
Robust Blockchain-Based Federated Learning
Aftab Akram
1 a
, Cl
´
ementine Gritti
2 b
, Mohd Hazali Mohamed Halip
3,4 c
,
Nur Diyana Kamarudin
3,4 d
, Marini Mansor
3
, Syarifah Bahiyah Rahayu
3,4 e
and Melek
¨
Onen
1 f
1
Department of Digital Security, EURECOM, 450 route des Chappes, 06410 Biot, France
2
CITI Lab, INSA Lyon – Inria, 69100 Villeurbanne, France
3
Faculty of Defence Science and Technology, University of Malaysia, 57000 Kem Sungai Besi, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
4
Cyber Security and Digital Industrial Revolution Centre, National Defence University of Malaysia, 57000 Kem Sungai
Besi, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
Keywords:
Federated Learning, Byzantine Nodes, Secure Aggregation, Privacy, Robustness, Blockchain.
Abstract:
In Federated Learning (FL), clients collaboratively train a global model by updating it locally. Secure Aggre-
gation (SA) techniques ensure that individual client updates remain protected, allowing only the global model
to be revealed while keeping the individual updates private. These updates are usually protected through ex-
pensive cryptographic techniques such as homomorphic encryption or multi-party computation. We propose a
new solution that leverages blockchain technology, specifically the Secret Network (SN), to provide privacy-
preserving aggregation with aggregate integrity through Smart Contracts in Trusted Execution Environments
(TEEs). Moreover, FL systems face the risk of Byzantine clients submitting poisoned updates, which can
degrade the model performance. To counter this, we integrate three state-of-the-art robust aggregation tech-
niques within the Smart Contract, namely Krum, Trim Mean and Median. Furthermore, we have evaluated the
performance of our framework which remains efficient in terms of computation and communication costs. We
have also exhibited similar accuracy results compared to state-of-the art scheme named SABLE.
1 INTRODUCTION
Collaborative Machine Learning (ML), including
Federated Learning (FL), has attracted a lot of in-
terest, recently. FL enables ML models to be
trained while restricting the access to the local train-
ing datasets, thus preventing the disclosure of sensi-
tive information. Informally, multiple clients jointly
train a global model by training it locally and se-
curely aggregating their updated parameters. Se-
cure Aggregation (SA) (Kairouz et al., 2021; Man-
souri et al., 2023) is conducted by a server such that
the latter learns nothing from local inputs but the
global model. Various techniques have been pro-
posed to achieve SA, including Homomorphic En-
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0003-2402-4058
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0835-8678
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8233-0219
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9018-7694
e
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1996-5166
f
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0269-9495
cryption (HE) (e.g., (Zhang et al., 2020)), masking
(e.g., (Bonawitz et al., 2017)), Multi-Party Computa-
tion (MPC) (e.g., (Corrigan-Gibbs and Boneh, 2017))
and Trusted Execution Environments (TEEs) (e.g.,
(Kalapaaking et al., 2023)).
While FL has carefully considered the challenge
of preserving the privacy of the clients’ updates, it
brings extra security concerns. As mentioned above,
multiple clients, including possibly compromised
ones, participate in the iterative training process. In
particular, a Byzantine client can aim to manipulate
the global model by poisoning local datasets or to
submit manipulated model updates. Consequently,
the accuracy of the FL training can be severely im-
pacted, making model poisoning a serious threat to
FL systems. Such Byzantine behavior introduces se-
rious concerns regarding the integrity and robustness
of FL systems, and thus has attracted more attention
over the last few years (Miao et al., 2022).
Defenses against such attacks mostly rely ei-
ther on anomaly detection (Fung et al., 2020; Shen
et al., 2016) or Byzantine-robust estimators (Blan-
Akram, A., Gritti, C., Halip, M. H. M., Kamarudin, N. D., Mansor, M., Rahayu, S. B. and Önen, M.
Robust Blockchain-Based Federated Learning.
DOI: 10.5220/0013188800003899
In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy (ICISSP 2025) - Volume 1, pages 59-70
ISBN: 978-989-758-735-1; ISSN: 2184-4356
Copyright © 2025 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
59

chard et al., 2017; Chen et al., 2018). Nevertheless,
such solutions remain expensive when integrated with
SA which usually rely on resource-expensive crypto-
graphic techniques such as MPC. Consequently, the
design of new SA protocols for FL systems should
incorporate practical defenses against model poison-
ing. One way is to enhance norm bounds on clients’
local updates (Naseri et al., 2022), which can easily
be adapted to secure FL systems. Norm bounds have
already been deployed as a countermeasure against
untargeted attacks (Shejwalkar et al., 2021) and tar-
geted attacks (Lycklama et al., 2023; Rathee et al.,
2023; Bell et al., 2023). However, existing solutions
come with limitations. Most of them imply the par-
ticipation of two (or more) non-colluding servers to
achieve the desired security properties (Rathee et al.,
2023). Other solutions have been designed in a single-
server setting (Lycklama et al., 2023; Bell et al., 2023)
but require the use of expensive mechanisms such as
Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKPs).
Furthermore, the integrity of correct aggregation
is another challenging task in existing FL solutions.
In the case of single-server FL systems, the result
from aggregation may be compromised by a poten-
tially malicious server whose aim can be to obtain in-
formation from local updates. Hence, verifying the
integrity of aggregation also becomes essential. Some
FL solutions with aggregation verifiability (Guo et al.,
2021; Buyukates et al., 2022) have been proposed but
incur large overheads in terms of computation and
communication.
1.1 Problem Statement
In this paper, we are interested in ensuring and imple-
menting three security guarantees and defenses:
• Protecting the privacy of clients’ local updates.
Each local update is kept private from the server while
the latter recovers the aggregated model through SA
mechanisms. Informally, each client hides its local
update before sending it to the server using techniques
such as HE and masking. The server aggregates hid-
den updates and recovers the global model but not in-
dividual updates.
• Ensuring the robustness of the global model
against Byzantine behavior. The global model is ex-
pected to be robust against Byzantine faults occurring
either in the training data (e.g. by a malicious client
who manipulates the training data) or during the pro-
tocol execution (e.g. from the information exchanged
during the protocol). A solution is to compare the lo-
cal updates received from clients and remove the out-
liers before the server proceeds with aggregation.
• Developing a solution with aggregation in-
tegrity. We aim to enable the correctness of local in-
puts’ aggregation: clients should be guaranteed that
their genuine local input has been correctly received
and used for the generation of the new global model.
A solution is to rely on consensus mechanisms from
blockchain technologies to ensure the correct execu-
tion of aggregation operations.
1.2 Our Contributions
With the aforementioned goals, we propose to take
advantage of blockchain technologies to inherently
ensure aggregation correctness. To ensure integrity
and input privacy at the same time, we choose the
particular Secret Network
1
(SN) framework. SN is a
public blockchain that relies on TEEs to execute smart
contract operations privately and correctly.
Therefore, in our solution, a network of nodes
maintain the blockchain to replace the traditional
FL server. This design choice prevents single point
of failure while guaranteeing aggregation correctness
and immutability through the use of consensus mech-
anisms. To ensure the privacy of clients’ training
updates, we enable SA inside TEEs. Client inputs
are first encrypted and sent to SN. They are then
decrypted inside a TEE where aggregation occurs.
Furthermore, to validate the legitimacy of a client’s
training update, we deploy and evaluate a specific
smart contract within SN which utilizes three state-of-
the-art robust aggregation techniques, namely Krum,
Trim Mean, and Median, to diminish the impact of
potentially Byzantine nodes.
To summarize, combining SN with our robust ag-
gregation smart contract simultaneously guarantees
the integrity and immutability of the aggregation op-
erations in a decentralized setting, client input privacy
and Byzantine robustness of the global model, while
preventing single point of failure.
We also test our solution in a real environment.
We consider a medical dataset used to train over
a Neural Network (NN) for arrhythmia prediction.
Training updates are sent to the testnet of SN and
taken as inputs in our smart contract to check their
genuineness. We show that our proposed solution
works in practice. We also evaluate the performance
of our solution with the classical MNIST scenario in
order to compare it with the closest related scheme
named SABLE (Choffrut et al., 2023).
1.3 Paper Outline
In Section 2, we explore the existing robust SA works.
In Section 3, we introduce the various concepts on
1
https://scrt.network/
ICISSP 2025 - 11th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy
60

which relies our blockchain-based FL solution. In
Section 4, we present our privacy-preserving and ro-
bust SA solution through the use of TEEs within the
blockchain SN. In Section 5, we analyse and evalu-
ate our solution to assess its robustness in practice,
from experiments based on a real (fully anonymised)
medical dataset and on the MNIST dataset. Finally,
in Section 6, we conclude our paper.
2 RELATED WORK
Multi-Party Computation (MPC): Several works
have previously explored privacy-preserving FL sys-
tems robust against Byzantine nodes. Approaches
such as (Corrigan-Gibbs and Boneh, 2017; Hao et al.,
2021; Nguyen et al., 2021; Zhang et al., 2022) use
MPC along with other cryptographic techniques, such
as Zero-Knowledge Proofs and Oblivious Transfer.
Nevertheless, those solutions assume the involvement
of two honest-but-curious servers that do not collude,
which can be seen as too restrictive.
Other robust FL MPC-based solutions (Hao et al.,
2021; Roy Chowdhury et al., 2022) implement
weaker robustness mechanisms, thereby compromis-
ing the convergence guarantees of the global mod-
els. For instance, the method proposed in (Hao et al.,
2021) is based on FLTrust framework (Cao et al.,
2020), which requires the server to have access to a
trusted and clean dataset, which is a strong assump-
tion compared to most of FL systems that leverage
solely client gradients. Similarly, while the solution
in (Roy Chowdhury et al., 2022) shows practical ef-
fectiveness, it lacks formal convergence guarantees,
which are essential for Byzantine-resilient FL sys-
tems (Allouah et al., 2023a; Khazbak et al., 2020).
Works in (Liu et al., 2021; Lu et al., 2019;
Arachchige et al., 2020) have employed MPC in
combination with blockchain to provide privacy.
However, these approaches primarily focus on
protecting the privacy of the participating clients,
without addressing the robustness needed to defend
against malicious clients attempting to poison global
models.
Differential Privacy (DP): Works such as (Allouah
et al., 2023b; Guerraoui et al., 2021; Zhu and Ling,
2022) have explored the use of Differential Privacy
(DP) in Byzantine-resilient FL algorithms to protect
client privacy from malicious servers. These methods
typically rely on noise injection into the gradients to
ensure privacy, though this often leads to an accept-
able but not an optimal trade-off between privacy
and model accuracy. For example, in (Guerraoui
et al., 2021), the authors, through theoretical analysis
and numerical experiments using publicly available
datasets, demonstrate that it is impractical to achieve
both DP and Byzantine resilience simultaneously.
Homomorphic Encryption (HE): A few prior works
(Wang et al., 2021; Rahulamathavan et al., 2023;
Miao et al., 2022; Bell et al., 2023) have explored
the use of HE to ensure privacy in FL systems. For
instance, the work in (Wang et al., 2021) proposes
a blockchain-based FL solution that employs Pail-
lier HE cryptosystem to implement the Multi-Krum
aggregator. However, this approach does not fully
implement Multi-Krum within the encrypted domain
due to operational limitations of the cryptosystem
(i.e., additions only). As a result, this partial imple-
mentation leads to considerable leakage towards the
aggregation nodes, significantly compromising the
privacy of the clients. Moreover, the method pro-
posed in (Rahulamathavan et al., 2023) grants the
server access to the evolving model at each step of
the learning process, threatening the privacy of the
clients. The solution in (Miao et al., 2022) presents
a blockchain-based FL system to ensure privacy and
robustness. The authors apply the Cheon-Kim-Kim-
Song (CKKS) scheme, which implements fully HE to
encrypt local gradients, thus enhancing privacy pro-
tection. Additionally, they utilize the FLTrust frame-
work (Cao et al., 2020) for robustness, which restric-
tively relies on a trusted server with access to a clean
dataset, as discussed earlier. Lastly, robust mecha-
nisms for SA are presented in (Bell et al., 2023) such
that malicious inputs can be first detected through
norm bounding techniques, and then discarded. Nev-
ertheless, extra overheads have a substantial impact
on the resulting FL system, making the latter not de-
ployable in practice.
A more recent work (Choffrut et al., 2023) uti-
lizes HE to implement privately robust aggregation
technique, more specifically, Trim Mean and Me-
dian. Since the solution sorts gradient values while
being homomorphically encrypted at the server side
for Trim Mean and Median, it incurs a high com-
putational cost, particularly at the server end. Our
blockchain-based approach shares strong similarities
with (Choffrut et al., 2023) as it uses Trim Mean to
deal with robustness issues. We choose to compare
this work with ours to better assess the deployability
of the latter in a real FL environment.
Robust Blockchain-Based Federated Learning
61

3 BACKGROUND
3.1 Federated Learning
FL consists of a distributed ML framework where
multiple clients collaboratively train a global model
under the supervision of a FL server. In a Syn-
chronous FL (SyncFL) setting (McMahan et al.,
2017), at each FL round, clients train a global model
on their private local data (e.g., through Stochastic
Gradient Descent) and forward their updates to the
server. When updates from all clients are received
by the server, the latter proceeds to the aggregation
phase by averaging those updates, resulting into a new
global model. This global model is sent back to the
clients for a new round of training. Rounds repeat
until the global model shows some desired level of
accuracy.
Buffered Asynchronous FL (BAsyncFL) (Nguyen
et al., 2022) enables clients to send their local updates
to the server without the need for synchronized
communication across all parties. Unlike SyncFL,
where all participating clients must complete their
local training before aggregation at each given round,
BAsyncFL allows clients to send updates when
ready, improving the scalability and efficiency of the
system. To handle this, updates are integrated into a
buffer such that their aggregation happens once the
buffer is full.
Secure Aggregation (SA): To obtain a global model
from multiple privacy-preserved locally-trained
models, SA has been widely used through various
techniques such as HE (e.g., (Zhang et al., 2020)),
masking (e.g., (Bonawitz et al., 2017)), MPC (e.g.,
(Corrigan-Gibbs and Boneh, 2017)) and TEEs (e.g.,
(Kalapaaking et al., 2023)).
Robustness: Among all participating clients, some
may behave maliciously and provide corrupted or
manipulated data to the server, to compromise the
integrity of the global model. We call such malicious
clients Byzantine nodes. As demonstrated in (Blan-
chard et al., 2017), even a single Byzantine node
can significantly disrupt the aggregation process,
especially when simple averaging is used, leading to
inaccurate outcomes. To mitigate this risk, robust
techniques can be used, such as Krum (Blanchard
et al., 2017), Trim Mean (Yin et al., 2018) and
Median (Yin et al., 2018).
Integrity: Privacy-preserving FL with verifiable ag-
gregation (Guo et al., 2021; Buyukates et al., 2022)
guarantees that the server cannot obtain information
from clients’ local updates by manipulating aggrega-
tion operations. Specifically, clients can be ensured
that the server has generated a new global model by
aggregating their inputs as expected.
3.2 Secret Network
Secret Network
2
(SN) is an interoperable blockchain
protocol offering privacy guarantees through the
execution of smart contract within TEEs. Informally,
SN encrypts the data before storing them in smart
contracts, preserving the privacy of the information
collected within dApps (decentralized applications).
A network of SN nodes is responsible of securely
processing smart contract computations through
consensus mechanisms. The native cryptocurrency
SCRT serves as a medium for participating in on-
chain governance, facilitating network transactions,
and rewarding users for securing the network through
staking. A major use case is in DeFi (decentralized
finance), where privacy-preserving smart contracts
enable confidential transactions while facilitating
various activities such as lending, borrowing and
trading. SN design relies on two main components,
namely the Cosmos SDK
3
and the Tendermint
4
con-
sensus engine. This combination provides a robust
foundation for scalable, private and permissionless
smart contracts that seamlessly integrate with the
broader interchain ecosystem.
Actors: The SN network consists of a set of nodes,
called delegates, who are elected by token hold-
ers, called delegators, to represent and validate
transactions on their behalf. Delegators participate
by staking or delegating their tokens to specific
delegates of their choice. The number of staked
tokens determines the weight of a delegator’s vote.
Delegates campaign for votes from delegators,
showcasing their technical competence, reliability
and contributions to the network to gain support. The
delegates with the most votes become active block
producers, called validators, taking turns to produce
blocks and validate transactions. The SN protocol
allows a limited number of 100 delegates.
Consensus: A consensus mechanism defines
how nodes in the network agree on the state of
a blockchain. SN utilizes the Delegated Proof of
Stake (DPoS) mechanism for consensus (Saad et al.,
2021). Here, users participate in the validation and
maintenance of the network by voting for a limited
2
https://scrt.network/
3
https://docs.cosmos.network/
4
https://tendermint.com/
ICISSP 2025 - 11th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy
62

number of delegates. These few selected delegates,
also known as the validators, are entrusted with the
responsibility of validating blocks and ensuring the
smooth operation of the network. This approach
enhances the speed of the network compared to other
Proof of Stake (PoS) systems, resulting in lower fees
and increased throughput.
Transactions and Blocks: Transactions are verified
and grouped into blocks by the active delegates. The
latter then propose those blocks to the network for
validation. Other nodes in the network, including
standby delegates, verify them. Once consensus is
reached, through the majority of the network (here,
at least 2/3 of the validators) agreeing on the validity
of the proposed blocks, the latter are added to the
blockchain. Delegates who successfully produce
blocks and participate in the consensus process
receive rewards. In particular, rewards are distributed
among both the validators and the delegators who
staked their tokens with the former.
Cryptocurrency: SCRT is the native cryptocurrency
of SN, enabling the following functions:
• Governance: SCRT holders participate in the
governance of SN by voting on proposals. Each
staked SCRT equals one vote, and validators vote
with the combined total of all their delegators’ staked
SCRT. Governance proposals require a simple major-
ity of staked SCRT to pass, and the voting period lasts
for 7 days.
• Gas Fees: Gas fees are paid in SCRT for
processing transactions. These fees compensate
validators and stakers on the network for their efforts
in securing and maintaining the network’s operation.
Trusted Execution Environments (TEEs): A TEE
creates a secure area within a processor where data is
isolated from other system components. This secure
area, called enclave, acts as a black box for computa-
tions, ensuring that the internal state remains hidden.
SN has chosen the Intel’s Software Guard Extensions
(SGX) implementation for its TEE framework (Will
and Maziero, 2023). In a smart contract, private meta-
data is encrypted before being sent to validators for
processing. Validators only decrypt this data within
their TEE, ensuring that it remains inaccessible to
them. Computations are then performed on the de-
crypted data, and the output is encrypted before being
sent off the TEE and stored on the blockchain. En-
claves in SN generate and store their attestation keys,
which are used only once during registration. The
enclaves create subsequent keys for communication
with the network, in particular to decrypt private in-
puts of smart contracts and encrypt resulting outputs.
4 ROBUST SN-BASED FL
SOLUTION
4.1 Overview
Multiple clients train locally their own dataset, result-
ing into local models. Those local models are then
sent encrypted to SN. The latter is in charge of ag-
gregating those local models to obtain a new global
model, in such a way that it learns nothing about the
individual models but only the resulting aggregate.
Moreover, SN is responsible of checking each submit-
ted individual model before aggregation. In particu-
lar, the blockchain verifies that every model proposed
by a client is correct and will not poison the future
global model.
Let N clients C
1
, ··· , C
n
be users of the blockchain
ecosystem. Each of these clients holds a pairwise key
shared with SN. One client, say C
1
, trains the model
locally using its own dataset and submits to SN the
resulting input, encrypted using its pairwise key k
1
shared with SN (1).
As soon as an encrypted input arrives, SN
launches the robust aggregation process (2). To do
so, inside the TEE, inputs are decrypted and possi-
bly ordered, and the robust techniques (e.g. Krum,
Trim Mean, Median) are calculated on those inputs.
For instance, the input from C
1
is decrypted using k
1
inside the TEE. SN first includes it into an initially
empty list that represents the buffer. SN collects other
inputs until the list is full. Steps (1) and (2) launch
the transaction Tr1, which is financially covered by
C
1
. Once the list is full, SN aggregates all inputs in
this list such that outliers are discarded (based on the
selected robust technique), resulting in a new global
model (3). This model can be queried by each client.
Then, the list becomes empty. This step triggers a
transaction since the global model has been updated
and the list has been emptied. This transaction is paid
by the owner of the smart contract.
We aim for deploying our solution in buffered FL
settings (Nguyen et al., 2022).Clients execute their
training as their pace as long as the used global model
is fresh enough (it does not need to be the latest model
accessible by query). When submitting their inputs
to SN, clients must include the hash of the trans-
action from which the global model was computed.
Hence, SN can check the freshness of the inputs be-
fore proceeding to the robust aggregation step, using
the transaction hash (giving the time and the block).
Moreover, the list plays the role of the buffer in our
Robust Blockchain-Based Federated Learning
63
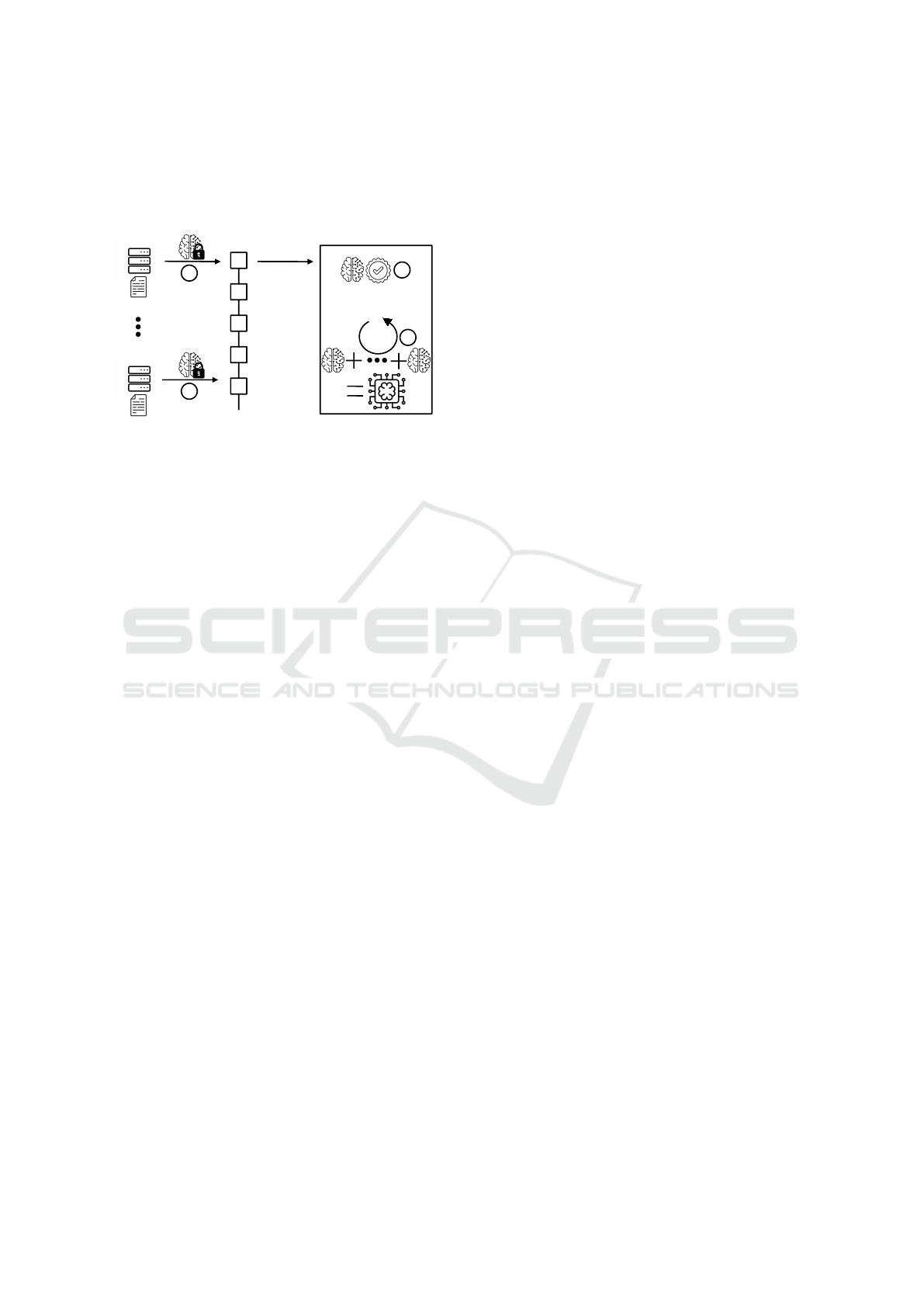
solution. SN is responsible of collecting enough cor-
rect inputs from clients before moving towards aggre-
gation. Figure 1 depicts the flow of our blockchain-
based scenario.
Tr1
Tr2
SN
blockchain
Client C
1
1
1
2
3
TEE
Client C
n
Figure 1: Overview of our FL scenario.
4.2 SN-Based System
4.2.1 System Phases
Setup: During the setup phase, the clients register to
the SN ecosystem. They become basic users of the
network, with some stake but without the intention
of participating in the maintenance of the blockchain
(i.e. through the roles of delegates and delegators).
Clients aim to launch transactions to submit their
local inputs to SN for robust aggregation. They also
receive the appropriate key material to communicate
with SN, allowing them to encrypt their inputs and
decrypt the outputs respectively.
Training: Clients locally train the model on their
own dataset. Once training is over, they submit their
updates to SN by encrypting them using a symmetric
key shared between each client and the network. This
kind of submission triggers a transaction, meaning
that clients must pay fees to SN where some are used
for gas and other for paying delegates.
Robust Aggregation: Clients’ inputs are stored in a
buffer of a FL-oriented smart contract until the buffer
is full. SN, through this smart contract, first ag-
gregates the stored inputs and obtains the aggregate.
The latter serves as the new global model and can be
queried by clients for another training round.
To enhance robust aggregation, the smart contract
embeds robust techniques, namely Krum, Trim Mean
and Median. More specifically, the smart contract re-
ceives local inputs from clients through transaction in
their encrypted form. Within the TEE, these inputs
are decrypted, ordered and aggregated following one
of the three techniques.
4.2.2 Smart Contract
Workflow: The smart contract proceeds as follows to
achieve robust aggregation. The smart contract first
receives local updates from clients and adds them
to its buffer. Note that only one input (i.e., vector)
is accepted per client per buffer round to prevent
DoS attacks. Once the buffer is full, it checks their
validity by ordering them according to the chosen
robust technique. For instance, a bound on the
number of corrupted clients is defined that excludes
the most left and right inputs in the ordered list. Once
input exclusion has happened, the smart contract
aggregates all the remaining updates, resulting into
a new global model. The latter can be queried by
clients.
Client Management: The smart contract is owned
by a party belonging to SN. The owner can add and
revoke clients. Clients are defined as authorised
when the smart contract is instantiated. This means
that only authorised clients can submit local inputs
through transactions. On the other side, any party
in SN, not only the authorised clients, can query the
smart contract. For instance, anyone can query the
list of authorised clients and the latest global model.
The size of the buffer is defined as being at least half
of the number of authorised clients.
Smart Contract Management: The owner is in
charge of activating the smart contract. Additionally,
she can deactivate it at any time. The smart contract
has been developed such that the owner can make
it not queriable (except to check whether the smart
contract is active) and not modifiable.
Input Management: Clients’ inputs are vectors
whose size can be consequent, of the order of thou-
sands. To fit within the SN framework, vectors can
be sent in smaller segments. Clients are asked to
append the round information of the current buffer.
They find such information when accessing the new
global model to train. Clients are restricted to sub-
mit one input per buffer round, even if this input is
rejected (not validated). Once the buffer is full (i.e.,
its maximum size is reached), the aggregation of all
inputs within the buffer is launched.
4.3 Robust Techniques
To manage Byzantine nodes, we employ and evalu-
ate three robust aggregation techniques, namely Krum
(Blanchard et al., 2017), Trim Mean (Yin et al., 2018),
and Median (Yin et al., 2018).
ICISSP 2025 - 11th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy
64

Krum selects the input that is the closest to the ma-
jority by calculating the Euclidean distance between
each pair of inputs. It then sums the distances of the
closest inputs and selects the one with the lowest total
distance, effectively filtering out outliers.
Trim Mean calculates the average of local inputs,
after discarding a predefined threshold of the highest
and lowest values among sorted inputs. This thresh-
old represents the hypothetical number of Byzantine
nodes in the system. Doing so, the influence of ex-
treme outliers is reduced. Median determines the
middle value of the sorted local inputs, providing ro-
bustness against extreme outliers w.r.t. predefined hy-
pothetical number of Byzantine nodes.
In practice, those robust techniques first consider
inputs as they arrive to SN. Then, inputs are ordered
to exclude a predetermined amount of outliers. This
amount represents the presumable number of cor-
rupted clients in the system. Finally, aggregation is
executed on the remaining inputs.
5 EXPERIMENTAL EVALUATION
5.1 Experimental Settings
Datasets and Distribution Among Clients: To
implement and evaluate our solution, we consider
two scenarios with two datasets: (i) a local med-
ical dataset that consists of 2126 patients’ (fully
anonymized) medical information such as age, blood
pressure, pulse, waist, uric acid, etc., and helps
predict heart arrhythmia; (ii) the MNIST dataset for
image classification (Deng, 2012). We consider a
cross-silo distributed system composed of SN (which
can be seen as a single server) and n clients. More
concretely, these two medical and MNIST datasets
are distributed among 10 and 15 FL clients, respec-
tively. In a realistic cross-silo environment, clients
often have different data distributions; hence, in our
setting, similar to the one in SABLE (Choffrut et al.,
2023), the dataset is partitioned among all clients
following a Dirichlet distribution parameterized with
α (Hsu et al., 2019). To capture the desired level of
data heterogeneity and examine its impact, we set α
in {0.5, 1, 5} for the medical dataset (the higher α the
more homogeneous the distribution among clients).
We choose α = 1 as in SABLE for the MNIST
dataset, reflecting a heterogeneous distribution.
Byzantine Nodes and Attacks: Training a FL model
on the medical and MNIST datasets while keeping it
privacy-protected becomes even more complex when
defending against a subset of Byzantine nodes who
try to deter the model’s performance. We have imple-
mented the four classes of Byzantine nodes that are
enumerated in SABLE:
• In a Fall Of Empires (FOE) attack (Xie et al.,
2020), Byzantine nodes send (1 − τ)v
t
, where v
t
is
the average of vectors sent by honest nodes at round t
and τ is the attack factor.
• In an A Little Is Enough (ALIE) attack (Baruch
et al., 2019), Byzantine nodes send v
t
+ τσ
t
, where
σ
t
is the coordinate-wise standard deviation of honest
vectors.
• In a Label Flipping (LF) attack (Allen-Zhu et al.,
2020), Byzantine nodes flip each label l to 9 − l,
where labels range from {0, . . . , 9}, and compute gra-
dients on these modified labels.
• In a mimic attack (Karimireddy et al., 2020),
Byzantine nodes imitate the honest node that incurs
the largest variance with respect to the gradients
and transmit the same values to SN. To evaluate the
impact of such attacks, we introduce f Byzantine
nodes in our two scenarios, with f varying from 0 to
3 and 0 to 5, respectively.
Models and Hyperparameters: For the medical sce-
nario, each client trains a Feed Forward Neural Net-
work (NN) composed of three fully connected layers
(FCLayers) with two activation functions, with model
batch size b = 32 and learning rate γ = 0.01.
Because SN only works with integers, we quantize
the model parameters and set the precision value δ =
10
4
. On the other hand, for the MNIST scenario, we
adopt the same setting of the one used in SABLE in
order to be able to compare easily. For both scenarios,
the model is trained in 100 rounds (we observe that
this number is sufficient for the model to converge).
5.2 Experimental Results
We first evaluate the performance of our SN-based FL
solution within the medical scenario. In particular,
we assess the learning performance of the model, in
comparison to its non-attacked counterpart, while
gradually increasing the number f of malicious
clients. We then evaluate our solution using the
MNIST dataset to accurately compare our results
with those obtained in SABLE. In both scenarios, we
also evaluate the communication and computation
costs.
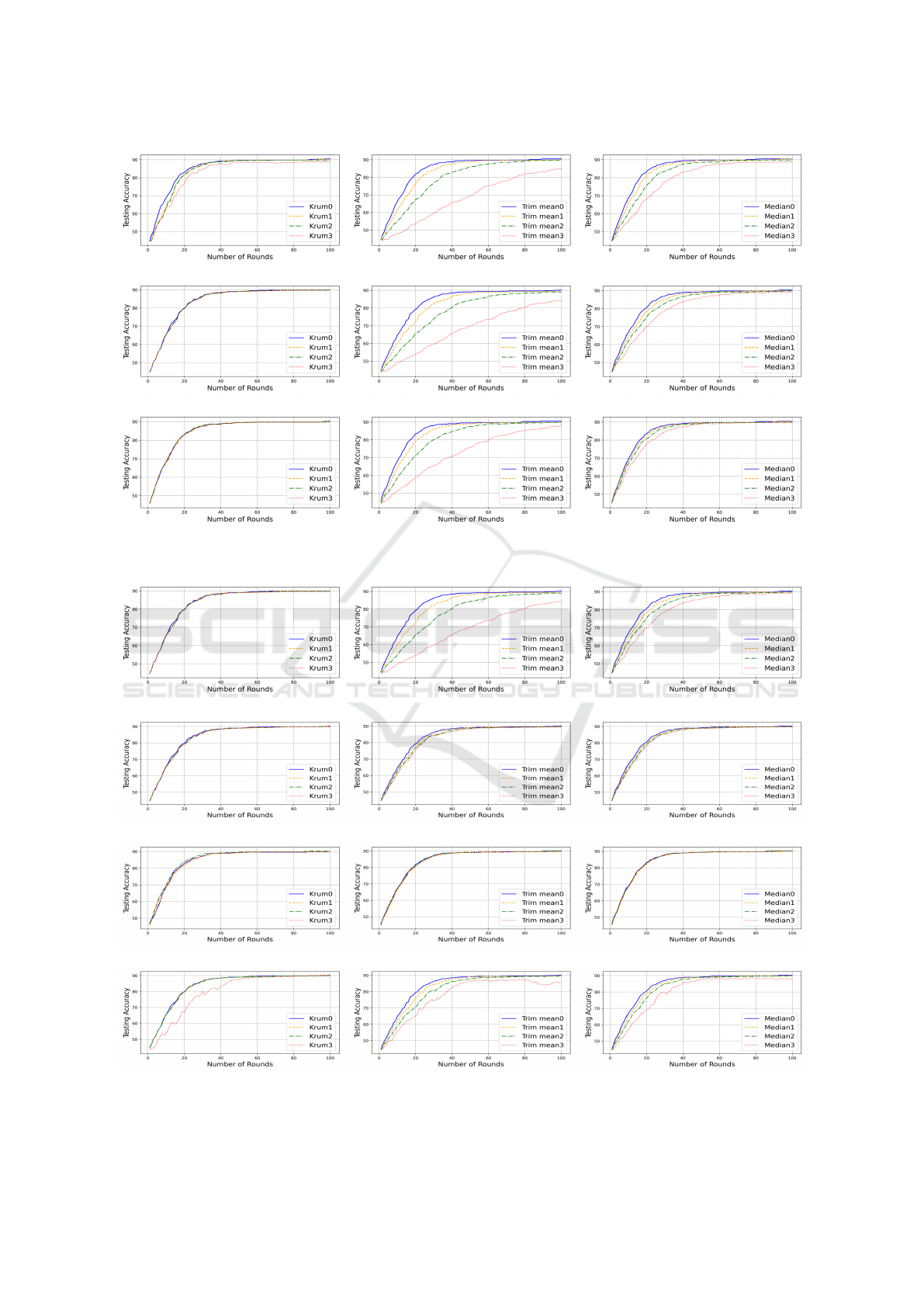
Medical Scenario: Firstly, in our experiments, we
notice that, when we move towards more homoge-
neous data distributions, all robust aggregation tech-
niques converge faster, independently of the under-
lying attack. This is depicted in Figure 2 for FOE
Robust Blockchain-Based Federated Learning
65
attacks (we observe the same behavior for the other
attacks but because of lack of space, we do not show
them here.). Therefore, we decide to set α = 1 for all
remaining experiments, as depicted in Figure 3.
Figure 3 then resents the accuracy results of the
trained model using the three robust aggregation tech-
niques (results with Krum, Trim Mean, and Median
are depicted in the first, second and last column, re-
spectively). Each row corresponds to the study of one
specific attack and each graph shows results with four
case-studies: one honest and three malicious cases,
i.e., f ∈ {0, 1, 2, 3}.
Regarding the quality of the aggregation tech-
nique, we observe that Krum shows the greatest re-
silience in more heterogeneous environments in the
case of FOE attacks. We believe the reason for this
performance is that changing the sign does not af-
fect the Euclidean distance between the values. On
the other hand, when ALIE or LF attacks are imple-
mented, all aggregation techniques seem to show sim-
ilar accuracy results, and compared to FOE attacks,
these two attacks do not create harm to the model.
Under the mimic attack, Figure 3(d) shows that the
Trim Mean aggregation technique is less robust than
Krum and Median techniques. Nevertheless, we re-
alize that the training still converges to an acceptable
accuracy level (≈ 90%).
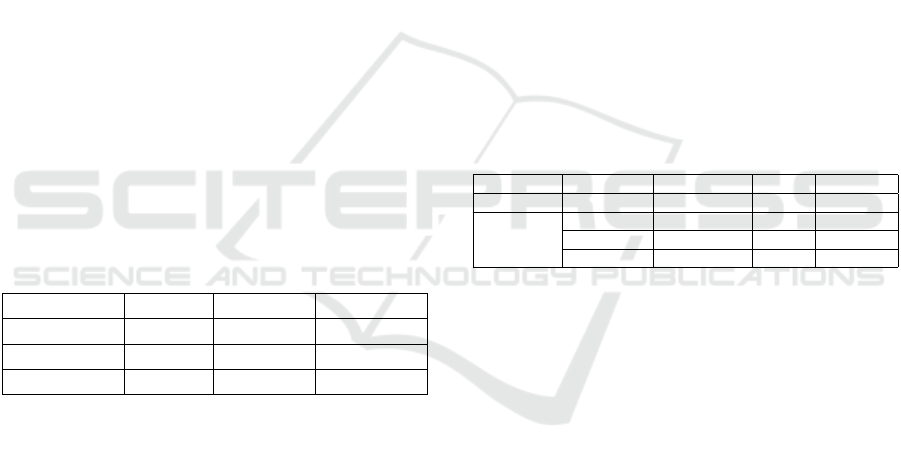
Table 1: Communication and computational costs of Krum,
Trim Mean and Median for the medical scenario. ”BW”
denotes bandwidth.
Technique t
tran
(s) t
agg
(ms) BW (KB)
Krum 4.2 120 13.67
Trim Mean 4.0 110 13.67
Median 4.1 100 13.67
The communication and computational costs for
the medical scenario are presented in Table 1, where
n = 10, f = 3 and δ = 10
4
. Here, t
tran
is defined as
the time required for each client to submit their local
update to SN, specifically the time needed to upload
their parameters to the blockchain via a transaction.
On the other hand, t
agg
denotes the time taken by SN
to execute the smart contract by applying the selected
robust technique to the clients’ updates, aggregating
them, and sending the updated values to all FL clients.
As seen in Table 1, the Trim Mean technique
achieves the best trade-off between communication
and computational costs, with a slightly lower t
tran
compared to the other methods. The Median tech-
nique requires marginally less aggregation time t
agg
.
Hence, the variations in computational are mainly
due to the processing complexities unique to each
technique. Moreover, all three techniques exhibit the
same bandwidth usage (i.e., 13.67 KB) since each
client utilizes the same CNN model for training,
resulting in identical gradient sizes. Each gradient
value is represented by an integer quantized with a
factor of 10
4
and can be stored in 16 bits.
MNIST Scenario: Figure 4 illustrates the learn-
ing performance of our solution on the MNIST sce-
nario, using the same model and hyperparameter set-
tings outlined in SABLE. In particular, n = 15, f ∈
{0, 1, 3, 5} and α = 1. We launch the four aforemen-
tioned attacks, as in SABLE, to properly compare our
solution with the latter. Table 2 offers a detailed com-
parison between our work and SABLE in terms of
communication and computational costs, based on the
MNIST dataset, with n = 15 and f = 5. This config-
uration simulates a realistic scenario in which up to
a third of the nodes may be compromised SABLE.
Within this context, t
tran
denotes the time each client
needs to submit its local update to the SN, while t
agg
indicates the time taken by the SN to execute the
smaer contract.
Table 2: Performance comparison on the MNIST dataset
with 79,510 model parameters. (
∗
Such a value is suggested
in (Choffrut et al., 2023) but is not explained.).
System Technique t
tran
(s) t
agg
(s) BW (KB)
SABLE Trim Mean not available 1040.4 5
∗
Our Work
Trim Mean 4.1 2.96 19.42
Median 4.1 2.61 19.42
Krum 4.2 3.48 19.42
SABLE aims to support robust aggregation tech-
niques over homomorphically encrypted data. It has
only been implemented with Trim Mean in practice.
Specifically, the Median method has been suggested
as an extension of Trim Mean, with similar results,
while Krum has not been deployed due to its potential
incompatibility with the HE scheme used in SABLE.
Moreover, in SABLE, the entire homomorphic aggre-
gation process is not completed at the server side as
expected. Instead, the final averaging step (i.e., divi-
sion by the total number of local inputs), is executed
by each client, introducing additional computational
overhead on the client side. Additionally, the band-
width usage is estimated to 5 KB in SABLE but not
explicitly confirmed neither theoretically nor experi-
mentally.
In contrast, our work offers a fully integrated and
practical implementation of three robust aggregation
techniques, namely Trim Mean, Median, and Krum.
Moreover, the full aggregation process (including di-
viding the aggregate by the number of updates) oc-
curs within the SN, and not at the client side. Our
solution also improves the overall system efficiency,
ICISSP 2025 - 11th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy
66
(a) α = 0.5.
(b) α = 1.
(c) α = 5.
Figure 2: Accuracy results for KRUM, Trim Mean, and Median under FOE attacks over the medical dataset.
(a) FOE attack.
(b) ALIE attack.
(c) LF attack.
(d) Mimic attack.
Figure 3: Accuracy results for KRUM, Trim Mean, and Median under the four attacks over the medical dataset.
Robust Blockchain-Based Federated Learning
67

(a) FOE attack.
(b) ALIE attack.
(c) LF attack.
(d) Mimic attack.
Figure 4: Accuracy results for KRUM, Trim Mean, and Median under the four attacks over the MNIST dataset.
as evidenced by the reduced aggregation times t
agg
by
a factor of approximately 300 compared to SABLE.
The bandwidth usage of our solution requires 19.42
KB (with 2-bit representation of parameters), while
authors of SABLE claim to consume approximately
5 KB (we had difficulties to compute this number
although adopting the same setting and quantization
strategy). The bandwidth cost, in our case, still re-
mains very low. On the other hand, we observe sub-
stantial gains in computational speed. Finally, we
have evaluated the performance of the three aggrega-
tion techniques (i.e., Trim Mean along with both Me-
dian and Krum), which does not vary much in terms
of computational and communication costs.
Regarding Figure 4, we show that we obtain a sim-
ilar behavior compared with SABLE, which only im-
plements Trim Mean. Moreover, as also observed in
the medical scenario, we realize that Krum is the most
suitable technique to overcome FOE attacks, whereas
all three methods perform similarly under ALIE and
LF attacks. Finally, the mimic attack seems to be the
most difficult attack to prevent, and for this one, the
worst aggregation method seems to be Trim Mean.
To summarize, based on this experimental study,
we can claim that Krum seems the most suitable tech-
nique to overcome the four types of attacks with a
negligible overhead in terms of computation and com-
munication.
5.3 Discussion and Future Work
Through designing our robust and privacy-preserving
solution over SN, we have met several challenges
from the latter. The first one is related to blockchain-
based storage fees. Clients submit their local input
to the smart contract through transactions. This im-
plies a financial cost, which is evaluated as gas fees
as in Ethereum
5
. Aggregation happens only once the
buffer is full, meaning that the smart contract keeps
received inputs until aggregation. Gas fees increase
with the number of inputs stored in the smart con-
tract. In particular, if the initial transaction launched
from the first vector has a cost worth x, then the sub-
sequent Nth transaction from the Nth vector has a cost
worth Nx. However, such a cost process has a limit in
SN. The SN simply rejects the transactions and thus
client vectors because the fees are seen as too high for
5
https://ethereum.org/
ICISSP 2025 - 11th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy
68

the network. Consequently, we aim to explore how to
overcome such a restrictive limitation to permit to op-
erate our solution over real but huge datasets such as
CIFAR.
Another problem that we have encountered is re-
lated to the selection of techniques to enable robust
aggregation. Other metrics exist, based on norm
bounding (e.g., L
2
, L
∞
, Cosine distance, Hamming
distance). Nevertheless, those metrics incur costly
operations, which reach the financial limits of SN
(i.e., costly operations require more gas fees). Con-
sequently, some local inputs could be rejected before
the buffer being full and thus, aggregation might never
happen. A second option for future work is to con-
sider more carefully how to deploy those norm bound-
ing metrics in our solution.
6 CONCLUSION
In this paper, we addressed key challenges in FL by
developing a solution that ensures the privacy of client
updates along with the robustness and integrity of the
global model. While SA within TEEs protects indi-
vidual updates, FL systems remain vulnerable to ma-
licious clients submitting poisoned updates that com-
promise model performance. To mitigate this, we
proposed three methods that filter out outlier updates
prior to aggregation, safeguarding the global model’s
robustness. Our framework also supports FL model
integrity through consensus mechanisms, guarantee-
ing genuine clients to have their updates used for
aggregation. By integrating blockchain technology
through SN and using smart contracts within TEEs,
our approach ensures privacy-preserving and robust
aggregation of updates. Experimental results using a
medical dataset and the MNIST dataset demonstrate
the effectiveness of our solution in protecting client
input privacy and preventing model poisoning, while
keeping a favorable performance in terms of compu-
tation and communication.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work has been partially supported by the TRAIN
project number ANR-22-FAI1-0003 and UPNM
short-term grant code UPNM/2023/GPJP/ICT/6.
REFERENCES
Allen-Zhu, Z., Ebrahimian, F., Li, J., and Alistarh, D.
(2020). Byzantine-resilient non-convex stochastic
gradient descent. arXiv preprint arXiv:2012.14368.
Allouah, Y., Farhadkhani, S., Guerraoui, R., Gupta, N.,
Pinot, R., and Stephan, J. (2023a). Fixing by mix-
ing: A recipe for optimal Byzantine ML under het-
erogeneity. In Int. Conf. on Artificial Intelligence and
Statistics, pages 1232–1300.
Allouah, Y., Guerraoui, R., Gupta, N., Pinot, R., and
Stephan, J. (2023b). On the privacy-robustness-utility
trilemma in distributed learning. In Int. Conf. on Ma-
chine Learning, pages 569–626.
Arachchige, P. C. M., Bertok, P., Khalil, I., Liu, D.,
Camtepe, S., and Atiquzzaman, M. (2020). A trust-
worthy privacy preserving framework for Machine
Learning in industrial IoT systems. IEEE Trans. on
Industrial Informatics, 16(9):6092–6102.
Baruch, G., Baruch, M., and Goldberg, Y. (2019). A lit-
tle is enough: Circumventing defenses for distributed
learning. Advances in Neural Information Processing
Systems, 32.
Bell, J., Gasc
´
on, A., Lepoint, T., Li, B., Meiklejohn, S.,
Raykova, M., and Yun, C. (2023). ACORN: Input
validation for secure aggregation. In 32nd USENIX
Security Symposium, pages 4805–4822.
Blanchard, P., El Mhamdi, E. M., Guerraoui, R., and
Stainer, J. (2017). Machine Learning with adversaries:
Byzantine tolerant gradient descent. Adv. in Neural
Information Processing Systems, 30:118–128.
Bonawitz, K., Ivanov, V., Kreuter, B., Marcedone, A.,
McMahan, H. B., Patel, S., Ramage, D., Segal, A., and
Seth, K. (2017). Practical secure aggregation for pri-
vacy preserving Machine Learning. Cryptology ePrint
Archive, Paper 2017/281.
Buyukates, B., So, J., Mahdavifar, H., and Avestimehr, S.
(2022). Lightverifl: Lightweight and verifiable secure
federated learning. In Workshop on Federated Learn-
ing: Recent Advances and New Challenges (in Con-
junction with NeurIPS 2022).
Cao, X., Fang, M., Liu, J., and Gong, N. Z. (2020). FLtrust:
Byzantine-robust Federated Learning via trust boot-
strapping. arXiv preprint arXiv:2012.13995.
Chen, L., Wang, H., Charles, Z., and Papailiopoulos, D.
(2018). DRACO: byzantine-resilient distributed train-
ing via redundant gradients.
Choffrut, A., Guerraoui, R., Pinot, R., Sirdey, R., Stephan,
J., and Zuber, M. (2023). Practical homomor-
phic aggregation for Byzantine ML. arXiv preprint
arXiv:2309.05395.
Corrigan-Gibbs, H. and Boneh, D. (2017). Prio: Private, ro-
bust, and scalable computation of aggregate statistics.
In 14th USENIX Symposium on Networked Systems
Design and Implementation, pages 259–282.
Deng, L. (2012). The MNIST database of handwritten digit
images for Machine Learning research. IEEE signal
processing magazine, 29(6):141–142.
Fung, C., Yoon, C. J. M., and Beschastnikh, I. (2020). Miti-
gating Sybils in Federated Learning Poisoning. arXiv
preprint arXiv:1808.04866.
Guerraoui, R., Gupta, N., Pinot, R., Rouault, S., and
Stephan, J. (2021). Differential Privacy and Byzantine
resilience in SGD: Do they add up? In ACM Sympo-
sium on Principles of Distributed Computing, pages
391–401.
Robust Blockchain-Based Federated Learning
69

Guo, X., Liu, Z., Li, J., Gao, J., Hou, B., Dong, C., and
Baker, T. (2021). Verifl: Communication-efficient
and fast verifiable aggregation for federated learning.
IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Se-
curity, 16:1736–1751.
Hao, M., Li, H., Xu, G., Chen, H., and Zhang, T. (2021). Ef-
ficient, private and robust Federated Learning. In 37th
Annual Computer Security Applications Conference,
pages 45–60.
Hsu, T.-M. H., Qi, H., and Brown, M. (2019). Mea-
suring the effects of non-identical data distribution
for federated visual classification. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1909.06335.
Kairouz, P., McMahan, H. B., Avent, B., and Bellet, A.
(2021). Advances and Open Problems in Federated
Learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:1912.04977.
Kalapaaking, A. P., Khalil, I., Rahman, M. S., Atiquz-
zaman, M., Yi, X., and Almashor, M. (2023).
Blockchain-Based Federated Learning With Secure
Aggregation in Trusted Execution Environment for
Internet-of-Things. IEEE Trans. on Industrial Infor-
matics, 19(2):1703–1714.
Karimireddy, S. P., He, L., and Jaggi, M. (2020). Byzantine-
robust learning on heterogeneous datasets via bucket-
ing. arXiv preprint arXiv:2006.09365.
Khazbak, Y., Tan, T., and Cao, G. (2020). MLGuard: mit-
igating poisoning attacks in privacy preserving dis-
tributed collaborative learning. In 29th Int. Conf. on
Computer Communications and Networks, pages 1–9.
Liu, J., He, X., Sun, R., Du, X., and Guizani, M. (2021).
Privacy-preserving data sharing scheme with FL via
MPC in financial permissioned blockchain. In IEEE
International Conf. on Communications, pages 1–6.
Lu, Y., Huang, X., Dai, Y., Maharjan, S., and Zhang,
Y. (2019). Blockchain and federated learning for
privacy-preserved data sharing in industrial IoT. IEEE
Trans. on Industrial Informatics, 16(6):4177–4186.
Lycklama, H., Burkhalter, L., Viand, A., K
¨
uchler, N., and
Hithnawi, A. (2023). RoFL: robustness of secure fed-
erated learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2107.03311.
Mansouri, M.,
¨
Onen, M., Ben Jaballah, W., and Conti, M.
(2023). SoK: secure aggregation based on crypto-
graphic schemes for federated learning. In 23rd Pri-
vacy Enhancing Technologies Symposium.
McMahan, B., Moore, E., Ramage, D., Hampson, S., and
y Arcas, B. A. (2017). Communication-efficient learn-
ing of deep networks from decentralized data. In 20th
Int. Conf. on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics.
Miao, Y., Liu, Z., Li, H., Choo, K.-K. R., and Deng, R. H.
(2022). Privacy-preserving Byzantine-robust feder-
ated learning via blockchain systems. IEEE Trans. on
Information Forensics and Security, 17:2848–2861.
Naseri, M., Hayes, J., and Cristofaro, E. D. (2022). Local
and central differential privacy for robustness and pri-
vacy in federated learning. In 29th Annual Network
and Distributed System Security Symposium.
Nguyen, J., Malik, K., Zhan, H., Yousefpour, A., Rabbat,
M., Malek, M., and Huba, D. (2022). Federated learn-
ing with buffered asynchronous aggregation. In In-
ternational Conference on Artificial Intelligence and
Statistics, pages 3581–3607.
Nguyen, T. D., Rieger, P., Chen, H., Yalame, H., M
¨
ollering,
H., Fereidooni, H., Marchal, S., Miettinen, M., Mirho-
seini, A., Zeitouni, S., Koushanfar, F., Sadeghi,
A.-R., and Schneider, T. (2021). FLGUARD: se-
cure and private federated learning. arXiv preprint
arXiv:2101.02281.
Rahulamathavan, Y., Herath, C., Liu, X., Lambotharan,
S., and Maple, C. (2023). FheFL: fully homo-
morphic encryption friendly privacy-preserving fed-
erated learning with byzantine users. arXiv preprint
arXiv:2306.05112.
Rathee, M., Shen, C., Wagh, S., and Popa, R. (2023).
ELSA: secure aggregation for federated learning with
malicious actors. In IEEE Symposium on Security and
Privacy, pages 1961–1979.
Roy Chowdhury, A., Guo, C., Jha, S., and van der Maaten,
L. (2022). Eiffel: Ensuring integrity for federated
learning. In ACM SIGSAC Conf. on Computer and
Communications Security, pages 2535–2549.
Saad, S. M. S., Radzi, R. Z. R. M., and Othman, S. H.
(2021). Comparative analysis of the blockchain con-
sensus algorithm between proof of stake and delegated
proof of stake. In International Conference on Data
Science and Its Applications, pages 175–180.
Shejwalkar, V., Houmansadr, A., Kairouz, P., and Ramage,
D. (2021). Back to the drawing board: A critical eval-
uation of poisoning attacks on production federated
learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2108.10241.
Shen, S., Tople, S., and Saxena, P. (2016). Auror: defending
against poisoning attacks in collaborative deep learn-
ing systems. In Annual Computer Security Applica-
tions Conference, page 508–519.
Wang, N., Yang, W., Guan, Z., Du, X., and Guizani, M.
(2021). BPFL: a blockchain based privacy-preserving
federated learning scheme. In IEEE Global Commu-
nications Conference, pages 1–6.
Will, N. C. and Maziero, C. A. (2023). Intel software guard
extensions applications: A survey. ACM Computing
Survey, 55.
Xie, C., Koyejo, O., and Gupta, I. (2020). Fall of empires:
Breaking byzantine-tolerant sgd by inner product ma-
nipulation. In Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence,
pages 261–270.
Yin, D., Chen, Y., Kannan, R., and Bartlett, P. (2018).
Byzantine-robust distributed learning: Towards opti-
mal statistical rates. In Int. Conf. on Machine Learn-
ing, pages 5650–5659.
Zhang, C., Li, S., Xia, J., Wang, W., Yan, F., and Liu, Y.
(2020). BatchCrypt: Efficient homomorphic encryp-
tion for Cross-Silo federated learning. In USENIX An-
nual Technical Conference, pages 493–506.
Zhang, Z., Wu, L., Ma, C., Li, J., Wang, J., Wang, Q.,
and Yu, S. (2022). LSFL: a lightweight and se-
cure federated learning scheme for edge computing.
IEEE Trans. on Information Forensics and Security,
18:365–379.
Zhu, H. and Ling, Q. (2022). Bridging differential pri-
vacy and byzantine-robustness via model aggregation.
arXiv preprint arXiv:2205.00107.
ICISSP 2025 - 11th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy
70
