
Cellular Automata-Based Model for Simulation of Collective Pedestrian
Dynamics in Indoor Environments with Surmountable Obstacles
Eduardo C. Silva
a
, Gabriela S. Damazo
b
, Gina M. B. Oliveira
c
and Luiz G. A. Martins
d
Faculty of Computer Science, Federal University of Uberl
ˆ
andia, Uberl
ˆ
andia, MG 38408-100, Brazil
Keywords:
Cellular Automata, Collective Pedestrian Dynamics, Modeling and Simulation, Surmountable Obstacles,
Impassable Diagonals.
Abstract:
Understanding and predicting human behavior in normal and emergency situations is a difficult task that
attracts the attention of many researchers. In this sense, modeling and simulation of collective pedestrian
dynamics (CPD) is essential in society, as it is used in various scenarios, such as urban planning and public
safety. Cellular Automata stand out as simple computational tools capable of identifying and reproducing
the complexity of various patterns, such as pedestrian movement, especially during evacuation in emergency
situations. Models of this type take several parameters into consideration, such as the strategy for choosing
the floor, the interaction between pedestrians, social phenomena, such as panic and the tendency to follow
crowds, among others. This work proposes a model based on cellular automata for modeling CPD, strongly
based on the Varas Model, which combines three changes to bring the simulation closer to reality. These are:
changing the movement dynamics, presenting the separation between surmountable and impassable obstacles,
and changing the permission to pass between objects diagonally. These updates speed up the pedestrian
evacuation process and increase the level of credibility of the simulations compared to reality.
1 INTRODUCTION
Collective pedestrian dynamics (CPD) models play a
crucial role in enhancing public safety and improv-
ing urban planning strategies. These models use dif-
ferent computing approaches, including social force,
fluid dynamics, agent-based, game theory and ani-
mal experimentation (Zheng et al., 2011). A notable
method used in modelling CPD are the cellular au-
tomata (CA), that can be considered multi-agent sys-
tems. The CA are computational structures, which
can interact with each other, presenting local connec-
tivity, and result in emerging computing.
Three different factors can be considered when de-
veloping this CPD models. First, the space in which
the simulation is conducted. Second, the representa-
tion of the pedestrians. Third, the situation described
by the model. It is particularly interesting to model
CPD in emergency situations because there are some
human behaviors (e.g. panic, surpassing obstacles)
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9042-2562
b
https://orcid.org/0009-0007-3364-7029
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0384-1879
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0168-1293
that should be considered in the simulation in order to
make it more trustworthy.
The literature contains several works using CA
for CPD. Historically, the first studies using CAs to
model human movement were published in the 1990s,
for example the work of (Nagel and Schreckenberg,
1992), although it was focused on modeling vehicle
traffic flow. During this period, contributions came
from several studies involving pedestrian simulations
through models based on social forces, such as (Hel-
bing and Moln
´
ar, 1995; Helbing et al., 1997a; Hel-
bing et al., 1997b; Helbing et al., 2000), in addi-
tion to the arrival of CA-based models focused on
modeling bidirectional traffic (Blue and Adler, 1999a;
Blue et al., 1997; Blue and Adler, 1999b; Blue
and Adler, 2000). Then, CA models that simulated
pedestrian traffic in multiple directions emerged, with
emphasis on the Euclidean distance-based model of
(Burstedde et al., 2001). The environments studied
also changed over time, with emphasis on the internal
scenarios of classrooms (Liu et al., 2009), elevators
(Ma et al., 2012), theaters (Gao et al., 2020), restau-
rants (Eng Aik and Wee Choon, 2012), aircraft (Giit-
sidis et al., 2017), ships (Hu and Cai, 2020), among
others (Li et al., 2019).
Silva, E. C., Damazo, G. S., Oliveira, G. M. B. and Martins, L. G. A.
Cellular Automata-Based Model for Simulation of Collective Pedestrian Dynamics in Indoor Environments with Surmountable Obstacles.
DOI: 10.5220/0013186300003890
In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2025) - Volume 2, pages 463-471
ISBN: 978-989-758-737-5; ISSN: 2184-433X
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
463

(Alizadeh, 2011) proposed a CDP model that in-
corporates the concept of a dynamic floor into the
deterministic perspective, being built considering the
distribution of pedestrians during the simulation and
recalculated at each iteration, by checking the num-
ber of people on floors closest to an exit. (Mrowin-
ski et al., 2012) proposed two approaches: individuals
can move according to a probability between follow-
ing the floor value or making random movements or
pedestrians minimize the number of neighbors. (Shi
et al., 2018a; Shi et al., 2018b) proposed a model that
extends the static floor from the microscopic scale to
the mesoscopic scale.
(Shi et al., 2019) proposed a model that calculates
the dynamic impatience level considering both the
self-growth and the impatience propagation among
pedestrians. (Cari
˜
no and Garciano, 2020) used dy-
namics to develop a model of Evacuation safety index
(ESI). (Huan-Huan et al., 2015) developed a model in
which pedestrians are treated as the movable obsta-
cles which will increase the value of the floor field.
(Alizadeh, 2011; Mrowinski et al., 2012; Shi
et al., 2018a; Shi et al., 2018b; Shi et al., 2019; Cari
˜
no
and Garciano, 2020; Huan-Huan et al., 2015) are
models that share in common the static floor proposed
by (Varas et al., 2007), that is, a simplified way of
calculating the distances between the cells of the grid
and the exit without disregarding the use of obstacles.
This method offers an alternative to the static floor
based on Euclidean distance (Burstedde et al., 2001;
Kirchner and Schadschneider, 2002; Kirchner et al.,
2003b; Kirchner et al., 2003a; Kirchner et al., 2004;
Nishinari et al., 2004), in this model the reproduction
of human behavior phenomena depends on the adjust-
ment of several parameters. In contrast, using only
the static floor field and rules for handling collisions
with obstacles, the (Varas et al., 2007) model can re-
produce simulations in complex scenarios. Finally,
(Varas et al., 2007) also relies on the panic parameter,
which makes the model non-deterministic.
The aim of this paper is to present a CA model
for CPD, strongly based on the (Varas et al., 2007)
model that improves the relationship of the pedestrian
with the space of simulation, especially with the ob-
stacles, changing the movement dynamics, presenting
the difference between surmountable and insurmount-
able obstacles and modifying the permission to pass
between insurmountable obstacles using the diagonal.
First, in Section 2, the reference model is de-
scribed. Second, in Section 3, the changes we made
in the model are presented. Third, in Section 4, we
explain the results comparing the alterations with the
reference model. Finally, in Section 5, we summarize
and explain future research points.
2 THE MODEL
The prototype presented in this article is based on
(Varas et al., 2007), a model that proposes a simpli-
fied method for calculating the distance from transi-
tion cells to exit cells (Mrowinski et al., 2012). In ad-
dition, the model supports obstacles, something that
is usually present in real scenarios. The next subsec-
tions detail the main aspects of the explored model.
2.1 Floor Field Calculation
In the (Varas et al., 2007) model, the room is de-
fined as a two-dimensional quadrangular lattice, so
that each floor cell represents an area of 0.4 × 0.4m
2
and can assume one of the following states: pedes-
trian, obstacle or empty. The cell size represents a
surface when occupied by a person in high-density sit-
uations (Li et al., 2019). In addition, the authors also
defined that the pedestrian speed is approximately 1
m/s, thus ∆t = 0.4s.
The initial grid is designed to determine the exit
locations, the empty cells, the positions of the individ-
uals and insurmountable obstacles. Each cell receives
a constant value that represents the distance from that
cell to the exit, so that the closer to the exit, the lower
the value of the cell is (Alizadeh, 2011). The values
of the cells of the initial grid are calculated as follows
(Varas et al., 2007):
1. The exit cell receives a value of 1;
2. The cells adjacent to those with previously de-
fined distances have their values calculated ac-
cording to the following rules:
• If the value of the cell is n, the adjacent cells
vertically or horizontally will receive a value of
n + 1, while the adjacent cells on the diagonals
will receive a value of n + λ, with λ > 1;
• If there is a conflict of values, the lowest value
is chosen for that cell;
3. Step 2 is repeated until all cells have their dis-
tances calculated;
4. Objects (walls, tables, chairs, etc.) receive a high
value so that pedestrians do not try to pass through
these cells.
The Figure 1 shows an initial grid representing the
floor of a 16 × 20 room, in which the cell distances
were calculated considering, λ = 1.5 and object with
the constant value of 500.
2.2 Transition Rules
The movement and interaction between pedestrians is
defined based on a transition rule that uses Moore
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
464
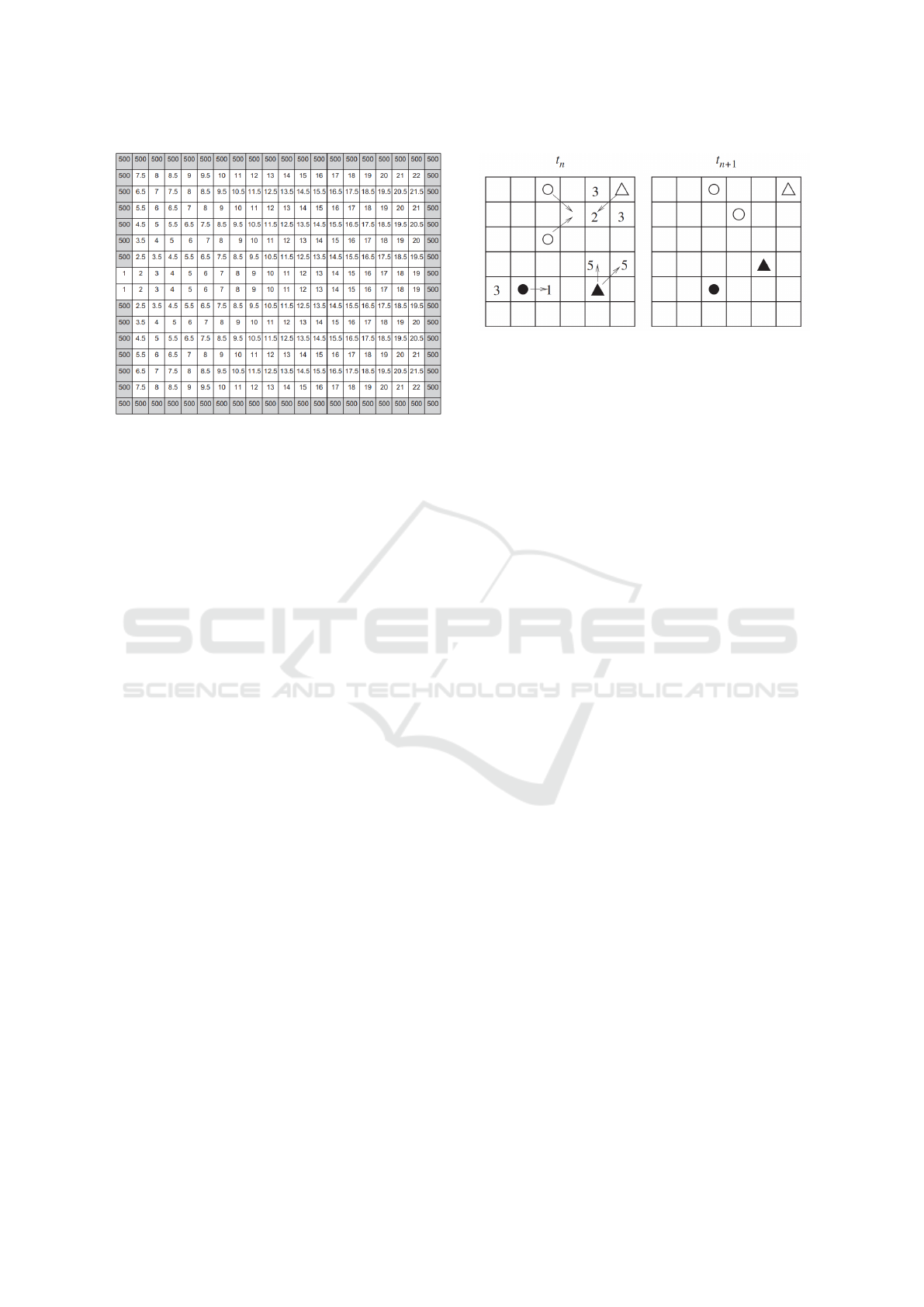
Figure 1: Calculation of the floor field of a 16 × 20 room
grid (Varas et al., 2007).
neighborhood and radius 1. At each step of the
CA evolution, all pedestrians move together to a cell
closer to the exit. Figure 2, demonstrates the move-
ment rules used, which are presented below (Al-
izadeh, 2011):
• Black circle: pedestrian moves to the cell with the
lowest value in its neighborhood;
• White circles: if two pedestrians want to go to the
same cell, this results in a conflict, resolved ran-
domly. The winner moves and the loser remains
still;
• Black triangle: if two or more cells in the neigh-
borhood of a pedestrian have the same value,
the pedestrian moves randomly to one of these
spaces;
• White triangle: introduction of the panic charac-
teristic. If a pedestrian panics at time t, he remains
still.
The last three rules introduce probability to the model,
so that it is not fully deterministic. It is worth men-
tioning that a pedestrian remains still when the cell
he wants to move to is occupied. In this sense, the
forms of interaction between pedestrians occur using
this last information and the rule of the white circles.
3 NEW MODEL RULES
One of the contributions of the (Varas et al., 2007)
model is the inclusion of obstacles in the simulations
so that the environment resembles real situations,
since it is more common for pedestrians to need to
evacuate rooms with obstacles than completely empty
rooms. However, there are a significant number of
simulations in rooms without obstacles, for example
Figure 2: Rules of pedestrian movement (Varas et al., 2007).
(Zheng et al., 2017). In addition, this model allows
the analysis of the influence of the location of doors
and their respective sizes on the evacuation of sim-
ulated scenarios. During the implementation of this
model, certain aspects were identified that could be
changed to bring the work even closer to real envi-
ronments. The modifications made will be detailed
below.
3.1 Cell Selection Dynamics
In the (Varas et al., 2007) model, the pedestrian
chooses to move to a cell with a lower value than
the one he is currently in. In addition, the authors
imposed some rules in which the pedestrian remains
still. There are three cases:
1. If he loses in the dispute against another pedes-
trian who wants to go to the same cell as him;
2. If he panics at that moment of the simulation;
3. If he chooses to go to a cell that already has a
pedestrian.
The first two items were demonstrated by the au-
thor in Figure 2. The original behavior of the third
rule is shown in Figure 3(a). In the grid on the
left, at t = 0, only a single pedestrian can move,
while the other pedestrians wait for the cell with the
best floor value to become available, which occurs
at t = 1. Therefore, a different approach is pre-
sented in this work, which is also explored in other
works, such as the model proposed by (Alizadeh,
2011). In it, the pedestrian always chooses the lowest
empty floor, which often avoids stopping by the third
rule. This choice-without-waiting (CWW) approach
is presented in Figure 3(b). Therefore, when using
the choice movement rule without waiting, all three
pedestrians are able to move. On the other hand, in
the choice with waiting, only one of the pedestrians
moves.
Cellular Automata-Based Model for Simulation of Collective Pedestrian Dynamics in Indoor Environments with Surmountable Obstacles
465
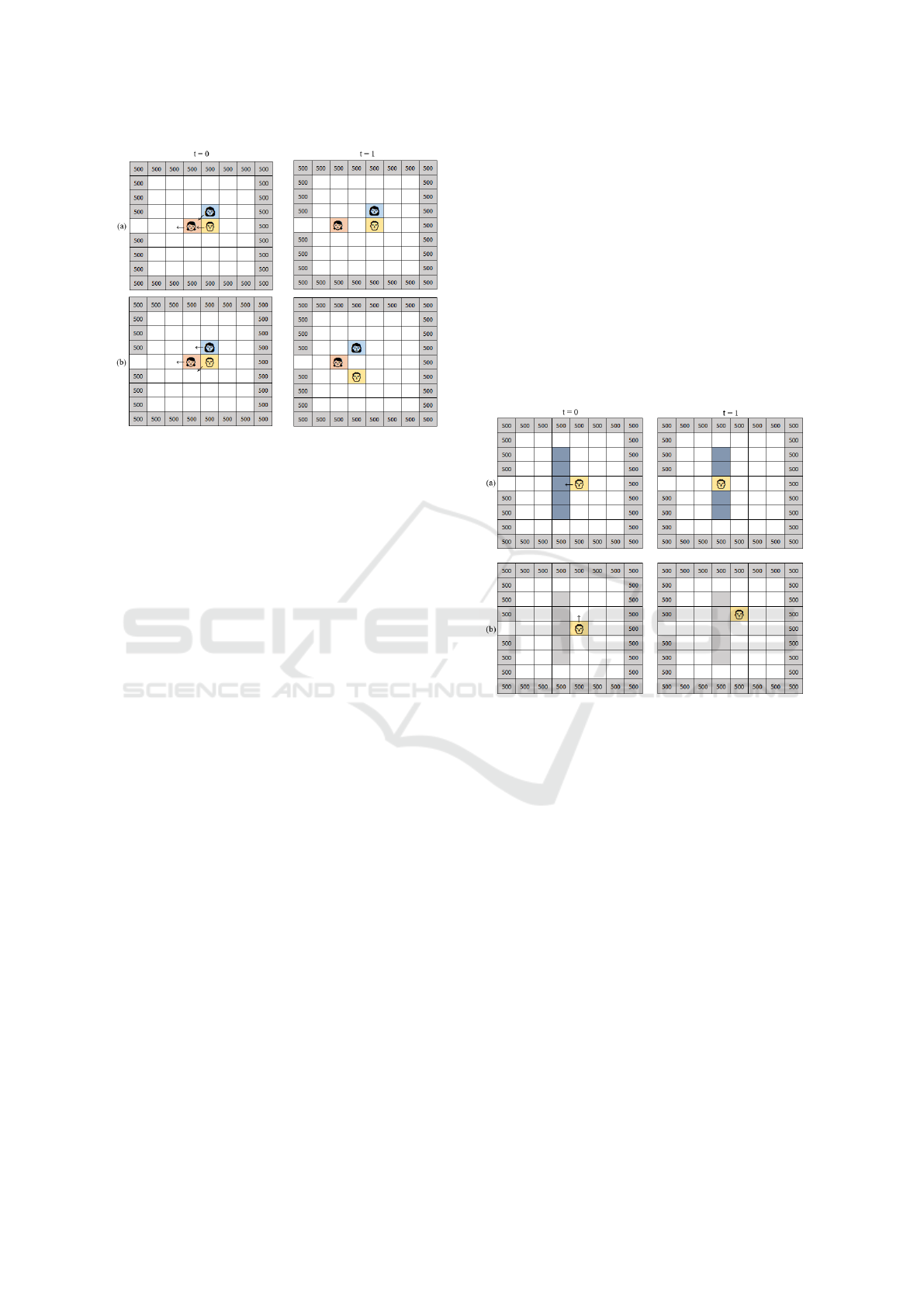
Figure 3: Comparison between pedestrian movement in a
9 × 8 room. (a) Choice of cell with waiting. (b) Choice of
cell without waiting (CWW).
3.2 Surmountable Obstacles
The (Varas et al., 2007) model supports the simula-
tion of obstacles in the simulation, in order to repro-
duce situations that are more faithful to reality. To
model obstacles, the model defines cells with con-
stant and unreachable values, making transitions to
these cells unfeasible. Therefore, these objects are
completely impassable, i.e., regardless of the items it
wanted to represent (walls, tables, chairs, etc.), pedes-
trians would not be able to overcome them.
The model proposed in this paper presents a dis-
tinction between two types of objects: impassable and
passable. The impassable objects are the objects of
the original (Varas et al., 2007; Alizadeh, 2011) mod-
els. The passable objects are introduced according to
some rules:
1. They have no impact on the structure of the grid,
that is, when the floor field values are calculated,
the passable objects are ignored and their cells are
treated as free and have their cost values calcu-
lated;
2. An overtaking rate z is defined at the beginning
of the simulations, which indicates the probabil-
ity of a pedestrian passing the object. It works as
follows:
• If the pedestrian ”wins” the overtaking, in the
next time step, he will occupy the obstacle cell,
representing a pedestrian on top of a chair or a
table;
• If the pedestrian ”loses” the overtaking, he re-
mains still.
Figure 4 demonstrates the difference in pedestrian
movement when considering the existence of sur-
mountable obstacles (proposed approach) and the
original model (with only insurmountable obstacles).
Figure 4(b) shows the movement of a pedestrian in
yellow, following the original version of (Varas et al.,
2007). In it, obstacles and walls are not distinguished,
therefore, to overcome the barrier, the pedestrian must
go around it. In Figure 4(a), according to the proposed
approach, the objects in blue represent surmountable
objects, while the walls in gray are insurmountable.
Assuming that at time t = 0, the pedestrian has gained
the overtaking, at time t = 1, he is on top of the bar-
rier. In the next time steps, he leaves the barrier floor
and goes to a cell according to the value of the lattice
and the transition rules.
Figure 4: Pedestrian movement in environments with sur-
mountable obstacles: (a) extended model and (b) original
model.
3.3 Changing Diagonal Movements
The (Varas et al., 2007) model allows pedestrians to
move diagonally. This feature is addressed in the tran-
sition rules and in the floor field calculation. De-
spite this, when obstacles are positioned diagonally,
the rules allow pedestrians to pass through the free
space between the barrier.
Figure 5(a) shows an initial grid of a room
that contains a diagonal barrier. As demonstrated,
the floor field calculation performed by the original
model considers the passage of obstacles through the
free cells on the opposite diagonals, which makes it
feasible for a pedestrian to move to such cells, illus-
trated in Figure 5(b).
A simple solution would be to use a double wall,
so that the obstacles are also included in the map mod-
eling. However, this representation may not be suit-
able for demonstrating real scenarios as it results in
more crowded environments.
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
466
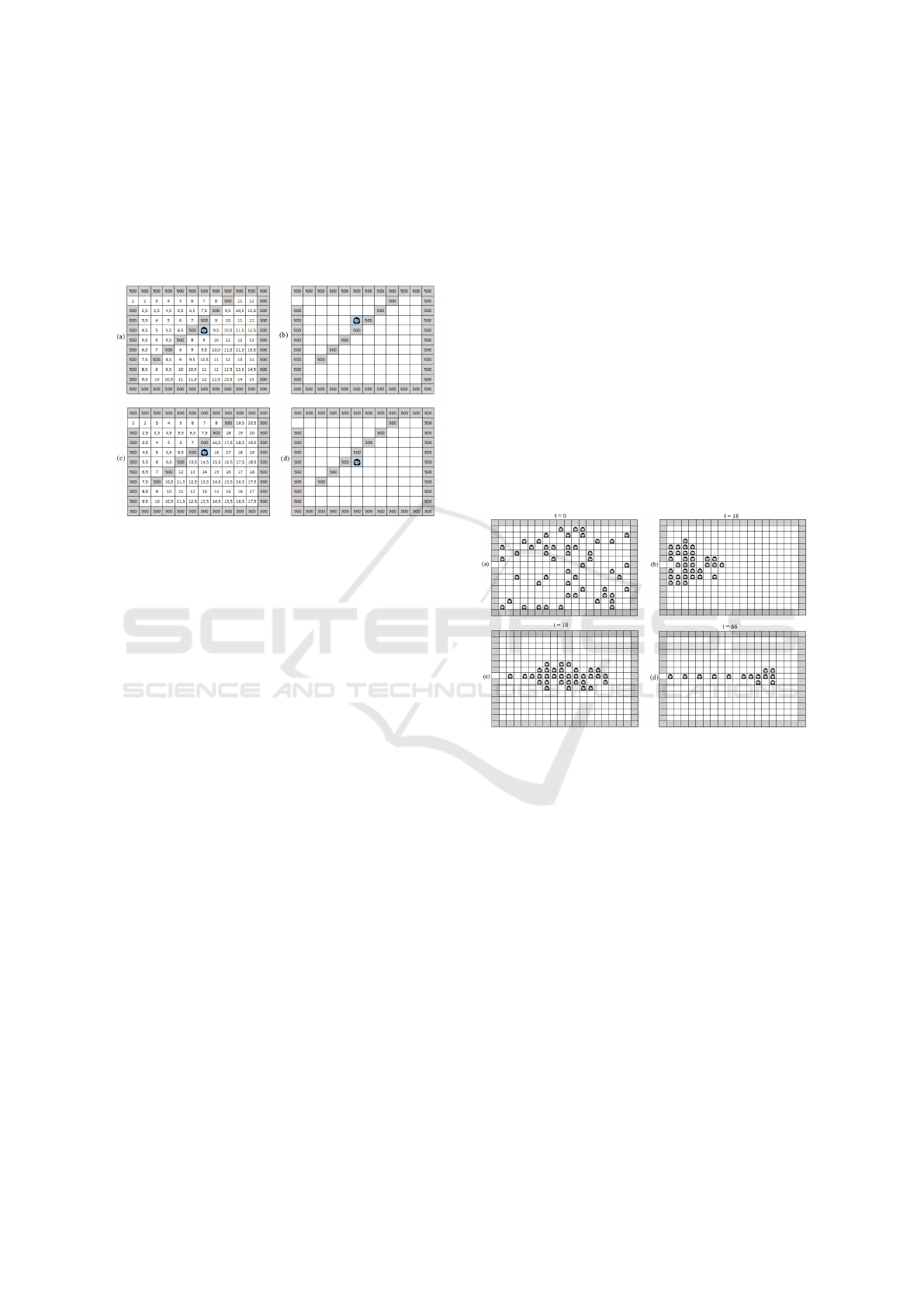
To solve this problem, the model improves the
floor field calculation to avoid movements through
barriers, i.e., the floor calculation is not propagated to
adjacent diagonal cells between obstacles. Figure 5(c)
shows the initial grid generated from this new floor
calculation strategy, resulting in the desired move-
ment, as demonstrated in Figure 5(d).
Figure 5: Pedestrian movement in scenarios with obstacles
arranged diagonally.
4 SIMULATION RESULTS
The analysis of CDS models involves several param-
eters that have a direct influence on the simulation re-
sults. The value of the diagonal rate was defined as
λ = 1.5. Another important consideration is that, in
all simulations, as in the paper by (Varas et al., 2007),
the panic rate was adopted as 5%, that is, each pedes-
trian, at each time step, has a 5% chance of stopping
due to having panicked. Another important character-
istic is that, in this implementation, it was considered
that a pedestrian, upon reaching the door, is no longer
inside the room.
The prototype was developed using the JAVA lan-
guage through an Integrated Development Environ-
ment (IDE). Simulations and data collection were per-
formed through the tool’s integrated console. A link
to the repository with a copy of the source code for
reproducing results can be found at appendix. Fur-
thermore, 30 runs were performed for each simula-
tion version and the values displayed refer to the av-
erage of these. Other important information will be
presented for each map.
4.1 Evacuation Dynamics in an Empty
Room
The grid used in the simulations to represent an
obstacle-free environment can be seen in 6(a). It con-
sists of a 16×20 room, with a cell-sized exit centered
on the leftmost wall. In the simulation, pedestrians
are randomly distributed. In the case of the image,
fifty pedestrians were placed in the simulation. This
map is used to compare the model of (Varas et al.,
2007) and the CWW version.
The Figures 6(c) and 6(d) present two different in-
stants (t = 18 and t = 66) of the simulation with the
original version of the Varas Model. A queue forma-
tion phenomenon occurs, because pedestrians choose
only the lowest floor value in their neighborhood and,
until it is clear, they remain still. Since the door is
located at a point further to the left of the room, the
queue follows that direction.
The Figure 6(b) shows a simulation instant (t =
18) with the CWW version. The difference between
the formations generated by the two models is clear.
It is clear that in the new version, pedestrians accu-
mulate closer to the exit and this causes them to leave
the room faster.
Figure 6: Comparison between the evacuation dynamics re-
sulting from the original and greedy versions of the Varas
model. (a) Initial lattice of a random simulation for 50
pedestrians in an empty room; (b) Lattice after 18 simu-
lation steps with the model in the CWW version; (c) Lat-
tice after 18 simulation steps with the model in the Original
Varas configuration; and (d) Lattice after 66 time steps in
the Original Varas configuration.
A quantitative analysis of this difference in behav-
ior is presented in Figure 7. This figure shows the av-
erage number of simulation time steps required for the
complete evacuation of pedestrians in the investigated
environment, for different numbers of people (25, 50,
100, 150). This average was obtained from 30 simula-
tions in each scenario (number of pedestrians) and for
each model investigated (Original Varas and CWW
version). The graph shows that the average number
of time steps differs between the two models as the
number of pedestrians increases. In the CWW ver-
sion, pedestrians always look for a cell smaller than
or equal to their value that is empty, which causes a
Cellular Automata-Based Model for Simulation of Collective Pedestrian Dynamics in Indoor Environments with Surmountable Obstacles
467
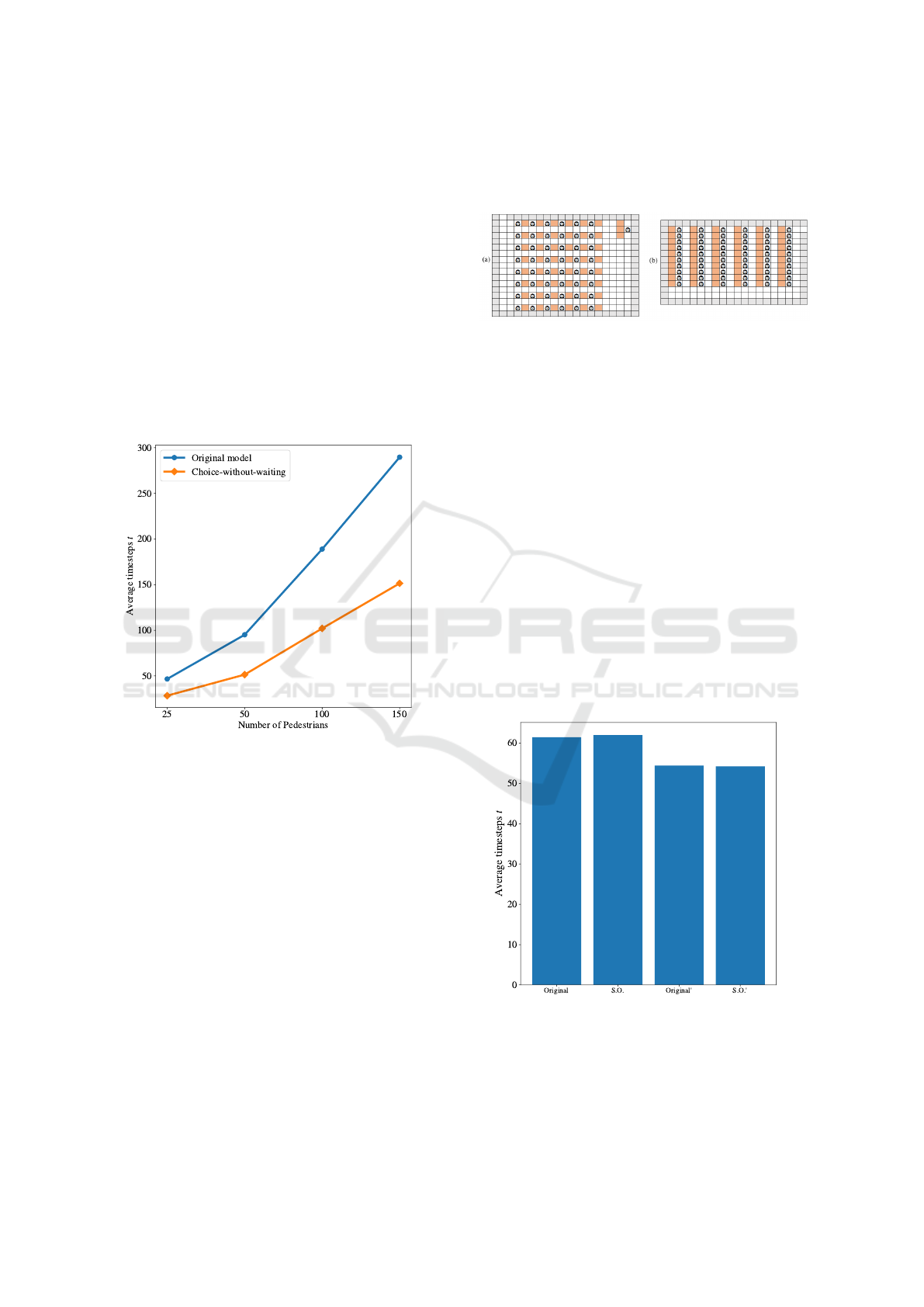
potential reduction in the average waiting time. In
the original version, they remain stationary until the
cell they want is free, which results in a considerably
longer waiting time, especially in traffic congestion
situations.
Furthermore, it is important to consider that the
observed discrepancy may also be influenced by the
way the model is implemented, as previously men-
tioned. In the implemented version, a pedestrian at
the door is no longer considered in the simulation. In
this sense, if there is a crowd, pedestrians escape more
quickly, since at each time step, a pedestrian can oc-
cupy the door cell. However, when considering sce-
narios without pedestrians accumulating around the
exit, for example, in the formation of queues, pedes-
trians do not necessarily leave at each time step.
Figure 7: Comparison between the original and CWW ver-
sions of the Varas model, considering simulations for 25,
50, 100 and 150 pedestrians.
4.2 Evacuation Dynamics in
Environments with Obstacles
To analyze the difference between surmountable and
impassable obstacles, it was necessary to think of en-
vironments that use different types of obstacles. The
map in Figure 8(a) was inspired by a university class-
room. The room is 17 × 20. Adding up all the pedes-
trians in the simulation (students and teacher), this
simulation has 49 people. In addition, 51 obstacles
were modeled to represent the students’ desks (1 cell
per desk) and the teacher’s desk (the only one that oc-
cupies 3 cells). The exit is located in the upper left
corner.
Another environment used for this modeling was
inspired by the university’s computer labs. In
this modeling, the grid is sized 14 × 20, with
60 traversable obstacles (representing the computer
benches) and 60 pedestrians. The exit is located in
the upper right corner (Figure 8).
Figure 8: Maps of the classroom (17×20 with 51 obstacles)
and computer lab (14 × 20 with 60 obstacles).
For both maps, an overtaking rate of 70% was
used. Figures 9 and 10 show the graphs correspond-
ing to the simulations performed for these maps.
These two configurations demonstrate that the ar-
rangement of pedestrians, objects and the exit of a
map can directly affect the average number of sim-
ulation time steps.
When observing Figure 9, it is noticeable that the
average times are very close. This is due to the ar-
rangement of the grid. In the case of the classroom
map, most pedestrians will prefer to walk diagonally,
heading northwest and avoiding obstacles, even when
they manage to overcome them, since the exit is lo-
cated at the highest point and to the left of the map.
In addition, the fact that the obstacles are of a sin-
gle size prevents them from making it too difficult for
pedestrians to move. Therefore, even though the orig-
inal version of (Varas et al., 2007) takes, on average,
more time steps, this difference is not so visible.
Figure 9: Average time steps for evacuation in the class-
room environment.
In Figure 10, the average decreases from the orig-
inal (Varas et al., 2007) model (slower) to the CWW
version with traversable objects (faster). The door
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
468
located in the upper right corner and the arrange-
ment of the obstacles forming continuous barriers is
what causes this discrepant difference between the
two simulations.
Figure 10: Average time steps for evacuation in the labora-
tory environment.
Figure 11(a) shows that, by making it impossible
to pass through the objects, the only option for pedes-
trians is to follow the corridor, which creates a large
crowd and, even with the CWW version, it is not pos-
sible to disperse these individuals to get closer to the
exit. In the case of Figure 11(b), the traversable ob-
jects are connected, in this case, it is clear that pedes-
trians prefer to try to pass obstacles, rather than follow
the corridor, which corresponds to the information in
the graphs.
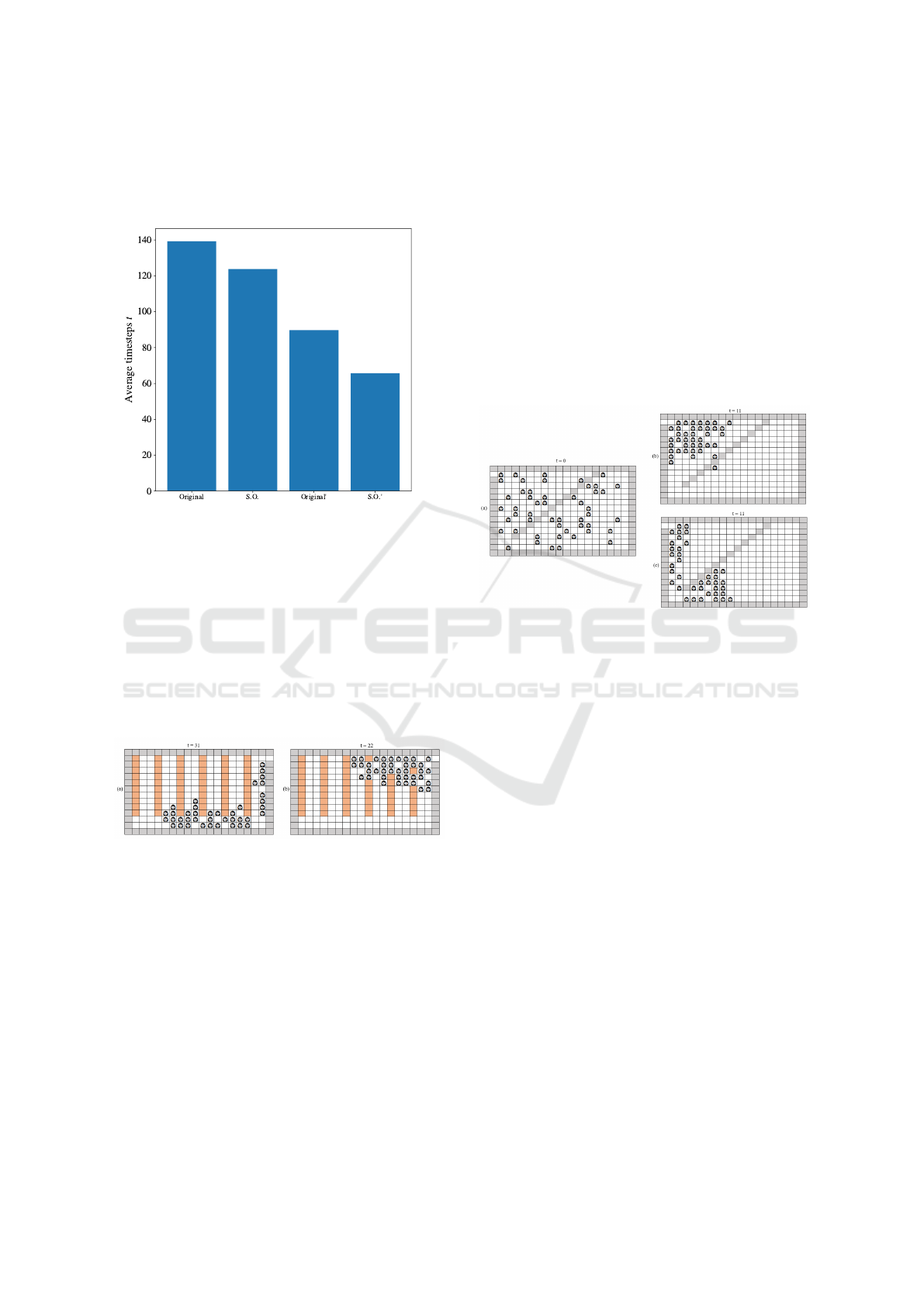
Figure 11: Laboratory evacuation dynamics according to
the type of obstacle modeled. (a) Simulation of the CWW
version with only insurmountable obstacles (t = 31); and
(b) Simulation of the CWW version model with both sur-
mountable and insurmountable obstacles (t = 22).
4.3 Evacuation Dynamics in an
Environment with Diagonal Wall
In order to assess the non-crossing of insurmountable
barriers diagonally, a map similar to the one shown in
Figure 5 was used. It has dimensions of 16 × 20 and
pedestrians are randomly allocated in the room.
Figure 12 shows two simulations that demonstrate
the difference in pedestrian flow when allowing or not
allowing the crossing of walls by free cells on the di-
agonals. These simulations were generated from the
original version of the Varas model and through the
CWW version, varying the way in which the distances
of the grid cells are calculated. In Figure 12(b), the
floor calculation of the original model was adopted,
which considers the adjacency between the diagonal
cells positioned on opposite sides of the wall. As
can be seen, in this simulation, pedestrians quickly
gathered at the exit, since they were able to cross the
barriers. On the other hand, in the situation shown
in Figure 12(c), the improved floor calculation was
adopted, which disregards the adjacency between di-
agonal cells on opposite sides of the walls, so that
pedestrians need to go around to reach the exit.
Figure 12: Pedestrian flow as a function of the strategy used
in the floor calculation. (a) Lattice at time t = 0 with 50
random pedestrians. (b) Simulation of the greedy strategy
model using the original floor calculation, at time t = 11. (c)
Simulation of the greedy strategy model using the adapted
floor calculation, at time t = 11.
By allowing this overtaking, the simulation be-
comes a little faster, since individuals do not need
to go around the wall. Despite this, as mentioned in
previous sections, this behavior does not come close
to reality. Furthermore, as can be seen in the graph
in Figure 13, the average number of steps does not
change significantly when using the CWW version of
the model.
Another noticeable result when analyzing the
graph is that using the ”double wall” version or the
”no diagonals” version does not affect the average
number of simulation steps, whether in the simulation
of the original model or the CWW version. Despite
this, removing the double wall frees up some cells on
the map, which allows more pedestrians or obstacles
to be represented in those locations.
5 CONCLUSION
Cellular automata-based CPD models are widely used
in this research area because they can effectively
Cellular Automata-Based Model for Simulation of Collective Pedestrian Dynamics in Indoor Environments with Surmountable Obstacles
469
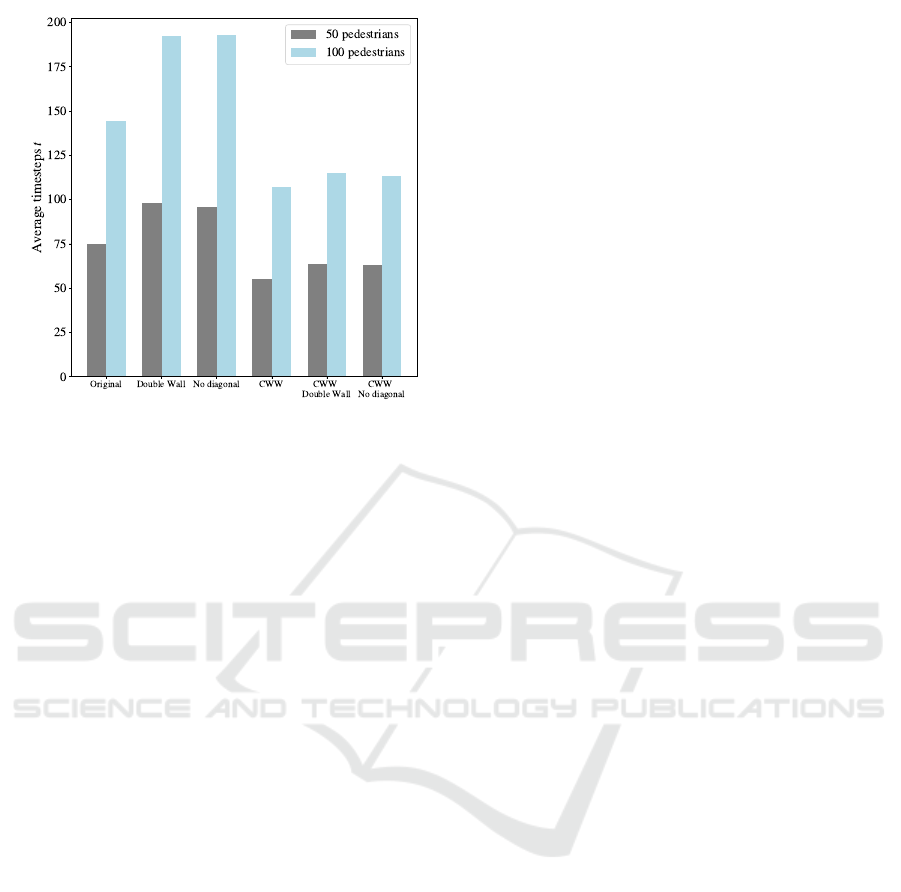
Figure 13: Comparison between simulations of the Room
with Diagonal Wall Map.
and simply represent complex pedestrian behaviors
in normal and emergency situations. In this sense,
this work implemented a precursor model in the area,
which is well known and used by several researchers,
the (Varas et al., 2007) model. In addition, changes
were made to this model: in the movement dynam-
ics, by presenting surmountable obstacles and by pro-
hibiting diagonal movements between impassable ob-
jects.
These modifications, when compared to the orig-
inal model, produced different results. The CWW
version significantly improves the average simulation
time steps as the number of pedestrians increases. The
second modification presents a separation between
surmountable and impassable obstacles. In this case,
it was observed that the room configuration produces
very different results for each simulation. Once these
obstacles were separated, the third modification pre-
vents people from passing through the diagonal be-
tween two impassable objects. This modification did
not demonstrate a significant difference in the aver-
age simulation time steps, but it is a more realistic
behavior when people encounter a diagonal wall. In
the original model, since it is possible to calculate the
cost of a neighboring diagonal cell, pedestrians can
pass through walls, which does not reflect reality.
These changes are an initial step towards refining
the model (Varas et al., 2007). In future work, this
research will be used to enhance the model’s ability
to represent real environments. One idea is to add
a dynamic floor so that pedestrians do not congre-
gate in one location, but can instead look for other
exits (Alizadeh, 2011; Xiao and Li, 2021; Strongylis
et al., 2019). Another investigation aims to further
distinguish between surmountable obstacles, present-
ing different difficulties for overcoming. Further-
more, one proposal is to add characteristics of exter-
nal environments, so that the model can be used in
different environments and can assist in the evacua-
tion of pedestrians in these locations (Zheng et al.,
2011; Zheng et al., 2017; Zhou et al., 2019).
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The work describe in this paper was supported by
CNPq (National Council for Scientific and Techno-
logical Development) and CAPES (Coordination of
Superior Level Staff Improvement). We also thank the
reviewers for their constructive comments and sug-
gested corrections.
REFERENCES
Alizadeh, R. (2011). A dynamic cellular automaton model
for evacuation process with obstacles. Safety Science,
49(2):315–323.
Blue, V. and Adler, J. (1999a). Bi-directional emergent
fundamental pedestrian flows from cellular automata
microsimulation. Transportation and traffic theory,
14:235–254.
Blue, V., Embrechts, M., and Adler, J. (1997). Cellular au-
tomata modeling of pedestrian movements. In Com-
putational Cybernetics and Simulation 1997 IEEE In-
ternational Conference on Systems, Man, and Cyber-
netics, volume 3, pages 2320–2323 vol.3.
Blue, V. J. and Adler, J. L. (1999b). Cellular Automata
Microsimulation of Bidirectional Pedestrian Flows.
Transportation Research Record, 1678(1):135–141.
Blue, V. J. and Adler, J. L. (2000). Cellular Automata Model
of Emergent Collective Bi-Directional Pedestrian Dy-
namics.
Burstedde, C., Klauck, K., Schadschneider, A., and Zittartz,
J. (2001). Simulation of pedestrian dynamics using a
two-dimensional cellular automaton. Physica A: Sta-
tistical Mechanics and its Applications, 295(3):507–
525.
Cari
˜
no, J. and Garciano, L. (2020). Proposed evacuation
safety index (ESI) for school buildings. International
Journal of Disaster Resilience in the Built Environ-
ment, 11(3):309–328.
Eng Aik, L. and Wee Choon, T. (2012). Simulating Evacu-
ations with Obstacles Using a Modified Dynamic Cel-
lular Automata Model. Journal of applied mathemat-
ics, 2012:1–17.
Gao, Q.-F., Tao, Y.-Z., Wei, Y.-F., Wu, C., and Dong, L.-Y.
(2020). Simulation-based optimization of inner lay-
out of a theater considering the effect of pedestrians*.
Chinese Physics B, 29(3):034501.
Giitsidis, T., Dourvas, N. I., and Sirakoulis, G. C. (2017).
Parallel implementation of aircraft disembarking and
ICAART 2025 - 17th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
470

emergency evacuation based on cellular automata.
The international journal of high performance com-
puting applications, 31(2):134–151.
Helbing, D., Farkas, I. J., and Vicsek, T. (2000). Freezing
by Heating in a Driven Mesoscopic System. Physical
Review Letters, 84(6):1240–1243.
Helbing, D., Keltsch, J., and Moln
´
ar, P. (1997a). Mod-
elling the evolution of human trail systems. Nature,
388(6637):47–50.
Helbing, D. and Moln
´
ar, P. (1995). Social force model for
pedestrian dynamics. Physical Review E, 51(5):4282–
4286.
Helbing, D., Schweitzer, F., Keltsch, J., and Moln
´
ar, P.
(1997b). Active walker model for the formation of
human and animal trail systems. Physical Review E,
56(3):2527–2539.
Hu, M. and Cai, W. (2020). Evacuation simulation and lay-
out optimization of cruise ship based on cellular au-
tomata. International Journal of Computers and Ap-
plications, 42(1):36–44.
Huan-Huan, T., Li-Yun, D., and Yu, X. (2015). Influence
of the exits’ configuration on evacuation process in
a room without obstacle. Physica A: Statistical Me-
chanics and its Applications, 420:164–178.
Kirchner, A., Kl
¨
upfel, H., Nishinari, K., Schadschneider,
A., and Schreckenberg, M. (2003a). Simulation of
competitive egress behavior: Comparison with air-
craft evacuation data. Physica A: Statistical Mechan-
ics and its Applications, 324(3):689–697.
Kirchner, A., Kl
¨
upfel, H., Nishinari, K., Schadschneider,
A., and Schreckenberg, M. (2004). Discretization
effects and the influence of walking speed in cellu-
lar automata models for pedestrian dynamics. Jour-
nal of Statistical Mechanics: Theory and Experiment,
2004(10):P10011.
Kirchner, A., Nishinari, K., and Schadschneider, A.
(2003b). Friction effects and clogging in a cellular
automaton model for pedestrian dynamics. Physical
Review E, 67(5):056122.
Kirchner, A. and Schadschneider, A. (2002). Simula-
tion of evacuation processes using a bionics-inspired
cellular automaton model for pedestrian dynamics.
Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications,
312(1):260–276.
Li, Y., Chen, M., Dou, Z., Zheng, X., Cheng, Y., and
Mebarki, A. (2019). A review of cellular automata
models for crowd evacuation. Physica A: Statistical
Mechanics and its Applications, 526:120752.
Liu, S., Yang, L., Fang, T., and Li, J. (2009). Evacuation
from a classroom considering the occupant density
around exits. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and
its Applications, 388(9):1921–1928.
Ma, J., Lo, S. M., and Song, W. G. (2012). Cellular au-
tomaton modeling approach for optimum ultra high-
rise building evacuation design. Fire Safety Journal,
54:57–66.
Mrowinski, M., Gradowski, T., and Kosinski, R. (2012).
Models of pedestrian evacuation based on cellular au-
tomata. Acta Physica Polonica A, 121(2 B):B95–
B100.
Nagel, K. and Schreckenberg, M. (1992). A cellular
automaton model for freeway traffic. Journal de
Physique I, 2(12):2221–2229.
Nishinari, K., Kirchner, A., Namazi, A., and Schadschnei-
der, A. (2004). Extended Floor Field CA Model for
Evacuation Dynamics. IEICE TRANSACTIONS on In-
formation and Systems, E87-D(3):726–732.
Shi, M., Lee, E. W. M., and Ma, Y. (2018a). A novel
grid-based mesoscopic model for evacuation dynam-
ics. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applica-
tions, 497:198–210.
Shi, M., Lee, E. W. M., and Ma, Y. (2019). A dynamic
impatience-determined cellular automata model for
evacuation dynamics. Simulation Modelling Practice
and Theory, 94:367–378.
Shi, M., Ming Lee, E. W., and Ma, Y. (2018b). A Newly de-
veloped Mesoscopic Model on Simulating Pedestrian
Flow. Procedia Engineering, 211:614–620.
Strongylis, D., Kouzinopoulos, C. S., Stavropoulos, G., Vo-
tis, K., and Tzovaras, D. (2019). Emergency Evacu-
ation Simulation in Open Air Events Using a Floor
Field Cellular Automata Model. In Moura Oliveira,
P., Novais, P., and Reis, L. P., editors, Progress in Ar-
tificial Intelligence, Lecture Notes in Computer Sci-
ence, pages 642–653, Cham. Springer International
Publishing.
Varas, A., Cornejo, M. D., Mainemer, D., Toledo, B., Ro-
gan, J., Mu
˜
noz, V., and Valdivia, J. A. (2007). Cellular
automaton model for evacuation process with obsta-
cles. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Appli-
cations, 382(2):631–642.
Xiao, Q. and Li, J. (2021). Pedestrian Evacuation Model
considering Dynamic Emotional Update in Direction
Perception Domain. Complexity, 2021:e5530144.
Zheng, Y., Jia, B., Li, X.-G., and Jiang, R. (2017). Evacua-
tion dynamics considering pedestrians’ movement be-
havior change with fire and smoke spreading. Safety
Science, 92:180–189.
Zheng, Y., Jia, B., Li, X.-G., and Zhu, N. (2011). Evacu-
ation dynamics with fire spreading based on cellular
automaton. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its
Applications, 390(18):3147–3156.
Zhou, Z., Zhou, Y., Pu, Z., Qi, Y., and Xu, Y. (2019).
An Integrated Cellular Automata Approach for Spa-
tial Evacuation Simulation on Metro Platforms with
Smoke Spreading. Transportation Research Record,
2673(11):851–864.
APPENDIX
A copy of the source code used in the simu-
lations was made available in a remote reposi-
tory at (https://github.com/eduardocassiano-ufu/
Cellular-Automata-with-Surmountable-Obstacles).
Additional instructions on compilation steps, soft-
ware dependencies and test execution are presented
on the repository’s home page.
Cellular Automata-Based Model for Simulation of Collective Pedestrian Dynamics in Indoor Environments with Surmountable Obstacles
471
