
Disease Estimation Using Gait Videos by Separating Individual Features
Based on Disentangled Representation Learning
Shiori Furukawa
a
and Noriko Takemura
b
Kyushu Institute of Technology, Fukuoka, Japan
Keywords:
Gait, Disease-Estimation, Image-Processing.
Abstract:
With the aging of society, the number of patients with gait disturbance is increasing. Lumbar spinal canal
stenosis (LCS) and cervical spondylotic myelopathy (CSM) are representative diseases that cause gait dis-
turbance. However, diagnosing these diseases takes a long time because of the wide variety of medical de-
partments and lack of screening tests. In this study, we propose a method to recognize LCS and CSM using
patients’ walking videos. However, the gait images of patients contain not only disease features but also indi-
vidual features, such as body shape and hairstyle. Such individual features may reduce the accuracy of disease
estimation. Therefore, we aim to achieve highly accurate disease estimation by separating and removing in-
dividual features from disease features using a deep learning model based on a disentangled representation
learning approach. In evaluation experiments, we confirmed the usefulness of the proposed method by verify-
ing the accuracy of different model structures and different diagnostic tasks to be estimated.
1 INTRODUCTION
Gait disturbance is one of the most common disor-
ders in an aging society. Gait disturbance not only
restricts the patient’s activities but also has psycho-
logical effects, such as memory loss and decreased
motivation caused by decreased walking time. From
a social point of view, it is also a problem that it re-
quires much effort to care for patients with gait dis-
turbance.
Typical diseases with gait disturbance include
lumbar spinal canal stenosis (LCS), cervical spondy-
lotic myelopathy (CSM), Parkinson’s disease, periph-
eral arterial disease, and cerebrovascular disease. Be-
cause of the wide variety of departments specializ-
ing in these diseases and the lack of simple screen-
ing tests, such as biomarkers, it can take considerable
time to receive a correct diagnosis; 43% of patients
with cervical spondylosis are initially diagnosed with
other diseases and patients with gait disorders visit
5.2 physicians on average before receiving an appro-
priate diagnosis (Wu et al., 2013). In this study, we
aim to automatically estimate these diseases based on
a person’s gait characteristics.
Several studies have been conducted on gait anal-
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0008-4614-6722
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1977-4690
ysis for diseases with gait disorders (Abdulhay et al.,
2018; Tahir and Manap, 2012; Kidzi
´
nski et al., 2020;
Nguyen et al., 2016). Tahir et al. (Tahir and Manap,
2012) used a motion capture system and floor reac-
tion force meter to extract features such as the joint
angle, stride length, and floor reaction force during
walking, and used a machine learning model to iden-
tify patients with Parkinson’s disease. However, this
method uses expensive sensors that require special-
ized knowledge, which makes it unsuitable for practi-
cal diagnosis and screening tests.
By contrast, Kidzi
´
nski (Kidzi
´
nski et al., 2020) es-
timated gait speed, cadence, the knee joint angle, and
other parameters using gait videos captured by a sin-
gle camera. Although this method is highly practi-
cal because gait features can be estimated simply by
capturing a person walking using a camera, it esti-
mates the above features based on a rough skeletal
model. It lacks information closely related to dis-
eases, such as a subtle bending of the neck and hips.
Furthermore, estimation errors and false positives for
the joint points may lead to a decrease in the accu-
racy of disease estimation. Therefore, in this study,
we adopt an appearance-based method with silhouette
features instead of a model-based method with skele-
tal features to estimate diseases from gait videos.
Appearance-based methods directly estimate a
disease from images; hence, little information about
Furukawa, S. and Takemura, N.
Disease Estimation Using Gait Videos by Separating Individual Features Based on Disentangled Representation Learning.
DOI: 10.5220/0013168200003912
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 20th International Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications (VISIGRAPP 2025) - Volume 2: VISAPP, pages
919-925
ISBN: 978-989-758-728-3; ISSN: 2184-4321
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
919

the disease is missing. However, simultaneously,
personal characteristics, such as hairstyle and body
shape, are also included in the images, and these
may affect the performance of disease estimation. In
this study, we address this problem using disentan-
gled representation learning (DRL), which can sep-
arate features. DRL is often used to generate face
images in which only facial expressions and poses
are changed (Tran et al., 2017; Higgins et al., 2016).
In this study, we apply the DRL framework used as
an image generator as a discriminator. As a DRL
model, the variational autoencoder (VAE) (Kingma
and Welling, 2013) is often used. However, a VAE-
based model includes a decoder for reconstructing
images, which is not necessary for the classification
tasks (Shiori Furukawa, 2024). In this study, we aim
to improve accuracy by modifying the network to a
convolutional neural network (CNN), which is used
as a feature extractor (Donahue et al., 2014) and spe-
cialized for classification tasks, and comparing it to
VAE. Using 263 people’s walking videos, LCS, CSM,
and healthy discrimination were analyzed to confirm
the usefulness of the proposed method.
2 PROPOSED METHOD
In this study, we estimate diseases using a mean sil-
houette image (gait energy image, GEI (Han and
Bhanu, 2005)) generated from walking videos. We
aim to improve accuracy using a VAE-based DRL
model and a CNN-based DRL model to separate dis-
ease features and individual features. The details of
the proposed method are described below.
2.1 Gait Features
Silhouettes are extracted from walking videos and an
average silhouette image normalized by height: GEI
(128 × 88 pixels) is generated. A graph transition
(Gong et al., 2019) is used for the person region seg-
mentation method. Because patients with gait disor-
ders have unstable gait cycles, the number of frames
used to generate the GEI was experimentally set to 40
frames.
GEI is a practical gait feature used in various stud-
ies on gait analysis and recognition because it repre-
sents static features, such as neck and back flexion,
and dynamic features, such as limb swing, in a sin-
gle image (Sakata et al., 2019; Takemura et al., 2018;
Liao et al., 2021). By contrast, as shown in Figure 1, it
also includes many individual features, such as body
shape and hairstyle; hence, it is necessary to consider
the effects of such individual differences when ana-
Figure 1: These GEIs all belong to different individuals.
GEIs include many individual features, such as body shape
and hairstyle; hence, it is necessary to consider the effects
of such individual differences when analyzing gait.
lyzing gait.
2.2 Disease Estimation Method Using a
VAE
2.2.1 DRL Model
In this study, we perform feature separation in the la-
tent space based on Guided-VAE (Ding et al., 2020).
The VAE-based DRL model consists of three net-
works: a VAE model, an excitation classifier, and an
inhibition classifier, as shown in Figure 2. The de-
tails of each network structure are the same as those
in (Ding et al., 2020).
VAE Model. The network reconstructs the same im-
age as the input image after compressing the input
image once. The loss function L
VAE
(Equation
3) is the sum of the reconstruction error (mean
squared error, Equation 1) of the input and out-
put images, and the Kullback-Leibler divergence
(KLD, Equation 2) measures the difference be-
tween two probability distributions. In the context
of Variational Autoencoders (VAE), we compare
the latent variable distribution as Q(z | x) with the
prior distribution as P(z), which is typically as-
sumed to be a standard normal distribution.
L
recon
=
1
N
N
∑
i=1
∥x
i
− ˆx
i
∥
2
(1)
L
KLD(P|Q)
=
∑
z
Q(z|x)log
Q(z|x)
P(z)
(2)
L
VAE
= L
recon
+ L
KLD
(3)
Excitation Classifier. The classifier is used when
learning so that a latent variable obtains specific
feature information, where the loss function L
exc
is Binary Cross-Entropy Loss (BCE) or Cross-
Entropy Loss (CE).
Inhibition Classifier. The classifier is used when
learning, so that the remaining latent variables do
not have specific feature information, and the loss
function L
inh
is BCE or CE, as is L
exc
.
VISAPP 2025 - 20th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
920
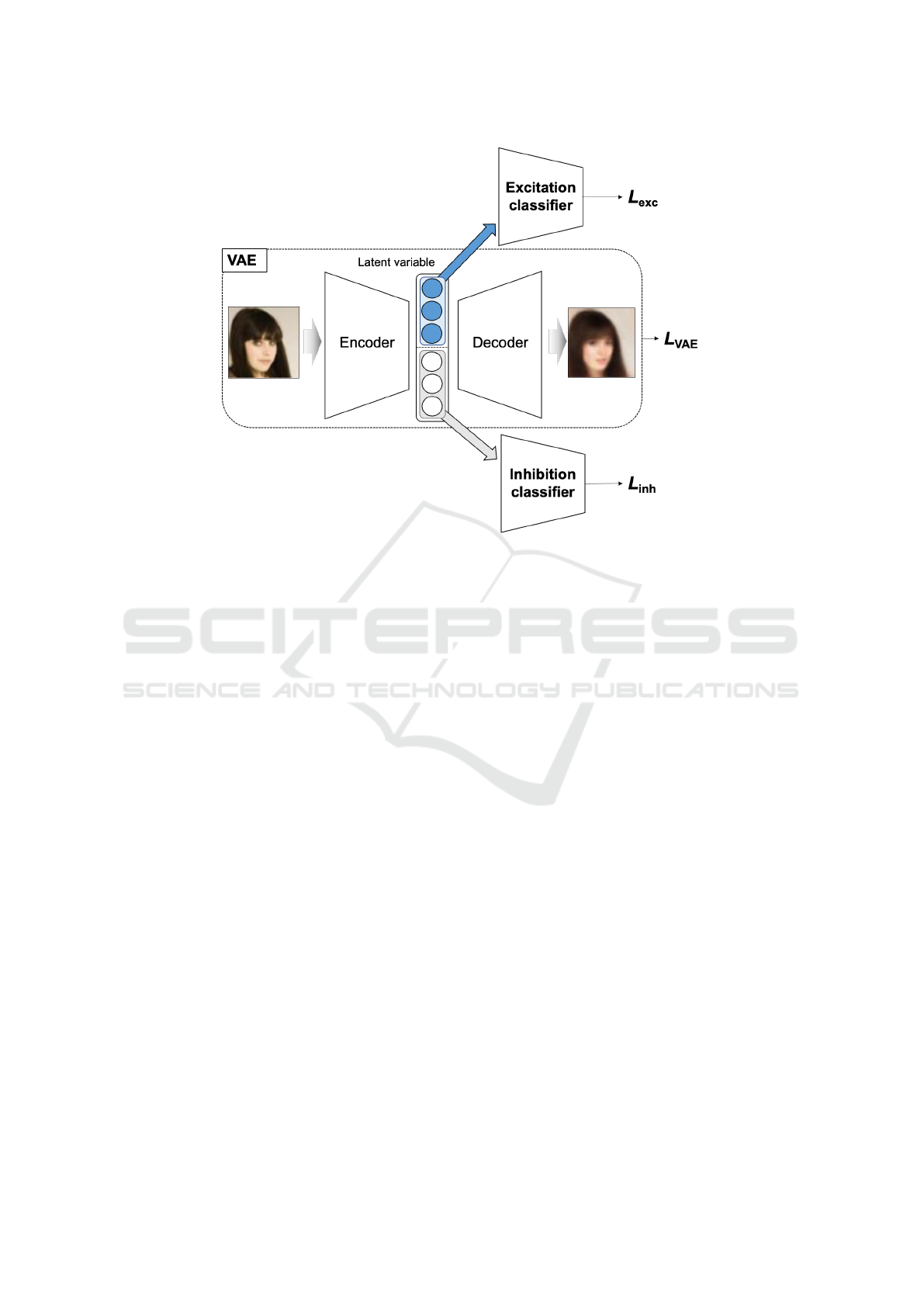
Figure 2: In this study, we perform feature separation in the latent space based on Guided-VAE (Ding et al., 2020).The VAE-
based DRL model consists of three networks: a VAE model, an excitation classifier, and an inhibition classifier. The details
of each network structure in our proposed method are the same this DRL model.
The learning procedure for this VAE-based DRL
model is shown below. Repeating this learning
procedure can separate latent variables with and
without specific feature information. In the proposed
method, the procedures are applied to both disease
features and individual features.
[Learning Procedure of VAE-Based DRL Model]
(1) The VAE and excitation classifier parameters are
trained with the loss function as L
VAE
+ αL
exc
,
where α is the weight of the sum of L
VAE
(Equa-
tion 3) and L
exc
. These are learned so that the ex-
citation classifier can classify feature labels cor-
rectly, the VAE can reconstruct the correct image,
and the latent variables contain features that the
excitation classifier can classify correctly.
(2) An inhibition classifier is trained with the loss
function as L
inh
. The inhibition classifier is
trained to classify feature labels correctly.
(3) The feature label (one-hot vector) is set to uniform
values (label value = 1/#classes) and the VAE is
trained with the loss function as L
inh
. Latent vari-
ables are trained so they do not have specific fea-
ture information.
Disease estimation is performed considering indi-
vidual features using the VAE-based DRL model indi-
cated above. The framework of the method is shown
in Figure 3. The input GEI for model training is la-
beled with the presence or absence of a disease and
an ID. In the proposed method, the above procedure
is repeated for both diseases and individuals. When
learning individual features, the latent variables used
as inputs for the excitation classifier and the inhibition
classifier are reversed compared to when learning dis-
ease features. Eventually, the excitation classifier for
disease features is used to estimate diseases. In this
way, disease estimation that accounts for individual
differences can be performed using latent variables
that capture disease features but exclude individual
features.
2.3 Disease Estimation Method Using a
CNN
Latent variables in the VAE include features that can
reconstruct the image, i.e., all features related to the
image. Therefore, it is necessary to separate the la-
tent variables into parts that have specific features
and parts that do not. By contrast, latent variables
in the CNN extract only features related to the spe-
cific feature; hence, there is no need to separate la-
tent variables unrelated to the specific feature. The
CNN model does not have the task of reconstructing
the image, which allows it to focus more on the clas-
sification task. Therefore, the learning procedure of
the CNN excludes some steps from the VAE learning
Disease Estimation Using Gait Videos by Separating Individual Features Based on Disentangled Representation Learning
921
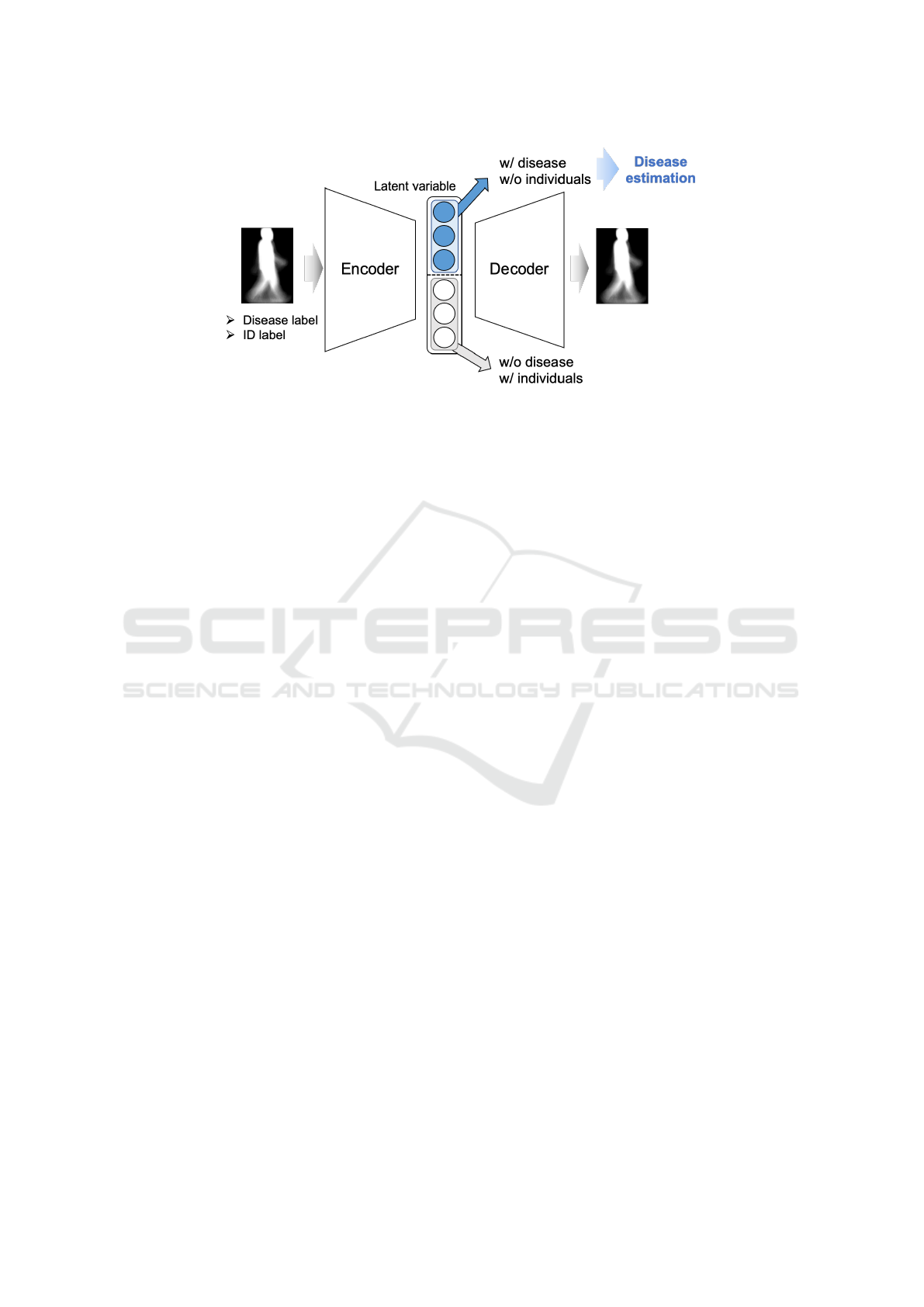
Figure 3: This is the framework of the proposed method utilizing a VAE. By applying [Learning Procedure of VAE-based
DRL model] with disease features, the latent variables are divided into those representing disease (w/ disease) and those not
representing disease (w/o disease). Similarly, by applying [Learning Procedure of VAE-based DRL model] with individual
features, the latent variables are divided into those excluding individual-specific features (w/o individuals) and those including
individual-specific features (w/ individuals).
procedure. The framework of the method is shown
in Figure 4. The CNN network shares the same ar-
chitecture as the encoder in the VAE and the loss
function L
KLD
represents the Kullback-Leibler diver-
gence. Unlike the VAE, the CNN does perform im-
age reconstruction; thus, reconstruction error is not
included. However, L
KLD
, which encourages dimen-
sional independence in the latent variable space, is
utilized.
The learning procedure for this CNN-based DRL
model is described below. Step (1) is applied to
disease features to enable disease identification,
while step (2) and step (3) are applied to individ-
ual features to ensure individuals cannot be identified.
[Learning Procedure of CNN-Based DRL Model]
(1) The CNN and excitation classifier parameters are
trained with the loss function as L
KLD
+ βL
exc
,
where β is the weight of the sum of L
KLD
(Equa-
tion 2) and L
exc
. These are learned so that the ex-
citation classifier can classify disease labels cor-
rectly, i.e., the latent variables contain features
that diseases can be classified correctly.
(2) An inhibition classifier is trained with the loss
function as L
inh
. The inhibition classifier is
trained to classify ID labels correctly.
(3) The feature label (one-hot vector) is set to uni-
form values (label value = 1/#ID) and the CNN is
trained with the loss function as L
inh
. Latent vari-
ables are trained so they do not have individual
features.
3 EVALUATION
For performance evaluation, we collected gait videos
of patients with gait disorders and normal subjects.
3.1 Dataset
A standard monocular RGB camera captured 4 me-
ters of the distance the people walked of LCS patients,
CSM patients, and healthy subjects (1288 × 964 pix-
els, 30 fps). Figure 5 shows an example of the cap-
tured gait videos. A total of 139 LCS patients, 59
CSM patients (19 of whom had both LCS and CSM),
and 84 healthy subjects had gait videos collected one
to four times per person, for a total of 896 times.
A physician’s diagnosis disease labels and ID labels
were assigned to each gait video. GEIs were gener-
ated from 40 frames of image sequences by stagger-
ing the images by one frame. The number of subjects
and the number of GEIs are shown in Table 1. Note
that the GEIs used for model training had an upper
limit of 200 images per video and were undersampled
to eliminate data bias.
3.2 Comparison Methods
To demonstrate the usefulness of the proposed dis-
ease estimation method that considers individual dif-
ferences, we evaluated its performance using the fol-
lowing comparative methods.
VISAPP 2025 - 20th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
922

Figure 4: This is the framework of the proposed method utilizing a CNN. In the [Learning Procedure of CNN-based DRL
model], step (1) is applied to disease features to enable disease identification (w/ disease), while step (2) and step (3) are
applied to individual features to ensure individuals cannot be identified (w/o individuals).
Figure 5: This is an example of a gait video. A stan-
dard monocular RGB camera captured 4 meters of the dis-
tance the people walked of LCS patients, CSM patients, and
healthy subjects (1288 × 964 pixels, 30 fps).
3.2.1 VAE-Based Model
Comparison Method 1 (Comp1). Only the
[Learning Procedure of VAE-Based DRL
Model] with disease features is performed;
those of individual features is not performed.
Comparison Method 2 (Comp2). Only the
[Learning Procedure of VAE-Based DRL
Model] step (1) with disease features is per-
formed. All latent variables were trained to
identify the disease using a disease excitation
classifier and VAE. However, to keep the la-
tent variable dimension used for disease esti-
mation the same as that for the other methods,
the number of latent variables is half that of
the other methods.
3.2.2 CNN-Based Model
Comparison Method 3 (Comp3). Only the
[Learning Procedure of CNN-Based DRL
Model] step (1) with disease features is per-
formed. All latent variables are trained to
identify the disease using a disease excitation
classifier and CNN.
Table 1: The number of subjects and the number of GEIs
are shown in the below table. Note that the GEIs used for
model training had an upper limit of 200 images per video
and were undersampled to eliminate data bias.
#Subjects #Movies #GEIs
LCS 139 504 48,456
CSM 59 192 26,970
healthy 84 269 28,609
3.3 Evaluation Method
Using gait data from LCS patients, CSM patients, and
healthy subjects, we generated the following four dis-
ease estimators and evaluated the performance of the
proposed and comparison methods, respectively.
LCS Estimator: LCS vs. {CSM, healthy}
CSM Estimator: CSM vs.{LCS, healthy}
Disease Estimator: {LCS, CSM} vs. healthy
Multi Class Estimator: LCS vs. CSM vs. healthy
For the performance evaluation, we divided
videos into ten groups and conducted 10-fold cross-
validation: one group was the test data, another was
the validation data, and the remaining eight were the
training data. The average F1 score of the 10 groups
was used for the evaluation.
The mini-batch size for training was set to 512
and the model’s performance was evaluated on the
test data using up to 100 epochs, selecting the epoch
where the F1 score of the validation data was max-
imized. Hyperparameters such as L
VAE
and L
exc
weights α, L
KLD
and L
exc
weights β, the initial learn-
ing rate, and weight decay for each network were de-
termined using the validation data at the first cross-
validation, and the same values were used for the
second and subsequent cross-validations. Adam was
used for model optimization(Kingma and Ba, 2014).
Disease Estimation Using Gait Videos by Separating Individual Features Based on Disentangled Representation Learning
923
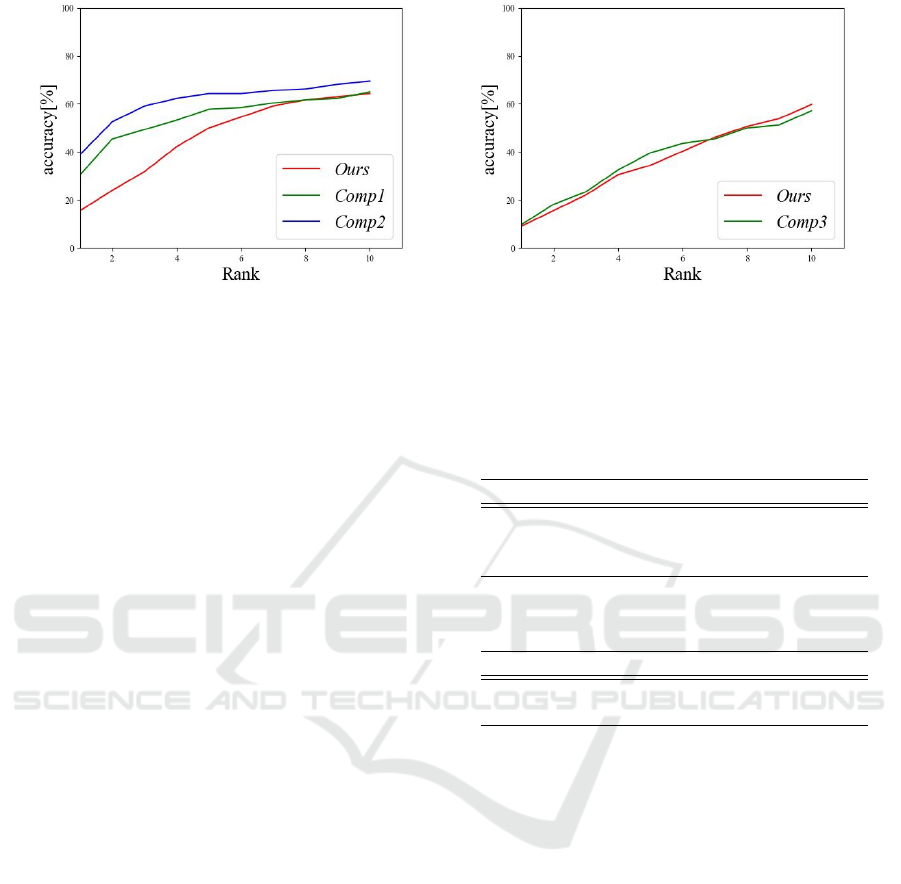
(a) VAE-based model (b) CNN-based model
Figure 6: Rank-N accuracy for individual identification.
3.4 Result
The results of the evaluation experiment are shown in
Table 2. For all estimators except Dis
est
of the CNN,
the proposed method was more accurate than the com-
parison methods. Therefore, we demonstrated the ef-
fectiveness of the proposed method for separating in-
dividual features in the latent space.
By contrast, Comp3 with the CNN obtained the
highest accuracy for Dis
est
. As their high average ac-
curacies indicate, the task were easier than those for
other estimators, and even a simple model achieved
sufficiently high accuracy. Therefore, it seems that the
disadvantages of complex models that make learning
more difficult outweigh the advantages of considering
individual differences in the proposed method.
The results of the VAE and CNN were compared.
The proposed method with the CNN was more ac-
curate than the proposed method with the VAE ex-
cept for Dis
est
. We demonstrated the effectiveness of
a CNN specialized for classification tasks.
Individual identification was also analyzed to ver-
ify the extent to which individual features were re-
moved from the latent variable used for disease esti-
mation. Figure 6 shows the rank-N accuracy of indi-
vidual identification. The intermediate layer output
of the individual identification classifier was a fea-
ture vector and the feature vectors of all subjects in
the dataset were obtained in advance as registration
data. The L2 norm computed by the feature vector
for a given input and the feature vector of each reg-
istered data were sorted in decreasing order and the
proportion of the same person in the top N subjects
was calculated(Phillips et al., 2000). The smaller the
proportion, the less identifiable the individual, that is,
the more separated the individual features. As Figure
6 shows, the proposed method separated individual
features better than the comparison methods.
Table 2: Average F1 score for each estimator that LCS esti-
mator (LCS
est
), CSM estimator (CSM
est
), Disease estima-
tor (Dis
est
), and Multi class estimator (Mul
est
). Bold indi-
cates the best value.
(a) VAE-based model
LCS
est
CSM
est
Dis
est
Mul
est
Ours 0.924 0.844 0.979 0.760
Comp1 0.916 0.843 0.971 0.744
Comp2 0.915 0.842 0.977 0.755
(b) CNN-based model
LCS
est
CSM
est
Dis
est
Mul
est
Ours 0.925 0.859 0.978 0.772
Comp3 0.914 0.857 0.979 0.765
4 CONCLUSION
In this study, we proposed a method for disease esti-
mation from gait videos. We aimed to improve dis-
ease estimation accuracy by separating disease and
individual features in the latent space of a VAE and
a CNN using the DRL model.
Almost all of the proposed methods were more ac-
curate than the comparison methods, which demon-
strates the effectiveness of the methods for separating
disease and individual features. Additionally, almost
all the proposed methods obtained better CNN accu-
racy than VAE, which indicates the effectiveness of
the specialized model for the classification tasks pro-
posed in this study.
We plan to expand the scope to include diseases
other than LCS and CSM, such as Parkinson’s. We
only used the side video of walking in the experi-
ments, but we aim to further improve accuracy by also
using features from the frontal video. Additionally,
VISAPP 2025 - 20th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
924

we aim to further improve accuracy using MRI and
CT images in addition to gait images. We will verify
the usefulness of this method for separating individ-
ual features for other tasks, such as facial expression
recognition. In this study, we conducted experiments
using VAE and CNN to verify the effectiveness of our
feature separation method. Furthermore, since our
feature separation method can be applied to various
backbones, we plan to apply it to more tasks using
existing networks.
REFERENCES
Abdulhay, E., Arunkumar, N., Narasimhan, K., Vellaiap-
pan, E., and Venkatraman, V. (2018). Gait and tremor
investigation using machine learning techniques for
the diagnosis of parkinson disease. Future Genera-
tion Computer Systems, 83:366–373.
Ding, Z., Xu, Y., Xu, W., Parmar, G., Yang, Y., Welling,
M., and Tu, Z. (2020). Guided variational autoen-
coder for disentanglement learning. In Proceedings
of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and
Pattern Recognition, pages 7920–7929.
Donahue, J., Jia, Y., Vinyals, O., Hoffman, J., Zhang, N.,
Tzeng, E., and Darrell, T. (2014). Decaf: A deep con-
volutional activation feature for generic visual recog-
nition. In International conference on machine learn-
ing, pages 647–655. PMLR.
Gong, K., Gao, Y., Liang, X., Shen, X., Wang, M., and
Lin, L. (2019). Graphonomy: Universal human pars-
ing via graph transfer learning. In Proceedings of the
IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pat-
tern Recognition, pages 7450–7459.
Han, J. and Bhanu, B. (2005). Individual recognition us-
ing gait energy image. IEEE transactions on pattern
analysis and machine intelligence, 28(2):316–322.
Higgins, I., Matthey, L., Pal, A., Burgess, C., Glorot, X.,
Botvinick, M., Mohamed, S., and Lerchner, A. (2016).
beta-vae: Learning basic visual concepts with a con-
strained variational framework. In International con-
ference on learning representations.
Kidzi
´
nski, Ł., Yang, B., Hicks, J. L., Rajagopal, A., Delp,
S. L., and Schwartz, M. H. (2020). Deep neural
networks enable quantitative movement analysis us-
ing single-camera videos. Nature communications,
11(1):4054.
Kingma, D. P. and Ba, J. (2014). Adam: A
method for stochastic optimization. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1412.6980.
Kingma, D. P. and Welling, M. (2013). Auto-encoding vari-
ational bayes. arXiv preprint arXiv:1312.6114.
Liao, R., Moriwaki, K., Makihara, Y., Muramatsu, D.,
Takemura, N., and Yagi, Y. (2021). Health indi-
cator estimation by video-based gait analysis. IE-
ICE TRANSACTIONS on Information and Systems,
104(10):1678–1690.
Nguyen, T.-N., Huynh, H.-H., and Meunier, J. (2016).
Skeleton-based abnormal gait detection. Sensors,
16(11):1792.
Phillips, P. J., Moon, H., Rizvi, S. A., and Rauss, P. J.
(2000). The feret evaluation methodology for face-
recognition algorithms. IEEE Transactions on pat-
tern analysis and machine intelligence, 22(10):1090–
1104.
Sakata, A., Takemura, N., and Yagi, Y. (2019). Gait-based
age estimation using multi-stage convolutional neural
network. IPSJ Transactions on Computer Vision and
Applications, 11:1–10.
Shiori Furukawa, N. T. (2024). Disease estimation based
on gait images by separating individual features us-
ing variational autoencoder. In AROB-ISBC-SWARM
2024.
Tahir, N. M. and Manap, H. H. (2012). Parkinson dis-
ease gait classification based on machine learning ap-
proach. Journal of Applied Sciences(Faisalabad),
12(2):180–185.
Takemura, N., Makihara, Y., Muramatsu, D., Echigo, T.,
and Yagi, Y. (2018). Multi-view large population gait
dataset and its performance evaluation for cross-view
gait recognition. IPSJ transactions on Computer Vi-
sion and Applications, 10:1–14.
Tran, L., Yin, X., and Liu, X. (2017). Disentangled repre-
sentation learning gan for pose-invariant face recogni-
tion. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Com-
puter Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR).
Wu, J.-C., Ko, C.-C., Yen, Y.-S., Huang, W.-C., Chen, Y.-
C., Liu, L., Tu, T.-H., Lo, S.-S., and Cheng, H. (2013).
Epidemiology of cervical spondylotic myelopathy and
its risk of causing spinal cord injury: a national cohort
study. Neurosurgical focus, 35(1):E10.
Disease Estimation Using Gait Videos by Separating Individual Features Based on Disentangled Representation Learning
925
