
Multimodal Stock Price Prediction
Furkan Karadaş
1
, Bahaeddin Eravcı
2
and Ahmet Murat Özbayoğlu
2
1
Department of Computer Engineering, TOBB University of Economics and Technology, Ankara, Turkey
2
Department of Artificial Intelligence Engineering, TOBB University of Economics and Technology, Ankara, Turkey
Keywords: Financial Forecasting, Stock Market Prediction, Deep Learning, Deep Neural Networks,
Multimodal Machine Learning, Large Language Models.
Abstract: In an era where financial markets are heavily influenced by many static and dynamic factors, it has become
increasingly critical to carefully integrate diverse data sources with machine learning for accurate stock price
prediction. This paper explores a multimodal machine learning approach for stock price prediction by
combining data from diverse sources, including traditional financial metrics, tweets, and news articles. We
capture real-time market dynamics and investor mood through sentiment analysis on these textual data using
both ChatGPT-4o and FinBERT models. We look at how these integrated data streams augment predictions
made with a standard Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM model) to illustrate the extent of performance gains.
Our study's results indicate that incorporating the mentioned data sources considerably increases the forecast
effectiveness of the reference model by up to 5%. We also provide insights into the individual and combined
predictive capacities of these modalities, highlighting the substantial impact of incorporating sentiment
analysis from tweets and news articles. This research offers a systematic and effective framework for applying
multimodal data analytics techniques in financial time series forecasting that provides a new perspective for
investors to leverage data for decision-making.
1 INTRODUCTION
In the modern world of finance today, investors and
fund managers find themselves confronting
considerable challenges in making the most
appropriate investment decisions possible in
complicated and dynamic environments. From
immediate-impact global economic events to political
development market reflections and transformative
industrial changes brought about by technological
advancement, there have been so many continuous
influences on financial markets that make predicting
investments all the more difficult. Because of these
reasons, traditional analysis methods often fail, and
investors latch on to promising tools and frameworks
that offer accurate and reliable forecasting.
Das et al. (Das, Behera, & Rath, 2018) and Peng
et al. (Peng & Jiang, 2015) have focused on individual
tweet content to predict stock prices using social
media sentiment. This work is outstanding in terms of
including broader data sources, news articles, and
tweet sentiment data. However, unlike these studies,
we enrich our sentiment analysis by incorporating
engagement metrics such as tweet likes, retweets,
comments and the tweeter's follower count into our
feature extraction process. These processes provide a
much more detailed view of market sentiment.
This study focuses on multimodal stock price
prediction by integrating traditional financial metrics
with data acquired from tweets from Twitter (now
X.com) and news articles from The New York Times.
We aim to capture real-time market dynamics and
gauge investor sentiment by analyzing these data
sources. Tweets provide non-moderated, real-time
insights from the public, while news articles from The
New York Times offer moderated, expert information.
To measure market sentiment and excitement, we
conducted sentiment analysis using both ChatGPT-
4o and FinBERT to include (Araci, 2019). ChatGPT-
4o is a recent, large-scale language model, whereas
FinBERT is a specialized, smaller model tailored for
financial text analysis. Our study evaluates the
predictive models on three stocks representing
various market states, including bull, bear, and
neutral markets. We compare results from these
integrated data sources with predictions made by a
standard Long-Short-Term Memory (LSTM) model
utilizing only price data as input. Then, we highlight
Karada¸s, F., Eravcı, B. and Özbayo
ˇ
glu, A. M.
Multimodal Stock Price Prediction.
DOI: 10.5220/0013174500003890
In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2025) - Volume 3, pages 687-694
ISBN: 978-989-758-737-5; ISSN: 2184-433X
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
687

the performance enhancements achieved through data
diversity and advanced sentiment analysis.
Experimental results show that integrating social
media data, such as tweets and news articles, with
technical indicators significantly enhances the
model's predictive accuracy, outperforming price data
alone. Additionally, sentiment analysis using
FinBERT and ChatGPT-4o produced very similar
results, further validating the robustness of sentiment
integration.
The following sections will provide a detailed
methodology, including the experimental setup and
analysis of results. We will also discuss the potential
implications of multimodal data processing in
financial predictions.
2 RELATED WORKS
Deep learning-based machine learning methods are
successfully applied in various fields, such as
medicine, computer vision, and telecommunications
(Ahmedt-Aristizabal, Armin, Denman, Fookes, &
Petersson, 2021). Due to their success in these areas,
machine learning and deep learning have recently
become popular among the methods used in finance,
especially in financial forecasting. The application of
machine learning and artificial intelligence
techniques to financial data analysis and statistical
analyses of temporal data (Boginski, Butenko, &
Pardalos, 2005; Keskin, Yilmaz, & Ozbayoglu, 2021;
Sezer, Gudelek, & Ozbayoglu, 2020; Tsay, 2005)
provides investors with insights and
recommendations when forming their portfolios.
LSTM (Hochreiter, 1997) is a variant of RNN
capable of retaining short-term and long-term
information. Deep learning researchers frequently
choose LSTM networks for sequence learning. These
models are mainly applied to time-series data and are
employed across various domains, including Natural
Language Processing (NLP), language modelling,
translation, speech recognition, sentiment analysis,
predictive analytics, and financial time series analysis
(Gao, Chai, & Liu, 2017; Greff, Srivastava, Koutník,
Steunebrink, & Schmidhuber, 2016; Wu, 2016).
A review of studies in the literature highlights the
complexity and dynamism of financial markets,
emphasizing that analyses based on a single feature
can be misleading (Saha, Gao, & Gerlach, 2022).
Pearson correlation reveals linear relationships but
overlooks the diversity of financial data across
different times. A single feature usually gives only a
particular indication, while the interaction of several
factors shapes financial markets. For example,
focusing solely on stock prices can lead to paying
attention to significant aspects such as the company's
financial condition, management quality, industry
trends, economic conditions, and competition.
Wang et al. (Wang, Yu, & Shen, 2020) utilize
online financial reviews to determine the daily
sentiment for each stock, finding a strong correlation
between positive sentiment and an increase in the
closing stock price. Akita et al. (Akita, Yoshihara,
Matsubara, & Uehara, 2016) present a method for
predicting stock prices using financial data metrics
and text-based information. It introduces a strategy
for forecasting stock prices that involves using
distributed representations of news articles and
examining the relationships between various
companies operating within the same industry.
Lavrenko et al. (Lavrenko et al., 2000) integrated
stock price trends with financial news articles to
predict market directions based on news content
before these trends materialized. Another study
analysed newspaper articles' sentiment added to the
dataset and concluded that incorporating a sentiment-
measuring feature improved model performance for
the testing dataset (Forecast, 2021).
Besides news articles, social media is used in an
array of studies (Cam, Cam, Demirel, & Ahmed,
2024; Das et al., 2018; Peng & Jiang, 2015). These
implemented sentiment analyses on crawled tweets
from Twitter along with stock data for forecasting in
the stock market and concatenated with price data.
While social media data, specifically tweets, has been
incorporated into stock market forecasting models,
these studies have typically limited their sentiment
analysis to the textual content of tweets themselves.
Recent studies (Avramelou, Nousi, Passalis, &
Tefas, 2024; Farimani, Jahan, & Fard, 2024; Taylor
& Ng, 2024) examined multimodal deep learning for
predicting financial markets, each using distinct
methods and data types. Avramelou et al. (Avramelou
et al., 2024) present a novel multimodal approach for
deep reinforcement learning in financial trading. This
specifically addresses the challenge of effectively
combining diverse online data sources like news
articles and social media websites. Their approach
leverages embeddings to merge price and sentiment
data, allowing the model to discover the best
combinations of these elements for enhanced trading
decisions. Taylor et al. (Taylor & Ng, 2024) explore
a multimodal approach to stock price prediction,
integrating news headlines and article sources with
stock price percentage change data. Their study
mainly examines how percentage change compares to
raw price values in effectiveness, while also
exploring how different combinations of these data
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
688
types contribute to prediction accuracy. Farimani et
al. (Farimani et al., 2024) propose an adaptive
multimodal learning model for market price
prediction, leveraging diverse data modalities to
address the financial time series. The data sources for
their models fetched from news content, sentiment
from specialized newsgroups, and technical
indicators.
3 METHOD
3.1 Dataset
The dataset for this study comprises three selected
stocks: Walmart Inc., Walt Disney Co., and
Microsoft. Despite analyzing a few stocks, we
ensured a more representative dataset by selecting
companies with significantly different market
capitalizations, sectors, and behaviors in market
states. Table 1 lists each stock's sector information,
market state, and capitalization.
Table 1: Selected Stocks.
Stock
Name
Sector State Market
Ca
p
2024
Walmart
Inc.
Consume
Defensive
Neutral
643.86B
$
Walt Disney
Co.
Communication
Services
Bear
170.71B
$
Microsoft Technolog
y
Bull 3.09T $
With their different market conditions, these
stocks represent bull, bear, and neutral states. Bull
market stocks include rising prices and investors'
confidence while falling prices and economic
challenges characterize bear market stocks. Neutral
market stocks have a stable nature with a moderate
fluctuation in price to give a balanced perspective.
These stocks represent various market dynamics and
how those dynamics may play into investment
strategy. We collected comprehensive financial data
for each company from Yahoo Finance, including
historical price movements and other relevant
financial indicators. The data gathered for each stock
ranges from 2018 to 2023. The parameters chosen for
analysis are Date, Open, High, Low, Close, Adjusted
Close, and Volume.
We collected tweets relevant to each stock to
understand public opinion on market dynamics by
filtering for specific keywords. Keywords included
the company name or stock ticker symbol, such as
"Microsoft or MSFT." We required each tweet to
have at least 100 likes to prioritize tweets with higher
engagement. Table 2 shows the total number of
tweets for each stock. These tweets and the stock
price data were gathered from 2018 to 2023.
Table 2: Number of Tweets for Stocks.
Stock Number of Tweets
Walmart Inc. 31.555
Walt Disne
y
Co. 183.406
Microsoft 53.446
We included another data source for analyzing
market insights with expert and moderated opinions
to augment our market understanding. We collected
news articles from The New York Times using its
API to access news articles about each stock's
significant events and developments that may affect
market sentiment or stock performance. We filtered
the news articles using the exact keywords used for
the tweets. Table 3 presents the total number of news
articles for each stock collected over the same period
as the tweet data.
Table 3: Number of News Articles for Stocks.
Stock Number of Tweets
Walmart Inc. 2.930
Walt Disne
y
Co. 5.821
Microsoft 3.629
3.2 Preprocessing Data
In the preprocessing data phase, due to the non-
uniform range of values in the historical trading data,
Min-Max normalization will be applied to scale the
data to a range between 0 and 1 before inputting it
into the LSTM model.
We cleaned the data using various techniques to
ensure the quality and relevance of text within tweets
and news articles. This step removed unnecessary
content or text around URLs, hashtags, mentions,
reserved words, emojis, and smileys. Additionally,
we eliminated stop words, punctuation, special
characters, and numbers, as they do not contribute
meaningful information to the text. Further, we
removed any extra spaces while converting all text to
lowercase. These steps were essential for the dataset,
making it suitable for the subsequent analysis.
To address missing data, we applied a data-filling
method to ensure the continuity and completeness of
the dataset. Using forward-filling techniques, we
effectively imputed missing values while preserving
the dataset's integrity.
Multimodal Stock Price Prediction
689

3.3 Feature Extraction
Firstly, we selected two models to analyse the
sentiment of the tweets and news: FinBERT (Araci,
2019) and ChatGPT-4o. These two models bring
significant innovations to natural language
processing (NLP). FinBERT is an adaptation of the
BERT architecture and is specifically trained to
process financial texts, which means it allows better
and quicker insights from financial documents like
market analyses. The other model is ChatGPT-4o,
which is a general language model used to answer
many different kinds of questions effectively. Besides
FinBERT, it is trained not only on financial data but
in more and larger open-source data for human
interaction; hence, it will generate creative solutions
during conversations. Each tweet was input into these
models to assess its sentiment, assigning a score
ranging from -1 to 1. A score of -1 represents a highly
negative sentiment, 0 signifies a neutral sentiment,
and 1 denotes a highly positive sentiment.
Additionally, the models provided an accuracy
percentage for the sentiment evaluation, allowing us
to quantify the models' confidence in classifying
sentiment accurately.
Furthermore, we introduced a weighted sentiment
score to enhance our sentiment analysis. This method
considers not only the sentiment score of each tweet
but also additional engagement metrics: likes,
retweets, and comments for tweets, along with the
follower count of the user who posted the tweet. We
defined the tweet interaction ( 𝑇
) such that
𝑇
= 𝛼∗𝑇
+𝛽∗𝑇
+𝛾∗𝑇
(1)
where 𝑇
number of retweets for the tweet, 𝑇
,
number of likes for the tweet, 𝑇
, and number of
comments for the tweet and also 𝛼,𝛽,𝛾 are
hyperparameters reflecting the weights assigned to
each metric. In this study, we set these parameters to
0.3 as an initial estimate without any optimization.
To account for the impact of the user who posted
the tweet, we calculated the user influence (𝑈
) based
on their follower count, capturing the potential reach
of their messages. This is expressed as
𝑈
= 𝛿∗𝐹
(2)
where 𝐹
number of followers for the user who
posted the tweet, 𝛿 is a hyperparameter determining
the influence of follower counts, chosen as 0.1 in this
study.
The sentiment (𝑆) is derived by multiplying the
sentiment label (𝑆
) with the accuracy percentage of
the sentiment classification (𝑆
), ensuring that the
calculated sentiment reflects both its evaluated value
and the confidence level.
𝑆=𝑆
∗𝑆
(3)
Total tweet interaction (𝑇𝑇
) aggregates the total
engagement across retweets, likes, and comments to
assess each tweet's overall impact
𝑇𝑇
=𝑇
+𝑇
+𝑇
(4)
where 𝑇
number of retweets for the tweet, 𝑇
,
number of likes for the tweet, 𝑇
, number of
comments for the tweet.
By employing these comprehensive formulas, we
could reflect not just the content of the tweets but also
their potential influence and effectiveness within the
social media landscape. The weighted sentiment
( 𝑊𝑆 ) formula integrates all these factors and is
calculated as follows:
𝑊𝑆=
∗
∗
(5)
Our approach incorporates weighted sentiment
analysis, which augments tweet sentiments by
considering tweet engagement (retweets, likes,
comments) and user influence (follower count). This
is represented by the hyperparameters α, β, γ, and δ
which are tuned to optimize model performance and
provide a more nuanced assessment of market
sentiment, as high engagement and influential users
are weighted more heavily. This approach is expected
to more accurately reflect the true impact of the
influence and engagement of tweets on stock prices
compared to just tweet content's sentiment.
To enhance our dataset, we incorporated financial
technical indicators and sentiment analysis. These
features include the Relative Strength Index (RSI)
and the Simple Moving Average (SMA), both of
popular in financial analysis. The RSI measures the
speed and change of price movements to determine
whether a stock is overbought or oversold, while the
SMA smooths price data to help identify trends over
specified time periods.
To integrate the news articles, tweets, and price
data, we faced the challenge of aligning datasets that
operate on different timeframes. Given that the price
data is recorded daily, while there can be hundreds of
tweets and news articles within a single day, we
needed to synchronize these varying data frequencies.
We calculated the average sentiment label and
accuracy percentage for all tweets and news articles
generated daily to achieve this. Additionally, we
included the number of tweets and news articles for
the respective day in the dataset. This approach
allowed us to convert all data into a daily format,
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
690
ensuring that each stock's sentiment analysis
corresponds accurately with the price movements and
providing a cohesive dataset for our analysis.
3.4 Model
Our predictive model uses a standard Long-Short-
Term Memory (LSTM) architecture, chosen
specifically for its general applicability in handling
sequential data and its robustness in time series
forecasting. We focused on predicting stock closing
prices, which are crucial indicators in financial
decision-making.
The LSTM model consists of a single layer with
256 units. We employed the ReLU activation
function and the Adam optimizer with a learning rate
0.001. To optimize computational resources and
facilitate effective learning, we selected a batch size
of 128. The model was trained over 100 epochs.
4 PERFORMANCE EVALUATION
AND DISCUSSIONS
4.1 Training Strategy
Our model was trained using data from 2018 to 2022,
while data from 2023 was reserved for testing. This
temporal split allows the model to learn from a
substantial period of historical data before being
evaluated on more recent data patterns and unseen
market dynamics. We selected the Mean Squared
Error (MSE) for the loss function. To enhance the
reliability of our findings, we trained the model 10
times for both the training and testing phases and then
averaged the results. This iterative approach
minimizes the effects of any random variances or
anomalies in the data, ensuring that the performance
metrics reflect a more stable and generalized model
performance.
4.2 Computational Model Performance
In evaluating the performance of our model, designed
to predict stock closing prices, we utilized two key
metrics: R-squared (R2) and Mean Absolute Error
(MAE). Both metrics were calculated using the
predicted and actual closing prices for each stock.
Table 4 presents the performance of stock price
prediction models using FinBERT sentiment
analysis, evaluated across various feature
combinations.
For Walmart, the combination of price data with
RSI and SMA yielded the best results (R² = 0.936,
MAE = 0.017). Similar observations were made for
Microsoft. The highest performance was achieved
using price data combined with RSI and SMA (R² =
0.964, MAE = 0.020).
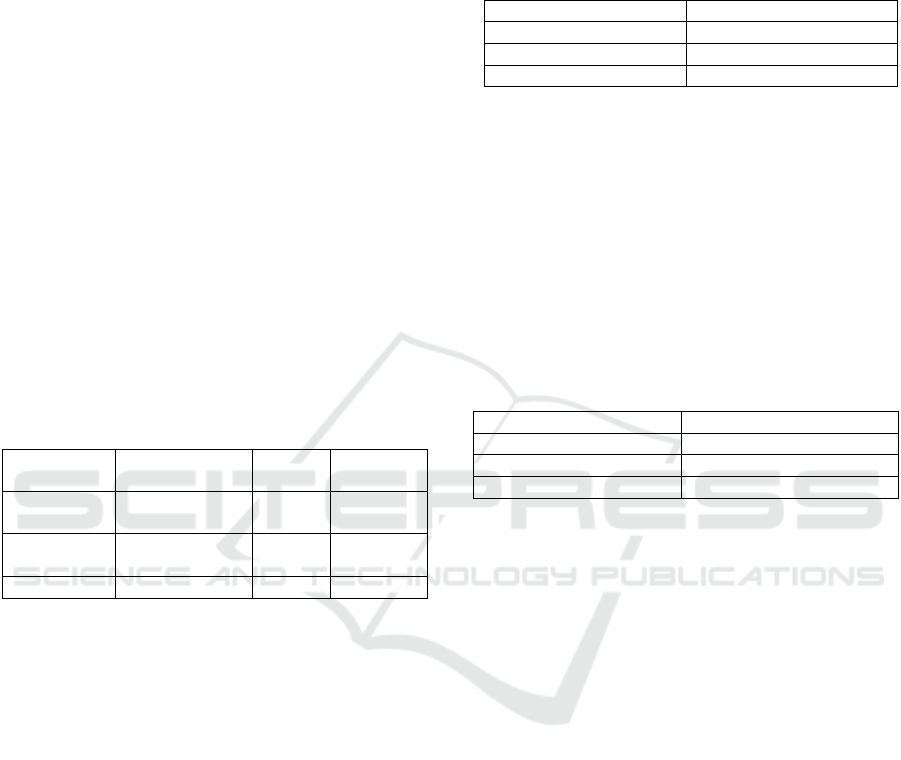
Table 4: Model Performance R² and MAE Scores
(FinBERT Sentiment).
Walmart Disney Microsoft
Metrics
Features
𝑹
𝟐
MAE
𝑹
𝟐
MAE
𝑹
𝟐
MAE
Prices
(Baseline)
0.928 0.018 0.892 0.017 0.950 0.023
Prices-
RSI-SMA
0.936 0.017 0.890 0.017 0.964 0.020
Prices-
News
0.889 0.023 0.860 0.019 0.812 0.036
Prices-
News-RSI-
SMA
0.904 0.021 0.829 0.021 0.960 0.021
Prices-
Tweets
0.891 0.023 0.889 0.017 0.949 0.023
Prices-
Tweets-
RSI-SMA
0.917 0.019 0.850 0.020 0.960 0.021
Prices-
Tweets-
News
0.889 0.023 0.829 0.022 0.940 0.025
Prices-
Tweets-
News-RSI-
SMA
0.904 0.021 0.846 0.020 0.964 0.019
Prices-
Weighted-
Tweets
0.872 0.026 0.909 0.015 0.952 0.023
Prices-
Weighted-
Tweets-
RSI-SMA
0.884 0.024 0.798 0.023 0.961 0.020
Prices-
Weighted-
Tweets-
News
0.873 0.025 0.871 0.018 0.943 0.025
Prices-
Weighted-
Tweets-
News-RSI-
SMA
0.910 0.021 0.863 0.019 0.946 0.024
In contrast, incorporating sentiment features
improved model performance for Disney predictions.
For instance, the model that combined price data with
the weighted sentiment score of tweets achieved
Multimodal Stock Price Prediction
691
higher R² scores (R² = 0.909, MAE = 0.015) than just
using price data (R² = 0.892, MAE = 0.017),
suggesting that sentiment data captures valuable
information about market perceptions and investor
sentiment specific to Disney.
It should be noticed that for Microsoft, the model
with combined data achieved better results with
tweets, news articles, and technical indicators (R² =
0.964, MAE = 0.019) compared to using only price
data (R² = 0.950, MAE = 0.023). This highlights the
significance of sentiment analysis for Microsoft's
stock predictions. Sentiment data can be beneficial
when combined with price data, enhancing the
model’s ability to capture market trends more
effectively.
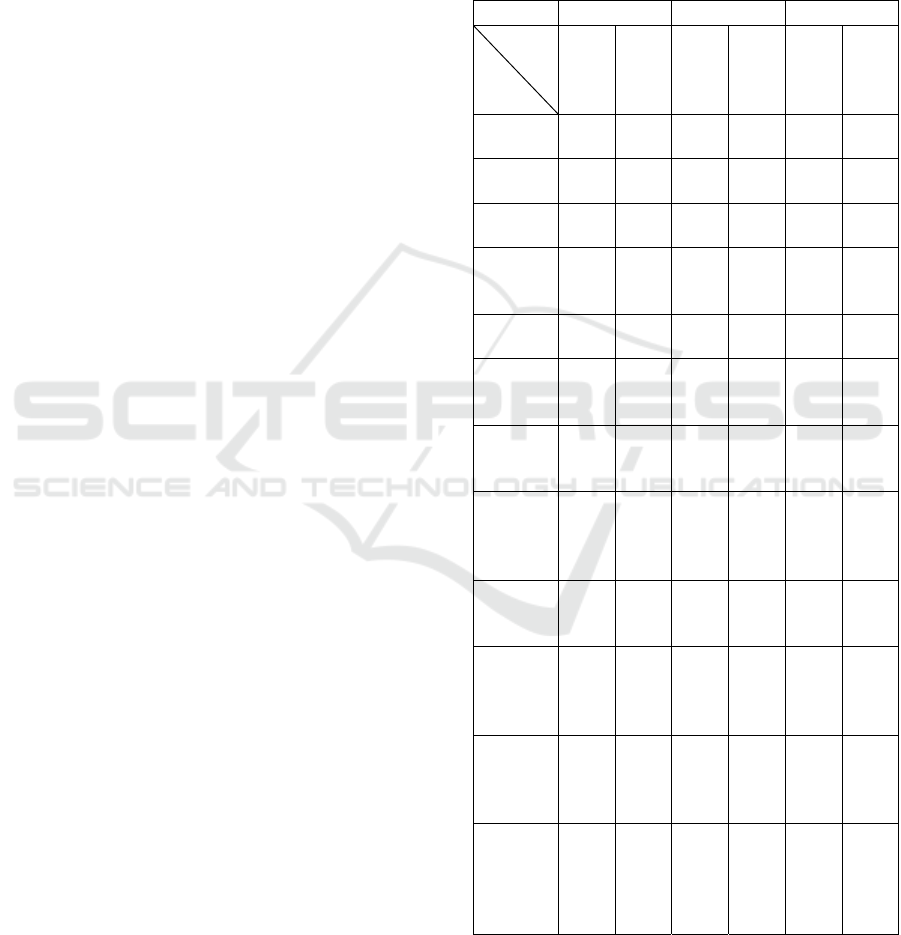
Table 5 summarizes the performance of models
utilizing ChatGPT-4o sentiment analysis features
across different stocks, revealing notable variations
depending on the features used.
For Walmart, the best results were again
achieved with technical indicators like RSI and SMA
(R² = 0.942, MAE = 0.016). Despite this being the
optimal outcome, when tweet sentiment data and
technical indicators are added, it yields better results
(R² = 0.935, MAE = 0.017) than using only price data
(R² = 0.892, MAE = 0.023). For Disney, it was
observed that using only price data was more
effective than including other features, such as
sentiment features from tweets, for improving the
overall model performance. The model performed
best for Microsoft using traditional technical
indicators with tweet sentiment data (R² = 0.959,
MAE = 0.021).
Both demonstrated strong performance when
comparing the FinBERT and ChatGPT-4o sentiment
analysis features. These indicators consistently led to
predictive performance across all stocks in both
models. Adding sentiment data, like news and tweets,
contributed positively in both models, though the
improvements were modest. FinBERT and ChatGPT-
4o performed well, with technical indicators playing
the dominant role and sentiment features adding
subtle yet consistent value.
4.3 Market Simulation
We implemented real-world stock trading using the
strategy outlined by Lavrenko et al. (Lavrenko et al.,
2000), which is defined as follows
𝑟
(𝑡)=
(
)
()
()
(6)
𝑔𝑎𝑖𝑛
(𝑡)=
𝑏𝑢𝑦→𝑠𝑒𝑙𝑙 (𝑟
(
𝑡
)
>0)
𝑠𝑒𝑙𝑙→𝑏𝑢𝑦 (𝑟
(
𝑡
)
<0)
(7)
Table 5: Model Performance R² and MAE Scores
(ChatGPT Sentiment).
Walmart Disney Microsoft
Metrics
Features
𝑹
𝟐
MAE
𝑹
𝟐
MAE
𝑹
𝟐
MAE
Prices
(Baseline)
0.892 0.023 0.916 0.014 0.947 0.024
Prices-
RSI-SMA
0.942 0.016 0.875 0.018 0.953 0.023
Prices-
News
0.876 0.025 0.878 0.018 0.932 0.028
Prices-
News-RSI-
SMA
0.893 0.023 0.749 0.027 0.955 0.022
Prices-
Tweets
0.893 0.023 0.903 0.016 0.953 0.023
Prices-
Tweets-
RSI-SMA
0.935 0.017 0.861 0.019 0.959 0.021
Prices-
Tweets-
News
0.876 0.025 0.836 0.021 0.935 0.026
Prices-
Tweets-
News-RSI-
SMA
0.899 0.022 0.739 0.027 0.956 0.022
Prices-
Weighted-
Tweets
0.921 0.020 0.898 0.016 0.951 0.023
Prices-
Weighted-
Tweets-
RSI-SMA
0.917 0.019 0.873 0.018 0.947 0.024
Prices-
Weighted-
Tweets-
News
0.881 0.024 0.799 0.023 0.948 0.023
Prices-
Weighted-
Tweets-
News-RSI-
SMA
0.909 0.021 0.715 0.029 0.951 0.023
where buy → sell denotes a transaction
purchasing stocks at the opening price, and sell →
buy denotes a transaction selling at the opening price.
Furthermore, shares are purchased at the closing price
if the opening price decreases by 2% relative to the
predicted closing price. In other cases, if a profit of
2% is achieved based on the price at which the stock
was initially bought, shares are sold at either the
opening or closing price, depending on which offers
the realized gain.
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
692
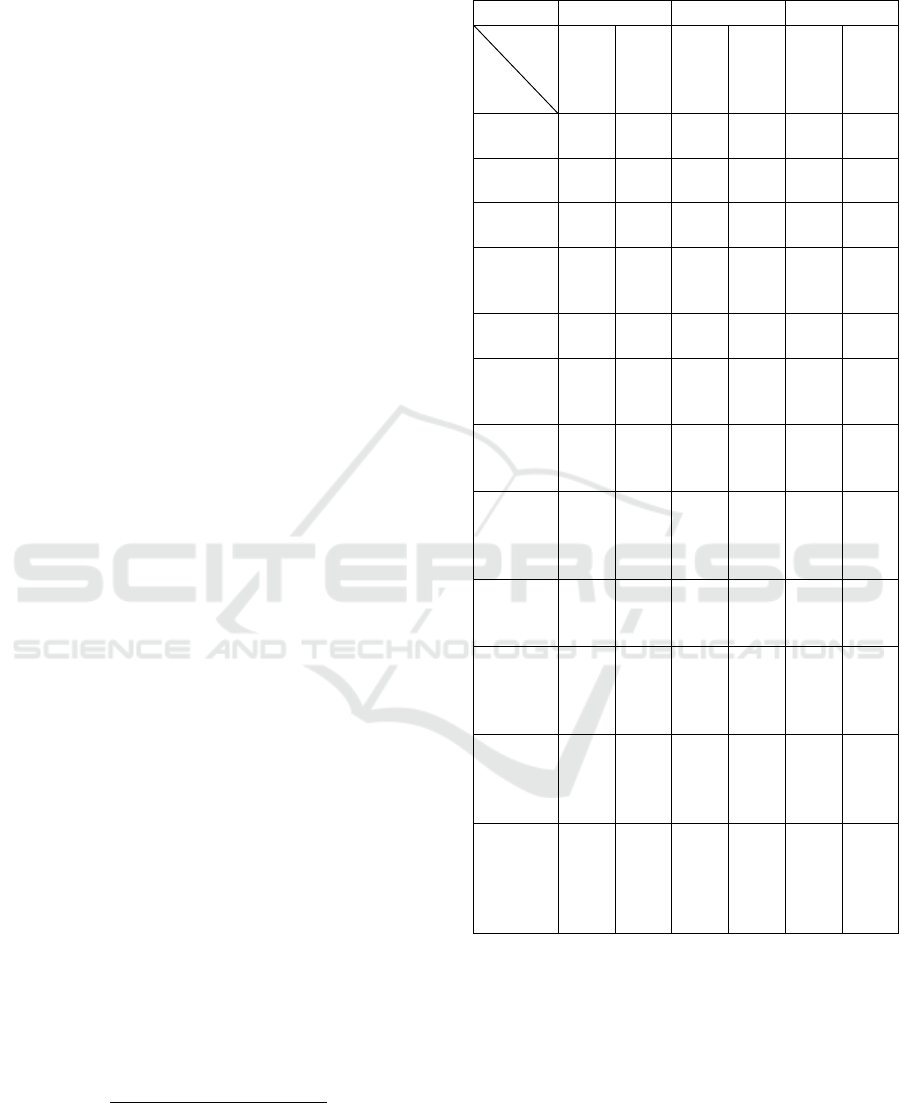
The market simulation results in Table 6 illustrate
the percentage gains achieved in various feature
combinations, starting with an initial capital of 1
million dollars for each stock. The table shows the
results of the profit we made at the end of the year.
Prices and news articles features achieved the
highest score, 12.4%, for Walmart using FinBERT
sentiment. For Disney, we observe that the tweets
obtained the highest score, 1.62% when weighted
sentiment analysis was used, which was done using
FinBERT sentiment analysis. When we look at the
Microsoft results, tweets, news articles, and technical
indicators, we see that they reached a peak score of
42.11% with sentiment analysis using FinBERT.
These results demonstrate that incorporating
technical indicators such as RSI and SMA and
sentiment analysis (especially news articles and
tweets) leads to higher returns than price data. While
price data provides a strong baseline, combining
technical indicators and sentiment analysis allows the
models to capture market trends more effectively and
generate higher profits. Thus, feeding the models with
these additional features proves to be a more effective
strategy for maximizing gains in the simulation.
Considering the results obtained in the market
simulation, FinBERT was the sentiment model with
the highest return among all three stocks. The results
indicate that FinBERT outperforms ChatGPT-4o in
sentiment analysis, particularly in stock price
prediction contexts. Although FinBERT is a small
model compared to ChatGPT-4o, it is considered to
provide better results since it is a domain-specific
model.
5 CONCLUSIONS
This paper has demonstrated how the use of
traditional financial data in conjunction with multiple
sources of text-based data, like tweets or news
articles, lead to more accurate financial forecasting.
By using insights from sentiment analysis of text-
based resources like tweets and news, this study also
emphasizes how crucial it is to comprehend market
sentiment and how it affects changes in stock prices.
In other words, a multimodal approach to financial
data analysis can enhance prediction accuracy and
result in more effective trading strategies.
To improve profit-making capacities, we want to
include macroeconomic information in future work,
such as GDP growth rates, inflation rates, and
unemployment statistics. In addition to incorporating
these information’s, we plan to explore advanced
embedding and fusion techniques with the integration
of LLMs (Large Language Models), to enhance our
model's performance compared to traditional LSTM
models.
Table 6: Market Simulation Score.
Walmart Disney Microsoft
Sentiment
Type
Features
FinBERT
ChatGPT-4o
FinBERT
ChatGPT-4o
FinBERT
ChatGPT-4o
Prices
(Baseline)
9.01 10.47 -0.67 -0.8 27.58 24.89
Prices-
RSI-SMA
5.24 6.19 -10.6 -11.4 30.92 26.33
Prices-
News
12.4 7.55 -2.72 -3.59 28.25 15.28
Prices-
News-RSI-
SMA
5.22 6.06 -2.53 -6.02 30.93 28.49
Prices-
Tweets
7.4 6.98 -2.94 -6.54 23.87 26.13
Prices-
Tweets-
RSI-SMA
6.84 7.91 -6.16 -8.17 30.73 27.82
Prices-
Tweets-
News
10.65 9.25 -2.15 -4.33 35.56 29.18
Prices-
Tweets-
News-RSI-
SMA
5.87 6.94 -6.24 -6.22 42.11 29.65
Prices-
Weighted-
Tweets
3.7 3.88 -2.03 -3.33 23.39 21.21
Prices-
Weighted-
Tweets-
RSI-SMA
2.80 7.79 -9.2 -8.73 33.69 22.66
Prices-
Weighted-
Tweets-
News
11.79 10.5 1.62 -1.39 27.7 19.76
Prices-
Weighted-
Tweets-
News-RSI-
SMA
5.78 6.59 -3.51 -4.8 25.5 29.77
REFERENCES
Ahmedt-Aristizabal, D., Armin, M. A., Denman, S.,
Fookes, C., & Petersson, L. (2021). Graph-based deep
Multimodal Stock Price Prediction
693

learning for medical diagnosis and analysis: past,
present and future. Sensors, 21(14), 4758.
Akita, R., Yoshihara, A., Matsubara, T., & Uehara, K.
(2016). Deep learning for stock prediction using
numerical and textual information. Paper presented at
the 2016 IEEE/ACIS 15th International Conference on
Computer and Information Science (ICIS).
Araci, D. (2019). FinBERT: Financial Sentiment Analysis
with Pre-trained Language Models. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1908.10063.
Avramelou, L., Nousi, P., Passalis, N., & Tefas, A. (2024).
Deep reinforcement learning for financial trading using
multi-modal features. Expert Systems with
Applications, 238, 121849.
Boginski, V., Butenko, S., & Pardalos, P. M. (2005).
Statistical analysis of financial networks.
Computational statistics & data analysis, 48(2), 431-
443.
Cam, H., Cam, A. V., Demirel, U., & Ahmed, S. (2024).
Sentiment analysis of financial Twitter posts on Twitter
with the machine learning classifiers. Heliyon, 10(1).
Das, S., Behera, R. K., & Rath, S. K. (2018). Real-time
sentiment analysis of twitter streaming data for stock
prediction. Procedia computer science, 132, 956-964.
Farimani, S. A., Jahan, M. V., & Fard, A. M. (2024). An
Adaptive Multimodal Learning Model for Financial
Market Price Prediction. IEEE Access.
Forecast, P. (2021). LSTM-based Sentiment Analysis for
Stock.
Gao, T., Chai, Y., & Liu, Y. (2017). Applying long short
term momory neural networks for predicting stock
closing price. Paper presented at the 2017 8th IEEE
international conference on software engineering and
service science (ICSESS).
Greff, K., Srivastava, R. K., Koutník, J., Steunebrink, B. R.,
& Schmidhuber, J. (2016). LSTM: A search space
odyssey. IEEE transactions on neural networks and
learning systems, 28(10), 2222-2232.
Hochreiter, S. (1997). Long Short-term Memory. Neural
Computation MIT-Press.
Keskin, M. M., Yilmaz, M., & Ozbayoglu, A. M. (2021). A
deep neural network model for stock investment
recommendation by considering the stock market as a
time graph. Paper presented at the 2021 2nd
International Informatics and Software Engineering
Conference (IISEC).
Lavrenko, V., Schmill, M., Lawrie, D., Ogilvie, P., Jensen,
D., & Allan, J. (2000). Mining of concurrent text and
time series. Paper presented at the KDD-2000
Workshop on text mining.
Peng, Y., & Jiang, H. (2015). Leverage financial news to
predict stock price movements using word embeddings
and deep neural networks. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1506.07220.
Saha, S., Gao, J., & Gerlach, R. (2022). A survey of the
application of graph-based approaches in stock market
analysis and prediction. International Journal of Data
Science and Analytics, 14(1), 1-15.
Sezer, O. B., Gudelek, M. U., & Ozbayoglu, A. M. (2020).
Financial time series forecasting with deep learning: A
systematic literature review: 2005–2019. Applied soft
computing, 90, 106181.
Taylor, K., & Ng, J. (2024). Natural Language Processing
and Multimodal Stock Price Prediction. arXiv preprint
arXiv:2401.01487.
Tsay, R. S. (2005). Analysis of financial time series. John
Eiley and Sons.
Wang, G., Yu, G., & Shen, X. (2020). The effect of online
investor sentiment on stock movements: an LSTM
approach. Complexity, 2020(1), 4754025.
Wu, Y. (2016). Google’s neural machine translation
system: Bridging the gap between human and machine
translation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1609.08144.
APPENDIX
We used a specific prompt to fetch the sentiment in
tweets and news articles from ChatGPT-4o. Below is
the prompt used to guide the ChatGPT-4o:
“You are an experienced financial analyst tasked
with analyzing tweets and news related to a specific
stock to gauge the overall sentiment and potential
impact on the stock's price. For each given tweet or
news snippet about the target stock, please:
1. Carefully consider the sentiment expressed,
looking at factors like: Positive or negative
language and tone; Mentions of financial
performance, profits/losses, business
developments; Discussion of stock price
movements, investor confidence; Overall
implications of the content for the stock.
2. Based on your analysis, provide the
sentiment label (positive, negative, or
neutral) and a sentiment score (between 0 and
1) representing the probability of the
sentiment label (e.g., a score of 0.8 for a
negative label means there is an 80%
probability that the tweet is negative).
3. Provide the sentiment score for each text
item, along with a one-sentence explanation
for your score.
Please look at the 'Content' column and analyze
each row. Then, add columns for sentiment label and
scoring (between 0 and 1) in the file. You should add
the sentiment label and score in the current file.
Remember to consider the financial and investing
context carefully, not just generic sentiment. Focus on
how the information may impact the stock and
investor perceptions.”
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
694
