
Gam-UNet for Semantic Segmentation
Rahma Aloui
1 a
, Pranav Martini
1 b
, Pandu Devarakota
2 c
, Apurva Gala
2 d
and Shishir K. Shah
1 e
1
University of Houston, Houston, TX, U.S.A.
2
Shell Information Technology International Inc., Houston, TX, U.S.A.
Keywords:
Image Segmentation, UNet Variants, Gabor Filters, Spatial-Channel Squeeze-and-Excitation, Multi-Scale
Feature Fusion, Gabor Convolution, Retinal Vessels Images, Seismic Images.
Abstract:
Accurate delineation of critical features, such as salt boundaries in seismic imaging and fine structures in med-
ical images, is essential for effective analysis and decision-making. Traditional convolutional neural networks
(CNNs) often face difficulties in handling complex data due to variations in scale, orientation, and noise. These
limitations become particularly evident during the transition from proof-of-concept to real-world deployment,
where models must perform consistently under diverse conditions. To address these challenges, we propose
GAM-UNet, an advanced segmentation architecture that integrates learnable Gabor filters for enhanced edge
detection, SCSE blocks for feature refinement, and multi-scale fusion within the U-Net framework. This ap-
proach improves feature extraction across varying scales and orientations. Trained using a combined Binary
Cross-Entropy and Dice loss function, GAM-UNet demonstrates superior segmentation accuracy and conti-
nuity, outperforming existing U-Net variants across diverse datasets.
1 INTRODUCTION
Segmentation tasks involving curved lines, such as
those in seismic and medical imaging, pose signifi-
cant challenges for traditional Convolutional Neural
Networks (CNNs), as shown in Figure 1. Poor pre-
dictions, often discontinuous or imprecise, can lead
to suboptimal results. These tasks demand high ac-
curacy for identifying boundaries amidst noisy back-
grounds while capturing fine details of varying shapes
and sizes. However, CNNs often struggle with vari-
ations in the orientation and scale of structures, re-
sulting in inconsistent performance and discontinu-
ous predictions, which are particularly detrimental in
fine-grained segmentation. While CNNs are adept at
capturing hierarchical spatial features, they inherently
lack the ability to manage geometric transformations,
often relying on extensive data augmentation. How-
ever, this can lead to overfitting and fails to fully ad-
dress the challenges posed by these tasks.
Previous techniques have explored Gabor filters
for their ability to capture multi-scale and multi-
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0008-2599-0553
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8871-9068
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1989-0261
d
https://orcid.org/0009-0005-2905-1113
e
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4093-6906
Figure 1: Examples of applications for curved lines seg-
mentation (a)Image (b) Ground Truth (c) Poor prediction.
orientation features, particularly for edge detection
and texture analysis. However, their application in
segmentation tasks remains underexplored. In this
work, we integrate learnable Gabor filters within
the U-Net architecture through a Gabor convolu-
tion mechanism, enabling the filters to adapt during
training and improving segmentation across varying
scales, orientations, and textures.
To complement Gabor filters, attention mecha-
nisms are incorporated into the U-Net architecture to
focus on critical regions, enhancing the detection of
relevant features. Additionally, multi-scale feature fu-
sion captures both fine details and broader contexts,
enabling the model to handle objects of varying sizes.
524
Aloui, R., Martini, P., Devarakota, P., Gala, A. and Shah, S. K.
Gam-UNet for Semantic Segmentation.
DOI: 10.5220/0013182000003912
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 20th International Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications (VISIGRAPP 2025) - Volume 3: VISAPP, pages
524-531
ISBN: 978-989-758-728-3; ISSN: 2184-4321
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

Together, these techniques ensure precise boundary
detection while maintaining a robust understanding of
overall image context.
Building on these advancements, we propose
GAM-UNet, a novel architecture that combines Ga-
bor Feature Extraction Modules (GFEM), attention
mechanisms, and multi-scale feature fusion within
the U-Net framework. SCSE (Spatial and Channel
Squeeze and Excitation) blocks dynamically recali-
brate feature maps, emphasizing spatial and channel-
wise information. This integrated approach signifi-
cantly improves segmentation continuity and robust-
ness, making GAM-UNet well-suited for challenging
segmentation tasks. The primary contributions of this
paper are as follows:
• Gabor Feature Extraction in UNet Integration
of Gabor Feature Extraction Modules (GFEM)
into the UNet architecture to improve edge and
texture detection in image segmentation tasks.
• SCSE Implementation. Incorporation of Spatial-
Channel Squeeze-and-Excitation (SCSE) blocks
to dynamically recalibrate feature maps, enhanc-
ing relevant feature extraction.
• Multi-Scale Feature Fusion. Implementation of
a multi-scale feature fusion framework, exploring
both Cascade and Skip Connection with Concate-
nation strategies to effectively capture contextual
information and reduce the semantic gap.
2 RELATED WORKS
Recent advances in semantic segmentation have fo-
cused on improving CNN-based architectures, par-
ticularly U-Net variants, using attention mechanisms,
Gabor filters, and multi-scale feature fusion. Our ap-
proach builds on these techniques, targeting feature
recalibration for complex tasks such as seismic and
medical image segmentation.
2.1 Gabor Filters in CNN
Gabor filters are widely recognized for their ability
to capture texture and edge details across specific ori-
entations and scales. Sarwar et al. (Sarwar et al.,
2017) demonstrated their use in CNNs for texture-
based classification, while Ozbulak et al. (Ozbulak
and Ekenel, 2018) refined Gabor filters for improved
classification on datasets like CIFAR-10. Luan et
al. (Luan et al., 2018b) embedded Gabor filters into
CNNs to enhance feature extraction and interpretabil-
ity in segmentation tasks. Trainable Gabor filters, in-
troduced by Alekseev and Bobe (Alekseev and Bobe,
2019), adapt dynamically to input data, improving ro-
bustness in texture-sensitive tasks. Yuan et al. (Yuan
et al., 2022) further refined this concept for greater
flexibility in various applications. For segmentation,
Wang and Alkhalifah (Wang and Alkhalifah, 2023)
employed adaptable Gabor kernels for seismic data,
while AGNet (Luan et al., 2018a) merged Gabor
and convolutional features to reduce semantic gaps.
Building on these developments, our method incor-
porates trainable Gabor filters that dynamically adjust
during training, enabling effective capture of edge and
texture features across diverse orientations and scales,
particularly in complex seismic and medical images.
2.2 Attention Mechanisms in U-Net
Attention mechanisms enhance U-Net models by
enabling them to focus on critical image features.
Squeeze and excitation (SE) blocks (Roy et al.,
2018) recalibrate feature channels, while the Con-
volutional Block Attention Module (CBAM) (Chen
et al., 2020) adds spatial attention for improved
foreground-background distinction. Coordinate At-
tention (CA) (Li et al., 2020) embeds positional
cues, enhancing segmentation precision. USE-Net
(Rundo et al., 2019) integrates SE blocks for prostate
zonal segmentation, and Shen et al. (Shen et al.,
2022) applied SE transformers to microvessel seg-
mentation. SSA-UNet (Jiang et al., 2024) combines
SE blocks with self-attention for brain segmentation,
demonstrating the effectiveness of feature recalibra-
tion in medical imaging. Our method integrates SCSE
blocks within the Gabor convolution layers to empha-
size spatial and channel-wise information. This recal-
ibration enables precise focus on important structures,
crucial for tasks involving seismic and medical data.
2.3 Multi-Scale Feature Fusion
Multi-scale feature fusion combines information from
different resolution levels, effectively integrating fine
details with broader contextual information. UNet++
(Zhou et al., 2018) improves this process by re-
designing skip connections, while U2-Net (Qin et al.,
2020) employs Residual U-blocks for better multi-
scale feature blending. MA-Unet (Cai and Wang,
2020) incorporates attention mechanisms to aggre-
gate multi-scale features, preserving detailed struc-
tures and larger patterns. Our model employs multi-
scale feature fusion in the decoder, merging features
from various levels to capture small-scale details and
overall context. This approach is particularly effective
for seismic and medical segmentation, where both
precision and contextual understanding are critical.
Gam-UNet for Semantic Segmentation
525

Figure 2: Model Architecture.
3 METHODOLOGY
3.1 GAM-UNet
GAM-UNet integrates key mechanisms to improve
segmentation in seismic and medical images. The
encoder features a Gabor Feature Extraction Module
(GFEM), combining Gabor convolution (GConv) and
SCSE (Spatial and Channel Squeeze-and-Excitation)
blocks to capture orientation- and scale-specific de-
tails while recalibrating feature importance. The de-
coder incorporates multi-scale feature fusion (MSFF)
to combine features across scales, minimizing in-
formation loss and enhancing segmentation perfor-
mance. Figure 2 illustrates the architecture, showing
GFEM in the encoder and MSFF in the decoder.
3.2 Gabor Feature Extraction Module
The Gabor Feature Extraction Module (GFEM) in-
tegrates Gabor convolution and standard convolution
filters in a dual-branch architecture to enhance fea-
ture extraction. The upper branch applies Gabor fil-
ters with SCSE blocks to focus on fine texture extrac-
tion, while the lower branch uses conventional 3 × 3
convolutions to capture broader spatial features. The
outputs of both branches are concatenated, merging
fine and general features for enriched representation.
A 1 × 1 convolution followed by a 3 × 3 convolution
further integrates these features, ensuring the network
effectively combines detailed and general information
for accurate segmentation.
3.2.1 Gabor Convolution
At the core of the GFEM is the Gabor convolu-
tion operation, as shown in Figure 3, where feature
maps from the previous encoder layer are convolved
channel-wise with a set of Gabor filters. The num-
ber of filters is determined by the product of the se-
lected orientations and scales, ensuring comprehen-
sive coverage of directional and multi-scale features
in the data. Here, C represents the number of input
Figure 3: Visualization of the GCONV operation.
feature maps, while C
′
denotes the number of feature
maps generated after applying the Gabor filters. A
ReLU activation is applied, followed by a 1 × 1 con-
volution to project the feature maps back to C dimen-
sions, maintaining consistency between input and out-
put feature map sizes. This design preserves feature
VISAPP 2025 - 20th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
526

map integrity while enabling effective detection of di-
rectional textures and edges.
The Gabor filters’ characteristics are influenced
by several key parameters, including their aspect ra-
tio (γ), which determines the filter’s shape. Smaller γ
values (e.g., 0.5) produce elongated filters that excel
in detecting directional edges, while values closer to
1 yield circular filters that capture broader textures.
Wavelength (λ), representing the spatial frequency,
is initialized with positive values greater than 0 and
less than the filter size. This constraint ensures that
λ aligns with the scale of the features in the data
and avoids unrealistic frequencies. Orientation (θ),
ranging from 0
◦
to 180
◦
, enables the filters to de-
tect features in all directions. Gaussian size (σ), set
within [0.5, 1.5], governs spatial localization, balanc-
ing fine and coarse feature detection. Phase offset (ψ)
is fixed at 0 to emphasize sharp transitions and im-
prove boundary detection. These parameters, updated
during training, allow the filters to dynamically adapt
to dataset-specific characteristics, capturing both fine
details and broader structures.
During training, λ, θ, σ, and γ are updated through
backpropagation. To ensure numerical stability, these
parameters are scaled during training and rescaled af-
ter each update, preventing extreme values that could
degrade performance.
Gabor filters remain consistent across all network
levels, maintaining coherence in feature extraction.
Future work will explore varying these parameters
across network levels to enhance hierarchical feature
extraction.
The filter size significantly impacts feature detec-
tion: smaller filters like 3 × 3 excel at highlighting
fine textures and directional edges, while larger sizes
(5 × 5 or 7 × 7) capture broader features but may lose
finer details. To balance this trade-off, filter sizes are
systematically tested, starting with 3 × 3.
The Gabor wavelet function is defined as:
g(x, y, λ, θ, ψ, σ, γ) = e
−
x
′2
+γ
2
y
′2
2σ
2
· e
i(2π
x
′
λ
+ψ)
, (1)
where x
′
and y
′
are rotated coordinates based on θ.
The Gaussian envelope provides spatial localization,
while the complex exponential captures frequency
and phase information.
By incorporating trainable Gabor filters, GAM-
UNet dynamically adapts to dataset characteristics,
effectively capturing both fine details and broader
structures for precise segmentation of complex tex-
tures, such as seismic top salt boundaries and thin
medical features like retinal vessels.
3.2.2 Spatial Channel Squeeze-and-Excitation
SCSE mechanisms recalibrate both spatial and chan-
nel information in the Gabor convolution outputs to
enhance feature selectivity. The SE block, illustrated
in Figure 2 in Section 3.1, uses global average pool-
ing to ”squeeze” feature maps into channel descrip-
tors that summarize their importance. A gating mech-
anism, comprising fully connected layers and a sig-
moid activation, adjusts the channel responses by am-
plifying important features and suppressing less rele-
vant ones. Additionally, spatial recalibration empha-
sizes critical regions such as fine textures and edges,
improving the model’s ability to capture subtle varia-
tions in complex segmentation tasks. Applying SCSE
to the Gabor-filtered outputs effectively enhances tex-
ture and edge detection, leveraging the strengths of
Gabor filters for precise segmentation.
3.3 Multi-Scale Feature Fusion (MSFF)
Figure 4: Multi-scale feature fusion: (a) Cascade connec-
tion (b) Skip Connection with Concatenation.
MSFF is essential for capturing both local and global
contexts, a widely used technique in segmentation
models (Zhou et al., 2018; Qin et al., 2020; Cai
and Wang, 2020). Our model employs a multi-scale
skip connection scheme that combines features from
various semantic levels via upsampling, concatena-
tion, and convolution in the decoder. Two connection
strategies are explored: Cascade and Skip Connection
with Concatenation, as illustrated in Figure 4.
• Cascade Connection. Features from multiple
scales are upsampled and concatenated into a uni-
fied representation.
• Skip Connection with Concatenation. Features
are upsampled and concatenated with the output
of the next block, forming a direct concatenated
pathway.
By progressively aggregating features from dif-
ferent decoder stages, our method reduces overfitting
and enhances fine detail capture. This structure im-
proves segmentation performance by maintaining ro-
bust feature representations across semantic levels.
Gam-UNet for Semantic Segmentation
527

3.4 Loss Function
To achieve precise segmentation, GAM-UNet em-
ploys a weighted combined loss function that inte-
grates Binary Cross-Entropy Loss (L
BCE
) for pixel-
wise accuracy and Dice Loss (L
DICE
) to enhance
structural similarity and address class imbalance.
This combination ensures a balance between pixel-
level accuracy and structural integrity, making GAM-
UNet highly effective for segmenting curvilinear
structures in seismic and medical images.
Binary Cross-Entropy Loss (L
BCE
) penalizes
pixel-wise differences between predicted probabili-
ties and the ground truth, while Dice Loss (L
DICE
)
measures the overlap between predicted segmenta-
tion and the ground truth, ensuring structural consis-
tency:
L
BCE
= −
1
N
N
∑
i=1
[y
i
log( ˆy
i
) + (1 − y
i
)log(1 − ˆy
i
)], (2)
L
DICE
= 1 −
2
∑
N
i=1
y
i
ˆy
i
∑
N
i=1
y
i
+
∑
N
i=1
ˆy
i
, (3)
where y
i
is the ground truth label and ˆy
i
is the pre-
dicted probability for pixel i.
4 EXPERIMENTS
We evaluated GAM-UNet on two segmentation tasks:
top salt layer in seismic images and retinal vessel in
medical images. The model, implemented in PyTorch
and optimized with the Adam optimizer (learning
rate: 0.0001), converged in approximately 80 epochs.
Key metrics—Dice Coefficient, Precision, and Re-
call—were used to assess segmentation accuracy and
structural consistency across diverse datasets.
4.1 Datasets
We evaluated GAM-UNet on two segmentation tasks:
top salt boundary in seismic images and retinal vessel
in medical images. Each task utilized datasets split
into 80% for training, 10% for validation, and 10%
for testing, without data augmentation to maintain the
original image characteristics.
• Seismic Image Datasets. Four seismic datasets
were used to assess the model’s robustness.
Datasets 1 to 3 are proprietary, containing 2D
slices extracted from 3D seismic cubes with sizes
ranging from 5k to 25k images. The fourth dataset
is the publicly available Dutch North Sea dataset
(DNS) (SEG SEAM Project, 2024), widely used
in seismic research. All datasets were prepared
by extracting 256 × 256 image slices along inline
and crossline sections, preserving geological de-
tails and curvilinear boundaries.
Figure 5: Seismic image slice and its label.
• Medical Image Datasets. To address the limited
availability of retinal vessel images online, six
datasets—ARIA, CHASE, DR-Hagis, DRIVE,
HRF, and STARE (Sarhan et al., 2021)—were
combined into a single dataset comprising ap-
proximately 400 images. This provided diverse
vessel structures with varying thickness, resolu-
tion, and background complexity.
Figure 6: Retinal vessel datasets.
4.2 Comparative Approaches
This section summarizes the key configurations of the
models used for comparative analysis:
• Fully Convolutional Network (FCN) (Long
et al., 2015). A model that replaces fully con-
nected layers with convolutions, enabling pixel-
wise predictions through upsampling while pre-
serving spatial information.
• UNet (Ronneberger et al., 2015). A symmetric
encoder-decoder architecture with skip connec-
tions, combining high-resolution encoder features
with decoder layers to enhance segmentation.
• UNet++ (Zhou et al., 2018). An extended UNet
with nested skip connections for refined feature
extraction and improved handling of complex
structures.
• Attention UNet (Att-UNet) (AlSalmi and
Elsheikh, 2024). Enhances segmentation by in-
corporating attention gates that focus on relevant
regions while suppressing irrelevant areas.
• Learnable Gabor Kernels for Seismic Inter-
pretation (LGK-UNet) (Wang and Alkhalifah,
2023). Employs learnable Gabor filters to adapt to
different scales and orientations, improving fea-
ture extraction for seismic image segmentation.
VISAPP 2025 - 20th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
528
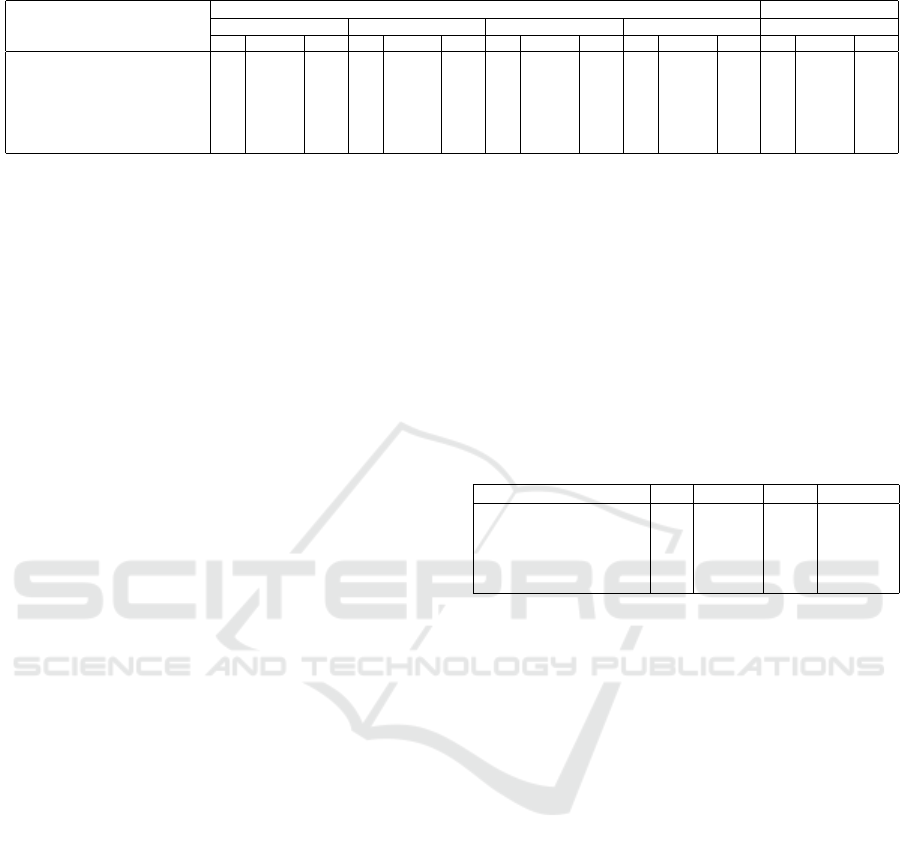
Table 1: Performance comparison for seismic and medical datasets across Dice, Precision, and Recall metrics.
Seismic Datasets Medical Dataset
Models Dataset 1 Dataset 2 Dataset 3 DNS Retinal Vessels
Dice Precision Recall Dice Precision Recall Dice Precision Recall Dice Precision Recall Dice Precision Recall
FCN (Long et al., 2015) 0.64 0.94 0.61 0.82 0.90 0.80 0.35 0.83 0.25 0.63 0.84 0.57 0.51 0.70 0.43
UNet (Ronneberger et al., 2015) 0.77 0.93 0.73 0.80 0.89 0.78 0.34 0.87 0.25 0.68 0.91 0.61 0.66 0.91 0.54
UNet++ (Zhou et al., 2018) 0.78 0.95 0.74 0.82 0.88 0.79 0.33 0.90 0.23 0.67 0.85 0.60 0.62 0.70 0.58
Att-UNet (AlSalmi and Elsheikh, 2024) 0.79 0.96 0.75 0.83 0.89 0.82 0.31 0.91 0.21 0.71 0.87 0.66 0.66 0.58 0.77
LGK-UNet (Wang and Alkhalifah, 2023) 0.80 0.95 0.76 0.83 0.89 0.81 0.34 0.90 0.24 0.72 0.88 0.67 0.65 0.64 0.69
Ours 0.89 0.88 0.91 0.84 0.89 0.82 0.65 0.78 0.59 0.85 0.86 0.85 0.70 0.61 0.83
5 RESULTS
This section compares our model’s performance with
other segmentation models using Dice, Precision, and
Recall metrics on seismic and medical datasets. Ab-
lation studies evaluate architectural components, and
the Gabor filters’ role in feature extraction is ana-
lyzed.
5.1 Models Performance Comparison
We assessed the performance of GAM-UNet on two
distinct dataset types: seismic datasets (Datasets 1
to 3 and DNS) and a combined medical dataset fo-
cused on retinal vessel segmentation. These datasets
present challenges such as noise, complex structures,
and high-resolution demands. For evaluation, GAM-
UNet was compared against the comparative models
cited in Section 4.2. Our model consistently achieves
higher Dice and Recall scores across both seismic and
medical datasets, as shown in Table 1. The Dice score
reflects accurate boundary and structure capture, bal-
ancing precision and recall. High Recall demonstrates
the model’s ability to identify target structures com-
prehensively, even in noisy or complex data. While
Precision scores are slightly lower due to the Gabor
filters enhancing edges but causing thicker bound-
aries, the strong Dice and Recall scores underscore
the model’s robustness and effectiveness in segmen-
tation tasks.
In seismic datasets, these improvements enable
accurate segmentation of top salt boundaries, ensur-
ing continuity and better detection in noisy geologi-
cal environments. As shown in Figure 7, GAM-UNet
provides more detailed and gap-free results compared
to other models, particularly in complex formations
where traditional approaches struggle.
For medical datasets, GAM-UNet excels in seg-
menting retinal vessels, effectively capturing finer
branching structures critical for diagnosis. Its abil-
ity to detect smaller vessels missed by other mod-
els demonstrates its strength in handling complex
vascular structures, making it suitable for precision-
demanding clinical applications.
5.2 Ablation Study
To evaluate the impact of different architectural com-
ponents on performance and parameter efficiency, we
conducted ablation studies on the Netherlands DNS
dataset. The analysis examined the contributions of
the Gabor Filter-based Feature Extraction Module
(GFEM), the SCSE mechanism, and multi-scale fea-
ture fusion with both cascade and Skip Connection
with Concatenation strategies.
Table 2: Ablation Study on Key Components.
Model Configuration Dice Precision Recall Param (M)
Baseline (UNet) 0.68 0.91 0.61 6.66
+ GFEM (Gabor Only) 0.80 0.89 0.76 6.99
+ GFEM (Gabor + SCSE) 0.83 0.90 0.79 7.02
+ GFEM + SCSE + Cascade 0.85 0.86 0.85 7.04
+ GFEM + SCSE + Residual 0.84 0.86 0.84 7.04
Each addition significantly enhanced the model’s
performance, as shown in Table 2. Introducing
the Gabor Filter-based Feature Extraction Module
(GFEM) increased Dice and Recall scores by +0.12
and +0.15, respectively, with a modest parameter rise
from 6.66M to 6.99M. Adding the SCSE mechanism
further improved feature maps, achieving a Dice score
of 0.83 with minimal parameter growth (7.02M),
highlighting the benefits of spatial and channel at-
tention. Incorporating multi-scale feature fusion with
cascade connections yielded the best results, reaching
a Dice score and Recall of 0.85 with 7.04M param-
eters. While the residual variant performed compa-
rably (Dice = 0.84), it fell short of the cascade con-
figuration. These findings validate the slight param-
eter increases by demonstrating substantial gains in
segmentation performance, particularly for complex
structures.
We further explored the influence of the loss func-
tion by conducting an ablation study on the different
weightings of the binary cross-entropy loss (L
BCE
)
and Dice loss (L
DICE
). As seen in Figure 8, the
weighting between L
BCE
and L
DICE
plays a crucial
role in the model’s performance. The optimal bal-
ance was found with α = 0.8 for L
BCE
and β = 0.2
for L
DICE
, yielding the best results. This indicates
that optimizing structural similarity through L
DICE
is
Gam-UNet for Semantic Segmentation
529

Figure 7: Segmentation results on DNS and retinal vessels datasets (a) Original image, (b) GT, (c) FCN, (d) UNet, (e) Att-
Unet, (f) Unet++, (g) GLK-Unet, (h) Ours
Figure 8: Ablation Study on Loss Function Weights.
essential for achieving high-quality segmentation, en-
suring accurate boundaries and overlap between the
predicted and ground truth segments.
Table 3: Ablation Study on Kernel Sizes, Orientations, and
Scales.
Kernel Size Orien Scales Dice Precision Recall
3 × 3
4 2 0.8321 0.8580 0.8105
8 4 0.8465 0.8649 0.8352
6 3 0.8560 0.8669 0.8521
12 6 0.8432 0.8601 0.8350
5 × 5
4 2 0.7742 0.8540 0.7200
8 4 0.7854 0.8673 0.7421
6 3 0.7920 0.8716 0.7502
12 6 0.7800 0.8600 0.7330
7 × 7
4 2 0.7595 0.8402 0.7101
8 4 0.7681 0.8455 0.7250
6 3 0.7750 0.8601 0.7203
12 6 0.7620 0.8500 0.7150
Our analysis evaluated Gabor filter configurations
by varying kernel sizes, orientations, and scales. As
shown in Table 3, the optimal configuration—6 orien-
tations, 3 scales, and a kernel size of 3 × 3—achieved
the highest Dice score (0.8560), Precision (0.8669),
and Recall (0.8521). The 3 × 3 kernels excelled in
capturing fine details and directional textures, which
are crucial for segmenting thin, curvilinear structures
like retinal vessels and top salt layers. Larger kernels
(5 × 5, 7 × 7) caused smoothing, leading to a loss of
critical edge details and occasionally blank, feature-
less images, which reduced segmentation accuracy.
The number of orientations, set to twice the num-
ber of scales, balanced feature coverage and redun-
dancy. Testing confirmed that the 3 × 3 setup offered
the best trade-off between computational efficiency
and segmentation accuracy, while larger configura-
tions provided diminishing returns.
5.3 Analysis of Gabor Filters for
Seismic and Medical Images
The Gabor filters adapt their parameters to the unique
characteristics of seismic and medical images. For
seismic datasets, filters focus on mid-range orienta-
tions (0.200π to 0.664π, or 36° to 120°), enabling
the detection of geological features like salt bound-
aries and faults. Lambda values (0.850 to 1.983) cap-
ture features across scales, while an elliptical Gamma
(0.547) emphasizes elongated structures. A Sigma of
1.0 balances fine and coarse feature detection, and a
Psi of 0.5π ensures sharp edge transitions, collectively
enhancing seismic feature representation (Figure 9).
Figure 9: Sample Gabor filters and their feature maps for
(right) DNS dataset and (left) Retinal vessels dataset.
For medical images, broader orientations (0.003π
to 0.648π, or 0.5° to 116°) address the multi-
directional nature of blood vessels and tissue bound-
aries. Lambda values (0.955 to 1.995) capture both
thin vessels and larger anatomical features. Un-
like seismic filters, a nearly circular Gamma (0.902)
suits rounded structures. The consistent Sigma (1.0)
and Psi (0.5π) ensure uniformity in phase transitions.
These domain-specific adaptations emphasize seismic
filters’ focus on elongated, stratified patterns, while
medical filters capture finer, multi-directional details
like branching vessels. This dynamic parameteriza-
tion enables the effective segmentation of intricate
patterns across both datasets.
VISAPP 2025 - 20th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
530

6 CONCLUSION
This paper presented GAM-UNet, a semantic seg-
mentation model integrating Gabor Feature Extrac-
tion Modules (GFEM), SCSE mechanisms, and
multi-scale feature fusion within the UNet frame-
work. This combination enhances the model’s ability
to capture fine edges and textures in complex tasks
involving seismic and medical images. The learn-
able Gabor filters dynamically adapt to the orientation
and scale of features, enabling the detection of fine,
elongated structures in seismic images and intricate,
multi-directional features in medical images, such as
blood vessels. Our experiments highlighted the su-
perior performance of the 3×3 Gabor filter configu-
ration, which preserved segmentation continuity and
reduced noise. Analysis across datasets demonstrated
the model’s adaptability—capturing broad, linear fea-
tures in seismic data and intricate textures in medical
images—underscoring its effectiveness in segmenting
fine, curvilinear structures within the tested datasets.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
We thank Shell Information Technology International
Inc. for providing the dataset, which was instrumental
in this research.
REFERENCES
Alekseev, A. and Bobe, A. (2019). Gabornet: Gabor fil-
ters with learnable parameters in deep convolutional
neural network. In 2019 International Conference on
Engineering and Telecommunication (EnT). IEEE.
AlSalmi, H. and Elsheikh, A. H. (2024). Automated seismic
semantic segmentation using attention u-net. GEO-
PHYSICS, 89(1).
Cai, Y. and Wang, Y. (2020). Ma-unet: An improved ver-
sion of unet based on multi-scale and attention mech-
anism for medical image segmentation. arXiv.
Chen, B., Zhang, Z., Liu, N., Tan, Y., Liu, X., and Chen, T.
(2020). Spatiotemporal convolutional neural network
with convolutional block attention module for micro-
expression recognition. Information, 11:380.
Jiang, S., Chen, X., and Yi, C. (2024). Ssa-unet:
Whole brain segmentation by u-net with squeeze-and-
excitation block and self-attention block from the 2.5d
slice image. IET Image Processing.
Li, H., Qiu, K., Chen, L., Mei, X., Hong, L., and Tao,
C. (2020). Scattnet: Semantic segmentation net-
work with spatial and channel attention mechanism
for high-resolution remote sensing images. IEEE
Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett., 18:905–909.
Long, J., Shelhamer, E., and Darrell, T. (2015). Fully con-
volutional networks for semantic segmentation. In
Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vi-
sion and Pattern Recognition, pages 3431–3440.
Luan, S., Chen, C., Zhang, B., Han, J., and Liu, J. (2018a).
Gabor convolutional networks. IEEE Transactions on
Image Processing, 27(9):4357–4366.
Luan, S., Zhang, B., Zhou, S., Chen, C., Han, J., Yang, W.,
and Liu, J. (2018b). Gabor convolutional networks.
IEEE Trans. Image Process., 27(9):4357–4366.
Ozbulak, G. and Ekenel, H. K. (2018). Gabor initialized
convolutional neural networks for transfer learning. In
Signal Processing and Communications Application
Conference.
Qin, X., Zhang, Z., Huang, C., Dehghan, M., Zaiane, O. R.,
and Jagersand, M. (2020). U2-net: Going deeper with
nested u-structure for salient object detection. Pattern
Recognition, 106:107404.
Ronneberger, O., Fischer, P., and Brox, T. (2015). U-net:
Convolutional networks for biomedical image seg-
mentation. 9351:234–241.
Roy, A. G., Navab, N., and Wachinger, C. (2018). Recali-
brating fully convolutional networks with spatial and
channel ‘squeeze and excitation’ blocks. IEEE Trans.
Med. Imaging, 38:540–549.
Rundo, L., Militello, C., Vitabile, S., Gilardi, M. C., and
Leonardi, R. (2019). Use-net: Incorporating squeeze-
and-excitation blocks into u-net for prostate zonal seg-
mentation of multi-institutional mri datasets. Neuro-
computing, 365:31–43.
Sarhan, A., Rokne, J., Alhajj, R., and Crichton, A. (2021).
Transfer learning through weighted loss function and
group normalization for vessel segmentation from
retinal images. In 2020 25th ICPR, pages 9211–9218.
IEEE.
Sarwar, S. S., Panda, P., and Roy, K. (2017). Gabor filter as-
sisted energy efficient fast learning convolutional neu-
ral networks. In IEEE ACM International Symposium
on Low Power Electronics and Design, pages 1–6.
SEG SEAM Project (2024). SEG SEAM Artifi-
cial Intelligence Dataset. https://seg.org/seam/
artificial-intelligence/.
Shen, X., Xu, J., Jia, H., Fan, P., Dong, F., Yu, B., and
Ren, S. (2022). Self-attentional microvessel segmen-
tation via squeeze-excitation transformer unet. Com-
puterized medical imaging and graphics : the official
journal of the Computerized Medical Imaging Society,
97:102055.
Wang, F. and Alkhalifah, T. (2023). Learnable gabor kernels
in convolutional neural networks for seismic interpre-
tation tasks. arXiv.
Yuan, Y., Wang, L.-N., Zhong, G., Gao, W., Jiao, W., Dong,
J., Shen, B., Xia, D., and Xiang, W. (2022). Adaptive
gabor convolutional networks. Pattern Recognition,
124:108495.
Zhou, Z., Rahman Siddiquee, M. M., Tajbakhsh, N., and
Liang, J. (2018). Unet++: A nested u-net architecture
for medical image segmentation. In Deep Learning
in Medical Image Analysis and Multimodal Learning
for Clinical Decision Support, DLMIA ML-CDS 2018,
volume 11045, pages 3–11. Springer, Cham.
Gam-UNet for Semantic Segmentation
531
