
Unified CNN-Transformer Model for Mental Workload Classification
Using EEG
Fiza Parveen
a
and Arnav Bhavsar
b
Indian Institute of Technology Mandi, Mandi, India
Keywords:
Mental Workload Classification, EEG, Convolutional Neural Network, Attention Mechanism, Transformers,
Ensemble Majority Voting.
Abstract:
The cognitive effort required for tasks requiring memory, attention, and decision-making is referred to as
mental workload. Preventing cognitive overload and increasing task efficiency rely on a reliable assessment
of mental workload. In this study, we present a CNN-Transformers hybrid model that uses EEG data for
multi-level Mental Workload classification. Our model uses 1D-CNN to extract spatial features from win-
dowed EEG signals followed by Transformers to capture temporal correlation.This combination improves our
comprehension of mental workload situations by capturing local spatial and both long-range temporal aspects.
We use a majority voting technique on the window based predictions to increase prediction reliability, making
sure the final accuracy represents a thorough assessment of mental workload at signal level. A rigorous 5-fold
cross-validation technique is used to evaluate the model on publicaly available STEW dataset.
1 INTRODUCTION
Mental workload refers to the cognitive effort re-
quired for executing tasks that involve attention,
memory, and decision-making processes. Assess-
ing cognitive stress particularly in real-time, is cru-
cial for enhancing task efficiency and avoiding cog-
nitive overwhelm. Electroencephalography (EEG) is
commonly employed for this objective because of
its capacity to record brain activity in real-time with
a high level of temporal precision. Machine learn-
ing and deep learning techniques, including Convo-
lutional Neural Networks (CNNs), have been effec-
tively used to classify EEG data for assessing men-
tal workload. CNNs have shown encouraging perfor-
mance in diverse applications related to EEG data in-
terpretation. They have a major advantage in being
able to automatically extract spatial characteristics
from raw EEG data by acquiring intricate hierarchical
patterns within the signals. CNNs are very proficient
at capturing spatial hierarchies and local dependen-
cies in EEG signals (Schirrmeister et al., 2017).
Nevertheless, CNNs encounter substantial obsta-
cles when used with time-series data, despite their
notable capabilities. The biomarkers of mental work-
a
https://orcid.org/0009-0003-2672-4656
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2849-4375
load may involve not only the local spatial patterns of
brain activity but also the temporal evolution of these
patterns. EEG signals possess an inherent sequential
nature, characterized by long range temporal depen-
dencies that manifest from the dynamic characteris-
tics of cognitive processes. Consequently, CNNs may
have difficulties in comprehending the sequential na-
ture of EEG data, which is crucial for appropriately
classifying levels of mental workload, especially in
activities that need constant monitoring and real-time
evaluation (Wang et al., 2020).
In order to address the limitations of CNNs in cap-
turing long range temporal relationships, researchers
have progressively shifted towards employing trans-
former models. Transformers, first designed for nat-
ural language processing, have fundamentally trans-
formed sequence modeling through the introduction
of the self-attention mechanism. The mechanism de-
scribed enables transformers to effectively capture re-
lationships that span across all time steps in a se-
quence, resulting in a thorough comprehension of
temporal dynamics (Vaswani et al., 2017). Trans-
formers have been shown reliability in classifying
cognitive states by considering several time periods
in the sequence and modeling how they evolve over
time (Roy et al., 2019).
Furthermore, the capacity of Transformers to han-
dle sequences concurrently, in contrast to the sequen-
928
Parveen, F. and Bhavsar, A.
Unified CNN-Transformer Model for Mental Workload Classification Using EEG.
DOI: 10.5220/0013190900003911
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 18th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2025) - Volume 1, pages 928-934
ISBN: 978-989-758-731-3; ISSN: 2184-4305
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

tial operation of RNNs, provides a notable computa-
tional benefit. The capacity of transformers to per-
form parallel processing allows for quicker training
and inference, making them highly suitable for real-
time applications that require rapid and precise evalu-
ations of mental exertion (Vaswani et al., 2017).
Combining transformers with CNNs has shown
significant promise in improving the effectiveness of
mental workload classification models. This hybrid
approach utilizes CNNs to extract spatial character-
istics from EEG data. CNNs are particularly effec-
tive in capturing local patterns and spatial hierarchies
which can lead to filtered embedding instead of us-
ing raw signals. The spatial features from CNN,
are subsequently fed into a transformer, which ana-
lyzes the sequence of spatial features and captures the
temporal relationships over the entire series (Huang
et al., 2019). This combination enables the model to
leverage the advantages of both CNNs and transform-
ers: CNNs offer a good quality spatial representation,
while transformers guarantee correct capture of tem-
poral correlations. A hybrid model is more capable of
managing the intricacies of EEG signals, resulting in
enhanced accuracy in classification and better gener-
alization across various tasks and people.
2 RELATED WORK
In this article, we examine recent studies that focus on
classifying mental workloads. The research by (Lim
et al., 2018) introduces the STEW dataset, which is
utilized in our analysis. This dataset is categorized
into three distinct classes: low, moderate, and high
workloads, based on ratings from 45 participants us-
ing a scale from 1 to 9. Power Spectral Density
(PSD) features are derived using Fast Fourier Trans-
form (FFT) across the delta, theta, alpha, and beta
frequency bands, applying a sliding window tech-
nique. The data is divided into training and testing
sets, allocating 80% (36 subjects) for training and
20% (9 subjects) for testing. Neighborhood Compo-
nent Analysis (NCA) is conducted to select features
from the training dataset for regression, utilizing 5-
fold cross-validation. The top 75% of features iden-
tified across all folds are used in Support Vector Re-
gression (SVR), which predicts ratings on the test data
that are later transformed into class labels.
In (Parveen and Bhavsar, 2023), the authors clas-
sify mental workloads into two and three levels. For
three-class classification, the data is segmented into
three mental workload categories based on the ratings
provided by subjects. Additionally, the dataset is split
into training and testing sets in a 9:1 ratio. After pre-
processing, the data is divided into windows of 512
samples with an overlap of 128 samples. These win-
dowed are input into a 1D-CNN network that includes
multiple horizontal and vertical CNN blocks for ex-
tracting spatial and temporal features from the EEG
data. A majority voting technique is employed to ob-
tain results for the entire signal rather than individual
windows. The model is validated using a 5-fold cross-
validation method.
In a different study by (Sharma and Ahirwal,
2021), the authors classify the STEW dataset into 2
and 3 classes based on ratings. For three-class classi-
fication, the dataset is divided into low, moderate, and
high workload categories. The low workload class
consists of respondents with ratings between 4 and
5, the moderate workload class includes subjects with
ratings between 6 and 7, and the high workload class
comprises individuals with ratings between 8 and 9.
The data is augmented by employing a window size of
512 with an overlap of 128 samples, generating a to-
tal of 6,615 samples. The classification process splits
the data into training (5,622 samples) and testing sets
(993 samples), maintaining a ratio of 85% for train-
ing and 15% for testing. A cascaded 1D-CNN and
Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory (Bi-LSTM)
model are used for classification, utilizing both 5-fold
and 7-fold cross-validation techniques.
In another study (Kingphai and Moshfeghi, 2023),
a sliding window approach with a size of 512 and an
overlap of 128 samples is utilized. Power Spectral
Density (PSD) is calculated for the alpha and theta
frequency bands. These features are extracted from
all 14 channels, resulting in a total of 84 features (14
channels multiplied by 6 features). A Bidirectional
Gated Recurrent Unit (BGRU-GRU) model is applied
to the time series EEG data, using the Rolling and
Expanding Window method for analysis.
Recent work demonstrated that transformers can
greatly improve the ability of EEG-based models to
analyze and understand changes over time, resulting
in more detailed and dependable evaluations of men-
tal workload (Sun et al., 2021). (Roy et al., 2019)
showed that a model built on transformers could sur-
pass typical recurrent neural networks (RNNs) in cap-
turing long-term relationships in EEG data, leading to
more accurate estimations of cognitive load. The pa-
per (Siddhad et al., 2024) explores the application of
transformer networks for classifying raw EEG data,
aiming to enhance accuracy while reducing the need
for extensive pre-processing. The study employed a
transformer model with a multi-head attention mech-
anism, embedding techniques, and positional encod-
ing. The STEW data, minimally pre-processed and
segmented into 0.25-second epochs, was used to train
Unified CNN-Transformer Model for Mental Workload Classification Using EEG
929

the transformer network. The model incorporated em-
bedding techniques to represent the input data and
positional encoding to maintain the order of the se-
quences. The transformer network was trained on the
raw EEG data for classification tasks.
In another work (Wang et al., 2024), the ap-
proach focus on the development of an Attention-
Based Recurrent Fuzzy Network (ARFN) to assess
mental workload using EEG data. EEG signals are
first processed through a fuzzy recursive module that
captures temporal dependencies, then passed into an
Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM), which produces
a feature vector. This vector is averaged across time
steps and fed into a fully connected layer with a Soft-
max function for classification. The model is trained
using a Mean Squared Error (MSE) loss function with
a regularization term to prevent overfitting, and the
optimization is handled by the Adaptive Moment Es-
timation (ADAM) algorithm. Performance was eval-
uated on STEW using k-fold cross-validation.
3 DATA DESCRIPTION
This study utilizes the open access STEW (Lim
et al., 2018) dataset, which includes EEG record-
ings of rest and multitasking mental workload activ-
ity. The recordings were obtained utilizing the Vi-
enna Test System (Bratfisch and Hagman, 2008) dur-
ing a single-session simultaneous capacity (SIMKAP)
experiment involving 48 male participants. The
SIMKAP activity is specifically developed to assess
an individual’s competence in effectively handling
numerous tasks in a challenging work environment.
The experiment is divided into two segments. At
the beginning, the participants are provided with spe-
cific instructions to adopt a calm position and en-
sure that their vision is not blocked for a period of
3 minutes. They are also instructed not to partici-
pate in any activities or tasks during this time. After-
wards, the participants engaged in the SIMKAP task,
in which they were directed to eliminate matching
panels, while also responding to auditory questions
that involved arithmetic, comparison, or data retrieval.
Certain auditory inquiries may require the subject to
delay their response, forcing them to keep an eye on
a clock in the upper right corner.
The task has a duration of three minutes. The se-
quence of questions in the challenge remains consis-
tent across all subjects. EEG was measured through-
out both the period of rest and the period of task per-
formance. To minimize the effect of any intermediate
task activity, the initial and concluding 15 seconds of
data from each recording are excluded. Out of the
48 participants, 45 individuals provided input on both
rest and task difficulty using a scale that ranged from
1 to 9. A numerical value ranging from 1 to 3 in-
dicates a workload that is considered low, whereas a
value ranging from 4 to 6 indicates a workload that is
considered moderate, and a rating ranging from 7 to 9
indicates a burden that is considered high.
The EEG data is acquired utilizing the Emotiv
EPOC EEG headset, which possesses a sampling fre-
quency of 128 Hz and a resolution of 16 bits analog-
to-digital conversion. The gadget is outfitted with 14
electrodes that are positioned according to the 10-20
international system at specified locations: AF3, F7,
F3, FC5, T7, P7, O1, O2, P8, T8, FC6, F4, F8, AF4.
In our study, which focuses on rating based com-
parisons between low, medium, and high levels, we
have excluded data from subjects S05, S24, and S42
due to the unavailability of ratings for these individu-
als.
4 METHODOLOGY
4.1 Pre-Processing
Pre-processing of EEG signals is an essential step
that improves the quality of the signals and stream-
lines data analysis. The accuracy and dependability
of the model may be jeopardized by noise and fluc-
tuations in the EEG data. EEG consists of discrete
frequencies, spatial patterns, and associations to dif-
ferent states of brain activity.
The commonly employed frequency ranges in-
clude delta (0.5 to 4 Hz), theta (4 to 7 Hz), alpha (8
to 12 Hz), and beta (13 to 30 Hz) (Lim et al., 2018).
These frequency ranges correspond to specific brain
states, including deep sleep, alertness, and anxiety.
Several filtering techniques are available for removing
artifacts, as shown in references (Chandrashekar and
Sahin, 2014), (Nitschke et al., 1998), (Iriarte et al.,
2003), (Lai et al., 2018). In this study, we utilize a 6th
order Butterworth filter to isolate frequencies ranging
from 1 to 60 Hz
Furthermore, we utilize the ADJUST algorithm
(Mognon et al., 2011) to reduce any artifacts. Over-
all, we implement the following sequential proce-
dures during the pre-processing phase (Parveen and
Bhavsar, 2023).
• EEG signals are typically recorded with respect to
one or more reference electrodes. In this study,
we utilized the technique of average referenc-
ing, which involves calculating the mean value of
each channel and then subtracting it from all data
points corresponding to that channel.
BIOSIGNALS 2025 - 18th International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
930

• EEG signals comprise a wide range of frequency
components that correspond to different types of
brain activity. We utilized a 6th order Butterworth
band-pass filter, especially an infinite impulse re-
sponse (IIR) filter, with a frequency range of 1-60
Hz. The strong cutoff in the stopband of this filter
effectively reduces low frequency drifts and high
frequency noise. We encompass the entire range
of frequencies, spanning from delta to gamma.
• To mitigate the disruption produced by line noise,
we utilize a 50 Hz notch filter on our EEG data.
• Eye blinks, muscular movements, and ambient
influences are examples of EEG artifacts that
come from sources besides brain activity. Arti-
fact removal is a crucial step in the processing of
EEG signals. This study employed the ADJUST
method (Mognon et al., 2011), which utilizes in-
dependent component analysis (ICA) to segregate
the EEG data into discrete components. Every el-
ement symbolizes a unique neural source of activ-
ity, some of which might involve artifacts.
4.2 Windowing
After pre-processing, we utilize sliding windows con-
sisting of 512 samples, with an overlap of 128 sam-
ples, over the entire duration of EEG data from each
participant. Each participant contributed a total of 147
windows, with each window measuring 14 units in
height and 512 units in width. We then divided the
data into three workload categories according to the
evaluations provided by 45 participants. We catego-
rized the EEG data according to the ratings, assign-
ing a label of ”low workload” to data with ratings 1-
3, ”moderate workload” to data with ratings 4-6, and
”high workload” to data with ratings 7-9. If the work-
load is moderate, we acquire 6,174 windows of EEG
data, with each window having dimensions of 14 x
512. When the workload is modest, we have a grand
total of 3,381 windows. Each window has dimensions
of 14 units in height and 512 units in width. In situ-
ations of high workload, we possess a grand total of
3,675 EEG samples that are windowed. These sam-
ples have dimensions of 14 x 512.
4.3 Model Description
The proposed framework, Figure 1, for classifying
mental workload combines the advantages of a Con-
volutional Neural Network (1D-CNN) with a Trans-
former network to accurately capture both local and
global relationships in the data. The model adheres
to a systematic pipeline to handle the incoming data,
extract pertinent features, and categorize the mental
workload into one of three types. Here is an elaborate
explanation of each constituent and its function in the
structure of the model.
4.3.1 CNN Based Features
In the initial phase of the model, an attention-based
1D-CNN is used to extract hierarchical features from
both the temporal and spectral dimensions, effectively
capturing the underlying patterns in the data. Max
pooling is utilized subsequent to the last convolu-
tional layer in order to decrease the size of the feature
maps, hence minimizing the computational complex-
ity while preserving the most essential information.
The extracted features exhibited the shape (11,613 x
3 x 252 x 50) and (1,617 x 3 x 252 x 50) for train
and test dataset respectively. In order to ensure com-
patibility with our proposed transformer network, the
retrieved features were reshaped by manipulating the
feature tensor. The tensor was reshaped to conform
to the input specifications of the transformer. Specif-
ically, it was transformed into the format (samples,
sequence length, feature dimension), where sequence
length is the result of multiplying the number of chan-
nels by the number of time samples, where sequence
length corresponds to the time samples, and feature
dimension is the product of channels and CNN filters,
resulted in features of shape (252x150). This reshap-
ing ensured that each time sample was represented by
a feature vector that encapsulated information across
all channels and CNN filters, making it suitable for
processing by the transformer network and feature di-
mension corresponds to the number of CNN filters.
The Transformer model was trained using the
following feature shapes (11,613 x 252 x 150) and
(1,617 x 252 x 150) for train and test respectively.
4.3.2 Transformer Block
We utilize only the encoder part of the Transformer in
order to capture information within the EEG signals.
Presence of a Multi-Head Attention block in the trans-
former network enables the model to simultaneously
focus on distinct segments of the sequence. In the
model, residual connections are also used which also
alleviate the issue of disappearing gradients and fa-
cilitate the propagation of gradients during backprop-
agation. Also the use of Layer Normalization makes
sure that the inputs for each layer is normalized, hence
enhancing the stability and speed of the training pro-
cess.
Following the Transformer block, the features un-
dergo flattening and then pass through a sequence of
fully connected layers. These layers have the purpose
of adding another level of abstraction to the informa-
Unified CNN-Transformer Model for Mental Workload Classification Using EEG
931

Figure 1: Proposed CNN-Transormer model.
tion and getting it ready for the classification task.
The output from the fully connected layer goes to a
softmax function, resulting in a probability distribu-
tion across the three classes.
4.3.3 Window Based Majority Voting
EEG is non-stationary in nature. Therefore to avoid
computing embeddings on complete signals, we uti-
lize window based estimates. The model produces
several predictions for each participant by using slid-
ing windows over the EEG signals. However, it is
more realistic to have the final result on entire signal.
So, we employ a majority voting approach to deter-
mine the final forecast based on the collective predic-
tions made across the windows for each EEG signal.
4.3.4 Summary of the Overall Approach
In summary the proposed model follows the following
sequence of steps:
• The model receives EEG segments that are dis-
played in separate windows.
• A 1D-CNN is utilized to extract local temporal in-
formation from the EEG inputs.
• Features are extracted from the last convolutional
layer following the process of max-pooling.
• The retrieved features are transformed into a suit-
able format for sequence processing.
• The modified characteristics undergo processing
in the Transformer block, which incorporates
multi-head attention, residual connections, layer
normalization, and a feed-forward network.
• The result of the Transformer block is flatten and
fed to fully connected layers.
• A softmax layer generates probability distribu-
tions for each class.
• The final class label for each subject is determined
by performing majority voting on the window-
level estimates.
5 EXPERIMENTS
For the three-class classification, we divided the data
into training and testing datasets with a 9:1 ratio be-
tween them. Following this, windowing has been
done on both the training and testing data, yielding
a combined total of 11,613 training EEG samples and
1,617 testing EEG samples.
This validation process employed a 5-fold cross-
validation technique.
6 RESULTS
The results of classification is presented in Table 1.
For three class level mental workload classification,
by integrating CNN with the transformer network,
the classification accuracy significantly increases to
85.46% on the 5-fold cross validation test data. This
demonstrates the substantial impact of the proposed
transformer network incorporating CNN features.
Table 1: Classification accuracy on cross-validation dataset
with proposed model.
Cross validation set Accuracy
CV-1 90.90%
CV-2 81.81%
CV-3 81.81%
CV-4 90.90%
CV-5 81.81%
Mean 85.46%
7 DISCUSSION AND
COMPARISSIONS
Table 2 presents a comparison of our results with
those utilizing the STEW dataset (Lim et al., 2018).
The findings demonstrate a significant improvement
BIOSIGNALS 2025 - 18th International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
932
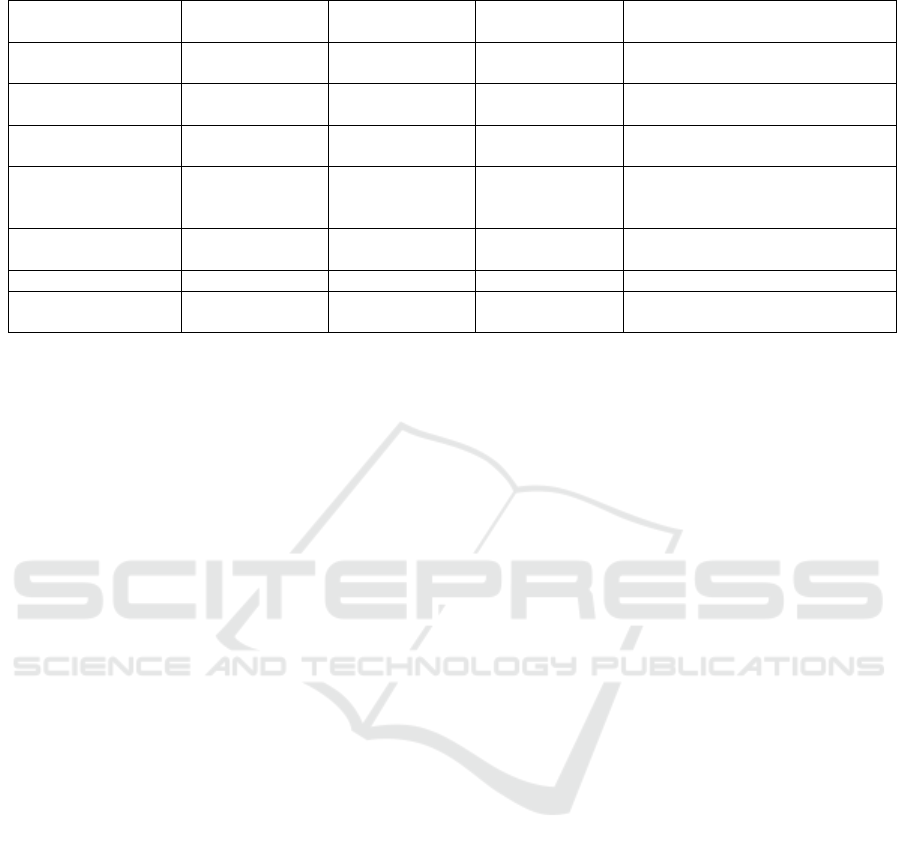
Table 2: Performance comparision with related work.
Paper Classifier Best Accuracy Average Accu-
racy
Remarks
(Lim et al., 2018) SVR 69.2% NA Subject wise train-test split and sig-
nal level classification
(Parveen and
Bhavsar, 2023)
Attention based
1D-CNN
81.81% 79.98% Subject wise train-test split and sig-
nal level classification
(Kingphai and Mosh-
feghi, 2023)
BGRU-GRU 84.56% NA Train-test split at window level
(Sharma and Ahir-
wal, 2021)
Cascaded 1D-
CNN and Bi-
LSTM mod
95.36% 94.68% Train-test split at window level
(Siddhad et al., 2024) Transformers 89.40% NA Subject wise train-test split, classi-
fication at window level
(Wang et al., 2024) LSTM 94.47% NA Test accuracy on single test data
Proposed Model Unified CNN-
Transformers
90.90% 85.46% Subject-wise train-test split along
with signal level classification
achieved by our proposed approach, which utilizes a
modern deep learning framework, as anticipated. Our
comparison focuses exclusively on three level mental
workload classification. Classification accuracy pro-
vided by (Lim et al., 2018) is 69.2%
(Parveen and Bhavsar, 2023) utilized CNN along
with attention on both time and channel axis in or-
der to extract features and classify small windows of
EEG data. In order to provide accuracy at the sig-
nal level, majority voting on windows is applied. An
average test accuracy of 79.98% is achieved on three
mental workload levels (low vs medium vs high), re-
spectively. This comparison indicates the clear advan-
tage of incorporating a CNN- Transformer approach.
The methodology employed in (Siddhad et al.,
2024) exhibits resemblances to our approach, specif-
ically in utilizing transformer neural networks for
the classification of STEW dataset. Authors in-
vestigate the application of transformer networks to
classify raw EEG data. It achieved an accuracy
of 89.40%. Although the approaches can be com-
pared, there are significant distinctions in the evalu-
ation process and results. The study presented find-
ings based on a conventional dataset, without employ-
ing cross-validation. Furthermore, our research uti-
lized a stricter evaluation process by employing a 5-
fold cross-validation dataset. This approach ensures
a more reliable assessment of the model’s capacity
to generalize. Hence, we compare our best accuracy
with approach. Our model attained the highest ac-
curacy of 90.90%, surpassing the performance of the
referenced approach.
The study (Wang et al., 2024) involves an
Attention-Based Recurrent Fuzzy Network (ARFN)
to evaluate mental workload through the analysis of
EEG data. The model employs an EEG signal pro-
cessing technique that integrates a fuzzy recursive
module and an LSTM layer. Performance evalua-
tion is carried out using k-fold cross-validation, based
on which, the best model is selected which is further
trained with entire training data (training and valida-
tion). Provided test accuracy of 94.47% on a single
test dataset. On the contrary, we have provided best as
well as averaged accuracy on 5-fold cross validation
dataset showcasing better generalization and reliabil-
ity of our approach.
While other studies, such as (Sharma and Ahirwal,
2021), and (Kingphai and Moshfeghi, 2023), have
also utilized the same dataset, they appear to divide
the training and testing data at the window level. This
means that when data is split at the window level, the
training and testing sets can include samples from the
same participants, which is impractical. In contrast,
our study, along with the above mentioned works,
partitions the data at the subject level. Although our
classification is conducted at the window level—with
signal-level labels determined through majority vot-
ing—we maintain a subject-based training and test-
ing split. This method poses greater challenges due to
inter-subject variability, but it reflects a more realistic
scenario.
Thus, overall the proposed approach is among
the better performing methods, and also one of the
few approaches which provide results based on cross-
validation in this domain. This, we believe that our
performance is encouraging enough to explore the po-
tential of such mixed models further.
8 CONCLUSION
In this work, we utilized a novel strategy to address
the difficulties of EEG data by introducing a hybrid
CNN-transformer model for mental workload classi-
Unified CNN-Transformer Model for Mental Workload Classification Using EEG
933

fication from EEG signals. Our model effectively an-
alyzes EEG signals by utilizing the strengths of CNNs
for extracting spatial features and Transformers for
capturing long-range temporal relationships.
Our methodology uses 1D-CNN to extract re-
silient characteristics from the EEG data which then
fed to the Transformer block. We implemented a ma-
jority voting method following the acquisition of pre-
dictions from the Transformer model. This method
guarantees that the ultimate precision reflects an ex-
tensive view of the mental workload condition, min-
imizing disruption and probable inaccuracies from
classifications based on windows. The suggested
model was assessed using a thorough 5-fold cross-
validation technique.
In summary, this study showcases the efficacy of
integrating spatial and temporal modeling methodolo-
gies, which enables the advancement of EEG-based
mental workload evaluation and creates opportunities
for further research in cognitive state classification.
Future studies could delve into additional enhance-
ments to the model and its utilization in various cog-
nitive activities, while also examining the feasibility
of real-time implementation for practical purposes in
monitoring and regulating mental workload.
REFERENCES
Bratfisch, O. and Hagman, E. (2008). Simkap–
simultankapazit
¨
at/multi-tasking. M
¨
odling: Schuhfried
GmbH.
Chandrashekar, G. and Sahin, F. (2014). A survey on feature
selection methods. Computers & Electrical Engineer-
ing, 40(1):16–28.
Huang, G., Zhang, Y., and Zhang, L. (2019). Cross-subject
mental workload assessment using transfer learning
with cnn. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 13:827.
Iriarte, J., Urrestarazu, E., Valencia, M., Alegre, M., Ma-
landa, A., Viteri, C., and Artieda, J. (2003). Indepen-
dent component analysis as a tool to eliminate artifacts
in eeg: a quantitative study. Journal of clinical neuro-
physiology, 20(4):249–257.
Kingphai, K. and Moshfeghi, Y. (2023). On time series
cross-validation for deep learning classification model
of mental workload levels based on eeg signals. In
Machine Learning, Optimization, and Data Science:
8th International Workshop, LOD 2022, Certosa di
Pontignano, Italy, September 19–22, 2022, Revised
Selected Papers, Part II, pages 402–416. Springer.
Lai, C. Q., Ibrahim, H., Abdullah, M. Z., Abdullah, J. M.,
Suandi, S. A., and Azman, A. (2018). Artifacts and
noise removal for electroencephalogram (eeg): A lit-
erature review. In 2018 IEEE Symposium on Com-
puter Applications & Industrial Electronics (ISCAIE),
pages 326–332. IEEE.
Lim, W., Sourina, O., and Wang, L. P. (2018). Stew: Simul-
taneous task eeg workload data set. IEEE Transac-
tions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineer-
ing, 26(11):2106–2114.
Mognon, A., Jovicich, J., Bruzzone, L., and Buiatti, M.
(2011). Adjust: An automatic eeg artifact detector
based on the joint use of spatial and temporal features.
Psychophysiology, 48(2):229–240.
Nitschke, J. B., Miller, G. A., and Cook, E. W. (1998). Dig-
ital filtering in eeg/erp analysis: Some technical and
empirical comparisons. Behavior Research Methods,
Instruments, & Computers, 30:54–67.
Parveen, F. and Bhavsar, A. (2023). Attention based 1d-
cnn for mental workload classification using eeg. In
Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on
PErvasive Technologies Related to Assistive Environ-
ments, pages 739–745.
Roy, Y., Banville, H., Albuquerque, I., Gramfort, A., Falk,
T. H., and Faubert, J. (2019). Deep learning-based
electroencephalography analysis: a systematic review.
Journal of neural engineering, 16(5):051001.
Schirrmeister, R. T., Springenberg, J. T., Fiederer, L. D. J.,
Glasstetter, M., Eggensperger, K., Tangermann, M.,
Hutter, F., Burgard, W., and Ball, T. (2017). Deep
learning with convolutional neural networks for eeg
decoding and visualization. Human Brain Mapping,
38(11):5391–5420.
Sharma, V. and Ahirwal, M. K. (2021). Quantifica-
tion of mental workload using a cascaded deep
one-dimensional convolution neural network and bi-
directional long short-term memory model.
Siddhad, G., Gupta, A., Dogra, D. P., and Roy, P. P. (2024).
Efficacy of transformer networks for classification of
eeg data. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control,
87:105488.
Sun, S., Chen, S., Wang, H., Zhang, S., and Zhang, H.
(2021). A transformer-based deep neural network for
eeg signal classification. IEEE Transactions on Neu-
ral Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 29:1574–
1584.
Vaswani, A., Shazeer, N., Parmar, N., Uszkoreit, J., Jones,
L., Gomez, A. N., Kaiser, Ł., and Polosukhin, I.
(2017). Attention is all you need. In Advances in
Neural Information Processing Systems, volume 30.
Wang, Y., Wang, L., Wang, X., and Wang, W. (2020). Deep
learning-based classification of eeg signals for cog-
nitive workload assessment. IEEE Access, 8:74262–
74272.
Wang, Z., Ouyang, Y., and Zeng, H. (2024). Arfn: An
attention-based recurrent fuzzy network for eeg men-
tal workload assessment. IEEE Transactions on In-
strumentation and Measurement.
BIOSIGNALS 2025 - 18th International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
934
