
From Noise Estimation to Restoration: A Unified Diffusion and Bayesian
Risk Approach for Unsupervised Denoising
Reeshad Khan
a
, Ukash Nakarmi
b
and John M. Gauch
c
Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, University of Arkansas, Fayetteville, Arkansas, U.S.A.
{rk010, unakarmi, jgauch}@uark.edu
Keywords:
Diffusion, Stein’s Unbiased Risk Estimator, Bayesian Loss, SURE, PURE, PGURE, MRI Denoising,
Unsupervised Learning.
Abstract:
Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) have revolutionized image denoising, challenging traditional methods such as
Stein’s Unbiased Risk Estimator (SURE) and its extensions (eSURE and PURE), along with Extended Poisson
Unbiased Risk Estimator (ePURE). These traditional approaches often struggle to generalize across different
noise types, especially when noise characteristics are unknown or vary widely, and they are not equipped
to handle mixed noise scenarios effectively. In response, we present a novel unsupervised learning strategy
that leverages an enhanced diffusion model combined with a dynamically trained Deep Convolutional Neural
Network (DnCNN). We introduce adaptive Bayesian loss functions—Bayesian-SURE, Bayesian-PURE, and
a newly developed Bayesian-Poisson-Gaussian Unbiased Risk Estimator (Bayesian-PGURE)—that adjust to
estimated noise levels and types without prior knowledge. This innovative method enables significant im-
provements in handling mixed noise conditions and ensures robustness across varied imaging scenarios. Our
comprehensive evaluations on MRI data corrupted by Gaussian, Poisson, and mixed noise demonstrate that
our approach outperforms existing algorithms, achieving superior denoising performance and image fidelity
under diverse, unpredictable conditions. Our contributions advance the state-of-the-art in medical imaging
denoising, establishing a new benchmark for unsupervised learning frameworks in managing complex noise
dynamics.
1 INTRODUCTION
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) serves as a criti-
cal tool in clinical diagnostics due to its non-ionizing
nature and superior tissue contrast capabilities, offer-
ing safe imaging without radiation exposure (Jalata
et al., 2024). Despite these advantages, MRI scans
are inherently affected by noise introduced during
the acquisition process, which often necessitates ad-
vanced denoising techniques to improve image qual-
ity (Manj
´
on and Coupe, 2019). While traditional
denoising methods like BM3D (Burger et al., 2012)
have been effective for synthetic noise types such as
Gaussian (Zhang et al., 2017a) and Poisson (Cherry
et al., 2012), the advent of Deep Learning (DL) has
shifted paradigms towards more adaptive, data-driven
approaches.
Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) have demon-
strated a remarkable ability to manage both synthetic
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0008-9870-022X
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5351-3956
c
https://orcid.org/0009-0008-7417-1212
and realistic noise scenarios, outperforming classical
methods under diverse conditions. However, the con-
ventional training of DNN-based denoisers often re-
lies on the availability of pristine, noiseless ground
truth images—a requirement seldom met in practi-
cal scenarios (Zhussip et al., 2019). This challenge
has led to the development of unsupervised learning
techniques such as Deep Image Prior (DIP) (Ulyanov
et al., 2020) and Noise2Noise (Lehtinen et al., 2018a),
which leverage the inherent capabilities of DNNs to
reconstruct high-quality images from noisy data with-
out needing clean examples (Ulyanov et al., 2018),
(Lehtinen et al., 2018b).
Building upon the foundations of Stein’s Unbiased
Risk Estimator (SURE) (Metzler et al., 2020) and its
variants eSURE (Zhussip et al., 2019), Poisson Unbi-
ased Risk Estimator (PURE) (Kim et al., 2022), and
Extended Poisson Unbiased Risk Estimator (ePURE)
(Kim et al., 2022), our work introduces an innovative
unsupervised framework that combines an enhanced
diffusion model (Ho et al., 2020) with a dynamically
trained DnCNN (Zhang et al., 2017b). This approach
Khan, R., Nakarmi, U. and Gauch, J. M.
From Noise Estimation to Restoration: A Unified Diffusion and Bayesian Risk Approach for Unsupervised Denoising.
DOI: 10.5220/0013187300003912
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 20th International Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications (VISIGRAPP 2025) - Volume 3: VISAPP, pages
547-555
ISBN: 978-989-758-728-3; ISSN: 2184-4321
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
547

not only addresses the limitations of existing meth-
ods—particularly their struggles with generalization
across unknown or mixed noise types—but also sets
new benchmarks in MRI denoising.
Our method leverages Bayesian-enhanced loss
functions—Bayesian-SURE, Bayesian-PURE, and
Bayesian-Poisson-Gaussian Unbiased Risk Estimator
(Bayesian-PGURE)—which dynamically adapt to the
estimated noise characteristics, thus allowing for ro-
bust denoising performance even when the noise type
and level are not a priori known. This adaptive capa-
bility is crucial for practical applications where noise
properties can significantly vary, such as in medical
imaging environments (Kim et al., 2020), (Kim et al.,
2022).
Furthermore, we extend the theoretical under-
standing of unsupervised denoising by drawing con-
nections between our Bayesian-enhanced methods
and the Noise2Noise framework, suggesting that our
Bayesian approaches can be viewed as a generaliza-
tion capable of handling correlated noise scenarios
more effectively (Lehtinen et al., 2018b). The experi-
mental validation of our models on MRI datasets con-
taminated with Gaussian, Poisson, and mixed noise
types demonstrates superior performance over tradi-
tional methods, particularly in scenarios where the
noise characteristics deviate from standard assump-
tions.
Our contributions not only advance the state-of-
the-art in image denoising but also open avenues
for future research into unsupervised learning models
that can seamlessly adapt to varied and dynamically
changing environmental conditions, thereby signifi-
cantly impacting both the theory and application of
machine learning in medical imaging.
2 BACKGROUND
The evolution of image denoising techniques, partic-
ularly for medical applications such as MRI, has re-
quired a deep understanding of both traditional and
advanced methodologies. This section introduces the
foundational concepts and established estimators, set-
ting the stage for the innovative approaches we de-
velop in subsequent sections. The core of our ap-
proach leverages Stein’s Unbiased Risk Estimator
(SURE) and its Monte Carlo variant (MC-SURE),
frameworks that have been extensively validated in
other domains. Our work extends the application of
these established methods to the complex noise char-
acteristics inherent in MRI data, a domain where the
acquisition of noise-free ground truth is notably chal-
lenging.
We review the principles of SURE (Metzler et al.,
2020) and MC-SURE, discussing their theoretical
underpinnings and the rationale behind their effec-
tiveness in scenarios lacking clean data. By adapt-
ing these methods to the realm of medical imaging,
specifically to MRI, we aim to demonstrate their ro-
bustness and utility in a field where accurate image
restoration is critical yet burdened by inherent noise.
This adaptation not only underscores the versatility of
these estimators across various applications but also
sets the stage for detailed examinations of their per-
formance in the subsequent sections of this study.
2.1 Stein’s Unbiased Risk Estimator
(SURE)
In the context of denoising Gaussian-contaminated
signals or images, a typical model involves a linear
equation:
y = x + n (1)
where x ∈ R
N
represents an unknown signal, y ∈
R
N
is the observed noisy measurement, and n ∈ R
N
denotes i.i.d. Gaussian noise with n ∼ N (0, σ
2
I),
where I is the identity matrix.
The SURE (Stein’s Unbiased Risk Estimator)
(Metzler et al., 2020) is a widely-used approach to es-
timate the mean squared error (MSE) associated with
an estimator h(y) of x. It is given by the expression:
η(h(y)) =
||y − h(y)||
2
N
− σ
2
+
2σ
2
N
N
∑
i=1
δh
i
(y)
δy
i
(2)
This equation suggests that the random variable
η(h(y)) is an unbiased estimator of the MSE of h(y),
given by:
E
n∼N (0,σ
2
)
||x − h(y)||
2
N
= E
n∼N (0,σ
2
)
{η(h(y))}
(3)
Obtaining an analytical solution for the divergence
term in equation (2) is limited to special cases, such as
when the estimator h(y) is a non-local mean or linear
filter. To utilize (2) in more general cases, an approx-
imate solution for the divergence term is necessary.
2.2 Poisson Unbiased Risk Estimator
(PURE)
The Poisson Unbiased Risk Estimator (PURE) (Kim
et al., 2022) is designed to address denoising scenar-
ios where the noise model is strictly Poissonian, often
relevant in medical imaging and photon-limited imag-
ing environments. The model for PURE (Kim et al.,
2022) is expressed by:
y = x + n
p
(4)
VISAPP 2025 - 20th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
548

where x ∈ R
N
denotes the true signal, y ∈ R
N
is
the observed image, and n
p
∈ R
N
represents Pois-
son noise, which is signal-dependent, differing from
Gaussian noise.
The PURE (Kim et al., 2022) estimator for the
mean squared error (MSE) of an estimator h(y) of x,
considering Poisson noise, is given by:
η
PU RE
(h(y)) =
N
∑
i=1
(h
i
(y) − y
i
log(h
i
(y))) (5)
This estimator effectively leverages the log-
likelihood of Poisson-distributed data, providing a
robust framework for noise estimation and image
restoration under Poisson noise conditions.
2.3 Poisson Unbiased Risk Estimator
(PURE) and Poisson-Gaussian
Unbiased Risk Estimator (PGURE)
Following the Gaussian noise scenario and inspired
by (Luisier et al., 2011), we extend our approach to
address mixed noise conditions commonly encoun-
tered in medical imaging and other photon-limited
imaging applications. PURE (Kim et al., 2022) and
PGURE provide frameworks to handle purely Pois-
son noise and a combination of Poisson and Gaussian
noise, respectively.
PGURE, in particular, is described by the follow-
ing loss function, adapted for noise levels that are not
known beforehand and may vary spatially or tempo-
rally across the image:
η
PGURE
(h(y)) =
N
∑
i=1
(h
i
(y) − y
i
log(h
i
(y)))
−
ˆ
σ
2
+
2
ˆ
σ
2
N
N
∑
i=1
δh
i
(y)
δy
i
(6)
This formulation incorporates the Bayesian ap-
proach to dynamically estimate both the parameters
of Poisson (λ) and Gaussian (σ
2
) noise components,
allowing for a more precise and adaptable denoising
process.
2.4 Monte-Carlo SURE (MC-SURE)
MC-SURE is a Monte Carlo method proposed by Ra-
mani et al. (Ramani et al., 2008) to estimate the di-
vergence and, consequently, the SURE loss.
Assume
˜
b ∼ N
0,1
∈ R
N
is a Gaussian vector which
is independent of n or y. Ramani et al(Ramani et al.,
2008) show that,
K
∑
i=1
δh
i
(y)
δy
i
= lim
ε→0
E
˜
b
˜
b
t
h(y + ε
˜
b) − h(y)
ε
(7)
Therefore, by applying this eq 7 to the divergence
term in eq 2:
1
N
N
∑
i=1
δh
i
(y)
δy
i
≈
1
εN
˜
b
T
(h(y + ε
˜
b) − h(y)) (8)
Here,
˜
b
T
is the transpose of
˜
b, and ε is a small
positive value to approximate the limit.
3 METHODS
This section outlines our innovative approach for un-
supervised image denoising, leveraging a diffusion-
based model (Ho et al., 2020) for dynamic noise
estimation combined with Bayesian formulations of
SURE, PURE, and PGURE for training our denoiser.
Our method significantly enhances the adaptability
and effectiveness of deep learning denoisers in han-
dling various real-world noise types without the need
for paired clean and noisy images.
3.1 Noise Estimation Using Diffusion
Models
Our approach utilizes a diffusion model (Ho et al.,
2020) as a dynamic noise estimator, which is trained
to predict both the type and level of noise directly
from noisy images. This model operates by gradually
adding noise to a clean image and learning to reverse
this process, thereby predicting the noise characteris-
tics at each step.
For Gaussian noise, the model adds and reverses
noise as follows:
Diffusion: x
t+1
=
p
1 − β
t
x
t
+
p
β
t
ε, ε ∼ N (0, I),
(9)
Reverse: x
t−1
=
x
t
−
p
β
t
ε
θ
(x
t
, t)
p
1 − β
t
, (10)
For Poisson noise, the diffusion equations adapt to
the signal-dependent nature:
Diffusion: x
t+1
=
p
1 − β
t
x
t
+
p
β
t
ε
p
,
ε
p
∼ Poisson(λ), (11)
Reverse: x
t−1
=
x
t
−
p
β
t
λ
θ
(x
t
, t)
p
1 − β
t
(12)
where β
t
are the variance schedules, ε and ε
p
rep-
resent Gaussian and Poisson noise, respectively, and
ε
θ
, λ
θ
are the noise levels predicted by the model.
From Noise Estimation to Restoration: A Unified Diffusion and Bayesian Risk Approach for Unsupervised Denoising
549

Noise Type and Level Prediction
Within the framework of the diffusion model (Ho
et al., 2020), the noise type (e.g., Gaussian, Poisson)
and its corresponding level (parameters such as σ for
Gaussian or λ for Poisson) are predicted by an auxil-
iary neural network module:
ˆ
σ,
ˆ
λ = f
θ
(x
t
, t) (13)
where f
θ
represents the neural network trained to
predict noise parameters based on the diffused image
x
t
and timestep t. This prediction enables tailoring
the denoising process to the specific characteristics of
the noise, enhancing the effectiveness of subsequent
denoising steps.
3.2 Bayesian SURE, PURE, and
PGURE
Utilizing the estimated noise parameters, we com-
pute the Bayesian versions of the SURE, PURE, and
PGURE losses for training our denoising network.
These losses adapt to the estimated noise levels and
types, providing a flexible framework for training un-
der varying noise conditions.
Custom Bayesian Loss Formulations
To address the variations in noise type and intensity,
we introduce custom Bayesian loss functions that dy-
namically adjust based on the estimated noise charac-
teristics:
Bayesian SURE (BSURE) is designed for Gaus-
sian noise environments and is formulated as:
L
BSURE
= MSE(y, ˆy) − σ
2
+ 2σ
2
· div(ˆy, y)
where MSE is the mean squared error, σ is the esti-
mated noise level, ˆy is the denoised image, y is the
noisy image, and div represents the divergence esti-
mated via a Monte Carlo approach.
Bayesian PURE (BPURE) applies to Poisson
noise conditions:
L
BPURE
= ˆy − y log(ˆy) + λ − y log(λ)
where λ is the estimated Poisson noise level.
Bayesian PGURE (BPGURE) is used for mixed
noise scenarios, combining the features of BSURE
and BPURE.
These loss functions are weighted dynamically
based on the predicted noise type, ensuring optimal
denoising performance across different imaging con-
ditions. This approach not only enhances the gener-
alizability of the model but also tailors the denoising
process to effectively handle the specific noise char-
acteristics present in medical imaging, where noise
types can vary significantly.
3.3 Modified Bayesian SURE
(Bayesian-SURE)
Our research introduces a Bayesian adaptation of
the SURE (Metzler et al., 2020) framework, termed
Bayesian-SURE, which incorporates a prior distribu-
tion on the noise level, allowing for a dynamic estima-
tion process that is more robust in practical settings
where the noise level might not be known a priori.
This approach utilizes a Bayesian inference method
to estimate the noise variance σ
2
dynamically:
η
Bayesian-SURE
(h(y)) =
||y − h(y)||
2
N
−
ˆ
σ
2
+
2
ˆ
σ
2
N
N
∑
i=1
δh
i
(y)
δy
i
(14)
Here,
ˆ
σ
2
represents the estimated noise variance
derived from the Bayesian posterior, enhancing the
flexibility and adaptability of the SURE method to
varying noise conditions.
3.4 Enhanced Monte-Carlo SURE
(MC-SURE)
In our project, we propose a modified Monte Carlo
SURE estimator to enhance the accuracy and reduce
the variance of the divergence estimation, crucial for
effective denoising performance. The traditional MC-
SURE, as described by Ramani et al. (Ramani et al.,
2008), relies on a single Gaussian perturbation vec-
tor
˜
b to estimate the divergence term crucial for the
SURE loss calculation.
Our enhancement involves averaging multiple in-
dependent estimations of the gradient, each derived
from a distinct Gaussian vector. This modification is
inspired by the Central Limit Theorem, which sug-
gests that averaging a set of independent estimates re-
duces variance, leading to a more robust and stable
estimator. The modified equation is as follows:
1
N
N
∑
i=1
δh
i
(y)
δy
i
≈
1
MεN
M
∑
j=1
˜
b
T
j
(h(y + ε
˜
b
j
)− h(y)) (15)
where M is the number of independent Gaussian vec-
tors
˜
b
j
, each sampled anew for the estimation. This
approach mitigates the noise in the gradient estima-
tion by averaging over multiple perturbations, thus
leading to a more accurate and reliable estimate of the
divergence.
This modification not only enhances the reliabil-
ity of the SURE loss estimate but also stabilizes the
optimization process in iterative denoising methods,
potentially resulting in higher quality reconstructions
VISAPP 2025 - 20th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
550

and improved generalization across different noise
conditions.
3.5 Modified Bayesian PURE
(Bayesian-PURE)
To enhance the PURE framework, we introduce a
Bayesian adaptation, termed Bayesian-PURE, which
incorporates Bayesian principles to dynamically esti-
mate the parameters of the Poisson distribution, par-
ticularly the rate parameter λ. This modification al-
lows for adapting to varying noise levels across dif-
ferent image regions, enhancing the estimator’s flexi-
bility and accuracy in practical imaging scenarios.
The Bayesian-PURE is formulated as follows:
η
Bayesian-PURE
(h(y)) =
N
∑
i=1
(h
i
(y) − y
i
log(h
i
(y)))
+
1
N
N
∑
i=1
(λ
i
− y
i
log(λ
i
))
(16)
Here, λ
i
represents the estimated Poisson rate for
each pixel, derived from a Bayesian posterior that ac-
counts for the observed data. This approach not only
improves the adaptability of the estimator to differ-
ent noise conditions but also enhances the accuracy
of denoising in environments where noise character-
istics may not be uniform or are unknown a priori.
3.6 Optimization of Deep Denoisers via
Enhanced SURE-Derived Losses
The integration of Stein’s Unbiased Risk Estimator
(SURE) and its variants, including Poisson Unbiased
Risk Estimator (PURE) and Poisson-Gaussian Unbi-
ased Risk Estimator (PGURE), has significantly ad-
vanced the unsupervised optimization of deep neural
network (DNN)-based denoisers. Our work extends
these methodologies by incorporating Bayesian prin-
ciples, which dynamically adjust to the noise charac-
teristics estimated from the data, thereby eliminating
the need for pristine ground truth images—a common
limitation in supervised learning paradigms.
We have developed modified Bayesian SURE,
PURE, and PGURE frameworks, which employ a
Bayesian approach to dynamically estimate noise pa-
rameters and apply these estimations to optimize the
training process of DNNs. These modifications al-
low for adaptive loss functions that are tailored to the
estimated type and level of noise, enhancing the flexi-
bility and effectiveness of the denoising process. The
Bayesian-enhanced loss functions are defined as fol-
lows:
η
Bayesian
(h
θ
(y)) =
1
M
M
∑
j=1
(
∥y
( j)
− h
θ
(y
( j)
)∥
2
−
ˆ
σ
2
j
+
2
ˆ
σ
2
j
ε
(
˜
b
( j)
)
T
h
θ
(y
( j)
+ ε
˜
b
( j)
) − h
θ
(y
( j)
)
)
. (17)
where M denotes the batch size, y
( j)
represents the
j-th noisy image in the batch,
ˆ
σ
2
j
is the dynamically
estimated noise variance for the j-th image, and
˜
b
( j)
is an auxiliary Gaussian perturbation vector indepen-
dent of the noise inherent in y. This reformulation not
only accounts for the direct error and the noise vari-
ance adjustment but also incorporates a Monte Carlo
estimation of the divergence term, providing a robust
and adaptive framework for the MSE, which is typi-
cally inaccessible in unsupervised settings.
Our experiments demonstrate that this approach
not only streamlines the training process by remov-
ing the necessity for clean data but also significantly
enhances the neural network’s ability to generalize
from noisy inputs. By effectively learning to de-
noise through a self-supervised learning framework,
our models achieve superior performance across var-
ious noise conditions, demonstrating robustness and
adaptability in real-world denoising tasks.
4 EXPERIMENTS AND RESULTS
In this section, we evaluate our proposed Bayesian-
enhanced diffusion model (Ho et al., 2020) and
DnCNN (Zhang et al., 2017b) framework on a chal-
lenging MRI dataset and compare its performance to
existing denoising methods. We first describe the
dataset and preprocessing steps, followed by prelim-
inary experiments with traditional methods. We then
present the results of our Bayesian approach under
various noise conditions and provide a detailed anal-
ysis of its performance.
4.1 Dataset and Preprocessing
We use fully-sampled 3T knee MRI scans from 22
subjects (11 males and 11 females) as described in
(Anonymous, 2013). Each subject’s volume is seg-
mented into 320×320×256 matrices and sliced into
320×256 axial planes. MRI acquisition was per-
formed using a 3T whole-body scanner, and raw k-
space data were preserved for authenticity.
From these volumes, we generated both axial and
coronal view PNG images for training and evalua-
tion. We used 1000 axial and 1000 coronal images for
training, with 100 images per view for testing. This
From Noise Estimation to Restoration: A Unified Diffusion and Bayesian Risk Approach for Unsupervised Denoising
551

setup ensures a diverse set of anatomical variations
and noise conditions.
4.2 Preliminary Experiments with
Traditional Methods
Before evaluating our Bayesian approach, we con-
ducted preliminary experiments using methods such
as SURE (Metzler et al., 2020), eSURE (Zhussip
et al., 2019), PURE (Kim et al., 2022), ePURE (Kim
et al., 2022), Noise2Noise (N2N) (Lehtinen et al.,
2018a), BM3D (Dabov et al., 2007), and DnCNN
(Zhang et al., 2017b) trained with standard MSE and
known ground truth. We tested these methods on con-
trolled Gaussian noise levels (σ = 25 and σ = 50) for
both axial and coronal views.
The Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio (PSNR) results
are presented in Table 1. As shown, eSURE (Zhus-
sip et al., 2019) and N2N methods perform strongly
under known Gaussian conditions, achieving high
PSNR values.
These preliminary results highlight the strengths
and limitations of traditional methods. While some
methods excel under known, controlled conditions,
they are not as robust when noise characteristics differ
from assumptions.
4.3 Bayesian-Enhanced Diffusion
Model Evaluation
We now evaluate our Bayesian-enhanced diffusion
model integrated with DnCNN (Zhang et al., 2017b)
under various unknown noise conditions (Gaussian,
Poisson, and mixed). Unlike the preliminary experi-
ments, our approach does not assume prior knowledge
of noise parameters.
Table 2 summarizes PSNR and SSIM results un-
der unknown Gaussian and Poisson noise levels, as
well as a mixed scenario. Our Bayesian approach
achieves notably higher PSNR and SSIM compared
to baseline methods, demonstrating its adaptability.
To visually illustrate these improvements, Fig-
ure 1 shows denoised axial views under Gaussian
noise. The Bayesian-enhanced model restores fine de-
tails and texture more faithfully than baseline meth-
ods.
Figure 2 highlights denoising performance on
coronal views. Again, our approach demonstrates ro-
bustness and edge fidelity, even under higher noise
levels.
Figure 1: Denoised results for axial views under Gaussian
noise (σ = 25 and 50). Our Bayesian model preserves de-
tails and edges more effectively.
Figure 2: Denoised results for coronal views under Gaus-
sian noise (σ = 25 and 50). The proposed method maintains
structural details better than competitors.
4.4 Visualizing Results on Poisson and
Mixed Noise
To further assess performance in complex scenarios,
we tested on Poisson and mixed noise. Figure 3 pro-
vides a comparison under Poisson noise at different
intensities using ePURE, and Figure 4 shows results
under Gaussian, Poisson, and mixed noise types with-
out prior knowledge of noise parameters. Our model
adapts seamlessly, producing high-quality reconstruc-
tions across all conditions.
4.5 Mixed Noise Scenarios and Gradual
Intensity Changes
In practical MRI settings, noise profiles may vary
across scans or within a single volume. Figure 5 illus-
trates our model’s performance on mixed noise with
gradually increasing intensity (from σ = 10 to 50 and
λ = 0.2 to 1.0). Even as noise intensity changes,
the Bayesian-enhanced approach retains stable per-
formance and reconstructs subtle structures that other
methods fail to recover.
Finally, Table 3 presents PSNR and SSIM results
under Poisson noise for ePURE, further validating the
competitiveness and adaptability of our approach.
VISAPP 2025 - 20th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
552
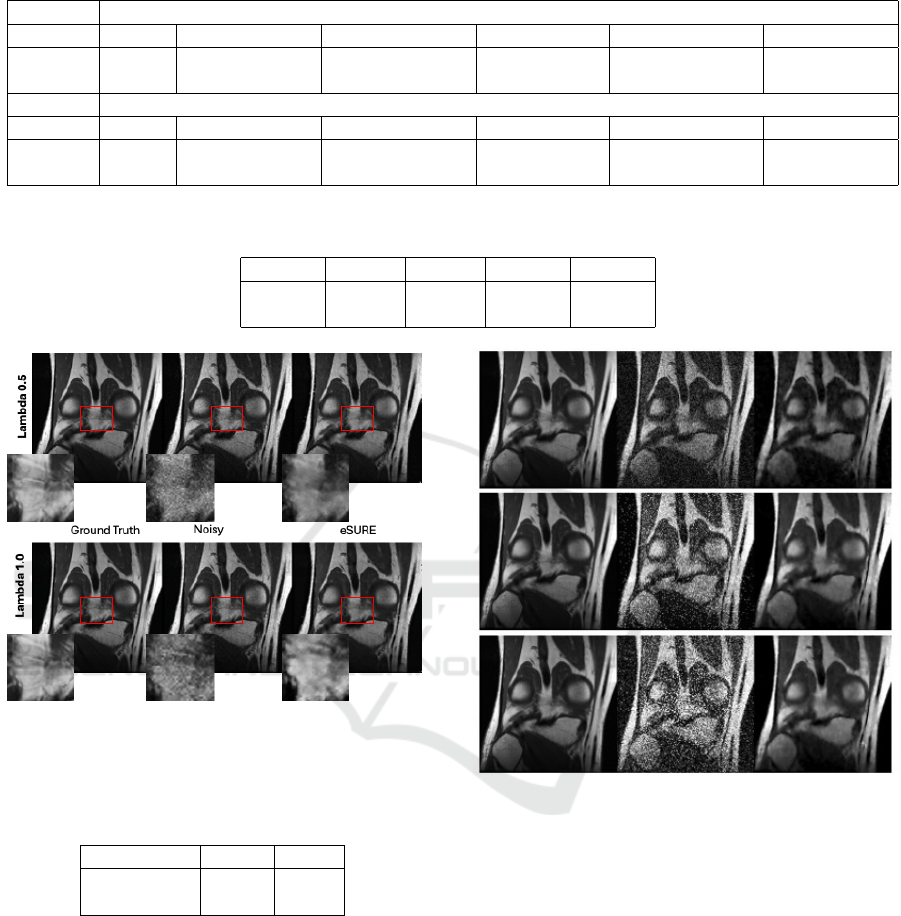
Table 1: PSNR results of blind denoisers in preliminary experiments on 3T Knee MRI. Higher is better.
3T Knee MRI Axial View
Methods BM3D DnCNN-SURE DnCNN-SURE* DnCNN-N2N DnCNN-eSURE DnCNN-MSE
σ = 25 29.10 31.56 29.00 33.96 33.96 29.20
σ = 50 27.75 31.55 26.07 31.53 31.63 26.22
3T Knee MRI Coronal View
Methods BM3D DnCNN-SURE DnCNN-SURE* DnCNN-N2N DnCNN-eSURE DnCNN-MSE
σ = 25 29.10 32.55 29.00 32.46 32.56 30.82
σ = 50 27.75 28.75 26.07 28.86 29.99 28.83
Table 2: PSNR and SSIM results of the Bayesian-enhanced diffusion model on MRI data. The method adapts to unknown
and mixed noise scenarios.
Metrics σ = 25 σ = 50 λ = 0.5 λ = 1.0
PSNR 35.05 32.80 33.25 30.00
SSIM 0.95 0.92 0.94 0.90
Figure 3: Visual comparison under Poisson noise at varying
intensities using ePURE. Our Bayesian approach adapts to
different noise levels, enhancing image fidelity.
Table 3: PSNR and SSIM results for ePURE on 3T Knee
MRI Coronal View under Poisson noise.
Noise Level PSNR SSIM
λ = 0.5 31.68 0.934
λ = 1.0 32.45 0.947
4.6 Discussion of Results
Our experiments demonstrate that the Bayesian-
enhanced diffusion framework outperforms tradi-
tional methods that rely on known noise models.
By dynamically estimating noise characteristics, the
model adapts to diverse conditions without ground
truth. The result is a more flexible, generalizable de-
noising tool suitable for real-world MRI scenarios.
The visual and quantitative evidence suggests that
this approach maintains structural integrity and detail
fidelity in conditions that break assumptions made by
Figure 4: Denoised results for Gaussian, Poisson, and
mixed noise (top to bottom) with unknown parameters. Our
method generalizes well, delivering consistent quality.
classical methods. Consequently, it sets a new stan-
dard for unsupervised denoising under complex, vari-
able noise patterns.
5 CONCLUSION
This work presents a novel unsupervised learning
framework for MRI denoising that integrates an en-
hanced diffusion model with a dynamically trained
Deep Convolutional Neural Network (DnCNN)
(Zhang et al., 2017b). By employing adaptive loss
functions that adjust to dynamically estimated noise
characteristics, our approach facilitates robust denois-
ing across a wide range of conditions without requir-
From Noise Estimation to Restoration: A Unified Diffusion and Bayesian Risk Approach for Unsupervised Denoising
553
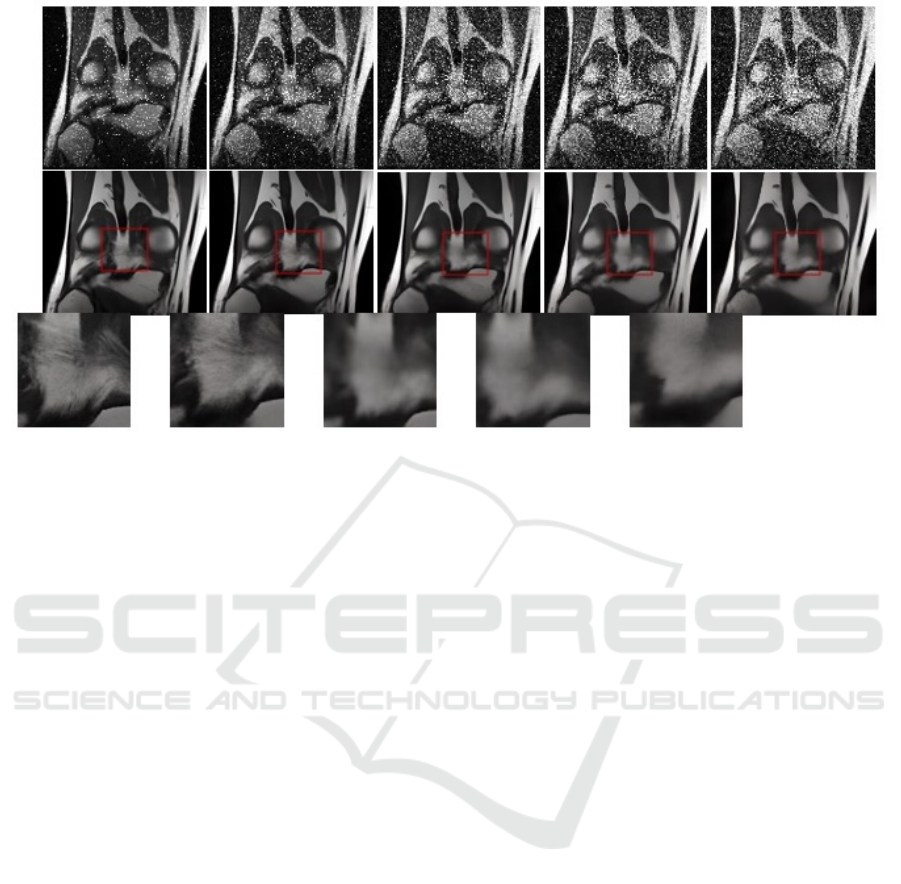
Figure 5: Denoised results for mixed noise with gradually increasing intensity. Our model maintains robust denoising quality
despite evolving noise characteristics.
ing prior noise distribution knowledge. Experimen-
tal results validate that our method outperforms tradi-
tional techniques, particularly in complex, real-world
medical imaging scenarios. It achieves high fidelity in
noise reduction while preserving essential image de-
tails, setting new benchmarks in both quantitative and
visual performance.
Future efforts will focus on applying this frame-
work to additional imaging modalities and incorpo-
rating cutting-edge neural architectures like genera-
tive adversarial networks (GANs) (Goodfellow et al.,
2014), potentially redefining the standards for medi-
cal image processing. Our results highlight the trans-
formative potential of advanced machine learning in
enhancing diagnostic accuracy and expanding clini-
cal applications, laying a robust groundwork for fu-
ture innovations in medical imaging technology.
REFERENCES
Anonymous (2013). Creation of fully sampled mr data
repository for compressed sensing of the knee. Proc.
SMRT 22nd Annu. Meeting.
Burger, H. C., Schuler, C. J., and Harmeling, S. (2012).
Image denoising: Can plain neural networks compete
with bm3d? In IEEE Conference on Computer Vision
and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pages 2392–2399.
Cherry, S. R., Sorenson, J. A., and Phelps, M. E. (2012).
Physics in nuclear medicine. Elsevier Health Sci-
ences.
Dabov, K., Foi, A., Katkovnik, V., and Egiazarian, K.
(2007). Image denoising by sparse 3-d transform-
domain collaborative filtering. IEEE Transactions on
Image Processing, 16(8):2080–2095.
Goodfellow, I. J., Pouget-Abadie, J., Mirza, M., Xu, B.,
Warde-Farley, D., Ozair, S., Courville, A., and Ben-
gio, Y. (2014). Generative adversarial networks.
arXiv.
Ho, J., Jain, A., and Abbeel, P. (2020). Denoising diffusion
probabilistic models.
Jalata, I. K., Khan, R., and Nakarmi, U. (2024). Learn-
ing from oversampling: A systematic exploitation of
oversampling to address data scarcity issues in deep
learning- based magnetic resonance image reconstruc-
tion. IEEE Access, 12:97621–97629.
Kim, H., Yie, S. Y., Chun, S. Y., and Lee, J. S. (2022). Pure-
comb: Poisson unbiased risk estimator based ensem-
ble of self-supervised deep denoisers for clinical bone
scan image. In IEEE 19th International Symposium on
Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), pages 1–5, Kolkata, India.
Kim, K., Soltanayev, S., and Chun, S. Y. (2020). Unsuper-
vised training of denoisers for low-dose ct reconstruc-
tion without full-dose ground truth. IEEE Journal
on Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 14(6):1112–
1125.
Lehtinen, J., Munkberg, J., Hasselgren, J., Laine, S., Karras,
T., Aittala, M., and Aila, T. (2018a). Noise2noise:
Learning image restoration without clean data.
Lehtinen, J., Munkberg, J., Hasselgren, J., Laine, S., Kar-
ras, T., Aittala, M., and Aila, T. (2018b). Noise2noise:
Learning image restoration without clean data. In
Proc. of the 35th Int. Conf. on Machine Learning
(ICML), pages 2965–2974.
Luisier, F., Blu, T., and Unser, M. (2011). Image denoising
in mixed poisson–gaussian noise. IEEE Transactions
on Image Processing, 20(3):696–708.
Manj
´
on, J. V. and Coupe, P. (2019). Mri denoising using
deep learning and non-local averaging. arXiv.
VISAPP 2025 - 20th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
554

Metzler, C. A., Mousavi, A., Heckel, R., and Baraniuk,
R. G. (2020). Unsupervised learning with stein’s unbi-
ased risk estimator. arXiv preprint arXiv:1805.10531.
Ramani, S., Blu, T., and Unser, M. (2008). Monte-carlo
sure: A black-box optimization of regularization pa-
rameters for general denoising algorithms. IEEE
Transactions on Image Processing, 17(9):1540–1554.
Ulyanov, D., Vedaldi, A., and Lempitsky, V. (2018). Deep
image prior. In IEEE Conference on Computer Vision
and Pattern Recognition, pages 9446–9454.
Ulyanov, D., Vedaldi, A., and Lempitsky, V. (2020). Deep
image prior. International Journal of Computer Vi-
sion, 128(7):1867–1888.
Zhang, K., Zuo, W., Chen, Y., Meng, D., and Zhang, L.
(2017a). Beyond a gaussian denoiser: Residual learn-
ing of deep cnn for image denoising. IEEE Transac-
tions on Image Processing, 26(7):3142–3155.
Zhang, K., Zuo, W., Chen, Y., Meng, D., and Zhang, L.
(2017b). Beyond a gaussian denoiser: Residual learn-
ing of deep cnn for image denoising. IEEE Transac-
tions on Image Processing, 26(7):3142–3155.
Zhussip, M., Soltanayev, S., and Chun, S. Y. (2019). Ex-
tending stein’s unbiased risk estimator to train deep
denoisers with correlated pairs of noisy images. In
Proceedings of the 33rd Conference on Neural In-
formation Processing Systems (NeurIPS), Vancouver,
Canada.
From Noise Estimation to Restoration: A Unified Diffusion and Bayesian Risk Approach for Unsupervised Denoising
555
