
Efficient Automatic Data Augmentation of CDT Images to Support
Cognitive Screening
Nina Hosseini-Kivanani
1 a
, In
ˆ
es Oliveira
1 b
, Sena Kilinc¸
2 c
and Luis A. Leiva
1 d
1
Department of Computer Science, University of Luxembourg, Esch-sur-Alzette, Luxembourg
2
Faculty of Science and Engineering, Sorbonne Universit
´
e, Paris, France
Keywords:
Drawing, Handwriting, Cognitive Impairments, Data Augmentation, Neural Networks.
Abstract:
We investigate the effectiveness of learnable and non-learnable automatic data augmentation (AutoDA) tech-
niques in enhancing Deep Learning (DL) models for classifying Clock Drawing Test (CDT) images used
in cognitive dysfunction screening. The classification is between healthy controls (HCs) and individuals with
mild cognitive impairment (MCI). Specifically, we evaluate TrivialAugment (TA) and UniformAugment (UA),
adapted for clinical image classification to address data scarcity and class imbalance. Our experiments across
three public datasets demonstrate significant improvements in model performance and generalization. Notably,
TA increased classification accuracy by up to 15 points, while UA achieved a 12-point improvement. These
techniques offer a computationally efficient alternative to learnable methods like RandAugment (RA), which
we also compare against, delivering comparable (and sometimes better) results with a much lower computa-
tional overhead. Our findings indicate that AutoDA techniques, particularly TA and UA, can be effectively
applied in clinical settings, providing robust tools for the early detection of cognitive disorders, including
Alzheimer’s disease and dementia.
1 INTRODUCTION
Data augmentation (DA) is crucial for Deep Learn-
ing (DL) models in clinical settings, where acquir-
ing large, labeled datasets is often challenging. By
applying transformations such as rotation, scaling,
and cropping, DA creates diverse training samples
that reduce overfitting and enhance model general-
ization (Frid-Adar et al., 2018; Shorten and Khosh-
goftaar, 2019). This is particularly vital in med-
ical applications where data is scarce and imbal-
anced, as seen in radiology and the screening for
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) (Hosseini-Kivanani et al.,
2024b; Kobayashi et al., 2022; Ogawa et al., 2019),
where DA can significantly improve accuracy. De-
spite these advantages, the success of DA relies on
preserving the clinical relevance of the images. In
some tasks, such as object detection for medical im-
age analysis, traditional DA techniques have shown
limitations (Kebaili et al., 2023). Indeed, improper
augmentation can introduce noise that disrupts the
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0821-9125
b
https://orcid.org/0009-0009-0043-4080
c
https://orcid.org/0009-0001-9529-7219
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5011-1847
learning process (Ko and Ok, 2021). Therefore, while
DA has demonstrated its value in healthcare (Chlap
et al., 2021; Nalepa et al., 2019), developing more
sophisticated augmentation strategies tailored to the
unique challenges of medical data remains a priority.
Several studies have explored the use of drawing
tasks to improve the detection of AD. These tasks cap-
ture different and complementary aspects of cognitive
impairment, enhancing the automated detection of
AD and mild cognitive impairment (MCI) (Hosseini-
Kivanani et al., 2024b; Kobayashi et al., 2022). How-
ever, there remains a gap in research that focuses
on customizing automatic data augmentation (Au-
toDA) techniques for cognitive assessment tools like
the Clock Drawing Test (CDT), widely used in cog-
nitive dysfunction screening. In this paper, we ad-
dress this gap by evaluating and adapting state-of-the-
art AutoDA techniques for CDT images. Our aim is
to maintain clinical relevance while improving model
robustness. Our key contributions are as follows:
• We adapt AutoDA techniques to the specific clin-
ical requirements of CDT images, preserving di-
agnostic relevance while achieving significant im-
provements in detection accuracy and model gen-
eralization across three public datasets.
600
Hosseini-Kivanani, N., Oliveira, I., Kilinç, S. and Leiva, L. A.
Efficient Automatic Data Augmentation of CDT Images to Support Cognitive Screening.
DOI: 10.5220/0013165100003890
In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2025) - Volume 3, pages 600-607
ISBN: 978-989-758-737-5; ISSN: 2184-433X
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

• By comparing learnable and non-learnable aug-
mentation methods, we provide practical insights
and guidelines for applying data augmentation ef-
fectively in cognitive dysfunction screening.
Our experimental results demonstrate that Au-
toDA methods achieve up to a 15% improvement in
accuracy compared to models without data augmenta-
tion, depending on the dataset. The results highlight
the effectiveness of applying tailored AutoDA tech-
niques for improving the early diagnosis of cognitive
impairments, such as AD and dementia. This work
supports enhanced clinical decision-making and lays
the foundation for more advanced diagnostic tech-
nologies in healthcare.
2 RELATED WORK
Traditional DA methods for images, such as random
cropping, flipping, and color jittering, require manual
design and domain expertise to be effective. While
these basic transformations are straightforward to im-
plement, they may not capture the complex variations
needed for specialized tasks or datasets. Special-
ized methods, including Cutout (Devries and Taylor,
2017), Mixup (Zhang et al., 2017), and CutMix (Yun
et al., 2019), have been proposed to enhance model
performance by introducing more sophisticated aug-
mentation techniques. Although effective for spe-
cific tasks, transferring these methods to other tasks
or datasets often requires extensive manual effort and
tuning. To alleviate this, recent advances have shifted
towards AutoDA strategies for designing and tuning
augmentation policies. Table 1 summarizes the state-
of-the-art.
AutoAugment (AA) (Cubuk et al., 2019) uses re-
inforcement learning to search for optimal policies,
which yields significant performance improvements
at the cost of heavy computational resources. Fast
AutoAugment (Fast AA) (Lim et al., 2019) reduces
this computational burden by using Bayesian Op-
timization (BO), while Population-Based Augmen-
tation (PBA) (Ho et al., 2019) introduces an evo-
lutionary algorithm to explore augmentation sched-
ules. Faster AutoAugment (Hataya et al., 2020) fur-
ther accelerates the process by employing a differen-
tiable policy search, but this comes with some per-
formance degradation. RandAugment (RA) (Cubuk
et al., 2020), inspired by the findings of Fast AA and
PBA, simplifies automated DA by removing the need
for an extensive search phase. However, RA still re-
quires a computationally intensive offline grid search
to find optimal hyperparameters. UniformAugment
(UA) (LingChen et al., 2020) and TrivialAugment
(TA) (Muller and Hutter, 2021) avoid the computa-
tional complexity of search-based techniques while
still benefiting from the diversity introduced by ran-
dom augmentations. They uniformly sample aug-
mentation operations from a predefined set and ap-
ply them with equal probability. (TA only considers
one operation at a time.) Augmentation-Wise Weight
Sharing (AWS) (Tian et al., 2020) uses Neural Ar-
chitecture Search (NAS) (Zoph and Le, 2017) for au-
tomatic augmentation search, reducing computational
costs while maintaining performance with a dynamic
augmentation policy that adapts during training. It
still demands significant computation in the initial
and fine-tuning phases. Model-Adaptive Data Aug-
mentation (MADAug) (Hou et al., 2023) adjusts aug-
mentation policies dynamically based on model per-
formance. Our work similarly explores when and
what augmentations should be applied during training
to optimize performance. Finally, BO-Aug (Zhang
et al., 2022) utilizes a continuous policy search space
and evaluates policy groups rather than individual
policies. It achieved state-of-the-art or comparable
performance with relatively low computational costs
compared to AA and RA.
Table 1: Overview of AutoDA techniques for DL models,
tested on ImageNet, sorted by error rate (lower is better).
†BO-Aug used Tiny ImageNet, a subset of 100k ImageNet
images.
AutoDA Error (%) Non-learnable
RandAugment (RA) 15.0 No
AutoAugment (AA) 16.5 No
AWS 18.5 No
Fast AA 19.4 No
UniformAugment (UA) 19.6 Yes
MADAug 21.5 No
TrivialAugment (TA) 21.9 Yes
Faster AA 23.5 No
BO-Aug† 36.8 No
Despite the significant amount of research focused
on AutoDA strategies, there is limited work specif-
ically targeting medical images. MedAugment (Liu
et al., 2023) is one of the few methods designed for
medical imaging. It employs two distinct augmenta-
tion spaces: pixel-level (photometric) and spatial (ge-
ometric) transformations. Unfortunately, MedAug-
ment focuses on X-ray data, which differs signifi-
cantly from hand-drawn data, such as the CDT images
that we are studying. Additionally, MedAugment re-
lies on ground-truth segmentations, which are not ap-
plicable to handwriting images and require learning a
DA policy, rendering it unsuitable for real-time appli-
cation in DL training pipelines.
Building on these insights, our work aims to ex-
Efficient Automatic Data Augmentation of CDT Images to Support Cognitive Screening
601

amine DA techniques for Computer Vision models
applied to drawing tasks for cognitive impairment as-
sessment, specifically AD. Our approach not only ad-
dresses the limitations of existing methods, but also
explores a novel domain in medical image augmen-
tation. We focus on creating augmentation strategies
that preserve the semantic content of hand-drawn ele-
ments while introducing sufficient variability to en-
hance model performance. By avoiding extensive
computational requirements and the reliance on spe-
cialized datasets, our method is suitable for real-time
use and contributes to the advancement of DL appli-
cations in medical imaging.
3 METHODOLOGY
Our task consists of spotting early signs of cognitive
decline via hand-drawn clock images. This is framed
as a binary classification problem between healthy
controls (HCs) and individuals with mild cognitive
impairment (MCI). This is a really challenging and
appealing task for several reasons. First, MCIs are at
high risk of progressing to dementia, although their
impairments do not severely impact daily or social
functioning. In fact, MCIs might remain stable or re-
verse to healthy cognition (Blair et al., 2022). Sec-
ond, the drawing abilities of HCs and MCIs are often
on par, making it difficult to differentiate both groups
with DL models. Third, being able to tell HCs and
MCIs apart means that practitioners could start treat-
ing the patients as soon as possible, as once they are
diagnosed with AD, it is irreversible.
3.1 Materials
The CDT is a paper-and-pencil cognitive screening
tool that is quick to apply, well accepted by patients,
easy to score, and independent of language, educa-
tion, and culture. It also has good inter-rater and
test-retest reliability, high levels of sensitivity and
specificity, concurrent validity, and predictive valid-
ity (Spenciere et al., 2017). In the CDT, subjects must
draw a clock, including the numbers 1 to 12, as well as
the clock hands, usually pointing to “10:00”, “11:10”,
or similar. The drawing is then scored according to a
normalized system, among which the Shulman (Shul-
man et al., 1993) and MoCA (Nasreddine et al., 2019)
scoring systems are the most popular ones.
We used three publicly available CDT datasets for
this study, each containing images from both HCs and
individuals with MCI. These datasets provide a rich
variety of clock images, enabling the exploration of
different augmentation strategies and deep-learning
models.
1. Dataset Chen (Chen et al., 2020) 2020 dataset. It
contains 1,021 images categorized as HCs (n=50)
and six subgroups of patients. Images in sub-
groups 1 (n=164) and 2 (n=233) correspond to
MCIs. The average age in both HCs and MCIs
is 69.8 years. There are 58% females and 42%
males.
2. Ruengchaijatuporn dataset (Ruengchaijatuporn
et al., 2022) 2022 dataset. It contains 918 im-
ages labeled according to the MoCA score. We se-
lected those of HCs (score of 26 or higher, n=550)
and MCIs (scores between 18 and 25, n=322).
The median age in both groups is 67 years. There
are 77% females and 23% males.
3. Raksasat dataset (Raksasat et al., 2023) 2023
dataset. It contains 3,108 images categorized as
six user groups. We consider group 5 (“perfect
clock”, n=1623) as HCs and group 4 (“minor vi-
suospatial deficits”, n=1047) as MCIs. The me-
dian age in both groups is 67 years. There are
66% females and 33% males.
To maintain consistency across all datasets, we en-
sured that all images had a square aspect ratio by crop-
ping each image to its shortest dimension. This step
was essential because DL models such as Efficient-
Net require square inputs to avoid distortion and en-
sure optimal performance. After cropping, the images
were resized to 224×224 px, matching the input size
required by pre-trained models. No additional pre-
processing, such as color normalization or denoising,
was applied, as the clock images are relatively clean.
3.2 AutoDA Methods
We systematically evaluate two non-learnable Au-
toDA methods, TA and UA, which have demonstrated
state-of-the-art performance in various computer vi-
sion tasks (Muller and Hutter, 2021; LingChen et al.,
2020). These methods are particularly appealing for
real-time applications because they do not require
learning augmentation policies during training, thus
reducing computational overhead. The augmentation
process in both methods follows three main steps:
• Random Sampling: A set of augmentations is ran-
domly chosen from a predefined list of operations
(Table 2) such as rotation, shear, etc.
• Magnitude Randomization: The intensity of each
selected augmentation is randomized within a
specified range.
• Application of Augmentation: The selected aug-
mentations are sequentially applied, resulting in a
modified version of the original input image.
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
602
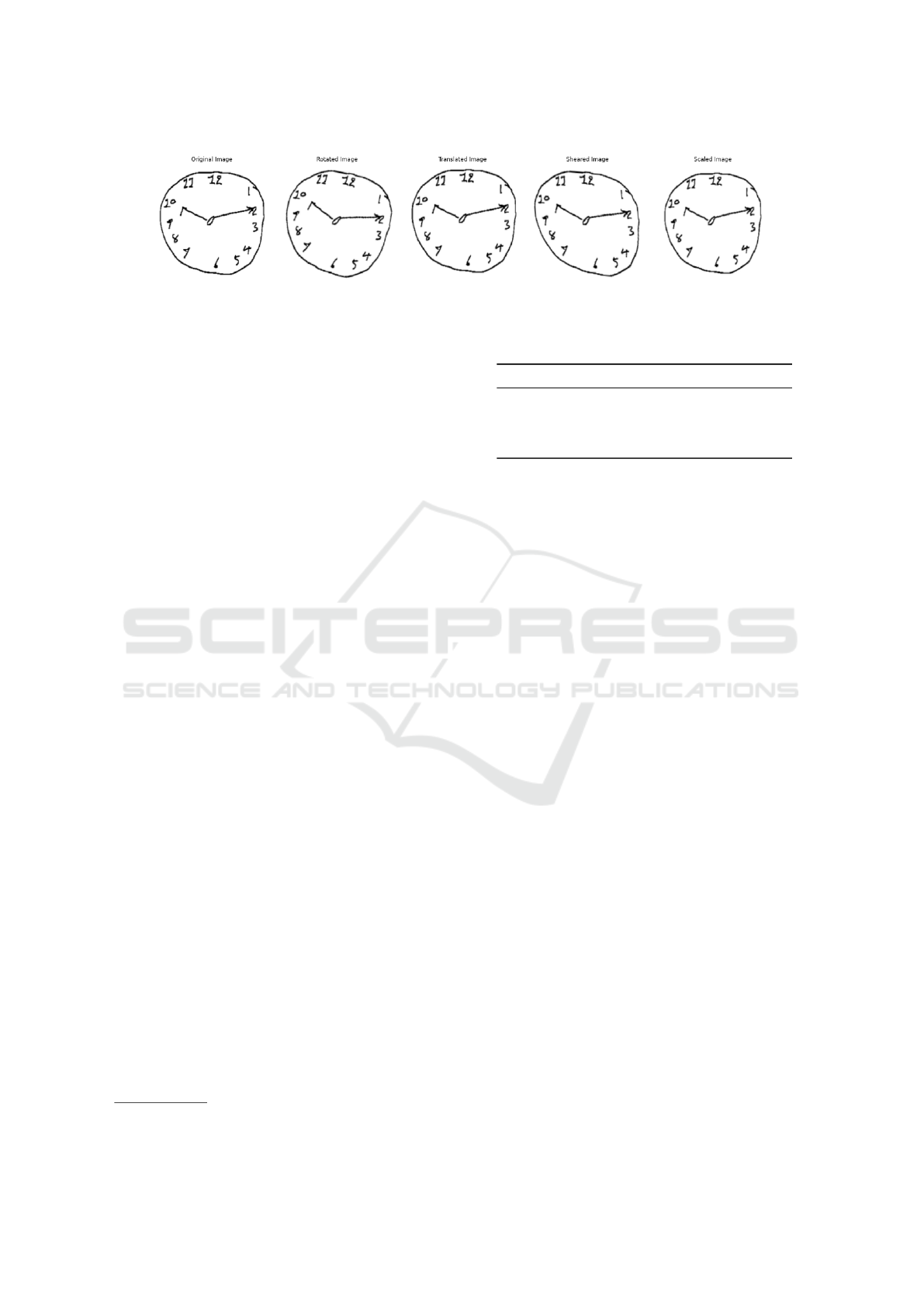
Figure 1: Examples of CDT images from Ruengchaijatuporn dataset before (original image) and after augmentation.
In TA, a single transformation is applied per aug-
mented image with a randomly chosen strength. In
UA, k transformations are selected, each of which
is applied with a probability of 0.5, with a ran-
domly picked magnitude. Following the original pa-
per (LingChen et al., 2020), we set k = 2.
For comparison, we also evaluate RA (Cubuk
et al., 2020), a state-of-the-art and widely used learn-
able AutoDA method that dynamically optimizes aug-
mentation strategies during training. Unlike TA and
UA, which rely on fixed augmentations, RA intro-
duces two key hyperparameters: the number of aug-
mentation operations and the magnitude, which are
optimized during the training process. This learnable
approach allows RA to adapt the augmentation poli-
cies based on the dataset’s characteristics, making it
particularly useful in domains such as medical imag-
ing, where data scarcity and class imbalance are com-
mon challenges. In our implementation, we search for
the RA hyperparameters N and M over discrete sets,
with N values ranging from 2 to 3 and M values rang-
ing from 4 to 5, as part of the optimization process to
find the best-performing augmentation combination.
While learnable methods like RA can potentially im-
prove model performance by adjusting augmentations
to the data, non-learnable methods such as TA and
UA provide a computationally efficient alternative by
avoiding the complexity and overhead associated with
policy optimization.
3.2.1 Transformation Operations
A key detail in AutoDA methods is the ”augmentation
pool,” i.e., the set of available transformation opera-
tions and their ranges.
autoreftab:transformations details the transformations
considered in the study. Only geometric transforma-
tions were applied in carefully curated ranges so as
not to destroy image semantics and thus ensure clini-
cal relevance. Transformations were applied using the
Albumentations library
1
.
1
https://albumentations.ai/
Table 2: Overview of considered augmentation operations
and transformation ranges.
Transformation Range Description
Rotation [-10, 10] degrees
Shear [0.2, 10] degrees
Scale [-0.05, 0.05] % of original size
Translation [-0.02, 0.02] % of bounding box
3.3 DL Models
We provide classification results according to Effi-
cientNet (Tan and Le, 2019) and DenseNet (Huang
et al., 2017) as a common benchmarking reference.
On the one hand, EfficientNet is a lightweight deep
learning model (5M parameters) that has demon-
strated state-of-the-art performance in various medi-
cal imaging applications. Its efficiency and scalabil-
ity make it an ideal choice for this study, particularly
given the relatively small size of the datasets involved.
On the other hand, DenseNet has a densely connected
architecture, where each layer is directly connected
to every other layer, promoting efficient feature reuse
and enhancing gradient flow. This structure enables
the extraction of richer and more detailed feature rep-
resentations. DenseNet’s design is particularly advan-
tageous for complex tasks like medical image classi-
fication, where capturing intricate patterns in the data
is critical for accurate diagnosis.
The models are trained using the Adam optimizer
with a learning rate of η = 0.0005. We used a batch
size of 32 images, and training was carried out for up
to 100 epochs. Early stopping is employed to prevent
overfitting, with a patience threshold of 10 epochs.
This approach ensures that training halts if the vali-
dation accuracy does not improve over 10 consecu-
tive epochs while retaining the best-performing model
weights. Balanced classification accuracy is used as
the monitoring metric. Additionally, the Area Under
the Receiver Operating Characteristic (AUC) curve is
used to evaluate the discriminative power of the clas-
sifier, providing further insight into its performance.
Efficient Automatic Data Augmentation of CDT Images to Support Cognitive Screening
603
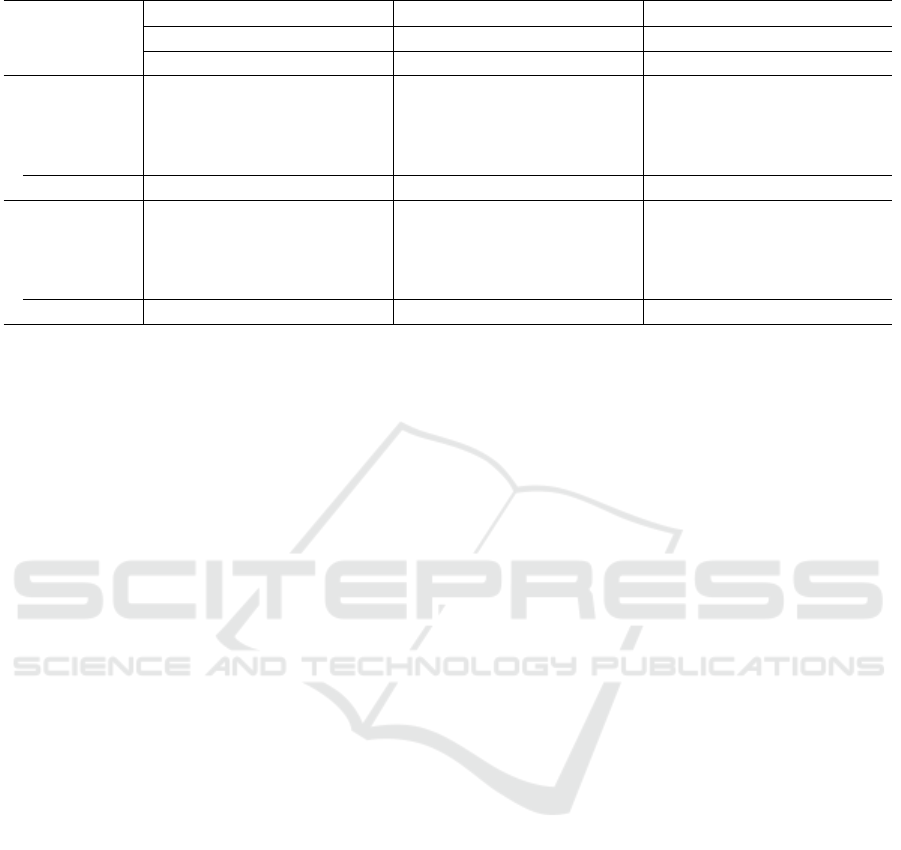
Table 3: Performance results on three public datasets. For each dataset, the best result is highlighted in boldface.
Chen dataset Ruengchaijatuporn dataset Raksasat dataset
TA UA RA TA UA RA TA UA RA
Acc. AUC Acc. AUC Acc. AUC Acc. AUC Acc. AUC Acc. AUC Acc. AUC Acc. AUC Acc. AUC
EfficientNet
DA train only 85 85 80 80 84 84 58 58 56 56 59 59 77 77 78 78 78 78
DA train + val. 95 95 90 90 80 80 58 58 58 58 60 60 80 80 77 77 79 79
DA val. only 85 85 85 85 85 85 62 62 60 60 57 57 76 76 77 77 77 77
DA all splits 90 90 91 91 90 90 62 62 60 60 64 64 78 78 76 76 78 78
No DA 80 Acc. 80 AUC 56 Acc. 56 AUC 77 Acc. 77 AUC
DenseNet
DA train only 90 90 89 89 89 89 53 53 59 59 50 50 71 71 68 68 67 67
DA train + val. 90 90 90 90 89 89 54 54 49 49 56 56 71 71 69 69 64 64
DA val. only 88 88 78 78 83 83 57 57 54 54 61 61 69 69 72 72 72 72
DA all splits 92 92 90 90 93 93 69 69 68 68 67 67 75 75 74 74 72 72
No DA 65 Acc. 65 AUC 55 Acc. 55 AUC 67 Acc. 67 AUC
3.4 Procedure
We split each dataset into three randomly disjoint sets:
70% training, 20% validation, and 10% testing. The
testing set is reserved as a held-out partition that is
used only after a model is trained since it simulates
unseen data. The splits are also stratified to ensure
that the HC and MCI images are evenly allocated to
the training/validation/testing sets.
In this work, we investigate five different DA con-
ditions for the training and evaluation of our models.
The baseline condition, No DA, involves no DA at all,
where the model is trained, validated, and tested on
the original, non-augmented data. The first augmen-
tation condition, DA train only, applies DA solely
to the training set, leaving the validation and test sets
unmodified. This allows the model to benefit from
augmented samples during training while preserving
the original, unaltered validation and test sets for un-
biased evaluation. The second condition, DA train
+ val., applies DA to both the training and validation
sets, enabling the model to generalize better by en-
countering augmented samples in both phases while
still maintaining a pristine test set. The third condi-
tion, DA val. only, applies augmentation solely to
the validation set, allowing the original training and
test sets to remain unaltered. Finally, in DA all splits,
DA is applied to all three partitions—training, valida-
tion, and test—offering the most challenging scenario
where the model is trained, validated, and evaluated
with real and augmented data. In each condition, DA
is applied by ensuring that the majority class has 10%
more instances than in the original dataset and match-
ing the number of instances in the minority class. In
this way, we address both class imbalance and data
scarcity issues during model training.
4 RESULTS
Table 3 compares the performance of various DA
strategies across two deep learning architectures
(EfficientNet and DenseNet) and three benchmark
datasets: Chen dataset, Ruengchaijatuporn dataset,
and Raksasat dataset. We evaluated the effects of TA,
UA, and RA under multiple augmentation regimes.
• Performance on Chen Dataset. EfficientNet’s
highest performance was achieved with the DA
train + val, reaching 95% accuracy and 95% AUC,
a significant improvement over the baseline (No
DA) of 80% accuracy and 80% AUC. Augment-
ing only the training set yielded an accuracy of
85%, demonstrating that augmenting the valida-
tion set can help mitigate overfitting and improve
generalization. DenseNet’s best performance was
observed with DA all splits, reaching 92% accu-
racy and 93% AUC.
• Performance on Ruengchaijatuporn Dataset.
EfficientNet’s largest improvement occurred with
TA, where accuracy improved from 56% (No DA)
to 62%. However, DenseNet outperformed Effi-
cientNet across all DA regimes, particularly un-
der DA all splits, where it reached 69% Accuracy
and AUC. UA also provided good results, with
DenseNet achieving 68% accuracy, demonstrat-
ing its robustness in handling this highly imbal-
anced dataset.
• Performance on Raksasat Dataset. Efficient-
Net’s best results were observed with the DA train
+ val, achieving 80% accuracy and AUC. When
RA was applied only to the training set, the ac-
curacy was 78% but its performance was incon-
sistent across other strategies. DenseNet achieved
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
604

the best performance under the DA all splits con-
dition with 75% accuracy and 75% AUC.
Overall, the results show that EfficientNet per-
forms well on datasets like Chen, achieving the high-
est accuracy and AUC, especially with the DA train +
val. While DenseNet performs better on more com-
plex datasets like Ruengchaijatuporn, consistently
achieving higher accuracy and AUC (69% accuracy,
69% AUC), EfficientNet outperforms DenseNet on
the Raksasat dataset, with its best performance in the
DA train + val. condition (80% accuracy, 79% AUC),
compared to DenseNet’s best performance of 75% ac-
curacy, 72% AUC under the DA all splits condition.
The improved generalization of the models, particu-
larly with TA and UA on Ruengchaijatuporn dataset,
highlights the potential for these techniques to be ap-
plied in real-world clinical environments.
5 DISCUSSION
Our results show that applying non-learnable data
augmentation techniques, particularly TA and UA,
significantly boosts the performance of DL models
for CDT image classification in cognitive dysfunc-
tion screening. These findings are evident across three
public datasets.
On the Chen dataset, EfficientNet demonstrated
superior performance, particularly when both the
training and validation splits were augmented, achiev-
ing an accuracy of 95% and an AUC of 95%. This
suggests that EfficientNet is highly effective in sim-
pler dataset structures, leveraging its architecture to
maximize the benefits of DA. Conversely, DenseNet
consistently outperforms EfficientNet in handling
more complex datasets such as Ruengchaijatuporn,
where it shows up to a 14% increase in accuracy
and a 14% improvement in AUC compared to Effi-
cientNet. This superior performance can be attributed
to DenseNet’s capacity to reuse features more ef-
fectively across layers, which enhances generaliza-
tion in complex clinical datasets characterized by lim-
ited data and inherent variability. However, on the
Raksasat dataset, the results slightly diverge. While
DenseNet achieved its best performance under the DA
all splits condition with 75% accuracy and 72% AUC,
EfficientNet slightly outperformed DenseNet under
the DA train + val. condition, achieving 80% accu-
racy and 80% AUC.
Our findings are consistent with prior work in
medical imaging, where augmentation strategies have
been shown to enhance model performance by diver-
sifying training data. Dutta et al. (Dutta et al., 2020)
reported similar performance improvements in radi-
ological classification tasks using data augmentation,
while Tufail et al. (Tufail et al., 2022) demonstrated
the role of augmentation in enhancing Alzheimer’s
disease detection. These results confirm the broad ap-
plicability of TA and UA beyond CDT screening, in-
dicating their potential utility across clinical domains
reliant on image-based diagnostics.
Moreover, the results of the Ruengchaijatuporn
dataset highlight the importance of selecting ap-
propriate augmentation strategies for imbalanced
datasets. TA led to an improvement in accuracy 12%,
demonstrating its ability to handle dataset imbalance
effectively. UA, while achieving robust performance
with a 68% accuracy, further demonstrates that sim-
pler augmentation strategies can be highly effective
in clinical applications where data are limited and
heavily skewed. This finding echoes prior research
by Shorten and Khoshgoftaar (Shorten and Khoshgof-
taar, 2019), who stressed the importance of augmen-
tation in handling class imbalances.
Although RandAugment provided some gains, es-
pecially in the Ruengchaijatuporn dataset (64% AUC
for EfficientNet), its improvements were less consis-
tent compared to TA and UA. This reinforces the prac-
tical benefits of non-learnable methods, which offer a
better balance between computational efficiency and
performance gains in clinical applications. Lim et
al. (Lim et al., 2019) demonstrated that simpler aug-
mentation methods, such as Fast AutoAugment, can
match or exceed the performance of more complex
learned strategies while requiring significantly fewer
computational resources. This aligns with our find-
ings, where non-learnable methods provided compa-
rable performance to RA, but with much lower com-
plexity and computational costs.
Another key takeaway from our results is the ef-
fectiveness of selective augmentation strategies. Ap-
plying augmentation to both training and valida-
tion sets (DA train + val.) consistently yielded the
best performance across all datasets for EfficientNet,
while DenseNet excelled with DA all splits in more
complex datasets. Conversely, augmenting only the
training set (DA train only) delivered strong results
on the Raksasat dataset for EfficientNet, with 80%
accuracy and AUC, underscoring the efficiency of
the targeted augmentation. These results suggest that
over-augmenting validation and test sets can intro-
duce noise, as observed in Ruengchaijatuporn, where
DA all splits resulted in only marginal improvements
(69% accuracy and AUC for DenseNet), consistent
with Chlap et al. (Chlap et al., 2021), who cautioned
against over-augmentation in medical imaging due to
potential overfitting and biased model evaluations.
Overall, this study presents strong evidence that
Efficient Automatic Data Augmentation of CDT Images to Support Cognitive Screening
605

non-learnable augmentation methods, such as TA and
UA, are not only computationally efficient but also
highly effective in improving model performance for
medical image classification tasks. By enhancing
model generalization across various datasets, these
techniques hold significant promise for real-time
healthcare applications where accurate and timely
decision-making is critical.
5.1 Limitations and Future Work
One limitation is that we chose AutoDA techniques
that are suitable for real-time (TA and UA) or near
real-time (RA) processing. There are many other ap-
proaches that are learnable and have achieved slightly
better performance on common benchmarks, such as
ImageNet (Table 1), but unfortunately, they are too
slow to be usable in practice. In addition, it re-
mains unclear whether the results achieved on Im-
ageNet would transfer to the medical domain. The
research literature suggests otherwise (Jonske et al.,
2023; Morid et al., 2021; Hosseinzadeh Taher et al.,
2021).
Another limitation of our work is that we have
considered only one type of drawing to support cog-
nitive dysfunction screening, albeit the most popular
one. Future work should go beyond CDTs to better
assess the generalizability of AutoDA methods. For
example, some drawings, like Pentagon Drawing Test
(PDT) images, allow other DA operations such as ver-
tical and horizontal flipping (Hosseini-Kivanani et al.,
2024a; Hosseini-Kivanani et al., 2023).
Furthermore, investigating the effectiveness of
AutoDA techniques across multiple domains can re-
veal further insights into their potential to improve
model performance in other computer vision applica-
tions. Future research could explore the integration of
non-learnable methods with semi-supervised learning
approaches to further improve performance, particu-
larly in scenarios where labeled data is scarce. Ex-
panding the application of these augmentation strate-
gies to other diagnostic fields, such as neuroimaging
and pathology, could unlock further potential and lead
to advances in clinical diagnostics.
6 CONCLUSION
Non-learnable AutoDA methods improve the perfor-
mance and generalization of DL models for cognitive
dysfunction screening using CDT images. Our results
indicate that DA strategies must be carefully tailored
to the input data and the task at hand, particularly in
the medical domain, where preserving the integrity of
diagnostic features is paramount. By addressing these
challenges, our work contributes to the advancement
of DL-based diagnostic tools in medical imaging.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
Research supported by the Horizon 2020 FET pro-
gram of the European Union through the ERA-NET
Cofund funding (grant CHIST-ERA-20-BCI-001) and
the European Innovation Council Pathfinder program
(SYMBIOTIK project, grant 101071147).
REFERENCES
Blair, E., Zahuranec, D., Langa, K. M., Forman, J., Reale,
B. K., Kollman, C., Giordani, B., and Levine, D. A.
(2022). Impact of patient mild cognitive impair-
ment on physician decision-making for treatment. J.
Alzheimer Dis., 78(4).
Chen, S., Stromer, D., Alabdalrahim, H. A., Schwab, S.,
Weih, M., and Maier, A. (2020). Automatic dementia
screening and scoring by applying deep learning on
clock-drawing tests. Scientific Reports, 10(1).
Chlap, P., Min, H., Vandenberg, N., Dowling, J., Holloway,
L., and Haworth, A. (2021). A review of medical im-
age data augmentation techniques for deep learning
applications. J. Med. Imaging Radiat. Oncol., 65.
Cubuk, E. D., Zoph, B., Man
´
e, D., Vasudevan, V., and Le,
Q. V. (2019). Autoaugment: Learning augmentation
strategies from data. In Proc. CVPR.
Cubuk, E. D., Zoph, B., Shlens, J., and Le, Q. (2020).
Randaugment: Practical automated data augmentation
with a reduced search space. In Proc. NeurIPS.
Devries, T. and Taylor, G. W. (2017). Improved regular-
ization of convolutional neural networks with cutout.
CoRR. arXiv:1708.04552.
Dutta, S., Prakash, P., and Matthews, C. (2020). Impact
of data augmentation techniques on a deep learning
based medical imaging task. In Proc. of SPIE Vol.
Frid-Adar, M., Klang, E., Amitai, M., Goldberger, J., and
Greenspan, H. (2018). Gan-based synthetic medical
image augmentation for increased cnn performance in
liver lesion classification. Neurocomputing, 321.
Hataya, R., Zdenek, J., Yoshizoe, K., and Nakayama, H.
(2020). Faster autoaugment: Learning augmentation
strategies using backpropagation. In Proc. ECCV.
Ho, D., Liang, E., Stoica, I., Abbeel, P., and Chen, X.
(2019). Population based augmentation: Efficient
learning of augmentation policy schedules. CoRR.
arXiv:1905.05393.
Hosseini-Kivanani, N., Salobrar-Garcia, E., Elvira-
Hurtado, L., Lopez-Cuenca, I., de Hoz, R., Ramirez,
J. M., Gil, P., Salas-Carrillo, M., Schommer, C., and
Leiva, L. A. (2024a). Ink of insight: Data augmen-
tation for dementia screening through handwriting
analysis. In Proc. ICMHI.
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
606

Hosseini-Kivanani, N., Salobrar-Garc
´
ıa, E., Elvira-
Hurtado, L., Salas, M., Schommer, C., and Leiva,
L. A. (2024b). Predicting alzheimer’s disease and
mild cognitive impairment with off-line and on-line
house drawing tests. In Proc. e-Science.
Hosseini-Kivanani, N., Salobrar-Grac
´
ıa, E., Elvira-
Hurtado, L., L
´
opez-Cuenca, I., de Hoz, R., Ram
´
ırez,
J. M., Gil, P., Salas, M., Schommer, C., and Leiva,
L. A. (2023). Better Together: Combining Different
Handwriting Input Sources Improves Dementia
Screening. In Proc. e-Science.
Hosseinzadeh Taher, M. R., Haghighi, F., Feng, R., Got-
way, M. B., and Liang, J. (2021). A systematic bench-
marking analysis of transfer learning for medical im-
age analysis. In Proc. DART and FAIR Workshops.
Hou, C., Zhang, J., and Zhou, T. (2023). When to learn
what: Model-adaptive data augmentation curriculum.
CoRR. arXiv:2309.04747.
Huang, G., Liu, Z., van der Maaten, L., and Weinberger,
K. Q. (2017). Densely Connected Convolutional Net-
works. In Proc. CVPR.
Jonske, F., Kim, M., Nasca, E., Evers, J., Haubold, J.,
Hosch, R., Nensa, F., Kamp, M., Seibold, C., Egger,
J., and Kleesiek, J. (2023). Why does my medical
ai look at pictures of birds? exploring the efficacy of
transfer learning across domain boundaries. ArXiv,
abs/2306.17555.
Kebaili, A., Lapuyade-Lahorgue, J., and Ruan, S. (2023).
Deep learning approaches for data augmentation in
medical imaging: A review. J. Imaging, 9.
Ko, B. and Ok, J. (2021). Time matters in using data aug-
mentation for vision-based deep reinforcement learn-
ing. CoRR. arXiv:2102.08581.
Kobayashi, M., Yamada, Y., Shinkawa, K., Nemoto, M.,
Nemoto, K., and Arai, T. (2022). Automated early
detection of alzheimer’s disease by capturing impair-
ments in multiple cognitive domains with multiple
drawing tasks. J. Alzheimer Dis., 88.
Lim, S., Kim, I., Kim, T., Kim, C., and Kim, S. (2019). Fast
autoaugment. In Proc. NeurIPS.
LingChen, T. C., Khonsari, A., Lashkari, A., Nazari, M. R.,
Sambee, J. S., and Nascimento, M. A. (2020). Unifor-
maugment: A search-free probabilistic data augmen-
tation approach. CoRR. arXiv:2003.14348.
Liu, Z., Lv, Q., Li, Y., Yang, Z., and Shen, L. (2023).
Medaugment: Universal automatic data augmenta-
tion plug-in for medical image analysis. CoRR.
arXiv:2306.17466.
Morid, M. A., Borjali, A., and Fiol, G. D. (2021). A scoping
review of transfer learning research on medical image
analysis using imagenet. Comput. Biol. Med.
Muller, S. G. and Hutter, F. (2021). Trivialaugment:
Tuning-free yet state-of-the-art data augmentation. In
Proc. ICCV.
Nalepa, J., Marcinkiewicz, M., and Kawulok, M. (2019).
Data augmentation for brain-tumor segmentation: A
review. Front. Comput. Neurosci., 13.
Nasreddine, Z. S., Phillips, N. A., B
´
edirian, V., Charbon-
neau, S., Whitehead, V., Collin, I., Cummings, J. L.,
and Chertkow, H. (2019). The montreal cognitive as-
sessment, moca: A brief screening tool for mild cog-
nitive impairment. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc., 11(1).
Ogawa, R., Kido, T., and Mochizuki, T. (2019). Effect of
augmented datasets on deep convolutional neural net-
works applied to chest radiographs. Clin. Radiol.
Raksasat, R., Teerapittayanon, S., Itthipuripat, S., Pradit-
pornsilpa, K., Petchlorlian, A., Chotibut, T., Chunha-
ras, C., and Chatnuntawech, I. (2023). Attentive pair-
wise interaction network for ai-assisted clock drawing
test assessment of early visuospatial deficits. Scientific
Reports, 13(1).
Ruengchaijatuporn, N., Chatnuntawech, I., Teerapit-
tayanon, S., Sriswasdi, S., Itthipuripat, S., Hemrun-
grojn, S., Bunyabukkana, P., Petchlorlian, A., Chu-
namchai, S., Chotibut, T., and Chunharas, C. (2022).
An explainable self-attention deep neural network for
detecting mild cognitive impairment using multi-input
digital drawing tasks. Alzheimers Res. Ther., 78(14).
Shorten, C. and Khoshgoftaar, T. M. (2019). A survey on
image data augmentation for deep learning. J. Big
Data, 6.
Shulman, K. I., Pushkar Gold, D., Cohen, C. A., and Zuc-
chero, C. A. (1993). Clock-drawing and dementia in
the community: a longitudinal study. Int. J. Geriatr.
Psychiatry, 8(6).
Spenciere, B., Alves, H., and Charchat-Fichman, H. (2017).
Scoring systems for the clock drawing test: A histori-
cal review. Dement. Neuropsychol., 11(1).
Tan, M. and Le, Q. (2019). EfficientNet: Rethinking Model
Scaling for Convolutional Neural Networks. In Tan,
Mingxing and Le, Quoc.
Tian, K., Lin, C., Sun, M., Zhou, L., Yan, J., and
Ouyang, W. (2020). Improving auto-augment
via augmentation-wise weight sharing. CoRR.
arXiv:2009.14737.
Tufail, A. B., Ullah, K., Khan, R. A., Shakir, M., Khan,
M. A., Ullah, I., Ma, Y.-K., and Ali, M. S. (2022). On
improved 3d-cnn-based binary and multiclass clas-
sification of alzheimer’s disease using neuroimag-
ing modalities and data augmentation methods. J.
Healthc. Eng., 2022.
Yun, S., Han, D., Chun, S., Oh, S. J., Yoo, Y., and Choe,
J. (2019). Cutmix: Regularization strategy to train
strong classifiers with localizable features. In Pro-
ceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference
on computer vision.
Zhang, C., Li, X., Zhang, Z., Cui, J., and Yang, B.
(2022). Bo-aug: learning data augmentation policies
via bayesian optimization. Appl. Intell., 53.
Zhang, H., Ciss
´
e, M., Dauphin, Y., and Lopez-Paz, D.
(2017). mixup: Beyond empirical risk minimization.
CoRR. arXiv:1710.09412.
Zoph, B. and Le, Q. V. (2017). Neural architec-
ture search with reinforcement learning. CoRR.
arXiv:1611.01578.
Efficient Automatic Data Augmentation of CDT Images to Support Cognitive Screening
607
