
Enhanced Guided Local Search for Addressing the Graph Burning
Problem
Lamia Sadeg-Belkacem
1 a
, Imad Tamelghaghet
2 b
and Fatima Benbouzid-Si Tayeb
2 c
1
Ecole Militaire Polytechnique (EMP), Bordj el Bahri, 16046, Algiers, Algeria
2
Laboratoire des M
´
ethodes de Conception de Syst
`
emes (LMCS), Ecole Nationale Sup
´
erieure d’Informatique (ESI),
BP 68M - 16270 Oued Smar, Algiers, Algeria
Keywords:
Social Networks, Graph Burning Problem, Optimization, Guided Local Search.
Abstract:
Information spread is crucial in network science, investigating how influence, data, or contagion propagates
through networks. Graph burning offers a simplified deterministic model for addressing the NP-complete
Graph Burning Problem. Acknowledging the unique characteristics of this problem, this paper introduces an
efficient guided local search approach, leveraging betweenness centrality to initialize the solution process and
integrating an augmented function with penalty terms to optimize the burning sequence. Using a binary search
mechanism, candidate values are iteratively tested. Experimental results on 15 benchmark graphs demonstrate
the algorithm’s superior performance compared to state-of-the-art methods.
1 INTRODUCTION
Social networks have become a key part of mod-
ern society, greatly influencing communication, com-
merce, and social interactions. Platforms like Face-
book, Twitter, and LinkedIn enable new levels of con-
nectivity and information sharing, changing how peo-
ple and organizations interact with each other. Social
network analysis (SNA) has emerged as a crucial tool
to leverage these intricate networks effectively. SNA
helps understand these networks’ complex relation-
ships and structures, revealing patterns of influence,
information flow, and community dynamics essential
for strategic decision-making and encouraging inno-
vation Wasserman (1994); Borgatti et al. (2013).
The spread of social influence is a key topic in
SNA, focusing on the propagation of emotions, mem-
bership, or contagion within social networks. Under-
standing the network’s structure is crucial for effec-
tively disseminating a message to all users in a net-
work, and determining the optimal strategy and speed
of message spread. Graph burning is an emerging pro-
cess that serves as a model for understanding and an-
alyzing how social influence or contagion spreads in
a graph.
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3205-6650
b
https://orcid.org/0009-0003-0403-9316
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7032-8544
In 2014, Bonato et al. Bonato et al. (2014,
2016)introduced the concept of the graph burning
problem (GBP), a combinatorial optimization prob-
lem that models the diffusion of contagion on social
networks, aiming to propagate influence across the
entire network as rapidly as possible. By represent-
ing networks as graphs, the contagion is likened to a
fire spreading through the graph’s vertices according
to its adjacency relations.
The GBP is NP-hard Bessy et al. (2017), imply-
ing that finding the optimal solution for large graphs
is computationally challenging. In response, re-
searchers have explored exact and approached meth-
ods to address this complexity. The exact methods
involve formulating the problem as an ILP (Integer
Linear Programming) or a CSP (Constraint Satisfac-
tion Problem) model, as detailed in Garc
´
ıa-D
´
ıaz et al.
(2022b). (Bonato and Kamali, 2019) proposed a 3-
approximation algorithm, with a time complexity of
O(M), where M is the number of edges.
Several heuristic approaches have also been devel-
oped. Among them are the Cutting Corner Heuristic
(CCH), the Maximum Eigenvector Centrality Heuris-
tic (MECH), and Greedy Algorithm with Forward-
Looking Search Strategy (GAFLSS)
ˇ
Simon et al.
(2019a), which are based on greedy techniques
ˇ
Simon
et al. (2019b). The most recent approximation al-
gorithm, BFF (Burning Farthest First) Garc
´
ıa-D
´
ıaz
et al. (2022a), provides a solution with a sequence
758
Sadeg-Belkacem, L., Tamelghaghet, I. and Tayeb, F. B.-S.
Enhanced Guided Local Search for Addressing the Graph Burning Problem.
DOI: 10.5220/0013179500003890
In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2025) - Volume 3, pages 758-765
ISBN: 978-989-758-737-5; ISSN: 2184-433X
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

length of at most 3 −
2
b(G)
, where b(G) is the burn-
ing number of the graph. With a time complexity
of O(n
3
), n being the number of nodes, it provides
an efficient approach for tackling the problem. Re-
cently, Tahmasbi et al. (2022) introduced new heuris-
tics based on a two-step process: first, selecting the
initial fire source, followed by determining the subse-
quent sources. Various strategies were proposed for
each step, and different combinations of these strate-
gies led to the development of distinct algorithms.
Morever, faster heuristics, such as BBGH (Backbone-
Based Greedy Heuristic), ICCH (Improved Cutting
Corner Heuristic), and CBRH (Component-Based
Recursive Heuristic), were introduced to enhance pre-
vious methods by incorporating more efficient selec-
tion strategies Gautam et al. (2022).
Metaheuristics have been employed very recently
to tackle the GBP, notably through the Centrality-
Based Genetic Algorithm (CBAG) Nazeri et al.
(2023), which tailors traditional genetic algorithm
techniques and operations specifically for addressing
this problem.
In this paper, we investigate the use of Guided Lo-
cal Search (GLS) algorithm to solve the GBP. GLS
is a metaheuristic algorithm developed by Voudouris
and Tsang Voudouris and Tsang (1996). We propose
an Adapted Guided Local Search for Graph Burn-
ing algorithm (AGLS − GB), which operates on a
given graph G and an integer parameter bg, to iden-
tify a burning sequence of size no greater than bg.
The method integrates an augmented function that in-
corporates penalty terms, which guide the optimiza-
tion process. A binary search mechanism is em-
ployed to iteratively test candidate values of bg. The
penalty terms are designed to encourage the selection
of smaller burning sequences, thereby minimizing the
sequence size.
The structure of the paper is as follows: Section
2 defines the burning graph problem and emphasizes
its importance in network analysis. Section 3 presents
the proposed guided local search algorithm. Section
4 details the experiments conducted on synthetic and
real datasets to assess the effectiveness of our ap-
proach, discusses the results obtained, and interprets
their significance. Lastly, Section 5 concludes the pa-
per, summarizing our findings and suggesting direc-
tions for future research.
2 THE GRAPH BURNING
PROBLEM FORMULATION
Graphs are popular representations that model social
networks of the real world. Let G = (V, E) be a graph
where V is the set of nodes representing individu-
als or entities and E is the set of edges representing
the relationships or interactions between them West
(2001). Formally V = {v
1
, . . . , v
N
} and E = e
i j
N
i, j=1
,
with N =
|
V
|
nodes, m =
|
E
|
edges and τ
k
(v
i
) =
u ∈ V | d(v
i
, u) ≤ k defines the k
th
closed neighbor-
hood of a node v
i
where d(v
i
, u) is the distance be-
tween the nodes v
i
and u
The GBP involves finding an optimal sequence of
nodes that have to be given information so that the
network is covered in the least number of steps. Given
a finite connected graph G, the burning process on G
is a discrete-time procedure defined as follows: Ini-
tially, all nodes are unburned. A node can be set on
fire directly or by its neighbouring nodes. Each step
selects only one node to be set on fire, and simultane-
ously, all nodes that were set on fire in the previous
step will burn their neighbours. This process contin-
ues until the entire graph is burned. Once a node is
burned, it remains in this state until the end of the
process.
The nodes chosen as sources of fire are termed
burning sequences, with the shortest sequence re-
ferred to as the optimum burning sequence. The
length of this optimum sequence is denoted as the
burning number b(G). A smaller burning number in-
dicates a faster spread of contagion (such as news or
gossip) throughout the network. Finding the optimum
burning sequence for a given network has significant
practical applications.
Given a sequence of fire sources S =
{v
1
, v
2
, . . . , v
k
}, where k ≥ 3, for a graph G , each
fire source v
i
burns all nodes u ∈ V that are within
a distance of at most i from v
i
. The GBP can then
be mathematically formulated as follows: finding
an optimal burning sequence for the graph entails
identifying a sequence of nodes S = {v
1
, v
2
, . . . , v
k
}
of minimal size such that:
τ
k−1
(v
1
) ∪ τ
k−2
(v
2
) ∪ ··· ∪ τ
0
(v
k
) = V
Additionally, for all 1 ≤ i ≤ j ≤ k, it must hold
that d(v
i
, v
j
) ≥ j − i.
The first condition ensures that all nodes of the
graph are burned by the sequence, while the second
condition guarantees that the nodes burned by source
v
j
are not burned by any earlier source v
i
Bonato et al.
(2014).
3 PROPOSED APPROACH TO
PROBLEM SOLVING
This section introduces our proposed approach,
Adapted Guided Local Search for Graph Burning,
Enhanced Guided Local Search for Addressing the Graph Burning Problem
759

hereinafter AGLS − GB, developed to address the
GBP. AGLS − GB tailors the principles of Guided
Local Search (GLS) to the unique characteristics of
GBP.
GLS is a metaheuristic optimization technique that
improves local search methods by applying penal-
ties to avoid local minima and explore the solution
space more efficiently. It starts from an initial solu-
tion and applies moves (small perturbations) to itera-
tively improve the solution. To prevent convergence
to local optima, GLS incorporates a penalty mecha-
nism for solutions exhibiting specific undesirable fea-
tures Voudouris and Tsang (1996). This is achieved
by modifying the original objective function into an
augmented objective function:
g(s) = f (s) + λ
∑
i∈I
p
i
· I
i
(s)
where f (s) is the original objective function, λ a pa-
rameter that regulates the influence of the penalty
term, p
i
the penalty associated with feature i, I
i
(s) an
indicator function equal to 1 if feature i is present in
the solution s, and 0 otherwise.
A cost c and a penalty p is assigned for each fea-
ture. As the search progresses, these penalties are up-
dated ) based on the notion of utility, defined as:
u
i
=
c
i
1 + p
i
where c
i
is the cost of feature i, p
i
the current penalty
of feature i (initially zero).
The feature with the highest utility is penalized by
increasing its penalty (p
i
← p
i
+ 1). This mechanism
ensures that features with high cost but not penalized
a lot in the past are prioritized.
The figure 1 illustrates the AGLS −GB processing
flowshart. The process begins with a pre-processing
step where the graph G = (V, E) and an integer bg are
provided as input. In this stage, two key metrics are
computed: betweenness centrality, which measures
node importance, and the shortest path between each
pair of nodes. Using this pre-processed information,
an initial solution is constructed. The algorithm then
proceeds with a local search phase aimed to identify
a local minimum solution S. To escape thislocal min-
ima and enhance solution quality, a penalty update is
performed, encouraging exploration of new regions of
the solution space. This iterative process continues
until a stopping criterion is met, upon which the min-
imum burning sequence of size at most bg (S best).
The subsequent sections provide a detailed anal-
ysis of AGLS − GB’s components, including solu-
tion representation, the pre-processing step, the local
search process, and penalty mechanisms.
Figure 1: AGLS − BG processing flowchart.
3.1 Solution Representation and
Objective Function
An alternative solution representation was proposed
in Nazeri et al. (2023), where a solution consists
of a partial sequence instead of the full burning se-
quence. This approach prioritizes the initial nodes
that burn the most graph nodes, as they are considered
the most critical to determine. In contrast, the later
nodes burn fewer nodes, with the last node burning
only itself, while the second-to-last node also burns
its neighbours. The selection of the initial nodes is of-
ten guided by graph characteristics such as centrality
and node distances. The final nodes in the sequence
are influenced by the earlier ones, as they depend on
the unburned nodes left by the initial parts of the se-
quence. The proposed AGLS − GB algorithm manip-
ulates these partial sequences, where the remaining
nodes (suffix) are determined by the nodes not burned
by the initial activators
We used the objective function from the CBAG al-
gorithm Nazeri et al. (2023), which calculates the to-
tal burning cost by summing the squares of the burn-
ing distances of each node as follows:
f (s) =
∑
u∈V
d
2
u
where d
u
≥ 0 represents the burning distance of a
node u, which is the minimum distance between the
node u and the nearest burned node and is given by :
d
u
= min
1≤ j≤bg
(d(u, v
j
) − (bg − j))
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
760

Nodes with d
u
= k ≥ 0 are not burned with the
sequence and require k additional steps to burn (with-
out adding new nodes), while nodes with d
u
≤ 0 are
already burned. This cost function considers the num-
ber of unburned nodes and the remaining steps needed
to burn each node. By penalizing solutions with
greater burning distances, it directs the algorithm to-
ward sequences that facilitate a more efficient burning
process.
During the evaluation phase, the partial solution
must be completed. This process involves identifying
the remaining activators from the unburned nodes. In
our algorithm, the final fire sources are chosen from
the unburned nodes within the incomplete sequence.
However, exploring all potential configurations can
be computationally inefficient, particularly when the
number of unburned nodes is large. To address this is-
sue, we complete the solution only when the number
of unburned nodes falls below a predefined threshold,
referred to as maxUnburned.
3.2 Preprocessing and Initial Solution
Generation
First, we calculate the distance between each pair of
nodes in the graph using a breadth-first search (BFS)
algorithm. Subsequently, the betweenness centrality
of each node is calculated. This measure quantifies
the importance of a node in controlling the flow of
information between other nodes in the network Bor-
gatti et al. (2013). Therefore, nodes with high be-
tweenness centrality are highly efficient in the spread
of the f ire in the graph. Furthermore, nodes with high
values are more widely distributed in the graph, which
facilitates propagation Nazeri et al. (2023).
AGLS − GB, like any improvement method, re-
quires a starting solution s
0
, which can be generated
randomly or using a heuristic. In our case, we chose to
construct the initial solution randomly. The solution’s
nodes are selected based on their centrality values B
c
.
The selection probability of a node v is given by the
following equation:
p(v) =
B
c
(v)
∑
u∈V
B
c
(u)
3.3 Fast Local Search
The local search employed in our algorithm utilizes
a first improvement strategy, where a node in the se-
quence is replaced by one of its neighbours. However,
evaluating the cost of each new solution obtained by
every possible movement can be computationally in-
efficient, particularly for large graphs. To address this
issue, we implement a fast local search that divides
the search space into sub-neighbourhoods, allowing
us to focus on the most promising areas to explore
Alsheddy et al. (2016). The sub-neighbourhoods are
represented by the positions of the nodes in the se-
quence N
1
, N
2
, . . . , N
k
, where k = bg − suffix. If a
movement is identified as an improvement, the neigh-
bourhood associated with the position of the changed
node is activated and can be explored in future iter-
ations. Additional sub-neighbourhoods may also be
activated based on the features presented by the solu-
tion.
3.4 Penalized Features
AGLS − GB defines three feature sets, the first of
which pertains to the distance between nodes in the
sequence S = {v
1
, v
2
, . . . , v
i
, . . . , v
j
, . . . , v
b
}. A key
condition for the validity of a burning sequence is
distance(v
j
, v
i
) ≥ j − i. That’s why we introduce a
parameter minDist, representing the minimum dis-
tance between activators. The costs c
i j
are defined
for 1 ≤ i, j ≤ bg as follows:
If d(v
j
, v
i
) ≤ minDist:
If B
c
(v
j
) ≤ B
c
(v
i
) : I
i j
= 1 and c
i j
=
minDist−d(v
j
,v
i
)
B
c
(v
i
)
Else: I
ji
= 1 and c
ji
=
minDist−d(v
j
,v
i
)
B
c
(v
j
)
This approach implies that lower centralities re-
sult in higher costs, prompting the algorithm to favour
nodes with higher centrality values and larger dis-
tances between activators to minimize overall costs.
We also activate the sub-neighbourhood associated
with the node with the lowest centrality values.
The second set of characteristics includes only the
maximum burning distance, which aims to minimize
the duration of the overall burning process. The asso-
ciated cost is defined as :
c
′
= max(d
u
) for u ∈ V
.
The third focuses only on the number of unburned
nodes, with the associated cost given by :
c
′′
=
nb unburned
bg
where nb unburned is the number of nodes that re-
main unburned.
These last two characteristics and their associ-
ated costs directly impact the base objective function,
guiding the search to reduce the number of unburned
nodes (to reach the threshold for solution comple-
tion) and to minimize the maximum burning distance,
thus facilitating a more rapid decrease in the objective
function’s overall cost.
Enhanced Guided Local Search for Addressing the Graph Burning Problem
761

4 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
AND DISCUSSION
This section presents the results of computational ex-
periments assessing the performance and effective-
ness of AGLS −GB for solving the GBP in social net-
works. All algorithms and tests were developed in
Python using TensorFlow and executed on a computer
equipped with a 64-bit Windows 10 system with an
Intel Core i7-8650U processor and 16 GB of RAM.
To conduct our analysis, we performed two sets of
experiments on a wide range of test problems. First,
we analyze the behavior of our proposed AGLS − GB
approach. Then, we compare AGLS − GB with state-
of-the-art algorithms to demonstrate its efficiency.
The following sections introduce the test problems
used in our experiments, along with their parameter
settings. We then describe the evaluation metrics and
finally provide an analysis of the experimental results.
4.1 Datasets and Evaluation Metrics
Our experiments cover a large number of test prob-
lems and compare them with published results. We
considered 31 graphs from the Data Network Repos-
itory Rossi and Ahmed (2015). They come from var-
ious fields and include biological, social, and techno-
logical networks, among others. They are commonly
used to test the effectiveness and robustness of algo-
rithms in solving complex problems due to their di-
versity in size, structure, and complexity (Table 1).
Table 1: benchmark graphs description
Graph |V| |E| Density
karate-club 34 78 0.139
soc-dolphins 62 159 0.084
rt-retweet 96 117 0.026
ia-infect-hyper 113 2196 0.347
C125-9 125 6963 0.898
ia-enron-only 143 623 0.061
c-fat200-1 200 1534 0.077
c-fat200-2 200 3235 0.163
c-fat200-5 200 8473 0.426
DD244 291 822 0.019
ca-netscience 379 914 0.013
infect-dublin 410 2765 0.033
c-fat500-1 500 4459 0.036
Continued on next page
Table 1: benchmark graphs description (Continued)
c-fat500-2 500 9139 0.073
c-fat500-5 500 23191 0.186
bio-diseasome 516 1188 0.009
polblogs 643 2280 0.011
twitter-copen 761 1029 0.004
DD68 775 2993 0.005
ia-crime-moreno 829 1475 0.007
DD199 841 1902 0.006
wiki-Vote 889 2914 0.041
DD497 903 2453 0.006
Reed98 962 18812 0.003
delaunay n10 1024 3056 0.012
tech-routers-rf 2113 6632 0.002
chameleon 2277 31421 0.015
tvshow 3892 17262 0.002
squirrel 5201 198493 0.015
politician 5908 41729 0.002
To assess the performance of our approach, we
employ several key evaluation metrics including:
• bg. An integer defining the size of the sequence
we aim to find. To determine the optimal bg, we
perform a binary search.
• maxUnberned. This parameter sets the threshold
for the number of unburned nodes beyond which
the solution is completed. The value of 20 is used,
as recommended in the CBAG algorithm Nazeri
et al. (2023).
• suffix. This parameter determines the number of
remaining nodes required to complete the solu-
tion. The value of 3 is used, as recommended in
the CBAG algorithm Nazeri et al. (2023).
• minDist. This parameter specifies the minimum
distance between nodes in the sequence.
• the GLS parameter λ
Each metric plays a crucial role in assessing the
effectiveness of the algorithm in finding optimal solu-
tions, guiding the search process and ensuring that the
proposed approach meets performance objectives. In
the rest of the study the behaviour of the method with
different values of lambda. The obtained results are
an average of the results obtained over 30 executions.
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
762
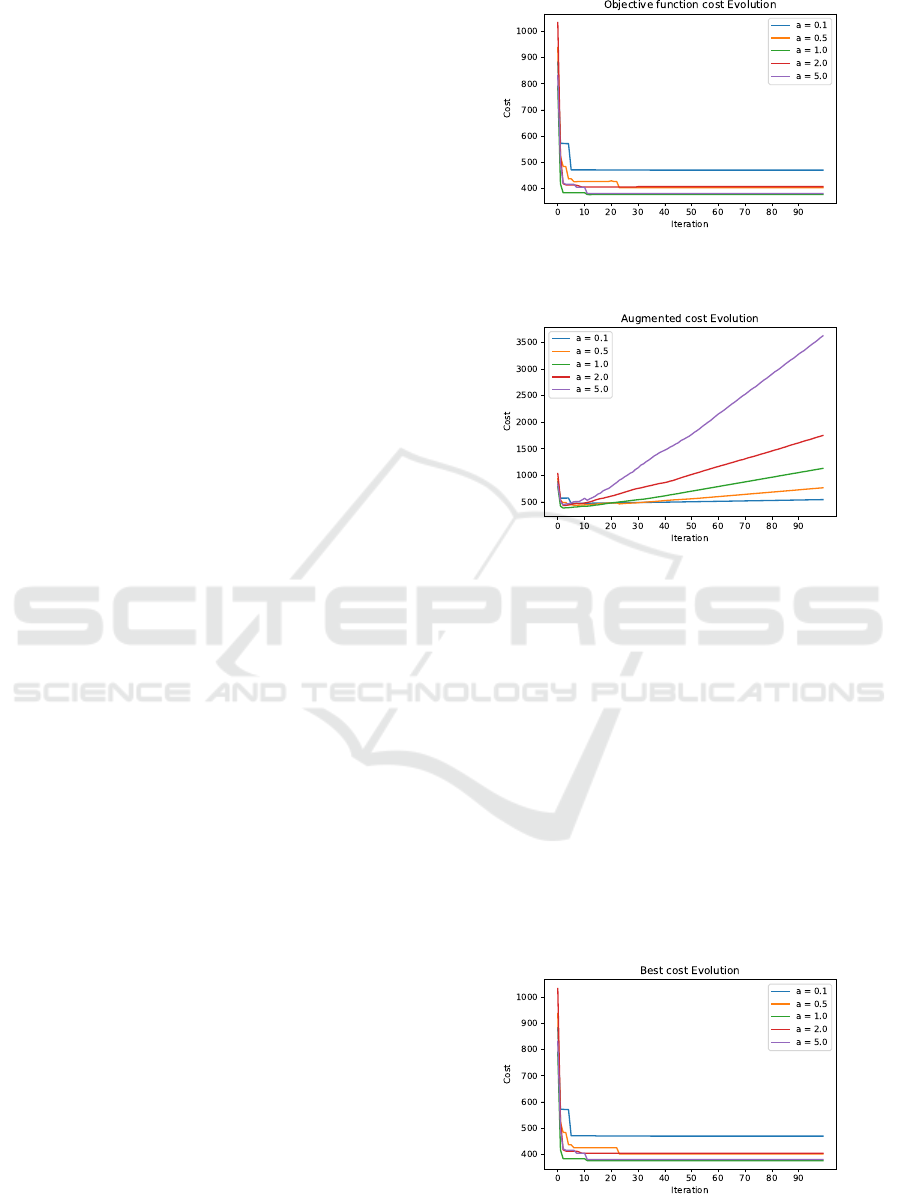
4.2 Behavioral Analysis of AGLS − GB
Algorithm
This section discusses the behaviour of the augmented
function (penalized objective function) and the initial
objective function in an optimization process using
Guided Local Search (GLS).
(a) According to Parameter λ. From Figure 3, one
can notice that the values of the augmented func-
tion increase with each iteration due to rising penalty
values when solutions exhibit specific characteristics.
Ideally, GLS should discover better solutions, lead-
ing to regular decreases in the curve, but in this case,
the curve increases linearly, indicating that the func-
tion struggles to escape local optima. However, early
vibrations in the curve suggest the discovery of new
solutions. The higher the penalty factor (a), the higher
the augmented function’s value.
Based on Figure 2, the values of the initial ob-
jective function oscillate with each iteration because
GLS prioritizes solutions based on the increased cost,
not the original objective function. This leads to find-
ing new, lower-quality solutions that are important
due to fewer penalizing features, enabling the algo-
rithm to escape local optima. When the penalty fac-
tor (a) is low (0.0 and 0.1), there is minimal oscilla-
tion, indicating that the penalties are not substantial
enough to encourage the discovery of interesting but
lower-quality solutions.
Figure 4 illustrates the cost evolution of the best
solution relative to the initial objective function. A
decreasing trend is observed, indicating that the al-
gorithm can escape local optima. Notably, the al-
gorithm successfully escapes local optima after the
oscillations observed in Figures 2. It should also be
noted that for large values of λ, the algorithm is less
able to escape local optima. This is due to the algo-
rithm’s tendency to prioritize cost minimization, par-
ticularly when the cost of constraints is multiplied by
this parameter. Consequently, an intermediate value
of λ was chosen for subsequent tests, and λ was set to
1.
(b) According to Parameter minDist. According
to figure 5, we can observe a growth in the increased
function as explained previously. However, it is worth
noting the difference between the curves. For large
values of minDist, there are many more vibrations on
the curves (Figures 9-12). This indicates that the al-
gorithm can find more interesting solutions to explore
when the sources explored are further apart.
Figure 6 illustrates a direct correlation between
minDist and the original cost. For low minDist values,
Figure 2: Evolution of the cost of the original function ac-
cording to the λ parameter on the c-fat500-1 instance.
Figure 3: Evolution of the cost of the augmented function
according to the λ parameter on the c-fat500-1 instance.
the original cost remains consistent (1, 3, 6). How-
ever, as minDist increases, the original cost exhibits
greater variability, suggesting a search for suboptimal
solutions. Notably, in early iterations, higher minDist
values often yield superior solutions, supporting our
hypothesis that increased source separation can en-
hance solution quality. This divergence can be at-
tributed to the algorithm’s prioritization of other con-
straints, potentially leading to the relaxation of dis-
tance constraints between sources.”
Figure 7 demonstrates that the algorithm is ca-
pable of escaping local optima. As previously dis-
cussed, the algorithm converges more rapidly with
larger values of minDist, supporting the hypothesis
Figure 4: Evolution of the cost of the best solution accord-
ing to the λ parameter on the c-fat500-1 instance.
Enhanced Guided Local Search for Addressing the Graph Burning Problem
763
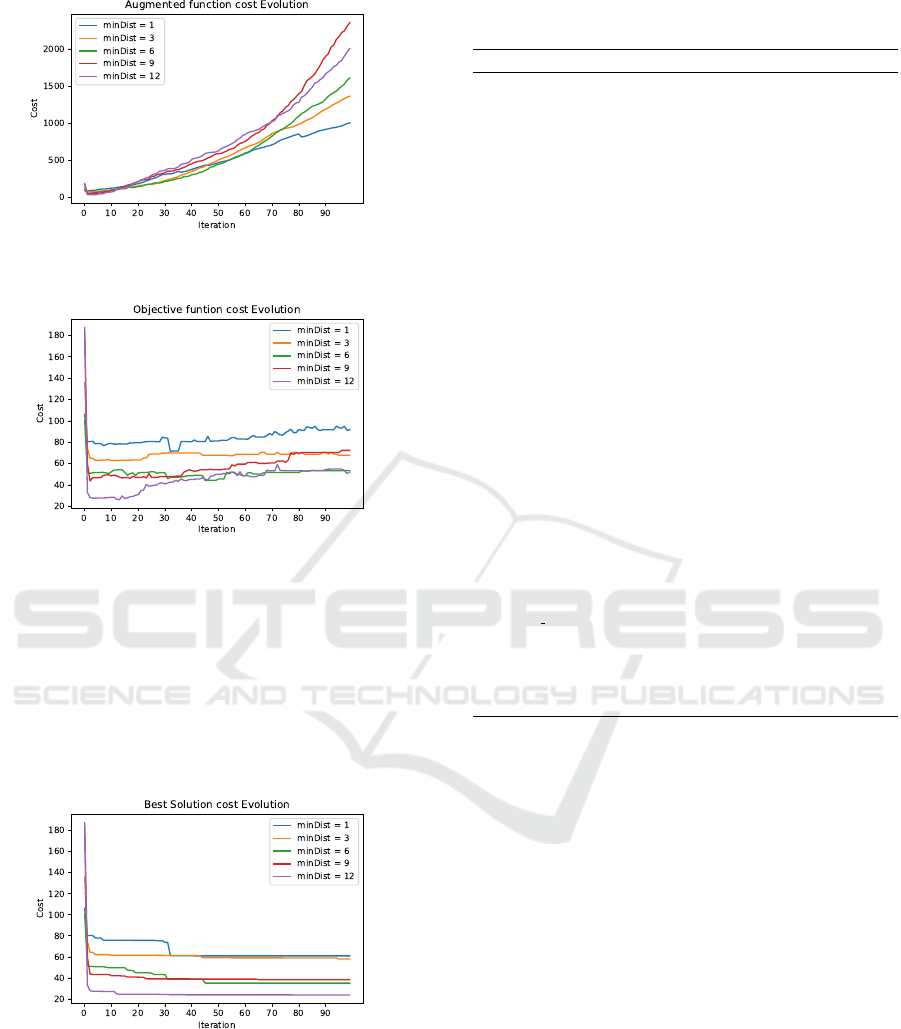
Figure 5: Evolution of the cost of the augmented function
according to the minDist parameter on the DD199 instance.
Figure 6: Evolution of the cost of the original function ac-
cording to the minDist parameter on the c-fat500-1 instance.
that sources should be well-separated. In subsequent
tests, we set minDist = bg − su f f ix. This is to ensure
the validity of sequences S = v
1
, ˙,v
i
, ˙,v
j
, ˙,v
b
, where
d(v
j
, v
i
) ≥ j − i. In our specific case, where (b =
bg - suffix), the minimum valid value for minDist is
bg − su f f ix −1 (considering the case where i = 1 and
j = b = bg = su f f ix, corresponding to the first and
last nodes respectively).
Figure 7: Evolution of the cost of the best solution accord-
ing to the minDist parameter on the D199 instance.
4.3 Performance Analysis of AGLS − GB
Algorithm
Table 2 shows a comparison of the performance of
the GLS−GB algorithm with several approximate and
heuristic algorithms from the literature.
Table 2: Comparative table of results between the GLS al-
gorithm and other approaches in the literature.
Nom Sbest BFF+ BBGH ICCH CBRH LS GLS
karate-club 3 3 3 3 4 3 3
soc-dolphins 4 4 5 4 5 4 4
rt-retweet 5 5 5 5 5 5 5
ia-infect-hyper 3 3 3 3 3 3 3
C125-9 3 3 3 3 3 3 3
ia-enron-only 4 5 4 5 4 5 5
c-fat200-1 7 7 7 7 7 7 7
c-fat200-2 5 5 5 5 5 6 5
c-fat200-5 3 3 3 3 3 3 3
DD244 7 9 7 7 7 7 7
ca-netscience 6 8 7 7 7 6 6
infect-dublin 5 5 5 5 5 5 5
c-fat500-1 9 10 9 10 9 11 10
c-fat500-2 7 5 7 7 7 7 7
c-fat500-5 5 7 5 5 5 5 5
bio-diseasome 7 7 8 7 8 8 8
polblogs 5 6 6 6 6 6 6
twitter-copen 7 7 7 7 7 7 7
DD68 9 11 10 10 10 12 12
ia-crime-
moreno
7 7 7 7 7 7 7
DD199 12 5 14 14 14 14 13
wiki-Vote 6 3 6 6 6 6 6
DD497 10 9 12 11 12 13 13
Reed98 4 8 4 4 4 4 4
delaunay n10 9 5 9 10 10 10 10
tech-routers-rf 6 6 7 7 7 7 6
chameleon 6 10 6 6 6 6 6
tvshow 9 6 10 10 10 11 11
squirrel 6 7 6 6 6 6 6
As demonstrated by the results presented in ta-
ble 2, the GLS algorithm was able to identify optimal
solutions for most graphs (21 out of 30). Notably,
it even discovered optimal solutions for large graphs
such as politician, squirrel, and chameleon (equally
achieved by local search). These findings highlight
the algorithm’s efficiency, primarily attributed to the
effectiveness of the implemented local search and the
quality of the initial solution.
Compared to the heuristics (BBGH, ICCH,
CBRH), GLS generally yields inferior results. Except
for three graphs (DD199, ca-netscience, and tech-
router), these heuristics provide solutions that are ei-
ther equal to or better than those of GLS. This is at-
tributed to the more effective source selection method
employed by these heuristics and the fact that GLS
occasionally becomes trapped in local optima during
the search. Regarding LS, it is generally observed
that GLS offers solutions that are equal to or better,
particularly for the graphs: DD199, tech-router, and
c-fat500-1. This demonstrates that the algorithm can
sometimes escape from local optima.
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
764

5 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
WORKS
This paper explored the application of the guided lo-
cal search (GLS) algorithm to solve the ’graph burn-
ing’ problem. GLS enhances traditional local search
methods by introducing a penalty mechanism that
helps escape local optima, making it particularly ef-
fective for tackling combinatorial optimization prob-
lems like graph burning. We began with a detailed
presentation of the GLS algorithm, outlining the ba-
sic concepts of local search and its limitations. We
then described the specific adaptations of GLS for the
graph burning problem, including the solution repre-
sentation and the definition of the objective function.
The results obtained with GLS were satisfactory,
showing that this method is promising and capable of
finding optimal solutions. Indeed, GLS yielded bet-
ter results than the approximate algorithms 3-approx
and BFF+ on this benchmark. However, the heuristics
BBGH, CBRH, and ICCH, as well as the metaheuris-
tic CBAG, offer better results.
As for future research, we intend to employ com-
munity detection techniques to deal with the graph
burning problem more effectively and investigate
other heuristics and metaheuristic approaches to im-
prove performance on larger and more complex graph
benchmarks.
REFERENCES
Alsheddy, A., Voudouris, C., Tsang, E. P. K., and Alhindi,
A. (2016). Guided Local Search, pages 1–37. Springer
International Publishing, Cham.
Bessy, S., Bonato, A., Janssen, J., Rautenbach, D., and
Roshanbin, E. (2017). Burning a graph is hard. Dis-
crete Applied Mathematics, 232:73–87.
Bonato, A., Janssen, J., and Roshanbin, E. (2014). Burning
a graph as a model of social contagion. In Algorithms
and Models for the Web Graph: 11th International
Workshop, WAW 2014, Beijing, China, December 17-
18, 2014, Proceedings 11, pages 13–22. Springer.
Bonato, A., Janssen, J., and Roshanbin, E. (2016). How to
burn a graph. Internet Mathematics, 12(1-2):85–100.
Bonato, A. and Kamali, S. (2019). Approximation algo-
rithms for graph burning. In Theory and Applications
of Models of Computation, pages 74–92. Springer In-
ternational Publishing.
Borgatti, S. P., Everett, M., and Johnson, J. (2013). Central-
ity. Analyzing social networks, pages 189–208.
Garc
´
ıa-D
´
ıaz, J., P
´
erez-Sansalvador, J. C., Rodr
´
ıguez-
Henr
´
ıquez, L. M. X., and Cornejo-Acosta, J. A.
(2022a). Burning graphs through farthest-first traver-
sal. IEEE Access, 10:30395–30404.
Garc
´
ıa-D
´
ıaz, J., Rodr
´
ıguez-Henr
´
ıquez, L. M. X., P
´
erez-
Sansalvador, J. C., and Pomares-Hern
´
andez, S. E.
(2022b). Graph burning: Mathematical formulations
and optimal solutions. Mathematics, 10(15):2777.
Gautam, R. K., Kare, A. S., and S., D. B. (2022). Faster
heuristics for graph burning. Applied Intelligence,
52(2):1351–1361.
Nazeri, M., Mollahosseini, A., and Izadi, I. (2023). A cen-
trality based genetic algorithm for the graph burning
problem. Applied Soft Computing, 144:110493.
Rossi, R. and Ahmed, N. (2015). The network data reposi-
tory with interactive graph analytics and visualization.
In Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial in-
telligence, volume 29. https://etworkrepository.com.
ˇ
Simon, M., Huraj, L., Dirgov
´
a Lupt
´
akov
´
a, I., and Posp
´
ıchal,
J. (2019a). Heuristics for spreading alarm throughout
a network. Applied Sciences, 9(16):3269.
ˇ
Simon, M., Huraj, L., Dirgov
´
a Lupt
´
akov
´
a, I., and Posp
´
ıchal,
J. (2019b). Heuristics for spreading alarm throughout
a network. Applied Sciences, 9(16):3269.
Tahmasbi, M., Rezai Farokh, Z., Buali, Y., and Tehrani, Z.
(2022). New heuristics for burning graphs. AUT Jour-
nal of Mathematics and Computing, 3(2):165–172.
Voudouris, C. and Tsang, E. (1996). Partial constraint satis-
faction problems and guided local search. Proc., Prac-
tical Application of constraint Technology (PACT’96),
London, pages 337–356.
Wasserman, S. (1994). Social network analysis: Methods
and applications. The Press Syndicate of the Univer-
sity of Cambridge.
West, D. (2001). Introduction to graph theory–prentice-hall.
New Jersey.
Enhanced Guided Local Search for Addressing the Graph Burning Problem
765
