
A Stochastic Location-Routing Problem for the Optimal Placement of
Lockers
Guido Barbieri
1
, Annarita De Maio
2 a
, Roberto Musmanno
1 b
and Sara Stoia
2 c
1
Department of Mechanical, Energy and Management Engineering, University of Calabria, Italy
2
Department of Economics, Statistics and Finance ”Giovanni Anania”, University of Calabria, Italy
Keywords:
Stochastic Location-Routing Problem, Parcel Lockers, Last-Mile Delivery, Vehicle Routing, Uncertainty,
Two-Stage Stochastic Programming.
Abstract:
This paper presents a Stochastic Location-Routing Problem aimed at optimizing the placement of parcel lock-
ers in last-mile delivery. The model integrates locker location decisions with vehicle routing, taking into
account customer preferences for home delivery or locker collection. It considers multiple scenarios of ser-
vice requests to address the uncertainty in customer behavior. The problem is formulated as a two-stage
stochastic program, where the first stage determines which lockers to activate, and the second stage optimizes
vehicle routes based on the service preferences for each scenario. Computational experiments are based on a
test problem used to validate the model’s effectiveness. Proposed future extensions include integrating multi-
period planning, introducing capacity constraints for both vehicles and lockers, enabling dynamic activation of
lockers, and optimizing the algorithm for multi-core architectures to enhance computational efficiency. These
advancements aim to enhance the model’s applicability and scalability in tackling complex logistics challenges
under uncertainty.
1 INTRODUCTION
In recent years, the rapid growth of online shopping
across various industries has created ongoing chal-
lenges for companies handling the delivery of high
volumes of parcels to increasingly demanding cus-
tomers.
In this scenario, optimizing last-mile delivery, par-
ticularly in densely populated urban areas, has be-
come essential for both business efficiency and envi-
ronmental sustainability. To reduce delivery costs and
minimize the ecological impact of last-mile logistics,
innovative strategies are being introduced, with one
prominent solution being the implementation of elec-
tronic, self-service lockers, placed in accessible pub-
lic locations and serving as convenient pick-up points
for online orders (Grabenschweiger et al., 2021).
The introduction of lockers offers benefits for both
companies and customers. Customers gain the flexi-
bility to customize their delivery experience by choos-
ing between home delivery or secure locker collection
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4650-3362
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8852-6933
c
https://orcid.org/0009-0001-1955-501X
at a convenient time. For companies, lockers enable
the consolidation of deliveries to fewer locations, re-
ducing inefficiencies such as missed deliveries when
customers are unavailable. Furthermore, placing par-
cel lockers in urban areas increases delivery capacity
without the need to expand the workforce, which also
helps to reduce the environmental footprint (Oren-
stein et al., 2019).
Today, various types of lockers exist. Schwerd-
feger and Boysen (2022) distinguishes between sta-
tionary and mobile infrastructures. Stationary lock-
ers, which are the most common, remain fixed after
installation, whereas Mobile Parcel Lockers (MPLs)
can be relocated as needed.
Determining the optimal location for installing a
parcel locker and planning deliveries at an operational
level are both complex and interdependent decisions.
It is important to note that the choice between deliv-
ery to a locker or directly to the customer’s home is
made by the customer, not the service provider. This
introduces a level of uncertainty that must be factored
into the decision-making process (Lai et al., 2022;
Rossolov, 2023).
Under this perspective, this work proposes a
stochastic model that integrates locker location and
Barbieri, G., De Maio, A., Musmanno, R. and Stoia, S.
A Stochastic Location-Routing Problem for the Optimal Placement of Lockers.
DOI: 10.5220/0013170500003893
In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Operations Research and Enterprise Systems (ICORES 2025), pages 123-132
ISBN: 978-989-758-732-0; ISSN: 2184-4372
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
123

vehicle routing costs, taking into account customer
time windows and variability in service type selection
to optimize operations comprehensively.
The problem can be modeled as a Stochastic
Location-Routing Problem (SLRP). The determinis-
tic version of the problem (LRP) has been discussed
in the literature for a long time. The earliest ex-
amples refer to Von Boventer (1961) and Maranzana
(1964). However, LRP has gained substantial pop-
ularity in the scientific community only recently, as
demonstrated in the surveys of Drexl and Schneider
(2015) and Mara et al. (2021).
Indeed, the location of a logistics node, if de-
termined without considering the impact on the re-
sulting routes, may lead to sub-optimal decisions in
terms of overall logistics costs. An integrated ap-
proach that accounts for both node location and route
optimization is therefore essential to minimize oper-
ational costs and enhance the efficiency of the distri-
bution network. This problem encompasses two NP-
hard problems, making LRP itself an NP-hard prob-
lem (Nagy and Salhi, 2007).
This class of problems has been used in the litera-
ture to model applications in different contexts. Some
recent examples in a deterministic setting are the fol-
lowing.
In Veenstra et al. (2021), lockers are used for phar-
maceutical deliveries without considering time win-
dows or locker capacities. Conversely, Liu et al.
(2021) apply lockers in a grocery distribution con-
text, taking into account both time windows and ca-
pacity constraints for lockers and depots. Wang et al.
(2022a) propose an LRP model for last-mile distribu-
tion, where customers can be served either by small
electric vehicles or through lockers, while consider-
ing the battery levels of the vehicles. Liu et al. (2015)
extend the LRP into the Location-Inventory-Routing
Problem, formulating a model that locates logistic
nodes for both parcel distribution and returns collec-
tion. The model also incorporates inventory deci-
sions, aiming to minimize the costs of location, trans-
portation, inventory, and parcel returns.
In the literature, the concept of lockers can be ex-
tended to include similar options, such as Collection-
and-Delivery Points (CDPs). These represent generic
logistic nodes for parcel collection and delivery,
which, unlike lockers, can include stores and private
postal services that offer such services during their
operating hours. Rautela et al. (2022) formulates a de-
terministic LRP model to locate CDPs within a com-
plex logistics network.
A paper addressing a problem similar to the one
under analysis is presented by Grabenschweiger and
Dorner (2022). They examine a multi-period LRP
for locker location, taking time windows into ac-
count. However, their model handles customer-to-
locker assignments without considering uncertainty in
customer service type selection. Liu et al. (2023b) ex-
plore a special case of LRP, focusing on the daily relo-
cation of MPLs to minimize overall operational costs
and enhance customer accessibility.
Although incorporating uncertain data makes
models more realistic, only a small portion of the
studies on LRP consider stochastic data, as high-
lighted by Mara et al. (2021). An example of a SLRP
is presented by Aghalari et al. (2023), who formu-
late an SLRP model for locating charging stations for
electric vehicles used in distribution. The model ac-
counts for uncertainty in customer demand and envi-
ronmental factors, which directly affect battery effi-
ciency. The objective is to minimize location costs
and the expected routing costs.
Other applications of SLRPs can be found in hu-
manitarian logistics, as discussed by de Veluz et al.
(2023), which focuses on the location of distribution
and evacuation centers while considering various dis-
aster scenarios. The model aims to minimize costs,
the number of vehicles used, and travel times.
This study contributes to the body of knowledge
on SLRPs as it is the first in the literature to address
locker location while considering customer time win-
dows, uncertainty in customer service selection, and
multi-period planning.
The remainder of the paper is organized as fol-
lows. In Section 2 we report a formal discussion of
the SLRP and the corresponding mathematical formu-
lation. In Section 3 we describe the solution method
proposed. In Section 4, we discuss the results of our
computational experiments. Conclusions and future
developments follow in Section 5.
2 MATHEMATICAL
FORMULATION
We consider a complete directed graph G = (N,A),
where N represents the set of nodes. Node 0 specif-
ically corresponds to the depot from which all routes
must start. Additionally, let the sets C and L be sub-
sets of N, where C represents the set of customers
(with each customer indexed by c), and L repre-
sents the set of potential sites for locker placement
(with each locker site indexed by l). Thus, we have
N = 0 ∪ C ∪ L. A represents the set of arcs, where
each arc (i, j) corresponds to the fastest path from
node i to node j in G.
For each customer c ∈ C, let π
c
represent the prob-
ability of serving the customer at their home. Conse-
ICORES 2025 - 14th International Conference on Operations Research and Enterprise Systems
124

quently, 1 − π
c
corresponds to the probability that the
customer will opt to collect their delivery from the
nearest locker. These probabilities can be estimated
using historical data on service preferences from the
previous purchases of each customer.
A binary constant g
c
is associated with each cus-
tomer, where g
c
= 1 if the customer is served at home
and g
c
= 0 if the service is provided through a locker.
This allows the formulation of a stochastic program-
ming problem to handle uncertainty by introducing a
set S of scenarios. Each scenario s ∈ S represents a
possible service configuration for all customers, de-
fined by a vector of |C| binary elements, with an asso-
ciated probability
p
(s)
=
∏
c∈C
p
(s)
c
,
where p
(s)
c
= π
c
if g
c
= 1 in scenario s, and p
(s)
c
=
1 − π
c
if g
c
= 0.
The total number of scenarios is therefore equal to
2
|C|
.
The stochastic programming problem is structured
as a two-stage model. In the first stage, decisions
are made regarding the placement of lockers, which
must be finalized before customers select their pre-
ferred service option (either home delivery or locker
collection). The second stage involves making rout-
ing decisions, which occur after customers have cho-
sen their service type.
The SLRP, in its most general form, can be multi-
period, with T representing the set of time periods that
define the planning horizon.
The input parameters of the problem are as fol-
lows:
• n: number of lockers to be activated (n ≤ |L|);
• d
i j
, (i, j) ∈ A: distance associated with arc (i, j);
• t
i j
, (i, j) ∈ A: travel time along arc (i, j);
• γ
i j
, (i, j) ∈ A: transportation cost along arc (i, j);
• δ
cl
, c ∈ C, l ∈ L: transportation penalty cost in-
curred when a customer c is served by a locker l
located at a distance d
cl
> ρ, where ρ is a thresh-
old set by the decision-maker. Specifically, ρ cor-
responds to the maximum distance a customer is
willing to travel to a locker. The penalty cost
δ
cl
= 0 if d
cl
≤ ρ, and δ
cl
= r(d
cl
− ρ) otherwise,
where r is a unit penalty cost;
• a
ct
, c ∈ C, t ∈ T : binary coefficient equal to 1 if
customer c must be served in time period t, 0 oth-
erwise;
• g
(s)
c
, c ∈ C, s ∈ S: binary coefficient indicating
whether, in scenario s, customer c is served at
home (g
(s)
c
= 1) or via a locker (g
(s)
c
= 0);
• e
i
, i ∈ N: earliest time at which service can start
at node i;
• l
i
, i ∈ N: latest time by which service must start at
node i;
• τ
i
, i ∈ N: service time at node i;
• f
l
, l ∈ L : activation cost of locker l;
• p
(s)
, s ∈ S : probability associated with scenario s;
• k: number of available vehicles;
• M: arbitrarily large constant.
The decision variables are the following.
First-stage variables:
• w
l
, l ∈ L: binary variable indicating whether a
locker is opened in site l.
Recourse variables:
• x
(s)
i jt
, (i, j) ∈ A, t ∈ T, s ∈ S : binary variable equal
to 1 if arc (i, j) is traversed by a vehicle during
time period t in scenario s, 0 otherwise;
• y
(s)
clt
, c ∈ C, l ∈ L, t ∈ T , s ∈ S: binary variable
equal to 1 if customer c is assigned to locker l
and served during time period t in scenario s, 0
otherwise;
• z
(s)
ct
, c ∈ C, t ∈ T , s ∈ S: binary variable equal to 1
if customer c is served at home during time period
t in scenario s, 0 otherwise;
• v
(s)
it
, i ∈ N, t ∈ T, s ∈ S: non-negative continuous
variable representing the start time of the visit to
node i during time period t in scenario s.
The objective of the SLRP is to minimize the total
cost, which is influenced by three components:
• transportation costs associated with vehicle routes
that visit both home customers and lockers:
z
(s)
1
=
∑
(i, j)∈A
∑
t∈T
γ
i j
x
(s)
i jt
;
• penalty costs related to the service level, reflecting
limitations on assigning customers to lockers that
are too distant:
z
(s)
2
=
∑
c∈C
∑
l∈L
∑
t∈T
δ
cl
y
(s)
clt
;
• locker activation costs:
z
3
=
∑
l∈L
f
l
w
l
.
Note that both the transportation costs and penalty
costs depend on recourse decisions and thus vary
across scenarios s ∈ S, whereas the locker activation
costs are invariant across scenarios, as they are asso-
ciated with the first-stage decisions.
A Stochastic Location-Routing Problem for the Optimal Placement of Lockers
125

The formulation of the two-stage model is the fol-
lowing:
min
∑
s∈S
p
(s)
(z
(s)
1
+ z
(s)
2
) + z
3
(1)
subject to
∑
j∈N\{i}
x
(s)
i jt
≤ 1, ∀ i ∈ N \ {0},∀ t ∈ T,∀ s ∈ S (2)
∑
j∈N\{0}
x
(s)
0 jt
≤ k, ∀ t ∈ T,∀ s ∈ S (3)
∑
j∈N\{i}
x
(s)
i jt
=
∑
j∈N\{i}
x
(s)
jit
, ∀ i ∈ N, ∀ t ∈ T,∀ s ∈ S (4)
y
(s)
clt
≤
∑
j∈N\{l}
x
(s)
l jt
, ∀ c ∈ C,∀ l ∈ L, ∀ t ∈ T,∀ s ∈ S (5)
z
(s)
ct
≤
∑
j∈N\{c}
x
(s)
c jt
, ∀ c ∈ C, ∀ t ∈ T, ∀ s ∈ S (6)
∑
j∈N\{l}
x
(s)
l jt
≤ w
l
, ∀ l ∈ L,∀ t ∈ T, ∀ s ∈ S (7)
∑
l∈L
w
l
= n (8)
∑
l∈L
(1 − g
(s)
c
) y
(s)
clt
+ g
(s)
c
z
(s)
ct
= a
ct
, ∀ c ∈ C, ∀ t ∈ T,∀ s ∈ S (9)
v
(s)
it
+ τ
i
+t
i j
− M (1 − x
(s)
i jt
) ≤ v
(s)
jt
, ∀ i ∈ N,
∀ j ∈ N \ {0},∀ t ∈ T, ∀ s ∈ S
(10)
v
(s)
it
+ τ
i
+t
i0
≤ l
0
, ∀ i ∈ N,∀ t ∈ T, ∀ s ∈ S (11)
v
(s)
it
≤ l
i
∑
j∈N\{i}
x
(s)
i jt
, ∀ i ∈ N \ {0},∀ t ∈ T,∀ s ∈ S (12)
v
(s)
it
≥ e
i
∑
j∈N\{i}
x
(s)
i jt
, ∀ i ∈ N, ∀ t ∈ T, ∀ s ∈ S (13)
x
(s)
i jt
∈ {0, 1}, ∀ (i, j) ∈ A,∀ t ∈ T,∀ s ∈ S (14)
y
(s)
clt
∈ {0,1}, ∀ c ∈ C,∀ l ∈ L, ∀ t ∈ T, ∀ s ∈ S (15)
z
(s)
ct
∈ {0,1}, ∀ c ∈ C,∀ t ∈ T,∀ s ∈ S (16)
w
l
∈ {0,1}, ∀ l ∈ L (17)
v
(s)
it
≥ 0, ∀ i ∈ N,∀ t ∈ T,∀ s ∈ S. (18)
In the objective function (1), the transportation
and penalty costs are weighted according to the prob-
abilities of the scenarios. Constraints (2) ensure that
each node (except the depot) is visited at most once
per time period in each scenario. Constraints (3) re-
strict the number of routes to the number of avail-
able vehicles in each time period and for each sce-
nario. Equations (4) represent the flow balance con-
straints for each node, in every time period and for
each scenario. Constraints (5) link the variables y
(s)
clt
to the variables x
(s)
l jt
, ensuring that for each scenario
s, if a customer c is served by locker l in time period
t, the node corresponding to that locker must be vis-
ited during that time period. Constraints (6) link the
variables z
(s)
ct
to the variables x
(s)
c jt
, ensuring that for
each scenario s, if a customer c is served at home in
time period t, the node corresponding to that customer
must be visited during that time period. Constraints
(7) ensure that for each time period and scenario, if
a locker is not opened, its corresponding node can-
not be visited. Constraint (8) imposes the required
number of lockers to be activated. Constraints (9) en-
sure that each customer is served either at home or
through a locker, depending on the scenario s. Con-
straints (10)−(11) ensure temporal continuity of ser-
vice and prevent the formation of sub-tours within the
routes. Additionally, constraints (11) ensure that the
time window for the depot is respected in every time
period and scenario. Constraints (12)−(13) impose
the satisfaction of time windows for each node, time
period, and scenario. Finally, constraints (14)−(18)
define the nature (binary or continuous) of the deci-
sion variables.
For simplicity, the remainder of this paper focuses
on a single time period within the planning horizon,
assuming that the available vehicle fleet is sufficiently
large to meet all customer demand.
3 SOLUTION METHOD
When solving the SLRP for locker location to opti-
mality, it is theoretically possible to approach the so-
lution by inspection, at least in principle. Specifically,
all possible
|L|
n
combinations of locker activations
from the set of potential sites are considered and ex-
amined individually. By defining the values of the
location variables w
l
for each combination, their ef-
fect on second-stage decisions can be evaluated by
solving a Vehicle Routing Problem with Time Win-
dows (VRP-TW) for each scenario. The nodes to be
visited in each VRP-TW include the activated lockers
and the customers who, in the corresponding scenario,
ICORES 2025 - 14th International Conference on Operations Research and Enterprise Systems
126

are scheduled for home delivery.
After solving the VRP-TW for each scenario s ∈ S,
the total solution cost for the SLRP can be calculated
using equation (1).
The pseudo-code of the proposed procedure for
solving the SLRP for each choice of n lockers to acti-
vate is presented below.
Algorithm 1: Procedure SLRP. (L, z).
begin
// L is the set of n lockers to
be activated
// z is the total cost of the
SLRP
1 z
3
=
∑
l∈L
f
l
;
2 z = z
3
;
3 for s = 1 to |S| do
4 Determine the list C
(s)
1
of customers
who, according to scenario s, request
home delivery;
// C
(s)
0
is the list of
customers served via lockers
5 C
(s)
0
= C \C
(s)
1
6 for c = 1 to |C
(s)
0
| do
7 Assign c to the nearest locker
l ∈ L;
8 Determine the penalty δ
cl
;
9 end
10 z
(s)
2
=
∑
c∈C
(s)
0
∑
l∈L
δ
cl
;
// Update z
11 z := z + p
(s)
z
(s)
2
;
// Define the set N of nodes
for which the VRP-TW will be
solved
12 N = 0 ∪C
(s)
1
∪ L;
13 Solve the VRP-TW on the complete
directed graph induced by N;
// z
(s)
1
is the cost of the
VRP-TW
// Update z
14 z := z + p
(s)
z
(s)
1
;
15 end
16 return z;
end
The time complexity of the entire algorithm
grows exponentially with the problem size, making it
quickly impractical even for moderately sized inputs,
as the execution time increases rapidly.
To keep execution times within acceptable limits,
three approaches can be applied simultaneously: 1)
reducing the number of configurations of n lockers
to test among the |L| possible choices (this reduces
the number of calls of the SLRP procedure); 2) re-
ducing the number of scenarios in the for loop 3−15
of the SLRP procedure; and 3) heuristically solving
the VRP-TW for each scenario (code line 13 of the
SLRP procedure). These three proposed approaches
are briefly outlined below.
3.1 Reduction of the Number of Locker
Configurations
For limiting the number of locker configurations to be
tested, geographical criteria are widely used and pro-
posed in literature to optimize placement and enhance
efficiency (Lagorio and Pinto (2020), Sawik (2024)
and Wang et al. (2022b)). Here are the two relevant
approaches:
• optimal geographical coverage: lockers should
be strategically placed to ensure even distribution
across the service area, minimizing coverage gaps
and guaranteeing accessibility in all key locations;
• proximity between lockers: it is possible to avoid
placing lockers too close to one another, prevent-
ing redundancy and enhancing the overall effi-
ciency of the locker network.
3.2 Reduction of the Number of
Scenarios
As observed in Section 2, the number of scenar-
ios grows exponentially with the number of cus-
tomers. To give an idea, considering 30 customers
would result in a number of scenarios equal to 2
30
=
1,073,741,824. This implies that only a representative
subset S of all possible scenarios may be considered.
To reduce the number of scenarios, the following
approach is proposed. First, the most likely scenario
s
∗
is considered. The probability p
(s
∗
)
of this scenario
is equal to the product of the probabilities associated
with each individual customer corresponding to the
most probable choice:
p
(s
∗
)
=
∏
c∈C
max{π
c
;1 − π
c
}.
Then, |S| scenarios are randomly generated, en-
suring that the overall probability (given by the sum
of the scenario probabilities) is greater than or equal
A Stochastic Location-Routing Problem for the Optimal Placement of Lockers
127

Algorithm 2: Procedure Scenario Generation.
begin
// Σ is a binary matrix of
scenarios, with size |S| × |C|
1 Randomly generate Σ;
2 Determine the cumulative probability
p
(Σ)
=
|S|
∑
s=1
p
(s)
associated with the
scenarios in Σ;
3 while p
(Σ)
< p
(s
∗
)
do
4 Randomly select an entry (s,c) of Σ;
5 if p
(s)
c
< max{π
c
;1 − π
c
} then
6 p
(s)
c
= max{π
c
;1 − π
c
};
7 Modify scenario s in Σ
accordingly;
8 Update p
(Σ)
;
9 end
10 end
end
to p
(s
∗
)
. The proposed procedure is illustrated in the
sequel.
Finally, to ensure consistent comparison between
solutions derived from different scenario subsets, we
normalize the associated probabilities so that the over-
all probability across all scenarios s ∈ S equals one.
This is achieved by replacing each value of p
(s)
for all
s ∈
S at the end of the Scenario Generation proce-
dure with the ratio p
(s)
/p
(Σ)
.
3.3 Heuristic Approaches for the
VRP-TW
Several methods can be applied to generate feasible
vehicle routes while respecting time windows con-
straints. As reported in Liu et al. (2023a), most
of these methods fall into three categories: exact,
heuristic, and metaheuristic approaches. Heuristic
and metaheuristic methods, starting with Solomon’s
constructive heuristics (Solomon, 1987), are widely
used in the literature due to their ability to efficiently
solve large-scale problems.
Exact methods are also worth mentioning, though
they are generally capable of optimally solving only
small to medium-sized problems (Desaulniers et al.,
2005) . Among them, the column generation method
stands out, as it can be adapted for the VRP-TW
to generate sub-optimal solutions within acceptable
computational times (Kallehauge et al., 2005).
4 COMPUTATIONAL
EXPERIMENTS
The solution method described in Section 3 was tested
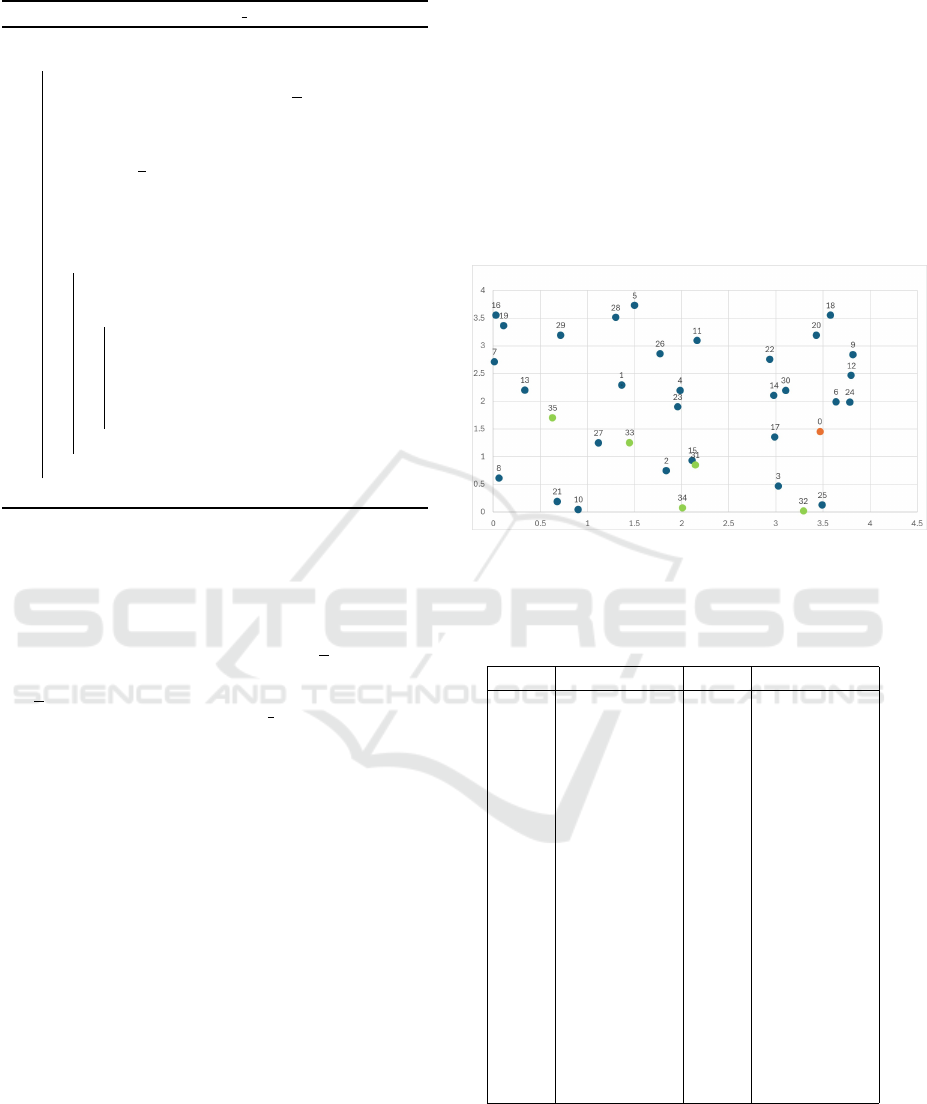
on a problem consisting of |N| = 36 nodes, where
their spatial distribution on the plane was randomly
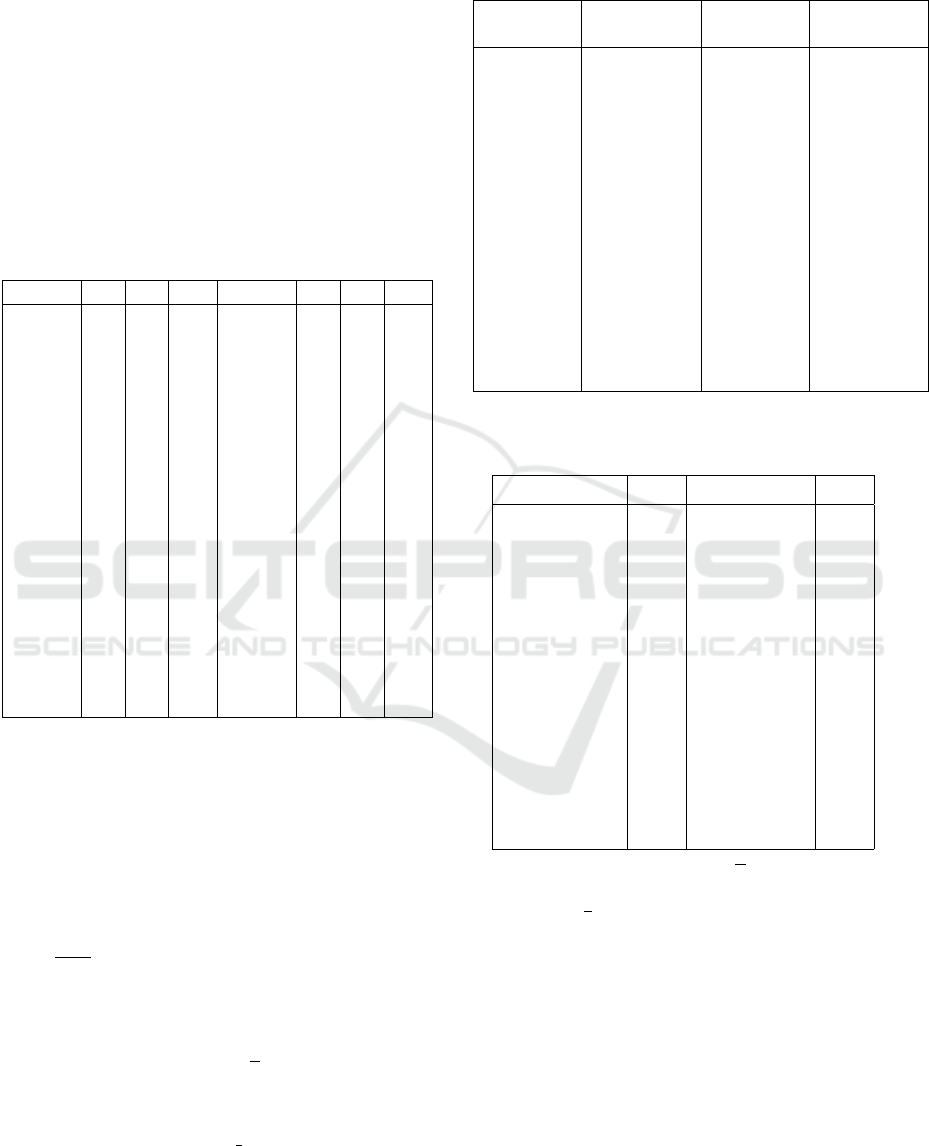
generated (see Figure 1). Table 1 presents the Carte-
sian coordinates of the nodes. Node 0 represents the
depot, nodes 1 to 30 correspond to the customers, and
nodes 31 to 35 indicate the potential sites for locker
locations.
Figure 1: Spatial distribution of the nodes of the test prob-
lem.
Table 1: Cartesian coordinates (in kilometres) of the nodes
of the test problem.
Node Coordinates Node Coordinates
0 (3.47, 1.46) 1 (1.36, 2.29)
2 (1.84, 0.75) 3 (3.03, 0.47)
4 (1.98, 2.20) 5 (1.50, 3.73)
6 (3.64, 1.99) 7 (0.02, 2.71)
8 (0.06, 0.61) 9 (3.82, 2.84)
10 (0.90, 0.05) 11 (2.17, 3.10)
12 (3.80, 2.47) 13 (0.34, 2.20)
14 (2.98, 2.10) 15 (2.11, 0.93)
16 (0.03, 3.55) 17 (2.99, 1.35)
18 (3.58, 3.55) 19 (0.11, 3.36)
20 (3.43, 3.19) 21 (0.68, 0.19)
22 (2.94, 2.76) 23 (1.96, 1.90)
24 (3.79, 1.98) 25 (3.49, 0.13)
26 (1.77, 2.86) 27 (1.12, 1.25)
28 (1.30, 3.51) 29 (0.72, 3.19)
30 (3.11, 2.19) 31 (2.15, 0.85)
32 (3.29, 0.02) 33 (1.45, 1.25)
34 (2.01, 0.08) 35 (0.63, 1.70)
The distances between nodes (in kilometers) are
Euclidean, thereby ensuring the triangular inequality
property. Table 2 presents the time windows and ser-
vice times for each node, expressed in hours. The
time windows are set starting from 00:00.
ICORES 2025 - 14th International Conference on Operations Research and Enterprise Systems
128
The transportation cost γ
i j
for each arc (i, j ) ∈ A
is defined as:
γ
i j
= 1.0 × d
i j
,
where 1.0 represents the unit transportation cost (in
e/km). The unit penalty cost is set to 0.60 e/km. The
fixed opening cost of a locker is assumed to be iden-
tical for each potential site ( f
l
= f ,∀ l ∈ L). As a
result, the cost z
3
in the objective function (1) is the
same for every locker configuration tested (z
3
= f n)
and is therefore omitted. The fleet consists of k = 4
vehicles.
Table 2: Time windows (e
i
, l
i
) and service times (τ
i
) for
each node i ∈ N.
Node i e
i
l
i
τ
i
Node i e
i
l
i
τ
i
0 0 24 0.0 1 10 15 0.1
2 9 13 0.1 3 14 17 0.1
4 12 16 0.1 5 8 15 0.1
6 9 11 0.1 7 10 14 0.1
8 16 18 0.1 9 10 13 0.1
10 11 15 0.1 11 12 17 0.1
12 15 16 0.1 13 10 13 0.1
14 10 14 0.1 15 8 10 0.1
16 9 13 0.1 17 15 17 0.1
18 14 16 0.1 19 12 14 0.1
20 13 16 0.1 21 10 11 0.1
22 9 12 0.1 23 14 16 0.1
24 12 13 0.1 25 14 16 0.1
26 12 15 0.1 27 10 11 0.1
28 12 14 0.1 29 8 9 0.1
30 15 16 0.1 31 9 18 0.3
32 9 18 0.3 33 9 18 0.3
34 9 18 0.3 35 9 18 0.3
The probabilities of home service for the 30 cus-
tomers are presented in Table 3.
Consequently, the most likely scenario s
∗
, corre-
sponding to the 30 binary entries reported in Table 4,
has a probability p
(s
∗
)
= 0.000354352.
We consider the case where two lockers are to be
activated out of the five potential sites. In this case,
the SLRP can be solved for each possible configura-
tion of locker activation, as the number is small, being
5
2
=
5!
2!×3!
= 10.
Regarding the scenarios, computational experi-
ments were conducted considering two situations: 1)
only scenario s
∗
, corresponding to the most likely ser-
vice configuration, for which the probability p
(s
∗
)
is
set to one; and 2) using a set S of 30 representative
scenarios, deemed sufficient to capture the stochas-
tic nature of the problem. These scenarios were
generated using the Scenario Generation procedure,
which produced the binary matrix Σ of size 30×30,
with a cumulative probability p
Σ
= 0.000381808. The
Table 3: Probabilities of service at home for the 30 cus-
tomers.
Customer Probability Customer Probability
(c) (π
c
) (c) (π
c
)
1 0.0449 2 0.9441
3 0.1970 4 0.6387
5 0.0678 6 0.3687
7 0.8344 8 0.8841
9 0.4342 10 0.9260
11 0.2256 12 0.0765
13 0.0425 14 0.7687
15 0.4447 16 0.7207
17 0.6687 18 0.8906
19 0.3913 20 0.2988
21 0.6518 22 0.9872
23 0.2420 24 0.9467
25 0.6288 26 0.6725
27 0.7480 28 0.0616
29 0.5331 30 0.8611
Table 4: Home delivery (1) or service via locker (0) for the
30 customers in the most likely scenario s
∗
.
Customer (c) g
(s
∗
)
c
Customer (c) g
(s
∗
)
c
1 0 2 1
3 0 4 1
5 0 6 0
7 1 8 1
9 0 10 1
11 0 12 0
13 0 14 1
15 0 16 1
17 1 18 1
19 0 20 0
21 1 22 1
23 0 24 1
25 1 26 1
27 1 28 0
29 1 30 1
probabilities of each scenario in S were then normal-
ized so that
∑
s∈S
p
(s)
= 1.
It is worth emphasizing that solving the SLRP by
considering only the most likely scenario effectively
transforms it into a deterministic problem, where ser-
vice decisions are made under the assumption that
each customer will always choose their most pre-
ferred service.
From this perspective, the ”single scenario” model
does not account for uncertainty and is therefore re-
ferred to as the deterministic case hereafter.
The entire algorithm was implemented in Python
3 using the Visual Studio Code IDE. To solve the
VRP-TW, we used the VRPy library, a package de-
A Stochastic Location-Routing Problem for the Optimal Placement of Lockers
129
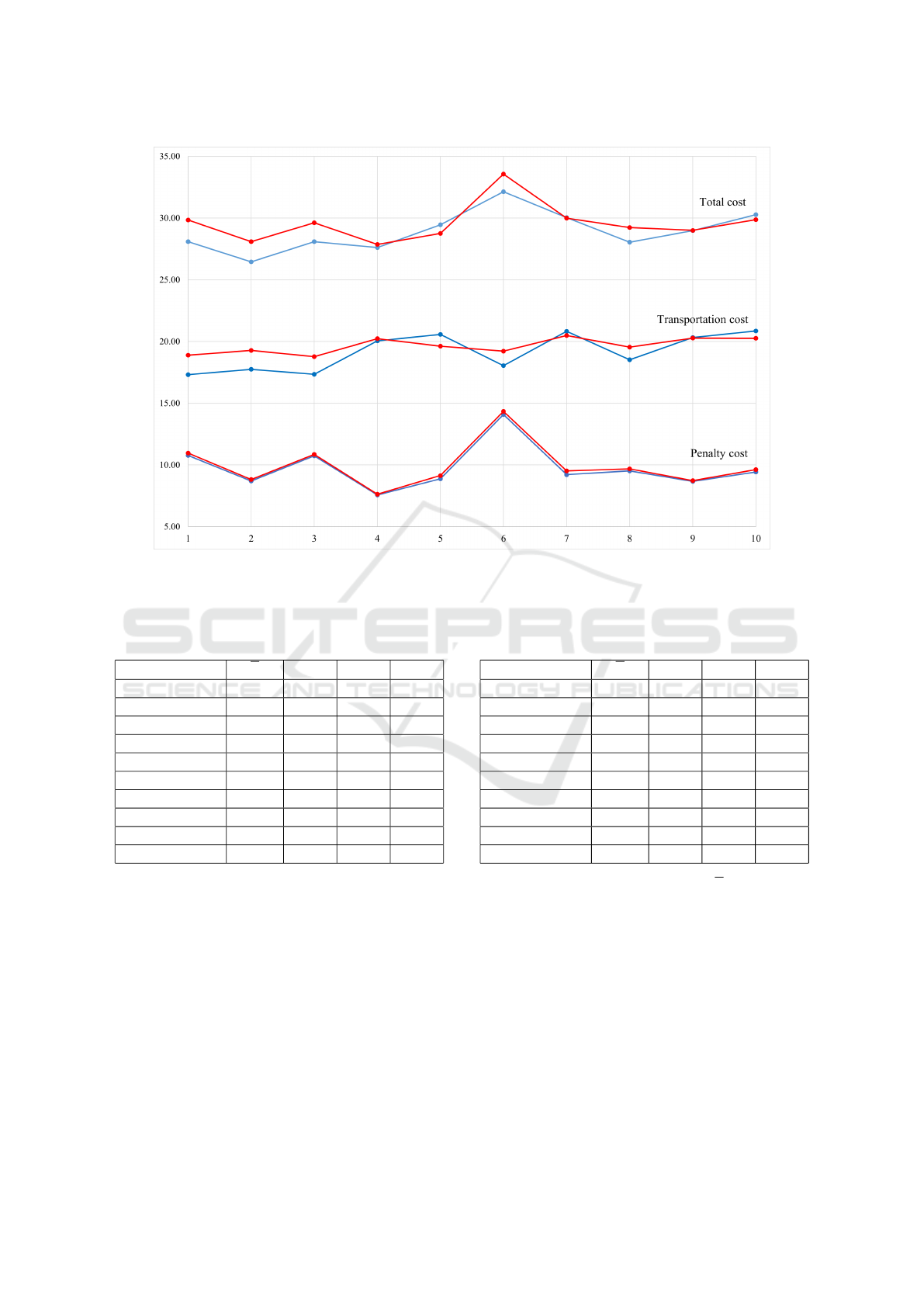
Figure 2: Costs obtained for each the ten tested locker configurations, both in the deterministic case (in blue) and the stochastic
case (in red).
Table 5: Pair of activated lockers, transportation cost (z
1
),
penalty cost (z
2
), and total cost (z) for each of the ten locker
configurations in the deterministic case.
Configuration L z
1
z
2
z
1 31, 32 17.32 10.77 28.09
2 31, 33 17.75 8.69 26.44
3 31, 34 17.34 10.74 28.08
4 31, 35 20.05 7.57 27.62
5 32, 33 20.57 8.88 29.45
6 32, 34 18.05 14.09 32.14
7 32, 35 20.83 9.21 30.04
8 33, 34 18.52 9.52 28.04
9 33, 35 20.31 8.66 28.97
10 34, 35 20.86 9.42 30.28
signed for solving various vehicle routing problems
through a column generation approach (Montagn
´
e
et al., 2020). In this method, routes (or columns)
are generated by solving a pricing problem and then
passed to a master problem, which selects the best
routes from a pool such that each vertex (except the
depot) is served exactly once. It is important to note
that VRPy does not necessarily return an optimal so-
lution, but feasibility is guaranteed.
The results are summarized in Tables 5 and 6 for
the deterministic and stochastic cases of the problem,
respectively. The tables are organized as follows:
column Configuration enumerates the ten configu-
Table 6: Transportation costs (z
1
), penalty costs (z
2
), and
total costs (z) for the ten activated locker configurations in
the stochastic case.
Configuration L z
1
z
2
z
1 31, 32 18.89 10.95 29.84
2 31, 33 19.27 8.81 28.08
3 31, 34 18.77 10.85 29.62
4 31, 35 20.23 7.63 27.86
5 32, 33 19.62 9.14 28.76
6 32, 34 19.22 14.34 33.56
7 32, 35 20.48 9.51 29.99
8 33, 34 19.55 9.68 29.23
9 33, 35 20.28 8.72 29.00
10 34, 35 20.26 9.61 29.87
rations of activated lockers, column L indicates the
nodes corresponding to the pairs of activated lock-
ers, columns z
1
and z
2
report the transportation and
penalty costs, respectively, while column z provides
the total costs. The results are also plotted in Figure
2, where, for each activated locker configuration, the
transportation, penalty, and total costs are shown for
both the deterministic (in blue) and stochastic (in red)
cases.
The SLRP with 30 scenarios effectively incorpo-
rates a degree of uncertainty regarding customer ser-
vice choices, making the model more realistic com-
pared to its simple deterministic counterpart. Conse-
ICORES 2025 - 14th International Conference on Operations Research and Enterprise Systems
130

quently, it is expected that the optimal solutions ob-
tained may differ. In fact, in the stochastic case, the
lockers identified as the best locations are at nodes 31
and 35, whereas in the deterministic case, the optimal
solution corresponds to lockers located at nodes 31
and 33.
5 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
DEVELOPMENTS
In this paper, we presented a stochastic location-
routing problem for the optimal placement of parcel
lockers, incorporating customer preferences between
home delivery and locker collection under uncertain
conditions. The model was formulated as a two-stage
stochastic program, with the first stage determining
locker locations and the second stage addressing ve-
hicle routing based on service requests across multi-
ple scenarios. Through computational experiments,
we demonstrated the differences between determinis-
tic and stochastic solutions, highlighting the ability of
the model to account for customer behavior variabil-
ity.
While the model offers a valuable framework for
addressing uncertainty in last-mile delivery, several
areas for future research and development remain un-
explored.
One possible extension involves the inclusion of
scenarios where some customers opt not to request
service at all. This reflects a real-world phenomenon
where, due to various factors such as pricing, deliv-
ery preferences, availability of alternatives, or per-
sonal circumstances, customers may decide not to en-
gage with the delivery network in a given time period.
Another extension would be to expand the model
to multi-period scenarios while incorporating capac-
ity constraints for both vehicles and lockers, making
the model more applicable to real-world logistics set-
tings.
Furthermore, the current model assumes a fixed
number of lockers to be activated. In future re-
search, this assumption could be relaxed, allowing
the number of lockers to be determined dynamically.
This would require the development of more sophis-
ticated procedures to determine which lockers to acti-
vate, such as ADD, DROP, or ADD-DROP heuristics.
Lastly, to enhance computational efficiency, the code
could be adapted to run on multi-core architectures,
enabling the generation of a greater number of sce-
narios. In this approach, the routing problem could be
decomposed into scenario subsets, with each subset
assigned to a different core, thereby reducing overall
computational time.
These future developments aim to improve the
practical applicability of the model, ensuring it re-
mains relevant for a wide range of logistics and last-
mile delivery problems under uncertainty.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The work of Annarita De Maio was partially sup-
ported by the Italian Minister of University and Re-
search under the grant H25F21001230004. This sup-
port is gratefully acknowledged.
REFERENCES
Aghalari, A., Salamah, D., Kabli, M., and Marufuzzaman,
M. (2023). A two-stage stochastic location–routing
problem for electric vehicles fast charging. Computers
and Operations Research, 158.
de Veluz, M. R. D., Redi, A. A. N. P., Maaliw III, R. R.,
Persada, S. F., Prasetyo, Y. T., and Young, M. N.
(2023). Scenario-based multi-objective location-
routing model for pre-disaster planning: A Philippine
case study. Sustainability, 15(6).
Desaulniers, G., Desrosiers, J., and Solomon, M. E. (2005).
Column Generation. GERAD 25th Anniversary Se-
ries. Springer Science & Business Media, Boston,
MA.
Drexl, M. and Schneider, M. (2015). A survey of variants
and extensions of the location-routing problem. Euro-
pean Journal of Operational Research, 241(2):283–
308.
Grabenschweiger, J., Doerner, K. F., Hartl, R. F., and
Savelsbergh, M. W. P. (2021). The vehicle routing
problem with heterogeneous locker boxes. Central
European Journal of Operations Research, 29.
Grabenschweiger, J. and Dorner, K. F. (2022). The multi-
period location routing problem with locker boxes.
Logisics Research, 15(1).
Kallehauge, B., Larsen, J., Madsen, O. B., and Solomon,
M. M. (2005). Vehicle Routing Problem with Time
Windows, pages 67–98. Springer US, Boston, MA.
Lagorio, A. and Pinto, R. (2020). The parcel locker location
issues: an overview of factors affecting their location.
International Conference on Information Systems, Lo-
gistics and Supply Chain.
Lai, P., Jang, H., Fang, M., and Peng, K. (2022). Determi-
nants of customer satisfaction with parcel locker ser-
vices in last-mile logistics. The Asian Journal of Ship-
ping and Logistics, 38(1):25–30.
Liu, B., Chen, H., Li, Y., and Liu, X. (2015). A
pseudo-parallel genetic algorithm integrating sim-
ulated annealing for stochastic location-inventory-
routing problem with consideration of returns in e-
commerce. Discrete Dynamics in Nature and Society,
2015(1):1258–1276.
A Stochastic Location-Routing Problem for the Optimal Placement of Lockers
131

Liu, D., Deng, Z., Zhang, W., Wang, Y., and Kaisar, E. I.
(2021). Design of sustainable urban electronic grocery
distribution network. Alexandria Engineering Jour-
nal, 60(1):145–157.
Liu, X., Chen, Y.-L., Por, L. Y., and Ku, C. S. (2023a). A
systematic literature review of vehicle routing prob-
lems with time windows. Sustainability, 15(15).
Liu, Y., Ye, Q., Escribano-Macias, J., Feng, Y., Candela,
E., and Angeloudis, P. (2023b). Route planning for
last-mile deliveries using mobile parcel lockers: A hy-
brid q-learning network approach. Transportation Re-
search Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review,
177.
Mara, S. T. W., Kuo, R., and Sri Asih, A. M. (2021).
Location-routing problem: a classification of recent
research. International Transactions in Operational
Research, 28(6):2941–2983.
Maranzana, F. (1964). On the location of supply points
to minimize transport costs. Operational Research
Quaterly, 15(3):261–270.
Montagn
´
e, R., Sanchez, D. T., and Storbugt, H. O. (2020).
Vrpy: A Python package for solving a range of vehicle
routing problems with a column generation approach.
The Journal of Open Source Software, 5(55).
Nagy, G. and Salhi, S. (2007). Location-routing: Issues,
models and methods. European Journal of Opera-
tional Research, 177(2):649–672.
Orenstein, I., Raviv, T., and Sadan, E. (2019). Flexible par-
cel delivery to automated parcel lockers: models, so-
lution methods and analysis. EURO Journal on Trans-
portation and Logistics, 8(5):683–711.
Rautela, H., Janjevic, M., and Winkenbach, M. (2022).
Investigating the financial impact of collection-and-
delivery points in last-mile e-commerce distribution.
Research in Trasportation Business and Management,
45(A).
Rossolov, A. (2023). A last-mile delivery channel choice
by e-shoppers: assessing the potential demand for au-
tomated parcel lockers. International Journal of Lo-
gistics Research and Applications, 26(8):983–1005.
Sawik, B. (2024). Optimizing last-mile delivery: A multi-
criteria approach with automated smart lockers, capil-
lary distribution and crowdshipping. Logistics, 8(2).
Schwerdfeger, S. and Boysen, N. (2022). Who moves the
locker? A benchmark study of alternative mobile par-
cel locker concepts. Transportation Research Part C:
Emerging Technologies, 142.
Solomon, M. M. (1987). Algorithms for the vehicle rout-
ing and scheduling problems with time window con-
straints. Operations Research, 35(2):254–265.
Veenstra, M., Roodbergen, K. J., Coelho, L. C., and Zhu,
S. X. (2021). A simultaneous facility location and ve-
hicle routing problem arising in health care logistics
in the Netherlands. Europen Journal of Operational
Research, 268(2):703–715.
Von Boventer, E. (1961). The relationship between trans-
portation costs and location rent in transportation
problems. Journal of Regional Science, 3(2):27–40.
Wang, M., Zhang, C., Bell, M. G., and Miao, L. (2022a). A
branch-and-price algorithm for location-routing prob-
lems with pick-up stations in the last-mile distribution
system. Europen Journal of Operational Research,
303(3):1258–1276.
Wang, Y., Zhang, Y., Bi, M., Lai, J., and Chen, Y. (2022b).
A robust optimization method for location selection
of parcel lockers under uncertain demands. Mathe-
matics, 10(22).
ICORES 2025 - 14th International Conference on Operations Research and Enterprise Systems
132
