
Cost Optimization Analysis of Retrial Machine Repair Problem with
Warm Standby Components and Imperfect Coverage
Tseng-Chang Yen
1
, Wei-Ping Lai
1
, Kuo-Hsiung Wang
2
and Chia-Huang Wu
3
1
Department of Applied Mathematics, National Chung Hsing University, Taichung 40227, Taiwan
2
Department of Business Administration, Asia University, Wufeng, Taichung 41354, Taiwan
3
Department of Industrial Engineering and Management, National Chiao Tung University, Hsinchu 300, Taiwan
Keywords: Cost Optimization, Imperfect Coverage, Matrix-Analytic Method, Particle Swarm Optimization, Retrial
Machine Repair Problem, Sensitivity Analysis.
Abstract: In this paper, we examine the cost optimization analysis of retrial machine repair problem with warm standby
components and imperfect coverage. This research suggests that failure times and repair times of the primary
and warm standby components are exponentially distributed and that the coverage factor is the same for a
primary component failure and a standby component failure. When the server is either busy with other tasks
or is repairing a failed component, the failed component will be sent to the retrial orbit. The steady-state
probabilities of the number of failed components in an orbit is developed by using the matrix-analytic method.
The particle swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm is implemented to simultaneously determine the joint
optimal values of the number of warm standbys, the repair rate, and the retrial rate at minimum cost. Under
optimal operating conditions, numerical experiments were presented to illustrate results. Sensitivity analysis
for system parameters is performed additionally.
1 INTRODUCTION
This paper studies a retrial machine repair problem
(RMRP) with warm standby components and
imperfect coverage. Retrial queue or RMRP with
imperfect coverage is a major issue. Artalejo (1999a,
1999b), Falin (1990), and Yang and Templeton
(1987) provided the foremost overall surveys and
ideas for retrial queues. Queueing systems in which
arriving failed components that cannot accept service
immediately enter orbit and retry for service again
after a random time is called retrial queue. Retrial
queueing problems are increasingly important
concerns and play a crucial role in many practical
applications, such as message switching systems,
manufacturing systems, telecommunication systems,
and production management. With an imperfect
coverage factor, the failed component is immediately
detected, located, and recovered by standby, and the
faults that exchange the failed component within the
standby component are called to be not covered.
Wang et al. (2014) examined an M/G/1 MRP with
imperfect coverage by constructing a cost function
and using direct search and the Quasi-Newton method
to find the optimal number of operating components,
the repair rate, and the coverage factor. Wang et al.
(2013) proposed the direct search method and PSO
algorithm to determine the joint optimal values at the
maximum profit function. After comparing these two
methods, using the PSO algorithm is a better choice
when dealing with optimization problems. Yen et al.
(2021) contrasted four retrial systems with imperfect
coverage and warm standbys. They presented the
comparative analysis of the cost-benefit ratio among
four retrial systems and provided the optimal retrial
system. Yen and Wang (2020) investigated the cost-
benefit analysis of four retrial systems with imperfect
coverage and warm standbys and made comparisons.
Wang et al. (2012) compared two availability systems
with imperfect coverage and warm standbys. This
paper also compares five different distributions of
repair time, which are exponential, normal, gamma,
uniform, and deterministic. Sherbeny and Hussien
(2019) studied the cost-benefit and the availability
analysis for three models with imperfect coverage and
mixed standby (cold and warm standby). Jain and
Meena (2017) analyzed a model of a fault-tolerant
system with imperfect coverage, applied the Runge-
Kutta method to evaluate system performance
measures, and conducted a numerical simulation of
the cost and sensitivity. Wang et al. (2013) conducted
a reliability and sensitivity analysis for the repair
system with imperfect coverage and service pressure
conditions, and studied the influence of different
Yen, T.-C., Lai, W.-P., Wang, K.-H. and Wu, C.-H.
Cost Optimization Analysis of Retrial Machine Repair Problem with Warm Standby Components and Imperfect Coverage.
DOI: 10.5220/0013172500003893
In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Operations Research and Enterprise Systems (ICORES 2025), pages 301-308
ISBN: 978-989-758-732-0; ISSN: 2184-4372
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
301

parameters on system reliability and MTTF.
Cost optimization is a major topic and much
research has been done using particle swarm
optimization (PSO) algorithm for cost optimization
analysis. The PSO algorithm was first proposed by
Kennedy and Eberhart (1995). Zhang et al. (2017)
investigated the retrial queue under the state-
dependent service policy and established a reward-
cost function, using the PSO algorithm to obtain the
optimal strategy. Compared with related service
strategies, managers get more benefits. Wang et al.
(2019) analyzed RMRP with working breakdowns
under the N policy, proposing a profit function and
using the PSO algorithm to determine the optimum
number of warm standbys, fast service rates, and slow
service rates. Yang et al. (2020) considered an M/M/2
queue with two heterogeneous servers. They
constructed a cost function and determined the
optimal solutions by using PSO algorithm. Zhang and
Wang (2017) studied an M/G/1 retrial queue with
setup times and used the PSO algorithm to find the
optimal reserved idle time for maximizing profit.
The rest of the paper is organized as follows. The
model descriptions and assumptions of the RMRP
with warm standby components and imperfect
coverage are presented in Section 2. By using the
matrix-analytic method, Section 3 provides the
derivations of the steady-state probabilities of the
number of failed components in the retrial orbit. The
effects of various system parameters on the system
performance measures are investigated in Section 4.
The total expected cost function to determine the
optimal solutions and perform sensitivity analysis is
shown in Section 5. Finally, the conclusion will be
shown in Section 6 of this paper.
2 THE MODEL DESCRIPTIONS
We consider the RMRP with
N=M+S
identical
components and a single server in the repair facility.
As many as
M
of these components can operate at
the same time, while the rest of the
S
components are
warm standbys. The assumptions of the model are
described as follows:
(1) Primary components are subject to breakdowns
according to the independent Poisson process
with parameter
λ
.
(2) Warm standby components are subject to
breakdowns according to independent Poisson
process with parameter
α
(
0<<
αλ
).
(3) When one of the primary components fails, it is
instantly replaced by an available warm standby
component. When a warm standby moves into
operating state, its failure characteristics will be
that of a primary component.
(4) Whenever a component fails, it will be sent to the
server immediately, where the repair is provided
in the order of their breakdowns, that is, the first-
come, first-served discipline.
(5) The repair times at this repair facility follow
exponential distribution with parameter
μ
.
(6) The server can only repair one failed component
at a time. Once a failed component is repaired, it
becomes as good as new.
(7) The probability of successful recovery on the
failure of a primary component (or warm standby
component) is denoted as
c
. Quantity
c
, which
is included in the probabilities of successful
detection, location, and recovery from a failure, is
known as the coverage factor or coverage
probability
(8) The unsafe failure state of the system in any one
of the breakdowns is not covered.
(9) Primary component (or warm standby component)
failure in the unsafe failure state is cleared by a
reboot. Reboot delay follows exponential
distribution with parameter
β
.
(10) When a primary or warm standby component
fails and finds that the server is busy in repairing
another failed component, it will be sent to the
retrial queue (orbit).
(11) Failed components in the retrial queue repeat its
request for service with an exponential random
period of retrial time at rate
γ
.
(12) When the time waiting in the retrial queue
terminates, the failed component will get the
repair if the server is idle; otherwise, it will
again be sent to the retrial queue for another
random period.
(13) The failure times, repair times, retrial times, and
reboot delay times are mutually independent
from each other.
3 STEADY-STATE RESULTS
In this RMRP with imperfect coverage, we describe
the system states by the pairs
(, )ij
.
0i =
means
that the server is idle,
1i =
shows that the server is
busy,
j
n=
denotes that there are
n
failed
components in the retrial orbit and the system is in a
safe failure state, and
n
juf=
represents that there
are
n
failed components in the retrial orbit and the
system is in an unsafe failure state.
The mean failure rate of a primary component
n
λ
is given by
(),0 1,
(), .
n
MSn nS
M
Sn S n N MS
λα
λ
λ
+− ≤≤−
=
+− ≤< = +
The following steady-state probabilities are
employed throughout this paper:
ICORES 2025 - 14th International Conference on Operations Research and Enterprise Systems
302
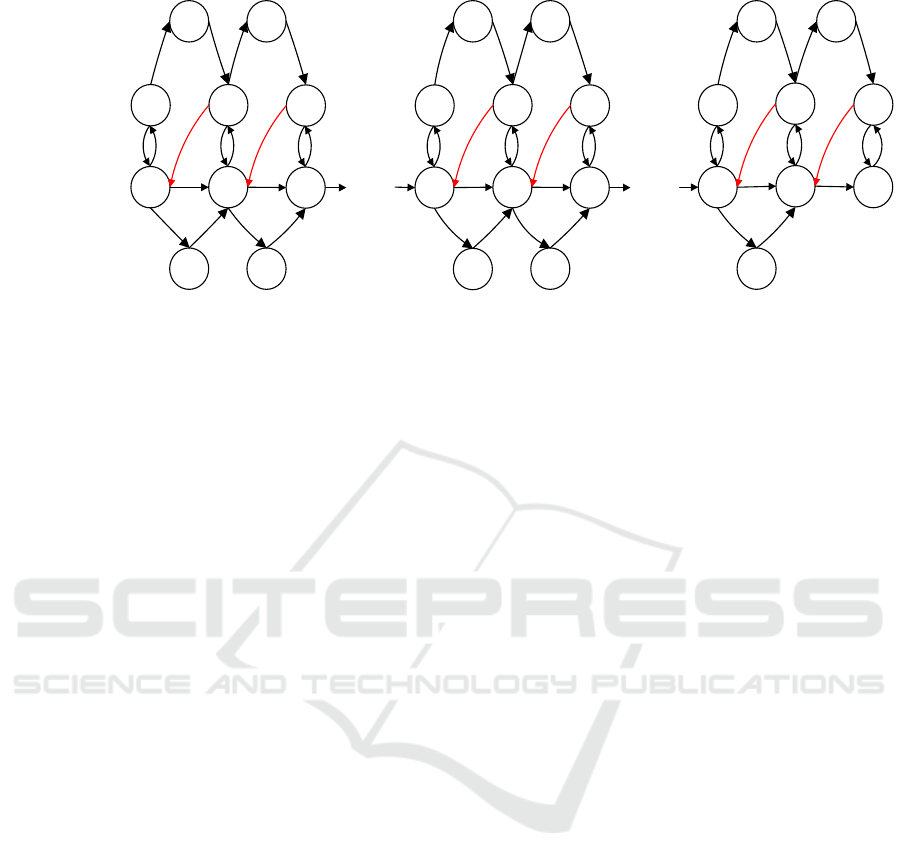
0,0 0,1
0,2
...
...
0, 1n −
0, n
0, 1n +
...
...
0, 3N −
1n
c
λ
−
N3
c
λ
−
0
c
λ
1,0 1,1
1,2
...
1, 1n −
1, n
1, 1n +
...
1, 3N −
1
c
λ
n
c
λ
1n
c
λ
+
... ...
Idle
Uncover
Idle
Cover
Busy
Cover
μ
μ
μ
μ
μ
μ
μ
Busy
Uncover
2
c
λ
γ
2
γ
n
γ
(1)n
γ
+
0
0, uf
1
0, uf
1
0,
n
uf
−
0,
n
uf
N
-3
0, uf
0
1, uf
1
1, uf
1
1,
n
uf
−
1,
n
uf
N
-3
1, uf
0, 2N −
1, 2N −
N-2
c
λ
μ
(N-2)
γ
1
c
λ
2
c
λ
n
c
λ
1n
c
λ
+
N-2
c
λ
β
β
β
β
β
β
β
β
β
β
0
(1- )c
λ
1
(1- )c
λ
1
(1- )c
λ
2
(1- )c
λ
n-1
(1- )c
λ
n
(1- )c
λ
n
(1- )c
λ
n+1
(1- )c
λ
N-2
(1- )c
λ
N-3
(1- )c
λ
N
-2
0, uf
0, 1N −
1, 1N −
N-2
(1- )c
λ
β
(N-1)
γ
N-1
λ
N-1
λ
μ
Figure 1: State-transition-rate diagram of RMRP with warm standby components and imperfect coverage.
0, n
P ≡ probability that there are
n
failed units in
the retrial orbit when the server is idle and
the system is in a safe failure state (cover),
where
n = 0, 1, 2, …,
N1−
;
1, n
P ≡ probability that there are
n
failed units in
the retrial orbit when the server is busy and
the system is in a safe failure state (cover),
where
n = 0, 1, 2, …,
N1−
;
,
n
0uf
P ≡ probability that there are
n
failed units in
the retrial orbit when the server is idle and
the system is in an unsafe failure state (not
covered), where
n = 0, 1, 2, …,
N2−
;
,
n
1uf
P ≡ probability that there are
n
failed
components in the retrial orbit when the
server is busy and the system is in an unsafe
failure state (not covered), where
n = 0, 1,
2, …,
N3−
.
3.1 Steady-State Equations
Referring to the diagram displayed in Figure 1, the
equilibrium equations are deduced as follows:
1,0 0 0,0
pp
μ
λ
= (1)
1
0,uf 1, 0,
(),1 1
j
jj j
pp jpjN
βμ
λ
γ
−
+=+ ≤≤− (2)
00,0 0,1 11,0
()cp p p
λ
γμ
λ
+=+ (3)
1
0, 1, 1 0, 1 1,uf
11,
()(1)
(),1 2
j
jjj j
jj
cp p j p p
pjN
λγβ
μλ
−
−+
+
+++ +
=+ ≤≤−
(4)
1 0,1 1,2 1,1
()
NN N N
pp p
λ
μ
−− − −
+= (5)
0, 0,uf
(1 c) , 0 2
j
jj
pp jN
λ
β
−= ≤≤− (6)
1, 1,uf
(1 c) , 0 3
j
j+1 j
pp jN
λ
β
−= ≤≤− (7)
3.2 Matrix-Analytic Method
The matrix-analytic method was first introduced by
Neuts (1981) while studying the embedded Markov
chains of many queueing systems. Because of the
high complexity of this RMRP with imperfect
coverage, the matrix-analytic method is employed to
derive the steady-state probabilities
,ij
p . By
appropriately arranging the system states, the
corresponding transition rate matrix
Q
of this
Markov chain can be established as the following
block tridiagonal form:
01
12
23
3
.
0
1
2
3
N4
N4 N3
N4 N3 N2
N3 N2 N1
N2 N1
−
−−
−−−
−−−
−−
=
Q
BC
ABC
ABC
AB
A
C
BC
ABC
ABC
AB
(8)
Each element of the matrix
Q
is a submatrix, which
may be listed as follows:
1
1
(1 ) 0 0
00
,0 ,
00
00 (1)
n
n
n
nn
n
c
n
nN3
c
c
βλ
λγ μ
λμλ
λβ
+
+
−−
−−
=≤≤−
−−
−−
B
(1 ) 0
0() ,
0
N2
N2 N2
N2 N1
c
N2
c
βλ
λγμ
λμλ
−
−−
−−
−−
=−−−
−−
B
,
N1
N1
N1
(N 1)
λγμ
λμ
−
−
−
−−−
=
−
B
Cost Optimization Analysis of Retrial Machine Repair Problem with Warm Standby Components and Imperfect Coverage
303

0000
0000
,1
000
0000
n
nN3
n
γ
=≤≤−
C
,
000
000
,
00
000
N2
(N 2)
γ
−
=
−
C
00
00,
0
N1
(N 1)
γ
−
=
−
C
00 0 0
000
,0 ,
00
00 0 0
n
n+1
nN4
c
β
λβ
=≤≤−
A
00 0 0
000,
00
N3
N2
c
β
λβ
−
−
=
A
00
.
00
N2
N1
β
λ
−
−
=
A
It should be noted that the matrix
Q
has a non-
homogeneous quasi-birth-death process. Let
P
denote the corresponding steady-state probability
vector of
Q
. By partitioning the vector
P
as
01 3 2 1
[,, , , , ]
T
NNN−−−
=Ppp p p p
, where
T
0, 0, 1, 1,
[,,,],
nn
nufnnuf
pppp=p
(
0 nN3≤≤ −
) are
column vectors with dimension
41×
,
0, 0, 1,
[,,]
N2
T
N2 uf N2 N2
ppp
−
−−−
=p
is a
31×
column
vector, and
0, 1,
[,]
T
N1 N1 N1
pp
−−−
=p
is a
21×
column vector, the equilibrium equation
43N −
=QP O
can be rewritten as follows:
00 11 4
,+=Bp Cp O
(9)
11 11 4
,1 3
nn nn nn
nN
−− ++
++ =≤≤−Ap Bp Cp O
(10)
33 22 11 3NN NN NN−− −− −−
++=Ap Bp Cp O
(11)
22 11 2NN NN−− −−
+=Ap Bp O
(12)
where
s
O
is a zero column vector with dimensions
1
s
×
.
3.3 Steady-State Solutions
Based on Equations (9)-(12), we have the following:
1
011 1 01
,where ,
−
==−pXp X BC
(13)
()
11
1
11 1
, where
,1 2
nnn
nnnnn
nN
++
−
+− +
=
=− + ≤ ≤ −
pXp
XAXBC
(14)
()
()
1
,where
N2 N1 N1 N1 2
N1 N3 N2 N2 N1
−− − −
−
−−−−−
+=
=− +
AX B p O
XAXBC
(15)
Consequently,
n
p
,
0 nN2≤≤ −
can be
represented in term of
N1−
p
as
1
12
1
,
n
nnn N1N1 iN1
iN1
nN1
+
++ −− −
=−
+−
==
=
∏
pXX Xp Xp
Φp
(16)
where
1
1
n
ni
iN1
+
+
=−
=
∏
ΦX
,
0,1, ...,nN2.=−
Finally, the probability
N1−
p
can be derived from
Equation (15). The following normalizing equation is
derived from:
0
1
0
1
N3
TT T
4n 3N2 2N1
n
N3
TT T
4n 3N1 2 N1
n
−
−−
=
−
+− −
=
++
=++=
ep ep ep
eΦ eΦ e p
(17)
where
s
e
denotes an identity column vector with
dimensions
1
s
×
. Once the probability
1N −
p
has
been determined, the remaining probability vectors
can be derived recursively according to Equation (16).
Then, the desired system performance measures can
be obtained on the basis of these probability vectors.
The solution algorithm for the steady-state
probability vectors is described in the following
subsection.
3.4 The Solution Algorithm
INPUT: Number of primary and warm standby
components
,)(M S
,
Q
matrix
OUTPUT: Steady-state probability vectors
Step 1: Set
1
101
−
=−XBC
.
Step 2: For
n
from 1 to
N2−
, set
()
1
11 1nnnnn
−
+− +
=− +XAXBC
.
Step 3: Set
()
1
N1 N3 N2 N2 N1
−
−−−−−
=− +XAXBC
.
Step 4: For
n
from 1 to
N1−
, set
1nn N3N2N−−−
=ΦXXXX
.
Step 5: Solve
()
N2 N1 N1 N1 2−− − −
+=AX B p O
and
the normalization condition
1
0
1
N3
TT T
4n 3N1 2 N1
n
−
+− −
=
++ =
eΦ eΦ e p
simultaneously, to obtain the probability
N1−
p
.
Step 6: For
0 nN2≤≤ −
, the probability
n
p
is
constructed as follows:
1nnN1+−
=pΦp
.
ICORES 2025 - 14th International Conference on Operations Research and Enterprise Systems
304
4 SYSTEM PERFORMANCE
MEASURES
We define system performance measures of the
RMRP with warm standby components and imperfect
coverage as follows:
[]EN ≡
the expected number of failed components in
the retrial orbit;
[]
C
EN ≡
the expected number of failed components
in the retrial orbit when the system is in a
safe failure state (cover);
[]
NC
EN ≡
the expected number of failed components
in the retrial orbit when and the system is
in an unsafe failure state (not cover);
[]ES ≡
the expected number of warm standby
components in the retrial orbit;
[]EO ≡
the expected number of primary components
in the retrial orbit;
NC
P ≡
the probability of failed components in the
retrial orbit when and the system is in an unsafe
failure state (not cover);
AV ≡
the probability of the number of failed units is
less than or equal to the number of warm
standby units.
We can compute
[]EN
,
[]
C
EN
,
[]
NC
EN
,
[]ES
, and
[]EO
from the following equations.
23
0, 1, 0,uf 1,uf
[] ( )
nn
N1 N N
nn
n0 n0 n0
EN np p np np
−−−
===
=+++
(18)
0, 1,
[] ( )
N1
Cnn
n0
EN np p
−
=
=+
(19)
23
0,uf 1,uf
[]
nn
NN
NC
n0 n0
E N np np
−−
==
=+
(20)
0,uf 0, 1, ,uf
0
[] ( )(
nn
S
nn1
n
ES S n p +p p +p )
=
=− +
(21)
[] [ ] [],EO N EN ES=− −
(22)
23
0,uf 1,uf
nn
NN
NC
n0 n0
P= p p
−−
==
+
(23)
0,uf 0, 1, ,uf
0
()
nn
S
nn1
n
AV= p +p p +p
=
+
(24)
The base case for the setting of system
parameters is listed below:
15,M =
10,S =
0.16,
λ
=
2.0,
μ
=
0.08,
α
=
6.0,
β
=
15.0,
γ
=
0.9c =
.
This section first studies how each parameter
affects system performance measures by the change
of each system parameter value. Except for
15M=
(which is always fixed), each system parameter takes
turn changing in a certain range while keeping other
system parameters fixed at the level of the base case.
We consider seven cases with various values of
system parameters. The numerical results are shown
in Figures 2-3.
Case 1:
2.0
μ
=
,
0.08
α
=
,
6.0
β
=
,
15.0
γ
=
,
0.9c =
,
λ
varies from 0.12 to 0.26;
Case 2:
0.16
λ
=
,
0.08
α
=
,
6.0
β
=
,
15.0
γ
=
,
0.9c =
,
μ
varies from 1.0 to 10.0;
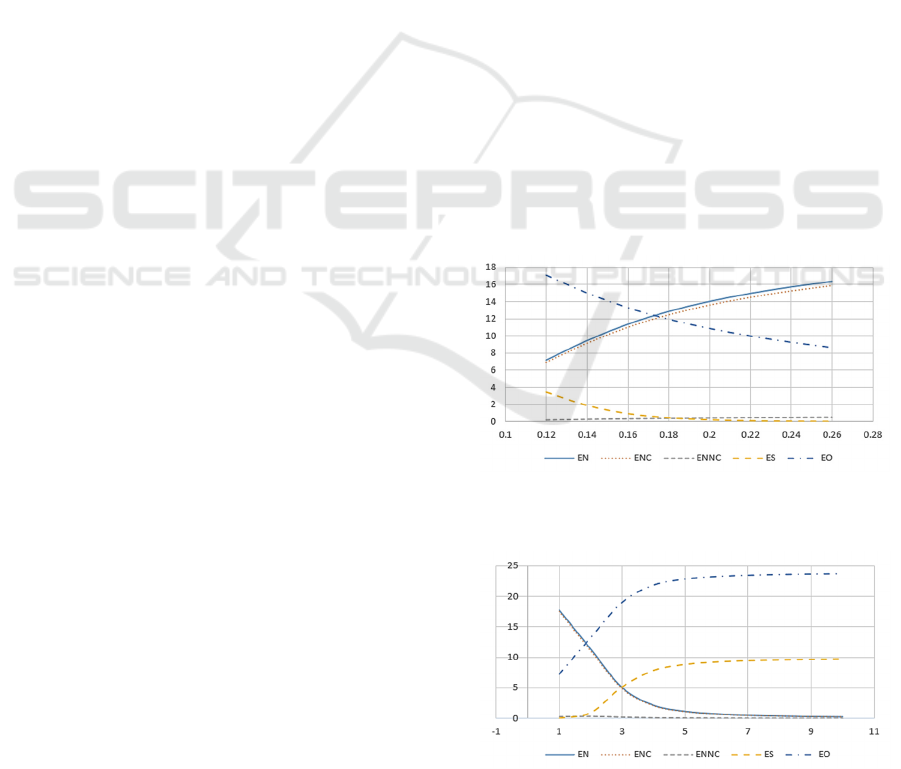
In Figure 2, we find that (i)
[]EN
,
[]
C
EN
,
[]EO
, and
AV
are significantly affected by
λ
; (ii)
[]ES
is slightly affected by
λ
; and (iii)
[]
NC
EN
and
NC
P
seems too insensitive to change in
λ
. In
Figure 3, we find that (i)
[]EN
,
[]
C
EN
,
[]ES
,
[]EO
,
AV
are significantly affected by
μ
; and (ii)
[]
NC
EN
and
NC
P
are slightly affected by
μ
.
Figure 2: System performance measures versus various
values of
λ
.
Figure 3: System performance measures versus various
values of
μ
.
Cost Optimization Analysis of Retrial Machine Repair Problem with Warm Standby Components and Imperfect Coverage
305
5 COST OPTIMIZATION
ANALYSIS
Several researchers have investigated the study of
retrial queue involving cost optimization analysis.
They aimed at determining the optimal number of
servers, optimal service rate, optimal repair rate, and
so on. We construct the expected cost function per
unit time for the RMRP with warm standby
components and imperfect coverage where
S
,
μ
,
and
γ
are decision variables. Our main goal is to
determine the optimal value of
(, ,)S
μγ
, say
ˆ
ˆ
ˆ
(, ,)S
μγ
, so as to minimize the cost function. The
cost elements are defined as follows:
1
C ≡
cost per unit time per failed component in the
retrial orbit when the system is in a safe failure
state (cover);
2
C ≡
cost per unit time per failed component in the
retrial orbit when the system is in an unsafe
failure state (not cover);
3
C ≡
cost per unit time of probability of
NC
P
;
4
C ≡
cost per unit time of unavailability
1 AV−
;
5
C ≡
cost per unit time of providing the service rate
μ
;
6
C ≡
cost per failed component in retrial orbit by
providing the retrial rate
γ
.
Based on all of the cost elements listed above,
the expected cost per unit time is constructed as
follows:
12 3
46
(, ,) [ ] [ ]
(1 ) .
CNCNC
5
TC S C E N C E N C P
C AV C +C
μγ
μγ
=+ +
+−+
(25)
Thus, the cost minimization problem can be
expressed mathematically as
,,
ˆ
ˆ
ˆ
(, ,) (, ,).
S
TC S Minimize TC S
μγ
μγ μγ
=
5.1 Sensitivity Analysis
As the following numerical examples, we consider
the cost elements as follows:
12 3 56
$60, $12 , $2 , $48 , $9 , $3 .
4
CC0C40C0C0C0== = = ==
To examine the effect of system parameters on
the cost function, a sensitivity analysis in six cases is
provided for
M=15
with various values of
S = 3, 5, 7,
respectively.
Case 1:
2.0
μ
=
,
0.08
α
=
,
6.0
β
=
,
15.0
γ
=
,
0.9c =
,
λ
varies from 0.12 to 0.26;
Case 2:
0.16=
λ
,
0.08
α
=
,
6.0
β
=
,
15.0
γ
=
,
0.9c =
,
μ
varies from 1.0 to 10.0;
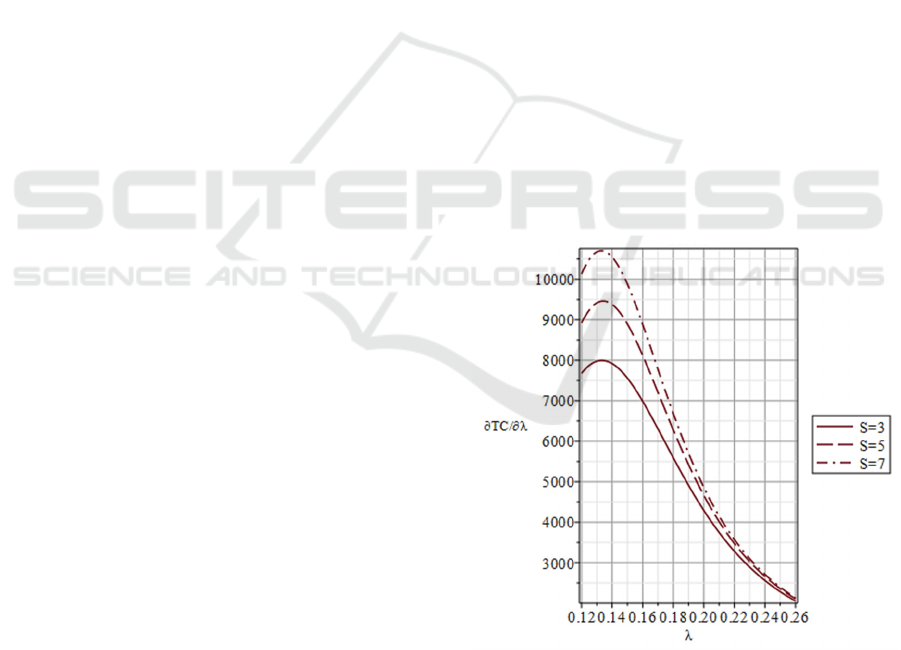
The numerical results of the above four cases are
shown in Figures 4-5, which depicts the sensitivity
performance of cost function
TC
o n
λ
,
α
,
β
,
μ
,
γ
, a n d
c
, respectively. It is important to note
that the sign of sensitivity indicates an increase or
decrease in the expected cost by changing the values
of system parameters. Figure 4 reveals that (i)
/TC
λ
∂∂
is positive, which means that
TC
increases as
λ
increases for all
S
; (ii)
/TC
λ
∂∂
has the highest point at around
0.13
λ
=
for all
S
;
and for (iii), as
λ
is fixed,
/TC
λ
∂∂
gets larger as
S
increases. Figure 5 shows that (i)
/TC
μ
∂∂
changes from negative to positive, which means that
TC
changes from a decrease to an increase on
μ
for all
S
; (ii) as
μ
is fixed,
/TC
μ
∂∂
gets
smaller as
S
increases; and when (iii) as
μ
i s
greater than 4,
/TC
μ
∂∂
is similar for all
S
.
Figure 4: Sensitivity analysis of
TC
with respect to
λ
for different
S
.
ICORES 2025 - 14th International Conference on Operations Research and Enterprise Systems
306
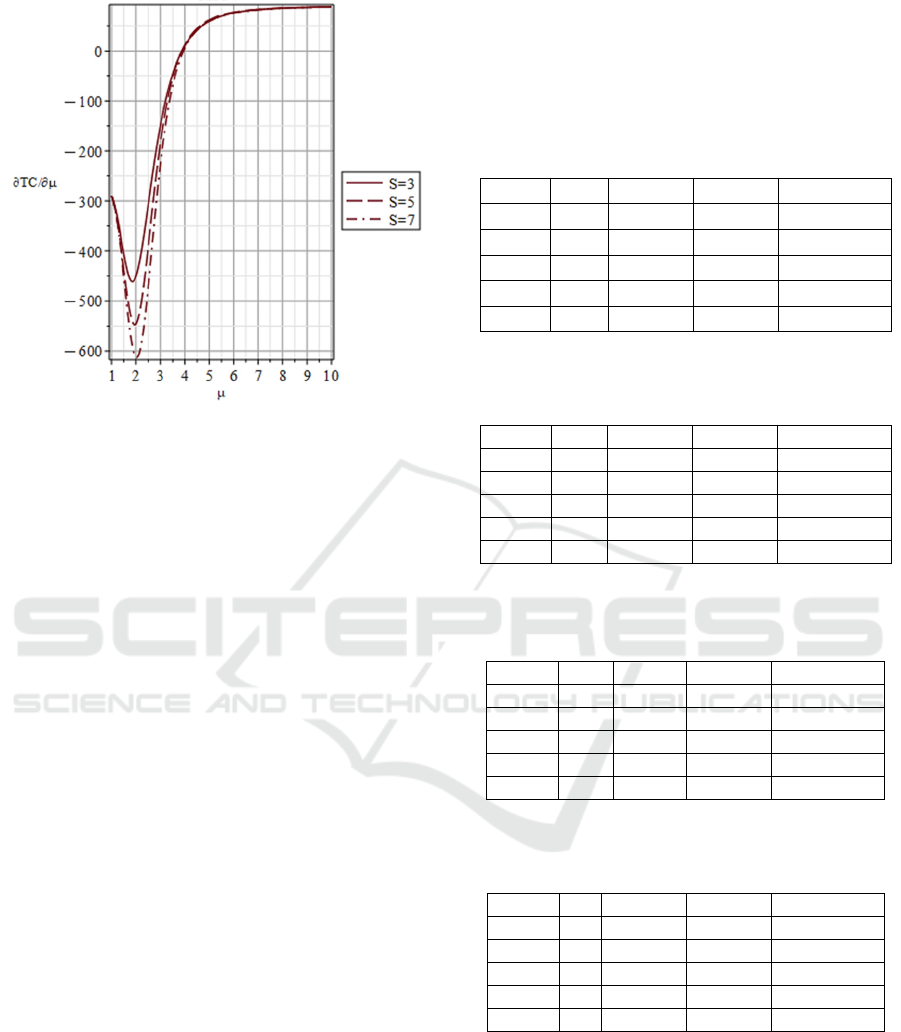
Figure 5: Sensitivity analysis of
TC
with respect to
μ
for different
S
.
5.2 Cost Optimization
The PSO algorithm was first proposed by Kennedy
and Eberhart (1995) and works with a population of
particles where one procedure includes exploitation
optimization searches. As the following numerical
examples, we consider the cost elements as follows:
12 3
56
$60, $12 , $2 ,
$48 , $9 , $3 .
4
CC0C40
C0C0C0
== =
===
The PSO algorithm is applied to find the approximate
optimization solution
ˆ
ˆ
ˆ
,,(S )
μγ
and minimum cost
ˆ
ˆ
ˆ
(, ,)TC S
μγ
. Since the PSO algorithm does not need
to compute the gradient, it is flexible for non-
differentiable cost functions. Moreover, it can be
implemented to handle optimization problems with a
mixture of discrete and continuous decision variables.
We first fix
15
M
=
and consider various values of
λ
,
α
,
β
, and
c
. Then, after setting the different
ranges of decision variables
S
,
μ
,
γ
by
110S≤≤
,
0.1 10.0
μ
≤≤
, a n d
0.1 20.0
γ
≤≤
, w e
use computer software Maple for numerical
investigation. The detailed optimal solution
ˆ
ˆ
ˆ
(, ,)S
μγ
, minimum cost
ˆ
ˆ
ˆ
(, ,)TC S
μγ
and related
parameters are shown in Tables 1-4. We observe from
Tables 1-4 that (i) the optimal number of warm
standby components
ˆ
S
increases as
λ
increases;
(ii) the optimal number of warm standby components
ˆ
S
decreases as
α
increases; (iii) the optimal
number of warm standby components
ˆ
S
is the same
even though
β
varies from 4.0 to 8.0 and
c
varies
from 0.6 to 1.0; (iv)
ˆ
ˆ
ˆ
(, ,)TC S
μγ
increases as
λ
or
α
increases; and (v)
ˆ
ˆ
ˆ
(, ,)TC S
μγ
decreases as
β
or
c
increases. Intuitively, the optimal number of
warm standby components
ˆ
S
is significantly
affected by
λ
and
α
, but seems too insensitive to
change in
β
and
c
.
Table 1: The optimal results for various values of
λ
with
0.08
α
=
,
6.0
β
=
, and
0.9c =
.
λ
ˆ
S
ˆ
μ
ˆ
γ
ˆ
ˆ
ˆ
(, ,)TC S
μγ
0.12 4 3.435 2.493 519.127
0.14 5 3.854 2.711 579.451
0.16 5 4.268 2.967 637.675
0.18 5 4.672 3.216 694.645
0.20 5 5.066 3.457 750.483
Table 2: The optimal results for various values of
α
with
0.16
λ
=
,
6.0
β
=
, and
0.9c =
.
α
ˆ
S
ˆ
μ
ˆ
γ
ˆ
ˆ
ˆ
(, ,)TC S
μγ
0.04 6 4.215 2.899 622.923
0.06 5 4.247 2.957 631.115
0.08 5 4.268 2.967 637.675
0.10 5 4.288 2.976 644.031
0.12 4 4.300 3.052 648.612
Table 3: The optimal results for various values of
β
with
0.16
λ
=
,
0.08
α
=
, and
0.9c =
.
β
ˆ
S
ˆ
μ
ˆ
γ
ˆ
ˆ
ˆ
(, ,)TC S
μγ
4.0 5 4.272 2.977 644.166
5.0 5 4.270 2.971 640.304
6.0 5 4.268 2.967 637.675
7.0 5 4.267 2.964 635.770
8.0 5 4.266 2.962 634.327
Table 4: The optimal results for various values of
c
with
0.16
λ
=
,
0.08
α
=
, and
6.0
β
=
.
c
ˆ
S
ˆ
μ
ˆ
γ
ˆ
ˆ
ˆ
(, ,)TC S
μγ
0.6 5 4.242 3.346 689.743
0.7 5 4.250 3.223 673.331
0.8 5 4.259 3.096 656.009
0.9 5 4.268 2.967 637.675
1.0 5 4.279 2.834 618.210
6 CONCLUSIONS
This article considers the RMRP with warm standby
components and imperfect coverage. Steady-state
results are computed numerically with the matrix-
analytic technique. We have performed the sensitivity
analysis of system performance measures with
Cost Optimization Analysis of Retrial Machine Repair Problem with Warm Standby Components and Imperfect Coverage
307

respect to various system parameters. By using the
PSO algorithm, we determine the joint optimal values
of the number of warm standbys, the repair rate, and
the retrial rate simultaneously to minimize the
expected cost. The PSO algorithm can be applied to
analyze the complex optimization problems that
occur in various retrial queues (or RMRP). Under
optimal operating conditions, we illustrate our results
by discussing several cases of numerical examples.
The experimented results are helpful for managers to
make decisions. Moreover, the results obtained
provide further insight into the RMRP with warm
standby components and imperfect coverage.
REFERENCES
Artalejo, J. R. (1999a). Accessible bibliography on retrial
queues. Mathematical and Computer Modelling: An
International Journal, 30(3-4), 1-6.
Artalejo, J. R. (1999b). A classified bibliography of
research on retrial queues: progress in 1990–1999. Top,
7(2), 187-211.
El-Sherbeny, M. S., & Hussien, Z. M. (2019). Cost analysis
of series systems with different standby components
and imperfect coverage. Operations Research and
Decisions, 29(2), 21-41.
Falin, G. (1990). A survey of retrial queues. Queueing
systems, 7, 127-167.
Jain, M., & Meena, R. K. (2017). Fault tolerant system with
imperfect coverage, reboot and server vacation. Journal
of Industrial Engineering International, 13, 171-180.
Kennedy, J., & Eberhart, R. (1995, November). Particle
swarm optimization. In Proceedings of ICNN'95-
international conference on neural networks (Vol. 4, pp.
1942-1948). ieee.
Neuts, M. F. (1981). Matrix Geometric Solutions in
Stochastic Models: An Algorithmic Approach, The
John Hopkins University Press, Baltimore.
Wang, K. H., Liou, C. D., & Lin, Y. H. (2013). Comparative
analysis of the machine repair problem with imperfect
coverage and service pressure condition. Applied
Mathematical Modelling, 37(5), 2870-2880..
Wang, K. H., Su, J. H., & Yang, D. Y. (2014). Analysis and
optimization of an M/G/1 machine repair problem with
multiple imperfect coverage. Applied Mathematics and
Computation, 242, 590-600.
Wang, K. H., Wang, J., Liou, C. D., & Zhang, X. (2019).
Particle swarm optimization to the retrial machine
repair problem with working breakdowns under the N
policy. Queueing Models and Service Management,
2(1), 61-82.
Wang, K. H., Yen, T. C., & Fang, Y. C. (2012). Comparison
of availability between two systems with warm standby
units and different imperfect coverage. Quality
Technology & Quantitative Management, 9(3), 265-
282.
Wang, K. H., Yen, T. C., & Jian, J. J. (2013). Reliability and
sensitivity analysis of a repairable system with
imperfect coverage under service pressure condition.
Journal of Manufacturing systems, 32(2), 357-363.
Wu, C. H., Yen, T. C., & Wang, K. H. (2021). Availability
and comparison of four retrial systems with imperfect
coverage and general repair times. Reliability
Engineering & System Safety, 212, 107642.
Yang, D. Y., Chen, Y. H., & Wu, C. H. (2020). Modelling
and optimisation of a two-server queue with multiple
vacations and working breakdowns. International
Journal of Production Research, 58(10), 3036-3048.
Yang, T., & Templeton, J. G. C. (1987). A survey on retrial
queues. Queueing systems, 2, 201-233.
Yen, T. C., & Wang, K. H. (2020). Cost benefit analysis of
four retrial systems with warm standby units and
imperfect coverage. Reliability Engineering & System
Safety, 202, 107006..
Zhang, Y., & Wang, J. (2017). Equilibrium pricing in an
M/G/1 retrial queue with reserved idle time and setup
time. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 49, 514-530.
Zhang, X., Wang, J., & Ma, Q. (2017). Optimal design for
a retrial queueing system with state-dependent service
rate. Journal of Systems Science and Complexity, 30(4),
883-900..
ICORES 2025 - 14th International Conference on Operations Research and Enterprise Systems
308
