
Impact of Feature Extraction Optimization on Machine Learning Models
for sEMG-Based Prosthesis Control
Ricardo Henrique Avelar Matheus and Maria Claudia F. Castro
a
Department of Electrical Engineering, Centro Universit
´
ario FEI, Brazil
Keywords:
sEMG, Machine Learning, Feature Extraction, LDA, RMS, Amputees.
Abstract:
One of the most significant challenges to the quality of life for amputees is the development of prostheses
that can closely simulate the capabilities of the lost limb. One possible solution to this problem is myo-
electric prostheses, which are devices that use myolectric signals as users’ intention to perform independent
movements. This study aims to investigate how optimizing feature extraction methods can impact the perfor-
mance of machine learning models in recognizing surface electromyogram (sEMG) signals from amputees.
The LibEMG library in Python, which offers a simple and robust API for developing sEMG-based projects,
was used alongside the DB8 dataset from the NINAPRO public database, which promotes machine-learning
research in human, robotic, and prosthetic hands. A total of twelve feature extraction methods and seven dif-
ferent classifiers were tested. The results showed the best mean accuracy of 79.18% using a Random Forest
classifier with a set of eleven time and frequency domain features, considering the data of an amputee with
experience in using myoelectric prostheses. However, the most affected models by feature optimization were
KNN, MLP, and SVM, with accuracy improvements up to 69.28%.
1 INTRODUCTION
One of the most discussed social issues today is ac-
cessibility and quality of life, particularly for individ-
uals with disabilities. Specifically, for people with
upper-limb amputations, one of the most significant
challenges is the development of prostheses that can
closely simulate the capabilities of the lost limb. One
possible solution to this problem is myoelectric pros-
theses, devices that use myolectric signals as users in-
tend to perform independent movements, mimicking
the functions of a healthy limb (Andrade, 2007).
The common and affordable myoelectric prosthe-
ses available today are primarily based on the tim-
ing and number of electrical pulses generated by the
user within a specific period, limiting their ability
to perform independent movements. Machine learn-
ing techniques can enhance the number of move-
ments required to make these prostheses increas-
ingly autonomous, natural, and more intuitive to the
user. Generally, classification techniques are em-
ployed to recognize patterns in surface electromyo-
graphy (sEMG) signals from various muscles so that
the prosthesis can identify the user’s intended move-
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2751-0014
ment and respond according to the signal.
One of the ongoing research efforts in this field is
the development of more efficient recognition mod-
els with higher accuracy for as many movements as
possible. However, most of the literature is applied
to health volunteer sEMG data (Sultana et al., 2023;
Song et al., 2023). Atzori et al. (2023) compared
the classification of 53 movements between one indi-
vidual with a transradial amputation and a database
of individuals with intact upper limbs. Using a K
— Nearest Neighbors (k-NN) classifier resulted in an
average accuracy of 61.51% for the amputee, com-
pared to 80.16% for the non-amputees. In the same
study, another test reducing the number of movements
to 13 resulted in 100% accuracy, exceeding those re-
ported in the literature by the author, such as 95%
accuracy for six movements using Principal Compo-
nent Analysis (PCA) and Support Vector Machine
(SVM) (Castellini et al., 2009), 84.4% accuracy for
ten movements using time-domain features and Lin-
ear Discriminant Analysis (LDA) (Li et al., 2010),
and 87.8% accuracy for twelve movements also us-
ing time-domain features but with MLP (Tenore et al.,
2009). Using MyoArmband, a device with a low-
frequency sEMG acquisition, Cognolato et al. (2018)
found significant accuracy discrepancies reached by
Matheus, R. H. A. and Castro, M. C. F.
Impact of Feature Extraction Optimization on Machine Learning Models for sEMG-Based Prosthesis Control.
DOI: 10.5220/0013173300003911
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 18th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2025) - Volume 1, pages 907-913
ISBN: 978-989-758-731-3; ISSN: 2184-4305
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
907

transradial amputees, ranging from 50% to 97.2%,
where a user of a myoelectric prosthesis achieved the
best.
The performance discrepancies between health
and amputees emphasize the importance of includ-
ing amputee data in developing these models. In the
literature, we also observed a significant variance in
the accuracies achieved with amputee data. Factors
such as user experience and training with myoelec-
tric prostheses, the number of movement classes, type
of movement, classifiers used, and feature extraction
methods also influence the classification outcome.
Thus, the general objective of this study was to an-
alyze a classification model using various classifiers
and feature extraction methods to achieve the best re-
sults in terms of accuracy, precision, recall, and F1
score. For this purpose, the dataset provided by the
NINAPRO online library, which included nine move-
ment classes and data from a single transradial am-
putee, was used.
2 METHODS
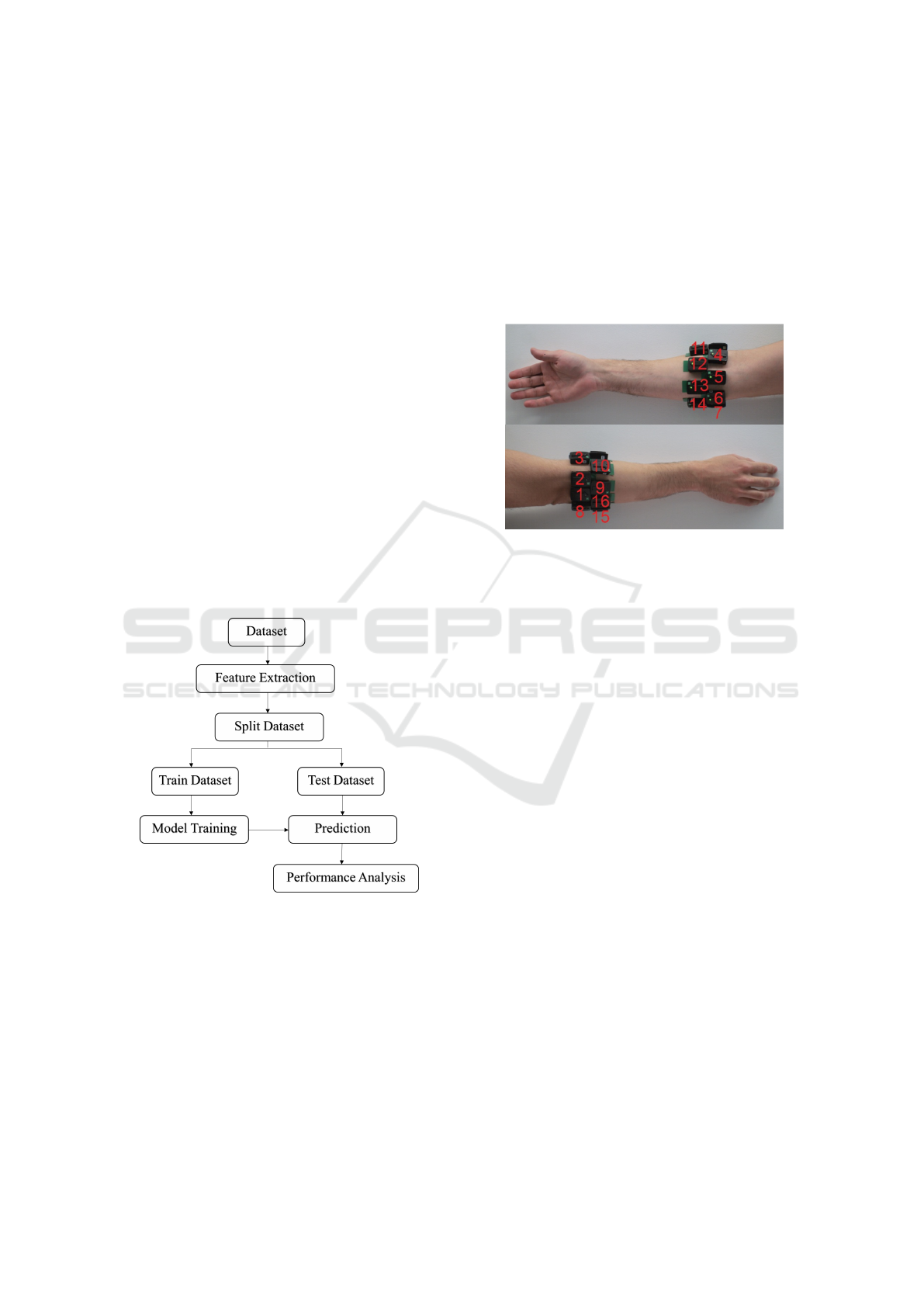
The proposed methodology is shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1: Methodology Workflow.
2.1 Dataset
The DB8 dataset, available in (NINAPRO multimodal
database, 2024) and described in detail in (Krasoulis
et al., 2019), consists of sEMG, IMU, and kinematic
data from 12 subjects, two of whom have transradial
amputations. For this study, only sEMG data from
both amputee subjects were considered. Both subjects
were male, with a right-hand amputation; subject 11
(S11) was 30 years old with no experience using my-
oelectric prostheses, while subject 12 (S12) was 56
with 2 years of experience using myoelectric prosthe-
ses.
Data acquisition was performed using 16 Delsys
Trigno IM Wireless sEMG system sensors placed on
the user’s forearm to capture the surface EMG at a
sampling frequency of 2kHz. No specific muscle was
chosen as the focus of acquisition. The positions of
the electrodes are shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2: sEMG sensors location (Krasoulis et al., 2019).
Three datasets were collected: the first two
with ten repetitions and the latter with two repeti-
tions of nine movements, including rest, thumb flex-
ion/extension and abduction/adduction, finger flex-
ion/extension (index, middle, and a combination of
ring and pinky fingers), and three types of functional
grasps: pointing index, cylindrical, lateral, and tripod
grip. All participants were asked to perform bilateral
mirrored movements (with both arms). These move-
ments are shown in figure 3.
2.2 LibEMG
For data processing, feature extraction methods, clas-
sifier testing, and evaluation, a Python library called
LibEMG was used. This library, created by (Eddy
et al., 2023), aims to provide a simple and robust API
for developing sEMG-based projects online and of-
fline.
The library offers several resources to streamline
the processes of signal reading and processing, filter-
ing, feature extraction, and selection, using various
methods commonly used in sEMG research, pattern
classification, and model result evaluation.
In this case, the built-in function of the library was
used to organize the datasets. The function separates
signals by their classes and repetitions, generating a
set of 90 files that were split into training and testing
datasets in an 80/20 ratio.
BIOSIGNALS 2025 - 18th International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
908

Figure 3: Acquisition protocol (Krasoulis et al., 2019).
2.3 Feature Extraction
Feature extraction aims to extract meaningful infor-
mation from the sEMG signal and is used later by the
classifiers (Spiewak et al., 2018). When dealing with
sEMG signals, owing to their time-based representa-
tion, feature-extraction methods commonly focus on
both the frequency and amplitude of the signal (Has-
san et al., 2020; Negi et al., 2016). Based on this,
LibEMG offers several methods commonly used in
the literature for sEMG signal analysis that can be ap-
plied individually or in groups. Twelve methods were
employed in this study.
• Discrete Fourier Transform Representation
(DFTR): Computes the energy within 6 frequency
bins of the sEMG power spectrum (Eddy et al.,
2024):
DFT R
bin
=
∑
i∈bin
M
i
(1)
• Root Mean Square (RMS): One of the most pop-
ular used in sEMG signal analysis, models the sig-
nal as an amplitude modulated Gaussian random
process that relates to constant force and non-
fatiguing contraction (Eddy et al., 2024; Phiny-
omark et al., 2012):
RMS =
s
1
N
N
∑
i=1
x
2
i
(2)
• Mean Absolute Value (MAV): Another popular
feature in sEMG signal analysis, represents the
average of the absolute values, providing a simple
measure of signal intensity over a specified time
interval (Eddy et al., 2024; Phinyomark et al.,
2012):
MAV =
1
N
N
∑
i=1
|x
i
| (3)
• Slope Sign Changes (SSC): Represent frequency
information of the sEMG signal. Can be defined
as the number of times that slope of the sEMG sig-
nal changes signs (Eddy et al., 2024; Phinyomark
et al., 2012):
SSC =
N−1
∑
i=2
f [(x
i
− x
i−1
) · (x
i
− x
i+1
)]; (4)
f (x) =
(
1, if x ≥ threshold
0, otherwise
(5)
• Integrated Absolute Value (IAV): The integral
of the absolute value (Eddy et al., 2024; Phiny-
omark et al., 2012):
IAV =
N
∑
i=1
|x
i
| (6)
• Log Detector (LD): Provides an estimate of
the muscle contraction force (Eddy et al., 2024;
Phinyomark et al., 2012):
LD = exp
1
N
N
∑
i=1
log(|x
i
|)
!
(7)
• Waveform Length (WL): Measures the com-
plexity of the sEMG signal. Defined as the cu-
mulative length of the sEMG waveform over time
(Eddy et al., 2024; Phinyomark et al., 2012):
WL =
N−1
∑
i=1
|x
i+1
− x
i
| (8)
• Autoregressive Coefficients (AR): Models the
sEMG signal as a linear combination of its previ-
ous values, capturing temporal dependencies and
serving as a predictive feature (Eddy et al., 2024;
Phinyomark et al., 2012):
a
i
=
P
∑
p=1
a
p
a
i−p
+ w
i
(9)
• Cepstral Coefficient (CC): Emphasizing peri-
odic patterns in the frequency domain by apply-
ing the inverse Fourier transform to the logarithm
Impact of Feature Extraction Optimization on Machine Learning Models for sEMG-Based Prosthesis Control
909

of the power spectrum (Eddy et al., 2024; Phiny-
omark et al., 2012):
c
1
= −a
1
; (10)
c
p
= −a
p
−
p−1
∑
l=1
1 −
l
p
a
p
c
p−l
(11)
• Spectral Moment (SM): A spectral moment
computed from the frequency domain. P is the
power spectrum of the signal, and f is the fre-
quencies associated with every sample of the
power spectrum (Eddy et al., 2024; Phinyomark
et al., 2012):
SM
1
=
M
∑
j=1
P
j
f
j
(12)
• Wavelet Energy (WENG): Time-frequency fea-
ture that extracts the number of possible wavelets
based on a given sampling frequency argument,
then calculates the average energy of a window
for each decomposition level. Given W
j
is the de-
composition for level j (Eddy et al., 2024):
WENG
j
=
∑
W
2
j
(13)
• Difference Absolute Standard Deviation Value
(DASDV): Standard deviation of the wavelength
(Eddy et al., 2024; Phinyomark et al., 2012):
DASDV =
s
1
N − 1
N−1
∑
i=1
(x
i+1
− x
i
)
2
(14)
2.4 Classifiers
After feature extraction, the data were used to train
the classification model. In this study, tests were con-
ducted using seven classification models based on the
reviewed literature (Eddy et al., 2024). The models
used were those defined below, set to the default con-
figurations of the scikit-learn library in Python, with
no modifications to their hyperparameters or other op-
timizations.
• Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA): Uses the
same covariance for all classes and assumes that
the data follows a normal distribution.
• k-Nearest Neighbors (KNN): Discriminates be-
tween inputs using the K closest samples in the
feature space. The LibEMG defaults to k = 5.
• Random Forest (RF): Utilizes a combination of
decision trees to differentiate between inputs.
• Quadratic Discriminant Analysis (QDA): A
quadratic classifier that uses covariances specific
to each class, assuming that classes are normally
distributed.
• Naive Bayes (NB): Assumes independence
among all input features while assuming that
classes are normally distributed.
• Multilayer Perceptron (MLP): Employs
human-like ”neurons” to model data, aiding in
the discrimination between inputs.
• Support Vector Machine (SVM): Uses a hyper-
plane to maximize the distance between classes,
serving as the decision boundary for classifica-
tion.
2.5 Experimental Protocol
LibEMG allows data separation into training and test-
ing sets using classes, repetitions, or subjects as pa-
rameters. The experiments were performed for each
subject using 5 k-fold cross-validation based on rep-
etitions. Two repetitions from each movement class
were randomly selected for testing, while the remain-
ing were used for model training.
An initial experiment was conducted using 5 com-
monly used time-domain feature extraction methods
(RMS, MAV, SSC, WL, and SM) across the six clas-
sifiers to obtain a preliminary understanding of the
performance of the models. This approach aimed to
assess the effectiveness of various methods without
any further preprocessing filtering, as well as to an-
alyze how these methods influence each model’s re-
sults to identify the best classifier for subsequent ex-
periments.
Key classification metrics were considered to
comprehensively evaluate the model. In this case, the
accuracy, error rate, and system instability were used.
Following the initial experiment, two additional
experiments were conducted. Each of the 12 features
was applied with the best classifier obtained previ-
ously, in terms of accuracy and stability, and finally, it
was selected those features that achieved an F1-score
higher than 60% to apply again with all the classifiers.
For both experiments, the common classification
metrics found in the literature were applied: accu-
racy, precision, recall, and F1-score. The equations
used are presented below, where TP represents true
positives, TN represents true negatives, FP represents
false positives, and FN represents false negatives:
• Classification Accuracy (CA): It is the percent-
age of correctly predicted samples.
CA =
1
N
N
∑
i=1
ˆy
i
== y
i
(15)
BIOSIGNALS 2025 - 18th International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
910
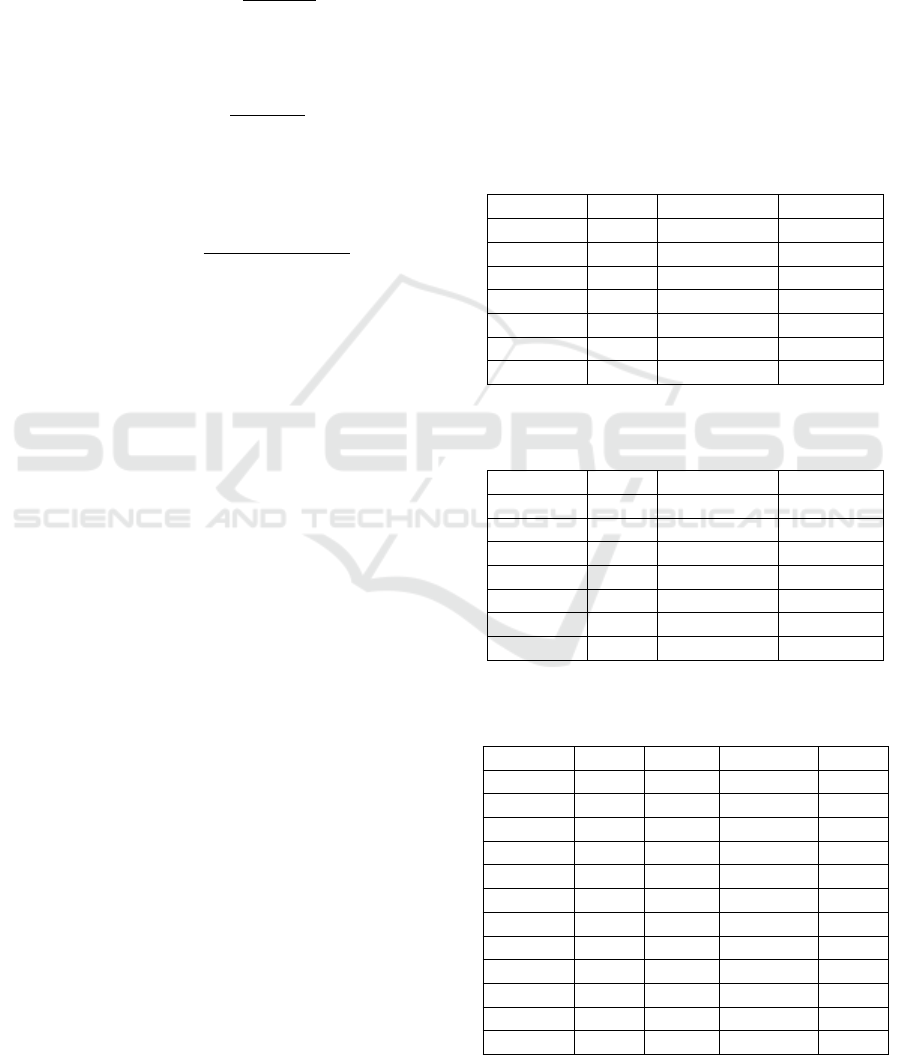
where N is the total number of data
frames/predictions, ˆy
i
is the predicted class
label for frame i, and y
i
is the true class label for
frame i.
• Precision: It is the proportion of TP relative to all
examples classified as positive (TP + FP).
Precision =
T P
T P + FP
(16)
• Recall: It is the proportion of TP relative to all
positive examples (TP + FN).
Recall =
T P
T P + FN
(17)
• F1-Score: It is the harmonic mean of precision
and recall, useful when a single metric that con-
siders both precision and recall is desired.
F1-score = 2 ×
Precision × Recall
Precision + Recall
(18)
Additionally, the error and instability of each clas-
sifier were also obtained. The active error is the per-
centage of incorrect predictions, ignoring “No Move-
ment” class predictions. This is valuable as the No
Movement class typically correlates to “do nothing”
functionality. The instability of a classifier is calcu-
lated by the number of times subsequent predictions
differ, normalized by the total number of predictions.
3 RESULTS
The results for experiment 1, using the five time-
domain features with each classifier, are presented in
Tables 1 and 2. In this initial test, RF and LDA were
the classifiers with the best results across the three
evaluation parameters. For the S12 data, mean ac-
curacies reached 76.39% and 73.38% (standard de-
viation - 3.66 and 4.33), and mean instabilities of
4.84 and 4.30, respectively. For the S11 data, in gen-
eral, the results were worse. The RF reached the best
mean accuracy of 73.29% (standard deviation - 12.82)
with instabilities of 6.91. For both subjects, SVM and
KNN showed the worst results, with error rates above
50% and high instability.
The results obtained with each feature using RF,
the best classifier in experiment 1, are presented in
Tables 3 and 4. For the S12 data, almost all features
achieved F1 scores greater than 60%, except for SSC,
which had a significantly lower result of 51.16%. In
contrast, for the S11 data, only half of the features
achieved at least 60% F1 scores.
Finally, to assess the impact of selecting relevant
features on the final model, the initial experiment with
the classifiers was redone. This time, the new features
with F1-scores above 60% were added. The results of
the final experiment are presented in Tables 5 and 6.
For the S12 data, the final tests improved the RF
and LDA accuracies. Despite a slight increase in in-
stability, RF remained the best overall model, achiev-
ing a mean accuracy of 79.18% (standard deviation
5.38) and instability of 5.24%. In contrast, for the S11
data, adding more features worsened the performance
of the RF despite it remaining the best overall model,
with 73.29% accuracy with a higher instability. The
most significant impact was observed in KNN, SVM,
and MLP cases.
Table 1: Classification results using five features (RMS,
MAV, SSC, WL, and SM) for the S12 data.
Classifier CA Active error Instability
RF 76.39 24.60 4.84
LDA 73.38 28.30 4.30
QDA 68.76 29.45 6.60
NB 55.86 43.97 4.25
MLP 55.07 46.51 13.18
SVM 50.29 50.64 14.16
KNN 43.79 56.94 28.87
Table 2: Classification results using five features (RMS,
MAV, SSC, WL, and SM) for the S11 data.
Classifier CA Active error Instability
RF 73.29 26.72 6.91
LDA 63.14 35.29 7.32
QDA 61.08 37.66 10.71
MLP 44.98 54.07 16.48
NB 42.28 51.34 6.32
SVM 41.93 57.34 14.78
KNN 38.31 60.85 31.14
Table 3: Performance metrics by each feature extraction
method with the S12 data.
Feature CA Recall Precision F1
DFTR 77.33 77.33 78.22 76.82
RMS 75.43 75.43 76.37 74.99
WENG 75.16 75.16 75.96 74.57
IAV 74.56 74.56 75.42 73.91
DASDV 74.41 74.41 75.41 73.85
MAV 73.48 73.48 75.07 72.82
WL 73.23 73.23 73.93 72.47
SM 73.17 73.17 74.36 72.63
CC 72.04 72.04 73.12 71.82
AR 71.58 71.58 72.77 71.37
LD 61.15 61.15 71.88 60.23
SSC 51.85 51.85 52.10 51.16
Impact of Feature Extraction Optimization on Machine Learning Models for sEMG-Based Prosthesis Control
911
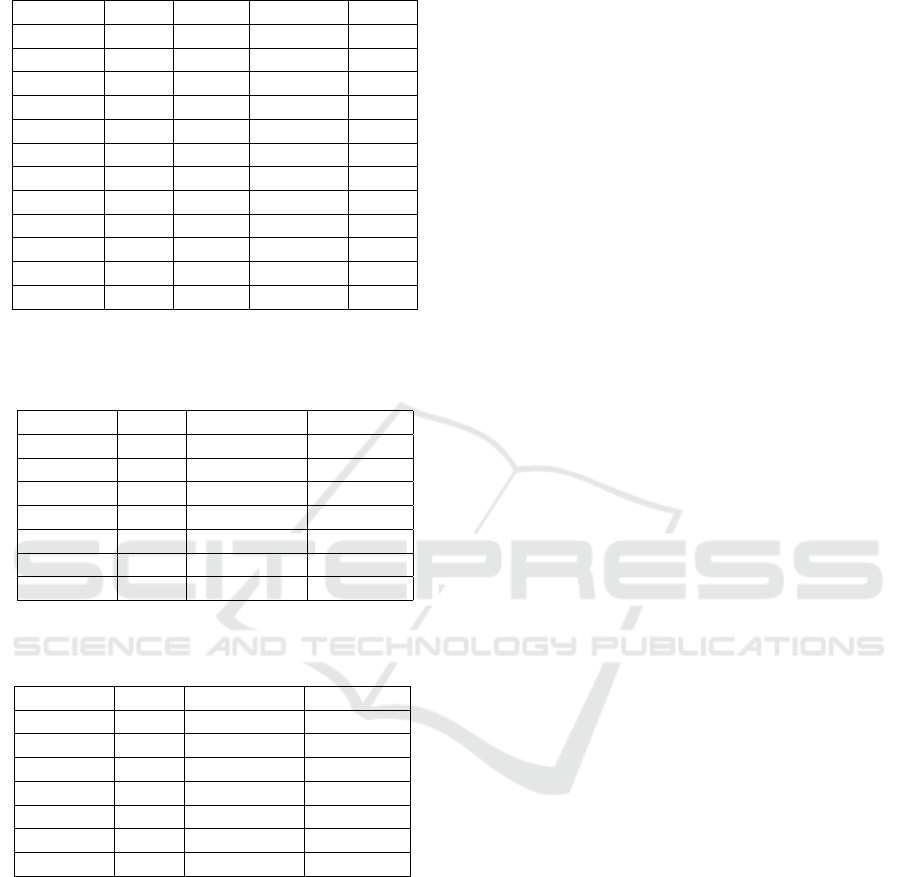
Table 4: Performance metrics by each feature extraction
method with the S11 data.
Feature CA Recall Precision F1
DFTR 73.43 73.43 74.22 73.36
WL 72.20 72.20 73.03 72.12
WENG 72.20 72.20 72.92 72.15
IAV 71.35 71.35 72.09 71.22
CC 60.32 60.32 61.12 60.19
AR 60.14 60.14 60.91 60.02
RMS 57.96 57.96 65.33 59.16
SM 54.24 54.24 64.56 59.16
DASDV 49.93 49.93 63.88 51.74
SSC 46.27 46.27 46.90 46.12
MAV 42.12 42.12 66.89 41.94
LD - - - -
Table 5: Classification results using 10 features (DFTR,
RMS, WENG, IAV, DASDV, MAV, WL, SM, CC, AR, and
LD) with the S12 data.
Classifier CA Active error Instability
RF 79.18 21.77 5.24
LDA 78.68 22.56 6.65
MLP 76.01 24.68 11.26
SVM 75.58 25.25 12.89
KNN 69.55 31.53 23.78
QDA 67.70 33.56 9.36
NB 55.90 45.06 7.35
Table 6: Classification results using 6 features (DFTR, WL,
WENG, IAV, CC, AR) with the S11 data.
Classifier CA Active error Instability
RF 72.45 27.43 8.97
MLP 69.54 30.81 16.03
LDA 66.91 33.09 12.72
SVM 66.65 33.82 19.21
KNN 64.85 33.80 32.24
NB 44.85 51.46 11.64
QDA 40.38 59.99 36.41
4 DISCUSSIONS
An important aspect noted in the literature is the need
to use amputee data. Individuals with intact limbs
generate sEMG signals based on isotonic contraction,
making it easier for the classifiers to recognize differ-
ent movement patterns. Instead, amputees perform
isometric contractions due to the lack of the limb.
Thus, it is fundamental to use amputee data to develop
such systems. Furthermore, their experience using
myoelectric prostheses allows for a more consistent
sEMG pattern generation. In addition, as the num-
ber of movement classes to be recognized increases,
it becomes more challenging for the model to achieve
high accuracy, particularly when classes involve sim-
ilar movements, especially for amputees. The liter-
ature shows significant variations in the number of
movements and accuracies. However, considering the
increased complexity due to the number of classes,
accuracies ranged from 79% to 87.8%, using time-
domain features with LDA and MLP (Li and Kuiken,
2009; Li et al., 2010; Tenore et al., 2009).
The results of this work agree with the literature,
showing the relevance of working with amputee data
and the impact of experience in using myoelectric
prostheses. However, as demonstrated by comparing
the accuracies and instabilities of the classifiers in ex-
periments 1 and 3, using a set of features capable of
capturing valuable data patterns for the proper classi-
fier can make this impact smaller.
The presented study achieved, for nine movement
classes, considering the data of the amputee with ex-
perience in the use of myoelectric prostheses (S12),
a final mean accuracy of 79.18% (standard deviation
5.38) using RF and 78.68% (standard deviation 5.54)
using LDA with eleven time and frequency features.
In contrast, the best result achieved, using the data of
the amputee with no experience in using myoelectric
prostheses (S11), was 73.29% accuracy (standard de-
viation 3.58), also using RF; however, with the five
time-domain features.
The results showed that each feature captures
specific and different patterns in the data and that
a combination of these patterns impacts each clas-
sifier differently due to how each one deals with
them. Using time and frequency-domain features in
the final experiment significantly impacted the KNN,
SVM, and MLP, which initially had the worst over-
all results. Considering the S12 data, increases of
58.83%, 50.29%, and 38.02% in accuracies, respec-
tively, made the SVM and MLP reach accuracy val-
ues closer to the best classifier performances. The
impact using the S11 data was higher for these clas-
sifiers (69.28%, 58.96%, and 54.61%, respectively).
However, using the same data, the addition had a neg-
ative impact in RF, and in QDA using the data of both
subjects, although individually, each feature resulted
in an accuracy higher than 60%.
It is important to highlight that this study did not
include any filtering or normalization steps in the data
preprocessing nor optimization of classifier hyperpa-
rameters that can improve the performance of the
classification model necessary for successful prosthe-
sis control by amputees.
BIOSIGNALS 2025 - 18th International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
912

5 CONCLUSIONS
The results demonstrate that optimizing the feature
set with a proper classifier can significantly impact
sEMG pattern recognition performance. Although the
RF had achieved the best performance in this study,
with the best mean accuracy of 79.18% using a set of
eleven features, considering the data of the amputee
with experience in the use of myoelectric prostheses,
and 73.29% using a set of six features, considering
the data of the amputee with no experience, the most
affected models by feature optimization were KNN,
MLP, and SVM, with accuracy improvements up to
69.28%.
A possible direction for future work would be to
explore filtering and normalization steps in the data
preprocessing, and deep learning classification mod-
els aim to improve performance.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
This study was financed in part by the Coordenac¸
˜
ao
de Aperfeic¸oamento de Pessoal de N
´
ıvel Superior –
Brasil (CAPES) – Finance Code 001. The authors
also thank FEI for their support.
REFERENCES
Andrade, N. A. (2007). Desenvolvimento de um sis-
tema de aquisic¸
˜
ao e processamento de sinais eletro-
miogr
´
aficos de superf
´
ıcie para a utilizac¸
˜
ao no controle
de pr
´
oteses motoras ativas. Master’s thesis, Universi-
dade de Bras
´
ılia.
Castellini, C., Gruppioni, E., Davalli, A., and Sandini, G.
(2009). Fine detection of grasp force and posture by
amputees via surface electromyography. Journal of
Physiology-Paris, 103(3):255–262.
Eddy, E., Campbell, E., Phinyomark, A., Bateman, S., and
Scheme, E. (2023). Libemg: An open source library to
facilitate the exploration of myoelectric control. IEEE
Access, 11:87380–87397.
Eddy, E., Campbell, E., Phinyomark, A., Bateman, S., and
Scheme, E. (2024). Libemg documentation: Feature
extraction. Accessed: 2024-09-21.
Hassan, H. F., Abou-Loukh, S. J., and Ibraheem, I. K.
(2020). Teleoperated robotic arm movement using
electromyography signal with wearable myo arm-
band. Journal of King Saud University - Engineering
Sciences, 32(6):378–387.
Krasoulis, A., Vijayakumar, S., and Nazarpour, K. (2019).
Effect of user practice on prosthetic finger control with
an intuitive myoelectric decoder. Frontiers in Neuro-
science, 13.
Li, G. and Kuiken, T. A. (2009). Emg pattern recogni-
tion control of multifunctional prostheses by transra-
dial amputees. In 2009 Annual International Confer-
ence of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biol-
ogy Society, pages 6914–6917.
Li, G., Schultz, A. E., and Kuiken, T. A. (2010). Quantify-
ing pattern recognition—based myoelectric control of
multifunctional transradial prostheses. IEEE Transac-
tions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineer-
ing, 18(2):185–192.
Negi, S., Kumar, Y., and Mishra, V. M. (2016). Feature
extraction and classification for emg signals using lin-
ear discriminant analysis. In 2nd International Con-
ference on Advances in Computing, Communication,
Automation (ICACCA) (Fall), pages 1–6. IEEE.
NINAPRO multimodal database (2024).
https://ninapro.hevs.ch/index.html.
Phinyomark, A., Phukpattaranont, P., and Limsakul, C.
(2012). Feature reduction and selection for emg sig-
nal classification. Expert Systems with Applications,
39(8):7420–7431.
Song, T., Yan, Z., Guo, S., Li, Y., Li, X., and Xi, F. (2023).
Review of semg for robot control: Techniques and ap-
plications. Applied Sciences, 13(17).
Spiewak, C., Islam, M., Zaman, M. A.-U., and Rahman,
M. H. (2018). A comprehensive study on emg fea-
ture extraction and classifiers. Open Access Journal
of Biomedical Engineering and Biosciences, pages 1–
10.
Sultana, A., Ahmed, F., and Alam, M. S. (2023). A system-
atic review on surface electromyography-based classi-
fication system for identifying hand and finger move-
ments. Healthcare Analytics, 3:100126.
Tenore, F. V., Ramos, A., Fahmy, A., Acharya, S., Etienne-
Cummings, R., and Thakor, N. V. (2009). Decoding
of individuated finger movements using surface elec-
tromyography. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical En-
gineering, 56(5):1427–1434.
Impact of Feature Extraction Optimization on Machine Learning Models for sEMG-Based Prosthesis Control
913
