com-
plex, context-dependent cases of toxicity.
The rise of deep learning further revolutionized
the field, offering more sophisticated techniques for
detecting toxic speech. Convolutional Neural Net-
worksand Recurrent Neural Networks became popu-
lar for their ability to automatically learn and repre-
sent features from raw text data (Garg et al., 2023).
Models like Long Short-Term Memory networks and
Transformer-based models such as Bidirectional En-
coder Representations from Transformers (BERT)
have proven especially effective by capturing intricate
semantic relationships and understanding the sub-
tleties of language (Malik et al., 2021). However, de-
spite their improved performance, these models are
resource-intensive, requiring large annotated datasets
and significant computational power to train and fine-
tune (Subramanian et al., 2023).
One of the most pressing challenges in toxic
speech detection is the multilingual and culturally nu-
anced nature of global communication. Toxicity is
contextually dependent not only on language but also
on cultural values and norms, making cross-linguistic
detection particularly complex (Leite et al., 2020).
Recent studies have shown that sentiment analysis can
be an effective tool for addressing these challenges,
especially in multilingual contexts. For example, re-
search by Proksch et al. (Proksch et al., 2019) demon-
strated how sentiment analysis applied to legislative
debates across different languages could capture un-
derlying political conflicts and nuances, suggesting
that sentiment-aware models could enhance toxicity
detection by providing additional contextual informa-
tion.
Despite these advances, handling ambiguous
cases in toxicity detection remains a significant chal-
lenge. Ambiguity often arises when language is nei-
ther clearly toxic nor benign, complicating classifica-
tion efforts. Sheth et al. (Sheth et al., 2022) high-
lighted the difficulty of defining the boundaries be-
tween toxic and non-toxic speech, while Subramanian
et al. (Subramanian et al., 2023) discussed the limita-
tions of current models in addressing these borderline
cases. Approaches such as multi-channel CNNs have
been proposed to address this issue, but accurately
classifying ambiguous content continues to pose dif-
ficulties.
Building on these advancements, our proposed
methodology integrates sentiment analysis with tradi-
tional binary classification models to address the chal-
lenge of ambiguous cases. By introducing a confu-
sion interval for uncertain toxicity scores, our model
redirects these cases to a sentiment analysis module,
which enriches the classification process with addi-
tional emotional and contextual information. This
dual-layered approach improves the robustness and
accuracy of toxic speech detection, particularly in
complex, politically charged environments where nu-
ance and sentiment play a critical role.
3 PROPOSAL ARCHITECTURE
To ensure robust and accurate detection of toxic
speech, we propose a comprehensive, modular frame-
work that integrates multiple components to enhance
the precision, adaptability, and reliability of toxicity
inference. This architecture is designed to handle the
challenges posed by complex, multilingual, and nu-
anced content, making it well-suited for both digital
platforms and politically charged environments. The
following section details the methodology and system
architecture, which together form the backbone of our
proposed solution.
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
556

3.1 Data Acquisition Module
The first step in the process is the Data Acquisition
Module, which is responsible for the automatic re-
trieval of textual data from diverse sources, includ-
ing digital platforms (social media, online forums)
and transcriptions of spoken interactions (e.g., parlia-
mentary debates). This module is designed to pro-
cess various types of input data, ensuring scalability
and adaptability to different environments and lan-
guages. By encompassing multiple sources, it allows
the framework to operate on both real-time streams
and historical archives, making it applicable to a wide
range of use cases, from online content moderation to
retrospective analysis of political speeches.
The acquisition process includes mechanisms to
handle noise in the data, such as filtering non-relevant
content and pre-processing steps like tokenization and
removal of stop words. This ensures that only perti-
nent text data are fed into subsequent modules, im-
proving the overall efficiency and accuracy of the sys-
tem.
3.2 Language Unification Module
Given the multilingual nature of modern discourse,
particularly in political settings such as the Valencian
Parliament, the Language Unification Module plays
a crucial role in standardizing text data before fur-
ther processing. This module automatically detects
the language of incoming text and translates it into a
unified language format (in this case, Spanish), en-
abling consistent and reliable analysis.
The challenge of multilingual text is twofold:
lexical variations across languages and the differing
cultural connotations of certain words. The Lan-
guage Unification Module addresses both by lever-
aging state-of-the-art machine translation models that
are sensitive to context. This ensures that translations
maintain the semantic integrity of the original speech,
preserving subtle nuances that are essential for accu-
rate toxicity detection. By addressing linguistic dis-
crepancies at this early stage, the framework is able
to avoid errors that might arise from handling multi-
ple languages simultaneously, ensuring a more coher-
ent and reliable toxicity assessment downstream.
3.3 Toxic Detection Module
The Toxic Detection Module serves as the core com-
ponent of the framework, responsible for evaluating
the toxicity of the standardized text. This module
utilizes advanced AI techniques, specifically binary
classification models, to determine whether a given
piece of text is likely to be toxic. In this study, we
employed the pre-trained Detoxify model (Hanu and
Unitary, 2023), which has demonstrated strong per-
formance in various toxic speech detection tasks.
Detoxify assigns a probability score to each text
sample, representing the likelihood that the content is
toxic. A score close to 0 indicates non-toxic content,
while a score closer to 1 suggests toxic speech. How-
ever, despite its effectiveness, the module can some-
times produce ambiguous results, especially when the
probability score falls within a certain range where the
classification is not definitively clear. To address this,
we introduce a predefined ”confusion zone,” typically
ranging between 42% and 58%. Texts with scores
within this zone are neither clearly toxic nor clearly
non-toxic, indicating a need for further analysis to
reach a confident conclusion.
This confusion zone is particularly relevant in the
context of political discourse, where language is of-
ten nuanced and may involve sarcasm, rhetorical de-
vices, or indirect speech. Such complexities can make
it difficult for the model to assign a clear classifica-
tion, resulting in borderline cases. To handle these,
the system flags these texts for additional processing
by the Sentiment Analysis Module, which provides
further contextual understanding to improve classifi-
cation accuracy.
3.4 Sentiment Analysis Module
To handle these uncertain cases, we introduce a sec-
ond layer of analysis: the Sentiment Analysis Module.
Once a text is flagged by the Toxic Detection Module
as ambiguous, it is redirected to this module for fur-
ther evaluation. The Sentiment Analysis Module per-
forms a deeper analysis of the emotional tone, provid-
ing additional context to aid in the final classification.
By assessing the emotional valence of the text, the
sentiment analysis adds a nuanced layer of interpre-
tation that binary classifiers typically overlook. For
instance, a politically charged statement with a highly
negative sentiment score is more likely to be toxic,
even if the initial classifier was uncertain. On the
other hand, a text with low sentiment intensity may
indicate sarcasm or rhetorical neutrality, reducing the
likelihood of it being classified as toxic.
This dual-layered approach—combining toxicity
classification with sentiment analysis—enables the
system to handle complex and ambiguous language
more effectively. Texts with strong negative sentiment
are reclassified as toxic, while those with more neu-
tral or positive sentiment are deemed non-toxic, thus
significantly reducing false positives and negatives in
the overall classification process.
Sentiment-Enriched AI for Toxic Speech Detection: A Case Study of Political Discourses in the Valencian Parliament
557
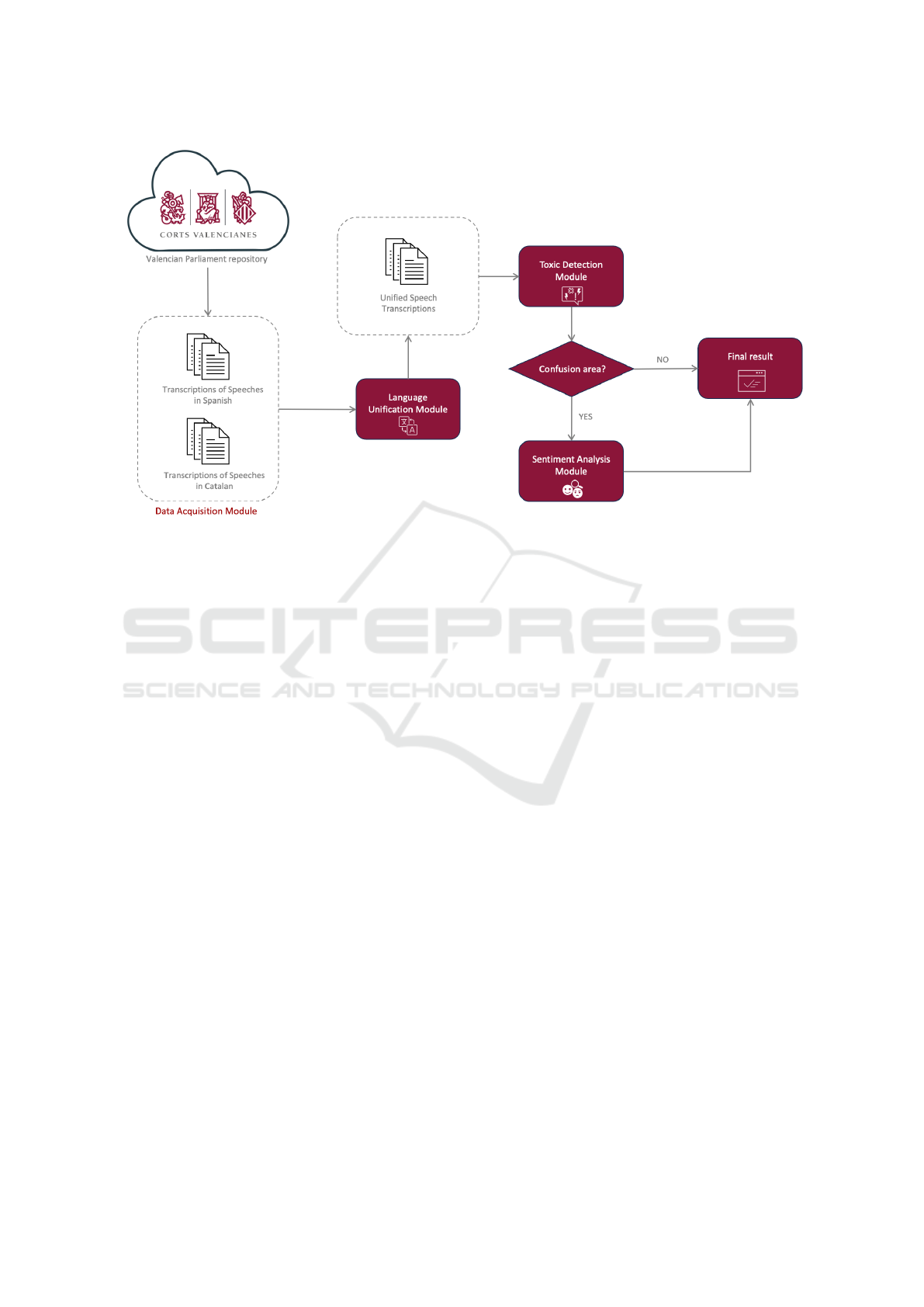
Figure 1: Architecture diagram of the proposed toxic speech detection framework.
3.5 System Integration and Scalability
The integration of the aforementioned modules forms
a robust system capable of accurately detecting toxic
speech across a wide variety of linguistic and con-
textual scenarios. The modular design allows for
flexibility, as each component can be updated or re-
placed as new models and techniques become avail-
able. For example, the Sentiment Analysis Module
can be easily swapped with more advanced models
like transformer-based sentiment classifiers as they
evolve.
Fig. 1 shows a general schematic of the proposed
solution, instantiated with the use case of the Valen-
cian Parliament. The proposed architecture not only
addresses the challenges of ambiguous toxicity infer-
ence but also paves the way for future advancements
in the field of toxic speech analysis.
4 CASE STUDY: THE
VALENCIAN PARLIAMENT
The Valencian Parliament, known as Les Corts Va-
lencianes, provides an ideal case study for analyz-
ing toxic speech detection, primarily due to its dual-
language environment (Spanish and Catalan) and the
increasing focus on monitoring political discourse.
As a legislative body where formal and respectful dis-
course is generally expected, parliamentary debates
often reflect broader societal trends, including polar-
ized speech and contentious rhetoric. This makes Les
Corts a valuable setting for studying the dynamics of
toxic speech and its impact on public perception and
societal attitudes.
Les Corts Valencianes serves as the legislative
body of the Valencian Community in Spain, where
both Spanish and Catalan hold official language sta-
tus. This bilingual context introduces unique chal-
lenges for toxic speech detection, as language-specific
nuances can affect how speech is perceived. Conse-
quently, robust language processing capabilities are
required to accurately assess toxic speech in such a
complex setting.
In this study, we applied a combination of the pre-
trained Detoxify model (Hanu and Unitary, 2023) and
the sentimentR library (Rinker, 2016) to enhance toxi-
city detection. The Detoxify model was chosen for its
strong performance in toxic speech detection, and we
integrated sentiment analysis to handle the complex-
ities inherent in political discourse. The combination
allowed us to create a more refined system capable
of distinguishing between overtly toxic language and
subtler, context-dependent forms of toxicity common
in political settings.
Our experiment involved analyzing ten plenary
sessions from the Valencian Parliament. The speeches
were segmented into individual sentences, which
were then used as samples for toxicity analysis. The
initial toxicity inference using Detoxify revealed that
the average level of toxicity across these sessions
ranged from 0.50% to 0.89%, indicating a generally
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
558
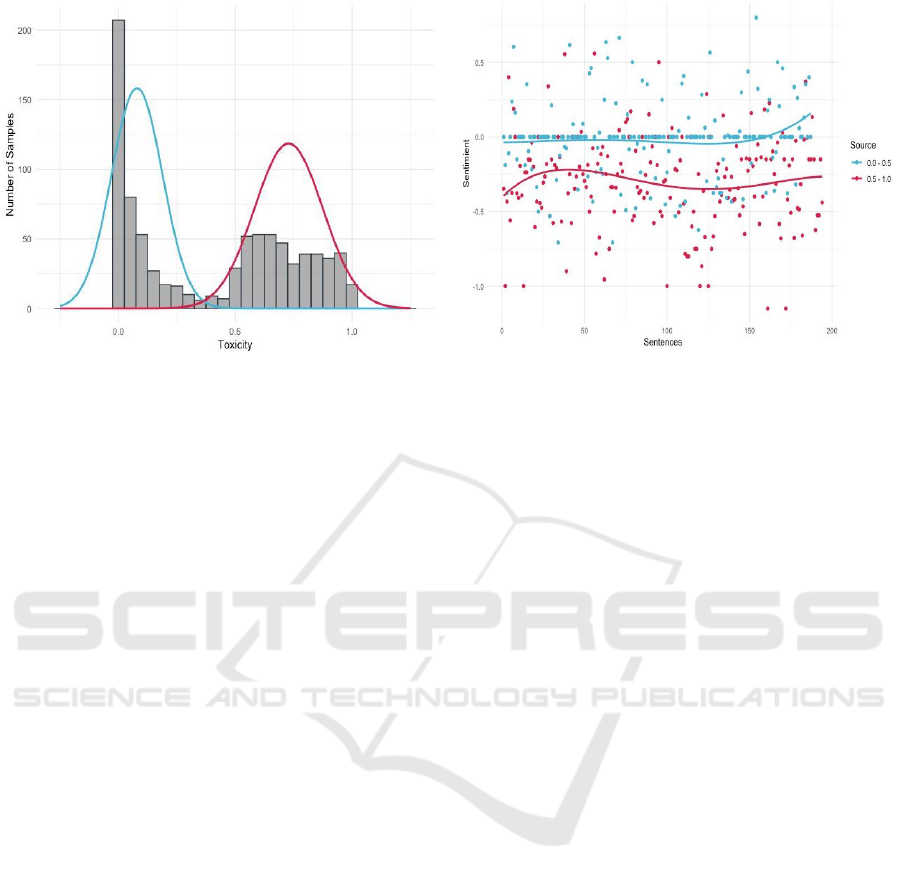
(a) Samples distribution. (b) Sentiment analysis results.
Figure 2: Distribution of samples and sentiment analysis results.
low but present occurrence of toxic speech in this for-
mal setting.
For this study, we selected 870 samples, half of
which (435) had a toxicity score greater than 50%, in-
dicating a higher likelihood of toxicity. The other half
had a toxicity score below 50%. These samples were
used to evaluate the performance of our sentiment-
enriched approach. The distribution of these samples
is shown in Fig. 2a, while the results of the sentiment
analysis are depicted in Fig. 2b.
From these 870 samples, we chose a subset of 80
for manual validation. The remaining samples were
divided into intervals based on their toxicity infer-
ence, with one group having scores below 0.25 and
another above 0.75. Fig. 2b shows two distinct clus-
ters in the sentiment analysis: one centered near a sen-
timent score of 0 (indicating neutral or non-toxic con-
tent) and the other near -0.33 (indicating toxic con-
tent).
For validation, we defined a confusion zone for
toxicity inference between 42% and 58%, represent-
ing ambiguous cases where classification was uncer-
tain. We compared the performance of the Detox-
ify model alone against our sentiment-enriched model
using this confusion zone. A group of three experts
(two in philology and one in sociology) manually la-
beled the samples for further validation.
The results indicated that without the confusion
zone, our model achieved an accuracy of 80.35%.
However, when the confusion zone was incorpo-
rated, along with sentiment reassignment, accuracy
improved significantly to 87.89%. This demonstrates
the effectiveness of adding a sentiment layer to re-
fine toxic speech detection, particularly in politically
charged and linguistically complex contexts such as
the Valencian Parliament.
To further benchmark our model, we compared
its performance against several other state-of-the-art
models, including Logistic Regression, BERT, and
HateBERT (Caselli et al., 2021). Table 1 provides
a comparison of key performance metrics, including
accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score.
As shown in Table 1, our sentiment-enriched
model outperformed baseline models in all metrics,
achieving an accuracy of 88%, a precision of 86%, a
recall of 87%, and an F1-score of 86%. The inclu-
sion of the confusion zone significantly improved the
overall performance, demonstrating the advantage of
using sentiment analysis to handle ambiguous cases.
5 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
WORK
In this preliminary study, we introduced a novel ap-
proach to toxic speech detection by integrating sen-
timent analysis into traditional binary classification
models. The proposed sentiment-enriched framework
significantly enhances the accuracy and robustness of
toxicity inference, particularly in handling ambigu-
ous cases where traditional models often struggle. By
adding a sentiment analysis layer, our approach of-
fers a more nuanced understanding of the emotional
and contextual elements of speech, which is critical
in complex and politically charged environments like
the Valencian Parliament.
The results from this study underscore the poten-
tial of combining toxicity detection with sentiment
analysis, especially in domains where language car-
ries significant emotional weight and subtlety, such
Sentiment-Enriched AI for Toxic Speech Detection: A Case Study of Political Discourses in the Valencian Parliament
559

Table 1: Comparison of performance metrics across different models. The table compares accuracy, precision, recall, and
F1-score for various models, showing the effectiveness of our sentiment-enriched model with and without the confusion zone.
Model Accuracy Precision Recall F1-Score
Logistic Regression 0.75 0.72 0.68 0.70
BERT 0.84 0.82 0.83 0.82
HateBERT 0.87 0.85 0.86 0.85
Our Model (without confusion zone) 0.80 0.78 0.79 0.78
Our Model (with confusion zone) 0.88 0.85 0.87 0.86
as political discourse. Our method not only improves
detection accuracy but also reduces the likelihood of
misclassifying borderline cases that often fall within
the “confusion zone” of probability scores.
One of the key areas for future improvement is
the sentiment analysis component. While the current
study utilized the sentimentR library, more sophisti-
cated techniques, such as transformer-based models
(e.g., BERT or GPT-like models) specifically fine-
tuned for sentiment analysis, could offer significant
improvements. Transformer models have shown ex-
ceptional capabilities in capturing the intricacies of
language, including context, irony, and sentiment po-
larity, making them ideal candidates for refining this
aspect of the framework. Fine-tuning such models on
domain-specific datasets, such as political speeches or
social media conversations, could further boost accu-
racy and adaptability.
Another promising direction for future work in-
volves the integration of additional contextual fea-
tures that go beyond the sentiment of the text itself.
For instance, speaker intent, tone, and audience re-
action could provide valuable cues for determining
toxicity. Analyzing speaker history (e.g., previous
inflammatory remarks or speech patterns) and audi-
ence engagement (e.g., applause, boos, or online sen-
timent in response to a speech) could offer deeper in-
sights into whether a statement is likely to be toxic or
merely provocative. Leveraging these contextual fea-
tures could enhance the model’s ability to distinguish
between different forms of aggressive or inflamma-
tory speech.
A further potential area of research is exploring
cross-modal toxicity detection, where textual data is
combined with other modalities such as audio, video,
or even social media interactions (Maity et al., 2024).
In many cases, tone of voice, body language, or visual
cues may reveal toxicity that is not explicitly present
in the text itself. For example, integrating acoustic
analysis from speeches or debates could capture vari-
ations in tone that indicate sarcasm, anger, or pas-
sive aggression—key indicators of underlying toxic-
ity. Video analysis of facial expressions or gestures
could similarly add depth to toxicity inference, par-
ticularly in live debates or interviews.
In parallel with advancing technical capabilities,
ensuring that these models are explainable and ethi-
cally sound is crucial. As toxic speech detection sys-
tems are increasingly used in sensitive domains, such
as political discourse or online moderation, it is im-
portant to make sure that the decision-making process
is transparent and justifiable (Mahajan et al., 2021).
Further research should explore methods for making
these models interpretable, allowing users or moder-
ators to understand why a particular piece of content
was flagged as toxic. Incorporating fairness measures
to prevent biases related to gender, race, or political
ideology will be vital for building trust and ensuring
that the models do not inadvertently perpetuate dis-
crimination.
In conclusion, this preliminary study presents a
promising approach for improving toxic speech de-
tection by integrating sentiment analysis with binary
classification models. While the current implemen-
tation has demonstrated success in a political context,
particularly within the Valencian Parliament, there are
ample opportunities for refinement and broader appli-
cation. As toxic speech continues to be a pressing
issue in both political and digital spaces, advancing
this methodology will contribute to fostering healthier
communication environments. Through further val-
idation, the integration of advanced sentiment mod-
els, contextual features, and multi-modal data, this ap-
proach has the potential to lead the way in addressing
the challenges of toxic speech detection and promot-
ing constructive dialogue in complex social settings.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We acknowledge the support and assistance of Alba
Gasc
´
on, Julia Palomares and Paula Gabarda in the
validation phase of this study.
This work has been developed with the financial
support of the Generalitat Valenciana under project
GV/2021/072 and by the MINECO under project
PRODIGIOUS PID2023-146224OB-I00.
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
560

REFERENCES
Arab, L. E. and D
´
ıaz, G. A. (2015). Impact of social
networks and internet in adolescence: strengths and
weaknesses. Revista M
´
edica Cl
´
ınica Las Condes,
26(1):7–13.
Bonetti, A., Mart
´
ınez-Sober, M., Torres, J. C., Vega, J. M.,
Pellerin, S., and Vila-Franc
´
es, J. (2023). Comparison
between Machine Learning and Deep Learning Ap-
proaches for the Detection of Toxic Comments on So-
cial Networks. Applied Sciences, 13(10):6038.
Buitrago L
´
opez, A., Pastor-Galindo, J., and Ruip
´
erez-
Valiente, J. A. How toxic is the Spanish information
environment? Exploring the sentimentalism and hate
speech in online news and public reactions.
Caselli, T., Basile, V., Mitrovi
´
c, J., and Granitzer, M.
(2021). HateBERT: Retraining BERT for abusive lan-
guage detection in English. In Proceedings of the 5th
Workshop on Online Abuse and Harms (WOAH 2021),
pages 17–25, Online. Association for Computational
Linguistics.
Chhabra, A. and Vishwakarma, D. K. (2023). A literature
survey on multimodal and multilingual automatic hate
speech identification. 29(3):1203–1230.
Garg, T., Masud, S., Suresh, T., and Chakraborty, T. (2023).
Handling Bias in Toxic Speech Detection: A Survey.
ACM Comput. Surv., 55(13s):264:1–264:32.
Hanu, L. and Unitary, t. (2023). Detoxify.
Islam, M. H., Farzana, K., Khalil, I., Ara, S., Shazid, M. A.,
and Kabir Mehedi, M. H. (2021). Unmasking toxicity:
A comprehensive analysis of hate speech detection in
banglish. In 2024 6th International Conference on
Electrical Engineering and Information & Communi-
cation Technology (ICEEICT), pages 963–968. ISSN:
2769-5700.
Leite, J. A., Silva, D. F., Bontcheva, K., and Scarton, C.
(2020). Toxic Language Detection in Social Media for
Brazilian Portuguese: New Dataset and Multilingual
Analysis.
Mahajan, A., Shah, D., and Jafar, G. (2021). Explainable
AI approach towards toxic comment classification. In
Hassanien, A. E., Bhattacharyya, S., Chakrabati, S.,
Bhattacharya, A., and Dutta, S., editors, Emerging
Technologies in Data Mining and Information Secu-
rity, pages 849–858. Springer Nature.
Maity, K., Poornash, A. S., Saha, S., and Bhattacharyya,
P. (2024). ToxVidLM: A multimodal framework for
toxicity detection in code-mixed videos.
Malik, P., Aggrawal, A., and Vishwakarma, D. K. (2021).
Toxic Speech Detection using Traditional Machine
Learning Models and BERT and fastText Embedding
with Deep Neural Networks. In 2021 5th Interna-
tional Conference on Computing Methodologies and
Communication (ICCMC), pages 1254–1259.
Proksch, S.-O., Lowe, W., W
¨
ackerle, J., and Soroka, S.
(2019). Multilingual Sentiment Analysis: A New Ap-
proach to Measuring Conflict in Legislative Speeches.
Legislative Studies Quarterly, 44(1):97–131.
Rinker, T. (2016). sentimentr: Calculate Text Polarity Sen-
timent.
Sheth, A., Shalin, V. L., and Kursuncu, U. (2022). Defining
and detecting toxicity on social media: context and
knowledge are key. Neurocomputing, 490:312–318.
Subramanian, M., Easwaramoorthy Sathiskumar, V.,
Deepalakshmi, G., Cho, J., and Manikandan, G.
(2023). A survey on hate speech detection and senti-
ment analysis using machine learning and deep learn-
ing models. Alexandria Engineering Journal, 80:110–
121.
Sentiment-Enriched AI for Toxic Speech Detection: A Case Study of Political Discourses in the Valencian Parliament
561
