
Automated News Scraping and AI-Powered Analysis for Municipal
Crime Mapping
Pedro Arthur P. S. Ortiz
a
and Leandro O. Freitas
b
Polytechnic School, Federal University of Santa Maria, Av Roraima 1000, Santa Maria - RS, Brazil
Keywords:
Web Scraping, Urban Crime Mapping, Data Extraction, AI-Powered Text Analytics, Crime Analysis.
Abstract:
This paper presents an innovative approach to urban crime mapping through automated web scraping and
data analysis techniques, addressing the challenge of limited crime data availability in smaller municipalities.
Focusing on Santa Maria, Brazil, we develop a methodology to extract, process, and visualize crime-related
information from local news sources. Our approach combines web scraping using Selenium, natural language
processing with the Claude API, and data visualization techniques to create a comprehensive crime dataset.
Through implementation, we present heat maps of crime hotspots, temporal analysis of crime patterns, and
statistical correlations between crime-related factors. The research examines hourly, daily, and seasonal crime
patterns, providing insights for law enforcement resource allocation. We discuss challenges and ethical con-
siderations of using web-scraped data, including privacy concerns, reporting bias, and verification challenges.
While acknowledging limitations such as data bias and accuracy concerns, this research provides a foundation
for data-driven urban crime prevention strategies. The methodology offers a scalable framework that could be
implemented across various urban environments, contributing to more effective crime prevention and public
safety strategies.
1 INTRODUCTION
The pervasive nature of urban crime has a profound
effect on the quality of life in cities and countries
around the world (Luca et al., 2023). Research in-
vestigates the impact of urban crime on leisure ac-
tivities and correlates fear and leisure capacity as in-
versely proportional propositions, for example, sport-
ing events experience an estimated 13.2% reduction
in attendance (Oliveira and Mendes Silva, 2021).
Crime has also become more prevalent in rural areas,
with a notable increase in fear of crime in rural ar-
eas of Brazil (Moreira and Ceccato, 2024). The im-
pacts of criminal activity range from social cohesion
and economic development to the general welfare of
communities and populations.
Despite its importance, tracking and analysing ur-
ban crime presents significant challenges, particu-
larly at the municipal level. Monitoring both lethal
and non-lethal criminal activities presents unexpected
challenges due to the scarcity of standardised city-
level data on criminal violence (Muggah and Aguirre,
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0002-2522-9568
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1112-3685
2024). This challenge is especially pronounced in
smaller cities and rural areas, where data collection
infrastructure may be less developed. In Brazil, for
example, violence patterns vary significantly by lo-
cation, with the North and Northeast experiencing
higher rates of violent deaths compared to the regions
of the south, southeast and central-west ((Lima et al.,
2021). The scarcity of reliable, timely data on ur-
ban crime, particularly in smaller municipalities, hin-
ders effective policy-making and intervention strate-
gies. Traditional methods of data collection and anal-
ysis often prove too slow or resource-intensive to pro-
vide actionable insights in a timely manner (Ceccato
and Brantingham, 2024). In this context, web scrap-
ing emerges as a potential tool to supplement exist-
ing data collection methods. The World Wide Web
has already become the biggest repository of human
knowledge, experiencing exponential growth in data
and information (Persson, 2019). Web scraping tech-
niques offer the possibility of navigating this digital
landscape to extract relevant information efficiently.
While not a replacement for official statistics or com-
prehensive sociological studies, web scraping could
potentially provide a means to gather data from lo-
cal news sources, offering insights into crime patterns
742
Ortiz, P. A. P. S. and Freitas, L. O.
Automated News Scraping and AI-Powered Analysis for Municipal Crime Mapping.
DOI: 10.5220/0013178200003890
In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2025) - Volume 3, pages 742-749
ISBN: 978-989-758-737-5; ISSN: 2184-433X
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
where official data may be lacking.
This paper presents an exploratory study into the
potential of web scraping techniques for urban crime
mapping. We focus on the city of Santa Maria, Rio
Grande do Sul, Brazil, as a case study, due to the
absence of a centralised crime statistics data source.
While our study focuses on Santa Maria, the method-
ology we’ve developed can be applied to any city
lacking standardized crime data. We selected this par-
ticular location due to its absence of comprehensive,
city-level criminal statistics. Our approach encom-
passes three key stages:
1. Data Collection: Scraping local news websites for
crime reports.
2. Data refining: Cleaning and organizing the ex-
tracted data on a dataset of urban crime.
3. Geographical Mapping and Analysis: Extracting
location data to visualise potential crime hotpots
and provide further analysis.
By applying these methodologies, we aim to in-
vestigate how automated tools might contribute to ur-
ban crime analysis. It is crucial to note that this
approach is not intended to replace human manual
analysis or address the complex, deep-rooted social
causes of urban crime (Silas Nogueira de Melo and
Matias, 2017). Rather, we present it as a potential
supplementary aid for monitoring and understanding
crime patterns.
Our implementation primarily uses Python with
the Selenium library, chosen for its capabilities in
handling dynamic web content and familiarity with
the language. Through this research, we explore
the intersection of web scraping, machine learning,
and criminology, examining how data extraction tech-
niques might be adapted to support urban crime anal-
ysis (Geetha et al., 2024). In this paper we detail our
methodology, implementation challenges, and obser-
vations from applying our tool in a real-world sce-
nario. We aim to contribute to the ongoing discussion
in the field of data-driven criminology and explore the
potential of web scraping and machine learning in ur-
ban safety research. We emphasise that our findings
should be viewed as preliminary and subject to further
validation and ethical consideration.
2 RELATED WORK
Web scraping is not a new concept and has been ex-
plored in the literature before. While web scraping
tools main objective is to automate data collection that
would otherwise require manual mining, researchers
often focus on the final data cleaning phase of these
projects. This section provides two different projects
that demonstrate effective approaches to automated
data extraction and refinement and so served as in-
spirations for the refinement of our proposed tool and
methodology.
2.1 Prediction of Crime Rate in Urban
Neighborhoods Based on Machine
Learning
(He and Zheng, 2021) analyzed over two million
crime incidents in Philadelphia (2006-2018) using a
generative adversarial network (GAN) to predict ur-
ban crime distribution. Their model generates crime
hotspot maps from city floor plans, demonstrating
machine learning’s potential in urban security plan-
ning. Their work emphasizes the importance of com-
prehensive crime datasets and web scraping tools for
collecting current crime data, enabling applications in
criminology and urban planning.
2.2 Chicago Crime Dataset
The Chicago Crime Dataset (City of Chicago, 2017),
available on Kaggle, comprises crime records from
2001-2021, extracted from the Chicago Police De-
partment’s CLEAR (Citizen Law Enforcement Anal-
ysis and Reporting) system. This dataset inspired
the Santa Maria project, though its accuracy for tem-
poral comparisons isn’t guaranteed it demonstrates
the potential for data-driven insights in urban crime
analysis. Key fields adopted include: unique key,
case number, date, block, iurc, primary type, descrip-
tion, location description, arrest and domestic.
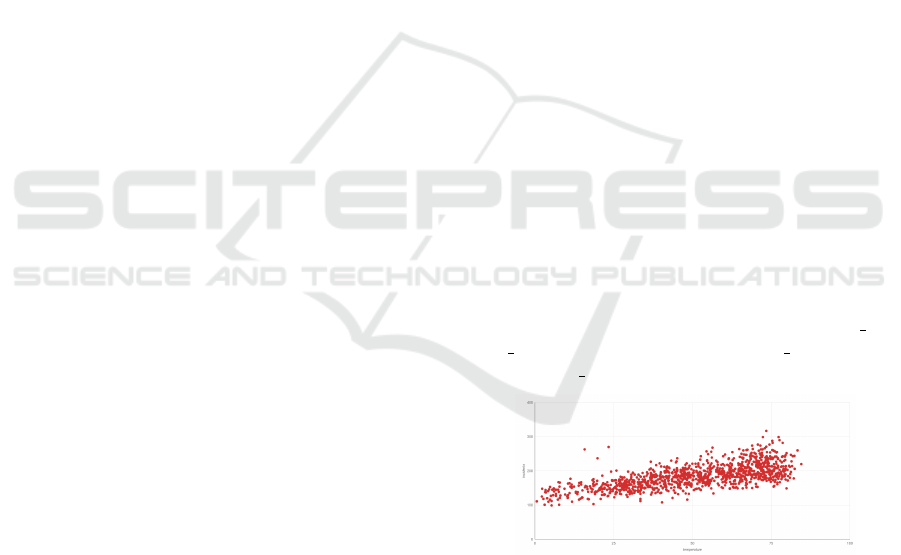
Figure 1: How does temperature affect the incident rate of
violent crime (assault or battery).
3 STATE OF THE ART
This section presents the current state of the art in web
scraping techniques and the AI-powered text analysis
tool utilised in this project.
Automated News Scraping and AI-Powered Analysis for Municipal Crime Mapping
743
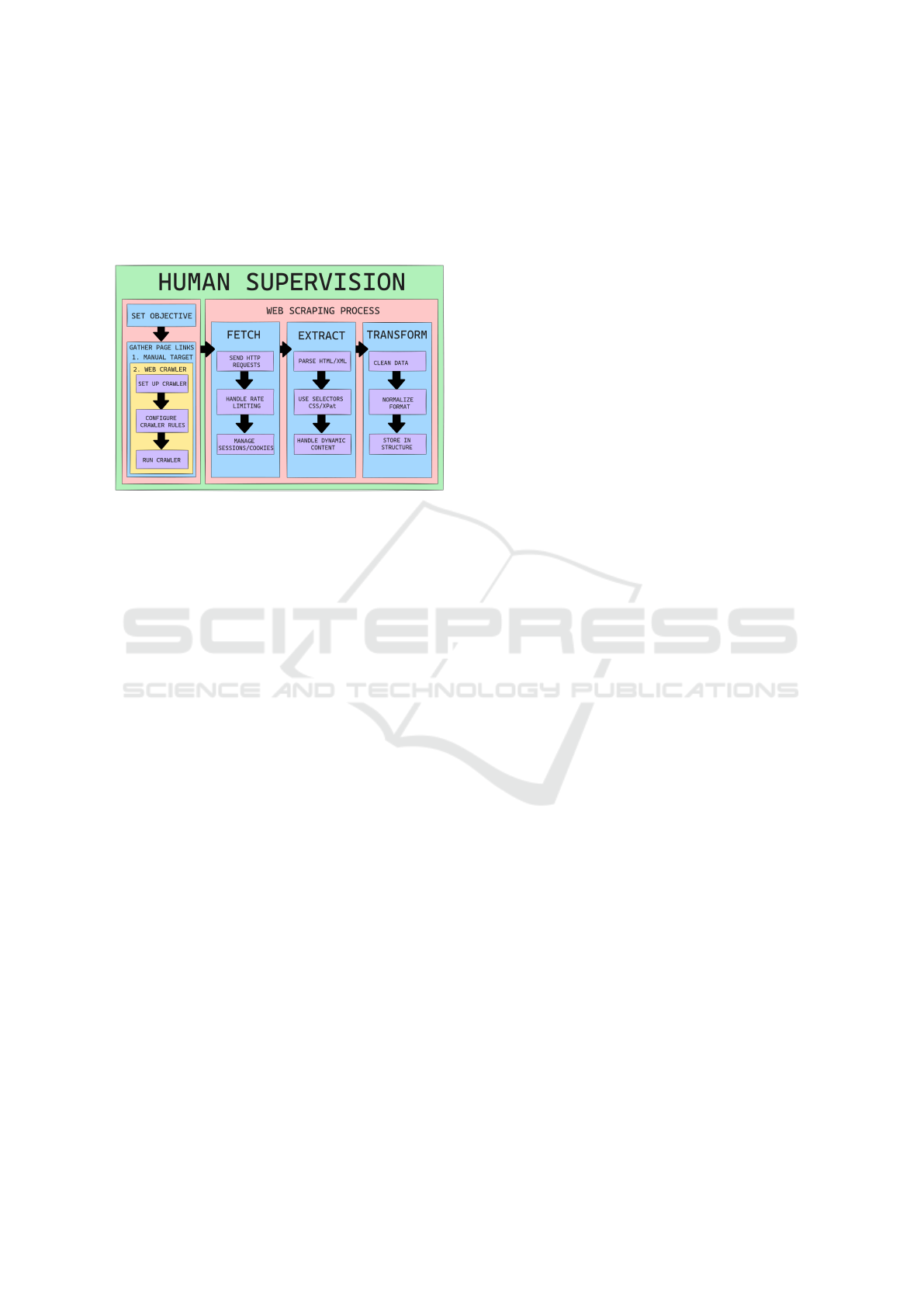
3.1 Web Scraping Process
While traditional web scraping involves fetching, ex-
traction, and transformation (Persson, 2019), we pro-
pose a supervised approach better suited for sensitive
urban crime data, as shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2: Proposed Methodology For The Web Scraping
Process.
The process begins with human supervision
through two steps:
1. Set Objective. Define goals for crime news ex-
traction
2. Gather Page Links. Manual targeting of Di
´
ario
de Santa Maria
The main stages include:
1. Fetch. HTTP requests, rate limiting, session man-
agement
2. Extract. Parse HTML/XML, use selectors, han-
dle dynamic content
3. Transform. Clean and normalize data for analy-
sis
We selected Selenium over alternatives like Beau-
tifulSoup due to its ability to handle JavaScript-
rendered content and simulate user interactions (Yuan
et al., 2023).. Selenium’s WebDriver enables us to:
1. Navigate through paginated news articles by auto-
matically clicking ”next page” buttons
2. Wait for dynamic content to load using explicit
waits
3. Handle cookie consent popups and other interac-
tive elements
4. Extract content from JavaScript-rendered DOM
elements
3.1.1 Challenges and Ethical Considerations
Key considerations include rate limit, legal and ethi-
cal compliance, and mainly data quality to ensure ac-
curacy and consistency (Andrews et al., 2024).
3.2 Anthropic API and Claude Model
The Anthropic API’s Claude model represents an
advancement in AI-powered text analysis (Asfour,
2024). For crime data analysis, Claude extracts and
categorizes information with high accuracy, comple-
menting traditional web scraping methods. Similar
to NCHRP’s improvements in WIM systems (Board
et al., 2023), Claude enhances data quality through
sophisticated analysis and pattern recognition (Hut-
son and Plate, 2023).
4 DATA EXTRACTION
As established in the previous chapter, our primary
objective with web scraping is to extract data from
a website and subsequently clean and save this data
in an urban crime mapped dataset. The chosen
city is Santa Maria, which encompasses an area of
1,780.194km² with a resident population of 271,735
people (Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statis-
tics, 2024). In 2024, a notable increase in violent
homicides has been observed, with a growth rate of
65% compared to the previous year. The city cur-
rently ranks fourth in the homicide statistics of Rio
Grande do Sul state (Riesgo, 2024).
The automation process systematically extracts
crime-related news articles through pattern matching
and data filtering. Figure 3 illustrates our methodol-
ogy from initial data collection through to final visu-
alisation. This process analyses articles individually
with the ’assalto’ (robbery) tag published between
2018 and 2024. We acknowledge this timespan repre-
sents a relatively modest sample size for our proposed
analysis, it serves as an experimental setup. Should
we elevate the scale of data extraction, we could po-
tentially access more news articles and information to
generate a more comprehensive dataset extending to
the city’s earliest publications. Furthermore, collabo-
ration with the local police department would facili-
tate access to official reports, enabling the creation of
a more elaborate database for analysing floor plans
and city locations, potentially contributing to inter-
vention planning and enhanced security measures.
Despite utilising the ’assalto’ tag, certain news ar-
ticles may be unrelated or mistakenly reference the
wrong city, as regional news outlets commonly re-
port on neighbouring cities’ events. As illustrated
in Figure 4, we have defined specific regex patterns
to exclude non-robbery-related articles and irrelevant
cities, ensuring our analysis remains focused on Santa
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
744
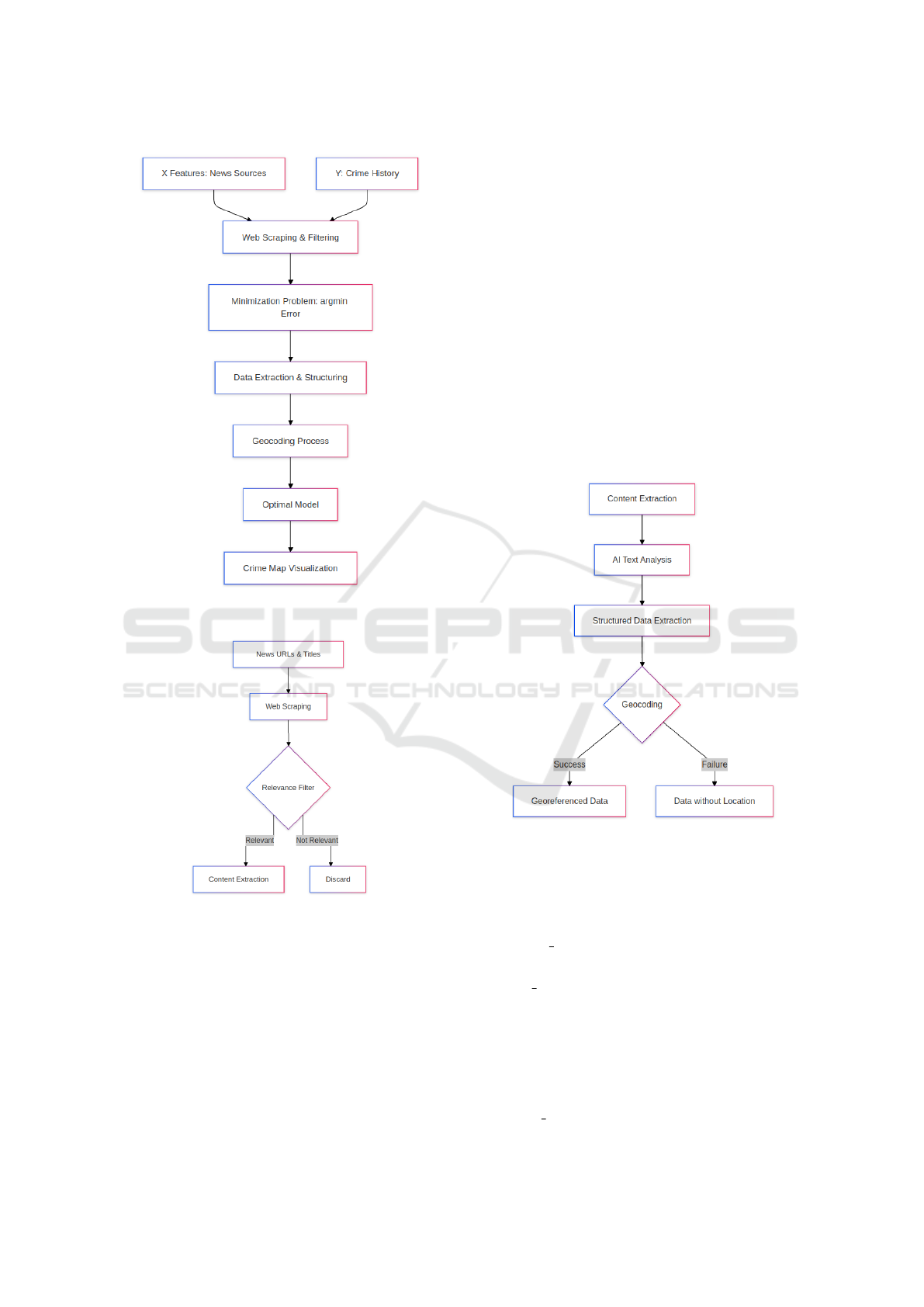
Figure 3: General Process of Crime Data Collection and
Analysis.
Figure 4: Reading, extracting and cleaning data.
Maria. Let us define our regex search patterns through
set theory and boolean logic:
R = (robbery|theft|burglary|·· ·|revolver) (1)
Where R represents the set of crime-related terms
in Portuguese, encompassing various forms of crimi-
nal activities, weapons, and related terminology.
E = (Restinga S
ˆ
eca|S
˜
ao Sep
´
e|· ··|Crici
´
uma) (2)
Where E represents the set of neighbouring cities
excluded from the analysis to maintain geographical
focus.
P = (?i)(R) ∧¬(E) (3)
The final pattern P combines crime terms with
geographic exclusions through logical AND (∧) and
negation (¬) operations.
Let A = {a
1
, a
2
, ..., a
n
} be the set of all scraped
articles. We define a filtering function:
f (a) =
(
1, if a contains relevant crime information
0, otherwise
(4)
The set of relevant articles R is defined as:
R = {a ∈ A| f (a) = 1} (5)
Figure 5: Data Processing and AI Analysis Pipeline.
As shown in Figure 5, we process the cleaned arti-
cles through AI text analysis using Anthropic Claude
to extract relevant information. The extracted infor-
mation comprises the following fields:
• unique key – Primary identifier for each crime
record
• date time – Date and time when the crime oc-
curred
• location – Specific address or location description
• neighbourhood – Name of the neighbourhood
where the crime occurred
• city – City where the incident took place
• crime type – Classification of the type of crime
Automated News Scraping and AI-Powered Analysis for Municipal Crime Mapping
745

• crime description – Detailed description of the
criminal incident
• weapon – Type of weapon used, if any
• victim info – Information about the victim(s)
• suspect info – Available information about the
suspect(s)
• vehicle involved – Details about any vehicles in-
volved
• arrest made – Whether an arrest was made (Yes,
No Or N/A)
Following the dataset creation, we can anal-
yse each row to generate reports and visualisations.
Whilst location data alone would suffice for map-
ping criminality throughout the city, we included ad-
ditional fields for comprehensive analysis purposes.
For each article r ∈ R, we define a transformation
function g : R → D, mapping to structured data points:
g(r) = (u, d, l, n, c, t, e, w, v, s, h, a) (6)
The components represent: u: unique identifier,
d: temporal information, l: geographic coordinates,
n: neighbourhood designation, c: city specification, t:
crime classification, e: event description, w: weapon
categorisation, v: victim demographics, s: suspect de-
scription, h: vehicle data, a: arrest status
Our final structured dataset S is defined as:
S = {g(r)|r ∈ R} (7)
The data extraction process employs Selenium for
web automation and the Claude API for natural lan-
guage processing. The implementation follows a se-
quential pipeline:
1. URL Collection. Systematic gathering of news
article URLs from the Di
´
ario de Santa Maria web-
site
2. Content Extraction. Automated parsing of arti-
cle content through web scraping
3. Pattern Application. Implementation of defined
regex patterns for filtering
4. Data Structuring. Transformation of unstruc-
tured text into the formal schema
5. Validation. Verification of extracted data against
predefined constraints
6. Storage. Persistence of structured data for subse-
quent analysis
The extracted data undergoes normalisation across
temporal, geographic, and categorical dimensions.
This ensures consistency in date formats, geographic
coordinates, and crime classifications whilst main-
taining the relationship between entities defined in our
formal schema. The normalisation process is crucial
for maintaining data integrity and facilitating mean-
ingful analysis across different temporal and spatial
scales.
5 RESULTS AND ANALYSIS
Following the generation of our crime dataset, we
conducted comprehensive analytical procedures to
extract meaningful patterns and insights. Our analy-
sis employed specialised Python libraries: Matplotlib
for statistical visualisations and Folium for interactive
geographical heatmaps. The geographical analysis re-
quired neighbourhood data extraction and geocoding
through Nominatim from geopy.geocoders. Figure 6
presents the resulting heatmap of Santa Maria, where
colour intensity corresponds to crime concentration
levels across different neighbourhoods.
5.1 Arrest Status Analysis
A crucial metric extracted from the news reports was
the arrest status classification. Each reported crime
outcome was categorised according to Equation 1:
Arrest Status =
True, if arrest was made
False, if no arrest was made
N/A, if info unavailable
(8)
Figure 7 illustrates the distribution of arrest out-
comes across the dataset. This visualisation pro-
vides insights into law enforcement effectiveness and
reporting comprehensiveness within the local media
ecosystem. The analysis of arrest outcomes reveals
significant patterns in law enforcement response and
success rates, offering valuable insights into the effi-
ciency of local policing strategies.
5.2 Temporal Pattern Analysis
Our temporal analysis revealed significant patterns in
both daily and seasonal crime distributions. Figure
8 demonstrates the frequency of criminal activities
throughout the day, whilst Figure 9 presents the evo-
lution of reported crimes across months and years.
The hourly distribution exhibits distinct peaks dur-
ing specific periods, suggesting strong correlations
with urban activity patterns and social behaviours.
These temporal clusters provide crucial insights into
the rhythms of criminal activity within the urban en-
vironment.
The analysis of monthly data indicates significant
seasonal influences on crime rates, with notable fluc-
tuations during particular periods. These seasonal
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
746
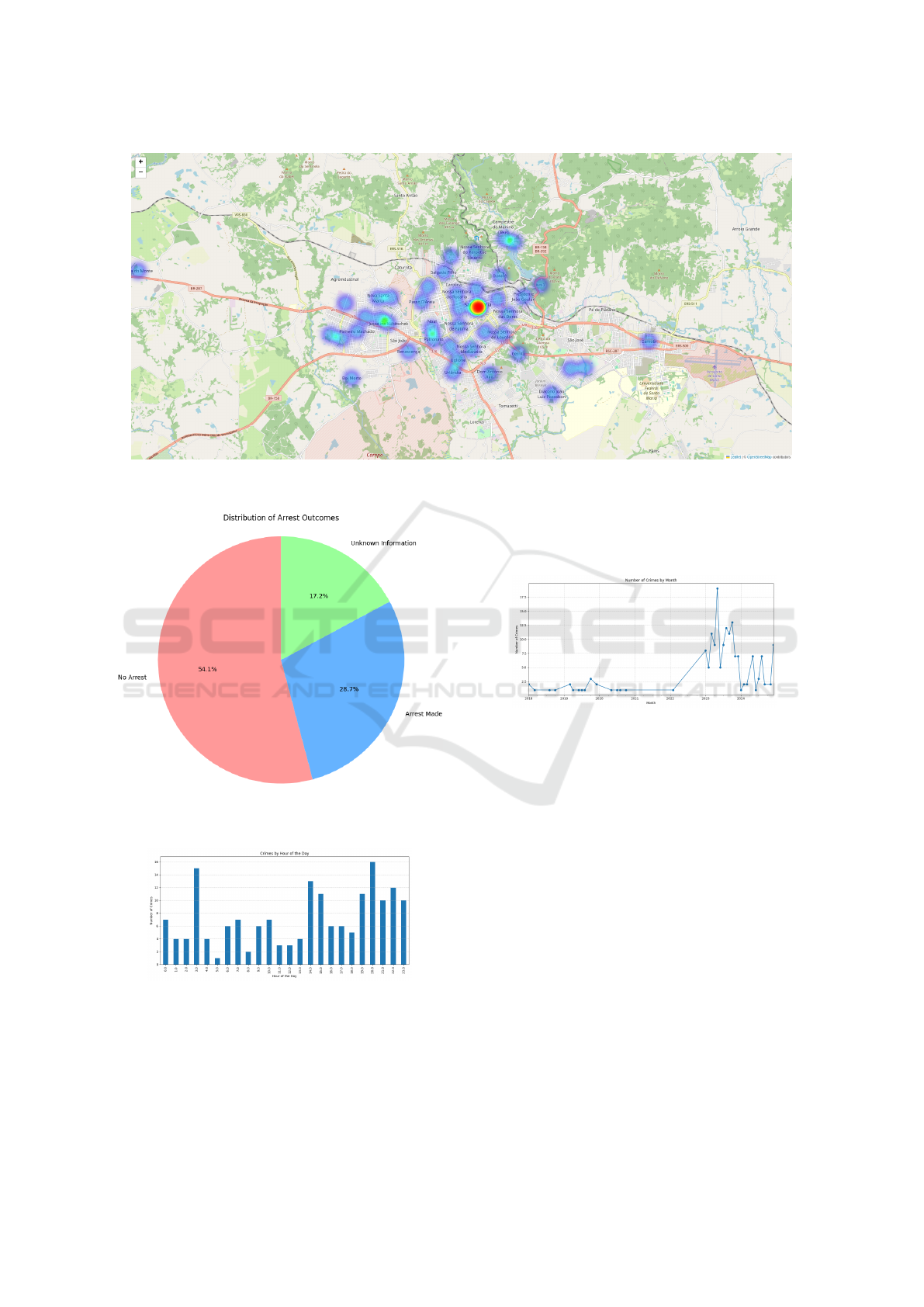
Figure 6: Heat map representation of urban crime distribution in Santa Maria, with colour intensity indicating crime concen-
tration across neighbourhoods.
Figure 7: Distribution analysis of arrest outcomes in re-
ported crimes, categorised by successful arrests, unsuccess-
ful arrests, and unreported status.
Figure 8: Hourly distribution of criminal activities, high-
lighting temporal patterns and peak occurrence periods.
variations appear to correlate with various environ-
mental and social factors, including weather patterns,
tourist seasons, and local events. Furthermore, the
long-term trend analysis reveals evolving patterns in
criminal activity and potential shifts in reporting prac-
tices over the studied timeframe, suggesting possible
changes in both criminal behaviour and law enforce-
ment responses.
Figure 9: Monthly crime frequency distribution across the
analysed timeframe, revealing seasonal patterns and long-
term trends.
5.3 Geographical Distribution Analysis
The geographical analysis reveals distinct patterns in
crime concentration across different neighbourhoods.
The heatmap visualisation identifies specific areas
with consistently higher crime rates, providing valu-
able insights for law enforcement resource alloca-
tion. These spatial patterns likely reflect a complex
interplay of socioeconomic factors, urban design el-
ements, and varying levels of police presence across
different areas of the city.
5.4 Methodological Considerations
The interpretation of our results must consider several
important factors that influence the data collection
and analysis process. News reporting practices, ed-
itorial priorities, and variations in coverage intensity
may affect the observed distributions of criminal ac-
Automated News Scraping and AI-Powered Analysis for Municipal Crime Mapping
747

tivities. The automated timestamp extraction process,
while efficient, may introduce minor imprecisions in
event timing. Additionally, news coverage can vary
significantly across different neighbourhoods, poten-
tially affecting the spatial distribution analysis in our
findings.
The reliance on public news sources introduces
certain limitations in data completeness, as some in-
cidents may go unreported or receive limited cover-
age. These constraints particularly affect the analysis
of less newsworthy crimes or incidents in areas with
reduced media attention. Furthermore, the temporal
accuracy of reported events may vary based on the
delay between occurrence and reporting, potentially
affecting the precision of our temporal analysis.
5.5 Implications and Future Directions
This experimental setup demonstrates the potential
for developing comprehensive crime analysis systems
at the municipal level, particularly beneficial for cities
lacking robust governmental crime tracking infras-
tructure. The methodology presented here offers a
foundation for developing more sophisticated crime
analysis tools, especially in regions where official
crime mapping resources are limited or unavailable.
Future enhancements to this methodology could
include integration with official police records to vali-
date and supplement news-based patterns. The imple-
mentation of advanced machine learning algorithms
could improve pattern prediction and anomaly detec-
tion capabilities, whilst real-time updating systems
could provide immediate insights for law enforce-
ment and public safety officials. Cross-validation
with similar-sized municipalities could help identify
common patterns and unique local characteristics, en-
abling more targeted intervention strategies.
The analysis framework developed in this study
shows particular promise for medium-sized cities
seeking to implement data-driven crime prevention
strategies. By combining news source analysis with
geographical information systems, cities can develop
more effective approaches to resource allocation and
crime prevention, even in the absence of sophisticated
governmental tracking systems.
Our findings demonstrate both the potential and
limitations of leveraging news-based data for urban
crime analysis. While the methodology provides
valuable insights into crime patterns, the inherent bi-
ases in news reporting must be carefully considered
when interpreting results. Nevertheless, this approach
offers a promising foundation for cities seeking to
develop data-driven crime prevention strategies, par-
ticularly in regions where official crime mapping re-
sources are limited. The framework established here
can serve as a template for other municipalities look-
ing to enhance their understanding of local crime pat-
terns through systematic analysis of publicly available
information.
6 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
This study has successfully developed a method to
generate an urban crime dataset for the city of Santa
Maria, addressing a significant gap in the availabil-
ity of structured crime data for analysis. The result-
ing dataset provides a valuable tool for crime analy-
sis in a city that previously lacked a formatted crime
database. Key achievements include the creation of
a structured crime dataset for Santa Maria, the de-
velopment of a methodology adaptable for generat-
ing new crime reports, and the provision of a tool for
validating existing crime data. While the method has
proven effective, several limitations and challenges
were identified. News repetition poses a significant
challenge, as the same crime event may be reported
multiple times, potentially skewing the dataset. Addi-
tionally, the accuracy of data presented in news con-
tent may not always perfectly align with reality. Tem-
poral consistency is another concern, as the coverage
and reporting of crimes in news outlets may vary over
time, affecting long-term trend analysis.
Despite these limitations, the dataset has already
yielded valuable insights. The heat map analysis in-
dicates that the city center experiences the highest
concentration of reported crimes, providing crucial
information for law enforcement resource allocation.
Analysis of crime occurrence by hour offers insights
into the most dangerous times in the city, which can
inform public safety strategies. With further refine-
ment, the dataset holds potential for more complex
correlations, such as examining the influence of tem-
perature on crime rates or identifying seasonal crime
patterns. To enhance the value and accuracy of this
dataset, several avenues for future work are proposed.
Collaboration with law enforcement is crucial; part-
nering with the local police department to validate and
refine the dataset will significantly improve its accu-
racy and comprehensiveness. Enhanced data clean-
ing techniques should be developed to identify and
remove duplicate reports while preserving unique in-
cidents. Integration with official records, combin-
ing this dataset with official police data, will create a
more complete and accurate picture of crime in Santa
Maria.
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
748

Future work should also focus on expanded analy-
sis, exploring additional correlations such as the rela-
tionship between crime rates and socio-economic fac-
tors, weather conditions, or urban development pat-
terns. The refined dataset could be utilized to de-
velop predictive models for crime hotspots or emerg-
ing crime trends, further enhancing its value for law
enforcement and urban planning. Additionally, devel-
oping a user-friendly interface, such as a dashboard
or application, would allow stakeholders to easily ex-
plore and analyze the crime data, making it more ac-
cessible and actionable for decision-makers. In con-
clusion, while this dataset and analysis tool are not
proposed as a final solution, they represent a signifi-
cant step towards more data-driven crime analysis and
prevention strategies in Santa Maria. By addressing
the identified limitations and pursuing the suggested
future work, this initiative has the potential to signifi-
cantly enhance public safety efforts and urban plan-
ning in the city. The methodology developed here
can serve as a model for other cities facing similar
challenges in crime data collection and analysis, con-
tributing to broader efforts in urban crime prevention
and management.
REFERENCES
Andrews, J., Zhao, D., Thong, W., Modas, A., Papakyri-
akopoulos, O., and Xiang, A. (2024). Ethical con-
siderations for responsible data curation. Advances in
Neural Information Processing Systems, 36.
Asfour, A. (2024). AI-Powered Productivity. Asma Asfour.
Board, T. R., National Academies of Sciences, E., and
Medicine (2023). LTPP Data Analysis: Practical
Tools and Procedures to Improve WIM Data Quality.
The National Academies Press, Washington, DC.
Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics (2024).
Santa maria. Accessed on [insert access date].
Ceccato, V. and Brantingham, P. (2024). What is the role
of architects and urban planners in crime prevention?
Security Journal, pages 1–26.
City of Chicago (2017). Chicago crime. Kaggle. Updated
7 years ago.
Geetha, V., Gomathy, C., Gollapalli, N., and Hemadri, S. L.
(2024). Web scraping using robotic process automa-
tion. In AIP Conference Proceedings, volume 3028.
AIP Publishing.
He, J. and Zheng, H. (2021). Prediction of crime rate
in urban neighborhoods based on machine learning.
Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence,
106:104460.
Hutson, J. and Plate, D. (2023). Enhancing institutional as-
sessment and reporting through conversational tech-
nologies: exploring the potential of ai-powered tools
and natural language processing. Journal of Artificial
Intelligence and Robotics, 1(1).
Lima, R. d., Bueno, S., and Alcadipani, R. (2021). Evoluc¸
˜
ao
das mortes violentas intencionais no brasil. F
´
ORUM
BRASILEIRO DE SEGURANC¸ A P
´
UBLICA–FBSP.
Anu
´
ario Brasileiro de Seguranc¸a P
´
ublica, pages 21–
35.
Luca, M., Campedelli, G. M., Centellegher, S., Tizzoni, M.,
and Lepri, B. (2023). Crime, inequality and public
health: a survey of emerging trends in urban data sci-
ence. Frontiers in Big Data, 6:1124526.
Moreira, G. and Ceccato, V. (2024). Increase of fear of
crime in rural brazil and police legitimacy. Journal of
Rural Studies, 110:103370.
Muggah, R. and Aguirre, K. (2024). Latin america’s murder
rates reveal surprising new trends. Americas Quar-
terly. Accessed: [Insert date of access here].
Oliveira, C. A. d. and Mendes Silva, D. (2021). Os impactos
do medo do crime sobre o consumo de atividades
de lazer no brasil. Revista Brasileira de Seguranc¸a
P
´
ublica, 15(1):156–173.
Persson, E. (2019). Evaluating tools and techniques for web
scraping.
Riesgo, G. (2024). A escalada da viol
ˆ
encia em santa maria:
aumento de 65% em homic
´
ıdios em 2024.
Silas Nogueira de Melo, M. A. A. and Matias, L. F. (2017).
Geography of crime in a brazilian context: an applica-
tion of social disorganization theory. Urban Geogra-
phy, 38(10):1550–1572.
Yuan, S. et al. (2023). Design and visualization of python
web scraping based on third-party libraries and sele-
nium tools. Academic Journal of Computing & Infor-
mation Science, 6(9):25–31.
Automated News Scraping and AI-Powered Analysis for Municipal Crime Mapping
749
