
Mobility: Promoting Health and Physical Activity
in School Environments
Mariana L. Moraes
1 a
, Maria Luiza C. Santos
1 b
, Maria das Grac¸as P. Silva
1 c
,
Edyellen L. S. Oliveira
1 d
, Rossana M. C. Andrade
2 e
and Pedro Almir M. Oliveira
1,2 f
1
Federal Institute of Maranh
˜
ao, Pedreiras, Brazil
2
Group of Computer Networks, Software Engineering, and Systems (GREat),
Federal University of Cear
´
a (UFC), Fortaleza, Brazil
{lopesmariana, luizacalisto, pereiramaria, eleal}@acad.ifma.edu.br,
Keywords:
Physical Activity, Health Promotion, Mobile Technology.
Abstract:
Technology, although it has brought many advances in various social spheres, has contributed to the popular-
ization of a sedentary lifestyle. The evolution of machines and the automation of daily processes have reduced
the need for daily physical activities, contributing to a serious public health problem. Given this scenario, it is
necessary to develop strategies that encourage adopting healthy practices in daily life. In this sense, this article
investigates the implementation of the ”Mobility” application in high schools, aiming to promote physical ac-
tivity among adolescents. By integrating technology with health promotion, Mobility stands out as a creative
tool to reduce cases of sedentary lifestyles and improve the quality of life of young people.
1 INTRODUCTION
Health, as one of the fundamental human rights,
is equated with other essential rights such as free-
dom, food, education, and security as established in
the Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR),
adopted by the United Nations (UN) in 1948. Recog-
nized as one of the key pillars for social, economic,
and personal development, health is considered a cru-
cial dimension of quality of life (Organization, 1995).
According to the (Nation, 1948), quality of life
is an individual’s perception of their position in life
within the context of the culture and value systems in
which they live and concerning their goals, expecta-
tions, standards, and concerns. In this context, the
WHO subdivides quality of life into four main do-
mains: physical, social, psychological, and environ-
mental. This study focuses on the physical domain,
covering aspects related to the motor skills of high
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0008-8084-8808
b
https://orcid.org/0009-0000-5017-9270
c
https://orcid.org/0009-0006-8130-9721
d
https://orcid.org/0009-0002-6488-2957
e
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0186-2994
f
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3067-3076
school students, their fitness for daily activities, and
their degree of mobility.
The Physical Activity Guide for the Brazilian Pop-
ulation, published by the Ministry of Health, states
that physical education can contribute significantly to
students’ health and personal development. During
periods of intense study, such as in the weeks leading
up to college exams, entrance exams, or the delivery
of a course completion paper, it is common for the stu-
dent to be anxious and overloaded and, also, the prac-
tice of physical activity may not be a priority during
this period, but it should be. Proper physical exercise
improves body health, which consequently benefits
brain health, increasing mental well-being and reduc-
ing symptoms of anxiety and depression (da Sa
´
ude,
2022).
When we think of neurocognitive aspects, such as
memory, it is through motor activities that new and
meaningful neural connections are formed. The psy-
chomotor approach already indicates that the com-
ponents of motor skills (a set of neural and muscu-
lar functions that enable voluntary or automatic body
movements) share common brain areas. This allows
students to transfer knowledge and skills acquired
through physical activity to academic tasks (Lisboa,
2022).
556
Moraes, M. L., Santos, M. L. C., Silva, M. D. G. P., Oliveira, E. L. S., Andrade, R. M. C. and Oliveira, P. A. M.
Mobility: Promoting Health and Physical Activity in School Environments.
DOI: 10.5220/0013164600003911
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 18th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2025) - Volume 2: HEALTHINF, pages 556-563
ISBN: 978-989-758-731-3; ISSN: 2184-4305
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

Physical education is mandatory in the primary
curriculum and optional in rare cases. Through cul-
ture and movement, in addition to its diversity of con-
tent, physical education seeks to sensitize and guide
students to reflect on their body mobility practices and
their impact on the environment in which they live.
Despite this, schools still need to encourage physical
exercise more, and little is said about its benefits for
students’ academic lives.
This study is necessary to help students become
more physically active since good performance in
school tasks is essential to achieving their goals. To
this end, the effectiveness of the Mobility app in the
school environment is investigated to promote better
habits in academic life. This investigation is con-
ducted by performing a usability test that evaluates
the quality and functionality of the app.
2 RELATED WORKS
To survey related studies, we searched the literature
using Google Scholar for approaches similar to the
proposal presented in this article. We aimed to iden-
tify studies related to promoting physical activity and
using technologies in the health area, resulting in se-
lecting five studies for discussion. The objective is to
provide a solid foundation for this article, highlight-
ing the need for technological innovations in health
and emphasizing the relevance of applications such
as Mobility.
In the foreground, the study by (Becchi et al.,
2021) discusses the practice of physical activities dur-
ing the COVID-19 pandemic. This scenario made it
challenging to maintain healthy habits due to social
distancing and the closure of public places, limiting
opportunities for physical activity and contributing to
a sedentary lifestyle. The article highlights the need
for digital tools to keep the population active amid the
lockdown. Despite the end of the pandemic, a seden-
tary lifestyle continues to be a reality for many people,
highlighting the need to encourage the population to
adopt healthier habits.
Similarly, the article by (Verzani and
de Souza Serapi
˜
ao, 2020) analyzes the impact
of smartphone applications on promoting physical
activity. The study highlights that these software
programs have great potential to encourage physical
activity and improve public health. Many appli-
cations incorporate gamification elements, such as
challenges and rewards, which can motivate users to
stay active and engaged. However, it is important to
overcome limitations such as dependence on tech-
nology, variation in effectiveness between different
users, and the possibility of disengagement over time.
It is concluded that applications have the potential to
encourage exercise. However, it is important to over-
come the aforementioned limitations to maximize
their impact.
Complementing the previous view, the (Silva
et al., 2020) review states that health apps are essential
in monitoring health conditions and promoting physi-
cal activities. They facilitate communication between
the healthcare professional and the patient and allow
health monitoring. However, challenges can be over-
come, such as prolonged user adoption, the need for
scientific validation, and ensuring data privacy. The
study shows that this software offers many benefits;
however, it is essential to emphasize the referential
challenges. Mobile health has promising results and
can help various public policies external to the pro-
motion of well-being and health.
Mobile health (mHealth) has been gaining in-
creasing attention in the health field. The study by
(Oliveira et al., 2018) explores the opportunities mo-
bile health offers in promoting physical activity and
improving health outcomes for the population. The
paper discusses how apps can monitor and encourage
physical exercise, supporting active lifestyles. As in
previous dissertations, it is found that there are obsta-
cles, such as accessibility, that need to be addressed
for the implementation of mobile health applications.
Contributing to the previous perspective, the text
by (Organization et al., 2007) is part of the WHO in-
formation series on school health and highlights the
importance of physical activities in the school con-
text as a fundamental component for promoting health
and well-being. The study states that implementing
school physical activity programs improves students’
physical, mental, and social development, improving
their academic performance and general well-being.
The document suggests that schools implement pro-
grams and policies that add physical activities to the
curriculum, creating an environment that encourages
healthy lifestyles.
Analyzing the approaches discussed, Mobility
shares the goal of integrating users through digital
tools. However, the app stands out among other ap-
plications for creating the practice of physical activi-
ties in a fun and interactive way, using tools such as
challenges and rankings combined with health moni-
toring, such as BMI calculation. In addition, it seeks
to overcome the challenges identified in the literature,
such as user disengagement and digital inclusion.
Mobility: Promoting Health and Physical Activity in School Environments
557

Figure 1: Mobility Prototype.
3 MOBILITY
The Mobility App aims to encourage mobility chal-
lenges that promote students’ physical health. The
project suggests mobility-related challenges inte-
grated with the infrastructure of “omitted for blind re-
view”. Initially, it was called MovPed and was being
developed on the App Inventor platform
1
, a web soft-
ware from the American university Massachusetts In-
stitute of Technology (MIT) for creating Android ap-
plications. Subsequently, the application was moved
to the Kodular tool
2
, inspired by App Inventor but
with more functionalities and components. The pro-
totype of the project’s screens was built in FigJam
3
1, an online whiteboard tool launched by the company
Figma
4
.
The application logo 2 features an image of a
cheetah, symbolizing mobility, as it is the fastest land
animal in the world. It also includes the slogan: ’You
in motion.’ The color scheme uses orange and its
complementary blue on the screens because the or-
ange hue symbolizes energy, vitality, movement, and
creativity. All interface elements of the app 3 were
sourced from the Flaticon website
5
, which provides
icons and stickers for download.
1
https://appinventor.mit.edu/
2
https://kodular.io/
3
https://figma.com/figjam/
4
https://figma.com/
5
https://flaticon.com/
Figure 2: Mobility app logo.
Figure 3: Icons from Flaticon.
The Mobility app includes the following screens:
Login/Register 4, Menu 7, Profile, Challenges 5,
Ranking 6, BMI Calculator 7, and Information.
• Login/Registration: The registration screen con-
tains fields to enter the full name, email, pass-
word, password confirmation, age, and gender.
All this data is sent and stored in Firebase 8 once
HEALTHINF 2025 - 18th International Conference on Health Informatics
558

the user fills out the fields and clicks the ”Create
account” button. After this step, when clicking
”Login,” the login screen will appear with fields to
enter the username and the previously registered
password in the database.
Figure 4: Splash screen, registration and login.
• Menu: This screen opens after the user has
logged in and clicked the ”Log In” button. It has
four buttons: Challenges, Ranking, BMI Calcu-
lator, and Information. It also displays the user
profile in the top section of the screen. Users are
redirected to the respective screen when they click
any button.
• Profile: This screen displays the user’s name, age,
and gender, retrieved from Firebase 8. The user
can edit these details by clicking the ”Edit data”
button. After making changes, the user clicks
”Save data,” and the fields will reflect the updated
information saved in the database.
• Challenges: This screen lists the proposed chal-
lenges in the app. Two challenges are listed: Max-
imum steps in 5 (five) minutes and Run from the
entrance to the announcement TV. The first chal-
lenge tracks the maximum number of steps the
user can achieve in five minutes. On this screen
is a step counter sensor that records the number
of steps taken and the distance covered in meters,
along with a timer that stops when five minutes
have passed, ending the challenge and saving the
result in the list below.
The second challenge is to run from the entrance
to the campus announcement TV as soon as pos-
sible. This screen shows the user’s current coordi-
nates and the distance in meters from the start and
end points of the challenge. Due to GPS accuracy,
there is a tolerance of up to 6 meters from the ref-
erence points to start or finish the challenge. After
completing the challenge by pressing the ”Finish
challenge” button, the time taken to complete the
path is recorded. The results of the challenges are
listed in descending and ascending order, respec-
tively.
Figure 5: Mobility Screens: Challenges.
• Ranking: The following screen displays all the
recorded results for each challenge, including the
name, score achieved, and the date the user com-
pleted the challenge. This data is retrieved from
Firebase, which is neatly saved for the sorting list.
Figure 6: Mobility Screens: Ranking.
• BMI Calculator: This screen presents fields to
enter height (cm) and weight (kg). When the
”Calculate” button is clicked, the user’s body
mass index and a classification table for health sta-
tus reference will appear. In the ”Clear” option,
the user can input new values and recalculate the
BMI.
Figure 7: Mobility Screen: Homescreen and BMI.
• Information: This screen contains a description
of the developers of the Mobility app and the pur-
pose of the application.
The Firebase Realtime Database
6
is used 8, which
is a cloud-hosted database that stores and syncs data
6
https://firebase.google.com/
Mobility: Promoting Health and Physical Activity in School Environments
559

among its users in real-time. The app settings are
stored on the platform (containing the latitudes and
longitudes of the two points in the running challenge
and the tolerance in meters, which can be modified),
the profiles (with the user’s name, age, and gender),
the records of the completion of each challenge (con-
taining the achieved value, the name of the person
who completed it, and the date), and the users (which
include the registered name, email, and password).
Figure 8: Mobility Database.
4 PRELIMINARY ASSESSMENT
It is important to note that the school did not offi-
cially implement Mobility. However, before the main
study was implemented, a preliminary evaluation was
conducted to test and identify possible challenges in
using the developed application. For this phase, two
exploratory questionnaires were applied through the
Google Forms platform: the pre-experiment question-
naire, which aimed to analyze the students’ physi-
cal activity habits, and the post-experiment question-
naire, which aimed to evaluate the app.
4.1 Methodology
To conduct the preliminary assessment, question-
naires created by the Mobility development team and
made available through the Google Forms platform
were used. Before the questionnaire was adminis-
tered, the students had not tested the application, al-
lowing a concrete analysis of the student’s first im-
pression of Mobility. No exclusion criteria were es-
tablished for participants in the preliminary assess-
ment.
The first form, a pre-experimental form, consisted
of 11 questions and took an average of five minutes
to complete. It sought to analyze participants’ aca-
demic data, including age, course, shift attended, year
in which they were enrolled, and study modality (inte-
grated, subsequent, or undergraduate). After collect-
ing this initial information, questions related to the
participants’ health were presented, such as ”Do you
have any chronic diseases or health problems?” and
”How physically active do you consider yourself?”,
in order to assess the participants’ general health sta-
tus and level of physical activity.
After completing the first form, the evaluation it-
self began. Participants tested all the software’s fea-
tures, including the proposed challenges. During this
phase, the tool’s usability, ease of access, and clarity
of the application’s instructions were observed, and
the effectiveness of the challenges in promoting ad-
herence to physical activities was evaluated. At the
end of the test, students were invited to answer a sec-
ond questionnaire: the post-experiment.
The Likert scale was used for the post-experiment
form, and an evaluation scale was used to measure
the participants’ opinions, motivations, and other as-
pects. It uses a series of response options ranging
from an extremely positive opinion to a highly neg-
ative one, sometimes including moderate or neutral
options. The questionnaire evaluated several aspects
of the application and included questions such as:
• ”How easy was it to use Mobility?”, with answers
ranging from 1 (very difficult) to 5 (very easy) 10;
• ”How interesting/appropriate did you find the
challenges?”, with options ranging from 1 (not
very interesting) to 5 (very interesting) 11;
• ”What would you rate the application?” with an-
swers ranging from 1 (poor) to 5 (excellent) 12.
In addition to these questions, the form contained
a section dedicated to suggestions, allowing partici-
pants to provide feedback and proposals for improv-
ing the application,. The post-experiment form took,
on average,, seven minutes to complete. Overall, con-
sidering the time spent on the questionnaires and the
evaluation itself, the application protocol lasted about
30 minutes.
4.2 Data Collected
The data collected in the pre-experiment and post-
experiment are shown in the following graphs 9, 10,
11, 12.
5 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Mobility aims to encourage students to practice phys-
ical exercise in a fun and accessible way within the
school environment. To ensure the app’s efficient use
at school, an evaluation period was conducted to en-
sure its effectiveness.
HEALTHINF 2025 - 18th International Conference on Health Informatics
560

Figure 9: Percentage distribution of students about the practice of physical exercises.
Figure 10: Level of ease of using Mobility.
Before introducing the application, a question-
naire was conducted using the Google Forms plat-
form to analyze aspects related to the students’ phys-
ical lives. The questionnaire was structured to col-
lect information on the frequency of physical activity
practices, mobility difficulties, and possible barriers
to performing exercises.
Based on the results obtained 9, it was ob-
served that 90.3% of the participants did not present
mobility-related problems. Furthermore, the data in-
dicate that 25.8% of the students do not perform
any physical activity, while 41.9% reported practic-
ing physical activities occasionally. On the other
hand, 25.8% reported practicing physical activities
frequently, and only 3.2% of the students reported
practicing physical activities regularly.
Therefore, the data obtained on physical activ-
ity practice indicate a worrying situation. The num-
ber of students who do not perform physical activ-
ity (25.8%) is high. This inactivity indicates that the
school has not encouraged or made students aware of
the benefits of regular physical activity.
In addition, the majority of the students (41.9%)
reported practicing physical activities only occasion-
ally, which may be insufficient to guarantee their ben-
efits. This occasional practice indicates that the stu-
dents understand the importance of physical exercise
but are not encouraged to do it.
Among the 31 participants in the experiment, only
3.2% practice physical activities regularly, indicating
that only a small portion of those being evaluated un-
derstand the real need to maintain a healthy routine.
5.1 Post-Assessment Form
After the preliminary assessment, another form was
proposed for the Mobility evaluation. This analysis
included the quality of the challenges and scores from
1 to 5 for application and ease of use.
The responses obtained from this questionnaire in-
dicated that the application is easy to use 10, with an
intuitive interface that makes navigation more acces-
sible for users. In addition, the feedback on the qual-
ity of the challenges was mostly favorable, indicat-
ing that the proposed activities are appropriate for the
app’s purpose 11.
On the other hand, some participants highlighted
the need to add other functions to the software. These
functionalities include creating more challenges and
an area reserved for meal tips and nutritional guide-
lines for better physical conditioning when practicing
mobility exercises. In addition, it was suggested that
the app integrate the Physical Education discipline so
that the challenges proposed in Mobility can also be
used as practical classes for the subject.
In general, the rating given to the application was
excellent, as shown in the graph 12. Considering the
suggestions presented by the participants, it is possi-
ble to improve the tool further, adapting it to different
lifestyles.
Mobility: Promoting Health and Physical Activity in School Environments
561
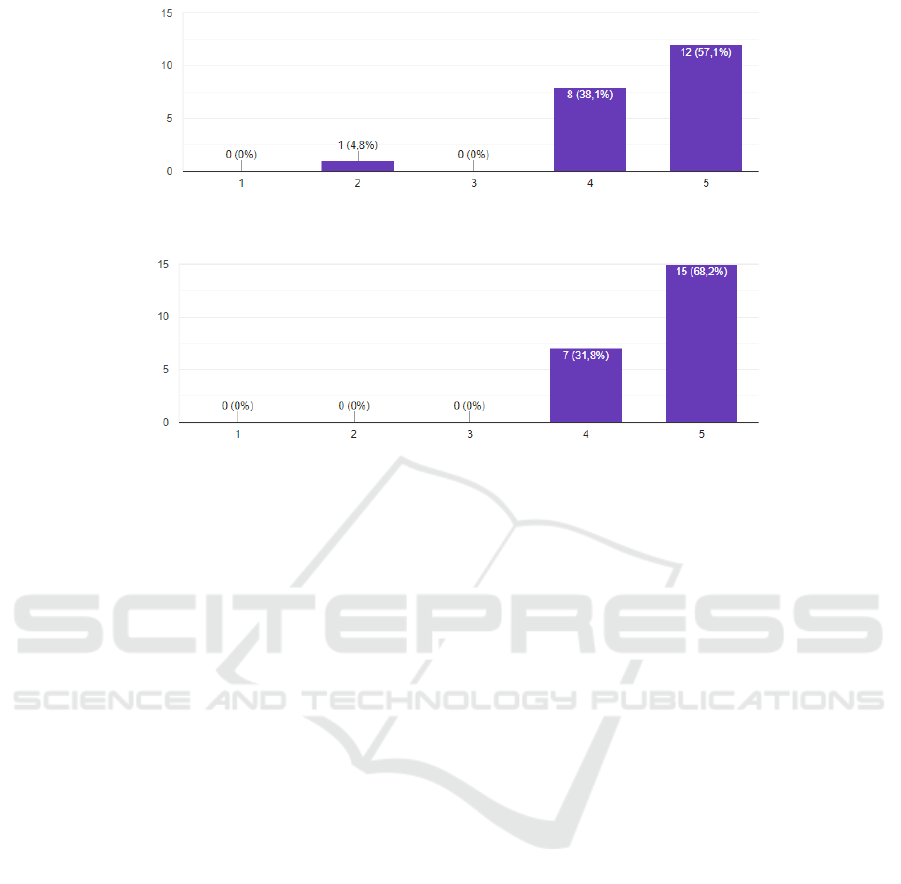
Figure 11: Level of suitability for Mobility challenges.
Figure 12: Mobility app general rating.
5.2 Study Limitations
One of the limitations of the study was the small num-
ber of people who participated in the test period, in
addition to the fact that it was conducted in a spe-
cific school environment with a limited age range. In
addition, several obstacles make it challenging to ap-
ply this software in schools, such as digital inclusion,
since not all students have the same level of knowl-
edge about using software, in addition to the suitabil-
ity of the environment for carrying out the challenges
proposed by Mobility. These factors restrict the gen-
eralization of the results, making it difficult to com-
pare with other institutions with different structural
conditions and socioeconomic contexts.
Another difficulty encountered is the lack of in-
terest in practicing physical activities. This bar-
rier may be related to individual issues (motivation,
self-esteem), social issues (influence of friends and
family), and environmental issues (access to suitable
spaces) (Ceschini and Junior, 2007). In the context
of the school in question, students feel overwhelmed
by the choice of a technical course integrated into
high school, which results in great academic de-
mands. Therefore, they naturally prefer more passive
lifestyles, which, in turn, generate a view of irrele-
vance regarding the application. For this reason, ini-
tially, the participants did not seem very interested in
participating in the preliminary evaluation.
During the application testing in the preliminary
evaluation phase, the software presented GPS-related
difficulties, which initially did not work correctly on
all cell phones. However, despite this obstacle, Mo-
bility proved to be successful in the testing phase,
proving to be easy to apply in practice.
5.3 Future Research
For future research, it is suggested that more compre-
hensive tests be conducted to obtain a broader view of
physical activity patterns among students. The effects
of programs that promote physical health in schools
should be observed, relating them to students’ aca-
demic performance and the associated psychological
implications. In addition to promoting training on us-
ing this type of software in schools, strategies to over-
come the aforementioned challenges must be created.
6 FINAL REMARKS
In summary, the study was based on the 17 UN
Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), emphasiz-
ing health and well-being. Thus, considering the
global scenario regarding the increase in the number
of young people facing problems related to a seden-
tary lifestyle and diseases resulting from this lifestyle,
it is essential to adopt effective measures to solve this
issue, leading to the creation of the Mobility applica-
tion.
Although the software has not been implemented
in schools, the results observed in the questionnaires
carried out indicate promising potential. However, al-
though the study presents excellent results, it is clear
HEALTHINF 2025 - 18th International Conference on Health Informatics
562

that there are several barriers related to implementing
this software in schools, such as digital inclusion and
the appropriate environment for carrying out the chal-
lenges, among others. In addition, a comprehensive
evaluation of the application discussed in this article
is still necessary.
The present study was based on the performance
of a usability test to assess the impact of Mobility in
schools. It is worth mentioning that before the prelim-
inary evaluation was carried out, all students involved
agreed to the consent terms present in the question-
naires.
To demonstrate the researchers’ commitment to
ensuring a viable project, it is emphasized that the cur-
rent study is under analysis by the Ethics Committee
and, if successful, will enter the process for more in-
depth research at the institute itself. Therefore, among
the main findings of this work is the need to integrate
technologies into educational networks to promote a
healthier environment that encourages the practice of
physical activities.
REFERENCES
Becchi, A. C., Mois
´
es, S. C. C., Lovato, N. S., Harami,
G. H., da Silva Alc
ˆ
antara, V. C., de Azevedo Bar-
bosa, V. C. A., and Machado, R. A. (2021). Incen-
tivo a pr
´
atica da atividade f
´
ısica: estrat
´
egias do nasf
em meio
`
a pandemia de covid-19. APS EM REVISTA,
3(3):176–181.
Ceschini, F. L. and Junior, A. F. (2007). Barreiras e deter-
minantes para a pr
´
atica de atividade f
´
ısica em adoles-
centes. Revista Brasileira de Ci
ˆ
encia e Movimento,
15(1):29–36.
da Sa
´
ude, M. (2022). Por que incentivar a participac¸
˜
ao
de crianc¸as e de adolescentes nas aulas de
educac¸
˜
ao f
´
ısica escolar? — minist
´
erio da sa
´
ude.
https://www.gov.br/saude/pt-br/assuntos/saude-
brasil/eu-quero-me-exercitar/noticias/2022/ por-
que-incentivar-a-participacao-de-criancas-e-de-
adolescentes-nas-aulas-de-educacao-fisica-escolar.
(Accessed on 10/13/2024).
Lisboa, T. (2022). Qual
´
e a relac¸
˜
ao entre a atividade f
´
ısica
e o desempenho escolar? — minist
´
erio da sa
´
ude.
https://www.gov.br/saude/pt-br/assuntos/saude-
brasil/eu-quero-me-exercitar/noticias/2022/ qual-e-
a-relacao-entre-a-atividade-fisica-e-o-desempenho-
escolar. (Accessed on 10/13/2024).
Nation, U. (1948). Constitution of the world health or-
ganization. https://www.who.int/about/governance/
constitution. (Accessed on 10/13/2024).
Oliveira, M. V. L. d. et al. (2018). mhealth: Possibilidades
no campo da atividade f
´
ısica e desfechos em sa
´
ude.
Organization, W. H. (1995). Universal declaration of
human rights — united nations. https://www.un.org/
en/about-us/universal-declaration-of-human-rights.
(Accessed on 10/13/2024).
Organization, W. H. et al. (2007). Promoting physical ac-
tivity in schools: an important element of a health-
promoting school. World Health Organization.
Silva, R. H., Gatti, M. A. N., Marta, S. N., Marafon, R.
G. C., Neto, G. G. G., de Andrade, E. B. d. O., de An-
drade, S. C., and das Neves Lopes, V. d. C. (2020).
Aplicativos de sa
´
ude para dispositivos m
´
oveis: Uma
revis
˜
ao integrativa. Brazilian Journal of Health Re-
view, 3(5):11754–11765.
Verzani, R. H. and de Souza Serapi
˜
ao, A. B. (2020).
Aplicativos de smartphones e atividades f
´
ısicas::
contribuic¸
˜
oes e limitac¸
˜
oes. Pensar a Pr
´
atica, 23.
Mobility: Promoting Health and Physical Activity in School Environments
563
